Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix Protein Is Sufficient and Necessary to Remodel Host Mitochondria in Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture, RSV Infection and RSV Growth
2.2. Plasmid Construction and Transfection
2.3. Immunofluorescence and Confocal Scanning Laser Microscopy (CLSM)
2.4. Quantitative Analysis of Mitochondrial Organisation/Distribution
2.5. Assessment of Mitochondrial Bioenergetics and Function
2.6. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential (Δψm) and mtROS
2.7. Quantitative PCR (qPCR) to Quantify Viral RNA
2.8. Reverse Transcription qPCR (RT-qPCR) to Quantify Host Gene mRNA Levels
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
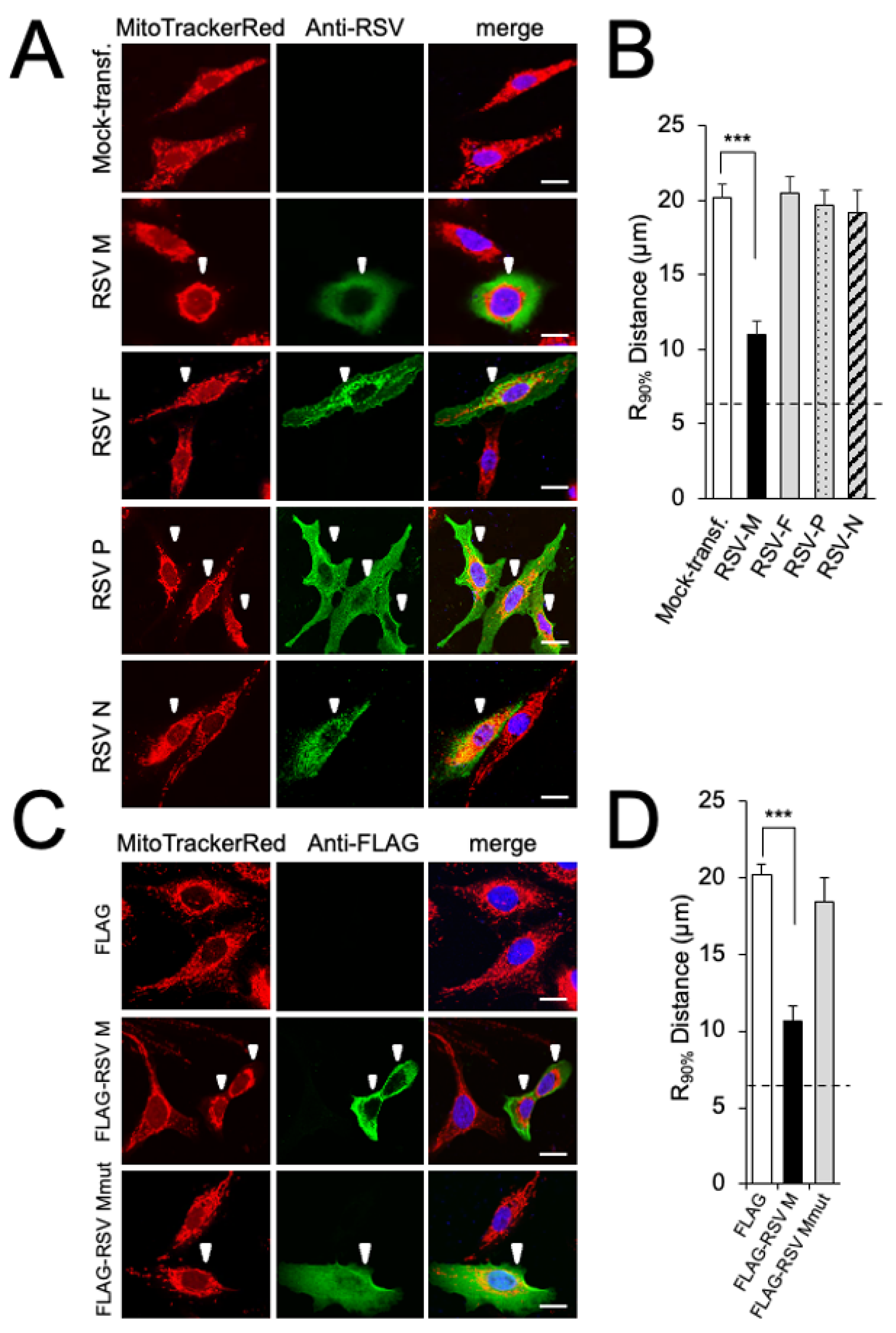
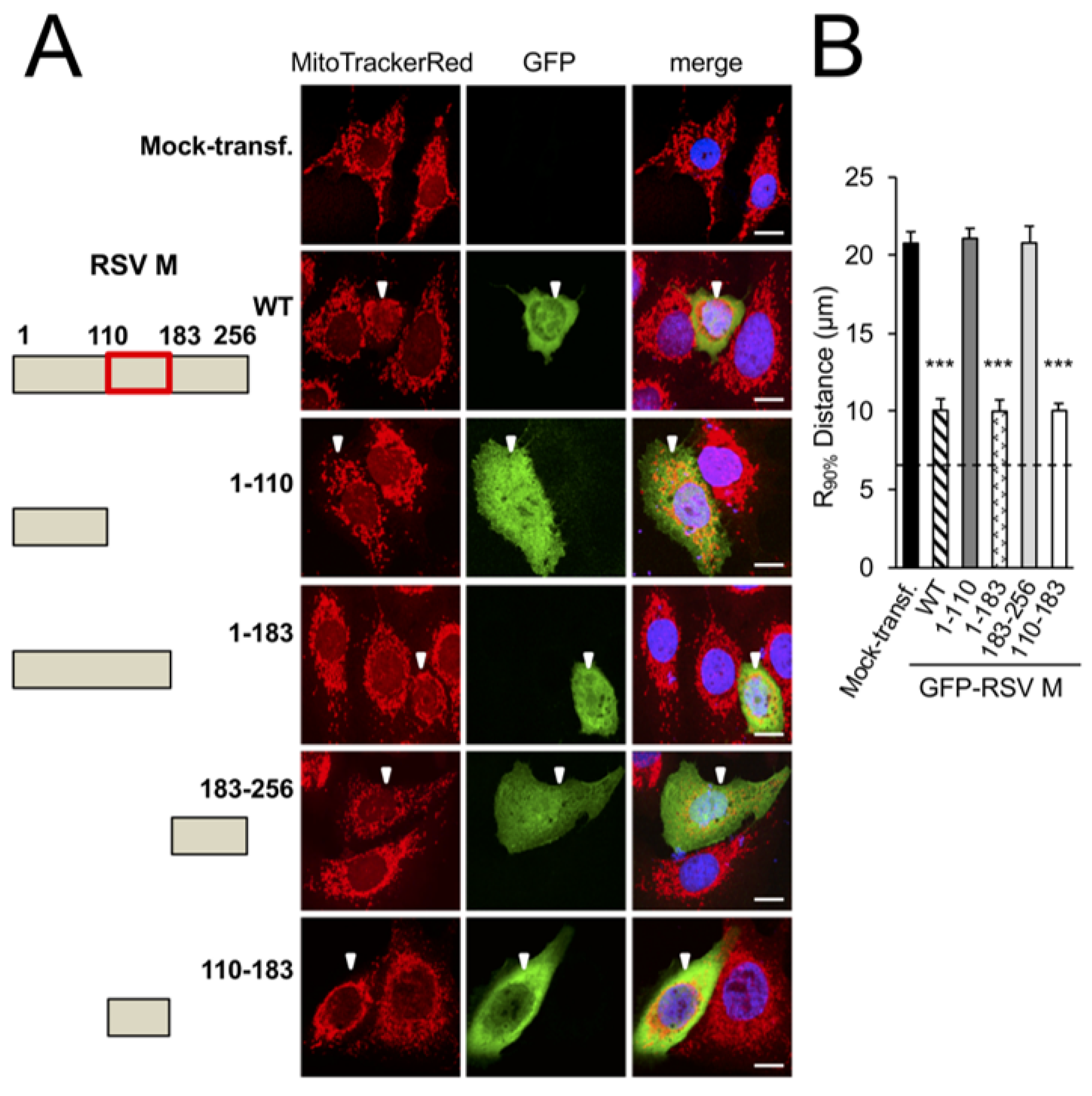
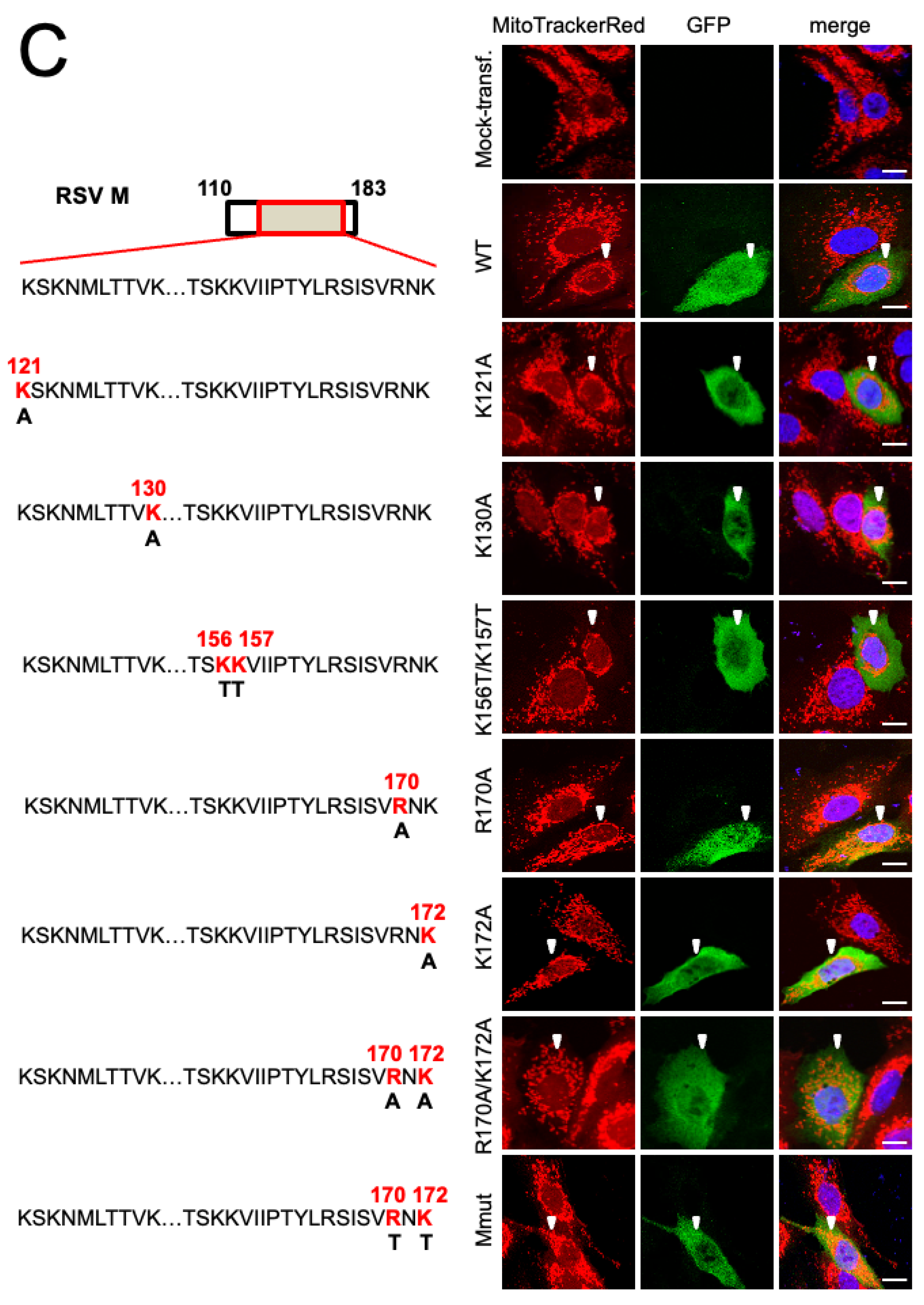
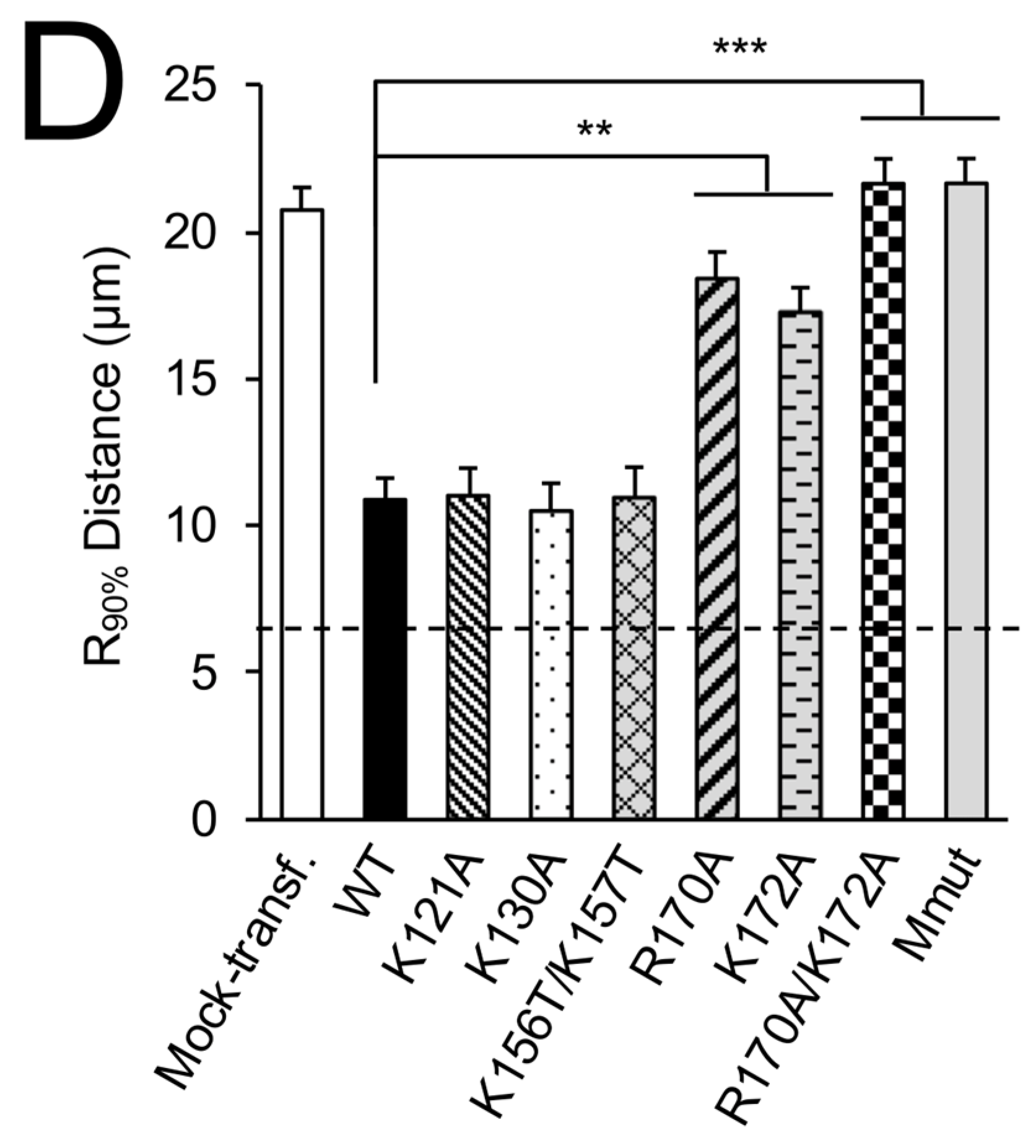
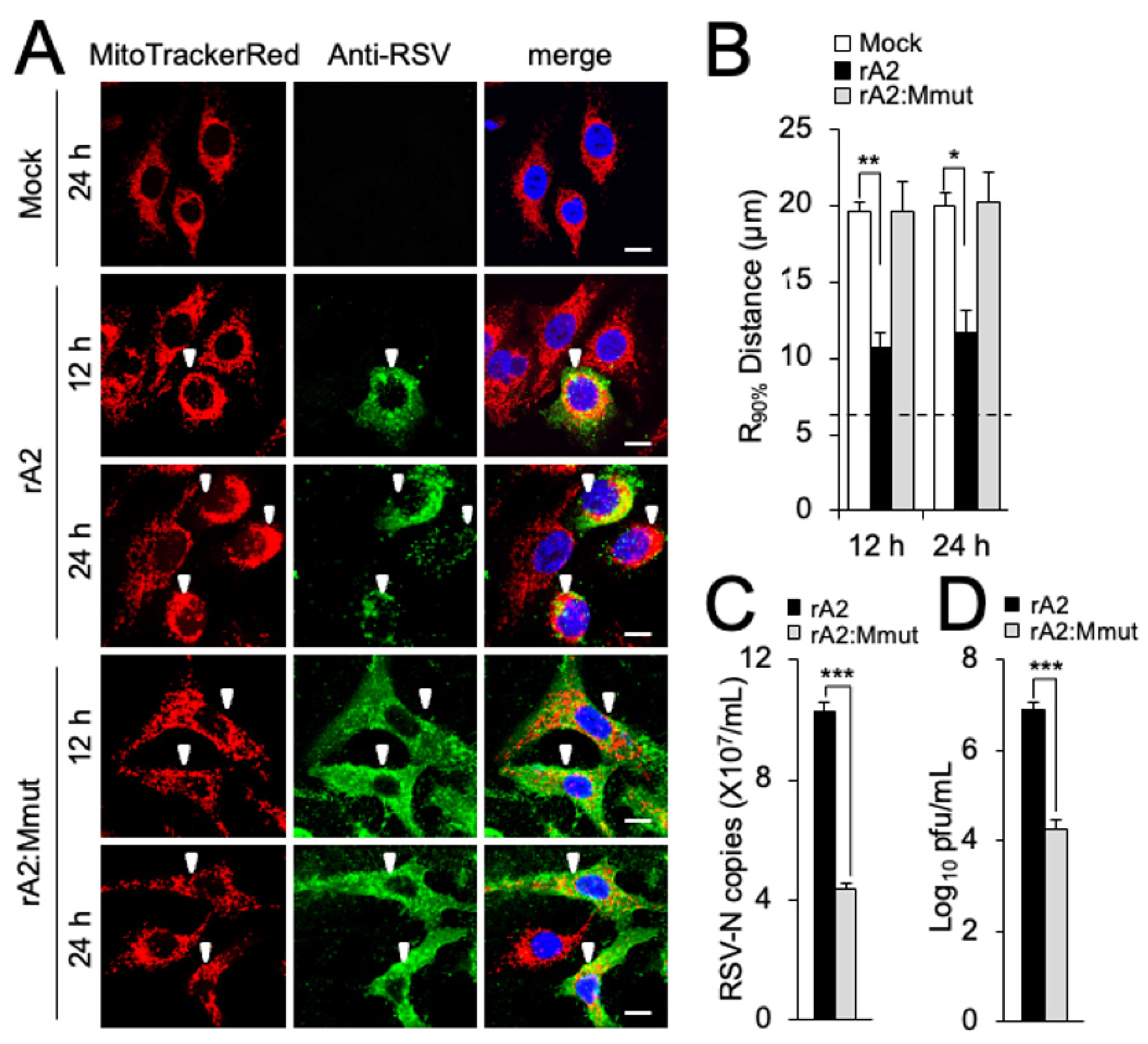
3.1. RSV Matrix Protein (M) Is Sufficient and Necessary to Induce Mitochondrial Perinuclear Clustering
3.2. RSV M Is Key to Inhibition of Mitochondrial Respiration in Infection
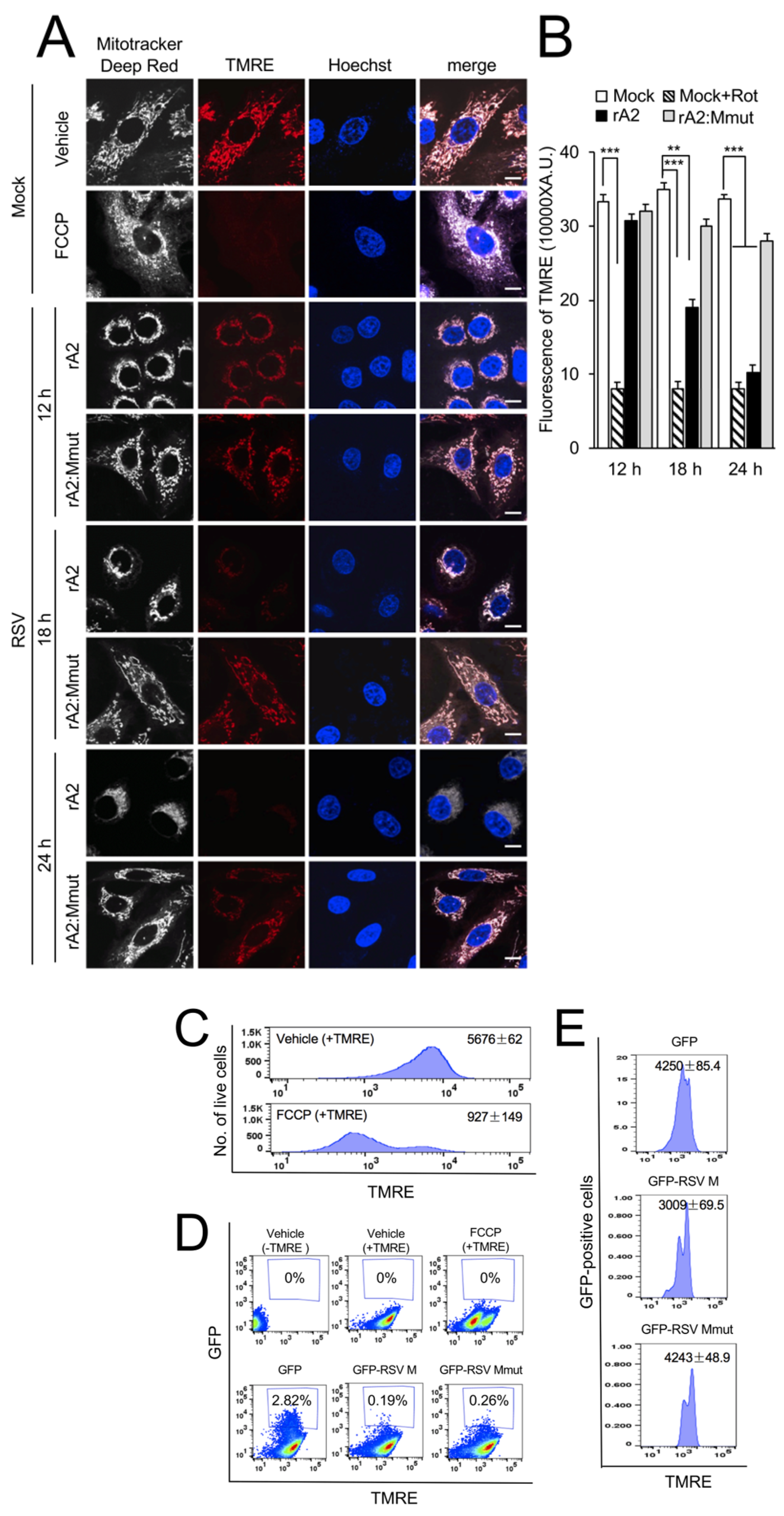
3.3. RSV M Is Necessary and Sufficient to Induce Loss of Δψm
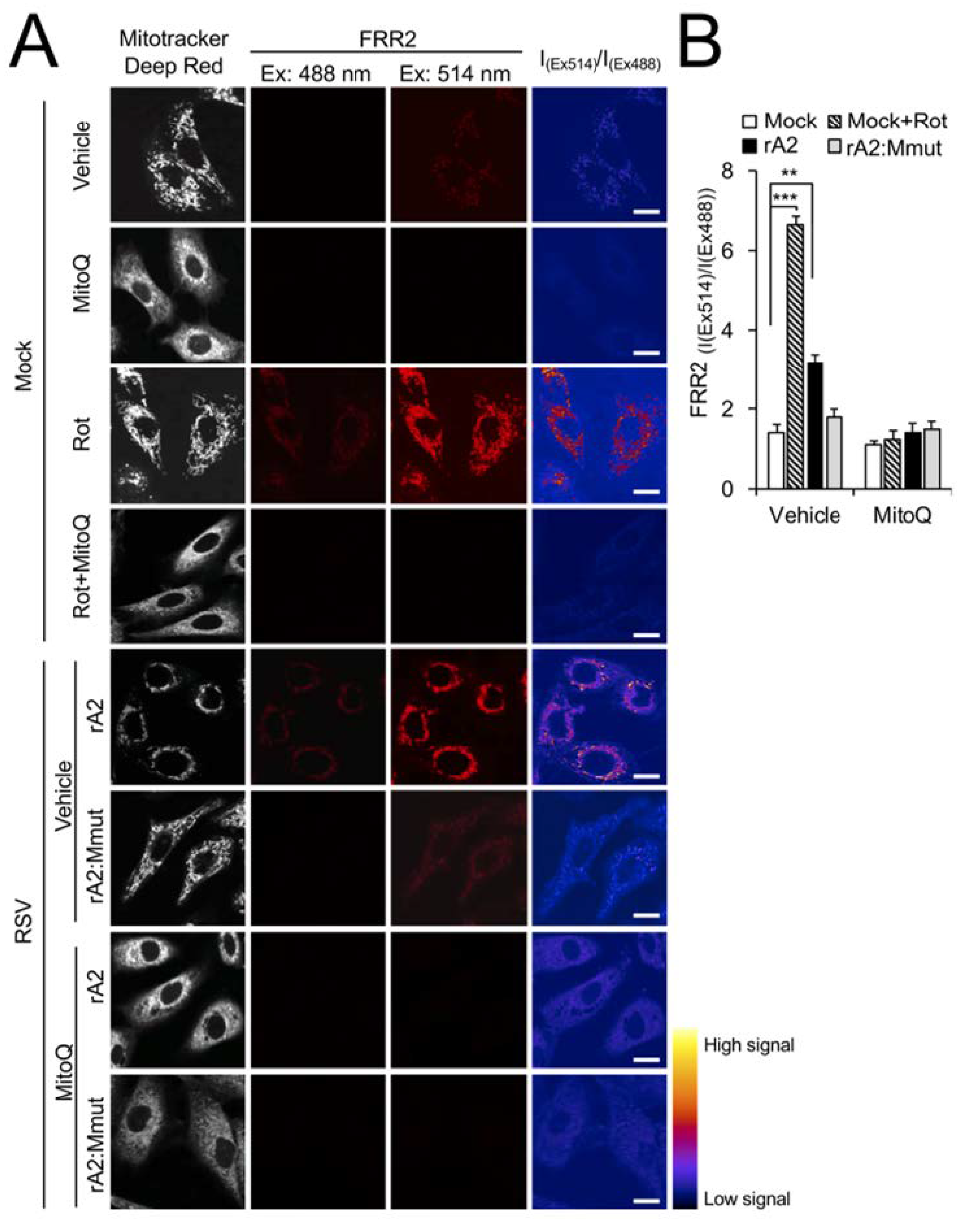
3.4. Wild-Type RSV M Contributes to Increased mtROS in Infection
3.5. RSV Infection Reduces Host Mitochondrial Gene Expression Dependent on Wild-Type M, and Can Be Reversed by a mtROS Scavenger
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lozano, R.; Naghavi, M.; Foreman, K.; Lim, S.; Shibuya, K.; Aboyans, V.; Abraham, J.; Adair, T.; Aggarwal, R.; Ahn, S.Y.; et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2095–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, H.; Nokes, D.J.; Gessner, B.D.; Dherani, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Singleton, R.J.; O’Brien, K.L.; Roca, A.; Wright, P.F.; Bruce, N.; et al. Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to respiratory syncytial virus in young children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2010, 375, 1545–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, C. Prospects for a respiratory syncytial virus vaccine. Science 1994, 265, 1393–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Littel-van den Hurk, S.v.D.; Mapletoft, J.W.; Arsic, N.; Kovacs-Nolan, J. Immunopathology of RSV infection: Prospects for developing vaccines without this complication. Rev. Med. Virol. 2007, 17, 5–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, P.L.; Fearns, R.; Graham, B.S. Respiratory Syncytial Virus: Virology, Reverse Genetics, and Pathogenesis of Disease. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013, 372, 3–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildyal, R.; Ho, A.; Jans, D.A. Central role of the respiratory syncytial virus matrix protein in infection. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 30, 692–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Jans, D.A. Impact of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Infection on Host Functions: Implications for Antiviral Strategies. Physiol. Rev. 2020, 100, 1527–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-M.; Ghildyal, R.; Hu, M.; Tran, K.C.; Starrs, L.M.; Mills, J.; Teng, M.N.; Jans, D.A. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix Protein-Chromatin Association Is Key to Transcriptional Inhibition in Infected Cells. Cells 2021, 10, 2786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildyal, R.; Ho, A.; Wagstaff, K.M.; Dias, M.M.; Barton, C.L.; Jans, P.; Bardin, P.; Jans, D.A. Nuclear Import of the Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix Protein Is Mediated By Importin beta1 Independent of Importin alpha. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 12887–12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildyal, R.; Mills, J.; Murray, M.; Vardaxis, N.; Meanger, J. Respiratory syncytial virus matrix protein associates with nucleocapsids in infected cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2002, 83, 753–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildyal, R.; Ho, A.; Dias, M.; Soegiyono, L.; Bardin, P.G.; Tran, K.C.; Teng, M.N.; Jans, D. The Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix Protein Possesses a Crm1-Mediated Nuclear Export Mechanism. J. Virol. 2009, 83, 5353–5362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, S.R.; Compans, R.W.; Wertz, G.W. Respiratory syncytial virus matures at the apical surfaces of polarized epithelial cells. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 2667–2673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrison, M.S.; Sakaguchi, T.; Schmitt, A.P. Paramyxovirus assembly and budding: Building particles that transmit infections. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 1416–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kipper, S.; Hamad, S.; Caly, L.; Avrahami, D.; Bacharach, E.; Jans, D.A.; Gerber, D.; Bajorek, M. New Host Factors Important for Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) Replication Revealed by a Novel Microfluidics Screen for Interactors of Matrix (M) Protein*. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2015, 14, 532–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Li, H.-M.; Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Jans, D.A. Mitochondrial protein p32/HAPB1/gC1qR/C1qbp is required for efficient respiratory syncytial virus production. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 489, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Schulze, K.E.; Ghildyal, R.; Henstridge, D.C.; Kolanowski, J.L.; New, E.J.; Hong, Y.; Hsu, A.C.; Hansbro, P.M.; Wark, P.A.B.; et al. Respiratory syncytial virus co-opts host mitochondrial function to favour infectious virus production. Elife 2019, 8, e42448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Jans, D.A. Subversion of Host Cell Mitochondria by RSV to Favor Virus Production is Dependent on Inhibition of Mitochondrial Complex I and ROS Generation. Cells 2019, 8, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caly, L.; Li, H.-M.; Jans, D. Host Factors Modulating RSV Infection: Use of Small Interfering RNAs to Probe Functional Importance. In Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus: Methods and Protocols; Tripp, R.A., Jorquera, P.A., Eds.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 93–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Clarke, D.; Zhou, H.Z.-Y.; Cheng, X.; Coelingh, K.; Bryant, M.; Li, S. Recombinant Human Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) from cDNA and Construction of Subgroup A and B Chimeric RSV. Virology 1998, 251, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, M.; Crawford, S.A.; Henstridge, D.C.; Ng, I.H.W.; Boey, E.J.H.; Xu, Y.; Febbraio, M.A.; Jans, D.A.; Bogoyevitch, M.A. p32 protein levels are integral to mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticulum morphology, cell metabolism and survival. Biochem. J. 2013, 453, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Walt, S.; Colbert, S.C.; Varoquaux, G. The NumPy Array: A Structure for Efficient Numerical Computation. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011, 13, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Walt, S.; Schönberger, J.L.; Nunez-Iglesias, J.D.; Boulogne, F.; Warner, J.; Yager, N.; Gouillart, E.; Yu, T. scikit-image: Image processing in Python. PeerJ 2014, 2, e453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, J.D. Matplotlib: A 2D graphics environment. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2007, 9, 90–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, P.; Gommers, R.; Oliphant, T.E.; Cournapeau, D.; Burovski, E.; Weckesser, W.; alexbrc; Peterson, P.; wnbell; mattknox_ca; et al. Scipy/Scipy: Scipy 0.18.1. 2016. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/154391#.ZFM686VBxPY (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Waskom, M.; Botvinnik, O.; Drewokane; Hobson, P.; Halchenko, Y.; Lukauskas, S.; Cole, J.B.; Warmenhoven, J.; De Ruiter, J.; Hoyer, S.; et al. Seaborn: V0.7.1 (June 2016). 2016. Available online: https://zenodo.org/record/54844#.ZFM7yKVBxPY (accessed on 1 February 2018).
- Van Bergeijk, P.; Adrian, M.; Hoogenraad, C.C.; Kapitein, L.C. Optogenetic control of organelle transport and positioning. Nature 2015, 518, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsu, N. A threshold selection method from gray-level histograms. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. 1979, 9, 62–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.H.; Lee, C.K. Minimum cross entropy thresholding. Pattern Recognit. 1993, 26, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejonghe, W.; Kuenen, S.; Mylle, E.; Vasileva, M.; Keech, O.; Viotti, C.; Swerts, J.; Fendrych, M.; Ortiz-Morea, F.A.; Mishev, K.; et al. Mitochondrial uncouplers inhibit clathrin-mediated endocytosis largely through cytoplasmic acidification. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCloy, R.A.; Rogers, S.; Caldon, C.E.; Lorca, T.; Castro, A.; Burgess, A. Partial inhibition of Cdk1 in G2phase overrides the SAC and decouples mitotic events. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1400–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potapova, T.A.; Sivakumar, S.; Flynn, J.N.; Li, R.; Gorbsky, G.J. Mitotic progression becomes irreversible in prometaphase and collapses when Wee1 and Cdc25 are inhibited. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 1191–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, R.A.; Murphy, M. Animal and human studies with the mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2010, 1201, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.; Jankowska, K.; Pilgrim, C.; Fraser, S.T.; New, E.J. Studies of Hematopoietic Cell Differentiation with a Ratiometric and Reversible Sensor of Mitochondrial Reactive Oxygen Species. Antioxidants Redox Signal. 2016, 24, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mehdi, A.-B.; Pastukh, V.M.; Swiger, B.M.; Reed, D.J.; Patel, M.R.; Bardwell, G.C.; Pastukh, V.V.; Alexeyev, M.F.; Gillespie, M.N. Perinuclear Mitochondrial Clustering Creates an Oxidant-Rich Nuclear Domain Required for Hypoxia-Induced Transcription. Sci. Signal. 2012, 5, ra47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mentel, R.; Wegner, U.; Bruns, R.; Gurtler, L. Real-time PCR to improve the diagnosis of respiratory syncytial virus infection. J. Med. Microbiol. 2003, 52, 893–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jans, D.; Bardin, P.G.; Meanger, J.; Mills, J.; Ghildyal, R. Association of Respiratory Syncytial Virus M Protein with Viral Nucleocapsids Is Mediated by the M2-1 Protein. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 8863–8870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Neilson, A.; Swift, A.L.; Moran, R.; Tamagnine, J.; Parslow, D.; Armistead, S.; Lemire, K.; Orrell, J.; Teich, J.; et al. Multiparameter metabolic analysis reveals a close link between attenuated mitochondrial bioenergetic function and enhanced glycolysis dependency in human tumor cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2007, 292, C125–C136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, S.; Oku, M.; Tsuda, M.; Hoseki, J.; Sakai, Y. Mitochondrial impairment triggers cytosolic oxidative stress and cell death following proteasome inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costes, S.V.; Daelemans, D.; Cho, E.H.; Dobbin, Z.; Pavlakis, G.; Lockett, S. Automatic and Quantitative Measurement of Protein-Protein Colocalization in Live Cells. Biophys. J. 2004, 86, 3993–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghildyal, R.; Baulch-Brown, C.; Mills, J.; Meanger, J. The matrix protein of Human respiratory syncytial virus localises to the nucleus of infected cells and inhibits transcription. Arch. Virol. 2003, 148, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez, I.; Lombardía, L.; García-Barreno, B.; Domínguez, O.; Melero, J.A. Distinct gene subsets are induced at different time points after human respiratory syncytial virus infection of A549 cells. J. Gen. Virol. 2007, 88, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, A.K.; Muehmer, M.; Mages, J.; Gueinzius, K.; Hess, C.; Heeg, K.; Bals, R.; Lang, R.; Dalpke, A.H. Differential Recognition of TLR-Dependent Microbial Ligands in Human Bronchial Epithelial Cells. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 3134–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Luxon, B.A.; Casola, A.; Garofalo, R.P.; Jamaluddin, M.; Brasier, A.R. Expression of Respiratory Syncytial Virus-Induced Chemokine Gene Networks in Lower Airway Epithelial Cells Revealed by cDNA Microarrays. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 9044–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Luxon, B.A.; Garofalo, R.P.; Casola, A.; Sinha, M.; Brasier, A.R. Identification of NF-kappaB-dependent gene networks in respiratory syncytial virus-infected cells. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 6800–6814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.-Y.; Imani, F.; Miller-DeGraff, L.; Walters, D.; Melendi, G.A.; Yamamoto, M.; Polack, F.P.; Kleeberger, S.R. Antiviral Activity of Nrf2 in a Murine Model of Respiratory Syncytial Virus Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 179, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaspar, J.W.; Niture, S.K.; Jaiswal, A.K. Nrf2:INrf2 (Keap1) signaling in oxidative stress. Free. Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 47, 1304–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammitt, L.L.; Dagan, R.; Yuan, Y.; Cots, M.B.; Bosheva, M.; Madhi, S.A.; Muller, W.J.; Zar, H.J.; Brooks, D.; Grenham, A.; et al. Nirsevimab for Prevention of RSV in Healthy Late-Preterm and Term Infants. New Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 837–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, E.A.F.; Madhi, S.A.; Muller, W.J.; Atanasova, V.; Bosheva, M.; Cabañas, F.; Cots, M.B.; Domachowske, J.B.; Garcia-Garcia, M.L.; Grantina, I.; et al. Efficacy of nirsevimab against respiratory syncytial virus lower respiratory tract infections in preterm and term infants, and pharmacokinetic extrapolation to infants with congenital heart disease and chronic lung disease: A pooled analysis of randomised controlled trials. Lancet Child Adolesc. Health 2023, 7, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, C.; Tamir, S.; Tripp, R.A.; Ghildyal, R. Reversible disruption of XPO1-mediated nuclear export inhibits respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) replication. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 19223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, M.; Bogoyevitch, M.A.; Jans, D.A. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix Protein Is Sufficient and Necessary to Remodel Host Mitochondria in Infection. Cells 2023, 12, 1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091311
Hu M, Bogoyevitch MA, Jans DA. Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix Protein Is Sufficient and Necessary to Remodel Host Mitochondria in Infection. Cells. 2023; 12(9):1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091311
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, MengJie, Marie A. Bogoyevitch, and David A. Jans. 2023. "Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix Protein Is Sufficient and Necessary to Remodel Host Mitochondria in Infection" Cells 12, no. 9: 1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091311
APA StyleHu, M., Bogoyevitch, M. A., & Jans, D. A. (2023). Respiratory Syncytial Virus Matrix Protein Is Sufficient and Necessary to Remodel Host Mitochondria in Infection. Cells, 12(9), 1311. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells12091311





