Adipo-Epithelial Transdifferentiation in In Vitro Models of the Mammary Gland
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Animals and Tissue Processing
2.3. Isolation of Mammary Epithelial Organoids
2.4. Isolation of Mammary Mature Adipocytes
2.5. Transwell Model for Co-Culturing Mammary Epithelial Organoids and Adipocytes
2.6. hMADS Cell Culture and Treatments
2.7. qRT-PCR
2.8. Western Blotting
2.9. miRNAseq Analysis in the Co-Culture Medium
2.10. Electron Microscopy
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
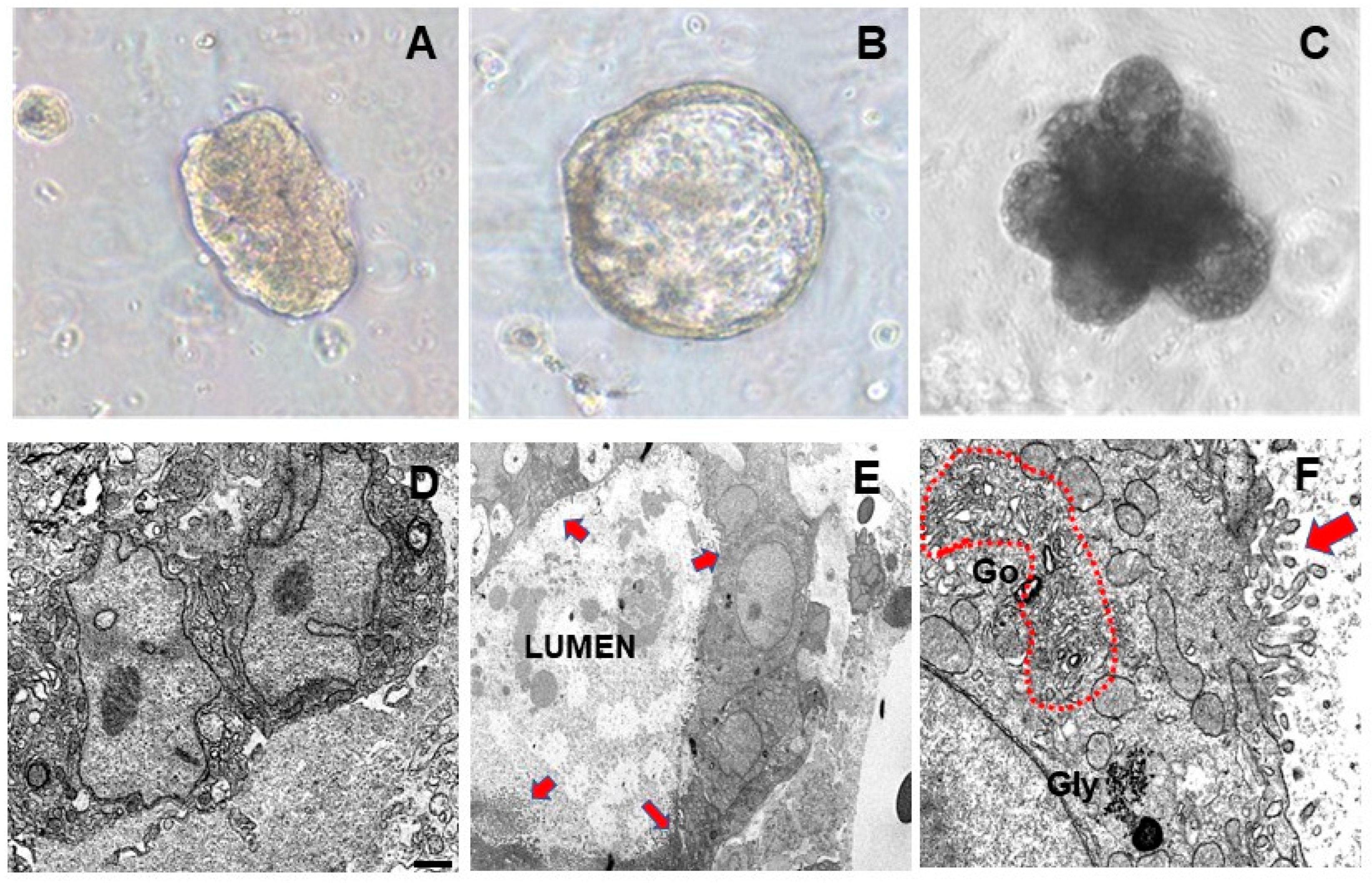
3.1. Pregnancy Hormones Affect Molecular and Morphological MEO Differentiation
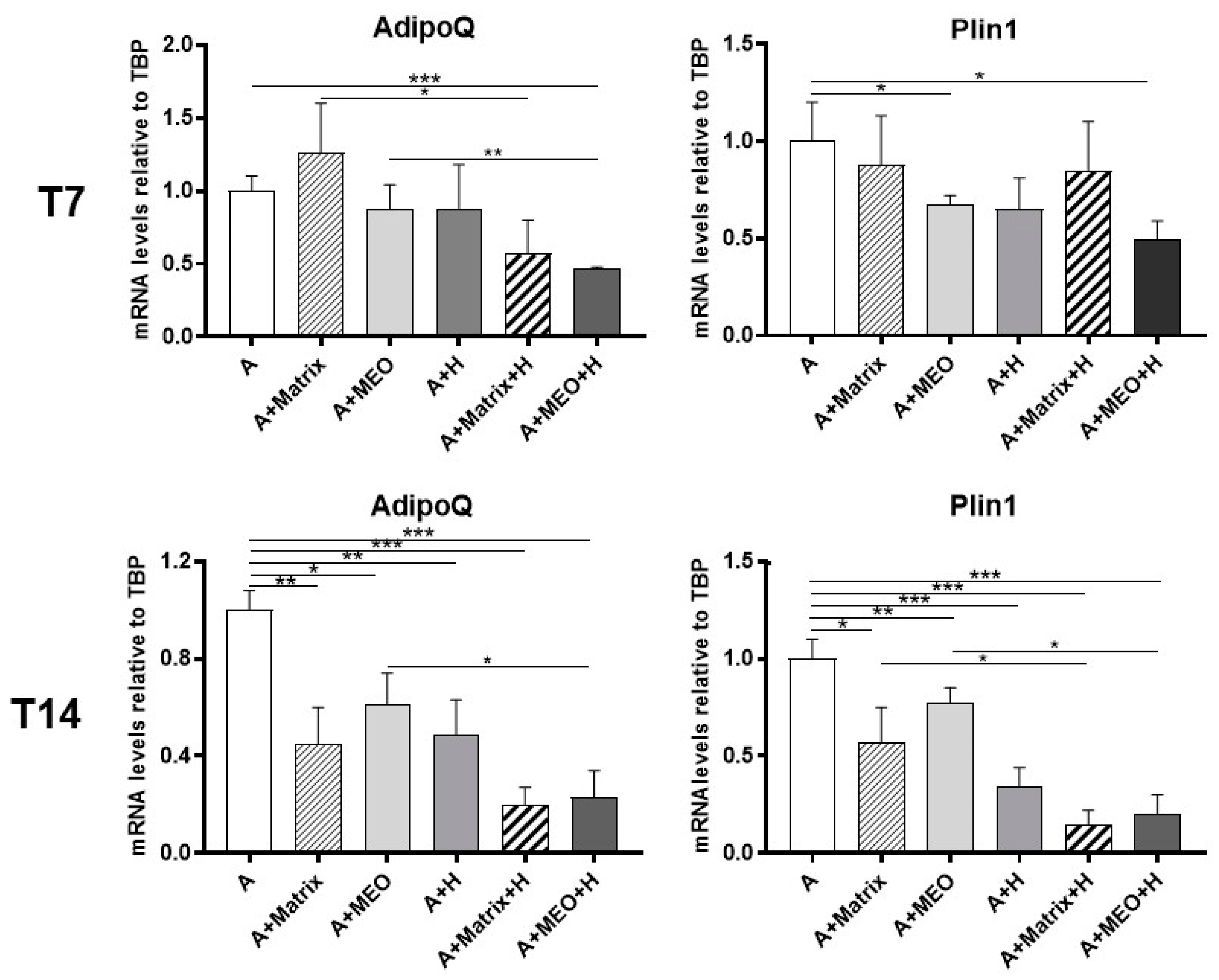
3.2. Mature Adipocytes under Co-Culture Conditions Lose Their Adipogenic Features and Acquire an Epithelial Mammary Phenotype
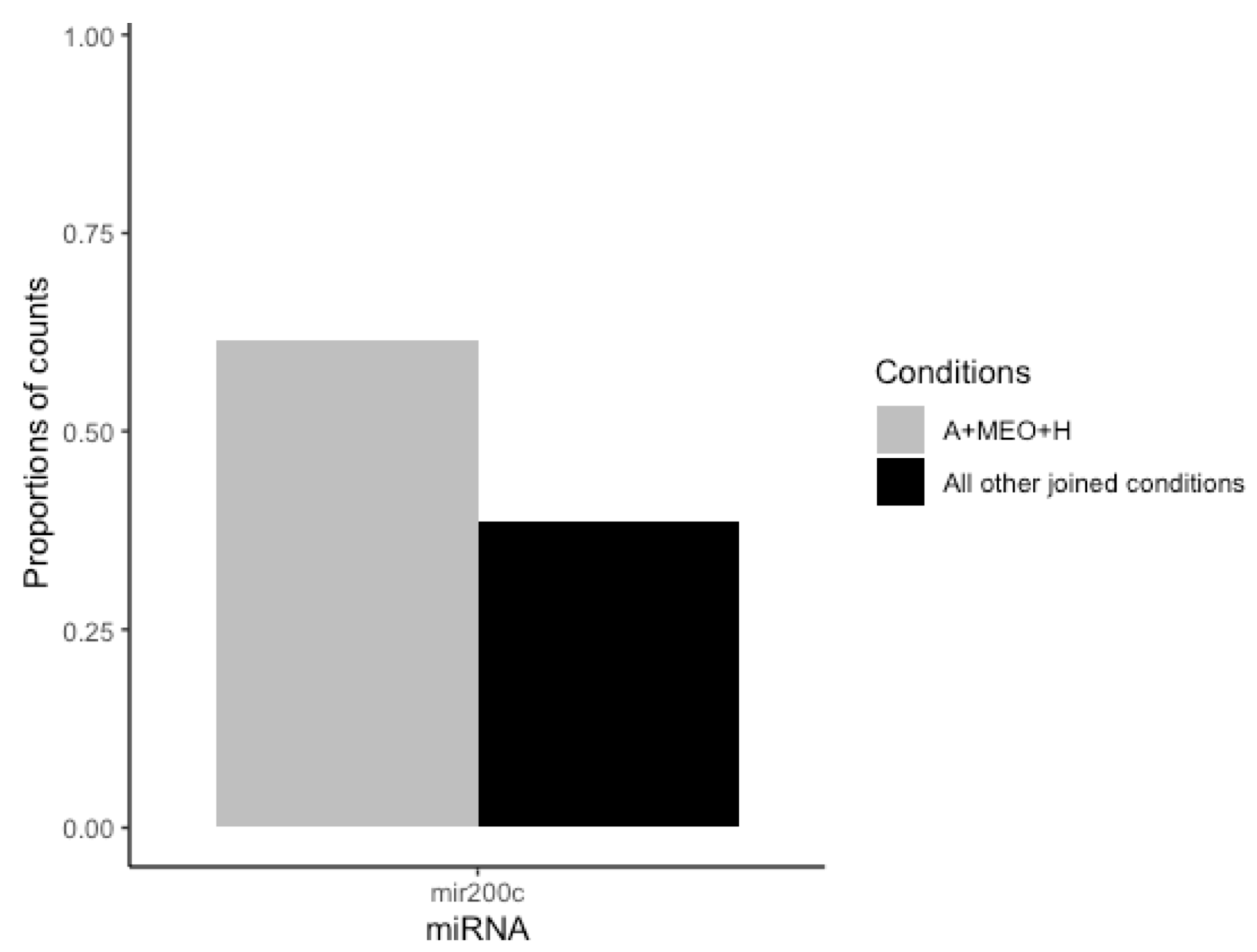
3.3. MEOs and Mammary Adipocytes Release miRNAs in the Co-Culture Supernatant
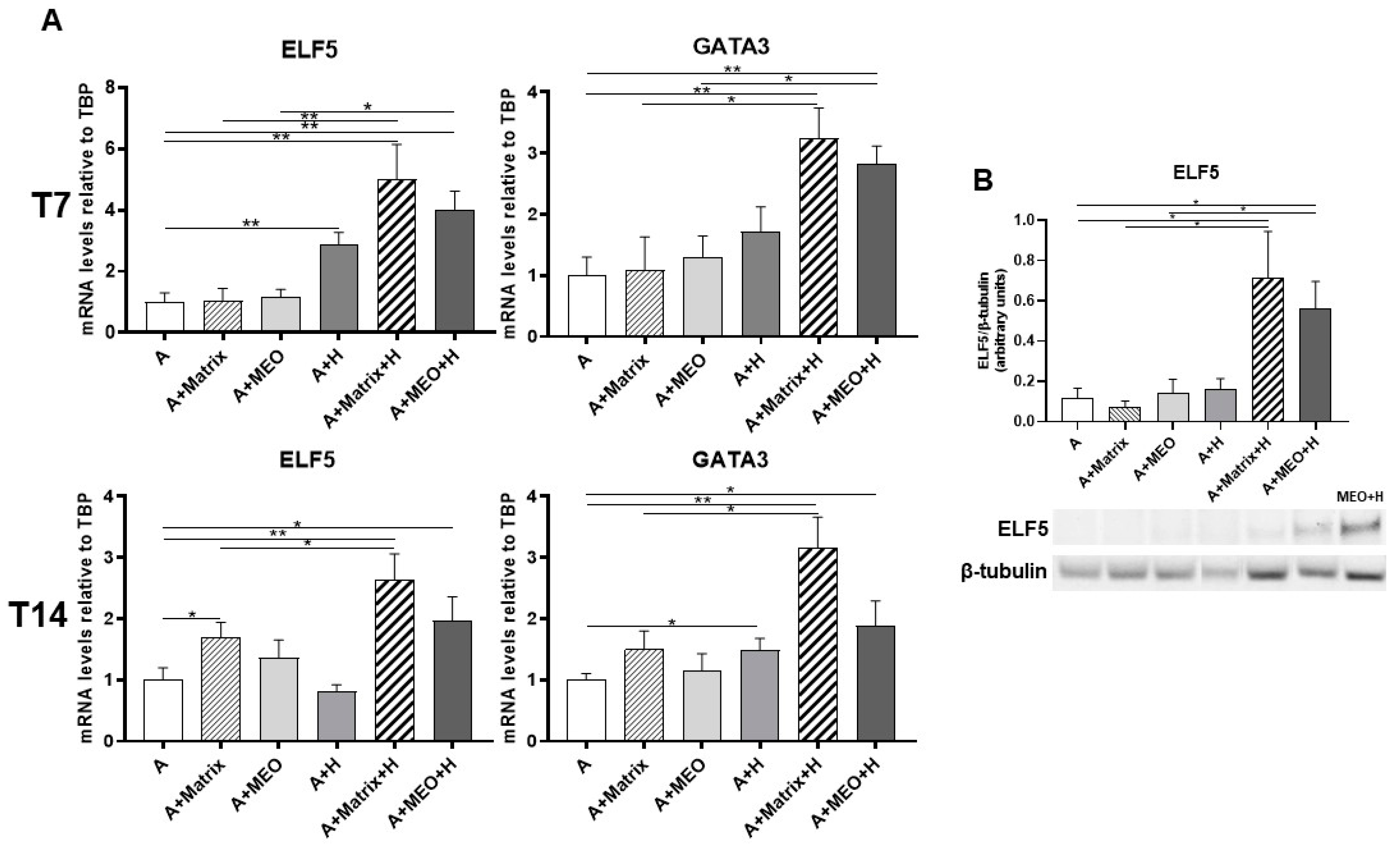
3.4. hMADS Adipocytes Acquire Adipo-Epithelial Transdifferentiation Markers under Pregnancy Stimuli
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Giordano, A.; Cinti, F.; Canese, R.; Carpinelli, G.; Colleluori, G.; Di Vincenzo, A.; Palombelli, G.; Severi, I.; Moretti, M.; Redaelli, C.; et al. The Adipose Organ Is a Unitary Structure in Mice and Humans. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, S. Adipose Organ Development and Remodeling. Compr Physiol. 2018, 8, 1357–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenwald, M.; Perdikari, A.; Rülicke, T.; Wolfrum, C. Bi-directional interconversion of brite and white adipocytes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 659–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betz, M.J.; Enerbäck, S. Targeting thermogenesis in brown fat and muscle to treat obesity and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajimura, S.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Seale, P. Brown and Beige Fat: Physiological Roles beyond Heat Generation. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 546–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richert, M.M.; Schwertfeger, K.L.; Ryder, J.W.; Anderson, S.M. An atlas of mouse mammary gland development. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia. 2000, 5, 227–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, B.A.; Gusterson, B.A. Human breast development. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia. 2000, 5, 119–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cinti, S. Pink Adipocytes. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 29, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwick, R.K.; Rudolph, M.C.; Shook, B.A.; Holtrup, B.; Roth, E.; Lei, V.; Van Keymeulen, A.; Seewaldt, V.; Kwei, S.; Wysolmerski, J.; et al. Adipocyte hypertrophy and lipid dynamics underlie mammary gland remodeling after lactation. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mongroo, P.S.; Rustgi, A.K. The role of the miR-200 family in epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korpal, M.; Kang, Y. The emerging role of miR-200 family of microRNAs in epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer metastasis. RNA Biol. 2008, 5, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darcy, K.M.; Shoemaker, S.F.; Lee, P.P.; Vaughan, M.M.; Black, J.D.; Ip, M.M. Prolactin and epidermal growth factor regulation of the proliferation, morphogenesis, and functional differentiation of normal rat mammary epithelial cells in three-dimensional primary culture. J. Cell Physiol. 1995, 163, 346–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahm, H.A.; Ip, M.M. Primary culture of normal rat mammary epithelial cells within a basement membrane matrix. I. Regulation of proliferation by hormones and growth factors. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. 1990, 26, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, C.S.; Postovit, L.M.; Lajoie, G.A. Matrigel: A complex protein mixture required for optimal growth of cell culture. Proteomics. 2010, 10, 1886–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorntorp, P.; Karlsson, M.; Gustafsson, L.; Smith, U.; Sjöström, L.; Cigolini, M.; Storck, G.; Pettersson, P. Quantitation of different cells in the epididymal fat pad of the rat. J. Lipid Res. 1979, 20, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zangani, D.; Darcy, K.M.; Shoemaker, S.; Ip, M.M. Adipocyte-epithelial interactions regulate the in vitro development of normal mammary epithelial cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1999, 247, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darcy, K.M.; Zangani, D.; Shea-Eaton, W.; Shoemaker, S.F.; Lee, P.P.; Mead, L.H.; Mudipalli, A.; Megan, R.; Ip, M.M. Mammary fibroblasts stimulate growth, alveolar morphogenesis, and functional differentiation of normal rat mammary epithelial cells. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2000, 36, 578–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imagawa, W.; Tomooka, Y.; Nandi, S. Serum-free growth of normal and tumor mouse mammary epithelial cells in primary culture. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 4074–4077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCave, E.J.; Cass, C.A.P.; Burg, K.J.L.; Booth, B.W. The normal microenvironment directs mammary gland development. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2010, 15, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, A.M.; Elabd, C.; Delteil, F.; Astier, J.; Vernochet, C.; Saint-Marc, P.; Guesnet, J.; Guezennec, A.; Amri, E.Z.; Dani, C.; et al. Adipocyte differentiation of multipotent cells established from human adipose tissue. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 315, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugini, J.; Di Mercurio, E.; Tossetta, G.; Severi, I.; Monaco, F.; Reguzzoni, M.; Tomasetti, M.; Dani, C.; Cinti, S.; Giordano, A. Biological effects of ciliary neurotrophic factor on hMADS adipocytes. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber-Hall, S.J.; Phippard, D.J.; Niemeyer, C.C.; Dale, T.C. Developmental and hormonal regulation of Wnt gene expression in the mouse mammary gland. Differentiation 1994, 57, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.J.; Gallego-Ortega, D.; Ledger, A.; Schramek, D.; Joshi, P.; Szwarc, M.M.; Cho, C.; Lydon, J.P.; Khokha, R.; Penninger, J.M.; et al. Progesterone drives mammary secretory differentiation via RankL-mediated induction of Elf5 in luminal progenitor cells. Development 2013, 140, 1397–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudolph, M.C.; Wellberg, E.A.; Anderson, S.M. Adipose-depleted mammary epithelial cells and organoids. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2009, 14, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyan, B.D.; Asmussen, N.C.; Lin, Z.; Schwartz, Z. The Role of Matrix-Bound Extracellular Vesicles in the Regulation of Endochondral Bone Formation. Cells 2022, 11, 1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, N.E.; Chen, Q.J.; Sickafoose, L.K.; Wood, M.B.; Gregg, J.P.; Ninnie, M.; Abrahamsson, N.M.; Engelberg, J.A.; Walls, J.E.; Borowsky, A.D. Transgenic mammary epithelial osteopontin (spp1) expression induces proliferation and alveologenesis. Genes Cancer 2013, 4, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faraldo, M.M.; Deugnier, M.A.; Thiery, J.P.; Glukhova, M.A. Development of mammary gland requires normal beta 1-integrin function. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2000, 480, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemir, M.; Bhattacharyya, D.; Li, X.; Singh, K.; Mukherjee, A.B.; Mukherjee, B.B. Targeted inhibition of osteopontin expression in the mammary gland causes abnormal morphogenesis and lactation deficiency. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neville, M.C.; Medina, D.; Monks, J.; Hovey, R.C. The mammary fat pad. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia. 1998, 3, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Li, B.; Li, M.; Niu, C.; Wang, G.; Li, T.; Król, E.; Jin, W.; Speakman, J.R. Brown adipocytes can display a mammary basal myoepithelial cell phenotype in vivo. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 1198–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandebourg, T.; Hugo, E.; Ben-Jonathan, N. Adipocyte prolactin: Regulation of release and putative functions. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2007, 9, 464–476. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez-Cuenca, S.; Gianotti, M.; Roca, P.; Proenza, A.M. Sex steroid receptor expression in different adipose depots is modified during midpregnancy. Mol. Cell Endocrinol. 2006, 249, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, D.A.; Werb, Z.; Zong, Y.; Goldstein, A.S. The Cleared Mammary Fat Pad Transplantation Assay for Mammary Epithelial Organogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Protoc. 2015, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, N.; McDonald, L.; Morris, J.S.; Cameron, E.R.; Blyth, K. RUNX2 in mammary gland development and breast cancer. J. Cell Physiol. 2013, 228, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Standal, T.; Borset, M.; Sundan, A. Role of osteopontin in adhesion, migration, cell survival and bone remodeling. Exp. Oncol. 2004, 26, 179–184. [Google Scholar]
- Kouros-Mehr, H.; Slorach, E.M.; Sternlicht, M.D.; Werb, Z. GATA-3 maintains the differentiation of the luminal cell fate in the mammary gland. Cell 2006, 127, 1041–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, Q.; Dalgin, G.; Xu, H.; Ting, C.N.; Leiden, J.M.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Function of GATA transcription factors in preadipocyte-adipocyte transition. Science 2000, 290, 134–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaret, K.S.; Carroll, J.S. Pioneer transcription factors: Establishing competence for gene expression. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 2227–2241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, S.R.; Naylor, M.J.; Asselin-Labat, M.L.; Blazek, K.D.; Gardiner-Garden, M.; Hilton, H.N.; Kazlauskas, M.; Pritchard, M.A.; Chodosh, L.A.; Pfeffer, P.L.; et al. The ETS transcription factor Elf5 specifies mammary alveolar cell fate. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.J.; Ormandy, C.J. Elf5, hormones and cell fate. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 23, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao-Ru, Y.; Tao, S.; Jia-Ying, X.; Ya-Fang, L.; Hui-Ling, Z. In vitro transdifferentiated signatures of goat preadipocytes into mammary epithelial cells revealed by DNA methylation and transcriptome profiling. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.L.; Zuk, P.; Berke, G.S.; Chhetri, D.K. Epithelial differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells for laryngeal tissue engineering. Laryngoscope 2010, 120, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, C.; Pond, X.B.; Torey, B.; Kevin, R.; Susan, H.; Jeffrey, M. Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor Signaling Is Essential for Normal Mammary Gland Development and Stem Cell Function. Stem Cells 2013, 31, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, E.M.; Yan, X.; John, M.S. Elf5 is an epithelium-specific, fibroblast growth factor-sensitive transcription factor in the embryonic lung. Dev. Dyn. 2007, 236, 1175–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, T.H.; Ha, Y.J.; Seung, Y.L.; Hyuk, S. Effects of the Insulin-like Growth Factor Pathway on the Regulation of Mammary Gland Development. Dev. Reprod. 2016, 20, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavallari, I.; Ciccarese, F.; Sharova, E.; Urso, L.; Raimondi, V.; Silic-Benussi, M.; D’Agostino, D.M.; Ciminale, V. The miR-200 Family of microRNAs: Fine Tuners of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Circulating Cancer Biomarkers. Cancers 2021, 13, 5874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, P.A.; Bracken, C.P.; Bert, A.G.; Goodall, G.J. MicroRNAs as regulators of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Cycle. 2008, 7, 3112–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Lamouille, S.; Derynck, R. TGF-beta-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, M.J.; Moorehead, R.A. The miR-200 family in normal mammary gland development. BMC Dev Biol. 2021, 21, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Experimental Condition | Acronym |
|---|---|
| Adipocytes | A |
| Adipocytes and hormones | A+H |
| Adipocytes and MEOs (embedded in Matrigel) | A+MEO |
| Adipocytes and MEOs (embedded in Matrigel) and hormones | A+MEO+H |
| Adipocytes and Matrigel (without MEOs) | A+Matrix |
| Adipocytes and Matrigel (without MEOs) and hormones | A+Matrix+H |
| Target Gene | Assay ID |
|---|---|
| AdipoQ | Mm00456425_m1 |
| AdipoQ | Hs00977214_m1 |
| FGF | Mm01285715_m1 |
| β-casein | Mm00839913_m1 |
| c-Myc | Mm01192721_m1 |
| E-cadherin | Mm01247357_m1 |
| ELF5 | Mm00468732_m1 |
| ELF5 | Hs00154971_m1 |
| GATA3 | Mm00484683_m1 |
| IGF | Mm00439564_m1 |
| K18 | Mm01601704_g1 |
| KLF4 | Mm00516104_m1 |
| NANOG | Mm02384862_g1 |
| Oct3/4 | Mm00305917_g1 |
| Plin1 | Mm00558672_m1 |
| Plin1 | Hs00160173_m1 |
| RANK-L | Mm00441906_m1 |
| SPP1 | Mm00436767_m1 |
| TBP | Mm00446973_m1 |
| TGFβ | Mm01178820_m1 |
| WAP | Mm00839664_m1 |
| Wnt6 | Mm00437353_m1 |
| Antibodies | Host * | Diluition | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| E-cadherin | R | 1:200 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology/sc-7870 |
| ELF5 | R | 1:200 | Thermo Fisher/720380 |
| β-casein | R | 1:100 | Thermo Fisher/PA5-109599 |
| β-Tubulin | M | 1:800 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology/sc-5274 |
| Conjugated to | React * | Dilution | Source | ID |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peroxidase | M | 1:5000 | Jackson ImmunoResearch | 715-036-150 |
| Peroxidase | R | 1:1000 | Vector Laboratories | PI-1000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perugini, J.; Smorlesi, A.; Acciarini, S.; Mondini, E.; Colleluori, G.; Pirazzini, C.; Kwiatkowska, K.M.; Garagnani, P.; Franceschi, C.; Zingaretti, M.C.; et al. Adipo-Epithelial Transdifferentiation in In Vitro Models of the Mammary Gland. Cells 2024, 13, 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110943
Perugini J, Smorlesi A, Acciarini S, Mondini E, Colleluori G, Pirazzini C, Kwiatkowska KM, Garagnani P, Franceschi C, Zingaretti MC, et al. Adipo-Epithelial Transdifferentiation in In Vitro Models of the Mammary Gland. Cells. 2024; 13(11):943. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110943
Chicago/Turabian StylePerugini, Jessica, Arianna Smorlesi, Samantha Acciarini, Eleonora Mondini, Georgia Colleluori, Chiara Pirazzini, Katarzyna Malgorzata Kwiatkowska, Paolo Garagnani, Claudio Franceschi, Maria Cristina Zingaretti, and et al. 2024. "Adipo-Epithelial Transdifferentiation in In Vitro Models of the Mammary Gland" Cells 13, no. 11: 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110943
APA StylePerugini, J., Smorlesi, A., Acciarini, S., Mondini, E., Colleluori, G., Pirazzini, C., Kwiatkowska, K. M., Garagnani, P., Franceschi, C., Zingaretti, M. C., Dani, C., Giordano, A., & Cinti, S. (2024). Adipo-Epithelial Transdifferentiation in In Vitro Models of the Mammary Gland. Cells, 13(11), 943. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13110943








