Identification of Genomic Predictors of Muscle Fiber Size
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Approval
2.2. Study Participants
2.2.1. The Russian Cohorts
2.2.2. The Japanese Cohorts
2.2.3. The UK Biobank Cohort
2.3. Assessment of the Cross-Sectional Area (CSA) of Fast-Twitch Muscle Fibers
2.4. Genotyping
2.4.1. Russian Study
2.4.2. Japanese Study
2.5. Weightlifting Performance Measurement
2.6. Handgrip Strength Measurement
2.7. Search for Genotype–Phenotype Associations Using UK Biobank
2.8. Analysis of Association of Muscle Fiber Size-Related SNPs with Gene Expression
2.9. Analysis of the Effects of Knockouts of Implicated Genes on Lean Mass and Strength in Mice
2.10. Analysis of the Effects of Strength Training on the Expression of Muscle Fiber Size-Related Genes
2.11. Statistical Analyses
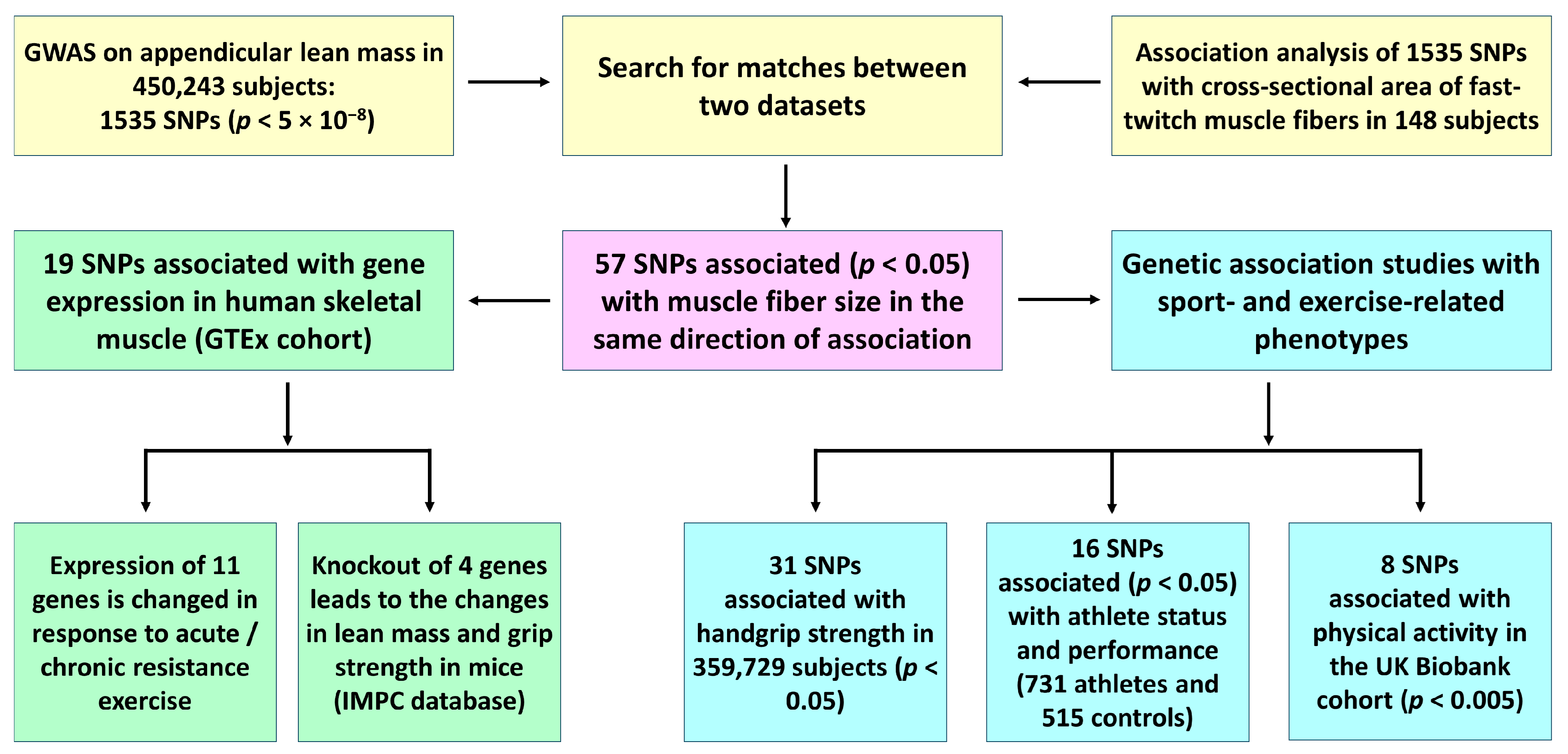
3. Results
3.1. Genomic Predictors of Both Appendicular Lean Mass and Muscle Fiber Size
3.2. Genetic Association Studies with Sport- and Exercise-Related Phenotypes
3.3. Bioinformatic Analyses Using Publicly Available Data
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, J.A.B.; Murach, K.A.; Dyar, K.A.; Zierath, J.R. Exercise metabolism and adaptation in skeletal muscle. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2023, 24, 607–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frontera, W.R.; Ochala, J. Skeletal muscle: A brief review of structure and function. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 96, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.; Balshaw, T.G.; Massey, G.J.; Maeo, S.; Lanza, M.B.; Johnston, M.; Allen, S.J.; Folland, J.P. The Muscle Morphology of Elite Sprint Running. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2021, 53, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.; Balshaw, T.G.; Massey, G.J.; Maeo, S.; Lanza, M.B.; Haug, B.; Johnston, M.; Allen, S.J.; Folland, J.P. The Muscle Morphology of Elite Female Sprint Running. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 2138–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trezise, J.; Blazevich, A.J. Anatomical and Neuromuscular Determinants of Strength Change in Previously Untrained Men Following Heavy Strength Training. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugisaki, N.; Kobayashi, K.; Tsuchie, H.; Kanehisa, H. Associations Between Individual Lower-Limb Muscle Volumes and 100-m Sprint Time in Male Sprinters. Int. J. Sports Physiol. Perform. 2018, 13, 214–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostron, Z.P.; Green, R.A.; Kingsley, M.; Zacharias, A. Associations Between Measures of Physical Activity and Muscle Size and Strength: A Systematic Review. Arch. Rehabil. Res. Clin. Transl. 2021, 3, 100124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanza, M.B.; Martins-Costa, H.C.; De Souza, C.C.; Lima, F.V.; Diniz, R.C.R.; Chagas, M.H. Muscle volume vs. anatomical cross-sectional area: Different muscle assessment does not affect the muscle size-strength relationship. J. Biomech. 2022, 132, 110956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamparo, P.; Minetti, A.E.; di Prampero, P.E. Interplay among the changes of muscle strength, cross-sectional area and maximal explosive power: Theory and facts. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 88, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.M.; Williams, H.; Ryan, K.J.; Wilson, T.L.; Daniel, Z.C.; Mareko, M.H.; Emes, R.D.; Harris, D.W.; Jones, S.; Wattis, J.A.; et al. Mitochondrial phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (PEPCK-M) and serine biosynthetic pathway genes are co-ordinately increased during anabolic agent-induced skeletal muscle growth. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, T.; Figueiredo, V.C.; Mobley, C.B.; McCarthy, J.J.; Vechetti, I.J., Jr. Evidence of myomiR regulation of the pentose phosphate pathway during mechanical load-induced hypertrophy. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e15137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumert, P.; Mäntyselkä, S.; Schönfelder, M.; Heiber, M.; Jacobs, M.J.; Swaminathan, A.; Minderis, P.; Dirmontas, M.; Kleigrewe, K.; Meng, C.; et al. Skeletal muscle hypertrophy rewires glucose metabolism: An experimental investigation and systematic review. J. Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle 2024, 15, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubal, M.J.; Gordish-Dressman, H.; Thompson, P.D.; Price, T.B.; Hoffman, E.P.; Angelopoulos, T.J.; Gordon, P.M.; Moyna, N.M.; Pescatello, L.S.; Visich, P.S.; et al. Variability in muscle size and strength gain after unilateral resistance training. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2005, 37, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Erskine, R.M.; Jones, D.A.; Williams, A.G.; Stewart, C.E.; Degens, H. Inter-individual variability in the adaptation of human muscle specific tension to progressive resistance training. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2010, 110, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahtiainen, J.P.; Walker, S.; Peltonen, H.; Holviala, J.; Sillanpää, E.; Karavirta, L.; Sallinen, J.; Mikkola, J.; Valkeinen, H.; Mero, A.; et al. Heterogeneity in resistance training-induced muscle strength and mass responses in men and women of different ages. Age 2016, 38, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stec, M.J.; Kelly, N.A.; Many, G.M.; Windham, S.T.; Tuggle, S.C.; Bamman, M.M. Ribosome biogenesis may augment resistance training-induced myofiber hypertrophy and is required for myotube growth in vitro. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 310, E652–E661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavin, K.M.; Bell, M.B.; McAdam, J.S.; Peck, B.D.; Walton, R.G.; Windham, S.T.; Tuggle, S.C.; Long, D.E.; Kern, P.A.; Peterson, C.A.; et al. Muscle transcriptional networks linked to resistance exercise training hypertrophic response heterogeneity. Physiol. Genom. 2021, 53, 206–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero, J.-L.L.; Barrey, E. Heritabilities and genetic and phenotypic parameters for gluteus medius muscle fibre type composition, fibre size and capillaries in purebred Spanish horses. Livest. Prod. Sci. 2001, 72, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Fan, W.; Xu, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, W.; Guo, Z.; Huang, W.; Zhou, Z.; Hou, S. Genome-wide association studies demonstrate that TASP1 contributes to increased muscle fiber diameter. Heredity 2021, 126, 991–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmetov, I.I.; Mozhayskaya, I.A.; Lyubaeva, E.V.; Vinogradova, O.L.; Rogozkin, V.A. PPARG Gene polymorphism and locomotor activity in humans. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 146, 630–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, E.C.R.; Semenova, E.A.; Bondareva, E.A.; Andryushchenko, L.B.; Larin, A.K.; Cięszczyk, P.; Generozov, E.V.; Ahmetov, I.I. Association of Genetically Predicted BCAA Levels with Muscle Fiber Size in Athletes Consuming Protein. Genes 2022, 13, 397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grishina, E.E.; Zmijewski, P.; Semenova, E.A.; Cięszczyk, P.; Humińska-Lisowska, K.; Michałowska-Sawczyn, M.; Maculewicz, E.; Crewther, B.; Orysiak, J.; Kostryukova, E.S.; et al. Three DNA Polymorphisms Previously Identified as Markers for Handgrip Strength Are Associated with Strength in Weightlifters and Muscle Fiber Hypertrophy. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2019, 33, 2602–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seaborne, R.A.; Hughes, D.C.; Turner, D.C.; Owens, D.J.; Baehr, L.M.; Gorski, P.; Semenova, E.A.; Borisov, O.V.; Larin, A.K.; Popov, D.V.; et al. UBR5 is a novel E3 ubiquitin ligase involved in skeletal muscle hypertrophy and recovery from atrophy. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 3727–3749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilherme, J.P.L.; Semenova, E.A.; Borisov, O.V.; Larin, A.K.; Moreland, E.; Generozov, E.V.; Ahmetov, I.I. Genomic predictors of testosterone levels are associated with muscle fiber size and strength. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2022, 122, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgay, C.; Kasakolu, A.; Kazan, H.H.; Mijaica, R.; Zorba, E.; Akman, O.; Bayraktar, I.; Ekmekci, R.; Koncagul, S.; Ulucan, K.; et al. Exome-Wide Association Study of Competitive Performance in Elite Athletes. Genes 2023, 14, 660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdijk, L.B.; Snijders, T.; Beelen, M.; Savelberg, H.H.; Meijer, K.; Kuipers, H.; Van Loon, L.J. Characteristics of muscle fiber type are predictive of skeletal muscle mass and strength in elderly men. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2010, 58, 2069–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Y.F.; Liu, Y.Z.; Yang, X.L.; Zhang, H.; Feng, G.J.; Wei, X.T.; Zhang, L. The genetic architecture of appendicular lean mass characterized by association analysis in the UK Biobank study. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, E.A.; Pranckevičienė, E.; Bondareva, E.A.; Gabdrakhmanova, L.J.; Ahmetov, I.I. Identification and Characterization of Genomic Predictors of Sarcopenia and Sarcopenic Obesity Using UK Biobank Data. Nutrients 2023, 15, 758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmetov, I.I.; Hakimullina, A.M.; Popov, D.V.; Lyubaeva, E.V.; Missina, S.S.; Vinogradova, O.L.; Williams, A.G.; Rogozkin, V.A. Association of the VEGFR2 gene His472Gln polymorphism with endurance-related phenotypes. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2009, 107, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khelaifi, F.; Yousri, N.A.; Diboun, I.; Semenova, E.A.; Kostryukova, E.S.; Kulemin, N.A.; Borisov, O.V.; Andryushchenko, L.B.; Larin, A.K.; Generozov, E.V.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Reveals a Novel Association Between MYBPC3 Gene Polymorphism, Endurance Athlete Status, Aerobic Capacity and Steroid Metabolism. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, N.; Moreland, E.; Homma, H.; Semenova, E.A.; Saito, M.; Larin, A.K.; Kobatake, N.; Yusupov, R.A.; Okamoto, T.; Nakazato, K.; et al. Genes and Weightlifting Performance. Genes 2022, 13, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Open Targets Genetics. Available online: https://genetics.opentargets.org (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- GTEx Portal. Available online: https://gtexportal.org/home/index.html (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- The International Mouse Phenotyping Consortium (IMPC) Database. Available online: https://www.mousephenotype.org/data/search (accessed on 25 May 2024).
- Pillon, N.J.; Gabriel, B.M.; Dollet, L.; Smith, J.A.B.; Sardón Puig, L.; Botella, J.; Bishop, D.J.; Krook, A.; Zierath, J.R. Transcriptomic profiling of skeletal muscle adaptations to exercise and inactivity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilwik, R.; Snijders, T.; Leenders, M.; Groen, B.B.; van Kranenburg, J.; Verdijk, L.B.; van Loon, L.J. The decline in skeletal muscle mass with aging is mainly attributed to a reduction in type II muscle fiber size. Exp. Gerontol. 2013, 48, 492–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guilherme, J.P.L.F.; Lancha, A.H., Jr. Total genotype score and athletic status: An exploratory cross-sectional study of a Brazilian athlete cohort. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2020, 84, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabbasov, R.T.; Arkhipova, A.A.; Borisova, A.V.; Hakimullina, A.M.; Kuznetsova, A.V.; Williams, A.G.; Day, S.H.; Ahmetov, I.I. The HIF1A Gene Pro582Ser Polymorphism in Russian Strength Athletes. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2013, 27, 2055–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciejewska-Skrendo, A.; Sawczuk, M.; Cięszczyk, P.; Ahmetov, I.I. Genes and power athlete status. In Sports, Exercise, and Nutritional Genomics: Current Status and Future Directions; Barh, D., Ahmetov, I., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 41–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, E.A.; Miyamoto-Mikami, E.; Akimov, E.B.; Al-Khelaifi, F.; Murakami, H.; Zempo, H.; Kostryukova, E.S.; Kulemin, N.A.; Larin, A.K.; Borisov, O.V.; et al. The association of HFE gene H63D polymorphism with endurance athlete status and aerobic capacity: Novel findings and a meta-analysis. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2020, 120, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Mei, T.; Duan, J.; Yan, X.; McNaughton, L.; He, Z. Genome-wide Association Study of Exercise-induced Skeletal Muscle Hypertrophy and the Construction of Predictive Model. Physiol. Genom. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semenova, E.A.; Hall, E.C.R.; Ahmetov, I.I. Genes and Athletic Performance: The 2023 Update. Genes 2023, 14, 1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Nearest Gene | SNP | Allele 1/Allele 2 | Favorable Allele | p Value (app. Lean Mass) | p Value (CSA of Fast-Twitch Muscle Fibers) | p Value (Phenotype) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AKAP13 | rs11632750 | A/C | C | 3.9 × 10−37 | 0.032 | 0.012 (HS); 0.048 (WL); 0.035 (WP); 0.00016 (PA) |
| LRP5 | rs2306862 | C/T | C | 1.4 × 10−46 | 0.041 | 3.4 × 10−9 (HS); 0.03 (POW); 0.0007 (PA) |
| CENPW | rs853985 | C/T | C | 4.7 × 10−121 | 0.017 | 0.000016 (HS); 0.014 (SPR); 0.0027 (WAL) |
| GIP | rs4794005 | G/A | A | 5.3 × 10−22 | 0.025 | 0.00043 (HS); 0.000094 (PA); 0.0011 (WAL) |
| IGFBP3 | rs13237404 | G/A | G | 5.6 × 10−27 | 0.045 | 0.0001 (HS); 0.006 (WP); 0.03 (WRS) |
| NADK | rs12040325 | G/A | A | 1.0 × 10−10 | 0.027 | 0.0013 (HS); 0.011 (SPR); 0.0035 (PA) |
| HMGA2 | rs1480474 | A/G | A | 1.1 × 10−139 | 0.023 | 1.5 × 10−12 (HS); 0.0042 (PA) |
| VPS52 | rs213225 | G/A | A | 6.8 × 10−9 | 0.00008 | 0.038 (SPR); 0.00068 (PA) |
| PRLR | rs6897259 | T/C | C | 9.6 × 10−14 | 0.018 | 0.00018 (HS); 0.03 (STR) |
| ADAMTS14 | rs1420524 | T/A | A | 1.0 × 10−12 | 0.042 | 0.007 (WL); 0.023 (STR) |
| MERTK | rs55812028 | C/T | T | 3.7 × 10−13 | 0.019 | 0.016 (WL); 0.049 (STR) |
| L3MBTL3 | rs7740107 | T/A | T | 7.5 × 10−99 | 0.046 | 6.3 × 10−21 (HS) |
| PHF20 | rs6121042 | C/T | C | 1.3 × 10−114 | 0.048 | 3.5 × 10−13 (HS) |
| TSBP1 | rs9268249 | T/A | T | 9.1 × 10−42 | 0.016 | 6.0 × 10−9 (HS) |
| CEP120 | rs34732995 | C/CTA | C | 2.2 × 10−55 | 0.017 | 4.6 × 10−8 (HS) |
| FIS1 | rs4729677 | A/G | A | 1.2 × 10−10 | 0.042 | 9.1 × 10−7 (HS) |
| MECOM | rs2115959 | A/C | C | 5.7 × 10−14 | 0.038 | 0.0000015 (HS) |
| DCST1 | rs150352963 | C/G | G | 1.3 × 10−17 | 0.042 | 0.000025 (HS) |
| IGF1 | rs35762 | T/C | T | 8.4 × 10−21 | 0.002 | 0.000055 (HS) |
| CAMKMT | rs343954 | T/C | C | 5.4 × 10−10 | 0.044 | 0.000062 (HS) |
| ZFAT | rs137957419 | I/D | D | 1.7 × 10−18 | 0.024 | 0.00012 (HS) |
| MLST8 | rs26866 | A/G | G | 2.9 × 10−28 | 0.006 | 0.00022 (HS) |
| NUDT6 | rs12509014 | C/T | C | 5.4 × 10−30 | 0.038 | 0.0007 (SPR) |
| FOXD2 | rs10749868 | C/T | C | 4.8 × 10−9 | 0.005 | 0.00085 (HS) |
| NDUFS4 | rs7727774 | A/G | A | 7.5 × 10−13 | 0.013 | 0.00094 (HS) |
| ATAD2B | rs4665244 | A/G | G | 1.5 × 10−31 | 0.027 | 0.001 (HS) |
| NTAN1 | rs3803573 | C/T | C | 1.8 × 10−15 | 0.019 | 0.0011 (HS) |
| TREH | rs472419 | C/T | T | 8.8 × 10−11 | 0.012 | 0.0013 (PA) |
| NOTCH4 | rs8192589 | G/T | T | 5.4 × 10−51 | 0.010 | 0.0023 (HS) |
| C4A | rs693906 | G/C | C | 2.2 × 10−54 | 0.015 | 0.0029 (HS) |
| BTNL2 | rs2227138 | C/T | T | 7.0 × 10−44 | 0.026 | 0.0036 (HS) |
| PMAIP1 | rs8086627 | C/A | A | 2.0 × 10−45 | 0.017 | 0.005 (HS) |
| HLA-DQA1 | rs9271657 | T/C | C | 4.1 × 10−34 | 0.046 | 0.006 (HS) |
| RAB18 | rs2477317 | A/G | G | 3.3 × 10−11 | 0.034 | 0.0065 (SPR) |
| FERMT1 | rs6054078 | A/C | C | 1.6 × 10−9 | 0.019 | 0.01 (WRS) |
| ADAMTS6 | rs9291834 | T/C | T | 2.8 × 10−8 | 0.019 | 0.012 (HS) |
| BOC | rs9810734 | A/T | T | 2.3 × 10−8 | 0.035 | 0.02 (STR) |
| E2F7 | rs10779153 | T/A | A | 1.5 × 10−9 | 0.00007 | 0.024 (SPR) |
| PITX2 | rs2595104 | T/G | T | 1.2 × 10−11 | 0.048 | 0.033 (HS) |
| MACF1 | rs2484749 | A/G | A | 4.9 × 10−10 | 0.046 | 0.038 (SPS) |
| MAPK1 | rs34550586 | A/G | G | 1.5 × 10−9 | 0.021 | 0.041 (WL) |
| RUNX2 | rs1321080 | G/T | G | 2.0 × 10−16 | 0.021 | 0.049 (HS) |
| CASZ1 | rs11121615 | C/T | C | 3.3 × 10−23 | 0.036 | NS |
| PABPC4 | rs3768320 | T/C | T | 3.0 × 10−10 | 0.034 | NS |
| PLPP3 | rs12140284 | T/C | C | 3.3 × 10−33 | 0.028 | NS |
| CIART | rs2318761 | A/G | A | 8.2 × 10−17 | 0.020 | NS |
| RPS6KC1 | rs182673203 | C/T | T | 6.2 × 10−11 | 0.029 | NS |
| DIS3L2 | rs79057767 | A/G | G | 3.2 × 10−21 | 0.004 | NS |
| CMSS1 | rs35225638 | T/TG | TG | 4.8 × 10−12 | 0.045 | NS |
| RBPJ | rs3109841 | G/T | T | 5.9 × 10−14 | 0.026 | NS |
| ADAMTS3 | rs72852033 | T/C | T | 2.4 × 10−10 | 0.006 | NS |
| WDR70 | rs4869505 | G/C | C | 6.5 × 10−31 | 0.032 | NS |
| VTI1A | rs11196067 | A/T | T | 2.1 × 10−9 | 0.004 | NS |
| STXBP6 | rs61981417 | C/T | C | 2.3 × 10−8 | 0.037 | NS |
| PAQR5 | rs2415040 | G/C | G | 1.0 × 10−8 | 0.028 | NS |
| TLE3 | rs2291982 | C/A | A | 6.4 × 10−9 | 0.039 | NS |
| NTN1 | rs7223668 | A/G | G | 2.2 × 10−11 | 0.049 | NS |
| Gene/Near Gene | SNP | Favorable Allele | Effect of Favorable Allele on Gene Expression |
|---|---|---|---|
| NADK | rs12040325 | A | NADK ↑ (β = 0.11; p = 1.3 × 10−8) |
| MACF1 | rs2484749 | A | MACF1 ↑ (β = 0.13; p = 0.00011) |
| PABPC4 | rs3768320 | T | PABPC4 ↓ (β = −0.12; p = 0.0000013) |
| CIART | rs2318761 | A | CIART ↓ (β = −0.068; p = 0.05) |
| ATAD2B | rs4665244 | G | ATAD2B ↑ (β = 0.045; p = 0.05) |
| CAMKMT | rs343954 | C | CAMKMT ↑ (β = 0.14; p = 0.0011) |
| NUDT6 | rs12509014 | C | NUDT6 ↑ (β = 0.20; p = 1.5 × 10−13) |
| NDUFS4 | rs7727774 | A | NDUFS4 ↓ (β = −0.043; p = 0.0091) |
| CEP120 | rs34732995 | C | CEP120 ↑ (β = 0.075; p = 0.0011) |
| C4A | rs693906 | C | C4A ↓ (β = −0.57; p = 8.2 × 10−22) |
| NOTCH4 | rs8192589 | T | NOTCH4 ↓ (β = −0.34; p = 5.2 × 10−11) |
| L3MBTL3 | rs7740107 | T | L3MBTL3 ↑ (β = 0.25; p = 6.5 × 10−10) |
| IGFBP3 | rs13237404 | G | IGFBP3 ↓ (β = −0.14; p = 0.0054) |
| AKAP13 | rs11632750 | C | AKAP13 ↓ (β = −0.051; p = 0.00027) |
| MLST8 | rs26866 | G | MLST8 ↑ (β = 0.24; p = 4.6 × 10−21) |
| NTAN1 | rs3803573 | C | NTAN1 ↑ (β = 0.072; p = 0.0031) |
| FERMT1 | rs6054078 | C | FERMT1 ↓ (β = −0.095; p = 0.024) |
| PHF20 | rs6121042 | C | PHF20 ↑ (β = 0.045; p = 0.037) |
| MAPK1 | rs34550586 | G | MAPK1 ↓ (β = −0.15; p = 5.0 × 10−10) |
| Gene/Near Gene | Effect of RE on Gene Expression | Effect of RT on Gene Expression |
|---|---|---|
| NADK | NADK ↑ | NS |
| MACF1 | MACF1 ↑ | MACF1 ↑ |
| PABPC4 | NS | PABPC4 ↓ |
| CIART | CIART ↓ | CIART ↓ |
| CAMKMT | CAMKMT ↑ | NS |
| NUDT6 | NS | NUDT6 ↑ |
| NDUFS4 | NS | NDUFS4 ↓ |
| NOTCH4 | NOTCH4 ↓ | NS |
| AKAP13 | NS | AKAP13 ↓ |
| NTAN1 | NS | NTAN1 ↑ |
| PHF20 | PHF20 ↑ | NS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guilherme, J.P.L.F.; Semenova, E.A.; Kikuchi, N.; Homma, H.; Kozuma, A.; Saito, M.; Zempo, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Kobatake, N.; Nakazato, K.; et al. Identification of Genomic Predictors of Muscle Fiber Size. Cells 2024, 13, 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13141212
Guilherme JPLF, Semenova EA, Kikuchi N, Homma H, Kozuma A, Saito M, Zempo H, Matsumoto S, Kobatake N, Nakazato K, et al. Identification of Genomic Predictors of Muscle Fiber Size. Cells. 2024; 13(14):1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13141212
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuilherme, João Paulo L. F., Ekaterina A. Semenova, Naoki Kikuchi, Hiroki Homma, Ayumu Kozuma, Mika Saito, Hirofumi Zempo, Shingo Matsumoto, Naoyuki Kobatake, Koichi Nakazato, and et al. 2024. "Identification of Genomic Predictors of Muscle Fiber Size" Cells 13, no. 14: 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13141212
APA StyleGuilherme, J. P. L. F., Semenova, E. A., Kikuchi, N., Homma, H., Kozuma, A., Saito, M., Zempo, H., Matsumoto, S., Kobatake, N., Nakazato, K., Okamoto, T., John, G., Yusupov, R. A., Larin, A. K., Kulemin, N. A., Gazizov, I. M., Generozov, E. V., & Ahmetov, I. I. (2024). Identification of Genomic Predictors of Muscle Fiber Size. Cells, 13(14), 1212. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13141212








