Synthetic mRNAs Containing Minimalistic Untranslated Regions Are Highly Functional In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production of Synthetic Messenger RNA by In Vitro Transcription
2.2. Cells and Transfection
2.3. CAR T-Cell Generation
2.4. In Vitro Lysis Assay
2.5. Animals and In Vivo Imaging
3. Results
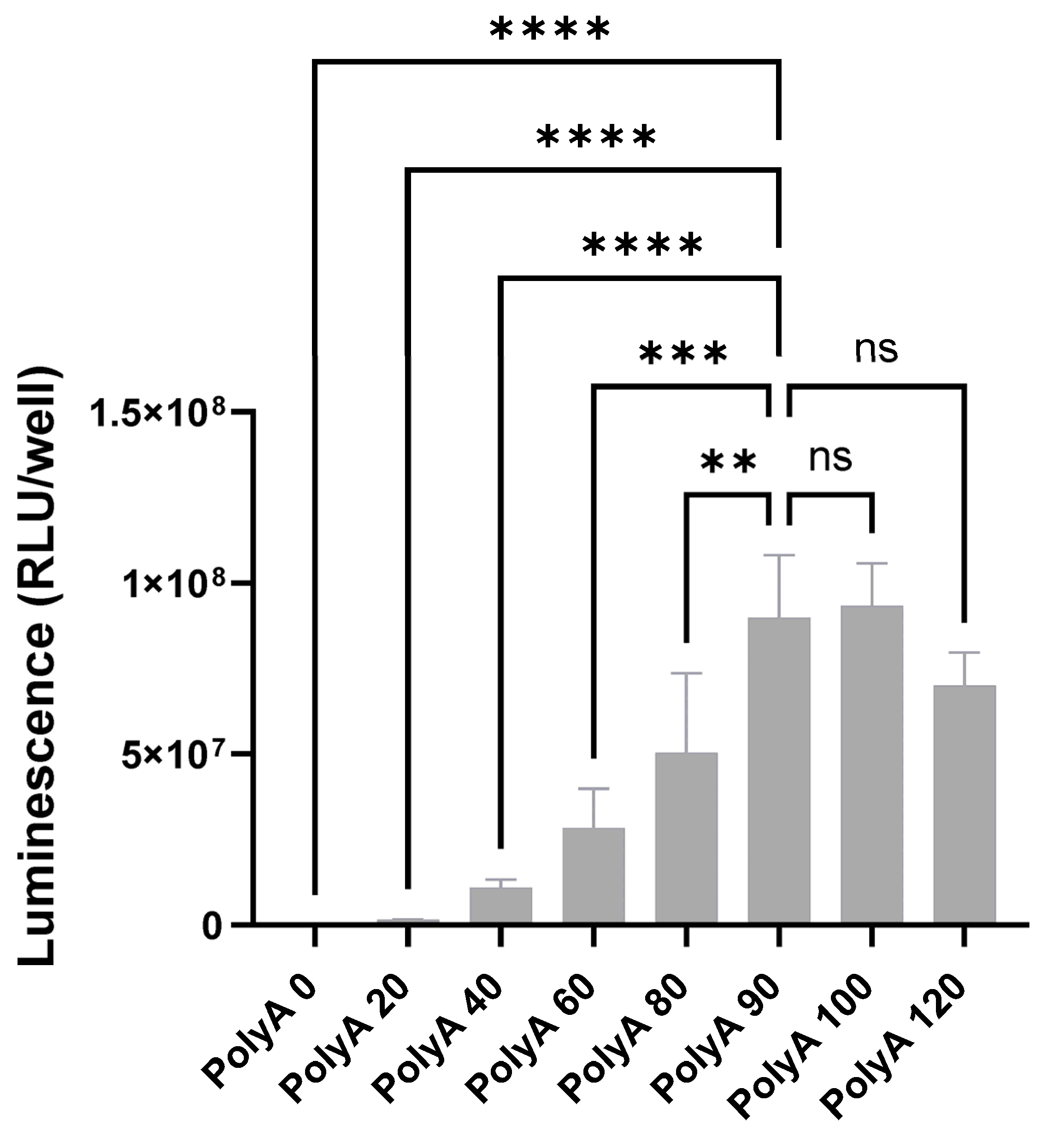
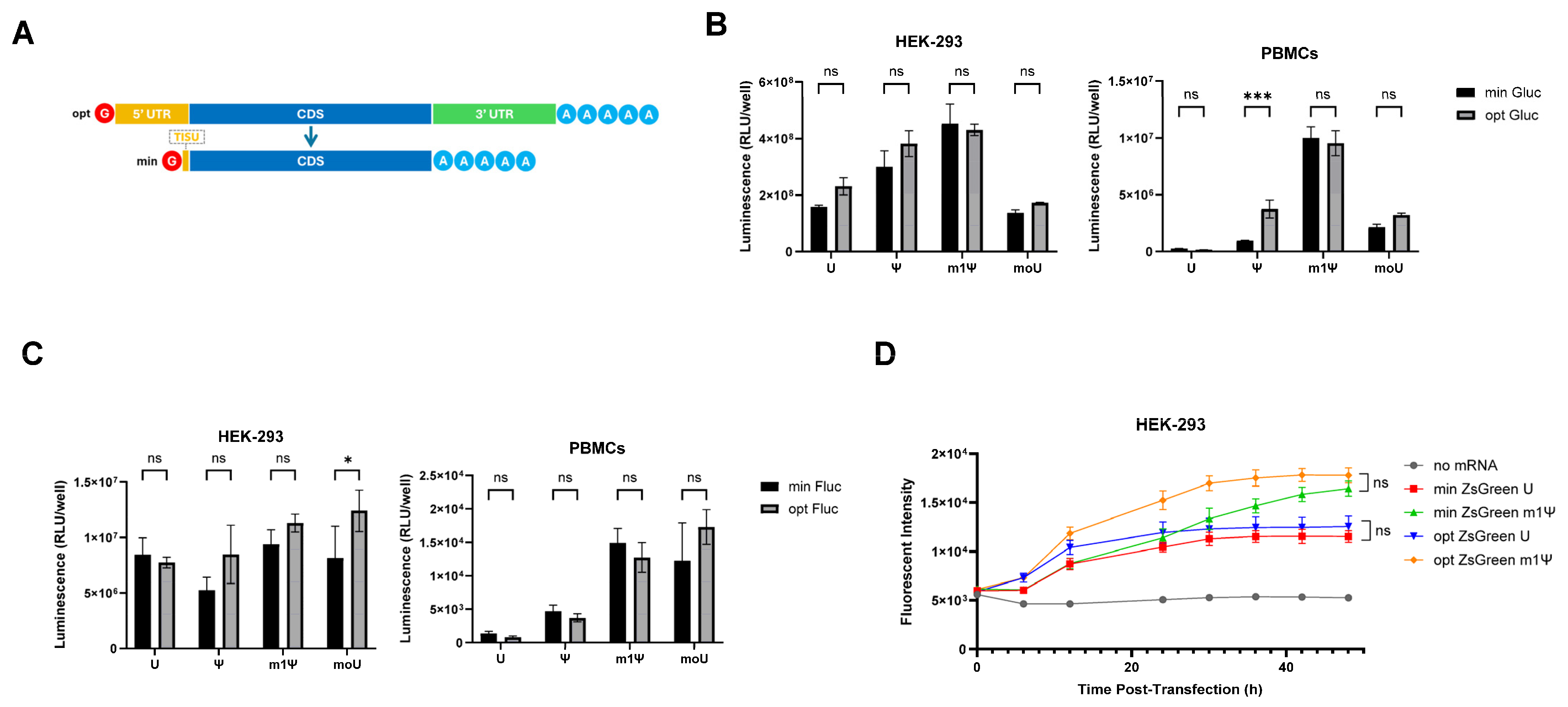
3.1. Minimal 5′ UTRs Are Compatible with the Translation of ivt mRNA
3.2. Comparing Minimised ivt mRNA (minRNA) to Classical Optimized ivt mRNAs
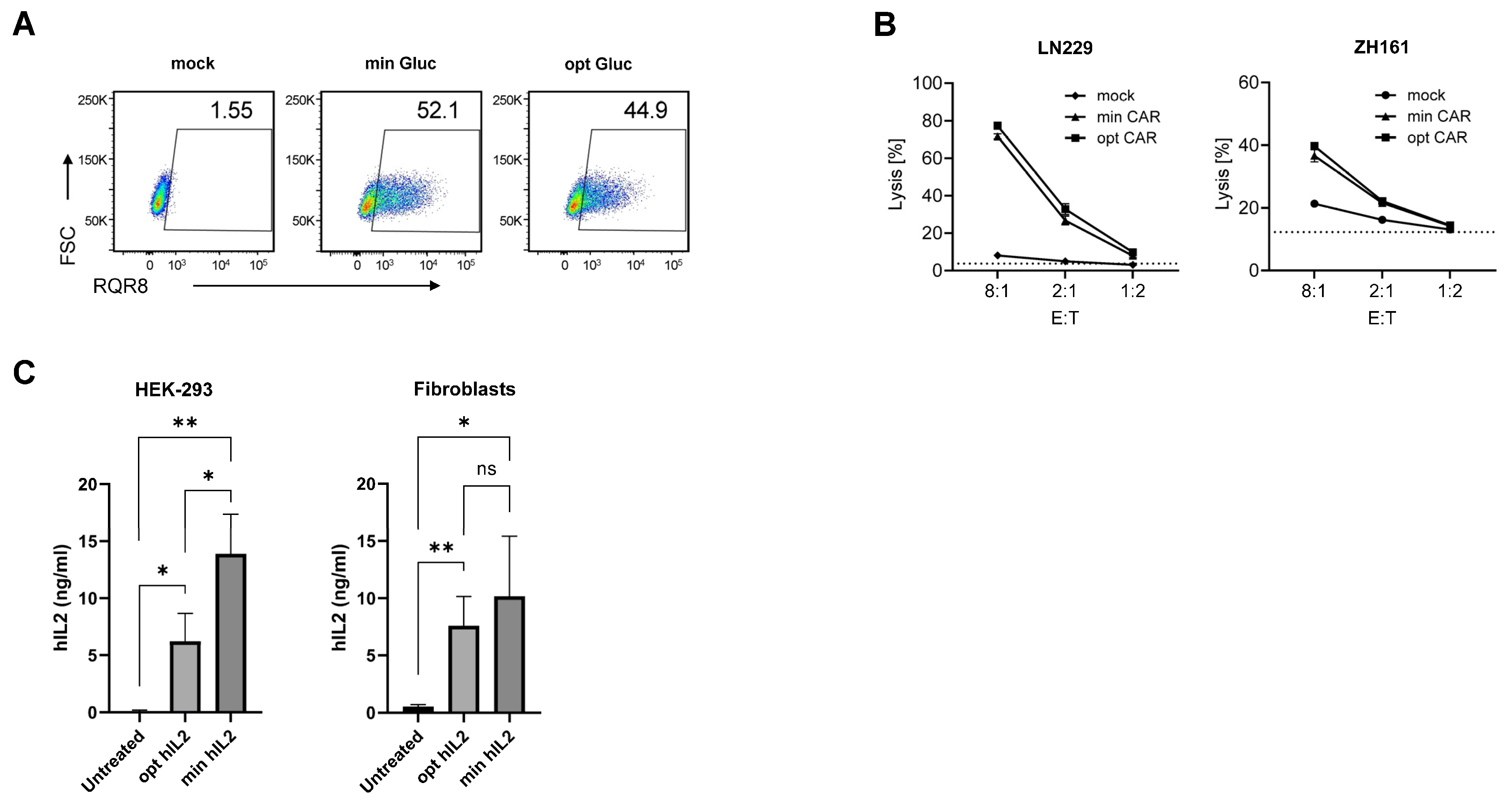
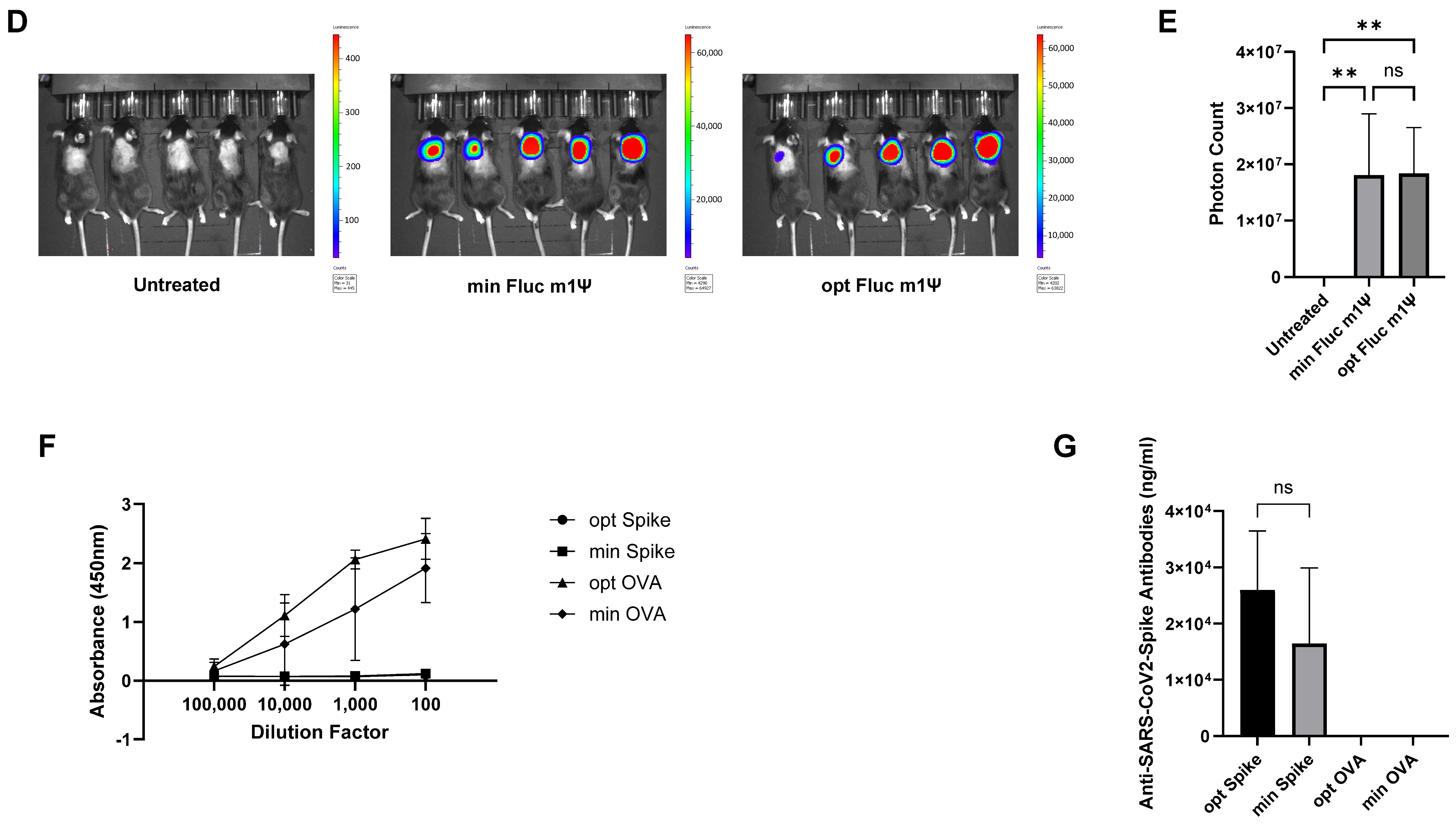
3.3. minRNA for Therapies and Vaccination
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sahin, U.; Kariko, K.; Tureci, Ö. mRNA-Based Therapeutics – Developing a New Class of Drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 759–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, K.; Grabowski, P.J.; Zaug, A.J.; Sands, J.; Gottschling, D.E.; Cech, T.R. Self-splicing RNA: Autoexcision and autocyclization of the ribosomal RNA intervening sequence of tetrahymena. Cell 1982, 31, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melton, D.; Krieg, P.; Rebagliati, M.; Maniatis, T.; Zinn, K.; Green, M. Efficientin vitrosynthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 7035–7056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, P.A.; Melton, D.A. Functional messenger RNAs are produced by SP6in vitrotranscription of cloned cDNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984, 12, 7057–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, J.A.; Malone, R.W.; Williams, P.; Chong, W.; Acsadi, G.; Jani, A.; Felgner, P.L. Direct gene transfer into mouse muscle in vivo. Science 1990, 247, 1465–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carralot, J.-P.; Probst, J.; Hoerr, I.; Scheel, B.; Teufel, R.; Jung, G.; Rammensee, H.-G.; Pascolo, S. Polarization of immunity induced by direct injection of naked sequence-stabilized mRNA vaccines. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2004, 61, 2418–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoerr, I.; Obst, R.; Rammensee, H.G.; Jung, G. In vivo application of RNA leads to induction of specific cytotoxic T lym-phocytes and antibodies. Eur. J. Immunol. 2000, 30, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carralot, J.-P.; Weide, B.; Schoor, O.; Probst, J.; Scheel, B.; Teufel, R.; Hoerr, I.; Garbe, C.; Rammensee, H.-G.; Pascolo, S. Production and characterization of amplified tumor-derived cRNA libraries to be used as vaccines against metastatic melanomas. Genet. Vaccines Ther. 2005, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weide, B.; Carralot, J.-P.; Reese, A.; Scheel, B.; Eigentler, T.K.; Hoerr, I.; Rammensee, H.-G.; Garbe, C.; Pascolo, S. Results of the First Phase I/II Clinical Vaccination Trial with Direct Injection of mRNA. J. Immunother. 2008, 31, 180–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuhn, A.N.; Diken, M.; Kreiter, S.; Vallazza, B.; Türeci, Ö.; Sahin, U. Determinants of intracellular RNA pharmacokinetics: Implications for RNA-based immunotherapeutics. RNA Biol. 2011, 8, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, E.E.; Frenck, R.W., Jr.; Falsey, A.R.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Neuzil, K.; Mulligan, M.J.; Bailey, R.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of Two RNA-Based COVID-19 Vaccine Candidates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2439–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbett, K.S.; Edwards, D.K.; Leist, S.R.; Abiona, O.M.; Boyoglu-Barnum, S.; Gillespie, R.A.; Himansu, S.; Schäfer, A.; Ziwawo, C.T.; DiPiazza, A.T.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine design enabled by prototype pathogen preparedness. Nature 2020, 586, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tusup, M.; French, L.E.; Guenova, E.; Kundig, T.M.; Pascolo, S. Optimizing the Functionality of in vitro-Transcribed mRNA. Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2018, 1, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Jarzebska, N.T.; Frei, J.; Lauchli, S.; French, L.E.; Guenova, E.; Gouttefangeas, C.; Kündig, T.M.; Mellett, M.; Pascolo, S. Lipofection with synthetic mRNA as a simple method for T-Cell immunomonitoring. Viruses 2021, 13, 1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meister, H.; Look, T.; Roth, P.; Pascolo, S.; Sahin, U.; Lee, S.; Hale, B.D.; Snijder, B.; Regli, L.; Ravi, V.M.; et al. Multifunctional mRNA-Based CAR T Cells Display Promising Antitumor Activity Against Glioblastoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 28, 4747–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarzebska, N.T.; Frei, J.; Mellett, M.; Kündig, T.M.; Pascolo, S.; Reichmuth, A.M. A Basic Method for Formulating mRNA-Lipid Nanoparticle Vaccines in the Lab. Methods Mol. Biol. 2024, 2786, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfakess, R.; Dikstein, R. A Translation Initiation Element Specific to mRNAs with Very Short 5′UTR that Also Regulates Transcription. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tusup, M.; Kundig, T.; Pascolo, S. An eIF4G-recruiting aptamer increases the functionality of in vitro transcribed mRNA. EPH-Int. J. Med. Health Sci. 2017, 3, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, B.; Kokalaki, E.; Mekkaoui, L.; Thomas, S.; Straathof, K.; Flutter, B.; Marin, V.; Marafioti, T.; Chakraverty, R.; Linch, D.; et al. A highly compact epitope-based marker/suicide gene for easier and safer T-cell therapy. Blood 2014, 124, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, J.D.; Diken, M.; Suchan, M.; Streuber, M.; Diken, E.; Kolb, L.; Allnoch, L.; Vascotto, F.; Peters, D.; Beißert, T.; et al. Long-lasting mRNA-encoded interleukin-2 restores CD8+ T cell neoantigen immunity in MHC class I-deficient cancers. Cancer Cell 2024, 42, 568–582.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Picciotto, S.; DeVita, N.; Hsiao, C.J.; Honan, C.; Tse, S.-W.; Nguyen, M.; Ferrari, J.D.; Zheng, W.; Wipke, B.T.; Huang, E. Selective activation and expansion of regulatory T cells using lipid encapsulated mRNA encoding a long-acting IL-2 mutein. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, J.D.; Reidenbach, D.; Salomon, N.; Sahin, U.; Türeci, Ö.; Vormehr, M.; Kranz, L.M. mRNA therapeutics in cancer immu-notherapy. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Niessen, A.G.O.; Poleganov, M.A.; Rechner, C.; Plaschke, A.; Kranz, L.M.; Fesser, S.; Diken, M.; Löwer, M.; Vallazza, B.; Beissert, T.; et al. Improving mRNA-Based Therapeutic Gene Delivery by Expression-Augmenting 3′ UTRs Identified by Cellular Library Screening. Mol. Ther. 2018, 27, 824–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; More, K.R.; Ojha, A.; Jackson, C.B.; Quinlan, B.D.; Li, H.; He, W.; Farzan, M.; Pardi, N.; Choe, H. Effect of mRNA-LNP components of two globally-marketed COVID-19 vaccines on efficacy and stability. npj Vaccines 2023, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henderson, J.M.; Ujita, A.; Hill, E.; Yousif-Rosales, S.; Smith, C.; Ko, N.; McReynolds, T.; Cabral, C.R.; Escamilla-Powers, J.R.; Houston, M.E. Cap 1 Messenger RNA Synthesis with Co-transcriptional CleanCap® Analog by In Vitro Transcription. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andries, O.; Mc Cafferty, S.; De Smedt, S.C.; Weiss, R.; Sanders, N.N.; Kitada, T. N1-methylpseudouridine-incorporated mRNA outperforms pseudouridine-incorporated mRNA by providing enhanced protein expression and reduced immunogenicity in mammalian cell lines and mice. J. Control. Release 2015, 217, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, R.; Lee, S.; Senavirathne, G.; Lai, E.C. microRNAs in action: Biogenesis, function and regulation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2023, 24, 816–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trulley, P.; Snieckute, G.; Bekker-Jensen, D.; Menon, M.B.; Freund, R.; Kotlyarov, A.; Olsen, J.V.; Diaz-Muñoz, M.D.; Turner, M.; Bekker-Jensen, S.; et al. Alternative Translation Initiation Generates a Functionally Distinct Isoform of the Stress-Activated Protein Kinase MK2. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 2859–2870.E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mangkalaphiban, K.; Fu, L.; Du, M.; Thrasher, K.; Keeling, K.M.; Bedwell, D.M.; Jacobson, A. Extended stop codon context predicts nonsense codon readthrough efficiency in human cells. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 2486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremsner, P.G.; Guerrero, R.A.A.; Arana-Arri, E.; Martinez, G.J.A.; Bonten, M.; Chandler, R.; Corral, G.; de Block, E.J.L.; Ecker, L.; Gabor, J.J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the CVnCoV SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine Candidate in Ten Countries in Europe and Latin America (HERALD): A Randomised, Observer-Blinded, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 2b/3 Trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022, 22, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kremsner, P.G.; Mann, P.; Kroidl, A.; Leroux-Roels, I.; Schindler, C.; Gabor, J.J.; Schunk, M.; Leroux-Roels, G.; Bosch, J.J.; Fendel, R.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of an mRNA-lipid nanoparticle vaccine candidate against SARS-CoV-2: A phase 1 randomized clinical trial. Wien. Klin. Wochenschr. 2021, 133, 931–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sáez-Llorens, X.; Lanata, C.; Aranguren, E.; Celis, C.R.; Cornejo, R.; DeAntonio, R.; Ecker, L.; Garrido, D.; Gil, A.I.; Gonzales, M.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of mRNA-LNP COVID-19 vaccine CVnCoV in Latin American adults: A phase 2 randomized study. Vaccine X 2022, 11, 100189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolz, O.-O.; Vahrenhorst, D.; Quintini, G.; Lemberg, C.; Koch, S.D.; Kays, S.-K.; Walz, L.; Kulkarni, N.; Fehlings, M.; Wengenmayer, P.; et al. Innate Responses to the Former COVID-19 Vaccine Candidate CVnCoV and Their Relation to Re-actogenicity and Adaptive Immunogenicity. Vaccines 2024, 12, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hồ, N.T.; Hughes, S.G.; Ta, V.T.; Phan, L.T.; Đỗ, Q.; Nguyễn, T.V.; Phạm, A.T.V.; Đặng, M.T.N.; Nguyễn, L.V.; Trịnh, Q.V.; et al. Safety, immunogenicity and efficacy of the self-amplifying mRNA ARCT-154 COVID-19 vaccine: Pooled phase 1, 2, 3a and 3b randomized, controlled trials. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 4081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Tang, X.; Chen, Y.; Chen, K.; Fan, N.; Xiao, W.; Zheng, Q.; Li, G.; Teng, Y.; Wu, M.; et al. mRNA-based therapeutics: Powerful and versatile tools to combat diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mamaghani, S.; Penna, R.R.; Frei, J.; Wyss, C.; Mellett, M.; Look, T.; Weiss, T.; Guenova, E.; Kündig, T.M.; Lauchli, S.; et al. Synthetic mRNAs Containing Minimalistic Untranslated Regions Are Highly Functional In Vitro and In Vivo. Cells 2024, 13, 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151242
Mamaghani S, Penna RR, Frei J, Wyss C, Mellett M, Look T, Weiss T, Guenova E, Kündig TM, Lauchli S, et al. Synthetic mRNAs Containing Minimalistic Untranslated Regions Are Highly Functional In Vitro and In Vivo. Cells. 2024; 13(15):1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151242
Chicago/Turabian StyleMamaghani, Shahab, Rocco Roberto Penna, Julia Frei, Conrad Wyss, Mark Mellett, Thomas Look, Tobias Weiss, Emmanuella Guenova, Thomas M. Kündig, Severin Lauchli, and et al. 2024. "Synthetic mRNAs Containing Minimalistic Untranslated Regions Are Highly Functional In Vitro and In Vivo" Cells 13, no. 15: 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151242
APA StyleMamaghani, S., Penna, R. R., Frei, J., Wyss, C., Mellett, M., Look, T., Weiss, T., Guenova, E., Kündig, T. M., Lauchli, S., & Pascolo, S. (2024). Synthetic mRNAs Containing Minimalistic Untranslated Regions Are Highly Functional In Vitro and In Vivo. Cells, 13(15), 1242. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151242







