A Comprehensive Insight and In Silico Analysis of CircRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Step toward ncRNA-Based Precision Medicine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CircRNA Nomenclature
3. CircRNA Classification
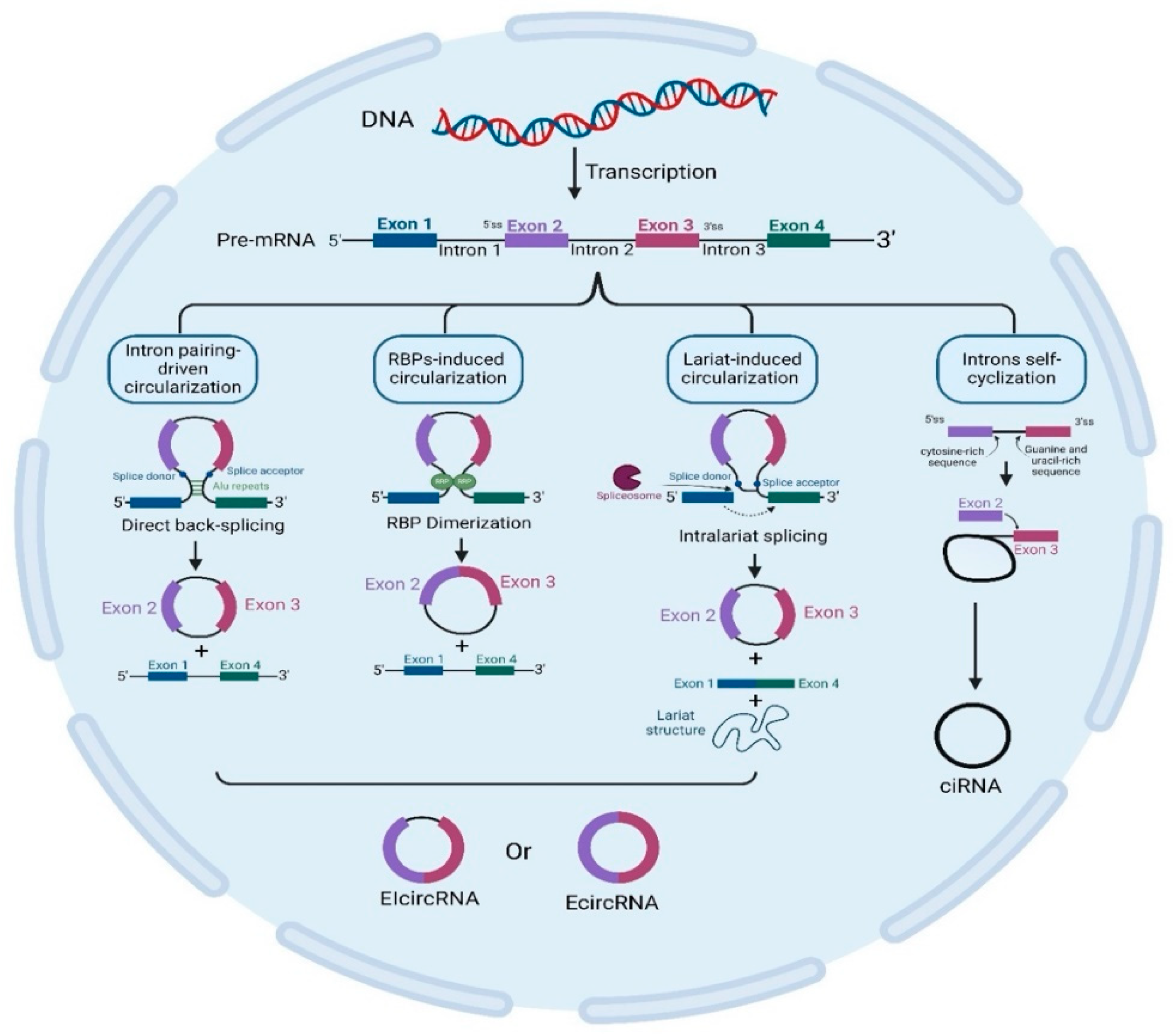
4. CircRNA Biogenesis
5. Mechanisms of CircRNA Biogenesis
6. CircRNAs and Cancer Pathology
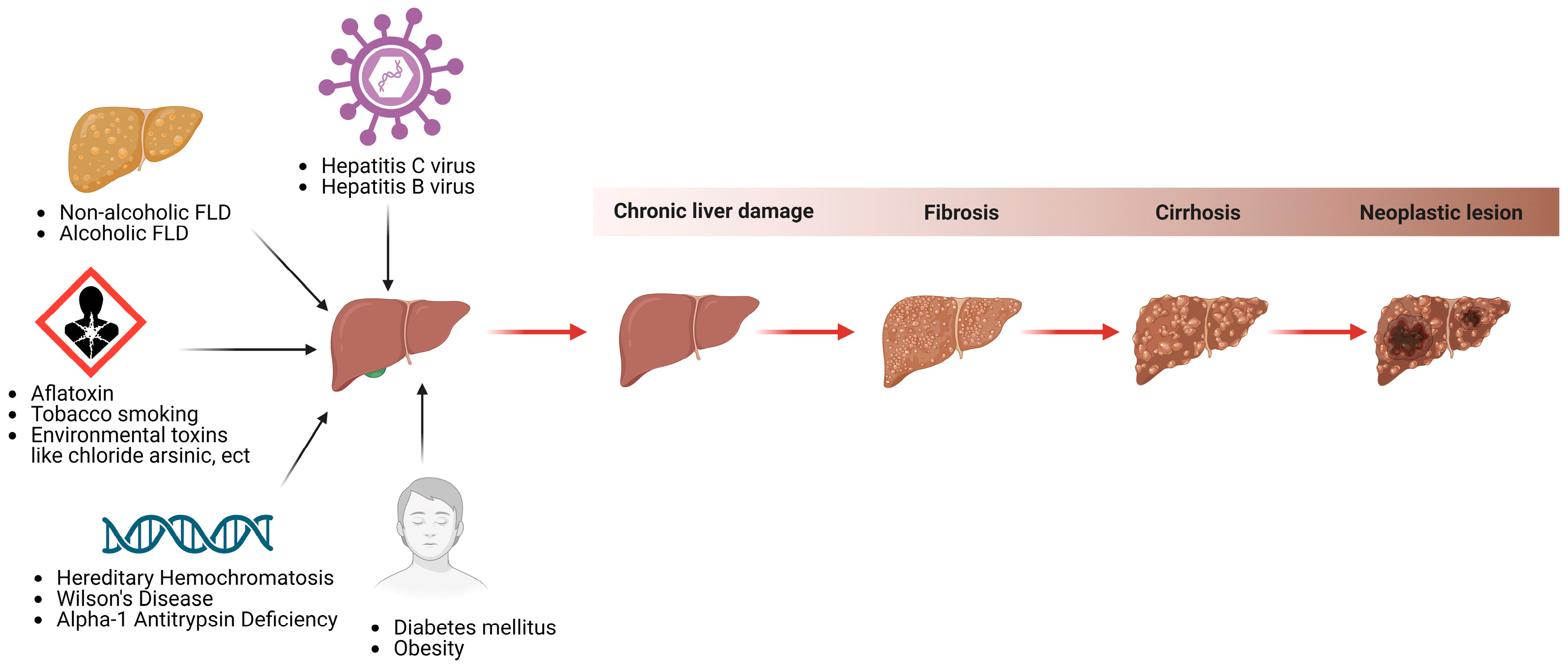
7. HCC Prevalence and Etiology
8. HCC Molecular Heterogeneity
9. Role of CircRNAs in HCC
10. CircRNAs Act as miRNA Sponges or Decoys
11. CircRNAs Function as Protein Sponges or Decoys
12. CircRNAs Can also Serve as Scaffolding for Proteins
13. CircRNA–Protein–mRNA Ternary Complexes
14. Are circRNAs Involved in Therapeutic Resistance Experienced by HCC Patients?
15. Could circRNAs Act as Theranostic Agents for HCC Patients?
16. Exosomal circRNA Is a New Hot Area of Research
17. CircRNAs in HCC: Bioinformatics Analysis
18. CircRNAs in Different Liver Diseases
19. Expert Authors’ Opinions, Recommendations, and Future Perspective
20. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pisignano, G.; Michael, D.C.; Visal, T.H.; Pirlog, R.; Ladomery, M.; Calin, G.A. Going circular: History, present, and future of circRNAs in cancer. Oncogene 2023, 42, 2783–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elemam, N.M.; Mekky, R.Y.; Rashid, G.; Braoudaki, M.; Youness, R.A. Pharmacogenomic and epigenomic approaches to untangle the enigma of IL-10 blockade in oncology. Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 2024, 26, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilusz, J.E. A 360 view of circular RNAs: From biogenesis to functions. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2018, 9, e1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Aziz, M.K.A.; Dawoud, A.; Kiriacos, C.J.; Fahmy, S.A.; Hamdy, N.M.; Youness, R.A. Decoding hepatocarcinogenesis from a noncoding RNAs perspective. J. Cell Physiol. 2023, 238, 1982–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawoud, A.; Ihab Zakaria, Z.; Hisham Rashwan, H.; Braoudaki, M.; Youness, R.A. Circular RNAs: New layer of complexity evading breast cancer heterogeneity. Noncoding RNA Res. 2023, 8, 60–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abaza, T.; El-Aziz, M.K.A.; Daniel, K.A.; Karousi, P.; Papatsirou, M.; Fahmy, S.A.; Hamdy, N.M.; Kontos, C.K.; Youness, R.A. Emerging Role of Circular RNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fahmy, S.A.; Dawoud, A.; Zeinelabdeen, Y.A.; Kiriacos, C.J.; Daniel, K.A.; Eltahtawy, O.; Abdelhalim, M.M.; Braoudaki, M.; Youness, R.A. Molecular Engines, Therapeutic Targets, and Challenges in Pediatric Brain Tumors: A Special Emphasis on Hydrogen Sulfide and RNA-Based Nano-Delivery. Cancers 2022, 14, 5244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Daly, S.M.; Talaat, R.M.; Braoudaki, M.; Youness, R.A.; Cho, W.C. Editorial: Recent breakthroughs in the decoding of circulating nucleic acids and their applications to human diseases. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1203495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ZeinElAbdeen, Y.A.; AbdAlSeed, A.; Youness, R.A. Decoding Insulin-Like Growth Factor Signaling Pathway From a Non-coding RNAs Perspective: A Step Towards Precision Oncology in Breast Cancer. J. Mammary Gland. Biol. Neoplasia 2022, 27, 79–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawoud, A.; Elmasri, R.A.; Mohamed, A.H.; Mahmoud, A.; Rostom, M.M.; Youness, R.A. Involvement of CircRNAs in regulating The “New Generation of Cancer Hallmarks”: A Special Depiction on Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2024, 196, 104312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glažar, P.; Papavasileiou, P.; Rajewsky, N. circBase: A database for circular RNAs. RNA 2014, 20, 1666–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wang, Q.; Shen, J.; Yang, B.B.; Ding, X. Circbank: A comprehensive database for circRNA with standard nomenclature. RNA Biol. 2019, 16, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri Moghaddam, M.; Maleki, M.; Oveisee, M.; Bagheri Moghaddam, M.; Arabian, M.; Malakootian, M. Circular RNAs: New Players in Cardiomyopathy. Genes 2022, 13, 1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sharpless, N.E. Detecting and characterizing circular RNAs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Q.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Liu, C.; Mao, L.; Ye, C.; Zhu, Q.-H.; Fan, L. PlantcircBase: A database for plant circular RNAs. Mol. Plant 2017, 10, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, G.; Khan, N.A.; Elsori, D.; Youness, R.A.; Hassan, H.; Siwan, D.; Seth, N.; Kamal, M.A.; Rizvi, S.; Babker, A.M.; et al. miRNA expression in PCOS: Unveiling a paradigm shift toward biomarker discovery. Arch. Gynecol. Obs. 2024, 309, 1707–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youness, R.A.; Habashy, D.A.; Khater, N.; Elsayed, K.; Dawoud, A.; Hakim, S.; Nafea, H.; Bourquin, C.; Abdel-Kader, R.M.; Gad, M.Z. Role of Hydrogen Sulfide in Oncological and Non-Oncological Disorders and Its Regulation by Non-Coding RNAs: A Comprehensive Review. Noncoding RNA 2024, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.-S.; Pan, F.; Mao, X.-D.; Liu, C.; Chen, Y.-J. Biological functions of circular RNAs and their roles in occurrence of reproduction and gynecological diseases. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huang, C.; Shan, G. Circular RNAs in physiology and non-immunological diseases. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2022, 47, 250–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, C.; Jia, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qing, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Xu, S.; Pan, Z. The role of circular rnas in the physiology and pathology of the mammalian ovary. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.O.; Chen, T.; Xiang, J.F.; Yin, Q.F.; Xing, Y.H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinelabdeen, Y.; Abaza, T.; Yasser, M.B.; Elemam, N.M.; Youness, R.A. MIAT LncRNA: A multifunctional key player in non-oncological pathological conditions. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024, 9, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashwan, H.H.; Taher, A.M.; Hassan, H.A.; Awaji, A.A.; Kiriacos, C.J.; Assal, R.A.; Youness, R.A. Harnessing the supremacy of MEG3 LncRNA to defeat gastrointestinal malignancies. Pathol. Res. Pr. 2024, 256, 155223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmasri, R.A.; Rashwan, A.A.; Gaber, S.H.; Rostom, M.M.; Karousi, P.; Yasser, M.B.; Kontos, C.K.; Youness, R.A. Puzzling out the role of MIAT LncRNA in hepatocellular carcinoma. Noncoding RNA Res. 2024, 9, 547–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, X.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Shi, L.; Li, Q.; Zang, A.; Wang, H. Circular RNA: Biogenesis, degradation, functions and potential roles in mediating resistance to anticarcinogens. Epigenomics 2020, 12, 267–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.O.; Dong, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.L.; Luo, Z.; Zhang, J.; Chen, L.L.; Yang, L. Diverse alternative back-splicing and alternative splicing landscape of circular RNAs. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1277–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.-Y.; Cai, Z.-R.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.-S.; Ju, H.-Q.; Xu, R.-H. Circular RNA: Metabolism, functions and interactions with proteins. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Yu, F.; Li, P.J.C. Circular RNAs: Characteristics, function and clinical significance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancers 2018, 10, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolha, L.; Ravnik-Glavač, M.; Glavač, D. Circular RNAs: Biogenesis, Function, and a Role as Possible Cancer Biomarkers. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017, 6218353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Errichelli, L.; Dini Modigliani, S.; Laneve, P.; Colantoni, A.; Legnini, I.; Capauto, D.; Rosa, A.; De Santis, R.; Scarfò, R.; Peruzzi, G.; et al. FUS affects circular RNA expression in murine embryonic stem cell-derived motor neurons. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, S.; Greenman, C.; Cook, P.R.; Papantonis, A. Exon Skipping Is Correlated with Exon Circularization. J. Mol. Biol. 2015, 427, 2414–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starke, S.; Jost, I.; Rossbach, O.; Schneider, T.; Schreiner, S.; Hung, L.H.; Bindereif, A. Exon circularization requires canonical splice signals. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, D.; Tatomer, D.C.; Luo, Z.; Wu, H.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L.; Cherry, S.; Wilusz, J.E. The Output of Protein-Coding Genes Shifts to Circular RNAs When the Pre-mRNA Processing Machinery Is Limiting. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 940–954.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragan, C.; Goodall, G.J.; Shirokikh, N.E.; Preiss, T. Insights into the biogenesis and potential functions of exonic circular RNA. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.-O.; Wang, H.-B.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.-L.; Yang, L. Complementary sequence-mediated exon circularization. Cell 2014, 159, 134–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, C.-Y.; Kuo, H.-C. The emerging roles and functions of circular RNAs and their generation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2019, 26, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, W.L.; Mohd Mohidin, T.B.; Shukla, K. Functional role of circular RNAs in cancer development and progression. RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 995–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.Q.; Zhou, S.L.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z.J.; Wang, P.C.; Xin, H.Y.; Mao, L.; Luo, C.B.; Yu, S.Y.; Huang, X.W. Circular RNA sequencing identifies CircASAP1 as a key regulator in hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis. Hepatology 2020, 72, 906–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Pan, X.; Zhu, D.; Deng, Z.; Jiang, R.; Wang, X. Circular RNA MAT2B promotes glycolysis and malignancy of hepatocellular carcinoma through the miR-338-3p/PKM2 axis under hypoxic stress. Hepatology 2019, 70, 1298–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Ji, L.; Liang, Y.; Wan, Z.; Zheng, W.; Song, X.; Gorshkov, K.; Sun, Q.; Lin, H.; Zheng, X. CircRNA-SORE mediates sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing YBX1. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wan, Z.; Tang, M.; Lin, Z.; Jiang, S.; Ji, L.; Gorshkov, K.; Mao, Q.; Xia, S.; Cen, D. N6-methyladenosine-modified CircRNA-SORE sustains sorafenib resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating β-catenin signaling. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Xu, Q.-g.; Wang, Z.-g.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Ma, J.-z.; Sun, S.-h.; Yang, F.; Zhou, W.-p. Circular RNA cSMARCA5 inhibits growth and metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 1214–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.-F.; Gao, C.; Huang, X.-Y.; Lu, J.-C.; Guo, X.-J.; Shi, G.-M.; Cai, J.-B.; Ke, A.-W. Cancer cell-derived exosomal circUHRF1 induces natural killer cell exhaustion and may cause resistance to anti-PD1 therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, L. Changes in the epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia. Cancers 2022, 14, 4473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.h.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, S.; Fan, J.; Gao, Q. Changing epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma in Asia. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 2029–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serraino, D.; Fratino, L.; Piselli, P. Epidemiological Aspects of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. In Hepatocellular Carcinoma; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switaerland, 2022; pp. 3–9. [Google Scholar]
- Shaalan, Y.M.; Handoussa, H.; Youness, R.A.; Assal, R.A.; El-Khatib, A.H.; Linscheid, M.W.; El Tayebi, H.M.; Abdelaziz, A.I. Destabilizing the interplay between miR-1275 and IGF2BPs by Tamarix articulata and quercetin in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Prod. Res. 2018, 32, 2217–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dikshit, R.; Eser, S.; Mathers, C.; Rebelo, M.; Parkin, D.M.; Forman, D.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: Sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 136, E359–E386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mesallamy, H.O.; Hamdy, N.M.; Sallam, A.A. Effect of obesity and glycemic control on serum lipocalins and insulin-like growth factor axis in type 2 diabetic patients. Acta Diabetol. 2013, 50, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khella, M.S.; Hamdy, N.M.; Amin, A.I.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. The (FTO) gene polymorphism is associated with metabolic syndrome risk in Egyptian females: A case- control study. BMC Med. Genet. 2017, 18, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youness, R.A.; Mohamed, A.H.; Efthimiadou, E.K.; Mekky, R.Y.; Braoudaki, M.; Fahmy, S.A. A Snapshot of Photoresponsive Liposomes in Cancer Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy: Opportunities and Challenges. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 44424–44436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiriacos, C.J.; Khedr, M.R.; Tadros, M.; Youness, R.A. Prospective Medicinal Plants and Their Phytochemicals Shielding Autoimmune and Cancer Patients Against the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic: A Special Focus on Matcha. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 837408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, S.S.; Abbas, E.; Youness, R.A.; Elemeery, M.N.; Nasr, A.S.; Seif, S. PNPLA3 and IL 28B signature for predicting susceptibility to chronic hepatitis C infection and fibrosis progression. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2022, 128, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, S.S.; Youness, R.A.; Abbas, E.A.E.; Osman, N.M.; ELFiky, A.; El-Kassas, M. miR-516a-3P, a potential circulating biomarker in hepatocellular carcinoma, correlated with rs738409 polymorphism in PNPLA3. Per. Med. 2022, 19, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mekky, R.Y.; El-Ekiaby, N.; El Sobky, S.A.; Elemam, N.M.; Youness, R.A.; El-Sayed, M.; Hamza, M.T.; Esmat, G.; Abdelaziz, A.I. Epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) and miR-548m reduce HCV entry through repression of CD81 receptor in HCV cell models. Arch. Virol. 2019, 164, 1587–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboouf, M.A.; Hamdy, N.M.; Amin, A.I.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. Genotype screening of APLN rs3115757 variant in Egyptian women population reveals an association with obesity and insulin resistance. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2015, 109, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mesallamy, H.O.; Hamdy, N.M.; Mostafa, D.M.; Amin, A.I. The serine protease granzyme B as an inflammatory marker, in relation to the insulin receptor cleavage in human obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014, 34, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekky, R.Y.; Elemam, N.M.; Eltahtawy, O.; Zeinelabdeen, Y.; Youness, R.A. Evaluating Risk: Benefit Ratio of Fat-Soluble Vitamin Supplementation to SARS-CoV-2-Infected Autoimmune and Cancer Patients: Do Vitamin-Drug Interactions Exist? Life 2022, 12, 1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youness, R.A.; Dawoud, A.; ElTahtawy, O.; Farag, M.A. Fat-soluble vitamins: Updated review of their role and orchestration in human nutrition throughout life cycle with sex differences. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 19, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, T.; Nguyen, M.H. Perspectives on the underlying etiology of HCC and its effects on treatment outcomes. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2023, 10, 413–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmoon, M.A.; Youness, R.A.; Gomaa, A.I.; Hamza, M.T.; Waked, I.; El Tayebi, H.M.; Abdelaziz, A.I. MiR-615-5p depresses natural killer cells cytotoxicity through repressing IGF-1R in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Growth Factors 2017, 35, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed Youness, R.; Amr Assal, R.; Mohamed Ezzat, S.; Zakaria Gad, M.; Abdel Motaal, A. A methoxylated quercetin glycoside harnesses HCC tumor progression in a TP53/miR-15/miR-16 dependent manner. Nat. Prod. Res. 2020, 34, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, N.A.; Hamdy, N.M.; Gibriel, A.A.; El Mesallamy, H.O. Investigation of the relationship between CTLA4 and the tumor suppressor RASSF1A and the possible mediating role of STAT4 in a cohort of Egyptian patients infected with hepatitis C virus with and without hepatocellular carcinoma. Arch. Virol. 2021, 166, 1643–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Derany, M.O.; Hamdy, N.M.; Al-Ansari, N.L.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. Integrative role of vitamin D related and Interleukin-28B genes polymorphism in predicting treatment outcomes of Chronic Hepatitis C. BMC Gastroenterol. 2016, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizk, H.H.; Hamdy, N.M.; Al-Ansari, N.L.; El-Mesallamy, H.O. Pretreatment Predictors of Response to PegIFN-RBV Therapy in Egyptian Patients with HCV Genotype 4. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Mesallamy, H.O.; Hamdy, N.M.; Rizk, H.H.; El-Zayadi, A.R. Apelin serum level in Egyptian patients with chronic hepatitis C. Mediat. Inflamm. 2011, 2011, 703031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mesallamy, H.O.; Hamdy, N.M.; Zaghloul, A.S.; Sallam, A.M. Serum retinol binding protein-4 and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin are interrelated in pancreatic cancer patients. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 2012, 72, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Mesallamy, H.O.; Hamdy, N.M.; Zaghloul, A.S.; Sallam, A.M. Clinical value of circulating lipocalins and insulin-like growth factor axis in pancreatic cancer diagnosis. Pancreas 2013, 42, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, S.S.; Hamdy, N.M. SOCS1 and pattern recognition receptors: TLR9 and RIG-I; novel haplotype associations in Egyptian fibrotic/cirrhotic patients with HCV genotype 4. Arch. Virol. 2017, 162, 3347–3354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, M.; Takeda, H.; Takai, A.; Seno, H. Risk factors and diagnostic biomarkers for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma: Current evidence and future perspectives. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 3410–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kew, M.C. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Epidemiology and risk factors. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2014, 1, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assal, R.A.; Elemam, N.M.; Mekky, R.Y.; Attia, A.A.; Soliman, A.H.; Gomaa, A.I.; Efthimiadou, E.K.; Braoudaki, M.; Fahmy, S.A.; Youness, R.A. A Novel Epigenetic Strategy to Concurrently Block Immune Checkpoints PD-1/PD-L1 and CD155/TIGIT in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2024, 45, 101961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, N.; Sawada, Y.; Endo, I.; Saito, K.; Uemura, Y.; Nakatsura, T. Biomarkers for the early diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2015, 21, 10573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.L.; Li, Y. Study on the hepatocellular carcinoma model with metastasis. Genes. Dis. 2020, 7, 336–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youness, R.A.; Gohar, A.; Kiriacos, C.J.; El-Shazly, M. Heat Shock Proteins: Central Players in Oncological and Immuno-Oncological Tracks. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023, 1409, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.D. Hepatitis C virus 1b viral factors (core, NS3, and NS5A) and increased risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 2013, 58, 491–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Gao, Y.; Hu, W.; Qu, Y.; Lou, N.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, H. Hepatitis C virus NS3 protein enhances hepatocellular carcinoma cell invasion by promoting PPM1A ubiquitination and degradation. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, M.M.; Sanad, E.F.; Hamdy, N.M. MicroRNAs’ role in the environment-related non-communicable diseases and link to multidrug resistance, regulation, or alteration. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 36984–37000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dykes, I.M.; Emanueli, C. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional gene regulation by long non-coding RNA. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2017, 15, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, L.; Ding, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, G.; Yang, J.; Zheng, H.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Xu, L. LncRNA structural characteristics in epigenetic regulation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.-Z.; Yan, G.-X.; Dong, D.-S.; Xin, H.; Liu, Z.-Y. LncRNA-ATB promotes autophagy by activating Yes-associated protein and inducing autophagy-related protein 5 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 5310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emam, O.; Wasfey, E.F.; Hamdy, N.M. Notch-associated lncRNAs profiling circuiting epigenetic modification in colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd El Fattah, Y.K.; Abulsoud, A.I.; AbdelHamid, S.G.; AbdelHalim, S.; Hamdy, N.M. CCDC144NL-AS1/hsa-miR-143-3p/HMGA2 interaction: In-silico and clinically implicated in CRC progression, correlated to tumor stage and size in case-controlled study; step toward ncRNA precision. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 253, 126739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldash, S.; Sanad, E.F.; Nada, D.; Hamdy, N.M. The Intergenic Type LncRNA (LINC RNA) Faces in Cancer with In Silico Scope and a Directed Lens to LINC00511: A Step toward ncRNA Precision. Non-Coding RNA 2023, 9, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldosoky, M.A.; Hammad, R.; Elmadbouly, A.A.; Aglan, R.B.; Abdel-Hamid, S.G.; Alboraie, M.; Hassan, D.A.; Shaheen, M.A.; Rushdi, A.; Ahmed, R.M.; et al. Diagnostic Significance of hsa-miR-21-5p, hsa-miR-192-5p, hsa-miR-155-5p, hsa-miR-199a-5p Panel and Ratios in Hepatocellular Carcinoma on Top of Liver Cirrhosis in HCV-Infected Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokolov, D.; Sharda, N.; Banerjee, A.; Denisenko, K.; Basalious, E.B.; Shukla, H.; Waddell, J.; Hamdy, N.M.; Banerjee, A. Differential Signaling Pathways in Medulloblastoma: Nano-biomedicine Targeting Non-coding Epigenetics to Improve Current and Future Therapeutics. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2024, 30, 31–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoud, M.M.; Sanad, E.F.; Elshimy, R.A.A.; Hamdy, N.M. Competitive Endogenous Role of the LINC00511/miR-185-3p Axis and miR-301a-3p From Liquid Biopsy as Molecular Markers for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 749753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammad, R.; Eldosoky, M.A.; Elmadbouly, A.A.; Aglan, R.B.; AbdelHamid, S.G.; Zaky, S.; Ali, E.; Abd El Hakam, F.E.; Mosaad, A.M.; Abdelmageed, N.A.; et al. Monocytes subsets altered distribution and dysregulated plasma hsa-miR-21-5p and hsa-miR-155-5p in HCV-linked liver cirrhosis progression to hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 15349–15364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, N.; Niu, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, H.; Wang, B.; Du, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S. Role of LncRNA-activated by transforming growth factor beta in the progression of hepatitis C virus-related liver fibrosis. Discov. Med. 2016, 22, 29–42. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Plissonnier, M.-L.; Herzog, K.; Levrero, M.; Zeisel, M.B. Non-coding RNAs and hepatitis C virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. Viruses 2018, 10, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Bao, H.; Huang, Z.; Liang, Z.; Wang, M.; Lin, N.; Ni, C.; Xu, Y. Little things with significant impact: miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1191070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Chen, B.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, H. UHRF1 Could Be a Prognostic Biomarker and Correlated with Immune Cell Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 6769–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Shi, Y.; Liu, M.; Sun, J. circHIPK3 regulates cell proliferation and migration by sponging miR-124 and regulating AQP3 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, G.; Yoon, J.S.; Jang, S.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Tak, W.Y.; Kweon, Y.-O.; Hur, K. Clinical significance of noncoding circHIPK3 RNA in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 2471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, X.; Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; Li, H.; Cheng, S.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, C.; Dong, J.; Zhang, L. The Circ_0001367/miR-545-3p/LUZP1 axis regulates cell proliferation, migration and invasion in glioma cells. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 781471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.-F.; Wei, C.-Y.; Huang, X.-Y.; Peng, R.; Yang, X.; Lu, J.-C.; Zhang, C.; Gao, C.; Cai, J.-B.; Gao, P.-T. Circular RNA circTRIM33–12 acts as the sponge of MicroRNA-191 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Li, J.; Wang, H.; Su, X.; Hou, J.; Gu, Y.; Qian, C.; Lin, Y.; Liu, X.; Huang, M. Circular RNA circMTO1 acts as the sponge of microRNA-9 to suppress hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Hepatology 2017, 66, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Guo, W.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Luo, Y.; Lyu, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Xue, H.; Li, Y.; Li, P.; Ma, F.; Liu, M.; Kong, S. HIPK3 circular RNA promotes metastases of HCC through sponging miR-338-3p to induce ZEB2 expression. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 3439–3447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, A.; Li, Q.; Chen, L. CircZFR promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression through regulating miR-3619–5p/CTNNB1 axis and activating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 661, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, N.; Peng, E.; Qiu, X.; Lyu, N.; Zhang, Z.; Tao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Z. circFBLIM1 act as a ceRNA to promote hepatocellular cancer progression by sponging miR-346. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Che, J. CircTP63 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by sponging miR-155-5p and upregulating ZBTB18. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, Y. CircRNA has_circ_0001806 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression via the miR-193a-5p/MMP16 pathway. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. Rev. Bras. Pesqui. Medicas E Biol. 2021, 54, e11459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, G.; Peng, D.; Wen, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, B.; Lu, J. CircYTHDF3 Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression through Modulating miR-136-5p/CBX4/VEGF Axis. 2023. Available online: https://susy.mdpi.com/user/assigned/production_form/eb3b73aef73bf6716a290b888d514329 (accessed on 10 July 2024).
- Chen, Z.; Du, J.; Yang, C.; Si, G.; Chen, Y. circ-CFH promotes the development of HCC by regulating cell proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion, and glycolysis through the miR-377-3p/RNF38 axis. Open Life Sci. 2022, 17, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, F.; Zhu, Z.; Ding, A.; Luo, J. CircRNA CDR1as/miR-1287/Raf1 axis modulates hepatocellular carcinoma progression through MEK/ERK pathway. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, 12, 8951–8964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Yang, G.; Wang, X.; Liu, J.; Lu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Xu, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, J. CircBACH1 (hsa_circ_0061395) promotes hepatocellular carcinoma growth by regulating p27 repression via HuR. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 6929–6941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.-J.; Zheng, B.; Luo, G.-J.; Ma, X.-K.; Lu, X.-Y.; Lin, X.-M.; Yang, S.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, T.; Li, Z.-X. Circular RNAs negatively regulate cancer stem cells by physically binding FMRP against CCAR1 complex in hepatocellular carcinoma. Theranostics 2019, 9, 3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.-G.; Awan, F.M.; Du, W.W.; Zeng, Y.; Lyu, J.; Wu, D.; Gupta, S.; Yang, W.; Yang, B.B. The circular RNA interacts with STAT3, increasing its nuclear translocation and wound repair by modulating Dnmt3a and miR-17 function. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 2062–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Du, W.W.; Wu, Y.; Yang, Z.; Awan, F.M.; Li, X.; Yang, W.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Q.; Yee, A. A circular RNA binds to and activates AKT phosphorylation and nuclear localization reducing apoptosis and enhancing cardiac repair. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Du, W.W.; Wu, N.; Yang, W.; Awan, F.M.; Fang, L.; Ma, J.; Li, X.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, Z. A circular RNA promotes tumorigenesis by inducing c-myc nuclear translocation. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1609–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Long, H.; Zheng, Q.; Bo, X.; Xiao, X.; Li, B. Circular RNA circRHOT1 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by initiation of NR2F6 expression. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, W.; Luo, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, B.; Han, S.; Li, X. Circular RNA circ-ADD3 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis through facilitating EZH2 degradation via CDK1-mediated ubiquitination. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2019, 9, 1695. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Liu, B.; Shen, D.-d.; Yan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Hou, L.; Jiang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, Y. A tumor-suppressive circular RNA mediates uncanonical integrin degradation by the proteasome in liver cancer. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabe5043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.; Wang, Y.; He, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Liu, N.; Wang, J.; Lu, T.; He, L.; Tian, Y. Circular RNA circIPO11 drives self-renewal of liver cancer initiating cells via Hedgehog signaling. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.-C.; Wong, C.-W.; Liang, P.-P.; Shi, M.; Cao, Y.; Rao, S.-T.; Tsui, S.K.-W.; Waye, M.M.-Y.; Zhang, Q.; Fu, W.-M. Translation of the circular RNA circβ-catenin promotes liver cancer cell growth through activation of the Wnt pathway. Genome Biol. 2019, 20, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Song, J.; Tang, B.; Fang, S.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, L.; Wu, F.; Gao, Y.; Chen, C.; Hu, X. CircSOD2 induced epigenetic alteration drives hepatocellular carcinoma progression through activating JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.-X.; Chen, X.; Xia, L.-P.; Zhang, J.-X.; Pan, Z.-Z.; Ma, X.-D.; Han, K.; Chen, J.-W.; Judde, J.-G.; Deas, O. N 6-methyladenosine modification of circNSUN2 facilitates cytoplasmic export and stabilizes HMGA2 to promote colorectal liver metastasis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarnerio, J.; Zhang, Y.; Cheloni, G.; Panella, R.; Mae Katon, J.; Simpson, M.; Matsumoto, A.; Papa, A.; Loretelli, C.; Petri, A. Intragenic antagonistic roles of protein and circRNA in tumorigenesis. Cell Res. 2019, 29, 628–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Qin, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Liu, L.; Lu, K.; Li, L.; Deng, X.; Liu, F. FNDC3B circular RNA promotes the migration and invasion of gastric cancer cells via the regulation of E-cadherin and CD44 expression. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 19895–19910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Kong, R.; Wu, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, S.; Chen, T.; Mao, C.; Liu, S. Circ-MALAT1 functions as both an mRNA translation brake and a microRNA sponge to promote self-renewal of hepatocellular cancer stem cells. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 1900949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, N.; Yuan, Z.; Du, K.Y.; Fang, L.; Lyu, J.; Zhang, C.; He, A.; Eshaghi, E.; Zeng, K.; Ma, J. Translation of yes-associated protein (YAP) was antagonized by its circular RNA via suppressing the assembly of the translation initiation machinery. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 2758–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Huang, F.; Feng, C. CircFoxo3 Promotes Adriamycin Resistance Through Regulation of miR-199a-5p/ATP Binding Cassette Subfamily C Member 1 Axis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2020, 13, 5113–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Liu, S.; Li, M.; Huang, P.; Li, X. circ_0003418 Inhibits Tumorigenesis And Cisplatin Chemoresistance Through Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway In Hepatocellular Carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 9539–9549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatsirou, M.; Artemaki, P.I.; Scorilas, A.; Kontos, C.K. The role of circular RNAs in therapy resistance of patients with solid tumors. Pers. Med. 2020, 17, 469–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, D.; Yu, C.; Sheng, J.; Lv, E.; Huang, W. The emerging roles of circFOXO3 in cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 659417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, D.; He, R.; Dang, Y.; Wu, H.; Feng, Z.; Chen, G. The latest overview of circRNA in the progression, diagnosis, prognosis, treatment, and drug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 608257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, R.; Liu, L.; Zhou, J.; Wei, X.; Huang, P. Current molecular biology and therapeutic strategy status and prospects for circRNAs in HBV-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 697747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.-P.; Xu, W.-X.; Hou, J.-C.; Xu, Q.; Wang, D.-D.; Tang, J.-H. The emerging role of the interactions between circular RNAs and RNA-binding proteins in common human cancers. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 5206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piñero, F.; Dirchwolf, M.; Pessôa, M.G. Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Diagnosis, Prognosis and Treatment Response Assessment. Cells 2020, 9, 1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janevska, D.; Chaloska-Ivanova, V.; Janevski, V. Hepatocellular carcinoma: Risk factors, diagnosis and treatment. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2015, 3, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.W.; Tsai, H.I.; Lee, W.C.; Huang, S.W.; Lin, C.Y.; Hsieh, Y.C.; Kuo, T.; Chen, C.W.; Yu, M.C. Normal Alpha-Fetoprotein Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Are They Really Normal? J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.S.; Chu, J.H.; Cui, S.X.; Song, Z.Y.; Qu, X.J. Des-γ-carboxy prothrombin (DCP) as a potential autologous growth factor for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2014, 34, 903–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparna, G.M.; Tetala, K.K.R. Recent Progress in Development and Application of DNA, Protein, Peptide, Glycan, Antibody, and Aptamer Microarrays. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabbish, A.M.; Abdelzaher, H.M.; Abohawya, M.; Shamma, S.; Mahmoud, Y.H.; Maged, A.; Manaa, M.; Hassany, M.; Kobeissy, F.; Bazgir, O.; et al. Prognostic MicroRNA Panel for HCV-Associated HCC: Integrating Computational Biology and Clinical Validation. Cancers 2022, 14, 3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonferoni, M.C.; Gavini, E.; Rassu, G.; Maestri, M.; Giunchedi, P. Chitosan nanoparticles for therapy and theranostics of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and liver-targeting. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Wu, M.; Xie, T.; Chen, J. Circular RNAs Sparkle in the Diagnosis and Theranostics of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front. Genet. 2021, 11, 628655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Lou, Y.; Qiu, Y.; Zhu, F. The mechanistic, diagnostic and therapeutic novel nucleic acids for hepatocellular carcinoma emerging in past score years. Brief. Bioinform. 2021, 22, 1860–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Quan, Y.; Fan, S.; Wang, H.; Liang, J.; Huang, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, Q.; He, P.; Ye, Y. Exosome-transmitted circular RNA hsa_circ_0051443 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Cancer Lett. 2020, 475, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hu, J.; Liao, J.; Su, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, B.; Li, C.; Wang, Z. exoRBase 2.0: An atlas of mRNA, lncRNA and circRNA in extracellular vesicles from human biofluids. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D118–D128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, K.; Wu, F.; Wang, W.; Zhang, K.; Hu, H.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, T. circRNA disease: A manually curated database of experimentally supported circRNA-disease associations. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Deng, L.; Zhuo, H.; Chen, X.; Tan, Z.; Han, S.; Tang, J.; Qian, X.; Yao, A. Circulating circRNA predicting the occurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with HBV infection. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 10216–10222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Difference | CircRNA | Linear mRNA |
|---|---|---|
| Splicing | Back | Normal |
| Pre-mRNA | Non-canonical | Canonical pre-mRNA |
| Production | By ligation | With a free 5′-cap and 3′-tail |
| Structure | No free cap and tail | With a free cap and tail |
| Final structure | Covalent closed-loop structure; circular | Linear |
| Formed from | Exons located in the cytoplasm or the nucleus increase nuclear protein retention, and circRNAs within introns remain in the nucleus | Pre-mRNA from a DNA template in the cell nucleus |
| Resistant to RNase R | Yes | No |
| CircRNA Biogenesis | CircRNA Product | Biogenesis Mechanism | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intron pairing-driven circularization | EcircRNAs or ElciRNAs | The method by which EcircRNA and EIcircRNA cyclize is known as “direct back splicing” or intron pairing-driven cyclization; pre-mRNA containing ALU repeats is sheared to form EcircRNA following reverse-base complementary pairing. EIciRNAs are produced if introns are kept in between exons. | [19,31] |
| RBP-induced circularization | RBPs (trans-acting factors) are Quaking, Muscleblind, and Fused-in Sarcoma. Circularization is facilitated by bridging comparable intronic regions. RBP dimerization links the 3′ and 5′ ends of circularized exons. | [32,33] | |
| Lariat-induced circularization driven by spliceosomes | Exon circularization is spliceosome-dependent and is collected at the back-splicing site to help join the 5′-3′ donor–acceptor sites. Within lariat, internal splicing releases EcircRNAs or EIcircRNAs. | [34,35,36,37] | |
| Intron self-cyclization | ciRNA | Intron self-cyclization is brought about by the 7 nucleotides of the G/U-rich sequence located near 1 exon and the 11 nucleotides of the C-rich sequence located near another exon in pre-mRNA. Three distinct kinds of circRNAs are produced: ciRNAs, EIcircRNAs, and EcircRNAs. A closed RNA loop (covalently EcircRNA) is formed when the 3′ end of an exon (5’ss) is joined to the 5′ end of either the same exon (single-exon circRNA) or an upstream exon (multiple-exon circRNA). | [22,38,39,40] |
| Functional Role | CircRNAs | Mechanism | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| MiR sponge or decoy | CircTRIM33-12 | increases the production of TET1 by the sponging of miR-191, lowering the levels of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in HCC cells | [100] |
| CircMTO1 | downregulates p21 level by sponging oncogenic miR-9 to inhibit HCC progression. | [101] | |
| CircHIPK3 | regulates AQP3 expression, sponges miR-124, alters cell proliferation and HCC migration | [97] | |
| CircZFR | regulates cell proliferation, epithelial–mesenchymal transition, Wnt/β-catenin via quenching miR-3619-5p, enhancing CTNNB1 expression and activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling | [104] | |
| CircFBLIM1 | ceRNA that enhances HCC progression via sponging miR-346 | [105] | |
| CircMAT2B | encourages HCC malignancy, glycolysis, and miR-338-3p quenching to activate the PKM2 axis under hypoxic conditions | [43] | |
| CircTP63 | sponges miR-155-5p and thus increases ZBTB18 expression, which is positively correlated with mortality rates in HCC patients | [106] | |
| CircSMARCA5 | TIMP3 expression via sponging miR-17-3p and miR-181b-5p | [46] | |
| Circ_0001806 | expedites HCC advancement by upregulating MMP-16 expression through the inhibition of miR-193a-5p | [107] | |
| CircYTHDF3 | fosters HCC via miR-136-5p/CBX4/VEGF pathway | [108] | |
| CircCFH | promotes HCC by influencing cellular proliferation, apoptosis, migration, invasion and glycolysis via miRNA 377-3p/RNF38 axis | [109] | |
| CDR1as | interacts with markers and miR-1287 bands within the Raf1 pathways to modulate HCC progression | [110] | |
| CircASAP1 | ceRNA for miR-326 and miR-532-5p regulates the expression of MAPK1 and CSF-1 targets, facilitating invasion, HCC cell proliferation and infiltration of tumor-associated macrophages | [42] | |
| CircSORE | induces sorafenib resistance by competitively activating the Wnt/β-catenin pathway through miR-103a-2-5p and miR-660-3p | [45] | |
| Protein sponge or decoy | CircBACH1 | interacts with HuR; RBP downregulates p27 expression, blocks translation in the p27 5′-untranslated region by an interferon-responsive sequence element, encourages HuR translocation and cytoplasmic accumulation | [111] |
| CircZKSCAN1 | competitively binding FMRP to modulate the translation of CCAR1 mRNA and inhibiting the Wnt signaling pathway | [112] | |
| Protein scaffold | CircAMOTL1 | combines with c-myc, STAT3, PDK1, and AKT1 to promote their translocation to the nucleus, modulating the expression of their target genes. | [113,114,115] |
| CircRHOT1 | recruits TIP60 to NR2F6, initiating NR2F6 transcription and HCC progression | [116] | |
| CircADD3 | protein scaffold inhibits HCC metastasis via CDK1-mediated EZH2 ubiquitination | [117] | |
| CircPABPC1 | a tumor suppressor, directly delivering ITGβ1 to the proteasome for HCC ubiquitin-independent destruction | [118] | |
| CircSORE | causes sorafenib resistance by binding oncogenic YBX1 and blocking its nuclear interaction with E3 ubiquitin ligase PRP19 | [44] | |
| Gene transcription regulation | CircIPO11 | binds TOP1 to trigger GLI1 transcription, with Hedgehog signaling activation. | [119] |
| Translation to proteins and peptides | CircCTNNB1 | creates 370 amino acid β-catenin isoform, uses circularization to block translation at a new stop codon, uses Wnt to stimulate HCC cell development | [120] |
| Epigenetic alterations’ regulation | CircSOD2 | induces epigenetic alteration to drive HCC progression by activating JAK2/STAT3 signaling. | [121] |
| circID | circBase ID | Genomic Position | Strand | Gene Symbol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exo_circ_11335 | NA | chr12:94169153-94186473 | + | PLXNC1 |
| exo_circ_23574 | hsa_circ_0041462 | chr17:3814322-3816270 | − | NCBP3 |
| exo_circ_71780 | hsa_circ_0006320 | chr8:22474954-22498112 | + | PPP3CC |
| exo_circ_79066 | hsa_circ_0001953 | chrY:2953909-2961646 | + | ZFY |
| Downregulated circRNAs | |||
| CircRNAs | Hepatic Disease/ Biological Function | Mechanism | Molecular Mechanism/Associated miR (Sponged miR) |
| circRNA_0046366 | Hepatocellular steatosis | - | circRNA_0046366/miR-34a/PPAR-a signaling |
| hsa_circ_0070963, hsa_circ_0061893 and hsa_circ_0013255 | Liver fibrosis | - | - |
| circRNAs_100395 | Liver cancer | inhibits cell proliferation, induces apoptosis | miR-1228 |
| circScd1 | NAFLD | encourages the JAK2/STAT5 pathway, which causes fatty liver disease | - |
| circCDK13 | Liver cancer | suppresses progression via JAK/STAT and PI3K/Akt signaling | - |
| circRNA_101764 | HBV-related HCC | - | hsa-miR-181 |
| circ_03848, circ_08236, circ_13398 and circ_15013 | Liver regeneration | - | - |
| circRNA-4099 | Hepatitis | unknown/triggers keap1/Nrf2 and p38MAPK | miR-706 aggravating H2O2-induced injury |
| Upregulated circRNAs | |||
| CircRNAs | Hepatic Disease/ Biological Function | Mechanism | Molecular Mechanism/ Associated miR (Sponged miR) |
| hsa_circRNA_0000657, hsa_circRNA_0000659, hsa_circRNA_0003247, hsa_circRNA_0001535 | Hepatotoxicity | - | - |
| hsa_circ_0072765, hsa_circ_0071410, hsa_circ_0054345 | Liver fibrosis | - | - miR-9-5p - |
| circZFR, circFUT8 circIPO11 | Liver cancer | - | - |
| circMEG3 | Liver cancer | inhibits telomerase activity, shortens telomere lifespan, reduces Cbf5 | - |
| circRNA-0067835 | Liver fibrosis | promotes cell proliferation, inhibits apoptosis | miR-155 to promote FOXO3a |
| circ_0091579 | Liver cancer | promotes proliferative and metastasis | miR-490-3p |
| hsa_circ_0003056 hsa_circ_0067127 | Carcinoma | - | - |
| circRNA-1984 | HSCs-related to fibrosis | - | miR-146b |
| circ_0015756 | Hepatoblastoma | - | - |
| hsa_circ_0000594 | Hepatoblastoma | - | mir-217/SIRT1 regulatory axis |
| circFBLIM1 | Hepatoblastoma | Promotes cell viability, proliferation, invasion | miR-346-ceRNA to regulate FBLIM1 expression |
| circHMGCS1 | Hepatoblastoma | Regulates proliferation, apoptosis and glutaminolysis | miR-503-5p/IGF/PI3K/AKT axis; regulates IGF2 and IGF1R expression |
| circ-PWWP2A | Fibrogenesis | Downstream reactor of TGF-ß and LPS | miR-203 and miR-223 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Youness, R.A.; Hassan, H.A.; Abaza, T.; Hady, A.A.; El Magdoub, H.M.; Ali, M.; Vogel, J.; Thiersch, M.; Gassmann, M.; Hamdy, N.M.; et al. A Comprehensive Insight and In Silico Analysis of CircRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Step toward ncRNA-Based Precision Medicine. Cells 2024, 13, 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151245
Youness RA, Hassan HA, Abaza T, Hady AA, El Magdoub HM, Ali M, Vogel J, Thiersch M, Gassmann M, Hamdy NM, et al. A Comprehensive Insight and In Silico Analysis of CircRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Step toward ncRNA-Based Precision Medicine. Cells. 2024; 13(15):1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151245
Chicago/Turabian StyleYouness, Rana A., Hossam A. Hassan, Tasneem Abaza, Ahmed A. Hady, Hekmat M. El Magdoub, Mohamed Ali, Johannes Vogel, Markus Thiersch, Max Gassmann, Nadia M. Hamdy, and et al. 2024. "A Comprehensive Insight and In Silico Analysis of CircRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Step toward ncRNA-Based Precision Medicine" Cells 13, no. 15: 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151245
APA StyleYouness, R. A., Hassan, H. A., Abaza, T., Hady, A. A., El Magdoub, H. M., Ali, M., Vogel, J., Thiersch, M., Gassmann, M., Hamdy, N. M., & Aboouf, M. A. (2024). A Comprehensive Insight and In Silico Analysis of CircRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Step toward ncRNA-Based Precision Medicine. Cells, 13(15), 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151245












