Discovery of Cell Number-Interstitial Fluid Volume (CIF) Ratio Reveals Secretory Autophagy Pathway to Supply eHsp90α for Wound Healing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
2.2. Reagents and Antibodies
2.3. Two Lentiviral Vector Systems for Up- or Downregulation of Target Genes
2.4. Fractionation of CM by Centrifugations
2.5. Trypsin Digestion
2.6. Western Immunoblotting Analysis and Band Quantitation
2.7. Cell Survival and Growth Assay
2.8. Animal Model and Tissue Samples
2.9. Wound-Healing Assay
2.10. Histology and Immunohistochemistry
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Result
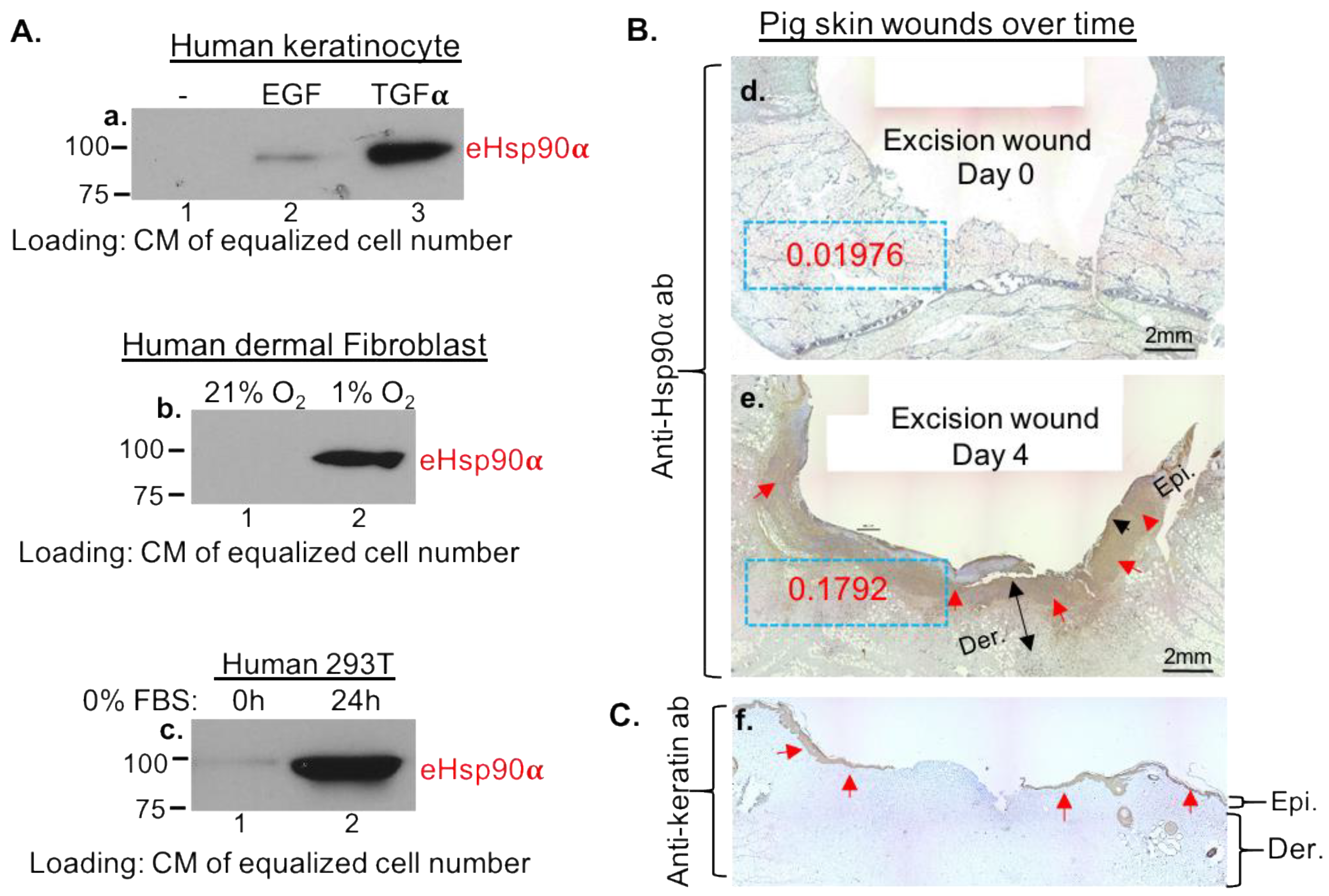
3.1. Massive Deposition of eHsp90α by Wounded Tissues and by Cultured Cells under Stress
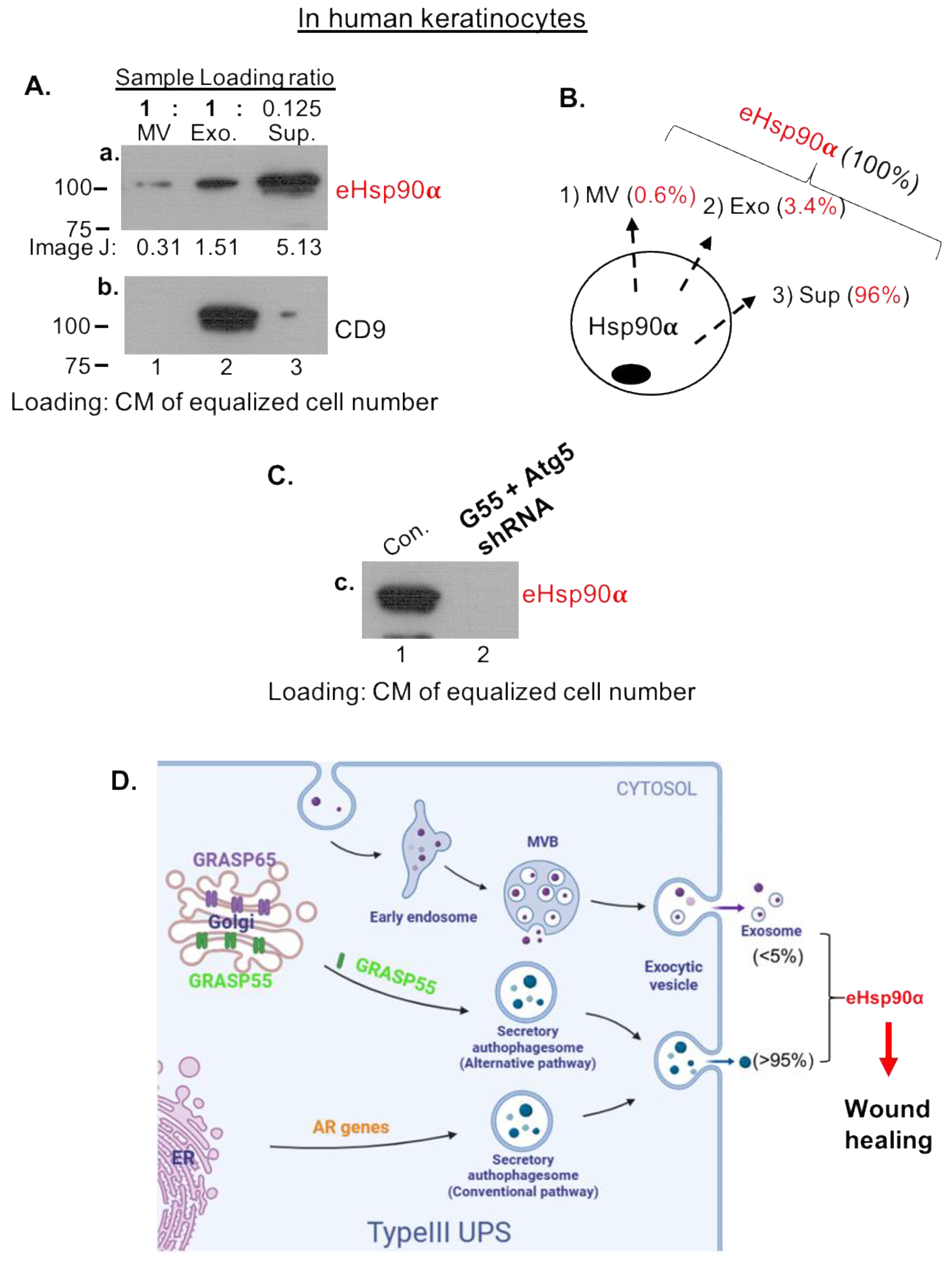
3.2. Majority of eHsp90α Is Not Associated with Secreted Extracellular Vesicles (EV)
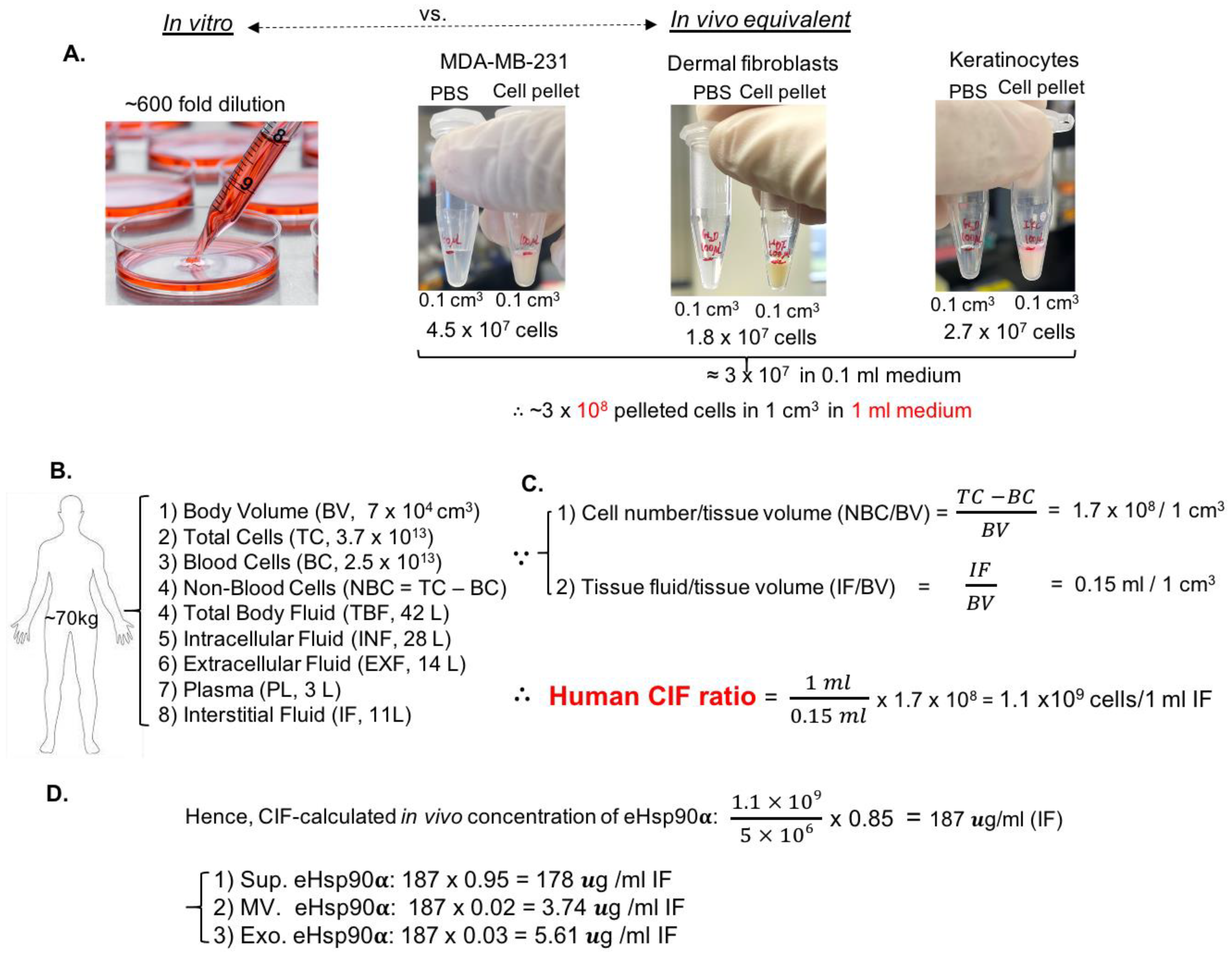
3.3. Establishment of Cell-Number-to-Interstitial-Fluid-Volume (CIF) Ratio for Human Tissue In Vivo to Predict Physiological Concentration of a Protein Target in CM of Cells In Vitro
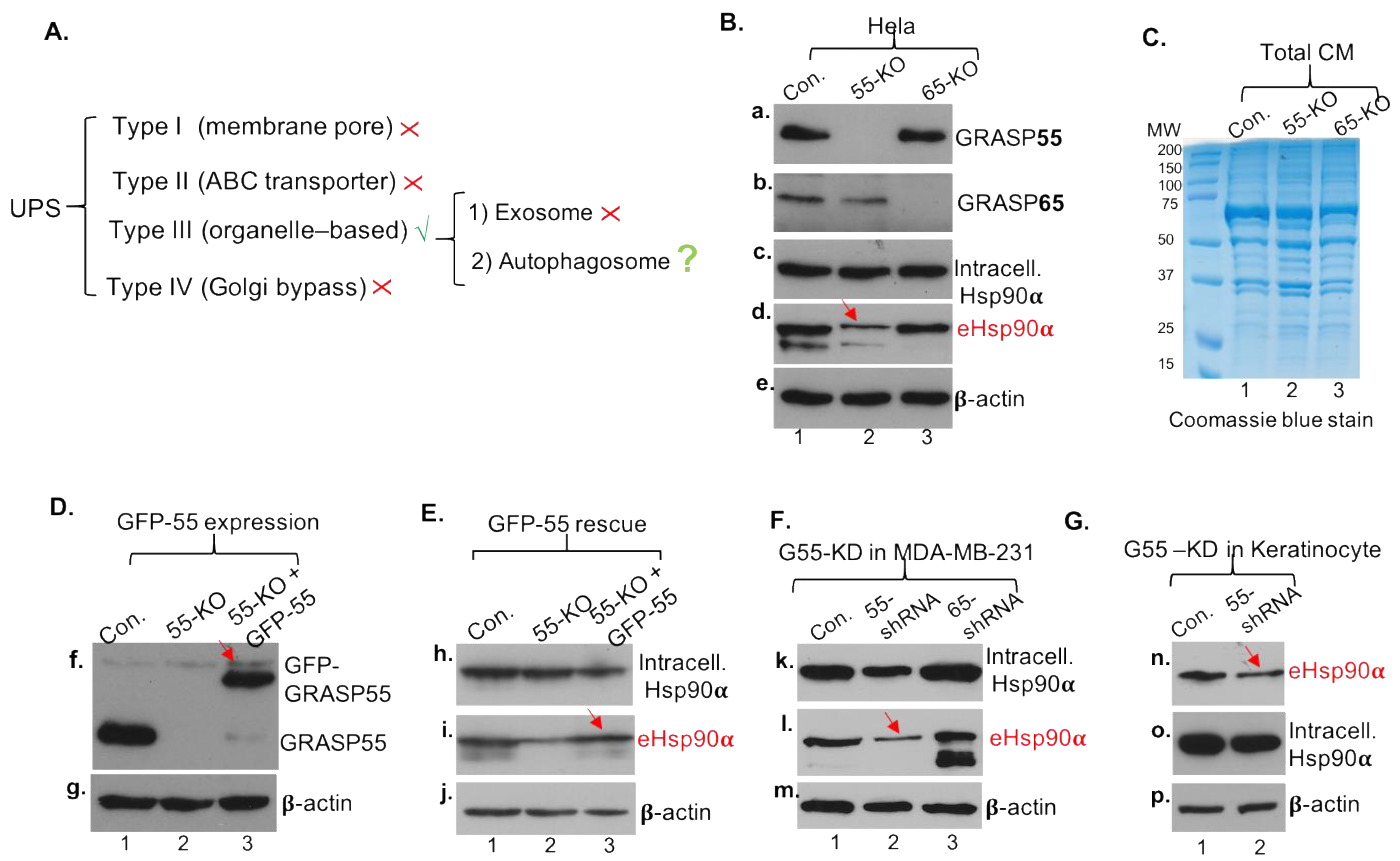
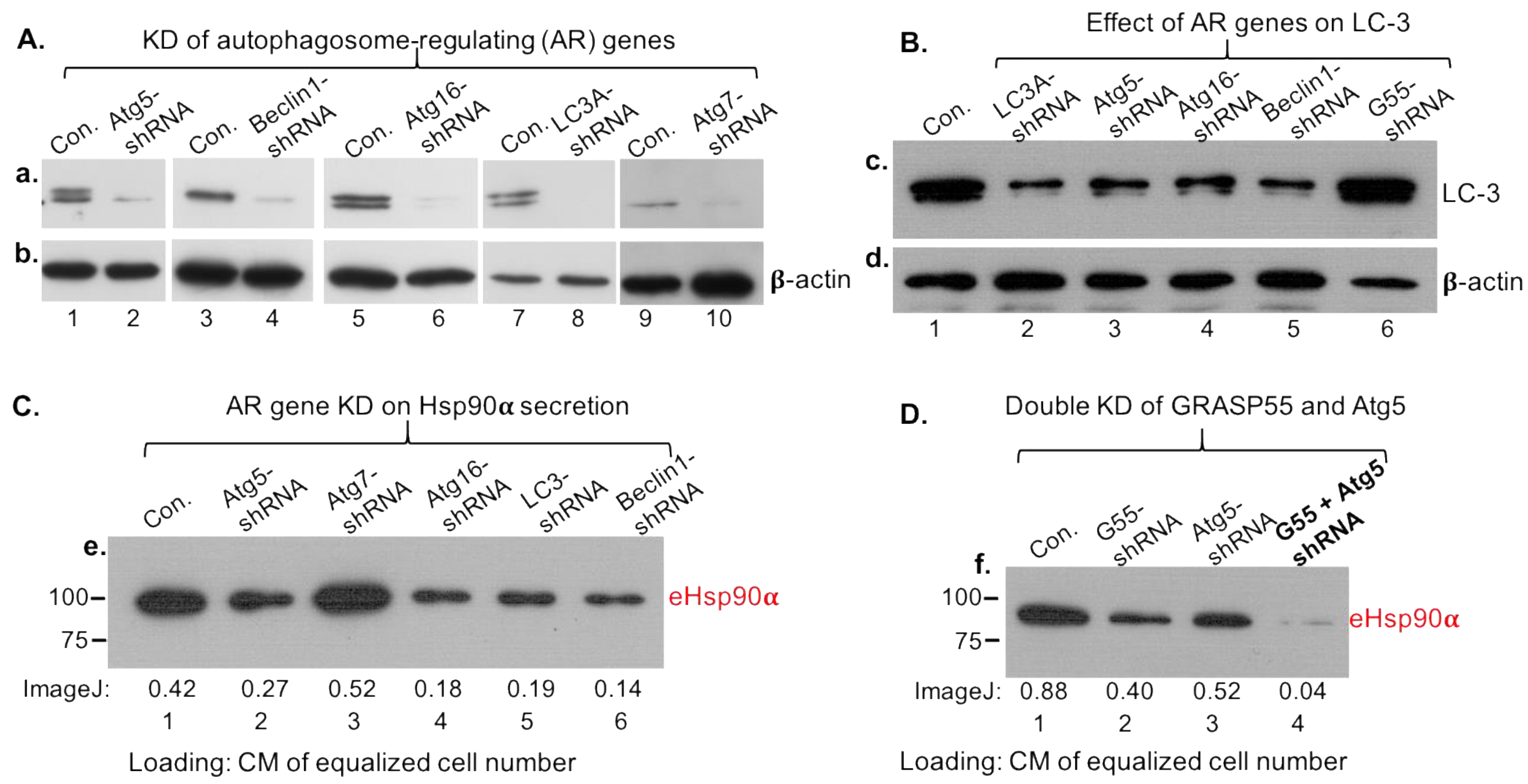
3.4. Secretory Autophagy, Not Exosomes, Supplies Functional Concentration of eHsp90α for Wound Healing
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tang, X.; Hao, M.; Chang, C.; Bhatia, A.; O’brien, K.; Chen, M.; Armstrong, D.G.; Li, W. Wound healing driver gene and therapeutic development: Political and scientific hurdles. Adv. Wound Care 2021, 10, 415–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, A.J.; Clark, R.A. Cutaneous wound healing. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 341, 738–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurtner, G.C.; Werner, S.; Barrandon, Y.; Longaker, M.T. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature 2008, 453, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eming, S.A.; Martin, P.; Tomic-Canic, M. Wound repair and regeneration: Mechanisms, signaling, and translation. Sci. Transl. Med. 2014, 6, 265sr6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, M.C.; Keith, B. The role of oxygen availability in embryonic development and stem cell function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.C.; Miller, E.A.; Goldberg, J.; Orci, L.; Schekman, R. Bi-directional protein transport between the ER and Golgi. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 20, 87–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nickel, W. Pathways of unconventional protein secretion. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 621–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabouille, C. Pathways of unconventional protein secretion. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filaquier, A.; Marin, P.; Parmentier, M.L.; Villeneuve, J. Roads and hubs of unconventional protein secretion. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2022, 75, 102072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tjalsma, H.; Antelmann, H.; Jongbloed, J.D.; Braun, P.G.; Darmon, E.; Dorenbos, R.; Dubois, J.Y.; Westers, H.; Zanen, G.; Quax, W.J.; et al. Proteomics of protein secretion by Bacillus subtilis: Separating the “secrets” of the secretome. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 207–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solursh, M.; Meier, S. A conditioned medium (CM) factor produced by chondrocytes that promotes their own differentiation. Dev. Biol. 1973, 30, 279–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, P.; Mani, S. Methodologies to decipher the cell secretome. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 2226–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dowling, P.; Clynes, M. Conditioned media from cell lines: A complementary model to clinical specimens for the discovery of disease-specific biomarkers. Proteomics 2011, 11, 794–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eustace, B.K.T.; Sakurai, J.K.; Stewart, D.; Yimlamai, C.; Unger, C.; Zehetmeier, B.; Lain, C.; Torella, S.W.; Henning, G.; Beste, B.T.; et al. Functional proteomic screens reveal an essential extracellular role for hsp90 alpha in cancer cell invasiveness. Nat. Cell Biol. 2004, 6, 507–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, Y.; Guan, S.; Fan, J.; Cheng, C.F.; Bright, A.M.; Chinn, C.; Chen, M.; Woodley, D.T. Extracellular heat shock protein-90alpha: Linking hypoxia to skin cell motility and wound healing. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 1221–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Sahu, D.; Tsen, F. Secreted heat shock protein-90 (Hsp90) in wound healing and cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 730–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Freitas, D.; Kim, H.S.; Fabijanic, K.; Li, Z.; Chen, H.; Mark, M.T.; Molina, H.; Martin, A.B.; Bojmar, L.; et al. Identification of distinct nanoparticles and subsets of extracellular vesicles by asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2018, 20, 332–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Fenix, A.M.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Ping, J.; Liu, Q.; Evans, R.; et al. Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell 2019, 177, 428–445.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.F.; Sahu, D.; Tsen, F.; Zhao, Z.; Fan, J.; Kim, R.; Wang, X.; O’Brien, K.; Li, Y.; Kuang, Y.; et al. A fragment of secreted Hsp90α carries properties that enable it to accelerate effectively both acute and diabetic wound healing in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4348–4361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, K.; Bhatia, A.; Tsen, F.; Chen, M.; Wong, A.K.; Woodley, D.T.; Li, W. Identification of the critical therapeutic entity in secreted Hsp90α that promotes wound healing in newly re-standardized healthy and diabetic pig models. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, A.; O’Brien, K.; Chen, M.; Wong, A.; Garner, W.; Woodley, D.T.; Li, W. Dual therapeutic functions of F-5 fragment in burn wounds: Preventing wound progression and promoting wound healing in pigs. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2016, 3, 16041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatia, A.; O’Brien, K.; Guo, J.; Lincoln, V.; Kajiwara, C.; Chen, M.; Woodley, D.T.; Udono, H.; Li, W. Extracellular and Non-Chaperone Function of Heat Shock Protein-90α Is Required for Skin Wound Healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 423–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.F.; Fan, J.; Fedesco, M.; Guan, S.; Li, Y.; Bandyopadhyay, B.; Bright, A.M.; Yerushalmi, D.; Liang, M.; Chen, M.; et al. Transforming growth factor alpha (TGFalpha)-stimulated secretion of HSP90alpha: Using the receptor LRP-1/CD91 to promote human skin cell migration against a TGFbeta-rich environment during wound healing. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 28, 3344–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woodley, D.T.; Fan, J.; Cheng, C.F.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Bu, G.; Li, W. Participation of the lipoprotein receptor LRP1 in hypoxia-HSP90alpha autocrine signaling to promote keratinocyte migration. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 1495–1498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Chang, C.; Hao, M.; Chen, M.; Woodley, D.T.; Schönthal, A.H.; Li, W. Heat shock protein-90alpha (Hsp90α) stabilizes hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) in support of spermatogenesis and tumorigenesis. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 1058–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Monte, U. Does the cell number 109 still really fit one gram of tumor tissue? Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianconi, E.; Piovesan, A.; Facchin, F.; Beraudi, A.; Casadei, R.; Frabetti, F.; Vitale, L.; Pelleri, M.C.; Tassani, S.; Piva, F.; et al. An estimation of the number of cells in the human body. Ann. Hum. Biol. 2013, 40, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sender, R.; Fuchs, S.; Milo, R. Revised estimates for the number of human and bacteria cells in the body. PLoS Biology 2016, 19, e1002533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogh-Andersen, N.; Altura, B.M.; Altura, B.T.; Siggaard-Andersen, O. Composition of interstitial fluid. Clin. Chem. 1995, 41, 1522–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkman, J.E.; Dorius, B.; Sharma, S. Physiology, Body Fluids. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2024; Bookshelf ID: NBK482447. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.J.; Chirico, W.J.; Lipke, P.N. Through the back door: Unconventional protein secretion. Cell Surf. 2020, 6, 100045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Dupont, N.; Castillo, E.F.; Deretic, V. Secretory versus degradative autophagy: Unconventional secretion of inflammatory mediators. J. Innate Immun. 2013, 5, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponpuak, M.; Mandell, M.A.; Kimura, T.; Chauhan, S.; Cleyrat, C.; Deretic, V. Secretory autophagy. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 35, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishida, Y.; Arakawa, S.; Fujitani, K.; Yamaguchi, H.; Mizuta, T.; Kanaseki, T.; Komatsu, M.; Otsu, K.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Shimizu, S. Discovery of Atg5/Atg7-independent alternative macroautophagy. Nature 2009, 461, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekier, M.E.; Wang, L.; Li, J.; Huang, H.; Tang, D.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y. Knockout of the Golgi stacking proteins GRASP55 and GRASP65 impairs Golgi structure and function. Mol. Biol. Cell 2017, 28, 2833–2842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guan, J.; Niu, X.; Hu, G.; Guo, S.; Li, Q.; Xie, Z.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y. Exosomes released from human induced pluripotent stem cells-derived MSCs facilitate cutaneous wound healing by promoting collagen synthesis and angiogenesis. J. Transl. Med. 2015, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Yu, M.; Xie, D.; Wang, L.; Ye, C.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, F.; Yang, L. Melatonin-stimulated MSC-derived exosomes improve diabetic wound healing through regulating macrophage M1 and M2 polarization by targeting the PTEN/AKT pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voss, A.K.; Thomas, T.; Gruss, P. Mice lacking HSP90beta fail to develop a placental labyrinth. Development 2000, 127, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhlén, M.; Fagerberg, L.; Hallström, B.M.; Lindskog, C.; Oksvold, P.; Mardinoglu, A.; Sivertsson, Å.; Kampf, C.; Sjöstedt, E.; Asplund, A.; et al. Proteomics. Tissue-based map of the human proteome. Science 2015, 347, 1260419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Lucas, D.A.; Chan, K.C.; Issaq, H.J.; Petricoin, E.F.; Liotta, L.A.; Veenstra, T.D.; Conrads, T.P. An investigation into the human serum “interactome”. Electrophoresis 2004, 25, 1289–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inal, J.M.; Kosgodage, U.; Azam, S.; Stratton, D.; Antwi-Baffour, S.; Lange, S. Blood/plasma secretome and microvesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1834, 2317–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Roybal, J.; Chaerkady, R.; Zhang, W.; Choi, K.; Alvarez, C.A.; Tran, H.; Creighton, C.J.; Yan, S.; Strieter, R.M.; et al. Identification of secreted proteins that mediate cell-cell interactions in an in vitro model of the lung cancer microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 7237–7245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Chang, C.; Mosallaei, D.; Woodley, D.T.; Schönthal, A.H.; Chen, M.; Li, W. Heterogeneous Responses and Isoform Compensation the Dim Therapeutic Window of Hsp90 ATP-Binding Inhibitors in Cancer. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 42, e0045921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chang, C.; Tang, X.; Schönthal, A.H.; Chen, M.; Woodley, D.T.; Wang, Y.; Liang, C.; Li, W. Discovery of Cell Number-Interstitial Fluid Volume (CIF) Ratio Reveals Secretory Autophagy Pathway to Supply eHsp90α for Wound Healing. Cells 2024, 13, 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151280
Chang C, Tang X, Schönthal AH, Chen M, Woodley DT, Wang Y, Liang C, Li W. Discovery of Cell Number-Interstitial Fluid Volume (CIF) Ratio Reveals Secretory Autophagy Pathway to Supply eHsp90α for Wound Healing. Cells. 2024; 13(15):1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151280
Chicago/Turabian StyleChang, Cheng, Xin Tang, Axel H. Schönthal, Mei Chen, David T. Woodley, Yanzhuang Wang, Chengyu Liang, and Wei Li. 2024. "Discovery of Cell Number-Interstitial Fluid Volume (CIF) Ratio Reveals Secretory Autophagy Pathway to Supply eHsp90α for Wound Healing" Cells 13, no. 15: 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151280
APA StyleChang, C., Tang, X., Schönthal, A. H., Chen, M., Woodley, D. T., Wang, Y., Liang, C., & Li, W. (2024). Discovery of Cell Number-Interstitial Fluid Volume (CIF) Ratio Reveals Secretory Autophagy Pathway to Supply eHsp90α for Wound Healing. Cells, 13(15), 1280. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13151280








