The Metabolomic Footprint of Liver Fibrosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Metabolomics
2.1. Early Studies Using NMR-Based Metabonomics
2.2. Recent Studies Using 13C and 31P NMR-Based Metabonomics
2.3. Recent Studies Using 1H NMR-Based Metabolomics
| Species | Fibrogen | Tissue | Upregulated Metabolites | Downregulated Metabolites | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rat | thioacetamide | liver | BCAA, lactate, alanine, acetate, acetoacetate, glutamine, TMA | - | [75] |
| rat | thioacetamide | serum urine | phenylalanine, N,N-dimethyl glycine, O-acetyl glycoprotein, N-acetyl glycoprotein choline 2-hydroxybutyrate, 3-hydroxybutyrate, adipate | - | [122] |
| rat | aflatoxin B1 | plasma liver | glucose, amino acids, choline, phosphocholine, glycerophosphocholine lipids, tyrosine, histidine, phenylalanine, BCAA, choline, inosine, adenosine, uridine | lipids glycogen, glucose | [76] |
| human human human human mouse (MRS) human (MRI) human human human | HBV HCV alcohol HBV thioacetamide HCV, MASLD, ASH, AIH HCV HCV HCV | serum liver serum serum liver liver serum serum serum | acetate, N-acetylglycoproteins, pyruvate, glutamine, 2-oxo-glutarate, taurine, glycerol, tyrosine, 1-methylhistidine, phenylalanine glutamate, phosphocholine, phosphoethanolamine lactate, pyruvate, glucose, BCAA, methionine, glutamine, citrate, creatinine glucose, lactate [1-13C]lactate/pyruvate, [1-13C]lactate/total carbon, [1-13C]alanine/pyruvate, [1-13C]alanine/total carbon glycerophosphatidylethanolamine VLDL1, citrate, lipid, glucose/sugars, phenylalanine histidine, methionine, tyrosine, methylsuccinate, formate, propionate, 2-hydroxy-isovalerate, 2-oxoisocaproate, methylguanidine, 1,7-dimethylxanthine, caffeine fucose, carnitine, lysine, 3-hydroxybutyrate, ornithine, glycerol, methionine, methanol, isopropanol | LDL, VLDL, BCAA, acetoacetate, choline, unsaturated lipid glucose - Lipids, choline inorganic phosphate, phosphatidylcholine LDL, acetoacetate, choline, BCAA, creatinine, creatine, glutamate, glutamine, HDL, asparagine, VLDL2, lysine, arginine, glycerol, 3-hydroxybutyrate, histidine N-acetylglycine, asparagine, creatinine, glutamine, glycine, methylhistidine, N-acetylaspartate, threonine, urea, adenosine proline, serine, valine, glutamine, creatinine | [77] [80] [82] [88] [93] [109] [110] [111] |
2.4. Summary of NMR Studies on Liver Fibrosis
2.5. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics
- (i)
- The stabilization of the collagen triple helix under physiological conditions is dependent upon the post-translational modification by proline 4-hydroxylation at -X-Pro-Gly sequences that require Fe2+, O2, ascorbate and 2-oxoglutarate, the last of which undergoes oxidative decarboxylation to succinate [165].
- (ii)
- In most mammals, excluding humans, certain primates and the guinea pig, ascorbate must be synthesized de novo, and the synthetic pathway involves the conversion of glucuronic acid via gulonic acid and gulonolactone, as depicted in Figure 1. Glucuronic acid is itself synthesized from the hexose precursors glucose, fructose and galactose as shown.
2.6. Summary of GC–MS Metabolomic Studies of Liver Fibrosis
2.7. Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry-Based Metabolomics
| Species | Fibrogen | Treatment | Tissue | Analytical Platform | Biochemical Pathways Affected by Fibrogen | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mouse mouse rat rat mouse rat mouse rat rat | TAA CCl4 CCl4 CCl4 CCl4 DMN CCl4 CCl4 CCl4 | picroside I phylligenin TACS Ganlong capsules YQJPF FHC curcumol - - - | serum urine liver feces feces liver serum urine feces serum serum urine serum serum | UPLC–QTOFMS GC–MS UPLC–TQMS UPLC–QTOFMS LC–MS LC–MS/MS LC–MS LC–MS UPLC–QTOFMS UPLC–QTOFMS | (PC, LPC) ↑ valine ↑ (glycerophospholipid metabolism, GSH, GSSG) ↑ SCFA ↓ BA (alloLCA, LCA, isoLCA, 7-ketoLCA, norDCA, CDCA, UDCA, HDCA, norCA, 6,7-diketoLCA, α-MCA, UCA, β-MCA; TCDCA) ↑ (5-phosphonooxy-L-lysine, 5-hydroxy-L-tryptophan, phosphoserine, 7-methylinosine, 3-methyl-2-(3-pyridyl)-1-indoleoctanoic acid *, β-alanyl-L-lysine, GCA, KCA, 7-sulfocholic acid, homomethionine, 3-methylindole, benzphetamine *) ↑ (glutathione, deoxyinosine, γ-glutamylglutamic acid, N2-acetyl-ornithine, CA, KDCA, CDCA, NCA, DCA, lysyltyrosine, N-acetyl-L-methionine) ↓ (5α-pregnane-3,20-dione, 4-(4-methyl-3-pentenyl)-3-cyclohexene-1-carboxaldehyde), PG(18:2(9Z,12Z)/18:2(9Z,12Z)), 6-hydroxy-1H-indole-3-acetamide, vanilloside, PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/P-18:0), PE(16:0/18:3(9Z,12Z,15Z)), 5-methylcytidine, L-carnitine, 2-hydroxy-6-pentadecylbenzoic acid **, m-coumaric acid, imidazoleacetic acid, uracil, prostaglandin E2, deoxycytidine, (R)-3-hydroxybutyric acid, pyroglutamic acid, γ-aminobutyric acid, myo-inositol, O-phosphoethanolamine) ↑ (DG(18:1(9Z)/18:4(6Z,9Z,12Z,15Z)), xanthosine, xanthine, N-acetylhistidine, β-D-glucosamine, N6-acetyl-L-lysine, γ-glutamylleucine, ascorbic acid, eicosapentaenoic acid, acetylglycine, citraconic acid, deoxyribose 5-phosphate, dihydrolipoate, prostaglandin B1, D-ribose, 2-furoic acid, isobutyrylglycine, L-iditol, fructose 1-phosphate, 2-ketobutyric acid, citramalic acid, D-mannose, S-adenosylhomocysteine) ↓ (thymine, PC(P-18:1(11Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)), PE(P-18:1(11Z)/22:5(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z)), PC(20:2(11Z,14Z)/20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)), PE(P-18:1(9Z)/ 20:4(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z)), PE(O-16:1(1Z)/22:6(4Z,7Z,10Z,13Z,16Z,19Z)), PC(20:4(8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)/P-18:0), vaccenylcarnitine, SM(d16:1/24:1(15Z)), (E)-5-tetradecanoylcarnitine, dodecanoylcarnitine, trimethylamine N-oxide, lysylvaline, hexylresorcinol *, maslinic acid *, thymidine, p-cresol) ↑ (dieporeticenin, 1H-indole-3-carboxaldehyde, 2-furoic acid, malonic acid) ↓ ginkgolide B * ↑ (dimethylhistamine, adrenochrome, N2-methylnorsalsolinol, vanillylamine, meconine, homovanillin, 3-methylpyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine *, β-D-glucosamine, isopentyl β-D-glucoside *, 2-methylbutyroylcarnitine, 4-trimethylammoniobutanoic acid, alanylproline, choline, naphthalene epoxide *, 2-acetylthiazole **, hydroxyprolylleucine, L-leucine, betaine aldehyde, lauroyl diethanolamide *) ↓ (4,4′-methylenebis(2,6-di-tert-butylphenol) *, mono(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate *, 2,3-dinor prostaglandin E1, mozenavir *, p-cresylsulfate) ↑ Paper in Chinese (soyasaponin I *, guggulsterone *, 3-ureidopropionic acid, 7-methylguanine, carnitine, N-acetylglutamic acid, N′2-benzylidene-5-hex-1-ynylfuran-2-carbohydrazide *, 3β,7β-dihydroxy-5-androsten-17-one, 4-oxoretinol, (Z)-9,10,11-trihydroxyoctadec-12-enoic acid *, 3-acetyl-11-keto-β-boswellic acid *, avocadyne 1-acetate, propionylcarnitine, 12,13-epoxy-9-octadecenoic acid, N-methylhydantoin ‡, 4-hexyloxyaniline *, methionine sulfoxide, aspartylglutamate, α-lapachone *, pantethine, O-acetylserine, 3-hydroxy-2-(3-nitro-4-piperidenylbenzyl)propanenitrile *, PC(4:0/18:5), PC(18:3/3:0), PC(14:1/24:1), PC(14:1/3:0), N5-(1,3,6-trimethyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)-1H-1,2,4-triazole-3,5-diamine *, histamine, glycyltyrosine, MAG(18:2), 2-deoxyuridine, 4-methyl-5-oxo-2-pentyl-2,5-dihydrofuran-3-carboxylic acid (striatisporolide A) *, cytidine, valproic acid *, 6-ketoprostaglandin F1α, indole-5,6-quinone) ↑ (methionine, leukotriene C4, norvaline, N-isobutyrylglycine, theophylline *, D-ala-D-ala, dihydroroseoside *, arginine, PE(16:0/22:6), cinnamoylglycine, pyroglutamic acid, isoniazid *, 5-[(10Z)-14-(3,5-dihydroxyphenyl)tetradec-10-en-1-yl)benzene-1,3-diol*, trimethyllysine, LPE(22:4)) ↓ (tryptophan, cis-aconitic acid, methylmalonic acid) ↑ (kynurenic acid, 5-hydroxyindoleacetylglycine, 3-methyldioxyindole, 4-(2-amino-3-hydroxyphenyl)-2,4-dioxobutanoic acid, isocitric acid, leucine) ↓ (valine, leucine, tryptophan, cholesterol, GCA) ↑ (sphinganine, lactosylceramide, sphingomyelin, lysoPC(17:0), PC (18:1(11Z)/20:5(5Z,8Z,11Z,14Z,17Z)) ↓ (β-MCA, cervonoyl ethanolamide, hydroxyethyl glycine, threonine, indoleacetic acid) ↑ | [166] [167] [168] [169] [170] [171] [172] [173] [174] |
2.8. Summary of LC–MS Metabolomic Studies of Liver Fibrosis
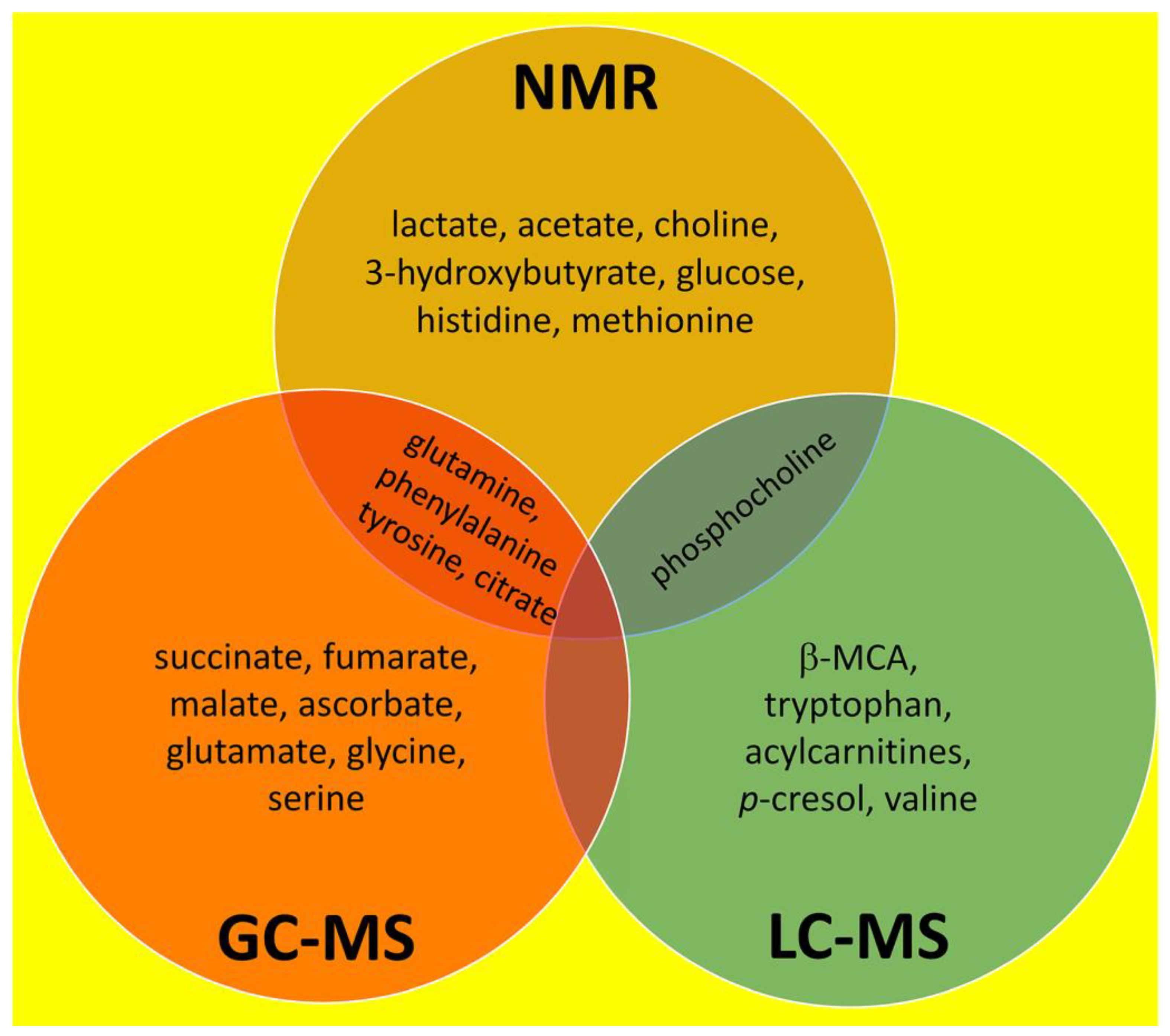
3. Overall Summary of NMR, GC–MS and LC–MS Investigations Into Liver Fibrosis
4. Brief Commentary on Medicinal Treatments for Liver Fibrosis
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bataller, R.; Brenner, D.A. Liver fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.D.; Zhou, J.; Chen, E.Q. Molecular Mechanisms and Potential New Therapeutic Drugs for Liver Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 787748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernon, G.; Baranova, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Systematic review: The epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 34, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arshad, T.; Paik, J.M.; Biswas, R.; Alqahtani, S.A.; Henry, L.; Younossi, Z.M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Prevalence Trends Among Adolescents and Young Adults in the United States, 2007–2016. Hepatol. Commun. 2021, 5, 1676–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angulo, P.; Kleiner, D.E.; Dam-Larsen, S.; Adams, L.A.; Bjornsson, E.S.; Charatcharoenwitthaya, P.; Mills, P.R.; Keach, J.C.; Lafferty, H.D.; Stahler, A.; et al. Liver Fibrosis, but No Other Histologic Features, Is Associated With Long-term Outcomes of Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 389–397.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dulai, P.S.; Singh, S.; Patel, J.; Soni, M.; Prokop, L.J.; Younossi, Z.; Sebastiani, G.; Ekstedt, M.; Hagstrom, H.; Nasr, P.; et al. Increased risk of mortality by fibrosis stage in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Hepatology 2017, 65, 1557–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, R.S.; Taylor, R.J.; Bayliss, S.; Hagstrom, H.; Nasr, P.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Ishigami, M.; Toyoda, H.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Peleg, N.; et al. Association Between Fibrosis Stage and Outcomes of Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1611–1625.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, A.J.; Van Natta, M.L.; Clark, J.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.A.; Diehl, A.; Dasarathy, S.; Loomba, R.; Chalasani, N.; Kowdley, K.; Hameed, B.; et al. Prospective Study of Outcomes in Adults with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1559–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Willoughby, C.E.; Singal, A.G.; Greten, T.F.; Heikenwalder, M.; El-Serag, H.B.; Finn, R.S.; Friedman, S.L. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Pathogenesis and treatment. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2023, 20, 487–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anstee, Q.M.; Reeves, H.L.; Kotsiliti, E.; Govaere, O.; Heikenwalder, M. From NASH to HCC: Current concepts and future challenges. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inverso, D.; Iannacone, M. Spatiotemporal dynamics of effector CD8+ T cell responses within the liver. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2016, 99, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glynn, L.E.; Himsworth, H.P.; Lindan, O. The experimental production and development of diffuse hepatic fibrosis, portal cirrhosis. Br. J. Exp. Pathol. 1948, 29, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hinton, D.E.; Williams, W.L. Hepatic fibrosis associated with aging in four stocks of mice. J. Gerontol. 1968, 23, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunn, M.A.; Rojkind, M.; Warren, K.S.; Hait, P.K.; Rifas, L.; Seifter, S. Liver collagen synthesis in murine schistosomiasis. J. Clin. Investig. 1977, 59, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scorza, C.; Scorza, J.V. Experimental study on the pathogenesis of hepatic fibrosis in rabbits infected with Schistosoma japonicum. Z. Tropenmed Parasitol. 1967, 18, 433–455. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paronetto, F.; Popper, H. Chronic liver injury induced by immunologic reactions. Cirrhosis following immunization with heterologous sera. Am. J. Pathol. 1966, 49, 1087–1101. [Google Scholar]
- Chaikoff, I.L.; Entenman, C.; Gillman, T.; Reichert, F.L. Hepatic fibrosis in the persistently non-fatty liver of the hypophysectomized dog. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1948, 67, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikoff, I.L.; Gillman, T.; Entenman, C.; Rinehart, J.F.; Reichert, F.L. Cirrhosis and other hepatic lesions produced in dogs by thyroidectomy and by combined hypophysectomy and thyroidectomy. J. Exp. Med. 1948, 88, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opie, E.L.; Alford, L.B. The Influence of Diet Upon Necrosis Caused by Hepatic and Renal Poisons: Part I. Diet and the Hepatic Lesions of Chloroform, Phosphorus, or, Alcohol. J. Exp. Med. 1915, 21, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, G.H.; Grove, R.C.; Gustafson, R.K.; Maire, E.D.; Thompson, M.J.; Wells, H.S.; Lamson, P.D. Studies on the pathological histology of experimental carbon tetrachloride poisoning. Bull. Johns. Hopkins Hosp. 1925, XXXVI, 107–133. [Google Scholar]
- Koch Weser, D.; Popper, H. Hepatic fibrosis produced by chronic ethionine feeding. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1952, 79, 34–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirayama, C.; Hartmann, F. On the biochemistry of liver connective tissue during the development of liver fibrosis induced in rats by thioacetamide. Acta Hepatosplenol. 1961, 8, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keppler, D.; Lesch, R.; Reutter, W.; Decker, K. Experimental hepatitis induced by D-galactosamine. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 1968, 9, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broitman, S.A.; Gottlieb, L.S.; Zamcheck, N. Influence of Neomycin and Ingested Endotoxin in the Pathogenesis of Choline Deficiency Cirrhosis in the Adult Rat. J. Exp. Med. 1964, 119, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, N.C. The Influence of Diet upon the Liver Injury produced by Carbon Tetrachloride. J. Med. Res. 1924, 44, 601–614.3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Best, C.H.; Huntsman, M.E. The effects of the components of lecithine upon deposition of fat in the liver. J. Physiol. 1932, 75, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Best, C.H.; Channon, H.J.; Ridout, J.H. Choline and the dietary production of fatty livers. J. Physiol. 1934, 81, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Channon, H.J.; Wilkinson, H. Choline and the "cholesterol" fatty liver. Biochem. J. 1934, 28, 2026–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorgy, P.; Goldblatt, H. Further observations on the production and prevention of dietary hepatic injury in rats. J. Exp. Med. 1949, 89, 245–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyorgy, P.; Goldblatt, H. Observations on the Conditions of Dietary Hepatic Injury (Necrosis, Cirrhosis) in Rats. J. Exp. Med. 1942, 75, 355–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Earle, D.P.; Kendall, F.E. Liver damage and urinary excretion of sulfate in rats fed l-cystine, dl-methionine, and cysteic acid. J. Exp. Med. 1942, 75, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, R.J.; Kent, G.; Barka, T.; Popper, H. Effect of methionine upon ethionine intoxication of the rat. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1960, 103, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farber, E.; Ichinose, H. The prevention of ethionine-induced carcinoma of the liver in rats by methionine. Cancer Res. 1958, 18, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cantoni, G.L. S-Adenosylmethionine; a new intermediate formed enzymatically from L-methionine and adenosinetriphosphate. J. Biol. Chem. 1953, 204, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cantoni, G.L. The nature of the active methyl donor formed enzymatically from L-methionine and adenosinetriphosphate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1952, 74, 2942–2943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loenen, W.A. S-adenosylmethionine: Jack of all trades and master of everything? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2006, 34, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parks, L.W. S-Adenosylethionine and ethionine inhibition. J. Biol. Chem. 1958, 232, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swann, P.F. The effect of ethionine on ribonucleic acid synthesis in rat liver. Biochem. J. 1975, 150, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villa-Trevino, S.; Shull, K.H.; Farber, E. The inhibition of liver ribonucleic acid synthesis by ethionine. J. Biol. Chem. 1966, 241, 4670–4674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swann, P.F.; Pegg, A.E.; Hawks, A.; Farber, E.; Magee, P.N. Evidence for ethylation of rat liver deoxyribonucleic acid after administration of ethionine. Biochem. J. 1971, 123, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, M.; Tarver, H. Studies on ethionine. III. Incorporation of ethionine into rat proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 192, 835–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.S.; Buck, M.; Houglum, K.; Chojkier, M. Activation of hepatic stellate cells by TGF alpha and collagen type I is mediated by oxidative stress through c-myb expression. J. Clin. Invest. 1995, 96, 2461–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camps, J.; Bargallo, T.; Gimenez, A.; Alie, S.; Caballeria, J.; Pares, A.; Joven, J.; Masana, L.; Rodes, J. Relationship between hepatic lipid peroxidation and fibrogenesis in carbon tetrachloride-treated rats: Effect of zinc administration. Clin. Sci. 1992, 83, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, I.; Auster, A.S.; Matsui, A.; Greenwel, P.; Geerts, A.; D’Amico, T.; Fujiwara, K.; Kessler, E.; Rojkind, M. Up-regulation of type I procollagen C-proteinase enhancer protein messenger RNA in rats with CCl4-induced liver fibrosis. Hepatology 1997, 26, 611–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, S.; Potter, J.J.; Geschwind, J.F.; Sur, S.; Hamilton, J.P.; Vogelstein, B.; Kinzler, K.W.; Mezey, E.; Ganapathy-Kanniappan, S. Deregulation of energy metabolism promotes antifibrotic effects in human hepatic stellate cells and prevents liver fibrosis in a mouse model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 469, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyoglu, D.; Idle, J.R. Metabolomic insights into the mode of action of natural products in the treatment of liver disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2020, 180, 114171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyoglu, D.; Idle, J.R. Metabolomic and Lipidomic Biomarkers for Premalignant Liver Disease Diagnosis and Therapy. Metabolites 2020, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyoglu, D.; Idle, J.R. The metabolomic window into hepatobiliary disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 59, 842–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patterson, A.D.; Maurhofer, O.; Beyoglu, D.; Lanz, C.; Krausz, K.W.; Pabst, T.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Dufour, J.F.; Idle, J.R. Aberrant lipid metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma revealed by plasma metabolomics and lipid profiling. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 6590–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyoglu, D.; Imbeaud, S.; Maurhofer, O.; Bioulac-Sage, P.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Dufour, J.F.; Idle, J.R. Tissue metabolomics of hepatocellular carcinoma: Tumor energy metabolism and the role of transcriptomic classification. Hepatology 2013, 58, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semmo, N.; Weber, T.; Idle, J.R.; Beyoglu, D. Metabolomics reveals that aldose reductase activity due to AKR1B10 is upregulated in hepatitis C virus infection. J. Viral Hepat. 2015, 22, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyoglu, D.; Simillion, C.; Storni, F.; De Gottardi, A.; Idle, J.R. A Metabolomic Analysis of Cirrhotic Ascites. Molecules 2022, 27, 3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyoglu, D.; Schwalm, S.; Semmo, N.; Huwiler, A.; Idle, J.R. Hepatitis C Virus Infection Upregulates Plasma Phosphosphingolipids and Endocannabinoids and Downregulates Lysophosphoinositols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C. Systems biology: Metabonomics. Nature 2008, 455, 1054–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliver, S.G.; Winson, M.K.; Kell, D.B.; Baganz, F. Systematic functional analysis of the yeast genome. Trends Biotechnol. 1998, 16, 373–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kell, D.B.; Oliver, S.G. The metabolome 18 years on: A concept comes of age. Metabolomics 2016, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiehn, O. Metabolomics--the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 48, 155–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E. ’Metabonomics’: Understanding the metabolic responses of living systems to pathophysiological stimuli via multivariate statistical analysis of biological NMR spectroscopic data. Xenobiotica 1999, 29, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hang, D.; Yang, X.; Lu, J.; Shen, C.; Dai, J.; Lu, X.; Jin, G.; Hu, Z.; Gu, D.; Ma, H.; et al. Untargeted plasma metabolomics for risk prediction of hepatocellular carcinoma: A prospective study in two Chinese cohorts. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 2144–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumas, M.E.; Kinross, J.; Nicholson, J.K. Metabolic phenotyping and systems biology approaches to understanding metabolic syndrome and fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2014, 146, 46–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakallioglu, I.T.; Tripp, B.; Kubik, J.; Casey, C.A.; Thomes, P.; Powers, R. Multiomics Approach Captures Hepatic Metabolic Network Altered by Chronic Ethanol Administration. Biology 2022, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ioannou, G.N.; Nagana Gowda, G.A.; Djukovic, D.; Raftery, D. Distinguishing NASH Histological Severity Using a Multiplatform Metabolomics Approach. Metabolites 2020, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.I.; Lo, C.J.; Zheng, C.W.; Lee, C.W.; Lee, W.C.; Lin, J.R.; Shiao, M.S.; Cheng, M.L.; Yu, H.P. A Lipidomics Study Reveals Lipid Signatures Associated with Early Allograft Dysfunction in Living Donor Liver Transplantation. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 8, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damadian, R.; Zaner, K.; Hor, D.; Dimaio, T. Human tumors by NMR. Physiol. Chem. Phys. 1973, 5, 381–402. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Damadian, R.; Zaner, K.; Hor, D.; DiMaio, T.; Minkoff, L.; Goldsmith, M. Nuclear magnetic resonance as a new tool in cancer research: Human tumors by NMR. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1973, 222, 1048–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunham, L.; Nichols, S.; Brunschwig, A. Potassium and calcium content of carcinomas and papillomas of the colon. Cancer Res. 1946, 6, 233. [Google Scholar]
- Brunschwig, A.; Dunham, L.; Nichols, S. Potassium and calcium content of gastric carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1946, 6, 230–232. [Google Scholar]
- Dunham, L.J.; Brunschwig, A. Calcium and potassium content of secretions from noncancerous and cancerous stomachs. Cancer Res. 1946, 6, 54–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bollard, M.E.; Garrod, S.; Holmes, E.; Lindon, J.C.; Humpfer, E.; Spraul, M.; Nicholson, J.K. High-resolution (1)H and (1)H-(13)C magic angle spinning NMR spectroscopy of rat liver. Magn. Reson. Med. 2000, 44, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waters, N.J.; Garrod, S.; Farrant, R.D.; Haselden, J.N.; Connor, S.C.; Connelly, J.; Lindon, J.C.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.K. High-resolution magic angle spinning (1)H NMR spectroscopy of intact liver and kidney: Optimization of sample preparation procedures and biochemical stability of tissue during spectral acquisition. Anal. Biochem. 2000, 282, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, A.W.; Nicholson, J.K.; Haselden, J.N.; Waterfield, C.J. A metabonomic approach to the investigation of drug-induced phospholipidosis: An NMR spectroscopy and pattern recognition study. Biomarkers 2000, 5, 410–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, D.G.; Reily, M.D.; Sigler, R.E.; Wells, D.F.; Paterson, D.A.; Braden, T.K. Metabonomics: Evaluation of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) and pattern recognition technology for rapid in vivo screening of liver and kidney toxicants. Toxicol. Sci. 2000, 57, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantinou, M.A.; Theocharis, S.E.; Mikros, E. Application of metabonomics on an experimental model of fibrosis and cirrhosis induced by thioacetamide in rats. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 218, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ye, Y.; An, Y.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H. Systems responses of rats to aflatoxin B1 exposure revealed with metabonomic changes in multiple biological matrices. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Lu, Q.; Liu, X.; Cong, H.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Lin, D. Application of 1H NMR-based metabonomics in the study of metabolic profiling of human hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis. Cancer Sci. 2009, 100, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrew, E.R.; Bradbury, A.; Eades, R.G. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectra from a Crystal rotated at High Speed. Nature 1958, 182, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.; Oldfield, E.; Doskocilova, D.; Schneider, B. NMR of gel and liquid crystalline phospholipids spinning at the ‘magic angle’. FEBS Lett. 1972, 25, 261–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Granados, B.; Morales, J.M.; Rodrigo, J.M.; Del Olmo, J.; Serra, M.A.; Ferrandez, A.; Celda, B.; Monleon, D. Metabolic profile of chronic liver disease by NMR spectroscopy of human biopsies. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2011, 27, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amathieu, R.; Nahon, P.; Triba, M.; Bouchemal, N.; Trinchet, J.C.; Beaugrand, M.; Dhonneur, G.; Le Moyec, L. Metabolomic approach by 1H NMR spectroscopy of serum for the assessment of chronic liver failure in patients with cirrhosis. J. Proteome Res. 2011, 10, 3239–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, S.W.; Tu, Z.G.; Peng, W.J.; Wang, L.X.; Ou-Yang, X.; Cai, A.J.; Dai, Y. (1)H NMR-based serum metabolic profiling in compensated and decompensated cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, L.; Lanz, B.; Andreola, F.; Ampuero, J.; Wijeyesekera, A.; Holmes, E.; Deutz, N. New technologies-new insights into the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 2016, 31, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qayyum, A. MR spectroscopy of the liver: Principles and clinical applications. Radiographics 2009, 29, 1653–1664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.J.; Ohliger, M.A.; Larson, P.E.Z.; Gordon, J.W.; Bok, R.A.; Slater, J.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Hess, C.P.; Kurhanewicz, J.; Vigneron, D.B. Hyperpolarized (13)C MRI: State of the Art and Future Directions. Radiology 2019, 291, 273–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deen, S.S. Metabolic Phenotyping of Prostate Cancer Using Hyperpolarized (13)C MRI. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2023, 5, e239001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deen, S.S.; Rooney, C.; Shinozaki, A.; McGing, J.; Grist, J.T.; Tyler, D.J.; Serrao, E.; Gallagher, F.A. Hyperpolarized Carbon 13 MRI: Clinical Applications and Future Directions in Oncology. Radiol. Imaging Cancer 2023, 5, e230005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, C.M.; Shin, S.S.; Heo, S.H.; Lim, H.S.; Moon, M.J.; Surendran, S.P.; Kim, G.E.; Park, I.W.; Jeong, Y.Y. Metabolic Changes in Different Stages of Liver Fibrosis: In vivo Hyperpolarized (13)C MR Spectroscopy and Metabolic Imaging. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2019, 21, 842–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardenkjaer-Larsen, J.H.; Fridlund, B.; Gram, A.; Hansson, G.; Hansson, L.; Lerche, M.H.; Servin, R.; Thaning, M.; Golman, K. Increase in signal-to-noise ratio of > 10,000 times in liquid-state NMR. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10158–10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, Z.; Ahmed, U.; Walayat, S.; Ren, J.; Martin, D.K.; Moole, H.; Koppe, S.; Yong, S.; Dhillon, S. Liver function tests in identifying patients with liver disease. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2018, 11, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yada, M.; Miyazaki, M.; Motomura, K.; Masumoto, A.; Nakamuta, M.; Kohjima, M.; Sugimoto, R.; Aratake, Y.; Higashi, N.; Morizono, S.; et al. The prognostic role of lactate dehydrogenase serum levels in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who are treated with sorafenib: The influence of liver fibrosis. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2016, 7, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National-Maglab. Sun Churn. Available online: https://nationalmaglab.org/magnet-academy/history-of-electricity-magnetism/places/magnetic-field-of-sun/ (accessed on 27 April 2024).
- Purvis, L.A.B.; Clarke, W.T.; Valkovic, L.; Levick, C.; Pavlides, M.; Barnes, E.; Cobbold, J.F.; Robson, M.D.; Rodgers, C.T. Phosphodiester content measured in human liver by in vivo (31) P MR spectroscopy at 7 tesla. Magn. Reson. Med. 2017, 78, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, M.M.; Varghese, R.S.; Ding, Y.; Ressom, H.W. Biomarker Discovery for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Liver Cirrhosis Using Untargeted Metabolomics and Lipidomics Studies. Metabolites 2023, 13, 1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisel, S.H. Dietary choline: Biochemistry, physiology, and pharmacology. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 1981, 1, 95–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Song, J.; Mar, M.H.; Edwards, L.J.; Zeisel, S.H. Phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase (PEMT) knockout mice have hepatic steatosis and abnormal hepatic choline metabolite concentrations despite ingesting a recommended dietary intake of choline. Biochem. J. 2003, 370, 987–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccatonda, A.; Andreetto, L.; D’Ardes, D.; Cocco, G.; Rossi, I.; Vicari, S.; Schiavone, C.; Cipollone, F.; Guagnano, M.T. From NAFLD to MAFLD: Definition, Pathophysiological Basis and Cardiovascular Implications. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.A. The prevalence and incidence of NAFLD worldwide: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francque, S.; De Maeght, S.; Adler, M.; Deltenre, P.; de Galocsy, C.; Orlent, H.; Van Steenbergen, W.; Bastens, B.; Wain, E.; Langlet, P.; et al. High prevalence of advanced fibrosis in association with the metabolic syndrome in a Belgian prospective cohort of NAFLD patients with elevated ALT. Results of the Belgian NAFLD registry. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 2011, 74, 9–16. [Google Scholar]
- Yip, T.C.; Lyu, F.; Lin, H.; Li, G.; Yuen, P.C.; Wong, V.W.; Wong, G.L. Non-invasive biomarkers for liver inflammation in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Present and future. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2023, 29, S171–S183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.L.; Jiang, S.W.; Hu, A.R.; Zhou, A.W.; Hu, T.; Li, H.S.; Fan, Y.; Lin, K. Non-invasive diagnosis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Current status and future perspective. Heliyon 2024, 10, e27325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halfon, P.; Bourliere, M.; Penaranda, G.; Cacoub, P. Noninvasive methods for predicting liver fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C: Alternatives to liver biopsy. Presse Med. 2007, 36, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manduca, A.; Oliphant, T.E.; Dresner, M.A.; Mahowald, J.L.; Kruse, S.A.; Amromin, E.; Felmlee, J.P.; Greenleaf, J.F.; Ehman, R.L. Magnetic resonance elastography: Non-invasive mapping of tissue elasticity. Med. Image Anal. 2001, 5, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, A.S.; Hasan, I.; Lesmana, C.R.A.; Kurniawan, J.; Jasirwan, C.O.M.; Nababan, S.; Kalista, K.F.; Hanifa, R.S.; Rachmani, D.; Gani, R.A. Diagnostic Performance of Mac-2-Binding Protein Glycosylation Isomer (M2BPGi), compared to Transient Elastography to Assess Liver Stiffness in Treatment Naive Chronic Hepatitis C Patients. Acta Med. Indones. 2022, 54, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aleman-Garcia, N.; Sanchez-Perez, C.; Perez-Garcia, A.; Duran-Pardilla, M.; Kershenobich, D.; Hernandez-Ruiz, J. Correlation of hepatic fibrosis assessed by Metavir score and digital morphometry in a murine model. Rev. Med. Hosp. Gen. Mexico 2020, 83, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.B.; Mehta, K.J. Liver biopsy for assessment of chronic liver diseases: A synopsis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2023, 23, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Embade, N.; Marino, Z.; Diercks, T.; Cano, A.; Lens, S.; Cabrera, D.; Navasa, M.; Falcon-Perez, J.M.; Caballeria, J.; Castro, A.; et al. Metabolic Characterization of Advanced Liver Fibrosis in HCV Patients as Studied by Serum 1H-NMR Spectroscopy. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0155094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarfaraz, M.O.; Myers, R.P.; Coffin, C.S.; Gao, Z.H.; Shaheen, A.A.; Crotty, P.M.; Zhang, P.; Vogel, H.J.; Weljie, A.M. A quantitative metabolomics profiling approach for the noninvasive assessment of liver histology in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Clin. Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, A.; Swaroop, S.; Dubey, D.; Rawat, A.; Verma, A.; Baisya, B.; Parihar, R.; Goel, A.; Rungta, S. The metabolic fingerprint of chronic hepatitis C progression: Metabolome shifts and cutting-edge diagnostic options. J. Mol. Recognit. 2024, 37, e3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.T.; Wimmer, R.; Le, V.Q.; Krarup, H.B. Metabolic fingerprint of progression of chronic hepatitis B: Changes in the metabolome and novel diagnostic possibilities. Metabolomics 2021, 17, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandrin, L.; Fourquet, B.; Hasquenoph, J.M.; Yon, S.; Fournier, C.; Mal, F.; Christidis, C.; Ziol, M.; Poulet, B.; Kazemi, F.; et al. Transient elastography: A new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2003, 29, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boursier, J.; Cales, P. Editorial. Clinical interpretation of Fibroscan(R) results: A real challenge. Liver Int. 2010, 30, 1400–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapper, E.B.; Castera, L.; Afdhal, N.H. FibroScan (vibration-controlled transient elastography): Where does it stand in the United States practice. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 13, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degos, F.; Perez, P.; Roche, B.; Mahmoudi, A.; Asselineau, J.; Voitot, H.; Bedossa, P.; group, F.s. Diagnostic accuracy of FibroScan and comparison to liver fibrosis biomarkers in chronic viral hepatitis: A multicenter prospective study (the FIBROSTIC study). J. Hepatol. 2010, 53, 1013–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manduca, A.; Bayly, P.J.; Ehman, R.L.; Kolipaka, A.; Royston, T.J.; Sack, I.; Sinkus, R.; Van Beers, B.E. MR elastography: Principles, guidelines, and terminology. Magn. Reson. Med. 2021, 85, 2377–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerunian, M.; Masci, B.; Caruso, D.; Pucciarelli, F.; Polici, M.; Nardacci, S.; De Santis, D.; Iannicelli, E.; Laghi, A. Liver Magnetic Resonance Elastography: Focus on Methodology, Technique, and Feasibility. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Manning, P.; Szeverenyi, N.; Wolfson, T.; Hamilton, G.; Middleton, M.S.; Vaida, F.; Yin, M.; Glaser, K.; Ehman, R.L.; et al. Repeatability and reproducibility of 2D and 3D hepatic MR elastography with rigid and flexible drivers at end-expiration and end-inspiration in healthy volunteers. Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 2843–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.C.; Nguyen, P.; Hernandez, C.; Bettencourt, R.; Ramirez, K.; Fortney, L.; Hooker, J.; Sy, E.; Savides, M.T.; Alquiraish, M.H.; et al. Magnetic Resonance Elastography vs Transient Elastography in Detection of Fibrosis and Noninvasive Measurement of Steatosis in Patients With Biopsy-Proven Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 598–607.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmuganathan, M.; Sarfaraz, M.O.; Kroezen, Z.; Philbrick, H.; Poon, R.; Don-Wauchope, A.; Puglia, M.; Wishart, D.; Britz-McKibbin, P. A Cross-Platform Metabolomics Comparison Identifies Serum Metabolite Signatures of Liver Fibrosis Progression in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 676349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, D.D.; Wang, J.S.; Wang, P.R.; Li, M.H.; Yang, M.H.; Kong, L.Y. Toxic effects of chronic low-dose exposure of thioacetamide on rats based on NMR metabolic profiling. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2014, 98, 334–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vinet, B. An enzymic assay for the specific determination of methanol in serum. Clin. Chem. 1987, 33, 2204–2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phuong, V.A.; Ngan, N.T.; Trang, D.T.; Luong, D.S.; Huong, N.T.A.; Anh, H.Q. Simultaneous determination of methanol, ethanol and isopropanol in human blood and white spirit samples. Viet J. Fd. Contr 2020, 3, 231–237. [Google Scholar]
- Bharti, S.K.; Roy, R. Quantitative 1H NMR spectroscopy. Trends Anal. Chem. 2012, 35, 5–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ACS. Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. A National Historic Chemical Landmark. Available online: https://www.acs.org/education/whatischemistry/landmarks/gas-chromatography-mass-spectrometry.html (accessed on 19 May 2024).
- Sparkman, O.D.; Penton, Z.; Kitson, F.G. Gas Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry: A Practical Guide; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2011; p. 632. [Google Scholar]
- Fiehn, O.; Kopka, J.; Dormann, P.; Altmann, T.; Trethewey, R.N.; Willmitzer, L. Metabolite profiling for plant functional genomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2000, 18, 1157–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiehn, O.; Kopka, J.; Trethewey, R.N.; Willmitzer, L. Identification of uncommon plant metabolites based on calculation of elemental compositions using gas chromatography and quadrupole mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2000, 72, 3573–3580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, J.; King, R.D.; Altmann, T.; Fiehn, O. Application of metabolomics to plant genotype discrimination using statistics and machine learning. Bioinformatics 2002, 18 (Suppl. 2), S241–S248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, X.; Tao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Peng, J.; Sun, S.; Cao, H.; Zheng, N.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, P. Urinary metabonomics characterization of liver fibrosis induced by CCl(4) in rats and intervention effects of Xia Yu Xue Decoction. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 74, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gou, X.; Tao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Peng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, J.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Liu, P. Urine metabolic profile changes of CCl4-liver fibrosis in rats and intervention effects of Yi Guan Jian Decoction using metabonomic approach. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 13, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.K.; Chung, H.W.; Lee, H.S.; Lim, J.; Park, J.H.; Lim, S.C.; Kim, J.M.; Hong, S.S.; Kwon, S.W. Investigation of metabolite alteration in dimethylnitrosamine-induced liver fibrosis by GC-MS. Bioanalysis 2013, 5, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Qiu, M.; Zhang, Y. Metabolomics combined with pattern recognition and bioinformatics analysis methods for the development of pharmacodynamic biomarkers on liver fibrosis. Mol. Biosyst. 2017, 13, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.N.; Dong, S.; Wei, B.; Liu, P.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Su, S.B. Metabolomic mechanisms of gypenoside against liver fibrosis in rats: An integrative analysis of proteomics and metabolomics data. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, T.; Li, H.; Jin, G.; Zhang, Y. Metabonomic profiling in study hepatoprotective effect of polysaccharides from Flammulina velutipes on carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury rats using GC-MS. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 110, 285–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Miao, H.; Yan, H.; Sheng, Y.; Ji, L. Hepatoprotective effect of Forsythiae Fructus water extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 218, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Li, H.; Zhao, H.; Wang, F.; He, Q.; Zhang, T.; Wang, S. Serum metabonomics study of the hepatoprotective effect of amarogentin on CCl(4)-induced liver fibrosis in mice by GC-TOF-MS analysis. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 149, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Teng, Y.; Li, G.; Yoshioka, S.; Yokota, J.; Miyamura, M.; Fang, H.; Zhang, Y. Metabonomics study of the protective effects of Lonicera japonica extract on acute liver injury in dimethylnitrosamine treated rats. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2010, 53, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, X.; Wang, X.; Xu, W.; Gong, M.; Zhou, C.; Jiang, E.; Tang, Y.; Jia, L.; Zeng, L.; Deng, S.; et al. Penthorum chinense Pursh leaf tea debittering mechanisms via green tea manufacturing process and its influence on NAFLD-alleviation activities. Food Chem. 2024, 445, 138715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.M.; Huo, G.M.; Cheng, J.; Zhang, Q.P.; Li, N.Z.; Guo, M.X.; Liu, Q.; Xu, G.H.; Zhu, J.X.; Li, C.F.; et al. Gypenoside XVII, an Active Ingredient from Gynostemma Pentaphyllum, Inhibits C3aR-Associated Synaptic Pruning in Stressed Mice. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.Y.; Huang, G.L.; Zhou, Z.L.; Chen, Z.M. Chemical Constituents from the Solid Culture of the Edible Mushroom Flammulina velutipes. Chem. Nat. Compd. 2022, 58, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Lu, X.; Tong, X.; Dong, Y.; Tang, L.; Liu, M. Forsythiae Fructus: A Review on its Phytochemistry, Quality Control, Pharmacology and Pharmacokinetics. Molecules 2017, 22, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinese_Pharmacopoeia_Commission. Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China; The Medicine Science and Technology Press of China: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer, H. Misinterpretation of the Fehling test for reducing sugars–From observation in chemistry class to evidence against the oxidation of the aldehyde group. Chemkon 2017, 24, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Peng, J.; Feng, Q.; Dai, J.; Sun, S.; et al. Gut Microbial Dysbiosis Is Associated with Altered Hepatic Functions and Serum Metabolites in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Qi, X.; Guo, X. Child-Pugh Versus MELD Score for the Assessment of Prognosis in Liver Cirrhosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies. Medicine 2016, 95, e2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, T.; Furube, M.; Hirano, S.; Takatori, K.; Iida, K.; Kajiwara, M. Evaluation of 13C-phenylalanine and 13C-tyrosine breath tests for the measurement of hepatocyte functional capacity in patients with liver cirrhosis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 49, 1507–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, M.Y.; Milsom, J.P.; Sherlock, S. Plasma ratio of valine, leucine and isoleucine to phenylalanine and tyrosine in liver disease. Gut 1978, 19, 1068–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, G.; Sorensen, M.; Buhl, M.; Sandahl, T.D.; Moller, N.; Ott, P.; Vilstrup, H. Muscle metabolism and whole blood amino acid profile in patients with liver disease. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 2015, 75, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lo, E.K.K.; Felicianna; Xu, J.H.; Zhan, Q.; Zeng, Z.; El-Nezami, H. The Emerging Role of Branched-Chain Amino Acids in Liver Diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni Lochlainn, M.; Bowyer, R.C.E.; Moll, J.M.; Garcia, M.P.; Wadge, S.; Baleanu, A.F.; Nessa, A.; Sheedy, A.; Akdag, G.; Hart, D.; et al. Effect of gut microbiome modulation on muscle function and cognition: The PROMOTe randomised controlled trial. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gojda, J.; Cahova, M. Gut Microbiota as the Link between Elevated BCAA Serum Levels and Insulin Resistance. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Qian, L.; Siliceo, S.L.; Long, X.; Nychas, E.; Liu, Y.; Ismaiah, M.J.; Leung, H.; Zhang, L.; Gao, Q.; et al. Resistant starch decreases intrahepatic triglycerides in patients with NAFLD via gut microbiome alterations. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1530–1547.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faquih, T.O.; van Klinken, J.B.; Li-Gao, R.; Noordam, R.; van Heemst, D.; Boone, S.; Sheridan, P.A.; Michelotti, G.; Lamb, H.; de Mutsert, R.; et al. Hepatic triglyceride content is intricately associated with numerous metabolites and biochemical pathways. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 1458–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanco-Grau, A.; Gabriel-Medina, P.; Rodriguez-Algarra, F.; Villena, Y.; Lopez-Martinez, R.; Augustin, S.; Pons, M.; Cruz, L.M.; Rando-Segura, A.; Enfedaque, B.; et al. Assessing Liver Fibrosis Using the FIB4 Index in the Community Setting. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldhier, M.C.; Almstetter, M.F.; Nurnberger, N.; Gruber, M.A.; Dettmer, K.; Oefner, P.J. Improved enantiomer resolution and quantification of free D-amino acids in serum and urine by comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography-time-of-flight mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 4537–4544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasabe, J.; Miyoshi, Y.; Rakoff-Nahoum, S.; Zhang, T.; Mita, M.; Davis, B.M.; Hamase, K.; Waldor, M.K. Interplay between microbial d-amino acids and host d-amino acid oxidase modifies murine mucosal defence and gut microbiota. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 16125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, F.F.; Song, Y.N.; Lu, Y.Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.Y.; Su, S.B. Analysis of plasma metabolic profile, characteristics and enzymes in the progression from chronic hepatitis B to hepatocellular carcinoma. Aging 2020, 12, 14949–14965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mocan, T.; Kang, D.W.; Molloy, B.J.; Jeon, H.; Sparchez, Z.A.; Beyoglu, D.; Idle, J.R. Plasma fetal bile acids 7alpha-hydroxy-3-oxochol-4-en-24-oic acid and 3-oxachola-4,6-dien-24-oic acid indicate severity of liver cirrhosis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, P.T.; Patel, E.; Lawson, A.M.; Carruthers, R.A.; Tanner, M.S.; Strandvik, B.; Egestad, B.; Sjovall, J. 3-Oxo-delta 4 bile acids in liver disease. Lancet 1988, 1, 1283–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setchell, K.D.; Suchy, F.J.; Welsh, M.B.; Zimmer-Nechemias, L.; Heubi, J.; Balistreri, W.F. Delta 4-3-oxosteroid 5 beta-reductase deficiency described in identical twins with neonatal hepatitis. A new inborn error in bile acid synthesis. J. Clin. Investig. 1988, 82, 2148–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaggini, M.; Carli, F.; Rosso, C.; Younes, R.; D’Aurizio, R.; Bugianesi, E.; Gastaldelli, A. Altered Metabolic Profile and Adipocyte Insulin Resistance Mark Severe Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyoglu, D.; Huang, P.; Skelton-Badlani, D.; Zong, C.; Popov, Y.V.; Idle, J.R. Metabolic Hijacking of Hexose Metabolism to Ascorbate Synthesis Is the Unifying Biochemical Basis of Murine Liver Fibrosis. Cells 2023, 12, 485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pihlajaniemi, T.; Myllyla, R.; Kivirikko, K.I. Prolyl 4-hydroxylase and its role in collagen synthesis. J. Hepatol. 1991, 13 (Suppl. 3), S2–S7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Shi, M.; Zhang, T.; Han, H. Protective effect of picroside I against hepatic fibrosis in mice via sphingolipid metabolism, bile acid biosynthesis, and PPAR signaling pathway. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 131, 110683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, C.; Fu, K.; Liu, Y.; Gong, L.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Hepatoprotective effect of phillygenin on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis and its effects on short chain fatty acid and bile acid metabolism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 296, 115478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Luo, Z.; Li, D.; Qin, J.; Pan, Z.; Guo, B.; Deng, L.; Nong, Y.; Huang, Z.; He, Y.; et al. Investigation of the Therapeutic Effect of Total Alkaloids of Corydalis saxicola Bunting on CCl(4)-Induced Liver Fibrosis in Rats by LC/MS-Based Metabolomics Analysis and Network Pharmacology. Metabolites 2022, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, C.; Li, Y.; Ou, L.; Zhou, J.; Peng, F.; Wu, D. Metabonomic analysis of the anti-hepatic fibrosis effect of Ganlong capsules. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1122118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Cheng, Y.; Wang, X.; Yue, S.; Wang, X.; Tang, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Xiong, Q.; Tan, S. Chinese herbal decoction, Yi-Qi-Jian-Pi formula exerts anti-hepatic fibrosis effects in mouse models of CCl(4)-induced liver fibrosis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e26129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.Y.; Zheng, X.Y.; Peng, Y.; Tao, Y.Y.; Liu, P.; Yang, T.; Liu, C.H. Effect of Fuzheng Huayu capsule on serum metabolomics in rats with liver fibrosis induced by dimethylnitrosamine. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2016, 41, 1725–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Jiang, R.; Zhao, T. Gut microbiota combined with metabolomics reveal the mechanism of curcumol on liver fibrosis in mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 152, 113204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.; Meng, H.Y.; Liu, S.M.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.X.; Lu, F.; Wang, H.Y. Identification of key metabolic changes during liver fibrosis progression in rats using a urine and serum metabolomics approach. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; He, J.Q.; Chen, D.Y.; Pan, Q.L.; Yang, J.F.; Cao, H.C.; Li, L.J. Dynamic changes of key metabolites during liver fibrosis in rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2019, 25, 941–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barupal, D.K.; Fiehn, O. Generating the Blood Exposome Database Using a Comprehensive Text Mining and Database Fusion Approach. Environ. Health Perspect. 2019, 127, 97008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.; Lee, J.G.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Kim, H.P. Anti-inflammatory activity of phylligenin, a lignan from the fruits of Forsythia koreana, and its cellular mechanism of action. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 118, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romer, A.S.; Parsons, T.S. The Vertebrate Body; Holt-Saunders International: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 1977. [Google Scholar]
- Higashiyama, H.; Uemura, M.; Igarashi, H.; Kurohmaru, M.; Kanai-Azuma, M.; Kanai, Y. Anatomy and development of the extrahepatic biliary system in mouse and rat: A perspective on the evolutionary loss of the gallbladder. J. Anat. 2018, 232, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, D.; Ge, K.; Qu, C.; Sun, T.; Wang, J.; Jia, W.; Zhao, A. Comparative profiling of serum, urine, and feces bile acids in humans, rats, and mice. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Zhu, S.; Jia, Q.; Yuan, D.; Ren, C.; Li, K.; Liu, S.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, H.; Cao, Y.; et al. The genomic and functional landscapes of developmental plasticity in the American cockroach. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayman_Chemical. Product Information. α-Ecdysone. Available online: https://cdn.caymanchem.com/cdn/insert/11711.pdf (accessed on 20 June 2024).
- Svoboda, J.A.; Kaplanis, J.N.; Robbins, W.E.; Thompson, M.J. Recent developments in insect steroid metabolism. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 1975, 20, 205–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, H.; Nakanishi, K.; King, D.S.; Okauchi, T.; Siddall, J.B.; Hafferl, W. On the origin and metabolic fate of alpha-ecdysone in insects. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 1970, 15, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, D.S.; Marks, E.P. The secretion and metabolism of alpha-ecdysone by cockroach (Leucophaea maderae) tissues in vitro. Life Sci. 1974, 15, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milner, M.J.; Sang, J.H. Relative activities of alpha-ecdysone and beta-ecdysone for the differentiation in vitro of Drosophila melanogaster imaginal discs. Cell 1974, 3, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Zhou, X.; Liu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, Y.; Li, K.; Wei, S.; Li, H.; Wang, L.; et al. Fuzheng Huayu capsule as an adjuvant treatment for HBV-related cirrhosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henneberry, A.L.; Wright, M.M.; McMaster, C.R. The major sites of cellular phospholipid synthesis and molecular determinants of Fatty Acid and lipid head group specificity. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 3148–3161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markus, V.; Paul, A.A.; Terali, K.; Ozer, N.; Marks, R.S.; Golberg, K.; Kushmaro, A. Conversations in the Gut: The Role of Quorum Sensing in Normobiosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goel, A.; Ahmad, F.J.; Singh, R.M.; Singh, G.N. 3-Acetyl-11-keto-beta-boswellic acid loaded-polymeric nanomicelles for topical anti-inflammatory and anti-arthritic activity. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2010, 62, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bongers, F.; Groenendijk, P.; Bekele, T.; Birhane, E.; Damtew, A.; Decuyper, M.; Eshete, A.; Gezahgne, A.; Girma, A.; Khamis, M.A.; et al. Frankincense in peril. Nat. Sustain. 2019, 2, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Sugimoto, K. Guggulsterone and Its Role in Chronic Diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2016, 929, 329–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumgartner, M.R.; Horster, F.; Dionisi-Vici, C.; Haliloglu, G.; Karall, D.; Chapman, K.A.; Huemer, M.; Hochuli, M.; Assoun, M.; Ballhausen, D.; et al. Proposed guidelines for the diagnosis and management of methylmalonic and propionic acidemia. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grammatikos, G.; Ferreiros, N.; Bon, D.; Schwalm, S.; Dietz, J.; Berkowski, C.; Fitting, D.; Herrmann, E.; Zeuzem, S.; Sarrazin, C.; et al. Variations in serum sphingolipid levels associate with liver fibrosis progression and poor treatment outcome in hepatitis C virus but not hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 2015, 61, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, S.; Xie, X.; Li, J.; Xu, X.; Chen, C.; Zou, G.; Lin, G.; Huang, T.; Hu, R.; Ran, T.; et al. Bile acids induce liver fibrosis through the NLRP3 inflammasome pathway and the mechanism of FXR inhibition of NLRP3 activation. Hepatol. Int. 2024, 18, 1040–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habermaass, V.; Gori, E.; Abramo, F.; Bartoli, F.; Pierini, A.; Mariti, C.; Lippi, I.; Marchetti, V. Serum Amino Acids Imbalance in Canine Chronic Hepatitis: Results in 16 Dogs. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstikov, V.V.; Fiehn, O. Analysis of highly polar compounds of plant origin: Combination of hydrophilic interaction chromatography and electrospray ion trap mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 2002, 301, 298–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beyoglu, D.; Idle, J.R. Metabolic Rewiring and the Characterization of Oncometabolites. Cancers 2021, 13, 2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, E.; Wijeyesekera, A.; Taylor-Robinson, S.D.; Nicholson, J.K. The promise of metabolic phenotyping in gastroenterology and hepatology. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 12, 458–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirnezami, R.; Kinross, J.M.; Vorkas, P.A.; Goldin, R.; Holmes, E.; Nicholson, J.; Darzi, A. Implementation of molecular phenotyping approaches in the personalized surgical patient journey. Ann. Surg. 2012, 255, 881–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.M.; Darzi, A.W.; Takats, Z.; Lindon, J.C. Metabolic phenotyping in clinical and surgical environments. Nature 2012, 491, 384–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, E.; Li, J.V.; Marchesi, J.R.; Nicholson, J.K. Gut microbiota composition and activity in relation to host metabolic phenotype and disease risk. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 559–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gathungu, R.M.; Kautz, R.; Kristal, B.S.; Bird, S.S.; Vouros, P. The integration of LC-MS and NMR for the analysis of low molecular weight trace analytes in complex matrices. Mass. Spectrom. Rev. 2020, 39, 35–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sunami, Y. NASH, Fibrosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Lipid Synthesis and Glutamine/Acetate Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, C.J.; Guha, I.N.; Kyriakides, M.; Wright, M.; Beckonert, O.; Holmes, E.; Rosenberg, W.M.; Coen, M. Metabolic phenotyping for enhanced mechanistic stratification of chronic hepatitis C-induced liver fibrosis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 110, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiele, M.; Suvitaival, T.; Trost, K.; Kim, M.; de Zawadzki, A.; Kjaergaard, M.; Rasmussen, D.N.; Lindvig, K.P.; Israelsen, M.; Detlefsen, S.; et al. Sphingolipids Are Depleted in Alcohol-Related Liver Fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2023, 164, 1248–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigstock, D.R. Extracellular Vesicles in Organ Fibrosis: Mechanisms, Therapies, and Diagnostics. Cells 2021, 10, 1596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heravi, M.M.; Zadsirjan, V. Prescribed drugs containing nitrogen heterocycles: An overview. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 44247–44311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, W.; Shao, X.; Maigret, B. Protein-ligand recognition using spherical harmonic molecular surfaces: Towards a fast and efficient filter for large virtual throughput screening. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2002, 20, 313–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feig, M.; Onufriev, A.; Lee, M.S.; Im, W.; Case, D.A.; Brooks, C.L., 3rd. Performance comparison of generalized born and Poisson methods in the calculation of electrostatic solvation energies for protein structures. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 265–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R.J.; Najmanovich, R.J.; Kahraman, A.; Thornton, J.M. Real spherical harmonic expansion coefficients as 3D shape descriptors for protein binding pocket and ligand comparisons. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2347–2355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahraman, A.; Morris, R.J.; Laskowski, R.A.; Thornton, J.M. Shape variation in protein binding pockets and their ligands. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 368, 283–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gines, P.; Castera, L.; Lammert, F.; Graupera, I.; Serra-Burriel, M.; Allen, A.M.; Wong, V.W.; Hartmann, P.; Thiele, M.; Caballeria, L.; et al. Population screening for liver fibrosis: Toward early diagnosis and intervention for chronic liver diseases. Hepatology 2022, 75, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graupera, I.; Thiele, M.; Ma, A.T.; Serra-Burriel, M.; Pich, J.; Fabrellas, N.; Caballeria, L.; de Knegt, R.J.; Grgurevic, I.; Reichert, M.; et al. LiverScreen project: Study protocol for screening for liver fibrosis in the general population in European countries. BMC Public Health 2022, 22, 1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graupera, I.; Thiele, M.; Serra-Burriel, M.; Caballeria, L.; Roulot, D.; Wong, G.L.; Fabrellas, N.; Guha, I.N.; Arslanow, A.; Exposito, C.; et al. Low Accuracy of FIB-4 and NAFLD Fibrosis Scores for Screening for Liver Fibrosis in the Population. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 2567–2576.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keam, S.J. Resmetirom: First Approval. Drugs 2024, 84, 729–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Causative | Preventative |
|---|---|
| Dietary restriction [13] High-fat diet [26] Aging [14] Dietary cystine [31] Proteins rich in cystine [31] Schistosoma mansoni infection [15] Schistosoma japonicum infection [16] Salmonella typhosa endotoxin [25] Foreign proteins [17] Hypophysectomy [18,19] Thyroidectomy [19] Chloroform [20] Carbon tetrachloride [21] Ethionine [22] Thioacetamide [23] Galactosamine [24] | High-protein diet [26] High-carbohydrate diet [26] Casein [30] Lecithin [27] Choline [27] Methionine [30,31] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Beyoğlu, D.; Popov, Y.V.; Idle, J.R. The Metabolomic Footprint of Liver Fibrosis. Cells 2024, 13, 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13161333
Beyoğlu D, Popov YV, Idle JR. The Metabolomic Footprint of Liver Fibrosis. Cells. 2024; 13(16):1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13161333
Chicago/Turabian StyleBeyoğlu, Diren, Yury V. Popov, and Jeffrey R. Idle. 2024. "The Metabolomic Footprint of Liver Fibrosis" Cells 13, no. 16: 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13161333
APA StyleBeyoğlu, D., Popov, Y. V., & Idle, J. R. (2024). The Metabolomic Footprint of Liver Fibrosis. Cells, 13(16), 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13161333









