Circadian Rhythms, Chrononutrition, Physical Training, and Redox Homeostasis—Molecular Mechanisms in Human Health
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Circadian Rhythms in the Regulation of Human Physiological and Behavioral Processes
2.1. The Circadian Clock and the Sleep Homeostasis
2.2. The Influence of Circadian Rhythms on Human Cognitive and Physical Performance
2.3. The Link between Circadian Rhythms and Exercise in Terms of Performance and Health Benefits
2.4. The Circadian Regulation of Glucose Metabolism
2.5. The Entrainment Effect of Exercise on Circadian Rhythms: Experimental and Clinical Proofs
3. Chrononutrition: The Connection between Circadian Rhythms, Nutrients, and the Timing of Food Intake
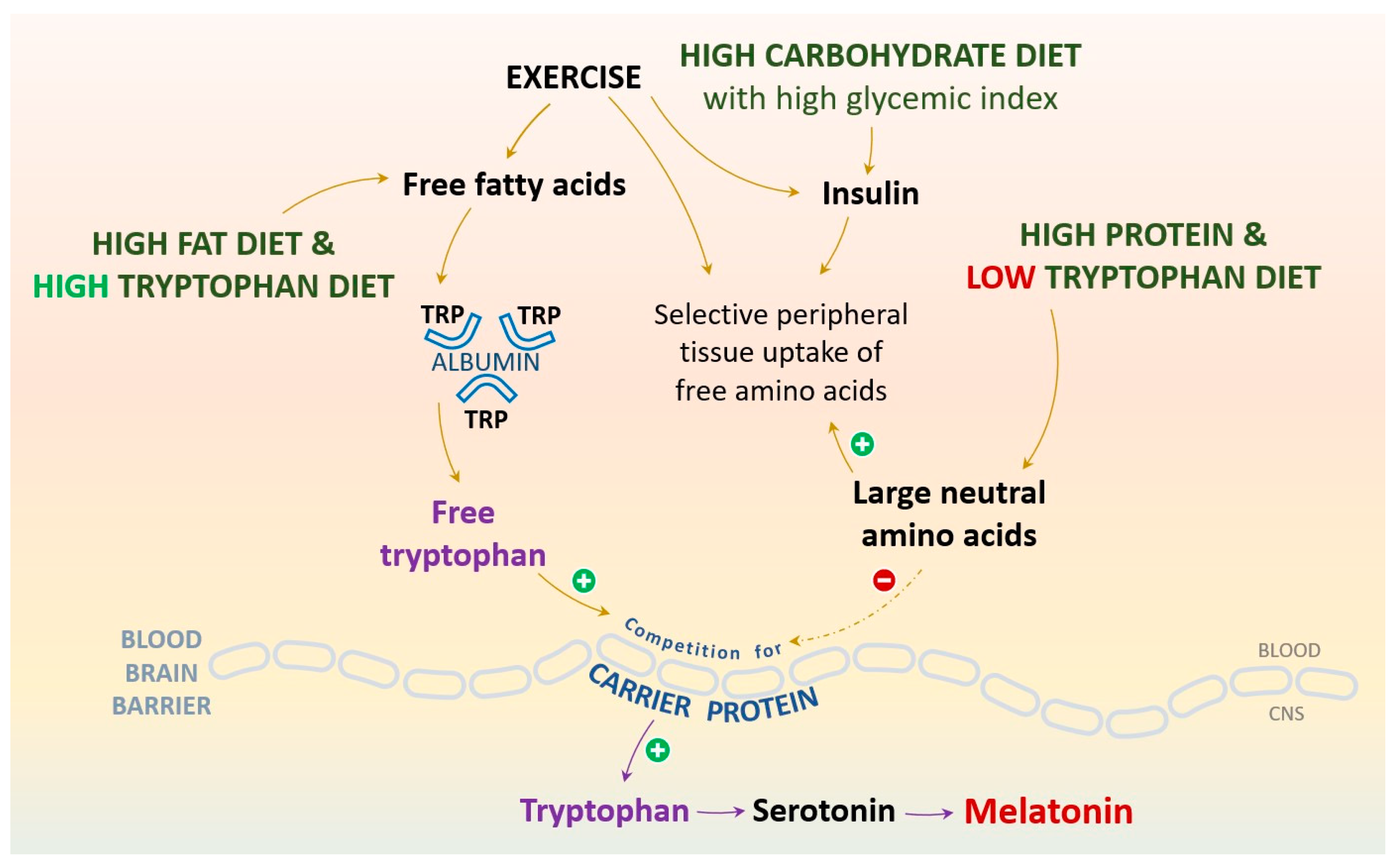
3.1. The Bidirectional Relationships among Tryptophan, Serotonin (5-HT), Physical Activity, Sleep, and Dietary Patterns
3.2. Melatonin, the Modulator of Cellular Redox Homeostasis, Human Circadian Rhythms, and Sleep-Wake Cycle
4. Physical Activity, Hormones, and Mood Interconnections
4.1. The Thyroid Hormones
4.2. The Adrenocorticotropic Hormone, Cortisol, and Growth Hormone
4.3. Insulin
4.4. Leptin
5. The Interchange between the Beneficial and Detrimental Roles of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species
5.1. Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species’ Impact on Sustaining the Biological Systems’ Homeostasis
5.2. ROS Over-Production and Effects’ Accumulation Can Exert a Significant Influence on the Pathogenesis and Progression of Chronic Diseases
6. Physical Exercise as a Key Element of the Oxygen Fate in the Human Organism
6.1. The Signaling Pathways Embodied in Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress
6.2. The Role of Antioxidant Molecules’ Supplementation in Sports Training
7. The Path Forward in Aligning Nutrition, Timing, and Physical Performance
7.1. The Implications of Caffeine Intake in Physical Training
7.2. Amino Acids and Carbohydrates Optimal Consumption Related to Physical Exercise
8. Promising Research Directions, Future Clinical Implications, and Possible Translations into Preventive or Therapeutic Strategies
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Budkowska, M.; Cecerska-Heryć, E.; Marcinowska, Z.; Siennicka, A.; Dołęgowska, B. The Influence of Circadian Rhythm on the Activity of Oxidative Stress Enzymes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClean, C.; Davison, G.W. Circadian Clocks, Redox Homeostasis, and Exercise: Time to Connect the Dots? Antioxidants 2022, 11, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, M.; Halson, S.L.; Weakley, J.; Hawley, J.A. Sleep, circadian biology and skeletal muscle interactions: Implications for metabolic health. Sleep. Med. Rev. 2022, 66, 101700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolae, A.C.; Dumitrescu, I.-B.; Diaconu, C.C.; Ritivoiu, M.E.; Sirbu, C.A.; Drăgoi, C.M. Chronotherapy Advances in the Management of Chronic Neurological and Cardiovascular Diseases: Complex Interactions of Circadian Rhythm Environmental Inputs, Nutrition and Drug Administration and Their Impact on Human Health. In Circadian Rhythm-New Insights Into Physiological and Pathological Implications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Patke, A.; Young, M.W.; Axelrod, S. Molecular mechanisms and physiological importance of circadian rhythms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 67–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voigt, R.M.; Forsyth, C.B.; Keshavarzian, A. Circadian rhythms: A regulator of gastrointestinal health and dysfunction. Expert. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 13, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, W.H.; Walton, J.C.; DeVries, A.C.; Nelson, R.J. Circadian rhythm disruption and mental health. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gradinaru, D.; Borsa, C.; Ionescu, C.; Margina, D. Advanced oxidative and glycoxidative protein damage markers in the elderly with type 2 diabetes. J. Proteom. 2013, 92, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungurianu, A.; Șeremet, O.; Grădinaru, D.; Ionescu-Tîrgoviște, C.; Margină, D.; Dănciulescu Miulescu, R. Spectrophotometric versus spectrofluorometric assessment in the study of the relationships between lipid peroxidation and metabolic dysregulation. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2019, 93, 1026–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagiani, F.; Di Marino, D.; Romagnoli, A.; Travelli, C.; Voltan, D.; Di Cesare Mannelli, L.; Racchi, M.; Govoni, S.; Lanni, C. Molecular regulations of circadian rhythm and implications for physiology and diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drăgoi, C.; Nicolae, A.C.; Dumitrescu, I.-B.; Popa, D.E.; Ritivoiu, M.; Arsene, A.L. DNA targeting as a molecular mechanism underlying endogenous indoles biological effects. Farmacia 2019, 67, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ooi, T.; Meramat, A.; Rajab, N.; Shahar, S.; Sharif, R. Antioxidant Potential, DNA Damage, Inflammation, Glycemic Control and Lipid Metabolism Alteration: A Mediation Analysis of Islamic Sunnah Intermittent Fasting on Cognitive Function among Older Adults with Mild Cognitive Impairment. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2022, 26, 272–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Lahens, N.F.; Ballance, H.I.; Hughes, M.E.; Hogenesch, J.B. A circadian gene expression atlas in mammals: Implications for biology and medicine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 16219–16224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doherty, R.; Madigan, S.; Warrington, G.; Ellis, J. Sleep and Nutrition Interactions: Implications for Athletes. Nutrients 2019, 11, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margaritelis, N.; Paschalis, V.; Theodorou, A.; Kyparos, A.; Nikolaidis, M. Redox basis of exercise physiology. Redox Biol. 2020, 35, 101499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drăgoi, C.M.; Dumitrescu, I.-B.; Nicolae, A.C. Introductory Chapter: Untangling the Essential Links among the Circadian Rhythm, Homeostasis of the Human Body, and the Nutritional, Behavioural, and Pathological Interferences. In Circadian Rhythm-New Insights Into Physiological and Pathological Implications; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Meyrem, O.; Nedime, S. Impact of circadian disruption on health; SIRT1 and Telomeres. DNA Repair. 2020, 96, 102993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyar, V.S.; Sukumaran, S. Circadian rhythms: Influence on physiology, pharmacology, and therapeutic interventions. J. Pharmacokinet. Pharmacodyn. 2021, 48, 321–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, A.; Alguacil, S.; Ciria, L.F.; Jiménez, A.; Ruz, M. Circadian rhythms and decision-making: A review and new evidence from electroencephalography. Chronobiol. Int. 2020, 37, 520–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barger, L.K.; Wright, K.P., Jr.; Hughes, R.J.; Czeisler, C.A. Daily exercise facilitates phase delays of circadian melatonin rhythm in very dim light. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2004, 286, R1077–R1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voiculescu, S.E.; Le Duc, D.; Rosca, A.E.; Zeca, V.; Chitimus, D.M.; Arsene, A.L.; Dragoi, C.M.; Nicolae, A.C.; Zagrean, L.; Schoneberg, T.; et al. Behavioral and molecular effects of prenatal continuous light exposure in the adult rat. Brain Res. 2016, 1650, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webb, A.B.; Angelo, N.; Huettner, J.E.; Herzog, E.D. Intrinsic, nondeterministic circadian rhythm generation in identified mammalian neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 16493–16498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, T.M.; Brainard, G.C.; Cajochen, C.; Czeisler, C.A.; Hanifin, J.P.; Lockley, S.W.; Lucas, R.J.; Münch, M.; O’Hagan, J.B.; Peirson, S.N.; et al. Recommendations for daytime, evening, and nighttime indoor light exposure to best support physiology, sleep, and wakefulness in healthy adults. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, A.; Hewins, B.; Bishop, C.; Fortin, A.; Wang, J.; Creamer, J.L.; Collen, J.; Werner, J.K., Jr. Traumatic Brain Injury, Sleep, and Melatonin-Intrinsic Changes with Therapeutic Potential. Clocks Sleep. 2023, 5, 177–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sejbuk, M.; Mirończuk-Chodakowska, I.; Witkowska, A.M. Sleep Quality: A Narrative Review on Nutrition, Stimulants, and Physical Activity as Important Factors. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumoto, H.; Ta, C.; Brown, S.M.; Mulcahey, M.K. Factors contributing to diurnal variation in athletic performance and methods to reduce within-day performance variation: A systematic review. J. Strength Cond. Res. 2021, 35, S119–S135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirizio, G.G.; Nunes, R.S.M.; Vargas, D.A.; Foster, C.; Vieira, E. Time-of-day effects on short-duration maximal exercise performance. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 9485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knaier, R.; Qian, J.; Roth, R.; Infanger, D.; Notter, T.; Wang, W.; Cajochen, C.; Scheer, F.A.J.L. Diurnal Variation in Maximum Endurance and Maximum Strength Performance: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2022, 54, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaman, G.S.; Abohashrh, M.; Ahmad, I.; Dera, A.A.; Alshahrani, M.S.; Ahmad, I.; Alam, M.M.; Mahmood, S.E.; Mansuri, N.; Irfan, S. The impact of body resistance training exercise on biomedical profile at high altitude: A randomized controlled trial. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 6684167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yuan, R.K.; Mitchell, J.; Zitting, K.-M.; Hilaire, M.A.S.; Wyatt, J.K.; Scheer, F.A.J.L.; Wright, K.P., Jr.; Brown, E.N.; Ronda, J.M.; et al. Using Kleitman’s Forced Desynchrony protocol to assess the intrinsic period of circadian oscillators and estimate the contributions of the circadian pacemaker and the sleep-wake homeostat to physiology and behavior in clinical research. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15602–15608. [Google Scholar]
- Freivalds, A.; Chaffin, D.B.; Langolf, G.D. Quantification of human performance circadian rhythms. Am. Ind. Hyg. Assoc. J. 1983, 44, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teo, W.; Newton, M.J.; McGuigan, M.R. Circadian rhythms in exercise performance: Implications for hormonal and muscular adaptation. J. Sports Sci. Med. 2011, 10, 600. [Google Scholar]
- Youngstedt, S.D.; Elliott, J.A.; Kripke, D.F. Human circadian phase–response curves for exercise. J. Physiol. 2019, 597, 2253–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, V.; Kumar, S. Effects Of Circadian Rhythm On Sports Performance In Different Seasons. Turk. Online J. Qual. Inq. 2021, 12, 12486. [Google Scholar]
- Budnick, C.J.; Stults-Kolehmainen, M.; Dadina, C.; Bartholomew, J.B.; Boullosa, D.; Ash, G.I.; Sinha, R.; Blacutt, M.; Haughton, A.; Lu, T. Motivation states to move, be physically active and sedentary vary like circadian rhythms and are associated with affect and arousal. Front. Sports Act. Living 2023, 5, 1094288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simmons, N.; Mandal, S.; Paton, B.; Ahmed, I. Are Circadian Rhythms a New Frontier in Athletic Performance? Curr. Sports Med. Rep. 2022, 21, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobari, H.; Azarian, S.; Saedmocheshi, S.; Valdés-Badilla, P.; Calvo, T.G. Narrative review: The role of circadian rhythm on sports performance, hormonal regulation, immune system function, and injury prevention in athletes. Heliyon 2023, 9, 19636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almoosawi, S.; Vingeliene, S.; Gachon, F.; Voortman, T.; Palla, L.; Johnston, J.D.; Van Dam, R.M.; Darimont, C.; Karagounis, L.G. Chronotype: Implications for epidemiologic studies on chrono-nutrition and cardiometabolic health. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montaruli, A.; Castelli, L.; Mulè, A.; Scurati, R.; Esposito, F.; Galasso, L.; Roveda, E. Biological rhythm and chronotype: New perspectives in health. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehinejad, M.A.; Wischnewski, M.; Ghanavati, E.; Mosayebi-Samani, M.; Kuo, M.-F.; Nitsche, M.A. Cognitive functions and underlying parameters of human brain physiology are associated with chronotype. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Choi, G.; Jang, L.; Kim, S.-W.; Jung, K.-H.; Park, H. Circadian rhythm gene expression and daily melatonin levels vary in athletes and sedentary males. Biol. Rhythm. Res. 2018, 49, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drăgoi, C.; Moroşan, E.; Dumitrescu, I.-B.; Nicolae, A.C.; Arsene, A.L.; Drăgănescu, D.; Lupuliasa, D.; Ioniţă, A.C.; Stoian, A.P.; Nicolae, C. Insights into chrononutrition: The innermost interplay amongst nutrition, metabolism and the circadian clock, in the context of epigenetic reprogramming. Farmacia 2019, 67, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, C.J.; Kaur, B.; Quek, R.Y.C. Chrononutrition in the management of diabetes. Nutr. Diabetes 2020, 10, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungurianu, A.; Zanfirescu, A.; Margina, D. Regulation of Gene Expression through Food-Curcumin as a Sirtuin Activity Modulator. Plants 2022, 11, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basti, A.; Yalçin, M.; Herms, D.; Hesse, J.; Aboumanify, O.; Li, Y.; Aretz, Z.; Garmshausen, J.; El-Athman, R.; Hastermann, M. Diurnal variations in the expression of core-clock genes correlate with resting muscle properties and predict fluctuations in exercise performance across the day. BMJ Open Sport. Exerc. Med. 2021, 7, e000876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, R.; Vasilaki, A. Age-related changes in skeletal muscle: Changes to life-style as a therapy. Biogerontology 2018, 19, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, M.L.; Zhang, H.; Mey, J.T.; Kirwan, J.P. Exercise Training Impacts Skeletal Muscle Clock in Adults with Prediabetes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2020, 52, 2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala, V.; Martínez-Bebia, M.; Latorre, J.A.; Gimenez-Blasi, N.; Jimenez-Casquet, M.J.; Conde-Pipo, J.; Bach-Faig, A.; Mariscal-Arcas, M. Influence of circadian rhythms on sports performance. Chronobiol. Int. 2021, 38, 1522–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drăgoi, C.M.; Arsene, A.L.; Dinu-Pîrvu, C.E.; Dumitrescu, I.B.; Popa, D.E.; Burcea-Dragomiroiu, G.T.; Udeanu, D.I.; Timnea, O.C.; Velescu, B.Ș.; Nicolae, A.C. Melatonin: A silent regulator of the glucose homeostasis. Carbohydrate 2017, 99, 66625. [Google Scholar]
- Ungurianu, A.; Seremet, O.; Gagniuc, E.; Olaru, O.T.; Gutu, C.; Gradinaru, D.; Ionescu-Tirgoviste, C.; Margina, D.; Danciulescu-Miulescu, R. Preclinical and clinical results regarding the effects of a plant-based antidiabetic formulation versus well established antidiabetic molecules. Pharmacol. Res. 2019, 150, 104522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragoi, C.M.; Nicolae, A.C.; Grigore, C.; Dinu-Pirvu, C.E.; Arsene, A.L. Characteristics of glucose homeostasis and lipidic profile in a hamster metabolic syndrome model, after the co-administration of melatonin and irbesartan in a multiparticulate pharmaceutical formation. In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Interdisciplinary Management of Diabetes Mellitus and its Complications, INTERDIAB 2016, Bucharest, Romania, 3–5 March 2016; pp. 221–229. [Google Scholar]
- Daniela, M.; Catalina, L.; Ilie, O.; Paula, M.; Daniel-Andrei, I.; Ioana, B. Effects of exercise training on the autonomic nervous system with a focus on anti-inflammatory and antioxidants effects. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzati, A.; Rosenkranz, S.K.; Horne, B.D. Importance of Intermittent Fasting Regimens and Selection of Adequate Therapy on Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Margina, D.; Ungurianu, A.; Purdel, C.; Nitulescu, G.M.; Tsoukalas, D.; Sarandi, E.; Thanasoula, M.; Burykina, T.I.; Tekos, F.; Buha, A.; et al. Analysis of the intricate effects of polyunsaturated fatty acids and polyphenols on inflammatory pathways in health and disease. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 143, 111558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbu, C.G.; Arsene, A.L.; Florea, S.; Albu, A.; Sirbu, A.; Martin, S.; Nicolae, A.C.; Burcea-Dragomiroiu, G.T.A.; Popa, D.E.; Velescu, B.S.; et al. Cardiovascular risk assessment in osteoporotic patients using osteoprotegerin as a reliable predictive biochemical marker. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 6059–6067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, R.; Ye, Z.; Wu, Q.; Xue, W.; Shi, S.; Du, Y.; Wu, H.; Wei, Y.; Hu, Y. Circadian rhythm in cardiovascular diseases: A bibliometric analysis of the past, present, and future. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdel, C.; Ungurianu, A.; Margina, D. Metabolic and Metabolomic Insights Regarding the Omega-3 PUFAs Intake in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 783065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamaguchi, Y.; Tahara, Y.; Hitosugi, M.; Shibata, S. Impairment of circadian rhythms in peripheral clocks by constant light is partially reversed by scheduled feeding or exercise. J. Biol. Rhythm. 2015, 30, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolff, G.; Esser, K.A. Scheduled exercise phase shifts the circadian clock in skeletal muscle. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2012, 44, 1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroeder, A.M.; Truong, D.; Loh, D.H.; Jordan, M.C.; Roos, K.P.; Colwell, C.S. Voluntary scheduled exercise alters diurnal rhythms of behaviour, physiology and gene expression in wild-type and vasoactive intestinal peptide-deficient mice. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 6213–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanaka, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Tanahashi, Y.; Nishide, S.-Y.; Honma, S.; Honma, K.-I. Physical exercise accelerates reentrainment of human sleep-wake cycle but not of plasma melatonin rhythm to 8-h phase-advanced sleep schedule. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2010, 298, R681–R691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, Y.; Hashimoto, S.; Masubuchi, S.; Natsubori, A.; Nishide, S.-Y.; Honma, S.; Honma, K.-I. Differential regulation of circadian melatonin rhythm and sleep-wake cycle by bright lights and nonphotic time cues in humans. Am. J. Physiol.-Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2014, 307, R546–R557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, J.M. The neurotransmitters of sleep. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2004, 65 (Suppl. 16), 4–7. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, P.; Marlene, C.; Muntaha, S.; Tomoki, S.; Alina, C.; Shogo, S.; Kevin, B.K.; Grace, P.; Yasmine, A.; Niklas, M.; et al. Tryptophan metabolism is a physiological integrator regulating circadian rhythms. Mol. Metab. 2022, 64, 101556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platten, M.; Nollen, E.A.; Röhrig, U.F.; Fallarino, F.; Opitz, C.A. Tryptophan metabolism as a common therapeutic target in cancer, neurodegeneration and beyond. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 379–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drăgoi, C.M.; Nicolae, A.C. Introductory Chapter: Melatonin, the Integrative Molecule within the Human Architecture. In Melatonin-Molecular Biology, Clinical and Pharmaceutical Approaches; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Zuraikat, F.M.; Wood, R.A.; Barragán, R.; St-Onge, M.P. Sleep and Diet: Mounting Evidence of a Cyclical Relationship. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 2021, 41, 309–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernstrom, J.D. Large neutral amino acids: Dietary effects on brain neurochemistry and function. Amino Acids 2013, 45, 419–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allegra, M.; Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.X.; Gentile, C.; Tesoriere, L.; Livrea, M.A. The chemistry of melatonin’s interaction with reactive species. J. Pineal Res. 2003, 34, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, G.; Akbulut, K.G.; Guney, S. Melatonin, aging, and COVID-19: Could melatonin be beneficial for COVID-19 treatment in the elderly? Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 50, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahbarghazi, A.; Alamdari, K.A.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Salehi-Pourmehr, H. Co-administration of exercise training and melatonin on the function of diabetic heart tissue: A systematic review and meta-analysis of rodent models. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Ramis, M.R.; Esteban, S.; Miralles, A.; Tan, D.X.; Reiter, R.J. Caloric restriction, resveratrol and melatonin: Role of SIRT1 and implications for aging and related-diseases. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2015, 146–148, 28–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, G. Linking the biological underpinnings of depression: Role of mitochondria interactions with melatonin, inflammation, sirtuins, tryptophan catabolites, DNA repair and oxidative and nitrosative stress, with consequences for classification and cognition. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 80, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardinali, D.P.; Hardeland, R. Inflammaging, Metabolic Syndrome and Melatonin: A Call for Treatment Studies. Neuroendocrinology 2017, 104, 382–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R. Melatonin and inflammation-Story of a double-edged blade. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 65, e12525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Rawi, N.; Madkour, M.; Jahrami, H.; Salahat, D.; Alhasan, F.; BaHammam, A.; Al-Islam Faris, M.E. Effect of diurnal intermittent fasting during Ramadan on ghrelin, leptin, melatonin, and cortisol levels among overweight and obese subjects: A prospective observational study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0237922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puchalski, S.S.; Green, J.N.; Rasmussen, D.D. Melatonin effect on rat body weight regulation in response to high-fat diet at middle age. Endocrine 2003, 21, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchio, C.; Baba, K.; Piccione, G.; Tosini, G. Removal of melatonin receptor type 1 signalling induces dyslipidaemia and hormonal changes in mice subjected to environmental circadian disruption. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2021, 4, e00171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolden-Hanson, T.; Mitton, D.R.; McCants, R.L.; Yellon, S.M.; Wilkinson, C.W.; Matsumoto, A.M.; Rasmussen, D.D. Daily melatonin administration to middle-aged male rats suppresses body weight, intraabdominal adiposity, and plasma leptin and insulin independent of food intake and total body fat. Endocrinology 2000, 141, 487–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaeini, Z.; Mirmiran, P.; Bahadoran, Z. Effects of Ramadan intermittent fasting on leptin and adiponectin: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hormones 2021, 20, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiță, M.; Botezatu, R.; Coman, C.; Vuță, V.; Gâjâilă, G.; Nicolae, A.C.; Drăgoi, C.M.; Cotor, G. Research regarding the effect of leptin upon the ratio of certain lymphocyte populations in rat. Farmacia 2021, 69, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamad, M.A.; Mitrea, N.; Nicolae, A.-C.; CONSTANTINESCU, Z.; Drăgoi, C.M.; Arsene, A.-L.; Barbu, C.G. The dynamics of adiponectin and leptin on metabolic syndrome patients and age matched healthy subjects. Blood Press. (BP) 2014, 130, 85mmHg. [Google Scholar]
- Chawla, S.; Beretoulis, S.; Deere, A.; Radenkovic, D. The window matters: A systematic review of time restricted eating strategies in relation to cortisol and melatonin secretion. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Liu, H.; Yang, B.; Pan, J.; Tang, L.; Zeng, H.; Yang, S. Circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorders and the risk of dyslipidemia among railway workers in southwest China: A cross-sectional study. Chronobiol. Int. 2023, 40, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dowling, G.A.; Burr, R.L.; Van Someren, E.J.; Hubbard, E.M.; Luxenberg, J.S.; Mastick, J.; Cooper, B.A. Melatonin and bright-light treatment for rest-activity disruption in institutionalized patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2008, 56, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.H.; Joo, Y.; Kim, M.-S.; Choe, H.K.; Tong, Q.; Kwon, O. Effects of intermittent fasting on the circulating levels and circadian rhythms of hormones. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 745–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vriend, J.; Sheppard, M.S.; Borer, K.T. Melatonin increases serum growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) levels in male Syrian hamsters via hypothalamic neurotransmitters. Growth Dev. Aging 1990, 54, 165–171. [Google Scholar]
- Abassi, W.; Ouerghi, N.; Ghouili, H.; Haouami, S.; Bouassida, A. Greater effects of high-compared with moderate-intensity interval training on thyroid hormones in overweight/obese adolescent girls. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2020, 41, 20200031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ataeinosrat, A.; Haghighi, M.M.; Abednatanzi, H.; Soltani, M.; Ghanbari-Niaki, A.; Nouri-Habashi, A.; Amani-Shalamzari, S.; Mossayebi, A.; Khademosharie, M.; Johnson, K.E. Effects of three different modes of resistance training on appetite hormones in males with obesity. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bekesiene, S.; Smaliukiene, R.; Vaičaitienė, R.; Mažeikienė, A.; Larsson, G.; Karčiauskaitė, D.; Mazgelytė, E. Three-faceted approach to perceived stress: A longitudinal study of stress hormones, personality, and group cohesion in the real-life setting of compulsory basic military training. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dote-Montero, M.; De-la-O, A.; Jurado-Fasoli, L.; Ruiz, J.R.; Castillo, M.J.; Amaro-Gahete, F.J. The effects of three types of exercise training on steroid hormones in physically inactive middle-aged adults: A randomized controlled trial. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2021, 121, 2193–2206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caplin, A.; Chen, F.S.; Beauchamp, M.R.; Puterman, E. The effects of exercise intensity on the cortisol response to a subsequent acute psychosocial stressor. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2021, 131, 105336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, K.P., Jr.; Drake, A.L.; Frey, D.J.; Fleshner, M.; Desouza, C.A.; Gronfier, C.; Czeisler, C.A. Influence of sleep deprivation and circadian misalignment on cortisol, inflammatory markers, and cytokine balance. Brain Behav. Immun. 2015, 47, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Ma, H.; Gan, X.; Li, S.; Ma, X.; Chen, S.; Yang, H.; Zhu, X.; Jiang, H.; Bi, Q.; et al. Circadian misalignment leads to changes in cortisol rhythms, blood biochemical variables and serum miRNA profiles. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 567, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekampe, J.; van Middendorp, H.; Biermasz, N.R.; Sweep, F.C.; Meijer, O.C.; Pelsma, I.C.; Pereira, A.M.; Hermus, A.R.M.M.; Evers, A.W.M. Conditioning cortisol in healthy young women—A randomized controlled trial. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2021, 124, 105081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, W.J.; Ratamess, N.A.; Hymer, W.C.; Nindl, B.C.; Fragala, M.S. Growth Hormone(s), Testosterone, Insulin-Like Growth Factors, and Cortisol: Roles and Integration for Cellular Development and Growth With Exercise. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Nys, L.; Anderson, K.; Ofosu, E.F.; Ryde, G.C.; Connelly, J.; Whittaker, A.C. The effects of physical activity on cortisol and sleep: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2022, 143, 105843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heden, T.D.; Kanaley, J.A. Syncing Exercise with Meals and Circadian Clocks. Exerc. Sport. Sci. Rev. 2019, 47, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wideman, L.; Weltman, J.Y.; Hartman, M.L.; Veldhuis, J.D.; Weltman, A. Growth hormone release during acute and chronic aerobic and resistance exercise: Recent findings. Sports Med. 2002, 32, 987–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, R.; Duff, W.; Chizen, D.; Zello, G.A.; Chilibeck, P.D. The effect of a low glycemic index pulse-based diet on insulin sensitivity, insulin resistance, bone resorption and cardiovascular risk factors during bed rest. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKeegan, K.; Mason, S.A.; Trewin, A.J.; Keske, M.A.; Wadley, G.D.; Della Gatta, P.A.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Parker, L. Reactive oxygen species in exercise and insulin resistance: Working towards personalized antioxidant treatment. Redox Biol. 2021, 44, 102005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, M.; Deng, X.; Guo, Z.; Laudon, M.; Hu, Z.; Liao, D.; Hu, X.; Luo, Y.; Shen, Q.; Su, Z.; et al. NEU-P11, a novel melatonin agonist, inhibits weight gain and improves insulin sensitivity in high-fat/high-sucrose-fed rats. Pharmacol. Res. 2009, 59, 248–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinedi, E.; Cardinali, D.P. Neuroendocrine-Metabolic Dysfunction and Sleep Disturbances in Neurodegenerative Disorders: Focus on Alzheimer’s Disease and Melatonin. Neuroendocrinology 2019, 108, 354–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, C.; Dalla Man, C.; Cobelli, C.; Groop, L.; Zhao, H.; Bale, A.E.; Shaw, M.; Duran, E.; Pierpont, B.; Caprio, S.; et al. A common variant in the MTNR1b gene is associated with increased risk of impaired fasting glucose (IFG) in youth with obesity. Obesity 2015, 23, 1022–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caldeira, R.S.; Panissa, V.L.G.; Inoue, D.S.; Campos, E.Z.; Monteiro, P.A.; de Melo Giglio, B.; Pimentel, G.D.; Hofmann, P.; Lira, F.S. Impact to short-term high intensity intermittent training on different storages of body fat, leptin and soluble leptin receptor levels in physically active non-obese men: A pilot investigation. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 28, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Assis, G.G.; Murawska-Ciałowicz, E. Exercise and Weight Management: The Role of Leptin—A Systematic Review and Update of Clinical Data from 2000–2022. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4490. [Google Scholar]
- Kiernan, K.; MacIver, N.J. The role of the adipokine leptin in immune cell function in health and disease. Front. Immunol. 2021, 11, 622468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kord, H.V.; Tinsley, G.M.; Santos, H.O.; Zand, H.; Nazary, A.; Fatahi, S.; Mokhtari, Z.; Salehi-Sahlabadi, A.; Tan, S.C.; Rahmani, J. The influence of fasting and energy-restricted diets on leptin and adiponectin levels in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 40, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsofliou, F.; Pitsiladis, Y.; Malkova, D.; Wallace, A.; Lean, M. Moderate physical activity permits acute coupling between serum leptin and appetite–satiety measures in obese women. Int. J. Obes. 2003, 27, 1332–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaccaria, M.; Ermolao, A.; Roi, G.; Englaro, P.; Tegon, G.; Varnier, M. Leptin reduction after endurance races differing in duration and energy expenditure. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2002, 87, 108–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuesta, S.; Kireev, R.; Garcia, C.; Rancan, L.; Vara, E.; Tresguerres, J.A. Melatonin can improve insulin resistance and aging-induced pancreas alterations in senescence-accelerated prone male mice (SAMP8). Age 2013, 35, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbownik, M.; Tan, D.; Manchester, L.C.; Reiter, R.J. Renal toxicity of the carcinogen δ-aminolevulinic acid: Antioxidant effects of melatonin. Cancer Lett. 2000, 161, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodella, L.F.; Favero, G.; Rossini, C.; Foglio, E.; Bonomini, F.; Reiter, R.J.; Rezzani, R. Aging and vascular dysfunction: Beneficial melatonin effects. Age 2013, 35, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K.; Kauppinen, A. Crosstalk between Oxidative Stress and SIRT1: Impact on the Aging Process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3834–3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Centner, C.; Gollhofer, A.; König, D. Effects of Dietary Strategies on Exercise-Induced Oxidative Stress: A Narrative Review of Human Studies. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sies, H.; Jones, D.P. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 363–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.A.; Khan, M.; Jo, M.H.; Jo, M.G.; Amin, F.U.; Kim, M.O. Melatonin Stimulates the SIRT1/Nrf2 Signaling Pathway Counteracting Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Oxidative Stress to Rescue Postnatal Rat Brain. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2017, 23, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, F.; Pang, J.; Pan, C.; Xu, F.; Chen, Y. Fundamental Mechanisms of the Cell Death Caused by Nitrosative Stress. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 742483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bandookwala, M.; Sengupta, P. 3-Nitrotyrosine: A versatile oxidative stress biomarker for major neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Neurosci. 2020, 130, 1047–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haseeb, A. 3-Nitrotyrosine: A biomarker of nitrogen free radical species modified proteins in systemic autoimmunogenic conditions. Hum. Immunol. 2013, 74, 1392–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niculae, D.; Dusman, R.; Leonte, R.A.; Chilug, L.E.; Dragoi, C.M.; Nicolae, A.; Serban, R.M.; Niculae, D.A.; Dumitrescu, I.B.; Draganescu, D. Biological Pathways as Substantiation of the Use of Copper Radioisotopes in Cancer Theranostics. Front. Phys. 2021, 8, 568296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolae, A.C.; Drăgoi, C.M.; Ceaușu, I.; Poalelungi, C.; Iliescu, D.; Arsene, A.L. Clinical implications of the indolergic system and oxidative stress in physiological gestational homeostasis. Farmacia 2015, 63, 46–51. [Google Scholar]
- Diaconu, C.C.; Cozma, M.-A.; Dobrică, E.-C.; Gheorghe, G.; Jichitu, A.; Ionescu, V.A.; Nicolae, A.C.; Drăgoi, C.M.; Găman, M.-A. Polypharmacy in the Management of Arterial Hypertension—Friend or Foe? Medicina 2021, 57, 1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.A.; Sandesara, P.B.; Dhindsa, D.S.; Mehta, A.; Arneson, L.C.; Dollar, A.L.; Taub, P.R.; Sperling, L.S. Intermittent Fasting: A Heart Healthy Dietary Pattern? Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarţa-Arsene, O.; Leanca, M.; Dică, A.; Bran, E.; Rad, F.; Timnea, O.; Păcurar, D.; Velescu, B.S.; Nicolae, A.C.; Drăgoi, C.M. Dietary omega-3 fatty acids supplimentation for attention deficit with hyperactivity disorder in epileptic children. Farmácia 2017, 65, 550–556. [Google Scholar]
- Zairi, I.; Bejar, M.A.; Mrad, I.B.; Mzoughi, K.; Kraiem, S. Effect of intermittent fasting and chronotherapy on blood pressure control in hypertensive patients during Ramadan. Arter. Hypertens. 2022, 26, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolae, A.C.; Mitrea, N.; Drăgoi, C.M.; Constantinescu, M.Z.; Ciofrângeanu, C.; Bărboi, G.; Arsene, A.L. Murine studies regarding the variation of oxidative status in serum, hepatic and brain samples, after administration of some CNS active drugs. Farmácia 2013, 61, 658–669. [Google Scholar]
- Patikorn, C.; Roubal, K.; Veettil, S.K.; Chandran, V.; Pham, T.; Lee, Y.Y.; Giovannucci, E.L.; Varady, K.A.; Chaiyakunapruk, N. Intermittent Fasting and Obesity-Related Health Outcomes: An Umbrella Review of Meta-analyses of Randomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Netw. Open 2021, 4, e2139558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlăsceanu, A.; Petraru, C.; Baconi, D.; Ghica, M.; Arsene, A.; Popa, L.; Nicolae, A.; Drăgoi, C.; Pavalache, G. Quantitative relationships of urinary cotinine levels in smoking diabetic patients. Farmacia 2015, 63, 349–356. [Google Scholar]
- Hernández-García, J.; Navas-Carrillo, D.; Orenes-Piñero, E. Alterations of circadian rhythms and their impact on obesity, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular diseases. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 1038–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungurianu, A.; Zanfirescu, A.; Nitulescu, G.; Margina, D. Vitamin E beyond Its Antioxidant Label. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruia, V.; Arama, C.; Mitrea, N.; Arsene, A.L.; Gradinaru, D.; Dragoi, C. The hplc plasmatic profile of some fat-soluble antioxidant micronutrients (all-trans-retinol, alpha-tocopherol, coenzime q10) in diabetic and dyslipidemic patients. Farmacia 2009, 57, 630–638. [Google Scholar]
- Khizhkin, E.A.; Ilyukha, V.A.; Vinogradova, I.A.; Antonova, E.P.; Morozov, A.V. Circadian Rhythms of Antioxidant Enzyme’s Activity in Young and Adult Rats under Light Deprivation Conditions. Adv. Gerontol. 2018, 8, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louzada, R.A.; Bouviere, J.; Matta, L.P.; Werneck-de-Castro, J.P.; Dupuy, C.; Carvalho, D.P.; Fortunato, R.S. Redox signaling in widespread health benefits of exercise. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2020, 33, 745–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaguti, M.; Angeloni, C.; Hrelia, S. Polyphenols in exercise performance and prevention of exercise-induced muscle damage. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 825928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P. Hormesis defined. Ageing Res. Rev. 2008, 7, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margină, D.; Ungurianu, A.; Purdel, C.; Tsoukalas, D.; Sarandi, E.; Thanasoula, M.; Tekos, F.; Mesnage, R.; Kouretas, D.; Tsatsakis, A. Chronic Inflammation in the Context of Everyday Life: Dietary Changes as Mitigating Factors. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zsolt, R.; Hae, Y.C.; Erika, K.; Albert, W.T.; Sataro, G. Exercise, oxidative stress and hormesis. Ageing Res. Rev. 2008, 7, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, E.J.; Bachmann, K.A.; Bailer, A.J.; Bolger, P.M.; Borak, J.; Cai, L.; Cedergreen, N.; Cherian, M.G.; Chiueh, C.C.; Clarkson, T.W.; et al. Biological stress response terminology: Integrating the concepts of adaptive response and preconditioning stress within a hormetic dose-response framework. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2007, 222, 122–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nosaka, K.; Muthalib, M.; Lavender, A.; Laursen, P.B. Attenuation of muscle damage by preconditioning with muscle hyperthermia 1-day prior to eccentric exercise. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 2007, 99, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.M.; Hsieh, C.C.; Paffenbarger, R.S., Jr. Exercise intensity and longevity in men. The Harvard Alumni Health Study. JAMA 1995, 273, 1179–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, K.; Farahmand, B.; Ahlbom, A.; Held, C.; Ljunghall, S.; Michaëlsson, K.; Sundström, J. Risk of arrhythmias in 52 755 long-distance cross-country skiers: A cohort study. Eur. Heart J. 2013, 34, 3624–3631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mankowski, R.T.; Anton, S.D.; Buford, T.W.; Leeuwenburgh, C. Dietary Antioxidants as Modifiers of Physiologic Adaptations to Exercise. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 1857–1868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ristow, M.; Zarse, K.; Oberbach, A.; Klöting, N.; Birringer, M.; Kiehntopf, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Kahn, C.R.; Blüher, M. Antioxidants prevent health-promoting effects of physical exercise in humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 8665–8670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trappe, T.A.; White, F.; Lambert, C.P.; Cesar, D.; Hellerstein, M.; Evans, W.J. Effect of ibuprofen and acetaminophen on postexercise muscle protein synthesis. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 282, E551–E556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peake, J.M.; Markworth, J.F.; Nosaka, K.; Raastad, T.; Wadley, G.D.; Coffey, V.G. Modulating exercise-induced hormesis: Does less equal more? J. Appl. Physiol. 2015, 119, 172–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, S.K.; Goldstein, E.; Schrager, M.; Ji, L.L. Exercise training and skeletal muscle antioxidant enzymes: An update. Antioxidants 2022, 12, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gouspillou, G.; Godin, R.; Piquereau, J.; Picard, M.; Mofarrahi, M.; Mathew, J.; Purves-Smith, F.M.; Sgarioto, N.; Hepple, R.T.; Burelle, Y.; et al. Protective role of Parkin in skeletal muscle contractile and mitochondrial function. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 2565–2579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugh, J.N.; Close, G.L. Nutritional Antioxidants for Sports Performance. In Oxidative Eustress in Exercise Physiology; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 115–122. [Google Scholar]
- Awang Daud, D.M.; Ahmedy, F.; Baharuddin, D.M.P.; Zakaria, Z.A. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Enzymes Activity after Cycling at Different Intensity and Duration. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Fasipe, B.; Laher, I. Potential harms of supplementation with high doses of antioxidants in athletes. J. Exerc. Sci. Fit. 2022, 20, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas-Mendoza, N.; Morales-González, Á.; Madrigal-Santillán, E.O.; Angeles-Valencia, M.; Anguiano-Robledo, L.; González-López, L.L.; Sosa-Gómez, A.; Fregoso-Aguilar, T.; Esquivel-Chirino, C.; Ruiz-Velazco-Benítez, Y.A. Phytochemicals and modulation of exercise-induced oxidative stress: A novel overview of antioxidants. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 8292. [Google Scholar]
- Drobnic, F.; Lizarraga, M.A.; Caballero-García, A.; Cordova, A. Coenzyme Q10 Supplementation and Its Impact on Exercise and Sport Performance in Humans: A Recovery or a Performance-Enhancing Molecule? Nutrients 2022, 14, 1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Bustamante-Sanchez, Á.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Martín-Rodríguez, A.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Antioxidants and Sports Performance. Nutrients 2023, 15, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Tsatsakis, A.; Mamoulakis, C.; Teodoro, M.; Briguglio, G.; Caruso, E.; Tsoukalas, D.; Margina, D.; Dardiotis, E.; Kouretas, D.; et al. Current evidence on the effect of dietary polyphenols intake on chronic diseases. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 110, 286–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirla, A.; Islam, F.; Islam, M.R.; Ioana Vicas, S.; Cavalu, S. New Insight and Future Perspectives on Nutraceuticals for Improving Sports Performance of Combat Players: Focus on Natural Supplements, Importance and Advantages over Synthetic Ones. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 8611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S. Polyphenols and athletic performance: A review on human data. In Plant Physiological Aspects of Phenolic Compounds; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2019; pp. 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Díaz, M.; Martín-Castellanos, A.; Fernández-Elías, V.E.; López Torres, O.; Lorenzo Calvo, J. Effects of Polyphenol Consumption on Recovery in Team Sport Athletes of Both Sexes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Angelo, S.; Tafuri, D. Nutraceutical: Their role in improving sports performance. Sport. Sci. 2020, 13, 7–12. [Google Scholar]
- Margina, D.; Ilie, M.; Gradinaru, D. Quercetin and epigallocatechin gallate induce in vitro a dose-dependent stiffening and hyperpolarizing effect on the cell membrane of human mononuclear blood cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4839–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, P.; Morales Marroquín, F.E.; Gann, J.; Andre, T.; McKinley-Barnard, S.; Kim, C.; Morita, M.; Willoughby, D.S. Eight weeks of resistance training in conjunction with glutathione and L-Citrulline supplementation increases lean mass and has no adverse effects on blood clinical safety markers in resistance-trained males. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2018, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabre, H.E.; Greenwalt, C.E.; Gould, L.M.; Smith-Ryan, A.E. The effects of L-Citrulline and Glutathione on Endurance performance in young adult trained males. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2023, 20, 2206386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guest, N.S.; VanDusseldorp, T.A.; Nelson, M.T.; Grgic, J.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Jenkins, N.D.M.; Arent, S.M.; Antonio, J.; Stout, J.R.; Trexler, E.T.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Caffeine and exercise performance. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2021, 18, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerksick, C.M.; Arent, S.; Schoenfeld, B.J.; Stout, J.R.; Campbell, B.; Wilborn, C.D.; Taylor, L.; Kalman, D.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Kreider, R.B.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Nutrient timing. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2017, 14, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagim, A.R.; Harty, P.S.; Tinsley, G.M.; Kerksick, C.M.; Gonzalez, A.M.; Kreider, R.B.; Arent, S.M.; Jager, R.; Smith-Ryan, A.E.; Stout, J.R.; et al. International society of sports nutrition position stand: Energy drinks and energy shots. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2023, 20, 2171314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charest, J.; Grandner, M.A. Sleep and Athletic Performance: Impacts on Physical Performance, Mental Performance, Injury Risk and Recovery, and Mental Health. Sleep. Med. Clin. 2020, 15, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, K.C.; Owens, R.; Hopkins, S.R.; Malhotra, A. Sleep Hygiene for Optimizing Recovery in Athletes: Review and Recommendations. Int. J. Sports Med. 2019, 40, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, C.S.; Nascimento, F.E.L. Isolated branched-chain amino acid intake and muscle protein synthesis in humans: A biochemical review. Einstein 2019, 17, eRB4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Church, D.D.; Hirsch, K.R.; Park, S.; Kim, I.Y.; Gwin, J.A.; Pasiakos, S.M.; Wolfe, R.R.; Ferrando, A.A. Essential Amino Acids and Protein Synthesis: Insights into Maximizing the Muscle and Whole-Body Response to Feeding. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hulmi, J.J.; Laakso, M.; Mero, A.A.; Häkkinen, K.; Ahtiainen, J.P.; Peltonen, H. The effects of whey protein with or without carbohydrates on resistance training adaptations. J. Int. Soc. Sports Nutr. 2015, 12, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadopoulou, S.K. Rehabilitation Nutrition for Injury Recovery of Athletes: The Role of Macronutrient Intake. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Drăgoi, C.M.; Nicolae, A.C.; Ungurianu, A.; Margină, D.M.; Grădinaru, D.; Dumitrescu, I.-B. Circadian Rhythms, Chrononutrition, Physical Training, and Redox Homeostasis—Molecular Mechanisms in Human Health. Cells 2024, 13, 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13020138
Drăgoi CM, Nicolae AC, Ungurianu A, Margină DM, Grădinaru D, Dumitrescu I-B. Circadian Rhythms, Chrononutrition, Physical Training, and Redox Homeostasis—Molecular Mechanisms in Human Health. Cells. 2024; 13(2):138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13020138
Chicago/Turabian StyleDrăgoi, Cristina Manuela, Alina Crenguţa Nicolae, Anca Ungurianu, Denisa Marilena Margină, Daniela Grădinaru, and Ion-Bogdan Dumitrescu. 2024. "Circadian Rhythms, Chrononutrition, Physical Training, and Redox Homeostasis—Molecular Mechanisms in Human Health" Cells 13, no. 2: 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13020138
APA StyleDrăgoi, C. M., Nicolae, A. C., Ungurianu, A., Margină, D. M., Grădinaru, D., & Dumitrescu, I.-B. (2024). Circadian Rhythms, Chrononutrition, Physical Training, and Redox Homeostasis—Molecular Mechanisms in Human Health. Cells, 13(2), 138. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13020138










