The Neural Correlations of Olfactory Associative Reward Memories in Drosophila
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Memory Formation in Drosophila
2.1. Experimental Approaches in Drosophila Olfactory Associative Learning
2.2. Different Types of Olfactory Associative Memory
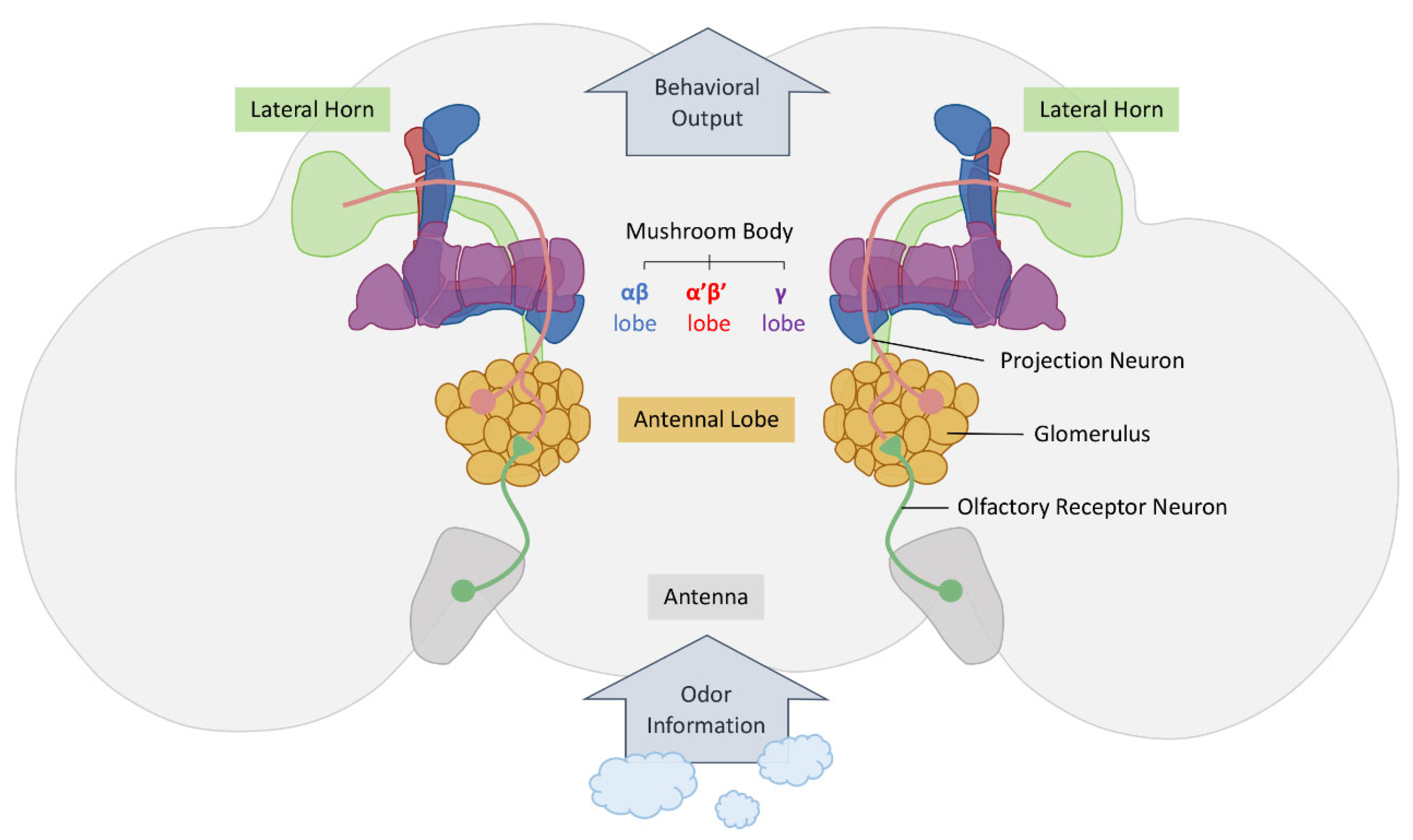
3. The Olfactory Nervous System
4. Olfactory Associative Reward Memories
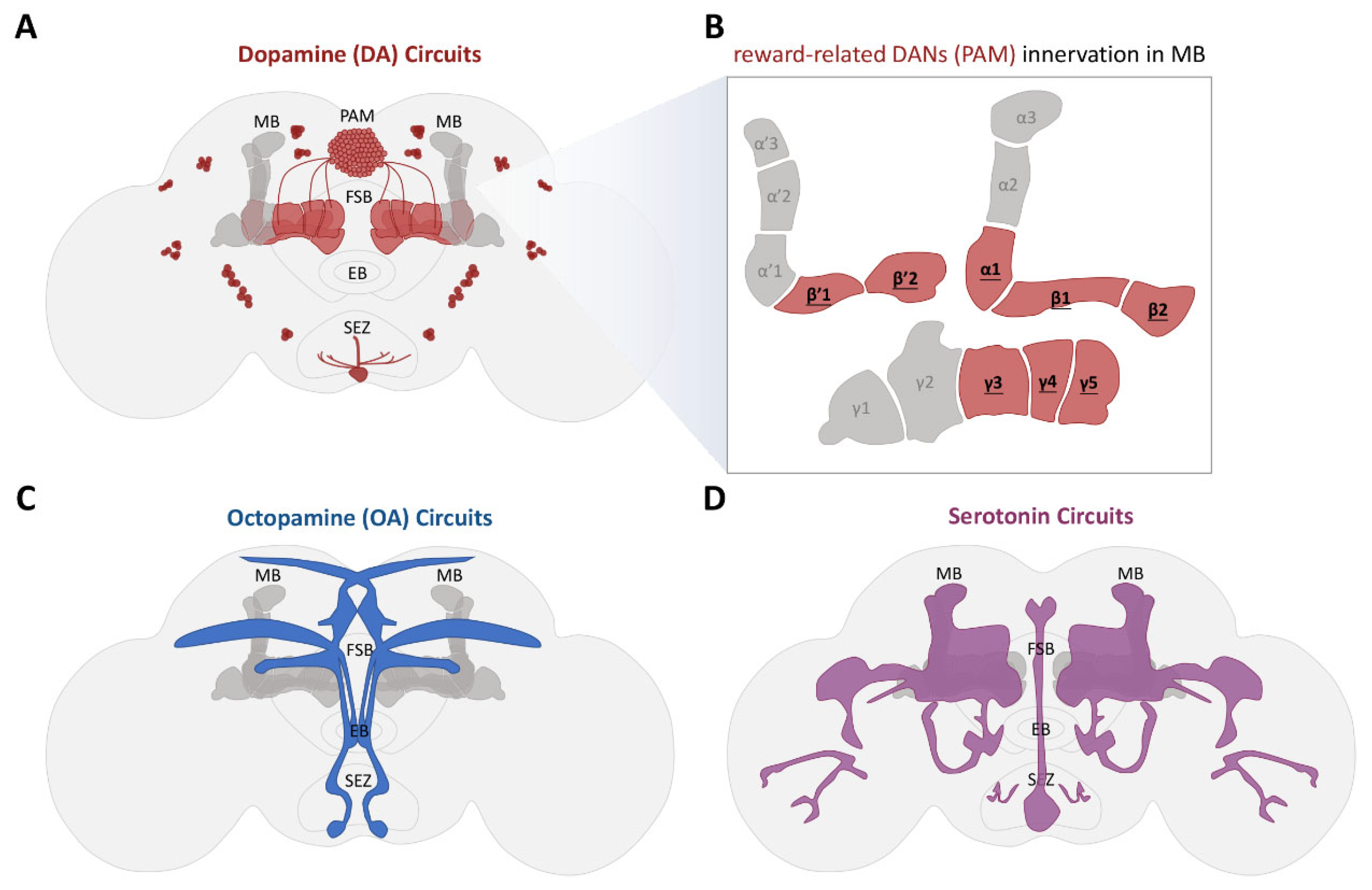
4.1. Neural Circuits Encoding Motivational States
4.2. Water-Reward Memory in Drosophila
4.3. Sucrose-Reward Memory in Drosophila
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Margulies, C.; Tully, T.; Dubnau, J. Deconstructing Memory in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, R700–R713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotas, M.E.; Medzhitov, R. Homeostasis, Inflammation, and Disease Susceptibility. Cell 2015, 160, 816–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaidya, N.; Marquand, A.F.; Nees, F.; Siehl, S.; Schumann, G. The Impact of Psychosocial Adversity on Brain and Behaviour: An Overview of Existing Knowledge and Directions for Future Research. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 3245–3267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citri, A.; Malenka, R.C. Synaptic Plasticity: Multiple Forms, Functions, and Mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 18–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.N.; Frank, M.J. Adaptive Control of Synaptic Plasticity Integrates Micro- and Macroscopic Network Function. Neuropsychopharmacology 2023, 48, 121–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahsai, L.; Zars, T. Learning and Memory in Drosophila: Behavior, Genetics, and Neural Systems. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2011, 99, 139–167. [Google Scholar]
- Jeibmann, A.; Paulus, W. Drosophila melanogaster as a Model Organism of Brain Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 407–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariano, V.; Achsel, T.; Bagni, C.; Kanellopoulos, A.K. Modelling Learning and Memory in Drosophila to Understand Intellectual Disabilities. Neuroscience 2020, 445, 12–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagni, C.; Zukin, R.S. A Synaptic Perspective of Fragile X Syndrome and Autism Spectrum Disorders. Neuron 2019, 101, 1070–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Duran, J.M.; Hejnol, A. A Developmental Perspective on the Evolution of the Nervous System. Dev. Biol. 2021, 475, 181–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diop, S.B.; Bodmer, R. Drosophila as a Model to Study the Genetic Mechanisms of Obesity-Associated Heart Dysfunction. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2012, 16, 966–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apidianakis, Y.; Rahme, L.G. Drosophila melanogaster as a Model for Human Intestinal Infection and Pathology. Dis. Model. Mech. 2011, 4, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amrein, H.; Thorne, N. Gustatory Perception and Behavior in Drosophila melanogaster. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, R673–R684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.H.; Ho, S.M.; Wu, H.Y.; Lin, Y.C.; Tsai, W.H.; Wu, T.; Lai, C.H.; Wu, C.L. Drosophila Model for Studying Gut Microbiota in Behaviors and Neurodegenerative Diseases. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, S.F.; Lee, P.S.; Fu, T.F.; Wu, T.; Wu, C.L. Independent Insulin Signaling Modulators Govern Hot Avoidance under Different Feeding States. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiang, M.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Wu, T.; Wu, C.L. Thermosensation and Temperature Preference: From Molecules to Neuronal Circuits in Drosophila. Cells 2023, 12, 2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, S.M.; Tsai, W.H.; Lai, C.H.; Chiang, M.H.; Lee, W.P.; Wu, H.Y.; Bai, P.Y.; Wu, T.; Wu, C.L. Probiotic Lactobacillus spp. Improves Drosophila Memory by Increasing Lactate Dehydrogenase Levels in the Brain Mushroom Body Neurons. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2316533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, R. Drosophila Olfaction: Past, Present and Future. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2022, 289, 20222054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabana-Dominguez, J.; Anton-Galindo, E.; Fernandez-Castillo, N.; Singgih, E.L.; O’Leary, A.; Norton, W.H.; Strekalova, T.; Schenck, A.; Reif, A.; Lesch, K.P.; et al. The Translational Genetics of ADHD and Related Phenotypes in Model Organisms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 144, 104949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugur, B.; Chen, K.; Bellen, H.J. Drosophila Tools and Assays for the Study of Human Diseases. Dis. Model. Mech. 2016, 9, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle Rodriguez, A.; Didiano, D.; Desplan, C. Power Tools for Gene Expression and Clonal Analysis in Drosophila. Nat. Methods 2011, 9, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, W.G.; Harris, W.A.; Benzer, S. Conditioned Behavior in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1974, 71, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.L. Learning and Memory Using Drosophila melanogaster: A Focus on Advances Made in the Fifth Decade of Research. Genetics 2023, 224, iyad085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, W.G.; Greenspan, R.J. Learning and Courtship in Drosophila: Two Stories with Mutants. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1984, 7, 67–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waddell, S.; Quinn, W.G. Flies, Genes, and Learning. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 1283–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, S.E.; Deshazer, M.; Davis, R.L. Thirty Years of Olfactory Learning and Memory Research in Drosophila melanogaster. Prog. Neurobiol. 2005, 76, 328–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, L.C.; Ejima, A. Courtship Learning in Drosophila melanogaster: Diverse Plasticity of a Reproductive Behavior. Learn. Mem. 2009, 16, 743–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, J.L.; DasGupta, S.; Krashes, M.J.; Leung, B.; Perrat, P.N.; Waddell, S. There Are Many Ways to Train a Fly. Fly 2009, 3, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masek, P.; Keene, A.C. Gustatory Processing and Taste Memory in Drosophila. J. Neurogenet. 2016, 30, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlov, P.I. Conditioned Reflexes: An Investigation of the Physiological Activity of the Cerebral Cortex. Ann. Neurosci. 2010, 17, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hershberger, W.A.; Smith, M.P. Conditioning in Drosophila melanogaster. Anim. Behav. 1967, 15, 259–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, T.; Quinn, W.G. Classical Conditioning and Retention in Normal and Mutant Drosophila melanogaster. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1985, 157, 263–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roman, G.; Davis, R.L. Molecular Biology and Anatomy of Drosophila Olfactory Associative Learning. Bioessays 2001, 23, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busto, G.U.; Cervantes-Sandoval, I.; Davis, R.L. Olfactory Learning in Drosophila. Physiology 2010, 25, 338–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perisse, E.; Burke, C.; Huetteroth, W.; Waddell, S. Shocking Revelations and Saccharin Sweetness in the Study of Drosophila Olfactory Memory. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R752–R763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walkinshaw, E.; Gai, Y.; Farkas, C.; Richter, D.; Nicholas, E.; Keleman, K.; Davis, R.L. Identification of Genes That Promote or Inhibit Olfactory Memory Formation in Drosophila. Genetics 2015, 199, 1173–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, A.C.; Krashes, M.J.; Leung, B.; Bernard, J.A.; Waddell, S. Drosophila Dorsal Paired Medial Neurons Provide a General Mechanism for Memory Consolidation. Curr. Biol. 2006, 16, 1524–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krashes, M.J.; Keene, A.C.; Leung, B.; Armstrong, J.D.; Waddell, S. Sequential Use of Mushroom Body Neuron Subsets during Drosophila Odor Memory Processing. Neuron 2007, 53, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krashes, M.J.; Waddell, S. Rapid Consolidation to a Radish and Protein Synthesis-Dependent Long-Term Memory after Single-Session Appetitive Olfactory Conditioning in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 3103–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempel, B.L.; Bonini, N.; Dawson, D.R.; Quinn, W.G. Reward Learning in Normal and Mutant Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1983, 80, 1482–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, W.G.; Dudai, Y. Memory Phases in Drosophila. Nature 1976, 262, 576–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudai, Y.; Corfas, G.; Hazvi, S. What Is the Possible Contribution of Ca2+-Stimulated Adenylate Cyclase to Acquisition, Consolidation and Retention of an Associative Olfactory Memory in Drosophila. J. Comp. Physiol. A 1988, 162, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folkers, E.; Drain, P.; Quinn, W.G. Radish, a Drosophila Mutant Deficient in Consolidated Memory. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 8123–8127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, T.; Boynton, S.; Brandes, C.; Dura, J.M.; Mihalek, R.; Preat, T.; Villella, A. Genetic Dissection of Memory Formation in Drosophila melanogaster. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1990, 55, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tully, T.; Preat, T.; Boynton, S.C.; Del Vecchio, M. Genetic Dissection of Consolidated Memory in Drosophila. Cell 1994, 79, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, P.F.; Waddell, S. Spaced Training Forms Complementary Long-Term Memories of Opposite Valence in Drosophila. Neuron 2020, 106, 977–991.e974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagani, M.R.; Oishi, K.; Gelb, B.D.; Zhong, Y. The Phosphatase SHP2 Regulates the Spacing Effect for Long-Term Memory Induction. Cell 2009, 139, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyashita, T.; Kikuchi, E.; Horiuchi, J.; Saitoe, M. Long-Term Memory Engram Cells Are Established by c-Fos/CREB Transcriptional Cycling. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 2716–2728.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, C.D.; Schroeder, B.; Davis, R.L. Learning Performance of Normal and Mutant Drosophila after Repeated Conditioning Trials with Discrete Stimuli. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 2944–2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandel, E.R. The Molecular Biology of Memory Storage: A Dialogue between Genes and Synapses. Science 2001, 294, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudai, Y.; Jan, Y.N.; Byers, D.; Quinn, W.G.; Benzer, S. Dunce, a Mutant of Drosophila Deficient in Learning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1976, 73, 1684–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.L.; Kiger, J.A., Jr. Dunce Mutants of Drosophila melanogaster: Mutants Defective in the Cyclic AMP Phosphodiesterase Enzyme System. J. Cell Biol. 1981, 90, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byers, D.; Davis, R.L.; Kiger, J.A., Jr. Defect in cyclic AMP Phosphodiesterase Due to the Dunce Mutation of Learning in Drosophila melanogaster. Nature 1981, 289, 79–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.L.; Davidson, N. Isolation of the Drosophila melanogaster Dunce Chromosomal Region and Recombinational Mapping of Dunce Sequences with Restriction Site Polymorphisms as Genetic Markers. Mol. Cell Biol. 1984, 4, 358–367. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.N.; Denome, S.; Davis, R.L. Molecular Analysis of cDNA Clones and the Corresponding Genomic Coding Sequences of the Drosophila Dunce+ Gene, the Structural Gene for cAMP Phosphodiesterase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 9313–9317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempel, B.L.; Livingstone, M.S.; Quinn, W.G. Mutations in the Dopa Decarboxylase Gene Affect Learning in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 3577–3581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, M.S.; Sziber, P.P.; Quinn, W.G. Loss of Calcium/Calmodulin Responsiveness in Adenylate Cyclase of Rutabaga, a Drosophila Learning Mutant. Cell 1984, 37, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yao, X.; Shuai, Y.; Huang, C.; Wang, L.; Jeong, S.H.; Zhong, Y. Dissociation of Rugose-Dependent Short-Term Memory Component from Memory Consolidation in Drosophila. Genes. Brain Behav. 2013, 12, 626–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Owald, D.; Chandra, V.; Talbot, C.; Huetteroth, W.; Waddell, S. Neural Correlates of Water Reward in Thirsty Drosophila. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoener, J.; Weiglein, A.; Gerber, B.; Schleyer, M. Optogenetically Induced Reward and ‘Frustration’ Memory in Larval Drosophila melanogaster. J. Exp. Biol. 2022, 225, jeb244565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naganos, S.; Ueno, K.; Horiuchi, J.; Saitoe, M. Dopamine Activity in Projection Neurons Regulates Short-Lasting Olfactory Approach Memory in Drosophila. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2022, 56, 4558–4571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.L. Olfactory learning. Neuron 2004, 44, 31–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jefferis, G.S.; Potter, C.J.; Chan, A.M.; Marin, E.C.; Rohlfing, T.; Maurer, C.R., Jr.; Luo, L. Comprehensive Maps of Drosophila Higher Olfactory Centers: Spatially Segregated Fruit and Pheromone Representation. Cell 2007, 128, 1187–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keene, A.C.; Waddell, S. Drosophila Olfactory Memory: Single Genes to Complex Neural circuits. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2007, 8, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaupp, U.B. Olfactory Signalling in Vertebrates and Insects: Differences and Commonalities. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 188–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallem, E.A.; Carlson, J.R. Coding of Odors by a Receptor Repertoire. Cell 2006, 125, 143–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clyne, P.J.; Warr, C.G.; Freeman, M.R.; Lessing, D.; Kim, J.; Carlson, J.R. A Novel Family of Divergent Seven-Transmembrane Proteins: Candidate Odorant Receptors in Drosophila. Neuron 1999, 22, 327–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Chess, A. Identification of Candidate Drosophila Olfactory Receptors from Genomic DNA Sequence. Genomics 1999, 60, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laissue, P.P.; Reiter, C.; Hiesinger, P.R.; Halter, S.; Fischbach, K.F.; Stocker, R.F. Three-Dimensional Reconstruction of the Antennal Lobe in Drosophila melanogaster. J. Comp. Neurol. 1999, 405, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vosshall, L.B.; Wong, A.M.; Axel, R. An Olfactory Sensory Map in the Fly Brain. Cell 2000, 102, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, K.; Brady, R., Jr.; Cravchik, A.; Morozov, P.; Rzhetsky, A.; Zuker, C.; Axel, R. A Chemosensory Gene Family Encoding Candidate Gustatory and Olfactory Receptors in Drosophila. Cell 2001, 104, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, A.; Alenius, M.; Dickson, B.J. Molecular, Anatomical, and Functional Organization of the Drosophila Olfactory System. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1535–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishilevich, E.; Vosshall, L.B. Genetic and Functional Subdivision of the Drosophila Antennal Lobe. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 1548–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, M.; Roorda, R.D.; Lima, S.Q.; Zemelman, B.V.; Morcillo, P.; Miesenbock, G. Transmission of Olfactory Information between Three Populations of Neurons in the Antennal Lobe of the Fly. Neuron 2002, 36, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.W.; Wong, A.M.; Flores, J.; Vosshall, L.B.; Axel, R. Two-Photon Calcium Imaging Reveals an Odor-Evoked Map of Activity in The Fly Brain. Cell 2003, 112, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisenberg, M.; Borst, A.; Wagner, S.; Byers, D. Drosophila Mushroom Body Mutants Are Deficient in Olfactory Learning. J. Neurogenet. 1985, 2, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Belle, J.S.; Heisenberg, M. Associative Odor Learning in Drosophila Abolished by Chemical Ablation of Mushroom Bodies. Science 1994, 263, 692–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.L. Olfactory Memory Formation in Drosophila: From Molecular to Systems Neuroscience. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 28, 275–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.L.; Han, K.A. Neuroanatomy: Mushrooming Mushroom Bodies. Curr. Biol. 1996, 6, 146–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubnau, J.; Chiang, A.S.; Tully, T. Neural Substrates of Memory: From Synapse to System. J. Neurobiol. 2003, 54, 238–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, Y.; Grubel, K.; Busch, S.; Friedrich, A.B.; Siwanowicz, I.; Tanimoto, H. The Mushroom Body of Adult Drosophila Characterized by GAL4 Drivers. J. Neurogenet. 2009, 23, 156–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heisenberg, M. Mushroom Body Memoir: From Maps to Models. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2003, 4, 266–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.; Lee, A.; Luo, L. Development of the Drosophila Mushroom Bodies: Sequential Generation of Three Distinct Types of Neurons from a Neuroblast. Development 1999, 126, 4065–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zars, T.; Fischer, M.; Schulz, R.; Heisenberg, M. Localization of a Short-Term Memory in Drosophila. Science 2000, 288, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual, A.; Preat, T. Localization of Long-Term Memory within the Drosophila Mushroom Body. Science 2001, 294, 1115–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isabel, G.; Pascual, A.; Preat, T. Exclusive Consolidated Memory Phases in Drosophila. Science 2004, 304, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connolly, J.B.; Roberts, I.J.; Armstrong, J.D.; Kaiser, K.; Forte, M.; Tully, T.; O’Kane, C.J. Associative Learning Disrupted by Impaired Gs Signaling in Drosophila Mushroom Bodies. Science 1996, 274, 2104–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuire, S.E.; Le, P.T.; Osborn, A.J.; Matsumoto, K.; Davis, R.L. Spatiotemporal Rescue of Memory Dysfunction in Drosophila. Science 2003, 302, 1765–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Roman, G.; Zong, L.; Davis, R.L. Pharmacogenetic Rescue in Time and Space of the Rutabaga Memory Impairment by Using Gene-Switch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, G.C.; Bazhenov, M.; Laurent, G. Olfactory Representations by Drosophila Mushroom Body Neurons. J. Neurophysiol. 2008, 99, 734–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guo, H.F.; Pologruto, T.A.; Hannan, F.; Hakker, I.; Svoboda, K.; Zhong, Y. Stereotyped Odor-Evoked Activity in the Mushroom Body of Drosophila Revealed by Green Fluorescent Protein-Based Ca2+ Imaging. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 6507–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, A.C.; Bygrave, A.M.; de Calignon, A.; Lee, T.; Miesenbock, G. Sparse, Decorrelated Odor Coding in the Mushroom Body Enhances Learned Odor Discrimination. Nat. Neurosci. 2014, 17, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta, R.; Nowotny, T. Fast and Robust Learning by Reinforcement Signals: Explorations in the Insect Brain. Neural Comput. 2009, 21, 2123–2151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wessnitzer, J.; Young, J.M.; Armstrong, J.D.; Webb, B. A Model of Non-Elemental Olfactory Learning in Drosophila. J. Comput. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 197–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardin, P.; Peng, F.; Mangan, M.; Lagogiannis, K.; Webb, B. Using an Insect Mushroom Body Circuit to Encode Route Memory in Complex Natural Environments. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1004683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Chittka, L. A Simple Computational Model of the Bee Mushroom Body Can Explain Seemingly Complex Forms of Olfactory Learning and Memory. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, J.; Nawrot, M.; Menzel, R.; Landgraf, T. A Neural Network Model for Familiarity and Context Learning during Honeybee Foraging Flights. Biol. Cybern. 2018, 112, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosqueiro, T.S.; Huerta, R. Computational Models to Understand Decision Making and Pattern Recognition in the Insect Brain. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2014, 6, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmuker, M.; Pfeil, T.; Nawrot, M.P. A neuromorphic Network for Generic Multivariate Data Classification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2081–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betkiewicz, R.; Lindner, B.; Nawrot, M.P. Circuit and Cellular Mechanisms Facilitate the Transformation from Dense to Sparse Coding in the Insect Olfactory System. eNeuro 2020, 7, ENEURO.0305-18.2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, Y.; Sitaraman, D.; Ichinose, T.; Kaun, K.R.; Vogt, K.; Belliart-Guerin, G.; Placais, P.Y.; Robie, A.A.; Yamagata, N.; Schnaitmann, C.; et al. Mushroom Body Output Neurons Encode Valence and Guide Memory-Based Action Selection in Drosophila. eLife 2014, 3, e04580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, N.K.; Tanimoto, H.; Ito, K. Neuronal Assemblies of the Drosophila Mushroom Body. J. Comp. Neurol. 2008, 508, 711–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, Y.; Hattori, D.; Yu, Y.; Johnston, R.M.; Iyer, N.A.; Ngo, T.T.; Dionne, H.; Abbott, L.F.; Axel, R.; Tanimoto, H.; et al. The Neuronal Architecture of the Mushroom Body Provides a Logic for Associative Learning. eLife 2014, 3, e04577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owald, D.; Waddell, S. Olfactory Learning Skews Mushroom Body Output Pathways to Steer Behavioral Choice in Drosophila. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2015, 35, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Chakraborty, S.; Sachse, S. Olfactory Processing in the Lateral Horn of Drosophila. Cell Tissue Res. 2021, 383, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das Chakraborty, S.; Chang, H.; Hansson, B.S.; Sachse, S. Higher-Order Olfactory Neurons in the Lateral Horn Support Odor Valence and Odor Identity Coding in Drosophila. eLife 2022, 11, e74637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimbeck, G.; Bugnon, V.; Gendre, N.; Keller, A.; Stocker, R.F. A Central Neural Circuit for Experience-Independent Olfactory and Courtship Behavior in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15336–15341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masse, N.Y.; Turner, G.C.; Jefferis, G.S. Olfactory Information Processing in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2009, 19, R700–R713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, H.; Lin, A.C. Neuronal Mechanisms Underlying Innate and Learned Olfactory Processing in Drosophila. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2019, 36, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, M.J.; Belliart-Guerin, G.; Bates, A.S.; Frechter, S.; Lampin-Saint-Amaux, A.; Aso, Y.; Roberts, R.J.V.; Schlegel, P.; Wong, A.; Hammad, A.; et al. Communication from Learned to Innate Olfactory Processing Centers Is Required for Memory Retrieval in Drosophila. Neuron 2018, 100, 651–668.e658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolan, M.J.; Frechter, S.; Bates, A.S.; Dan, C.; Huoviala, P.; Roberts, R.J.; Schlegel, P.; Dhawan, S.; Tabano, R.; Dionne, H.; et al. Neurogenetic Dissection of the Drosophila Lateral Horn Reveals Major Outputs, Diverse Behavioural Functions, and Interactions with the Mushroom Body. eLife 2019, 8, 43079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S. Internal-State-Dependent Modulation of Olfactory Responses: A Tale of Dopamine Neurons in the Adult Drosophila Mushroom Body. Curr. Opin. Insect Sci. 2023, 59, 101104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eschbach, C.; Fushiki, A.; Winding, M.; Afonso, B.; Andrade, I.V.; Cocanougher, B.T.; Eichler, K.; Gepner, R.; Si, G.; Valdes-Aleman, J.; et al. Circuits for Integrating Learned and Innate Valences in the Insect Brain. eLife 2021, 10, e62567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caron, S.J.; Ruta, V.; Abbott, L.F.; Axel, R. Random Convergence of Olfactory Inputs in the Drosophila Mushroom Body. Nature 2013, 497, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lindsey, J.W.; Marin, E.C.; Otto, N.; Dreher, M.; Dempsey, G.; Stark, I.; Bates, A.S.; Pleijzier, M.W.; Schlegel, P.; et al. The Connectome of the Adult Drosophila Mushroom Body Provides Insights into Function. eLife 2020, 9, e62576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Li, F.; Fisher, C.; Ali, I.J.; Sharifi, N.; Calle-Schuler, S.; Hsu, J.; Masoodpanah, N.; Kmecova, L.; Kazimiers, T.; et al. Structured Sampling of Olfactory Input by the Fly Mushroom Body. Curr. Biol. 2022, 32, 3334–3349.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Owald, D.; Felsenberg, J.; Talbot, C.B.; Das, G.; Perisse, E.; Huetteroth, W.; Waddell, S. Activity of Defined Mushroom Body Output Neurons Underlies Learned Olfactory Behavior in Drosophila. Neuron 2015, 86, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perisse, E.; Owald, D.; Barnstedt, O.; Talbot, C.B.; Huetteroth, W.; Waddell, S. Aversive Learning and Appetitive Motivation Toggle Feed-Forward Inhibition in the Drosophila Mushroom Body. Neuron 2016, 90, 1086–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noyes, N.C.; Davis, R.L. Innate and Learned Odor-Guided Behaviors Utilize Distinct Molecular Signaling Pathways in a Shared Dopaminergic Circuit. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, Y.; Herb, A.; Ogueta, M.; Siwanowicz, I.; Templier, T.; Friedrich, A.B.; Ito, K.; Scholz, H.; Tanimoto, H. Three Dopamine Pathways Induce Aversive Odor Memories with Different Stability. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, C.J.; Huetteroth, W.; Owald, D.; Perisse, E.; Krashes, M.J.; Das, G.; Gohl, D.; Silies, M.; Certel, S.; Waddell, S. Layered Reward Signalling through Octopamine and Dopamine in Drosophila. Nature 2012, 492, 433–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Placais, P.Y.; Yamagata, N.; Pfeiffer, B.D.; Aso, Y.; Friedrich, A.B.; Siwanowicz, I.; Rubin, G.M.; Preat, T.; Tanimoto, H. A Subset of Dopamine Neurons Signals Reward for Odour Memory in Drosophila. Nature 2012, 488, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, N.; Hiroi, M.; Kondo, S.; Abe, A.; Tanimoto, H. Suppression of Dopamine Neurons Mediates Reward. PLoS Biol. 2016, 14, e1002586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sejourne, J.; Placais, P.Y.; Aso, Y.; Siwanowicz, I.; Trannoy, S.; Thoma, V.; Tedjakumala, S.R.; Rubin, G.M.; Tchenio, P.; Ito, K.; et al. Mushroom Body Efferent Neurons Responsible for Aversive Olfactory Memory Retrieval in Drosophila. Nat. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 903–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Placais, P.Y.; Trannoy, S.; Friedrich, A.B.; Tanimoto, H.; Preat, T. Two Pairs of Mushroom Body Efferent Neurons Are Required for Appetitive Long-Term Memory Retrieval in Drosophila. Cell Rep. 2013, 5, 769–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aso, Y.; Ray, R.P.; Long, X.; Bushey, D.; Cichewicz, K.; Ngo, T.T.; Sharp, B.; Christoforou, C.; Hu, A.; Lemire, A.L.; et al. Nitric Oxide Acts as a Cotransmitter in a Subset of dopaminergic Neurons to Diversify Memory Dynamics. eLife 2019, 8, e49257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, D.; Maeyama, Y.; Tabata, T. Combinatory Actions of Co-transmitters in Dopaminergic Systems Modulate Drosophila Olfactory Memories. J. Neurosci. 2023, 43, 8294–8305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krashes, M.J.; DasGupta, S.; Vreede, A.; White, B.; Armstrong, J.D.; Waddell, S. A Neural Circuit Mechanism Integrating Motivational State with Memory Expression in. Cell 2009, 139, 416–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plaçais, P.Y.; Preat, T. To Favor Survival Under Food Shortage, the Brain Disables Costly Memory. Science 2013, 339, 440–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senapati, B.; Tsao, C.H.; Juan, Y.A.; Chiu, T.H.; Wu, C.L.; Waddell, S.; Lin, S.W. A Neural Mechanism for Deprivation State-Specific Expression of Relevant Memories in Drosophila. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 2029–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyu, W.H.; Chiu, T.H.; Chiang, M.H.; Cheng, Y.C.; Tsai, Y.L.; Fu, T.F.; Wu, T.; Wu, C.L. Neural Circuits for Long-Term Water-Reward Memory Processing in Thirsty. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albin, S.D.; Kaun, K.R.; Knapp, J.M.; Chung, P.; Heberlein, U.; Simpson, J.H. A Subset of Serotonergic Neurons Evokes Hunger in Adult. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 2435–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaplen, K.M.; Kaun, K.R. Reward from Bugs to Bipeds: A Comparative Approach to Understanding How Reward Circuits Function. J. Neurogenet. 2016, 30, 133–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, P.; Hiroi, M.; Ngai, J.; Scott, K. The Molecular Basis for Water Taste in Drosophila. Nature 2010, 465, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z. The Amiloride-Sensitive Epithelial Na+ Channel PPK28 Is Essential for Drosophila Gustatory Water Reception. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 6247–6252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enjin, A.; Zaharieva, E.E.; Frank, D.D.; Mansourian, S.; Suh, G.S.; Gallio, M.; Stensmyr, M.C. Humidity Sensing in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2016, 26, 1352–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, F.; Zhu, Y. A Novel Assay Reveals Hygrotactic Behavior in Drosophila. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, R.; Mabuchi, Y.; Mizunami, M.; Tanaka, N.K. Convergence of Multimodal Sensory Pathways to the Mushroom Body Calyx in Drosophila melanogaster. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 29481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Lee, H.G.; Han, K.A. D1 Dopamine Receptor dDA1 is Required in the Mushroom Body Neurons for Aversive and Appetitive Learning in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 7640–7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.P.; Chiang, M.H.; Chang, L.Y.; Shyu, W.H.; Chiu, T.H.; Fu, T.F.; Wu, T.; Wu, C.L. Serotonin Signals Modulate Mushroom Body Output Neurons for Sustaining Water-Reward Long-Term Memory in Drosophila. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 755574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitman, J.L.; Huetteroth, W.; Burke, C.J.; Krashes, M.J.; Lai, S.L.; Lee, T.; Waddell, S. A Pair of Inhibitory Neurons Are Required to Sustain Labile Memory in the Drosophila Mushroom Body. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 855–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernandez, J.S.; Brown, T.M.; Kaun, K.R. Drosophila Reward Circuits; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budnik, V.; White, K. Genetic Dissection of Dopamine and Serotonin Synthesis in the Nervous System of Drosophila melanogaster. J. Neurogenet. 1987, 4, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; Davis, R.L. Eight Different Types of Dopaminergic Neurons Innervate the Drosophila Mushroom Body Neuropil: Anatomical and Physiological Heterogeneity. Front. Neural Circuits 2009, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassel, D.R.; Elekes, K. Aminergic Neurons in the Brain of Blowflies and Drosophila: Dopamine- and Tyrosine Hydroxylase-Immunoreactive Neurons and Their Relationship with Putative Histaminergic Neurons. Cell Tissue Res. 1992, 267, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, M.T.; Lin, Y.Q.; Kisling, S.; Cotterell, J.; Wilson, Y.A.; Wang, Q.P.; Khuong, T.M.; Bakhshi, N.; Cole, T.A.; Oyston, L.J.; et al. A Simple High Throughput Assay to Evaluate Water Consumption in the Fruit Fly. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, N.; Ichinose, T.; Aso, Y.; Placais, P.Y.; Friedrich, A.B.; Sima, R.J.; Preat, T.; Rubin, G.M.; Tanimoto, H. Distinct Dopamine Neurons Mediate Reward Signals for Short- and Long-Term Memories. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 578–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, W.P.; Chiang, M.H.; Chang, L.Y.; Lee, J.Y.; Tsai, Y.L.; Chiu, T.H.; Chiang, H.C.; Fu, T.F.; Wu, T.; Wu, C.L. Mushroom Body Subsets Encode CREB2-Dependent Water-Reward Long-Term Memory in Drosophila. PLoS Genet. 2020, 16, e1008963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Zhang, X.; Hu, W.; Liang, X.; Zhang, F.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.J.; Zhong, Y. Importin-7 Mediates Memory Consolidation through Regulation of Nuclear Translocation of Training-Activated MAPK in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 3072–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- May, C.E.; Rosander, J.; Gottfried, J.; Dennis, E.; Dus, M. Dietary Sugar Inhibits Satiation by Decreasing the Central Processing of Sweet Taste. eLife 2020, 9, e54530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huetteroth, W.; Perisse, E.; Lin, S.; Klappenbach, M.; Burke, C.; Waddell, S. Sweet Taste and Nutrient Value Subdivide Rewarding Dopaminergic Neurons in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2015, 25, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaplen, K.M.; Talay, M.; Nunez, K.M.; Salamon, S.; Waterman, A.G.; Gang, S.; Song, S.L.; Barnea, G.; Kaun, K.R. Circuits That Encode and Guide Alcohol-Associated Preference. eLife 2020, 9, e48730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siju, K.P.; Stih, V.; Aimon, S.; Gjorgjieva, J.; Portugues, R.; Grunwald Kadow, I.C. Valence and State-Dependent Population Coding in Dopaminergic Neurons in the Fly Mushroom Body. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 2104–2115.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landayan, D.; Feldman, D.S.; Wolf, F.W. Satiation State-Dependent Dopaminergic Control Of Foraging in Drosophila. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, N.; Pleijzier, M.W.; Morgan, I.C.; Edmondson-Stait, A.J.; Heinz, K.J.; Stark, I.; Dempsey, G.; Ito, M.; Kapoor, I.; Hsu, J.; et al. Input Connectivity Reveals Additional Heterogeneity of Dopaminergic Reinforcement in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2020, 30, 3200–3211.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichinose, T.; Aso, Y.; Yamagata, N.; Abe, A.; Rubin, G.M.; Tanimoto, H. Reward Signal in a Recurrent Circuit Drives Appetitive Long-Term Memory Formation. eLife 2015, 4, e10719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.; Scott, K. Serotonergic Neurons Translate Taste Detection into Internal Nutrient Regulation. Neuron 2022, 110, 1036–1050.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burke, C.J.; Waddell, S. Remembering Nutrient Quality of Sugar in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 746–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebreton, S.; Witzgall, P.; Olsson, M.; Becher, P.G. Dietary Glucose Regulates Yeast Consumption in Adult Drosophila Males. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luersen, K.; Roder, T.; Rimbach, G. Drosophila melanogaster in Nutrition Research-The Importance of Standardizing Experimental Diets. Genes Nutr. 2019, 14, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Moon, S.J.; Wang, X.; Ren, Q.; Montell, C. Gr64f Is Required in Combination with Other Gustatory Receptors for Sugar Detection in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 1797–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slone, J.; Daniels, J.; Amrein, H. Sugar Receptors in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 1809–1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.L.; Motevalli, D.; Stern, U.; Yang, C.H. A Functional Division of Drosophila Sweet Taste Neurons That Is Value-Based and Task-Specific. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2110158119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzo, A.; Silies, M.; Gohl, D.M.; Scott, K. Motor Neurons Controlling Fluid Ingestion in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6307–6312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liman, E.R.; Zhang, Y.V.; Montell, C. Peripheral Coding of Taste. Neuron 2014, 81, 984–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trannoy, S.; Redt-Clouet, C.; Dura, J.M.; Preat, T. Parallel Processing of Appetitive Short- and Long-Term Memories in Drosophila. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, Y.F.; Bilican, A.; Bruggmann, R.; Sprecher, S.G. Regulators of Long-Term Memory Revealed by Mushroom Body-Specific Gene Expression Profiling in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 2018, 209, 1167–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagata, N.; Ezaki, T.; Takahashi, T.; Wu, H.; Tanimoto, H. Presynaptic Inhibition of Dopamine Neurons Controls Optimistic Bias. eLife 2021, 10, e64907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohn, R.; Morantte, I.; Ruta, V. Coordinated and Compartmentalized Neuromodulation Shapes Sensory Processing in Drosophila. Cell 2015, 163, 1742–1755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chouhan, N.S.; Sehgal, A. Consolidation of Sleep-Dependent Appetitive Memory Is Mediated by a Sweet-Sensing Circuit. J. Neurosci. 2022, 42, 3856–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo-Garcia, T.R.; Gu, K.; Woerner, R.K.R.; Dus, M. Food Memory Circuits Regulate Eating and Energy Balance. Curr. Biol. 2023, 33, 215–227.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, G.; Yan, J.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Cai, D. Metabolic Learning and Memory Formation by the Brain Influence Systemic Metabolic Homeostasis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chia, J.; Scott, K. Activation of Specific Mushroom Body Output Neurons Inhibits Proboscis Extension and Sucrose Consumption. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0223034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.C.; Lee, H.G.; Lim, J.; Han, K.A. Appetitive Learning Requires the alpha1-like Octopamine Receptor OAMB in the Drosophila Mushroom Body Neurons. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 1672–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwaerzel, M.; Monastirioti, M.; Scholz, H.; Friggi-Grelin, F.; Birman, S.; Heisenberg, M. Dopamine and Octopamine Differentiate between Aversive and Appetitive Olfactory Memories in Drosophila. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 10495–10502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitaraman, D.; LaFerriere, H.; Birman, S.; Zars, T. Serotonin Is Critical for Rewarded Olfactory Short-Term Memory in Drosophila. J. Neurogenet. 2012, 26, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Saver, M.; Chung, P.; Ren, Q.; Lee, T.; Kent, C.F.; Heberlein, U. Dissection of the Drosophila Neuropeptide F Circuit Using a High-Throughput Two-Choice Assay. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E8091–E8099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, T.; Parrish, C.A.; Xu, D.; Wu, Q.; Shen, P. Drosophila Neuropeptide F and Its Receptor, NPFR1, Define a Signaling Pathway That Acutely Modulates Alcohol Sensitivity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2141–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapek, S.; Kahsai, L.; Winther, A.M.; Tanimoto, H.; Nassel, D.R. Short Neuropeptide F Acts as a Functional Neuromodulator for Olfactory Memory in Kenyon Cells of Drosophila Mushroom Bodies. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 5340–5345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyutova, R.; Selcho, M.; Pfeuffer, M.; Segebarth, D.; Habenstein, J.; Rohwedder, A.; Frantzmann, F.; Wegener, C.; Thum, A.S.; Pauls, D. Reward Signaling in a Recurrent Circuit of Dopaminergic Neurons and Peptidergic Kenyon Cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannell, E.; Dornan, A.J.; Halberg, K.A.; Terhzaz, S.; Dow, J.A.T.; Davies, S.A. The Corticotropin-Releasing Factor-Like Diuretic Hormone 44 (DH44) and Kinin Neuropeptides Modulate Desiccation and Starvation Tolerance in Drosophila melanogaster. Peptides 2016, 80, 96–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovejoy, D.A.; Jahan, S. Phylogeny of the Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Family of Peptides in the Metazoa. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2006, 146, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Huang, R.; Fu, X.; Wang, G.; Qi, W.; Mao, D.; Shi, Z.; Shen, W.L.; Wang, L. A Post-Ingestive Amino Acid Sensor Promotes Food Consumption in Drosophila. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dus, M.; Lai, J.S.; Gunapala, K.M.; Min, S.; Tayler, T.D.; Hergarden, A.C.; Geraud, E.; Joseph, C.M.; Suh, G.S. Nutrient Sensor in the Brain Directs the Action of the Brain-Gut Axis in Drosophila. Neuron 2015, 87, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergarden, A.C.; Tayler, T.D.; Anderson, D.J. Allatostatin—A Neurons Inhibit Feeding Behavior in Adult Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3967–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Water-Reward Memory | |
| Neurons/Molecules | References |
| PAM-β′1 and PAM-γ4 | [59,131] |
| Dop1R1 receptor in the γ neurons | [59] |
| Dop1R1 receptor in the α′β′ neurons | [131] |
| cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) | [148] |
| DPM neurons > MBON-γ3β′1, MBON-α′2, and MBON-α′1α′3 | [140] |
| αβ surface and γ dorsal neurons | [148] |
| MBON-γ5β′2a and MBON-α3 | [131] |
| Sucrose-Reward Memory | |
| Neurons/Molecules | References |
| cAMP-responsive element-binding protein (CREB) | [39] |
| PAM-γ5 > MBON-γ5β′2a | [147,155,156] |
| PAM-α1 > α1 Kenyon cells > MBON-α1 | |
| Octopamine β-2 Receptor (Octβ2R) in γ1pedc DANs | [121] |
| Serotoninergic neurons | [132,157] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lin, Y.-C.; Wu, T.; Wu, C.-L. The Neural Correlations of Olfactory Associative Reward Memories in Drosophila. Cells 2024, 13, 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13201716
Lin Y-C, Wu T, Wu C-L. The Neural Correlations of Olfactory Associative Reward Memories in Drosophila. Cells. 2024; 13(20):1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13201716
Chicago/Turabian StyleLin, Yu-Chun, Tony Wu, and Chia-Lin Wu. 2024. "The Neural Correlations of Olfactory Associative Reward Memories in Drosophila" Cells 13, no. 20: 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13201716
APA StyleLin, Y.-C., Wu, T., & Wu, C.-L. (2024). The Neural Correlations of Olfactory Associative Reward Memories in Drosophila. Cells, 13(20), 1716. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13201716






