A Combinatory Therapy of Metformin and Dexamethasone Reduces the Foreign Body Reaction to Intraneural Electrodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surgical Procedure
2.2. Drug Administration
2.3. Electrophysiological and Functional Evaluation
2.4. Histological Evaluation
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
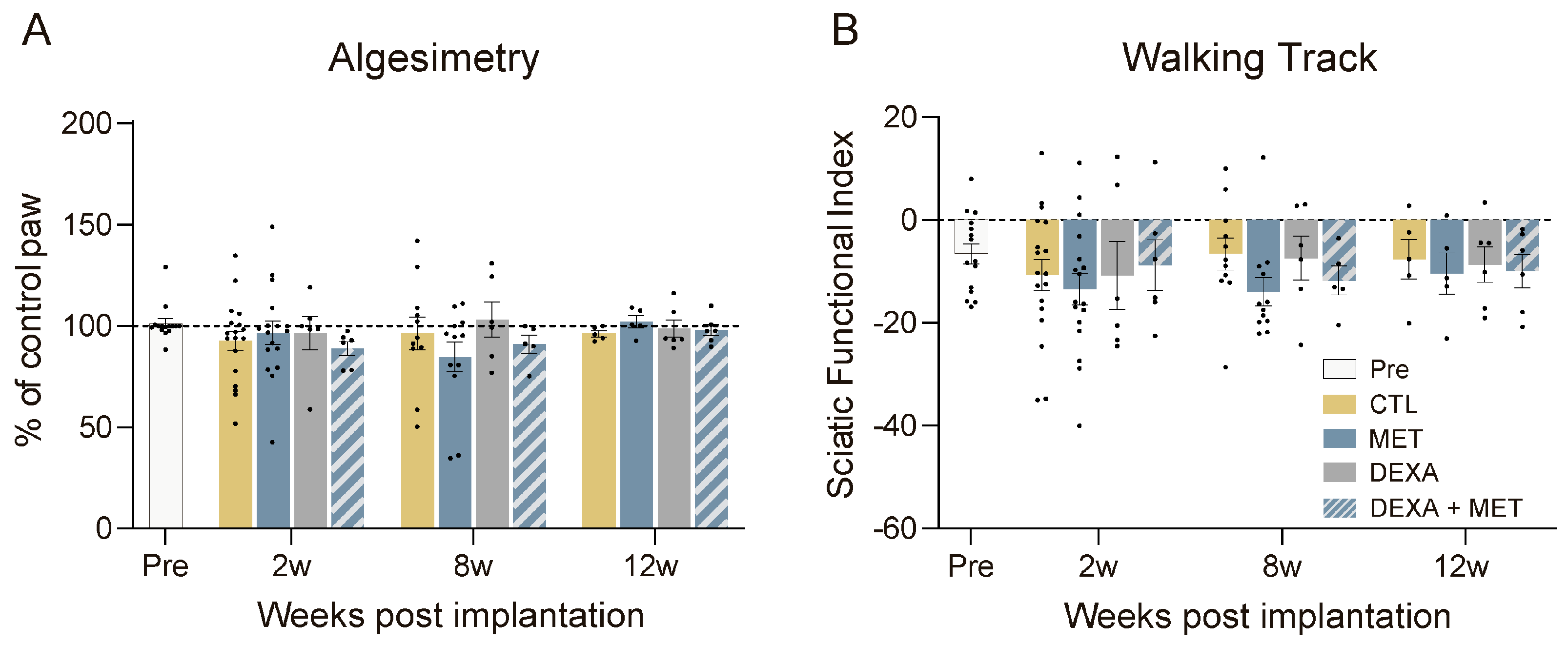
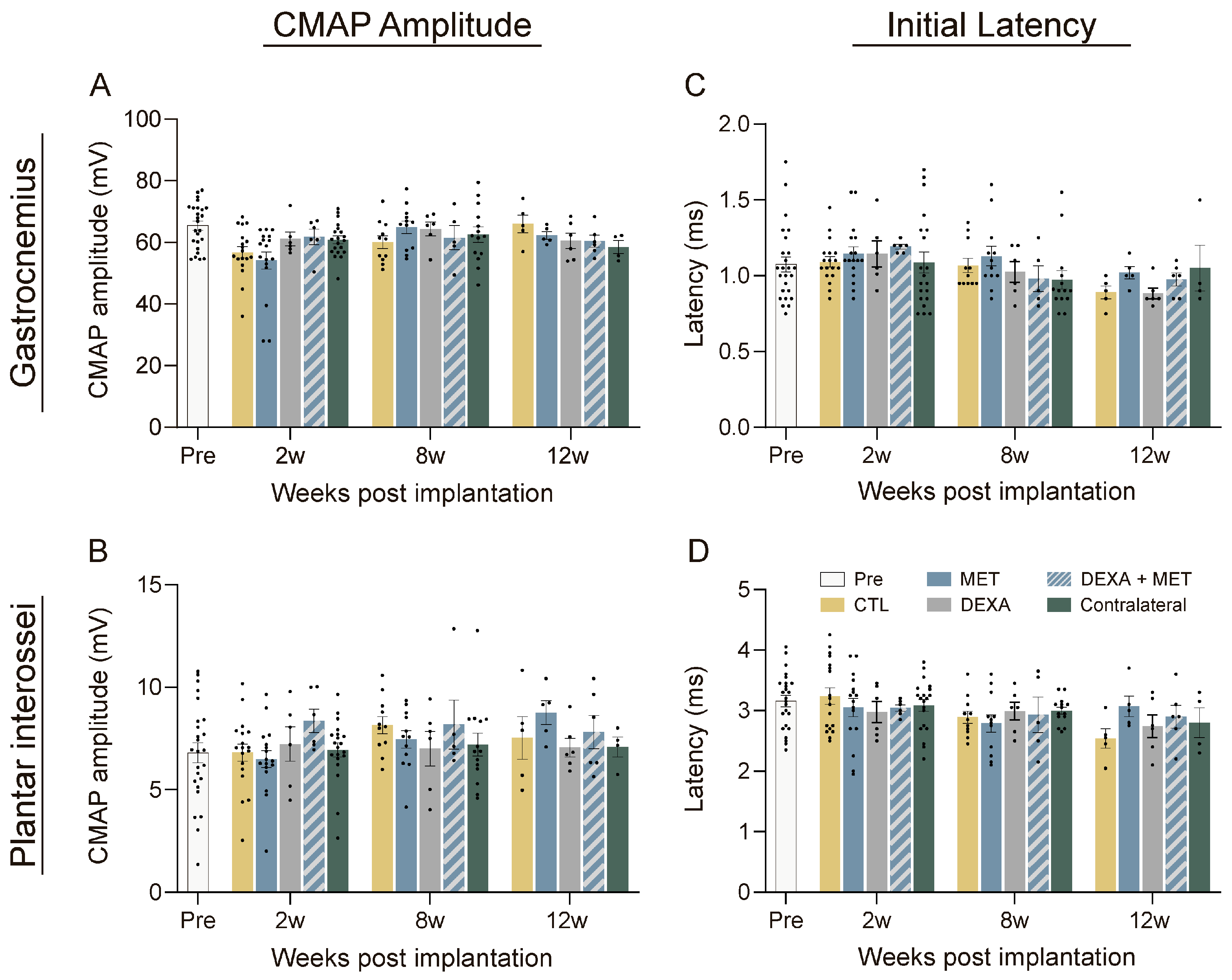
3.1. Functional Evaluation
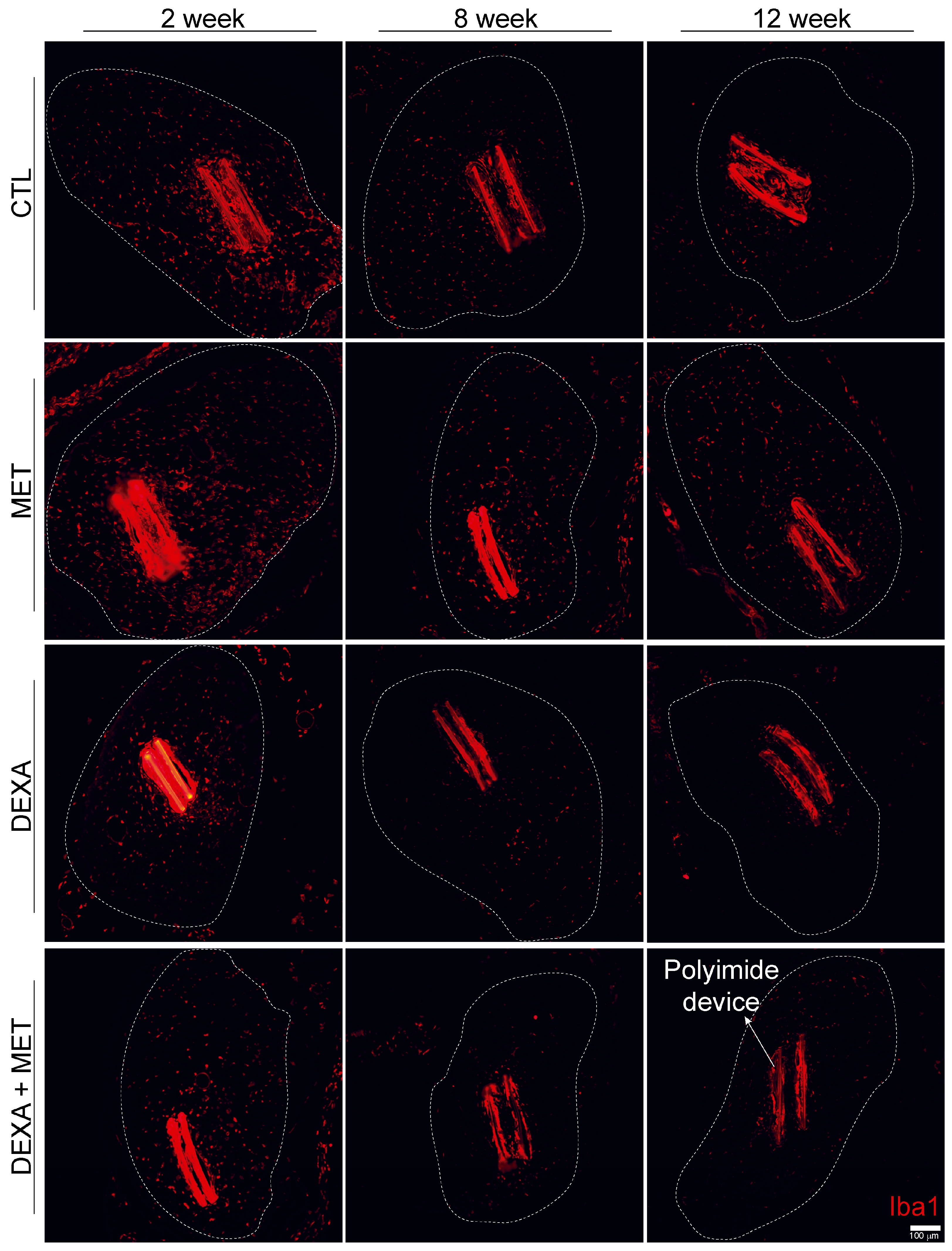
3.2. Inflammatory Response
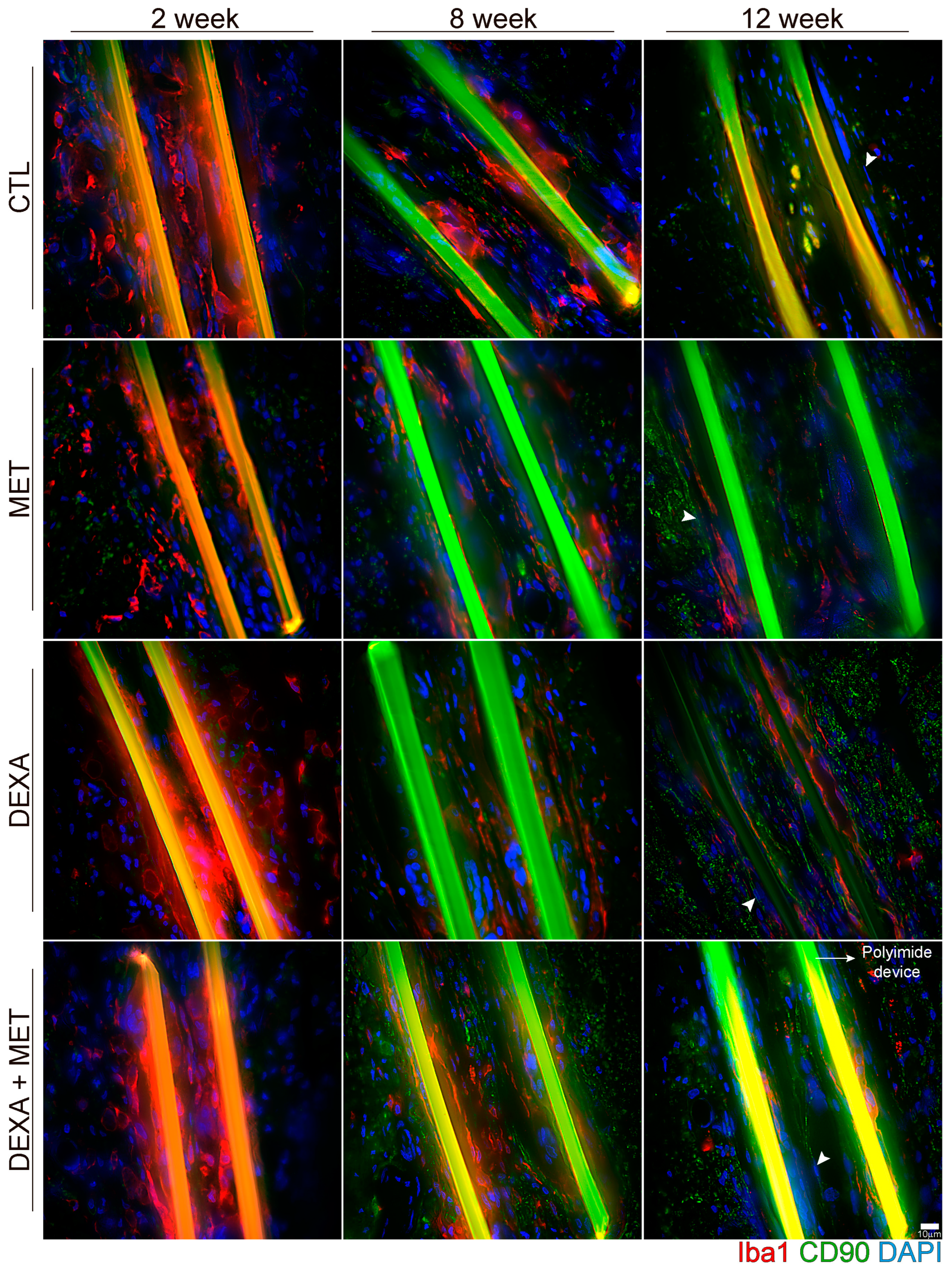
3.3. Capsule Formation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- del Valle, J.; Navarro, X. Interfaces with the Peripheral Nerve for the Control of Neuroprostheses, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 109, ISBN 9780124200456. [Google Scholar]
- Grill, W.M.; Thomas Mortimer, J. Electrical Properties of Implant Encapsulation Tissue. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1994, 22, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotti, F.; Ranieri, F.; Vadalà, G.; Zollo, L.; Di Pino, G. Invasive Intraneural Interfaces: Foreign Body Reaction Issues. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Oliva, N.; del Valle, J.; Delgado-Martínez, I.; Mueller, M.; Stieglitz, T.; Navarro, X.; Delgado-Martinez, I.; Mueller, M.; Stieglitz, T.; Navarro, X.; et al. Long-Term Functionality of Transversal Intraneural Electrodes Is Improved By Dexamethasone Treatment. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2019, 27, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulino, M.; Kim, D.; Pané, S.; Santos, S.D.; Pêgo, A.P. Tissue Response to Neural Implants: The Use of Model Systems toward New Design Solutions of Implantable Microelectrodes. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnicer-Lombarte, A.; Chen, S.T.; Malliaras, G.G.; Barone, D.G. Foreign Body Reaction to Implanted Biomaterials and Its Impact in Nerve Neuroprosthetics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 622524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grill, W.M.; Mortimer, J.T. Neural and Connective Tissue Response to Long-Term Implantation of Multiple Contact Nerve Cuff Electrodes. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2000, 50, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurth, S.; Capogrosso, M.; Raspopovic, S.; Gandar, J.; Federici, G.; Kinany, N.; Cutrone, A.; Piersigilli, A.; Pavlova, N.; Guiet, R.; et al. Long-Term Usability and Bio-Integration of Polyimide-Based Intra-Neural Stimulating Electrodes. Biomaterials 2017, 122, 114–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, E.; Li, J.; Won, S.M.; Bai, W.; Rogers, J.A. Materials for Flexible Bioelectronic Systems as Chronic Neural Interfaces. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 590–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Oliva, N.; Navarro, X.; del Valle, J. Dexamethasone Reduces the Foreign Body Reaction to Intraneural Electrode Implants in the Peripheral Nerve of the Rat. Anat. Rec. 2018, 301, 1722–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desgeorges, T.; Caratti, G.; Mounier, R.; Tuckermann, J.; Chazaud, B. Glucocorticoids Shape Macrophage Phenotype for Tissue Repair. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangarajan, S.; Bone, N.B.; Zmijewska, A.A.; Jiang, S.; Park, D.W.; Bernard, K.; Locy, M.L.; Ravi, S.; Deshane, J.; Mannon, R.B.; et al. Metformin Reverses Established Lung Fibrosis in a Bleomycin Model. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lago, N.; Yoshida, K.; Koch, K.P.; Navarro, X. Assessment of Biocompatibility of Chronically Implanted Polyimide and Platinum Intrafascicular Electrodes. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2007, 54, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Oliva, N.; Navarro, X.; Del Valle, J. Time Course Study of Long-Term Biocompatibility and Foreign Body Reaction to Intraneural Polyimide-Based Implants. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2018, 106, 746–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Oliva, N.; Mueller, M.; Stieglitz, T.; Navarro, X.; Del Valle, J. On the Use of Parylene C Polymer as Substrate for Peripheral Nerve Electrodes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- del Valle, J.; Santos, D.; Delgado-Martínez, I.; de la Oliva, N.; Giudetti, G.; Micera, S.; Navarro, X.; Delgado-Martinez, I. Segregation of Motor and Sensory Axons Regenerating through Bicompartmental Tubes by Combining Extracellular Matrix Components with Neurotrophic Factors. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, 1991–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Medinaceli, L.; Freed, W.J.; Wyatt, R.J. An Index of the Functional Condition of Rat Sciatic Nerve Based on Measurements Made from Walking Tracks. Exp. Neurol. 1982, 77, 634–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Y.; Bellamkonda, R.V. Dexamethasone-Coated Neural Probes Elicit Attenuated Inflammatory Response and Neuronal Loss Compared to Uncoated Neural Probes. Brain Res. 2007, 1148, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, D.G.; Carnicer-Lombarte, A.; Tourlomousis, P.; Hamilton, R.S.; Prater, M.; Rutz, A.L.; Dimov, I.B.; Malliaras, G.G.; Lacour, S.P.; Robertson, A.A.B.; et al. Prevention of the Foreign Body Response to Implantable Medical Devices by Inflammasome Inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2115857119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, S.; Rabiee, N.; Bagherzadeh, M.; Elmi, F.; Fatahi, Y.; Farjadian, F.; Baheiraei, N.; Nasseri, B.; Rabiee, M.; Dastjerd, N.T.; et al. Stimulus-Responsive Sequential Release Systems for Drug and Gene Delivery. Nano Today 2020, 34, 100914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Zhang, L.; Xia, W.; Chen, L.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, W. Fabrication of Graphene Oxide-Modified Chitosan for Controlled Release of Dexamethasone Phosphate. Appl. Phys. A 2016, 122, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, W.H.; Zhou, C.H.; Ju, X.J.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, L.; Xie, R.; Wang, W.; Liu, Z.; Chu, L.Y. Dual-Functional Polyetheretherketone Surface with Programmed Sequential Drug Release Coating. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2022, 219, 112806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rennaker, R.L.; Miller, J.; Tang, H.; Wilson, D.A. Minocycline Increases Quality and Longevity of Chronic Neural Recordings. J. Neural Eng. 2007, 4, L1–L5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercanzini, A.; Reddy, S.T.; Velluto, D.; Colin, P.; Maillard, A.; Bensadoun, J.C.; Hubbell, J.A.; Renaud, P. Controlled Release Nanoparticle-Embedded Coatings Reduce the Tissue Reaction to Neuroprostheses. J. Control. Release 2010, 145, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Heo, D.N.; Kwon, I.K.; Yun, K.-S.S.; Kang, J.Y.; Lee, S.H. Functional Nerve Cuff Electrode with Controllable Anti-Inflammatory Drug Loading and Release by Biodegradable Nanofibers and Hydrogel Deposition. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 215, 133–141. [Google Scholar]
- Heo, D.N.; Song, S.J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, Y.J.; Ko, W.K.; Lee, S.H.S.J.S.H.S.J.S.H.; Lee, D.; Park, S.J.; Zhang, L.G.; Kang, J.Y.; et al. Multifunctional Hydrogel Coatings on the Surface of Neural Cuff Electrode for Improving Electrode-Nerve Tissue Interfaces. Acta Biomater. 2016, 39, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, J.J. Suppression of Scarring in Peripheral Nerve Implants by Drug Elution. J. Neural Eng. 2016, 13, 026006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gori, M.; Giannitelli, S.M.; Vadalà, G.; Papalia, R.; Zollo, L.; Sanchez, M.; Trombetta, M.; Rainer, A.; Di Pino, G.; Denaro, V. A Soft Zwitterionic Hydrogel as Potential Coating on a Polyimide Surface to Reduce Foreign Body Reaction to Intraneural Electrodes. Molecules 2022, 27, 3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gori, M.; Vadalà, G.; Giannitelli, S.M.; Denaro, V.; Di Pino, G. Biomedical and Tissue Engineering Strategies to Control Foreign Body Reaction to Invasive Neural Electrodes. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 659033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spataro, L.; Dilgen, J.; Retterer, S.; Spence, A.J.; Isaacson, M.; Turner, J.N.; Shain, W. Dexamethasone Treatment Reduces Astroglia Responses to Inserted Neuroprosthetic Devices in Rat Neocortex. Exp. Neurol. 2005, 194, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrchen, J.M.; Roth, J.; Barczyk-Kahlert, K. More than Suppression: Glucocorticoid Action on Monocytes and Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coutinho, A.E.; Chapman, K.E. The Anti-Inflammatory and Immunosuppressive Effects of Glucocorticoids, Recent Developments and Mechanistic Insights. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2011, 335, 2–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Normansell, R.; Kew, K.M.; Mansour, G. Different Oral Corticosteroid Regimens for Acute Asthma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD011801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.; Katerelos, M.; Gleich, K.; Galic, S.; Kemp, B.E.; Mount, P.F.; Power, D.A. Phosphorylation of Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase by AMPK Reduces Renal Fibrosis and Is Essential for the Anti-Fibrotic Effect of Metformin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 2326–2336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biondo, L.A.; Batatinha, H.A.; Souza, C.O.; Teixeira, A.A.S.; Silveira, L.S.; Alonso-Vale, M.I.; Oyama, L.M.; Alves, M.J.; Seelaender, M.; Neto, J.C.R. Metformin Mitigates Fibrosis and Glucose Intolerance Induced by Doxorubicin in Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xu, H.; Liu, J.; Tan, X.; Wan, S.; Guo, M.; Long, Y.; Xu, Y. Metformin and Fibrosis: A Review of Existing Evidence and Mechanisms. J. Diabetes Res. 2021, 2021, 6673525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Lu, X.; Liu, N.; Ma, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Z.; Yang, K.; Jiang, M.; Zheng, Z.; Qiao, Y.; et al. Metformin Decelerates Aging Clock in Male Monkeys. Cell 2024, 187, 6358–6378.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.; Shi, J.; Li, M.; Gui, B.; Fu, R.; Yao, G.; Duan, Z.; Lv, Z.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; et al. Activation of AMPK by Metformin Inhibits TGF-β-Induced Collagen Production in Mouse Renal Fibroblasts. Life Sci. 2015, 127, 59–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, H.; Huang, C.; Shi, Y.; Cao, Q.; Chen, J.; Chen, X.M.; Pollock, C.A. Metformin Attenuates Renal Fibrosis in a Mouse Model of Adenine-Induced Renal Injury Through Inhibiting TGF-Β1 Signaling Pathways. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 603802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, N.; Takasaka, N.; Yoshida, M.; Tsubouchi, K.; Minagawa, S.; Araya, J.; Saito, N.; Fujita, Y.; Kurita, Y.; Kobayashi, K.; et al. Metformin Attenuates Lung Fibrosis Development via NOX4 Suppression. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, S.; Viswanadhapalli, S.; Kopp, J.B.; Shi, Q.; Barnes, J.L.; Block, K.; Gorin, Y.; Abboud, H.E. Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase Prevents TGF-Β1-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Myofibroblast Activation. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 2168–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Miao, N.; Xu, J.; Gan, X.; Xu, D.; Zhou, L.; Xue, H.; Zhang, W.; Lu, L. Metformin Prevents Renal Fibrosis in Mice with Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction and Inhibits Ang II-Induced ECM Production in Renal Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xavier, D.O.; Amaral, L.S.; Gomes, M.A.; Rocha, M.A.; Campos, P.R.; Cota, B.D.C.V.; Tafuri, L.S.A.; Paiva, A.M.R.; Silva, J.H.; Andrade, S.P.; et al. Metformin Inhibits Inflammatory Angiogenesis in a Murine Sponge Model. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2010, 64, 220–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kheirollahi, V.; Wasnick, R.M.; Biasin, V.; Vazquez-Armendariz, A.I.; Chu, X.; Moiseenko, A.; Weiss, A.; Wilhelm, J.; Zhang, J.S.; Kwapiszewska, G.; et al. Metformin Induces Lipogenic Differentiation in Myofibroblasts to Reverse Lung Fibrosis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisson, T.H.; Christensen, P.J.; Muraki, Y.; Dils, A.J.; Chibucos, L.; Subbotina, N.; Tohyama, K.; Horowitz, J.C.; Matsuo, T.; Bailie, M.; et al. Phosphodiesterase 4 Inhibition Reduces Lung Fibrosis Following Targeted Type II Alveolar Epithelial Cell Injury. Physiol. Rep. 2018, 6, e13753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ursini, F.; Grembiale, R.D.; D’Antona, L.; Gallo, E.; D’Angelo, S.; Citraro, R.; Visca, P.; Olivieri, I.; De Sarro, G.; Perrotti, N.; et al. Oral Metformin Ameliorates Bleomycin-Induced Skin Fibrosis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1892–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Song, J.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, S.; Ruan, H.; Fan, C. Metformin Prevents Peritendinous Fibrosis by Inhibiting Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 101784–101794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cao, Z.; Bai, T.; Carr, L.; Ella-Menye, J.R.; Irvin, C.; Ratner, B.D.; Jiang, S. Zwitterionic Hydrogels Implanted in Mice Resist the Foreign-Body Reaction. Nat. Biotechnol. 2013, 31, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, T.; Nocon, A.; Fry, J.; Sherban, A.; Rui, X.; Jiang, B.; Xu, X.J.; Han, J.; Yan, Y.; Yang, Q.; et al. AMPK Activation by Metformin Suppresses Abnormal Extracellular Matrix Remodeling in Adipose Tissue and Ameliorates Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2295–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.X.; Li, C.; Pang, X.R.; Zhang, J.; Yu, G.C.; Yeo, A.J.; Lavin, M.F.; Shao, H.; Jia, Q.; Peng, C. Metformin Attenuates Silica-Induced Pulmonary Fibrosis by Activating Autophagy via the AMPK-MTOR Signaling Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 719589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karatas, A.; Oz, B.; Celik, C.; Akar, Z.A.; Akkoc, R.F.; Etem, E.O.; Dagli, A.F.; Koca, S.S. Tofacitinib and Metformin Reduce the Dermal Thickness and Fibrosis in Mouse Model of Systemic Sclerosis. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tikoo, K.; Sharma, E.; Amara, V.R.; Pamulapati, H.; Dhawale, V.S. Metformin Improves Metabolic Memory in High Fat Diet (HFD)- Induced Renal Dysfunction. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 21848–21856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.S.; Ko, J.; Kim, D.A.; Ryu, E.S.; Ryu, H.M.; Park, S.H.; Kim, Y.L.; Oh, E.S.; Kang, D.H. Metformin Ameliorates the Phenotype Transition of Peritoneal Mesothelial Cells and Peritoneal Fibrosis via a Modulation of Oxidative Stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fertala, J.; Rivlin, M.; Wang, M.L.; Beredjiklian, P.K.; Steplewski, A.; Fertala, A. Collagen-rich Deposit Formation in the Sciatic Nerve after Injury and Surgical Repair: A Study of Collagen-producing Cells in a Rabbit Model. Brain Behav. 2020, 10, e01802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassif, R.M.; Chalhoub, E.; Chedid, P.; Hurtado-Nedelec, M.; Raya, E.; Dang, P.M.C.; Marie, J.C.; El-Benna, J. Metformin Inhibits ROS Production by Human M2 Macrophages via the Activation of AMPK. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Wu, F.; Li, D.; Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Li, R. Metformin Improves Obesity-Associated Inflammation by Altering Macrophages Polarization. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 461, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Shang, F.; Hui, L.; Zang, K.; Sun, G. The Alleviative Effects of Metformin for Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Lung Injury Rat Model and Its Underlying Mechanism. Saudi Pharm. J. 2017, 25, 666–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macias, S.L.; Palmer, O.; Simonovich, J.A.; Clark, R.A.; Hudalla, G.A.; Keselowsky, B.G. Immunometabolic Approaches Mitigating Foreign Body Response and Transcriptome Characterization of the Foreign Body Capsule. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2024, e2400602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Psarianos, P.; Ghoraie, L.S.; Yip, K.; Goldstein, D.; Gilbert, R.; Witterick, I.; Pang, H.; Hussain, A.; Lee, J.H.; et al. Metabolic Regulation of Dermal Fibroblasts Contributes to Skin Extracellular Matrix Homeostasis and Fibrosis. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Drug Group | Treatment Duration | Implant Duration | Dose | Administration | n |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CTL | – | 2 w | – | – | 7 |
| 8 w | 6 | ||||
| 12 w | 5 | ||||
| MET | 2 w | 2 w | 125 mg/kg/day | p.o. | 5 |
| 8 w | 8 w | 7 | |||
| 12 w | 12 w | 5 | |||
| DEXA | 2 w | 2 w | 0.2 mg/kg/s.i.d. | s.c. | 7 |
| 8 w | 7 | ||||
| 12 w | 6 | ||||
| DEXA + MET | 2 w (D) + 2 w (M) | 2 w | 0.2 mg/kg/s.i.d. (D) 125 mg/kg/day (M) | s.c. (D) p.o. (M) | 6 |
| 2 w (D) + 8 w (M) | 8 w | 5 | |||
| 2 w (D) + 12 w (M) | 12 w | 5 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Meana, B.; del Valle, J.; Navarro, X. A Combinatory Therapy of Metformin and Dexamethasone Reduces the Foreign Body Reaction to Intraneural Electrodes. Cells 2024, 13, 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13242112
Rodríguez-Meana B, del Valle J, Navarro X. A Combinatory Therapy of Metformin and Dexamethasone Reduces the Foreign Body Reaction to Intraneural Electrodes. Cells. 2024; 13(24):2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13242112
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Meana, Bruno, Jaume del Valle, and Xavier Navarro. 2024. "A Combinatory Therapy of Metformin and Dexamethasone Reduces the Foreign Body Reaction to Intraneural Electrodes" Cells 13, no. 24: 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13242112
APA StyleRodríguez-Meana, B., del Valle, J., & Navarro, X. (2024). A Combinatory Therapy of Metformin and Dexamethasone Reduces the Foreign Body Reaction to Intraneural Electrodes. Cells, 13(24), 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13242112






