A Mapping Review of the Pathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis: The Biofilm-Mediated Inflammation and Bone Dysregulation (BIND) Hypothesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
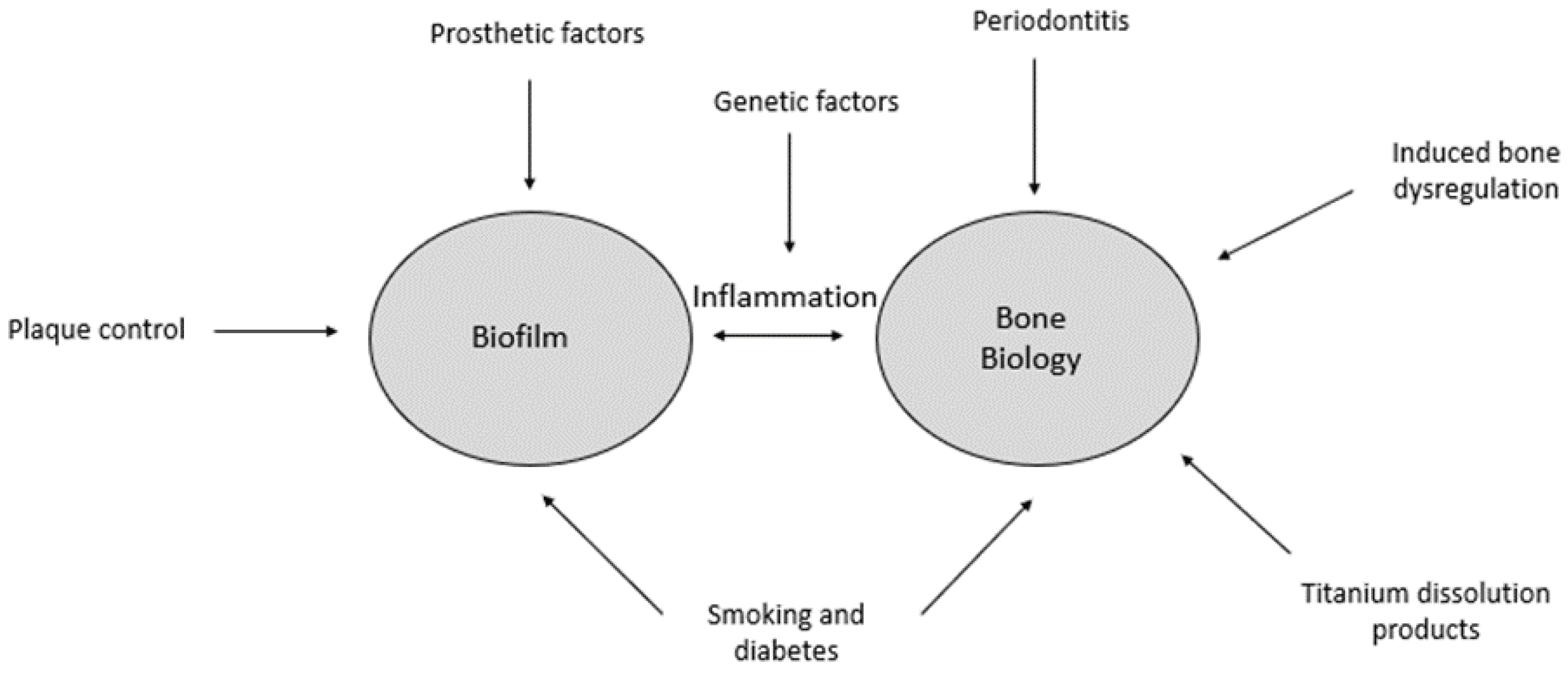
2. The Biofilm-Mediated Inflammation and Bone Dysregulation (BIND) Hypothesis
3. Bone Biology
4. Bone Biology Is Disrupted by Altered Peri-Implant Bone Metabolism
4.1. Medical History and Medications
4.2. Smoking and Diabetes Mellitus
4.3. Radiation Therapy
5. Implant Biofilm May Further Disrupt Already Disequilibrated Peri-Implant Bone
Factors Predisposing to Biofilm Accumulation
6. Wound Healing in the Presence of a Foreign Body Results in Subclinical Inflammation
7. Genetic Risk Factors Could Predispose Patients to Peri-Implantitis
8. Macrophage Polarisation May Be the ‘Switch’ That Activates Osteolysis and Drives Pathogenesis in the Bone Dysregulation-Inflammation-Biofilm Model
9. Clinical Implications and Further Research
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Joda, T.; Gintaute, A.; Bragger, U.; Ferrari, M.; Weber, K.; Zitzmann, N.U. Time-efficiency and cost-analysis comparing three digital workflows for treatment with monolithic zirconia implant fixed dental prostheses: A double-blinded RCT. J. Dent. 2021, 113, 103779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimkhaokham, A.; Jiaranuchart, S.; Kaboosaya, B.; Arunjaroensuk, S.; Subbalekha, K.; Mattheos, N. Can computer-assisted implant surgery improve clinical outcomes and reduce the frequency and intensity of complications in implant dentistry? A critical review. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 90, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, D.; Ofec, R.; Levin, L. Long term clinical performance of 10 871 dental implants with up to 22 years of follow-up: A cohort study in 4247 patients. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2021, 23, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knofler, W.; Barth, T.; Graul, R.; Krampe, D. Retrospective analysis of 10,000 implants from insertion up to 20 years-analysis of implantations using augmentative procedures. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2016, 2, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chappuis, V.; Buser, R.; Bragger, U.; Bornstein, M.M.; Salvi, G.E.; Buser, D. Long-term outcomes of dental implants with a titanium plasma-sprayed surface: A 20-year prospective case series study in partially edentulous patients. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2013, 15, 780–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derks, J.; Tomasi, C. Peri-implant health and disease. A systematic review of current epidemiology. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42 (Suppl. 16), S158–S171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renvert, S.; Lindahl, C.; Persson, G.R. Occurrence of cases with peri-implant mucositis or peri-implantitis in a 21–26 years follow-up study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Renvert, S.; Persson, G.R.; Pirih, F.Q.; Camargo, P.M. Peri-implant health, peri-implant mucositis, and peri-implantitis: Case definitions and diagnostic considerations. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S304–S312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heitz-Mayfield, L.J.A.; Salvi, G.E. Peri-implant mucositis. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S257–S266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renvert, S.; Polyzois, I. Risk indicators for peri-implant mucositis: A systematic literature review. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2015, 42 (Suppl. 16), S172–S186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, F.; Derks, J.; Monje, A.; Wang, H.L. Peri-implantitis. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S267–S290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belibasakis, G.N. Microbiological and immuno-pathological aspects of peri-implant diseases. Arch. Oral Biol. 2014, 59, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jansson, L.; Lundmark, A.; Modin, C.; Abadji, D.; Yucel-Lindberg, T. Intra-individual cytokine profile in peri-implantitis and periodontitis: A cross-sectional study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2021, 32, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvi, G.E.; Aglietta, M.; Eick, S.; Sculean, A.; Lang, N.P.; Ramseier, C.A. Reversibility of experimental peri-implant mucositis compared with experimental gingivitis in humans. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, S.; Giannopoulou, C.; Courvoisier, D.; Schimmel, M.; Muller, F.; Mombelli, A. Experimental mucositis and experimental gingivitis in persons aged 70 or over. Clinical and biological responses. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derks, J.; Schaller, D.; Hakansson, J.; Wennstrom, J.L.; Tomasi, C.; Berglundh, T. Peri-implantitis—Onset and pattern of progression. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2016, 43, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz-Arad, D.; Laviv, A.; Levin, L. Failure causes, timing, and cluster behavior: An 8-year study of dental implants. Implant Dent. 2008, 17, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrcanovic, B.R.; Kisch, J.; Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Analysis of risk factors for cluster behavior of dental implant failures. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.; Ivanovski, S.; Latcham, N.; Mattheos, N. The impact of cantilevers on biological and technical success outcomes of implant-supported fixed partial dentures. A retrospective cohort study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2014, 25, 175–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.; Tay, J.R.H.; Balan, P.; Ong, M.M.A.; Bostanci, N.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Seneviratne, C.J. Metagenomic sequencing provides new insights into the subgingival bacteriome and aetiopathology of periodontitis. J. Periodontal Res. 2021, 56, 205–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartold, P.M.; Van Dyke, T.E. Host modulation: Controlling the inflammation to control the infection. Periodontol. 2000 2017, 75, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, E.; Tay, J.R.H.; Ong, M.M.A. Minimally Invasive Periodontology: A Treatment philosophy and suggested Approach. Int. J. Dent. 2021, 2021, 2810264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonze, D.; Lahti, L.; Raes, J.; Faust, K. Multi-stability and the origin of microbial community types. ISME J. 2017, 11, 2159–2166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.; Dubinkina, V.; Maslov, S. Multiple stable states in microbial communities explained by the stable marriage problem. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2823–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubinkina, V.; Fridman, Y.; Pandey, P.P.; Maslov, S. Multistability and regime shifts in microbial communities explained by competition for essential nutrients. eLife 2019, 8, e49720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khazaei, T.; Williams, R.L.; Bogatyrev, S.R.; Doyle, J.C.; Henry, C.S.; Ismagilov, R.F. Metabolic multistability and hysteresis in a model aerobe-anaerobe microbiome community. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba0353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangal, U.; Noh, K.; Lee, S.; Cha, J.K.; Song, J.S.; Cha, J.Y.; Lee, K.J.; Kim, K.M.; Kwon, J.S.; Choi, S.H. Multistability and hysteresis in states of oral microbiota: Is it impacting the dental clinical cohort studies? J. Periodontal Res. 2023, 58, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mombelli, A.; van Oosten, M.A.; Schurch, E., Jr.; Land, N.P. The microbiota associated with successful or failing osseointegrated titanium implants. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 1987, 2, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berglundh, T.; Armitage, G.; Araujo, M.G.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Blanco, J.; Camargo, P.M.; Chen, S.; Cochran, D.; Derks, J.; Figuero, E.; et al. Peri-implant diseases and conditions: Consensus report of workgroup 4 of the 2017 World workshop on the classification of periodontal and peri-implant diseases and conditions. J. Periodontol. 2018, 89 (Suppl. 1), S313–S318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monje, A.; Pons, R.; Amerio, E.; Wang, H.L.; Nart, J. Resolution of peri-implantitis by means of implantoplasty as adjunct to surgical therapy: A retrospective study. J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 110–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, D.; Berglundh, T.; Schwarz, F.; Chapple, I.; Jepsen, S.; Sculean, A.; Kebschull, M.; Papapanou, P.N.; Tonetti, M.S.; Sanz, M.; et al. Prevention and treatment of peri-implant diseases-The EFP S3 level clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2023, 50 (Suppl. S26), 4–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.M. An overview of bone cells and their regulating factors of differentiation. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2008, 15, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sims, N.A.; Vrahnas, C. Regulation of cortical and trabecular bone mass by communication between osteoblasts, osteocytes and osteoclasts. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 561, 22–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langdahl, B.; Ferrari, S.; Dempster, D.W. Bone modeling and remodeling: Potential as therapeutic targets for the treatment of osteoporosis. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2016, 8, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardone, V.; D’Asta, F.; Brandi, M.L. Pharmacological management of osteogenesis. Clinics 2014, 69, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creecy, A.; Damrath, J.G.; Wallace, J.M. Control of bone matrix properties by osteocytes. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 578477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aarden, E.M.; Burger, E.H.; Nijweide, P.J. Function of osteocytes in bone. J. Cell Biochem. 1994, 55, 287–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, H.A.; Albrektsson, T.; Branemark, P.I. Structural aspects of the interface between tissue and titanium implants. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1983, 50, 108–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakahama, K. Cellular communications in bone homeostasis and repair. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 4001–4009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.Y.; Sim, J.H.; Yeo, I.L. Characteristics of contact and distance osteogenesis around modified implant surfaces in rabbit tibiae. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2017, 47, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Branemark, P.I.; Hansson, H.A.; Kasemo, B.; Larsson, K.; Lundstrom, I.; McQueen, D.H.; Skalak, R. The interface zone of inorganic implants In vivo: Titanium implants in bone. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 1983, 11, 1–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, O.; Angelov, N.; Gallez, F.; Jung, R.E.; Weber, F.E. The zirconia implant-bone interface: A preliminary histologic evaluation in rabbits. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2008, 23, 691–695. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Depprich, R.; Zipprich, H.; Ommerborn, M.; Naujoks, C.; Wiesmann, H.P.; Kiattavorncharoen, S.; Lauer, H.C.; Meyer, U.; Kubler, N.R.; Handschel, J. Osseointegration of zirconia implants compared with titanium: An in vivo study. Head Face Med. 2008, 4, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depprich, R.; Zipprich, H.; Ommerborn, M.; Mahn, E.; Lammers, L.; Handschel, J.; Naujoks, C.; Wiesmann, H.P.; Kubler, N.R.; Meyer, U. Osseointegration of zirconia implants: An SEM observation of the bone-implant interface. Head Face Med. 2008, 4, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monzavi, M.; Zhang, F.; Meille, S.; Douillard, T.; Adrien, J.; Noumbissi, S.; Nowzari, H.; Chevalier, J. Influence of artificial aging on mechanical properties of commercially and non-commercially available zirconia dental implants. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 101, 103423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, M.K.; Kang, Y.S.; Kwak, J.M.; Jo, Y.H.; Han, J.S.; Yeo, I.L. Comparison between bone-implant interfaces of microtopographically modified zirconia and titanium implants. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 11142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Insua, A.; Monje, A.; Wang, H.L.; Miron, R.J. Basis of bone metabolism around dental implants during osseointegration and peri-implant bone loss. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2017, 105, 2075–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, T.G.; Lee, C.O.; Park, J.W.; Choi, S.Y.; Rijal, G.; Shin, H.I. Osteonecrosis associated with dental implants in patients undergoing bisphosphonate treatment. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2014, 25, 632–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo-Pouso, A.I.; Bagan, J.; Bagan, L.; Gandara-Vila, P.; Chamorro-Petronacci, C.M.; Castelo-Baz, P.; Blanco-Carrion, A.; Blanco-Fernandez, M.A.; Alvarez-Calderon, O.; Carballo, J.; et al. Medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: A critical narrative review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, S.; Pautke, C.; Opelz, C.; Westphal, I.; Drosse, I.; Schwager, J.; Bauss, F.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Schieker, M. Osteonecrosis of the jaw: Effect of bisphosphonate type, local concentration, and acidic milieu on the pathomechanism. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 68, 2837–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Troeltzsch, M.; Cagna, D.; Stahler, P.; Probst, F.; Kaeppler, G.; Troeltzsch, M.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Otto, S. Clinical features of peri-implant medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Is there an association to peri-implantitis? J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2016, 44, 1945–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, J.; Ryu, J.I.; Shim, G.J.; Kwon, Y.D. Effect of agents affecting bone homeostasis on short- and long-term implant failure. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2023, 34 (Suppl. S26), 143–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tempesta, A.; Capodiferro, S.; Mauceri, R.; Lauritano, D.; Maiorano, E.; Favia, G.; Limongelli, L. Peri-implantitis-like medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw: Clinical considerations and histological evaluation with confocal laser scanning microscope. Oral Dis. 2022, 28, 1603–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsigarida, A.A.; Dabdoub, S.M.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Kumar, P.S. The influence of smoking on the peri-implant microbiome. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 1202–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cyprus, G.N.; Overlin, J.W.; Hotchkiss, K.M.; Kandalam, S.; Olivares-Navarrete, R. Cigarette smoke increases pro-inflammatory markers and inhibits osteogenic differentiation in experimental exposure model. Acta Biomater. 2018, 76, 308–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Matthews, C.R.; Joshi, V.; de Jager, M.; Aspiras, M. Tobacco smoking affects bacterial acquisition and colonization in oral biofilms. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 4730–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pimentel, S.P.; Fontes, M.; Ribeiro, F.V.; Correa, M.G.; Nishii, D.; Cirano, F.R.; Casati, M.Z.; Casarin, R.C.V. Smoking habit modulates peri-implant microbiome: A case-control study. J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Niazi, S.A.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Cao, X.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Q. Smoking by altering the peri-implant microbial community structure compromises the responsiveness to treatment. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 1040765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buduneli, N.; Scott, D.A. Tobacco-induced suppression of the vascular response to dental plaque. Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2018, 33, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holde, G.E.; Jonsson, B.; Oscarson, N.; Muller, H.P. To what extent does smoking affect gingival bleeding response to supragingival plaque? Site-specific analyses in a population-based study. J. Periodontal Res. 2020, 55, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chrcanovic, B.R.; Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Smoking and dental implants: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Dent. 2015, 43, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, I.; do Amaral, G.; Hassan, M.A.; Villar, C.C.; Romito, G.A.; Spin-Neto, R.; Pannuti, C.M. The influence of smoking on the incidence of peri-implantitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2023, 34, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquel, F.J.; Lansang, M.C.; Dhatariya, K.; Umpierrez, G.E. Management of diabetes and hyperglycaemia in the hospital. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.N.A.; Casarin, M.; Monajemzadeh, S.; Bezerra, B.B.; Lux, R.; Pirih, F.Q. The Microbiome in Periodontitis and Diabetes. Front. Oral Health 2022, 3, 859209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Lu, Z.; Sun, H. Impact of diabetes mellitus on the poor prognosis in patients with osseointegrated dental implants: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 2023, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, J.; Spille, J.H.; Wiltfang, J.; Naujokat, H. Systematic review on diabetes mellitus and dental implants: An update. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2022, 8, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karbach, J.; Callaway, A.; Kwon, Y.D.; d’Hoedt, B.; Al-Nawas, B. Comparison of five parameters as risk factors for peri-mucositis. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2009, 24, 491–496. [Google Scholar]
- Neckel, N.; Wagendorf, P.; Sachse, C.; Stromberger, C.; Vach, K.; Heiland, M.; Nahles, S. Influence of implant-specific radiation doses on peri-implant hard and soft tissue: An observational pilot study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2021, 32, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Feng, K.; Ye, L.; Liu, Y.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Y. Influence of radiotherapy on dental implants placed in individuals before diagnosed with head and neck cancer: Focus on implant-bed-specific radiation dosage. Clin. Oral Investig. 2022, 26, 5915–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, F.; Spoerl, S.; Gottsauner, M.; Klingelhoffer, C.; Spanier, G.; Kolbeck, C.; Reichert, T.E.; Hautmann, M.G.; Ettl, T. Significance of site-specific radiation dose and technique for success of implant-based prosthetic rehabilitation in irradiated head and neck cancer patients—A cohort study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2021, 23, 444–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acharya, A.; Chan, Y.; Kheur, S.; Kheur, M.; Gopalakrishnan, D.; Watt, R.M.; Mattheos, N. Salivary microbiome of an urban Indian cohort and patterns linked to subclinical inflammation. Oral Dis. 2017, 23, 926–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Payne, J.B.; Johnson, P.G.; Kok, C.R.; Gomes-Neto, J.C.; Ramer-Tait, A.E.; Schmid, M.J.; Hutkins, R.W. Subgingival microbiome colonization and cytokine production during early dental implant healing. mSphere 2017, 2, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabdoub, S.M.; Tsigarida, A.A.; Kumar, P.S. Patient-specific analysis of periodontal and peri-implant microbiomes. J. Dent. Res. 2013, 92, 168S–175S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robitaille, N.; Reed, D.N.; Walters, J.D.; Kumar, P.S. Periodontal and peri-implant diseases: Identical or fraternal infections? Mol. Oral Microbiol. 2016, 31, 285–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belibasakis, G.N.; Manoil, D. Microbial Community-Driven Etiopathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis. J. Dent. Res. 2021, 100, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibli, J.A.; Melo, L.; Ferrari, D.S.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Faveri, M.; Feres, M. Composition of supra- and subgingival biofilm of subjects with healthy and diseased implants. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2008, 19, 975–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffen, A.L.; Beall, C.J.; Campbell, J.H.; Firestone, N.D.; Kumar, P.S.; Yang, Z.K.; Podar, M.; Leys, E.J. Distinct and complex bacterial profiles in human periodontitis and health revealed by 16S pyrosequencing. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1176–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Martin, I.; Doolittle-Hall, J.; Teles, R.P.; Patel, M.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Hammerle, C.H.F.; Jung, R.E.; Teles, F.R.F. Exploring the microbiome of healthy and diseased peri-implant sites using Illumina sequencing. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyanagi, T.; Sakamoto, M.; Takeuchi, Y.; Maruyama, N.; Ohkuma, M.; Izumi, Y. Comprehensive microbiological findings in peri-implantitis and periodontitis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2013, 40, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.S.; Feres, M.; Figueiredo, L.C.; Shibli, J.A.; Ramiro, F.S.; Faveri, M. Microbiological diversity of peri-implantitis biofilm by Sanger sequencing. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2014, 25, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, N.; Ochi, M.; Miyakawa, H.; Nakazawa, F. Analysis of bacterial flora associated with peri-implantitis using obligate anaerobic culture technique and 16S rDNA gene sequence. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2013, 28, 1521–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albertini, M.; Lopez-Cerero, L.; O’Sullivan, M.G.; Chereguini, C.F.; Ballesta, S.; Rios, V.; Herrero-Climent, M.; Bullon, P. Assessment of periodontal and opportunistic flora in patients with peri-implantitis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2015, 26, 937–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafaurie, G.I.; Sabogal, M.A.; Castillo, D.M.; Rincon, M.V.; Gomez, L.A.; Lesmes, Y.A.; Chambrone, L. Microbiome and microbial biofilm profiles of peri-implantitis: A Systematic Review. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 1066–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, A.; Koh, M.L.; Kheur, S.; Watt, R.M.; Jin, L.; Mattheos, N. Salivary IL-1β and red complex bacteria as predictors of the inflammatory status in sub-peri-implant niches of subjects with peri-implant mucositis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2016, 27, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattheos, N.; Vergoullis, I.; Janda, M.; Miseli, A. The implant supracrestal complex and its significance for long-term successful clinical outcomes. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2021, 34, 88–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serino, G.; Strom, C. Peri-implantitis in partially edentulous patients: Association with inadequate plaque control. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2009, 20, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katafuchi, M.; Weinstein, B.F.; Leroux, B.G.; Chen, Y.W.; Daubert, D.M. Restoration contour is a risk indicator for peri-implantitis: A cross-sectional radiographic analysis. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2018, 45, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Koo, K.T.; Schwarz, F.; Ben Amara, H.; Heo, S.J. Association of prosthetic features and peri-implantitis: A cross-sectional study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2020, 47, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rungtanakiat, P.; Thitaphanich, N.; Chengprapakorn, W.; Janda, M.; Arksornnukit, M.; Mattheos, N. Association of prosthetic angles of the implant supracrestal complex with peri-implant tissue mucositis. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2023, 9, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.; Pelekos, G.; Ho, D.; Cortellini, P.; Tonetti, M.S. The depth of the implant mucosal tunnel modifies the development and resolution of experimental peri-implant mucositis: A case-control study. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derks, J.; Schaller, D.; Hakansson, J.; Wennstrom, J.L.; Tomasi, C.; Berglundh, T. Effectiveness of implant therapy analyzed in a Swedish population: Prevalence of peri-implantitis. J. Dent. Res. 2016, 95, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linkevicius, T.; Vindasiute, E.; Puisys, A.; Linkeviciene, L.; Maslova, N.; Puriene, A. The influence of the cementation margin position on the amount of undetected cement. A prospective clinical study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2013, 24, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho-Puchades, M.; Crameri, D.; Ozcan, M.; Sailer, I.; Jung, R.E.; Hammerle, C.H.F.; Thoma, D.S. The influence of the emergence profile on the amount of undetected cement excess after delivery of cement-retained implant reconstructions. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 1515–1522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Karasan, D.; Park, K.; Kwon, H.B.; Han, J.S.; Lee, J.H. Abutment margin levels and residual cement occurrence in cement-retained implant restorations: An observational study. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2023, 34, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staubli, N.; Walter, C.; Schmidt, J.C.; Weiger, R.; Zitzmann, N.U. Excess cement and the risk of peri-implant disease—A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2017, 28, 1278–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattheos, N.; Janda, M.; Acharya, A.; Pekarski, S.; Larsson, C. Impact of design elements of the implant supracrestal complex (ISC) on the risk of peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis: A critical review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2021, 32 (Suppl. S21), 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sailer, I.; Karasan, D.; Todorovic, A.; Ligoutsikou, M.; Pjetursson, B.E. Prosthetic failures in dental implant therapy. Periodontol. 2000 2022, 88, 130–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbella, S.; Morandi, B.; Calciolari, E.; Alberti, A.; Francetti, L.; Donos, N. The influence of implant position and of prosthetic characteristics on the occurrence of peri-implantitis: A retrospective study on periapical radiographs. Clin. Oral Investig. 2023, 27, 7261–7271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahardawi, B.; Jiaranuchart, S.; Damrongsirirat, N.; Arunjaroensuk, S.; Mattheos, N.; Somboonsavatdee, A.; Pimkhaokham, A. The lack of keratinized mucosa as a risk factor for peri-implantitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanauskaite, A.; Schwarz, F.; Sader, R. Influence of width of keratinized tissue on the prevalence of peri-implant diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2022, 33 (Suppl. S23), 8–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thoma, D.S.; Naenni, N.; Figuero, E.; Hammerle, C.H.F.; Schwarz, F.; Jung, R.E.; Sanz-Sanchez, I. Effects of soft tissue augmentation procedures on peri-implant health or disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29 (Suppl. S15), 32–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavelli, L.; Barootchi, S.; Avila-Ortiz, G.; Urban, I.A.; Giannobile, W.V.; Wang, H.L. Peri-implant soft tissue phenotype modification and its impact on peri-implant health: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. J. Periodontol. 2021, 92, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarraga-Vinueza, M.E.; Tavelli, L. Soft tissue features of peri-implant diseases and related treatment. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2023, 25, 661–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnicer-Lombarte, A.; Chen, S.T.; Malliaras, G.G.; Barone, D.G. Foreign body reaction to Implanted biomaterials and its impact in nerve neuroprosthetics. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 622524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrektsson, T.; Dahlin, C.; Jemt, T.; Sennerby, L.; Turri, A.; Wennerberg, A. Is marginal bone loss around oral implants the result of a provoked foreign body reaction? Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2014, 16, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trindade, R.; Albrektsson, T.; Galli, S.; Prgomet, Z.; Tengvall, P.; Wennerberg, A. Osseointegration and foreign body reaction: Titanium implants activate the immune system and suppress bone resorption during the first 4 weeks after implantation. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.M.; Rodriguez, A.; Chang, D.T. Foreign body reaction to biomaterials. Semin. Immunol. 2008, 20, 86–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosshardt, D.D.; Chappuis, V.; Buser, D. Osseointegration of titanium, titanium alloy and zirconia dental implants: Current knowledge and open questions. Periodontol. 2000 2017, 73, 22–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chappuis, V.; Cavusoglu, Y.; Gruber, R.; Kuchler, U.; Buser, D.; Bosshardt, D.D. Osseointegration of zirconia in the presence of multinucleated giant cells. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2016, 18, 686–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emecen-Huja, P.; Eubank, T.D.; Shapiro, V.; Yildiz, V.; Tatakis, D.N.; Leblebicioglu, B. Peri-implant versus periodontal wound healing. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2013, 40, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericsson, I.; Lindhe, J. Probing depth at implants and teeth. An experimental study in the dog. J. Clin. Periodontol. 1993, 20, 623–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, M.; Almlin, S.; Romanos, G.E.; Johansson, A. Ti Ions Induce IL-1β release by activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome in a human macrophage cell line. Inflammation 2022, 45, 2027–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chackartchi, T.; Zaydel, L.; Shapira, L.; Shany-Kdoshim, S.; Polak, D. Biofilm formation, its removal, and consequent effect on the osteoblast response to titanium surfaces: A model for re-osseointegration. J. Periodontol. 2022, 94, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanovski, S.; Bartold, P.M.; Huang, Y.S. The role of foreign body response in peri-implantitis: What is the evidence? Periodontol. 2000 2022, 90, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, M.T.; Barão, V.A.; Yuan, J.C.; Assunção, W.G.; Sukotjo, C.; Wimmer, M.A. What is the role of lipopolysaccharide on the tribocorrosive behavior of titanium? J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2012, 8, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, M.; Kelk, P.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Bylund, D.; Molin Thoren, M.; Johansson, A. Titanium ions form particles that activate and execute interleukin-1β release from lipopolysaccharide-primed macrophages. J. Periodontal Res. 2017, 52, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dini, C.; Costa, R.C.; Sukotjo, C.; Takoudis, C.G.; Mathew, M.T.; Barão, V.A.R. Progression of bio-tribocorrosion in implant dentistry. Front. Mech. Eng. 2020, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, M.T.; Abbey, S.; Hallab, N.J.; Hall, D.J.; Sukotjo, C.; Wimmer, M.A. Influence of pH on the tribocorrosion behavior of CpTi in the oral environment: Synergistic interactions of wear and corrosion. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2012, 100, 1662–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansone, V.; Pagani, D.; Melato, M. The effects on bone cells of metal ions released from orthopaedic implants. A review. Clin. Cases Miner. Bone Metab. 2013, 10, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Shi, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, X.; Hao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. The unfavorable role of titanium particles released from dental implants. Nanotheranostics 2021, 5, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajikawa, T.; Mastellos, D.C.; Hasturk, H.; Kotsakis, G.A.; Yancopoulou, D.; Lambris, J.D.; Hajishengallis, G. C3-targeted host-modulation approaches to oral inflammatory conditions. Semin. Immunol. 2022, 59, 101608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotsakis, G.A.; Olmedo, D.G. Peri-implantitis is not periodontitis: Scientific discoveries shed light on microbiome-biomaterial interactions that may determine disease phenotype. Periodontol. 2000 2021, 86, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noronha Oliveira, M.; Schunemann, W.V.H.; Mathew, M.T.; Henriques, B.; Magini, R.S.; Teughels, W.; Souza, J.C.M. Can degradation products released from dental implants affect peri-implant tissues? J. Periodontal Res. 2018, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Messous, R.; Henriques, B.; Bousbaa, H.; Silva, F.S.; Teughels, W.; Souza, J.C.M. Cytotoxic effects of submicron- and nano-scale titanium debris released from dental implants: An integrative review. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 1627–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubert, D.M.; Pozhitkov, A.E.; Safioti, L.M.; Kotsakis, G.A. Association of global DNA methylation to titanium and peri-implantitis: A Case-Control Study. JDR Clin. Trans. Res. 2019, 4, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubert, D.; Pozhitkov, A.; McLean, J.; Kotsakis, G. Titanium as a modifier of the peri-implant microbiome structure. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganesan, S.M.; Dabdoub, S.M.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Mariotti, A.J.; Ludden, C.W.; Kumar, P.S. Biome-microbiome interactions in peri-implantitis: A pilot investigation. J. Periodontol. 2022, 93, 814–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez-Lopez Del Amo, F.; Garaicoa-Pazmino, C.; Fretwurst, T.; Castilho, R.M.; Squarize, C.H. Dental implants-associated release of titanium particles: A systematic review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29, 1085–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safioti, L.M.; Kotsakis, G.A.; Pozhitkov, A.E.; Chung, W.O.; Daubert, D.M. Increased levels of dissolved titanium are associated with peri-implantitis—A Cross-Sectional Study. J. Periodontol. 2017, 88, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersson, M.; Pettersson, J.; Johansson, A.; Molin Thoren, M. Titanium release in peri-implantitis. J. Oral Rehabil. 2019, 46, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombelli, A.; Hashim, D.; Cionca, N. What is the impact of titanium particles and biocorrosion on implant survival and complications? A critical review. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2018, 29 (Suppl. S18), 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delgado-Ruiz, R.; Romanos, G. Potential causes of titanium particle and ion release in implant dentistry: A systematic review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrak, F.; Li, S.; Muntane, A.; Bhatia, M.; Crossthwaite, K.; Jones, J. Particle release from dental implants immediately after placement—An ex vivo comparison of different implant systems. Dent. Mater. 2022, 38, 1004–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettersson, M.; Pettersson, J.; Molin Thoren, M.; Johansson, A. Release of titanium after insertion of dental implants with different surface characteristics—An ex vivo animal study. Acta Biomater. Odontol. Scand. 2017, 3, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvim-Pereira, F.; Montes, C.C.; Mira, M.T.; Trevilatto, P.C. Genetic susceptibility to dental implant failure: A critical review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implants 2008, 23, 409–416. [Google Scholar]
- Dereka, X.; Mardas, N.; Chin, S.; Petrie, A.; Donos, N. A systematic review on the association between genetic predisposition and dental implant biological complications. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2012, 23, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, K.; Jian, F.; He, T.; Tang, H.; Huang, B.; Wei, N. Analysis of the association of TNF-α, IL-1A, and IL-1B polymorphisms with peri-implantitis in a Chinese non-smoking population. Clin. Oral Investig. 2020, 24, 693–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, Y. Genetic involvement in dental implant failure: Association with polymorphisms of genes modulating inflammatory responses and bone metabolism. J. Oral Implant. 2019, 45, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobi-Gresser, E.; Huesker, K.; Schutt, S. Genetic and immunological markers predict titanium implant failure: A retrospective study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 42, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schminke, B.; Vom Orde, F.; Gruber, R.; Schliephake, H.; Burgers, R.; Miosge, N. The pathology of bone tissue during peri-implantitis. J. Dent. Res. 2015, 94, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Chen, G. Interleukin-16 rs4072111 polymorphism is associated with the risk of peri-implantitis in the Chinese population. Pharmgenom. Pers. Med. 2021, 14, 1629–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Teng, F.; Cheng, Z. Association between common polymorphisms in IL-1 and TNFα and risk of peri-implant disease: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0258138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, J.M.; Ribeiro, A.C.; Palos, C.; Proenca, L.; Noronha, S.; Alves, R.C. Association between IL-1A and IL-1B gene polymorphisms with peri-implantitis in a Portuguese population-a pilot study. PeerJ 2022, 10, e13729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafuente-Ibanez de Mendoza, I.; Setien-Olarra, A.; Garcia-De la Fuente, A.M.; Aguirre-Urizar, J.M.; Marichalar-Mendia, X. Role of proinflammatory mutations in peri-implantitis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2022, 8, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaw, A.; Liu, C.; Ivanovski, S.; Han, P. The relevance of DNA methylation and histone modification in periodontitis: A scoping review. Cells 2022, 11, 3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dereka, X.; Akcali, A.; Trullenque-Eriksson, A.; Donos, N. Systematic review on the association between genetic polymorphisms and dental implant-related biological complications. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2022, 33, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miron, R.J.; Bosshardt, D.D. OsteoMacs: Key players around bone biomaterials. Biomaterials 2016, 82, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chehroudi, B.; Ghrebi, S.; Murakami, H.; Waterfield, J.D.; Owen, G.; Brunette, D.M. Bone formation on rough, but not polished, subcutaneously implanted Ti surfaces is preceded by macrophage accumulation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 93, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, D. The role of macrophages in osseointegration of dental implants: An experimental study in vivo. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2020, 108, 2206–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.C.; Zou, X.B.; Chai, Y.F.; Yao, Y.M. Macrophage polarization in inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2014, 10, 520–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mills, C.D. M1 and M2 Macrophages: Oracles of health and disease. Crit. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 32, 463–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, M.; Desnues, B.; Mege, J.L. Macrophage polarization in bacterial infections. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 3733–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Zhao, M.; Jia, S. Macrophage: Key player in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1080310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruber, R. Osteoimmunology: Inflammatory osteolysis and regeneration of the alveolar bone. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2019, 46 (Suppl. S21), 52–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eger, M.; Hiram-Bab, S.; Liron, T.; Sterer, N.; Carmi, Y.; Kohavi, D.; Gabet, Y. Mechanism and prevention of titanium particle-induced inflammation and osteolysis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, Y.; Cheng, H.; Li, D. Macrophage polarization in aseptic bone resorption around dental implants induced by Ti particles in a murine model. J. Periodontal Res. 2019, 54, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachi, T.; Shuto, T.; Shinohara, Y.; Matono, Y.; Makihira, S. Release of titanium ions from an implant surface and their effect on cytokine production related to alveolar bone resorption. Toxicology 2015, 327, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolzer, C.; Muller, M.; Gosau, M.; Henningsen, A.; Fuest, S.; Aavani, F.; Smeets, R. Do titanium dioxide particles stimulate macrophages to release proinflammatory cytokines and increase the risk for peri-implantitis? J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 81, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kudo, O.; Sabokbar, A.; Pocock, A.; Itonaga, I.; Fujikawa, Y.; Athanasou, N.A. Interleukin-6 and interleukin-11 support human osteoclast formation by a RANKL-independent mechanism. Bone 2003, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fretwurst, T.; Garaicoa-Pazmino, C.; Nelson, K.; Giannobile, W.V.; Squarize, C.H.; Larsson, L.; Castilho, R.M. Characterization of macrophages infiltrating peri-implantitis lesions. Clin. Oral Implants Res. 2020, 31, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarraga-Vinueza, M.E.; Obreja, K.; Ramanauskaite, A.; Magini, R.; Begic, A.; Sader, R.; Schwarz, F. Macrophage polarization in peri-implantitis lesions. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 2335–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viniegra, A.; Goldberg, H.; Cil, C.; Fine, N.; Sheikh, Z.; Galli, M.; Freire, M.; Wang, Y.; Van Dyke, T.E.; Glogauer, M.; et al. Resolving macrophages counter osteolysis by anabolic actions on bone cells. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Athanasou, N.A. The pathobiology and pathology of aseptic implant failure. Bone Jt. Res. 2016, 5, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciuffi, S.; Donati, S.; Marini, F.; Palmini, G.; Luzi, E.; Brandi, M.L. Circulating microRNAs as novel biomarkers for osteoporosis and fragility fracture risk: Is there a use in assessment risk? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Patil, S.; Qian, A. The role of microRNAs in bone metabolism and disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottani, M.; Banfi, G.; Lombardi, G. Perspectives on miRNAs as epigenetic markers in osteoporosis and bone fracture risk: A step forward in personalized diagnosis. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuai, Y.; Liao, L.; Su, X.; Sha, N.; Li, X.; Wu, Y.; Jing, H.; Kuang, H.; Deng, Z.; Li, Y.; et al. Circulating microRNAs in serum as novel biomarkers for osteoporosis: A case-control study. Ther. Adv. Musculoskelet. Dis. 2020, 12, 1759720X20953331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarecki, P.; Hackl, M.; Grillari, J.; Debono, M.; Eastell, R. Serum microRNAs as novel biomarkers for osteoporotic vertebral fractures. Bone 2020, 130, 115105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Peri-implant tissue health | The absence of clinical signs of inflammation, and can include successfully treated peri-implant disease with variable levels of bone support |
| Peri-implant disease | Collective term for peri-implant mucositis and peri-implantitis |
| Risk factor | An environmental, behavioural, or biological factor that if present directly increases the probability of a disease occurring and, if absent or removed, reduces that probability, based on epidemiologic evidence, usually in prospective cohort studies |
| Risk indicator | Putative risk factors tested until their significance as true risk factors are proven or rejected |
| Microbial dysbiosis | The change in abundance of species that were already present at baseline or from health, peri-implant mucositis to peri-implantitis |
| Microbiota | Describes the situation of a mixed microbial population |
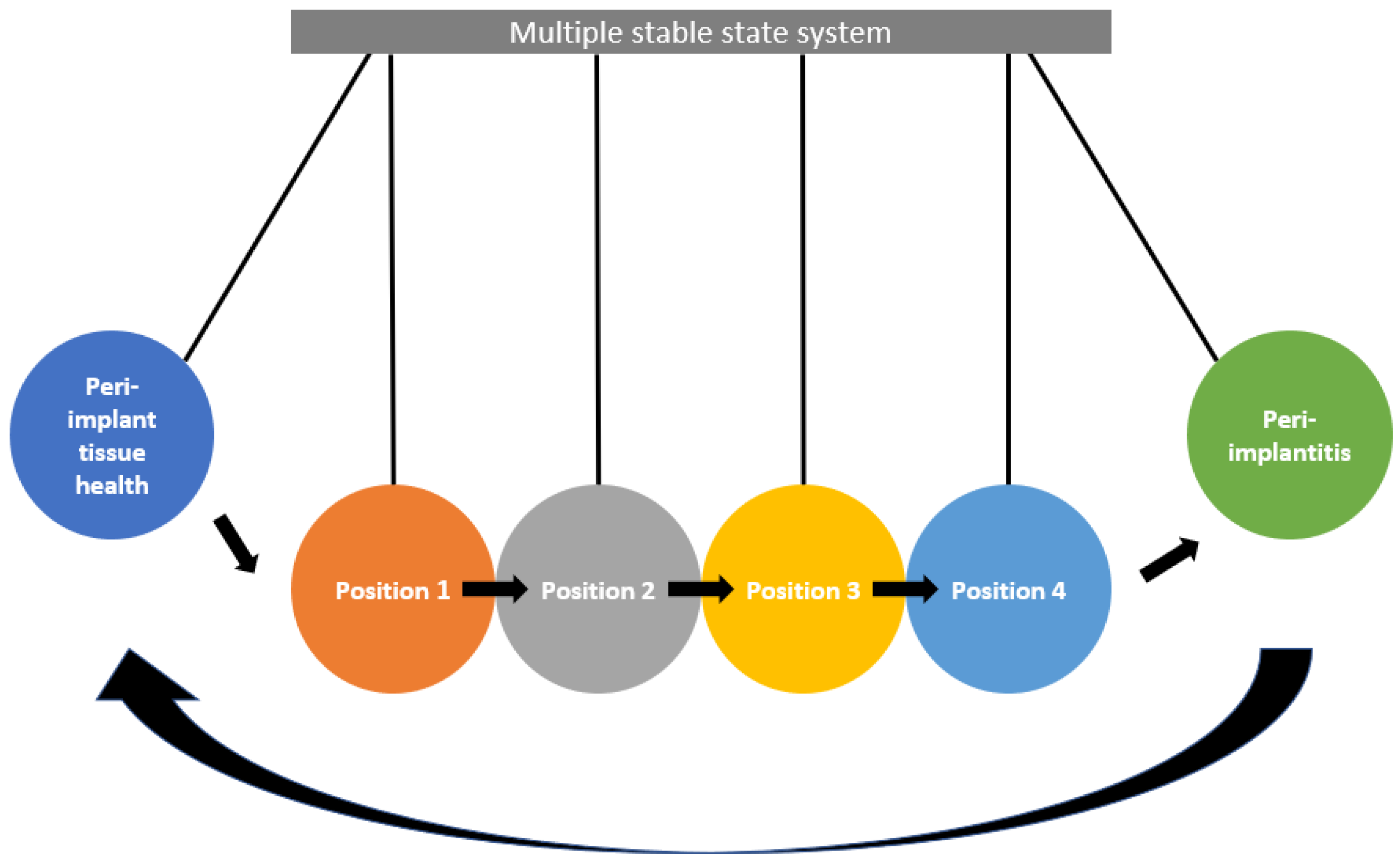
| Multi-stable state system | The dynamic property of a system that exhibits multiple mutually exclusive stable states. Microbial communities for each state exist with different species abundance profiles |
| Hysteresis | The innate resistance in a system before reaching a different state |
| Non-susceptible individuals | Individuals with various exposure to the presented factors, who are less likely to develop clinical disease due to a well-regulated homeostatic immune response |
| Susceptible individuals | Individuals with various exposure to the presented factors, who are more likely to develop early (mucositis) or late (peri-implantitis) disease due to a dysregulated homeostatic immune response |
| Bio-tribocorrosion | The combination of tribology (friction and wear), and corrosion with the biological environment |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ng, E.; Tay, J.R.H.; Mattheos, N.; Bostanci, N.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Seneviratne, C.J. A Mapping Review of the Pathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis: The Biofilm-Mediated Inflammation and Bone Dysregulation (BIND) Hypothesis. Cells 2024, 13, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13040315
Ng E, Tay JRH, Mattheos N, Bostanci N, Belibasakis GN, Seneviratne CJ. A Mapping Review of the Pathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis: The Biofilm-Mediated Inflammation and Bone Dysregulation (BIND) Hypothesis. Cells. 2024; 13(4):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13040315
Chicago/Turabian StyleNg, Ethan, John Rong Hao Tay, Nikos Mattheos, Nagihan Bostanci, Georgios N. Belibasakis, and Chaminda Jayampath Seneviratne. 2024. "A Mapping Review of the Pathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis: The Biofilm-Mediated Inflammation and Bone Dysregulation (BIND) Hypothesis" Cells 13, no. 4: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13040315
APA StyleNg, E., Tay, J. R. H., Mattheos, N., Bostanci, N., Belibasakis, G. N., & Seneviratne, C. J. (2024). A Mapping Review of the Pathogenesis of Peri-Implantitis: The Biofilm-Mediated Inflammation and Bone Dysregulation (BIND) Hypothesis. Cells, 13(4), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13040315










