Cutting-Edge Therapies for Lung Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Targeted Therapies
2.1. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) Inhibitors
| Representative Drugs | Target Mutation Site | Approved Indication | OS (Months) | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gefitinib | EGFR Ex19del, L858R | Advanced or metastatic NSCLC | 30.5–38.8 | [21,28] |
| Erlotinib | EGFR Ex19del, L858R | Advanced NSCLC | 19.3 | [29,30,31] |
| Icotinib | EGFR Ex19del, L858R | Advanced NSCLC | 30.5 | [32,33] |
| Afatinib | EGFR Ex19del, L858R | Locally advanced or metastatic NSCLC | 19.6–27.6 * 30.7–33.3 * | [34,35,36] |
| Dacomitinib | EGFR Ex19del, L858R | Advanced or metastatic NSCLC | 34.1 | [37,38] |
| Osimertinib | EGFR Ex19del, L858R, T790M | Advanced or metastatic NSCLC | 38.6 | [15,39] |
| Aumolertinib | EGFR Ex19del, L858R, T790M | Advanced NSCLC | NR | [40] |
| Mobocertinib | EGFR exon 20 insertion | Advanced or metastatic NSCLC | 24.0 | [41] |
| Cetuximab | EGFR | Advanced NSCLC | 10.9 | [42] |
| Amivantamab | EGFR exon 20 insertion | Advanced NSCLC | 11.4 | [43] |
2.2. Kirsten Rat Sarcoma Viral Oncogene Homologue (KRAS) Inhibitors
2.3. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase (ALK) Inhibitors
2.4. ROS Proto-Oncogene 1, Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (ROS1) Inhibitors
2.5. BRAF V600E Mutation Inhibitors
2.6. Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (HER2 or ERBB2) Mutation Inhibitors
3. Immunotherapy
3.1. Adoptive Cell Transfer
3.2. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
3.3. Cancer Vaccines
3.4. Oncolytic Viruses (OVs)
3.5. Targeting Immune Checkpoint Receptors (ICRs)
4. Radiation Therapy
4.1. Intensity-Modulated Radiation Therapy (IMRT) and Volumetric-Modulated Arc Therapy (VMAT)
4.2. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT)
4.3. Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy (SBRT)
5. Cryoablation
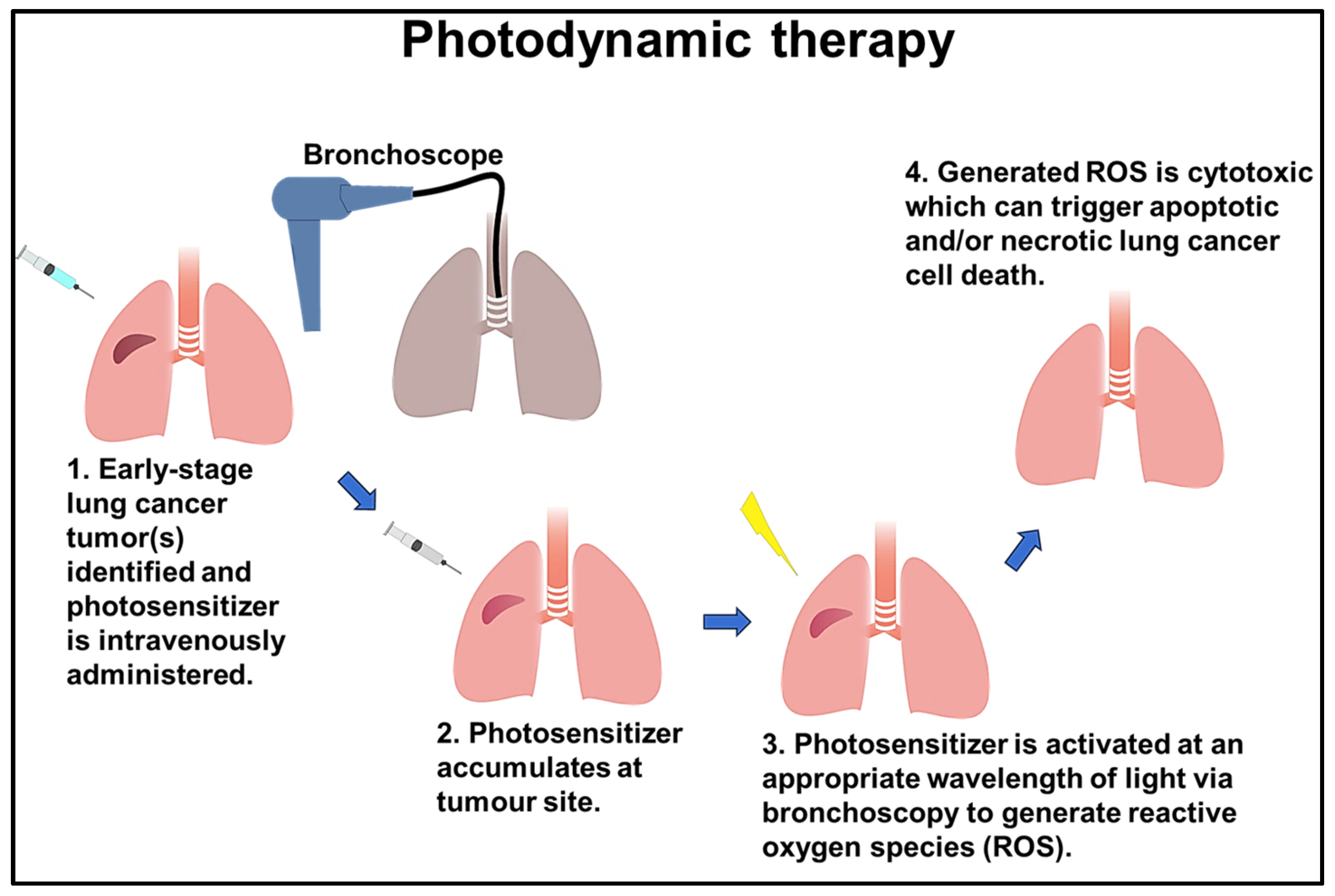
6. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT)
7. Hyperthermia Therapy
8. Nanoparticles as a Tool for Targeted Therapy
8.1. Hafnium Oxide Nanoparticles (HfO2 NPs)
8.2. Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs)
8.3. Lipid Nanoparticles (LNPs)
8.4. Polymeric Nanoparticles (PNPs)
9. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fu, F.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H. Treating lung cancer: Defining surgical curative time window. Cell Res. 2023, 33, 649–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, H.; Jiang, Y.; Fu, W.; Liu, X.; Zhong, R.; Cheng, B.; Zhu, F.; Xiang, Y.; He, J.; et al. Advances in lung cancer screening and early detection. Cancer Biol. Med. 2022, 19, 591–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, S.; Qin, C.; Hu, H.; Liu, T.; He, Y.; Guo, H.; Yan, H.; Zhang, J.; Tang, S.; Zhou, H. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Progress, Challenges, and Prospects. Cells 2022, 11, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lahiri, A.; Maji, A.; Potdar, P.D.; Singh, N.; Parikh, P.; Bisht, B.; Mukherjee, A.; Paul, M.K. Lung cancer immunotherapy: Progress, pitfalls, and promises. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koinis, F.; Kotsakis, A.; Georgoulias, V. Small cell lung cancer (SCLC): No treatment advances in recent years. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2016, 5, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; de Camargo Correia, G.S.; Wang, J.; Manochakian, R.; Zhao, Y.; Lou, Y. Emerging Targeted Therapies in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcila, M.E.; Nafa, K.; Chaft, J.E.; Rekhtman, N.; Lau, C.; Reva, B.A.; Zakowski, M.F.; Kris, M.G.; Ladanyi, M. EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations in lung adenocarcinomas: Prevalence, molecular heterogeneity, and clinicopathologic characteristics. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xing, Y.; Li, B.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Wang, Y. Molecular pathways, resistance mechanisms and targeted interventions in non-small-cell lung cancer. Mol. Biomed. 2022, 3, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westover, D.; Zugazagoitia, J.; Cho, B.; Lovly, C.; Paz-Ares, L. Mechanisms of acquired resistance to first-and second-generation EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, i10–i19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, K.; Xie, F.; Wang, F.; Fu, L. Therapeutic strategies for EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer patients with osimertinib resistance. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Yang, J.; Lee, C.K.; Kurata, T.; Kim, D.-W.; John, T.; Nogami, N.; Ohe, Y.; Mann, H.; Rukazenkov, Y.; et al. Osimertinib as first-line treatment of EGFR mutation—Positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanna, N.; Johnson, D.; Temin, S.; Baker, S., Jr.; Brahmer, J.; Ellis, P.M.; Giaccone, G.; Hesketh, P.J.; Jaiyesimi, I.; Leighl, N.B.; et al. Systemic therapy for stage IV non–small-cell lung cancer: American Society of Clinical Oncology clinical practice guideline update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 832–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D.; Popat, S.; Kerr, K.; Novello, S.; Smit, E.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Mok, T.S.; Reck, M.; Van Schil, P.E.; Hellmann, M.D.; et al. Metastatic non-small cell lung cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, iv192–iv237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soria, J.-C.; Ohe, Y.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Chewaskulyong, B.; Lee, K.H.; Dechaphunkul, A.; Imamura, F.; Nogami, N.; Kurata, T.; et al. Osimertinib in Untreated EGFR-Mutated Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D.; Loriot, Y.; André, F.; Gobert, A.; Auger, N.; Lacroix, L.; Soria, J.C. EGFR-independent mechanisms of acquired resistance to AZD9291 in EGFR T790M-positive NSCLC patients. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26, 2073–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-C.; Shih, J.-Y.; Yu, C.-J.; Ho, C.-C.; Liao, W.-Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Tsai, T.-H.; Su, K.-Y.; Hsieh, M.-S.; Chang, Y.-L.; et al. Outcomes in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer and acquired Thr790Met mutation treated with osimertinib: A genomic study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2018, 6, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thress, K.S.; Paweletz, C.P.; Felip, E.; Cho, B.C.; Stetson, D.; Dougherty, B.; Lai, Z.; Markovets, A.; Vivancos, A.; Kuang, Y.; et al. Acquired EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to AZD9291 in non–small cell lung cancer harboring EGFR T790M. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 560–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, S.; Ahn, J.; Hong, M.-H.; Kim, T.; Jung, H.-A.; Ou, S.-H.; Jeong, S.; Lee, Y.-H.; Yim, E.; Jung, S.; et al. MA07. 09 BBT-176, a 4th generation EGFR TKI, for Progressed NSCLC after EGFR TKI Therapy: PK, Safety and Efficacy from Phase 1 Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, S70–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derijcke, S.; Vansteenkiste, J.F. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Breathe 2009, 6, 10. [Google Scholar]
- Mitsudomi, T.; Morita, S.; Yatabe, Y.; Negoro, S.; Okamoto, I.; Tsurutani, J.; Seto, T.; Satouchi, M.; Tada, H.; Hirashima, T.; et al. Gefitinib versus cisplatin plus docetaxel in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring mutations of the epidermal growth factor receptor (WJTOG3405): An open label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirker, R.; Pereira, J.R.; Szczesna, A.; von Pawel, J.; Krzakowski, M.; Ramlau, R.; Vynnychenko, I.; Park, K.; Yu, C.-T.; Ganul, V.; et al. Cetuximab plus chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (FLEX): An open-label randomised phase III trial. Lancet 2009, 373, 1525–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khambata-Ford, S.; Harbison, C.T.; Hart, L.L.; Awad, M.; Xu, L.-A.; Horak, C.E.; Dakhil, S.; Hermann, R.C.; Lynch, T.J.; Weber, M.R. Analysis of potential predictive markers of cetuximab benefit in BMS099, a phase III study of cetuximab and first-line taxane/carboplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 918–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.C.; Simi, A.; Sabari, J.; Vijayaraghavan, S.; Moores, S.; Spira, A. Amivantamab, an Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor (EGFR) and Mesenchymal-epithelial Transition Factor (MET) Bispecific Antibody, Designed to Enable Multiple Mechanisms of Action and Broad Clinical Applications. Clin. Lung Cancer 2023, 24, 89–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.; Lee, K.; Cho, E.; Kim, D.-W.; Lee, J.-S.; Han, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Spira, A.; Haura, E.; Sabari, J.; et al. 1258O Amivantamab (JNJ-61186372), an EGFR-MET bispecific antibody, in combination with lazertinib, a 3rd-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), in advanced EGFR NSCLC. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, S813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Zhou, C.C. Targeted therapies for patients with advanced NSCLC harboring wild-type EGFR: What’s new and what’s enough. Chin. J. Cancer 2015, 34, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araghi, M.; Mannani, R.; Maleki, A.H.; Hamidi, A.; Rostami, S.; Safa, S.H.; Faramarzi, F.; Khorasani, S.; Alimohammadi, M.; Tahmasebi, S.; et al. Recent advances in non-small cell lung cancer targeted therapy; an update review. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maemondo, M.; Inoue, A.; Kobayashi, K.; Sugawara, S.; Oizumi, S.; Isobe, H.; Gemma, A.; Harada, M.; Yoshizawa, H.; Kinoshita, I.; et al. Gefitinib or chemotherapy for non–small-cell lung cancer with mutated EGFR. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosell, R.; Carcereny, E.; Gervais, R.; Vergnenegre, A.; Massuti, B.; Felip, E.; Palmero, R.; Garcia-Gomez, R.; Pallares, C.; Sanchez, J.M.; et al. Erlotinib versus standard chemotherapy as first-line treatment for European patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (EURTAC): A multicentre, open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2012, 13, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Wu, Y.-L.; Chen, G.; Feng, J.; Liu, X.-Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, J.; Zhou, S.; Ren, S.; et al. Erlotinib versus chemotherapy as first-line treatment for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (OPTIMAL, CTONG-0802): A multicentre, open-label, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2011, 12, 735–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steins, M.; Thomas, M.; Geißler, M. Erlotinib. In Small Molecules in Oncology; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, L.; Liu, X.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, S.; Wang, D.; Li, Q.; Qin, S.; Hu, C.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Icotinib versus gefitinib in previously treated advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (ICOGEN): A randomised, double-blind phase 3 non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 953–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.K.; Wang, L.; Han, B.H.; Li, W.; Yu, P.; Liu, Y.P.; Ding, C.M.; Song, X.; Ma, Z.Y.; Ren, X.L.; et al. First-line icotinib versus cisplatin/pemetrexed plus pemetrexed maintenance therapy for patients with advanced EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (CONVINCE): A phase 3, open-label, randomized study. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2443–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.-P.; Feng, J.; Lu, S.; Huang, Y.; Li, W.; Hou, M.; Shi, J.H.; Lee, K.Y.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin plus gemcitabine for first-line treatment of Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer harbouring EGFR mutations (LUX-Lung 6): An open-label, randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.C.-H.; Wu, Y.-L.; Schuler, M.; Sebastian, M.; Popat, S.; Yamamoto, N.; Zhou, C.; Hu, C.-P.; O’Byrne, K.; Feng, J.; et al. Afatinib versus cisplatin-based chemotherapy for EGFR mutation-positive lung adenocarcinoma (LUX-Lung 3 and LUX-Lung 6): Analysis of overall survival data from two randomised, phase 3 trials. Lancet Oncol. 2015, 16, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Tan, E.-H.; O’Byrne, K.; Zhang, L.; Hirsh, V.; Boyer, M.; Yang, J.-H.; Mok, T.; Lee, K.H.; Lu, S.; et al. Afatinib versus gefitinib in patients with EGFR mutation-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: Overall survival data from the phase IIb LUX-Lung 7 trial. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.-L.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Tsuji, F.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Dacomitinib versus gefitinib as first-line treatment for patients with EGFR-mutation-positive non-small-cell lung cancer (ARCHER 1050): A randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1454–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mok, T.S.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, X.; Lee, K.H.; Nakagawa, K.; Niho, S.; Lee, M.; Linke, R.; Rosell, R.; Corral, J.; et al. Improvement in overall survival in a randomized study that compared dacomitinib with gefitinib in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer and EGFR-activating mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 2244–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramalingam, S.S.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.C.; Gray, J.E.; Ohe, Y.; Zhou, C.; Reungwetwattana, T.; Cheng, Y.; Chewaskulyong, B.; et al. Overall survival with osimertinib in untreated, EGFR-mutated advanced NSCLC. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.; Dong, X.; Jian, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.; Sun, Y.; Ji, Y.; Wang, Z.; Shi, J.; Lu, J.; et al. AENEAS: A randomized phase III trial of aumolertinib versus gefitinib as first-line therapy for locally advanced or metastaticnon–small-cell lung cancer with EGFR exon 19 deletion or L858R mutations. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lam, D.; Yang, J.; Hu, L. Discovery of mobocertinib, a new irreversible tyrosine kinase inhibitor indicated for the treatment of non-small-cell lung cancer harboring EGFR exon 20 insertion mutations. Med. Chem. Res. 2022, 31, 1647–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirker, R.; Filipits, M. Cetuximab in non-small-cell lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2012, 1, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Haura, E.B.; Leighl, N.B.; Mitchell, P.; Shu, C.A.; Girard, N.; Viteri, S.; Han, J.-Y.; Kim, S.-W.; Lee, C.K.; et al. Amivantamab in EGFR Exon 20 Insertion-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Progressing on Platinum Chemotherapy: Initial Results from the CHRYSALIS Phase I Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3391–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goebel, L.; Müller, M.P.; Goody, R.S.; Rauh, D. KRasG12C inhibitors in clinical trials: A short historical perspective. RSC Med. Chem. 2020, 11, 760–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Sullivan, É.; Keogh, A.; Henderson, B.; Finn, S.P.; Gray, S.G.; Gately, K. Treatment Strategies for KRAS-Mutated Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2023, 15, 1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCormick, F. KRAS as a Therapeutic Target. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1797–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA. Approves First KRAS Inhibitor: Sotorasib. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, Of4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skoulidis, F.; Li, B.T.; Dy, G.K.; Price, T.J.; Falchook, G.S.; Wolf, J.; Italiano, A.; Schuler, M.; Borghaei, H.; Barlesi, F.; et al. Sotorasib for Lung Cancers with KRAS p.G12C Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 2371–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gort, E.; Johnson, M.L.; Hwang, J.J.; Pant, S.; Dünzinger, U.; Riemann, K.; Kitzing, T.; Janne, P.A. A phase I, open-label, dose-escalation trial of BI 1701963 as monotherapy and in combination with trametinib in patients with KRAS mutated advanced or metastatic solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38 (Suppl. S15), TPS3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, G.; Khurshid, F.; Lu, K.; Woodward, B.; Husain, H. Selective KRAS G12C inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: Chemistry, concurrent pathway alterations, and clinical outcomes. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2021, 5, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Schlessinger, J. Cell signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Cell 2010, 141, 1117–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, D.S.-W.; Araújo, A.; Zhang, J.; Signorovitch, J.; Zhou, Z.-Y.; Cai, X.; Liu, G. Comparative Efficacy of Ceritinib and Crizotinib as Initial ALK-Targeted Therapies in Previously Treated Advanced NSCLC: An Adjusted Comparison with External Controls. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 1550–1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaw, A.T.; Felip, E.; Bauer, T.M.; Besse, B.; Navarro, A.; Postel-Vinay, S.; Gainor, J.F.; Johnson, M.; Dietrich, J.; James, L.P.; et al. Lorlatinib in non-small-cell lung cancer with ALK or ROS1 rearrangement: An international, multicentre, open-label, single-arm first-in-man phase 1 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2017, 18, 1590–1599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.J.; Tran-Dubé, M.; Shen, H.; Nambu, M.; Kung, P.-P.; Pairish, M.; Jia, L.; Meng, J.; Funk, L.; Botrous, I.; et al. Structure based drug design of crizotinib (PF-02341066), a potent and selective dual inhibitor of mesenchymal-epithelial transition factor (c-MET) kinase and anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK). J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6342–6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Xiong, Q.; Cui, Z.; Tao, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Cui, P.; Chen, S.; Huang, D.; Yang, B.; et al. Efficacy and safety of crizotinib plus bevacizumab in ALK/ROS-1/c-MET positive non-small cell lung cancer: An open-label, single-arm, prospective observational study. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 1526–1534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Felip, E.; Kim, D.; Mehra, R.; Tan, D.; Chow, L.; Camidge, D.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Sharma, S.; De Pas, T.; Riely, G.; et al. Efficacy and safety of ceritinib in patients (pts) with advanced anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK)-rearranged (ALK+) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): An update of ASCEND-1. Ann. Oncol. 2014, 25, iv456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solomon, B.J.; Mok, T.; Kim, D.-W.; Wu, Y.-L.; Nakagawa, K.; Mekhail, T.; Felip, E.; Cappuzzo, F.; Paolini, J.; Usari, T.; et al. First-line crizotinib versus chemotherapy in ALK-positive lung cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 2167–2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.-J.; Zhou, J.; Cheng, Y.; Li, M.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, Z.; Zang, A.; Fan, Y.; Hui, A.-M.; Zhou, Y.; et al. SAF-189s in advanced, ALK-positive, non–small cell lung cancer: Results from a first-in-human phase 1/2, multicenter study. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Song, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wu, G.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yu, X.; Gao, F.; et al. First-in-human phase I results of APG-2449, a novel FAK and third-generation ALK/ROS1 tyrosine kinase inhibitor (TKI), in patients (pts) with second-generation TKI-resistant ALK/ROS1+ non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) or mesothelioma. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, K.D.; Doebele, R.C. Molecular pathways: ROS1 fusion proteins in cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 4040–4045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.J.; Cho, B.C.; Springfeld, C.; Camidge, D.R.; Solomon, B.; Baik, C.; Velcheti, V.; Kim, Y.-C.; Moreno, V.; van der Wekken, A.J.; et al. Abstract P224: Update from the Phase 2 registrational trial of repotrectinib in TKI-pretreated patients with ROS1+ advanced non-small cell lung cancer and with NTRK+ advanced solid tumors (TRIDENT-1). Mol. Cancer Ther. 2021, 20 (Suppl. S12), P224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yang, N.; Ma, H.; Fan, H.; Li, K.; Wu, H.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Meng, X.; Wang, X.; et al. The efficacy and safety of taletrectinib in patients with TKI-naïve or crizotinib-pretreated ROS1-positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 8572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Ngoc, T.; Bouchaab, H.; Adjei, A.A.; Peters, S. BRAF Alterations as Therapeutic Targets in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 1396–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Torres, J.M.; Viteri, S.; Molina, M.A.; Rosell, R. BRAF mutant non-small cell lung cancer and treatment with BRAF inhibitors. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2013, 2, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyman, D.M.; Puzanov, I.; Subbiah, V.; Faris, J.E.; Chau, I.; Blay, J.-Y.; Wolf, J.; Raje, N.S.; Diamond, E.L.; Hollebecque, A.; et al. Vemurafenib in Multiple Nonmelanoma Cancers with BRAF V600 Mutations. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 726–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D.; Kim, T.M.; Mazieres, J.; Quoix, E.; Riely, G.; Barlesi, F.; Souquet, P.-J.; Smit, E.F.; Groen, H.J.M.; Kelly, R.J.; et al. Dabrafenib in patients with BRAF(V600E)-positive advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: A single-arm, multicentre, open-label, phase 2 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Planchard, D.; Besse, B.; Groen, H.J.; Hashemi, S.M.; Mazieres, J.; Kim, T.M.; Quoix, E.; Souquet, P.-J.; Barlesi, F.; Baik, C.; et al. Phase 2 study of dabrafenib plus trametinib in patients with BRAF V600E-mutant metastatic NSCLC: Updated 5-year survival rates and genomic analysis. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riely, G.J.; Smit, E.F.; Ahn, M.-J.; Felip, E.; Ramalingam, S.S.; Tsao, A.; Johnson, M.; Gelsomino, F.; Esper, R.; Nadal, E.; et al. Phase II, open-label study of encorafenib plus binimetinib in patients with BRAF V600-mutant metastatic non–small-cell lung cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 3700–3711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive molecular profiling of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passaro, A.; Peters, S. Targeting HER2-Mutant NSCLC—The Light Is On. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Li, H.; Fan, Y. Targeting HER2 alterations in non-small cell lung cancer: Therapeutic breakthrough and challenges. Cancer Treat Rev. 2023, 114, 102520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uy, N.F.; Merkhofer, C.M.; Baik, C.S. HER2 in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Review of Emerging Therapies. Cancers 2022, 14, 4155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, J.; Shu, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fan, Y.; Fang, J.; et al. Pyrotinib in HER2-mutant advanced lung adenocarcinoma after platinum-based chemotherapy: A multicenter, open-label, single-arm, phase II study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 2753–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Prelaj, A.; Baik, C.; Le, X.; Garassino, M.; Wollner, M.; Haura, E.; Piotrowska, Z.; Socinski, M.; Dreiling, L.; et al. 26MO Efficacy and safety of poziotinib in treatment-naïve HER2 exon 20 insertion (ex20ins) mutated non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): ZENITH20-4. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, S13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Che, X.; Wang, X.; Ma, C.; Wu, G. Tumor Vaccines: Unleashing the Power of the Immune System to Fight Cancer. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.L.; Basu, S.; Soni, V.; Jaiswal, R.K. Immunotherapy: An alternative promising therapeutic approach against cancers. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2022, 49, 9903–9913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Huang, L. mRNA vaccine for cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Cancer 2021, 20, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, S.A.; Parkhurst, M.R.; Robbins, P.F. Adoptive cell transfer immunotherapy for patients with solid epithelial cancers. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chocarro, L.; Arasanz, H.; Fernández-Rubio, L.; Blanco, E.; Echaide, M.; Bocanegra, A.; Teijeira, L.; Garnica, M.; Morilla, I.; Martínez-Aguillo, M.; et al. CAR-T Cells for the Treatment of Lung Cancer. Life 2022, 12, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, S.; Cui, Y.; Liu, Q.; Chen, S. CAR-T cell therapy for lung cancer: A promising but challenging future. J. Thorac. Dis. 2020, 12, 4516–4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, F.; Li, J.; Pu, Y.; Yang, C.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Huang, Y. CAR-T cell therapy for lung cancer: Potential and perspective. Thorac. Cancer 2022, 13, 889–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Sun, J.; Chen, K.; Ma, P.; Lei, Q.; Xing, S.; Cao, Z.; Sun, S.; Yu, Z.; Liu, Y.; et al. Perspectives of tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte treatment in solid tumors. BMC Med. 2021, 19, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluch, C.; Santos, A.M.; Anzilotti, C.; Cornall, R.J.; Davis, S.J. Immune Checkpoints as Therapeutic Targets in Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivares-Hernández, A.; del Portillo, E.G.; Tamayo-Velasco, Á.; Figuero-Pérez, L.; Zhilina-Zhilina, S.; Fonseca-Sánchez, E.; Miramontes-González, J.P. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in non-small cell lung cancer: From current perspectives to future treatments-a systematic review. Ann. Transl. Med. 2023, 11, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiravand, Y.; Khodadadi, F.; Kashani, S.M.A.; Hosseini-Fard, S.R.; Hosseini, S.; Sadeghirad, H.; Ladwa, R.; O’byrne, K.; Kulasinghe, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 3044–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellmann, M.D.; Paz-Ares, L.; Bernabe Caro, R.; Zurawski, B.; Kim, S.-W.; Carcereny Costa, E.; Park, K.; Alexandru, A.; Lupinacci, L.; de la Mora Jimenez, E.; et al. Nivolumab plus Ipilimumab in Advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 381, 2020–2031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rodríguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csőszi, T.; Fülöp, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Migden, M.R.; Rischin, D.; Schmults, C.D.; Guminski, A.; Hauschild, A.; Lewis, K.D.; Chung, C.H.; Hernandez-Aya, L.F.; Lim, A.M.; Chang, A.L.S.; et al. PD-1 Blockade with Cemiplimab in Advanced Cutaneous Squamous-Cell Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fehrenbacher, L.; Spira, A.; Ballinger, M.; Kowanetz, M.; Vansteenkiste, J.; Mazieres, J.; Park, K.; Smith, D.; Artal-Cortes, A.; Lewanski, C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel for patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (POPLAR): A multicentre, open-label, phase 2 randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016, 387, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rittmeyer, A.; Barlesi, F.; Waterkamp, D.; Park, K.; Ciardiello, F.; von Pawel, J.; Gadgeel, S.M.; Hida, T.; Kowalski, D.M.; Dols, M.C.; et al. Atezolizumab versus docetaxel in patients with previously treated non-small-cell lung cancer (OAK): A phase 3, open-label, multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2017, 389, 255–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paz-Ares, L.; Spira, A.; Raben, D.; Planchard, D.; Cho, B.; Özgüroğlu, M.; Daniel, D.; Villegas, A.; Vicente, D.; Hui, R.; et al. Outcomes with durvalumab by tumour PD-L1 expression in unresectable, stage III non-small-cell lung cancer in the PACIFIC trial. Ann. Oncol. 2020, 31, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, M.L.; Cho, B.C.; Luft, A.; Alatorre-Alexander, J.; Geater, S.L.; Laktionov, K.; Kim, S.-W.; Ursol, G.; Hussein, M.; Lim, F.L.; et al. Durvalumab with or without Tremelimumab in Combination with Chemotherapy as First-Line Therapy for Metastatic Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: The Phase III POSEIDON Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Liu, L.; Lv, Z.; Zhao, K.; Yi, Q.; Zhang, J. Recent Advances in DNA Vaccines against Lung Cancer: A Mini Review. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.J.; Svensson-Arvelund, J.; Lubitz, G.S.; Marabelle, A.; Melero, I.; Brown, B.D.; Brody, J.D. Cancer vaccines: The next immunotherapy frontier. Nat. Cancer 2022, 3, 911–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, W.; Xu, Y.; Chen, X.; Jiang, H. Characteristics of clinical trials for non-small cell lung cancer therapeutic vaccines registered on ClinicalTrials.gov. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 936667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butts, C.; Socinski, M.A.; Mitchell, P.L.; Thatcher, N.; Havel, L.; Krzakowski, M.; Nawrocki, S.; Ciuleanu, T.E.; Bosquée, L.; Trigo, J.M.; et al. Tecemotide (L-BLP25) versus placebo after chemoradiotherapy for stage III non-small-cell lung cancer (START): A randomised, double-blind, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2014, 15, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apolonio, J.S.; de Souza Gonçalves, V.L.; Santos, M.L.C.; Luz, M.S.; Souza, J.V.S.; Pinheiro, S.L.R.; de Souza, W.R.; Loureiro, M.S.; de Melo, F.F. Oncolytic virus therapy in cancer: A current review. World J. Virol. 2021, 10, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakhi, H.; Arabi, M.; Ghaemi, A.; Movafagh, A.; Sheikhpour, M. Oncolytic viruses in lung cancer treatment: A review article. Immunotherapy 2024, 16, 75–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zolaly, M.A.; Mahallawi, W.; Khawaji, Z.Y.; A Alahmadi, M. The Clinical Advances of Oncolytic Viruses in Cancer Immunotherapy. Cureus 2023, 15, e40742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.N.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Tian, M.; Chen, L.L.; Miao, L.Y.; Zhou, Y.J. Recombinant human adenovirus type 5 (Oncorine) reverses resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitor in a patient with recurrent non-small cell lung cancer: A case report. Thorac. Cancer 2021, 12, 1617–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villalona-Calero, M.A.; Lam, E.; Otterson, G.A.; Zhao, W.; Timmons, M.; Subramaniam, D.; Hade, E.M.; Gill, G.M.; Coffey, M.; Selvaggi, G.; et al. Oncolytic reovirus in combination with chemotherapy in metastatic or recurrent non-small cell lung cancer patients with KRAS-activated tumors. Cancer 2016, 122, 875–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, J.; Maurice-Dror, C.; Lee, D.H.; Kim, D.W.; Nagrial, A.; Voskoboynik, M.; Chung, H.; Mileham, K.; Vaishampayan, U.; Rasco, D.; et al. First-in-human phase 1 study of the anti-TIGIT antibody vibostolimab as monotherapy or with pembrolizumab for advanced solid tumors, including non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curigliano, G.; Gelderblom, H.; Mach, N.; Doi, T.; Tai, D.; Forde, P.M.; Sarantopoulos, J.; Bedard, P.L.; Lin, C.-C.; Hodi, F.S.; et al. Phase I/Ib Clinical Trial of Sabatolimab, an Anti-TIM-3 Antibody, Alone and in Combination with Spartalizumab, an Anti-PD-1 Antibody, in Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 3620–3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, D.; Gilmour, C.; Patnaik, S.; Wang, L.L. Combinatorial blockade for cancer immunotherapy: Targeting emerging immune checkpoint receptors. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1264327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.E.; Ahn, S.D.; Je, H.U. Usability and necessity of a novel hybrid radiation therapy technique based on volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) in stage III lung cancer treatment. Radiat. Phys. Chem. 2022, 195, 110054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bree, I.; van Hinsberg, M.G.; van Veelen, L.R. High-dose radiotherapy in inoperable nonsmall cell lung cancer: Comparison of volumetric modulated arc therapy, dynamic IMRT and 3D conformal radiotherapy. Med. Dosim. 2012, 37, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Yang, R.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, J. An IMRT/VMAT Technique for Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 613060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steber, J.; Silva, S.; Harkenrider, M.; Surucu, M.; Choi, M. Clinical Application of a Hybrid Volumetric Arc Therapy Technique for Locally Advanced Lung Cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2015, 93, E595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Miao, L.; Li, Y. Boron Neutron Capture Therapy: Current Status and Challenges. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 788770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alberti, D.; Protti, N.; Toppino, A.; Deagostino, A.; Lanzardo, S.; Bortolussi, S.; Altieri, S.; Voena, C.; Chiarle, R.; Crich, S.G.; et al. A theranostic approach based on the use of a dual boron/Gd agent to improve the efficacy of Boron Neutron Capture Therapy in the lung cancer treatment. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivillin, V.A.; Garabalino, M.A.; Colombo, L.L.; González, S.J.; Farías, R.O.; Monti Hughes, A.; Pozzi, E.; Bortolussi, S.; Altieri, S.; Itoiz, M.; et al. Biodistribution of the boron carriers boronophenylalanine (BPA) and/or decahydrodecaborate (GB-10) for Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) in an experimental model of lung metastases. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2014, 88, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TrivTrivillin, V.A.; Serrano, A.; Garabalino, M.A.; Colombo, L.L.; Pozzi, E.C.; Hughes, A.M.; Curotto, P.M.; Thorp, S.I.; Farías, R.O.; González, S.J.; et al. Translational boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) studies for the treatment of tumors in lung. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019, 95, 646–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiger, J.L.; Kiger, W.S.; Patel, H.; Binns, P.J.; Riley, K.J.; Hopewell, J.W.; Harling, O.K.; Coderre, J.A. Effects of boron neutron capture irradiation on the normal lung of rats. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2004, 61, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, M.; Suzuki, O.; Sakurai, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Kondo, N.; Kinashi, Y.; Masunaga, S.-I.; Maruhashi, A.; Ono, K. Reirradiation for locally recurrent lung cancer in the chest wall with boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Int. Cancer Conf. J. 2012, 1, 235–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, M.; Endo, K.; Satoh, H.; Sakurai, Y.; Kumada, H.; Kimura, H.; Masunaga, S.; Kinashi, Y.; Nagata, K.; Maruhashi, A.; et al. A novel concept of treatment of diffuse or multiple pleural tumors by boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT). Radiother. Oncol. 2008, 88, 192–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masunaga, S.-I.; Sakurai, Y.; Tanaka, H.; Takata, T.; Suzuki, M.; Sanada, Y.; Tano, K.; Maruhashi, A.; Ono, K. Usefulness of combination with both continuous administration of hypoxic cytotoxin and mild temperature hyperthermia in boron neutron capture therapy in terms of local tumor response and lung metastatic potential. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019, 95, 1708–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hearn, J.W.; Videtic, G.M.; Djemil, T.; Stephans, K.L. Salvage stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for local failure after primary lung SBRT. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2014, 90, 402–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valakh, V.; Miyamoto, C.; Micaily, B.; Chan, P.; Neicu, T.; Li, S. Repeat stereotactic body radiation therapy for patients with pulmonary malignancies who had previously received SBRT to the same or an adjacent tumor site. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2013, 9, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andruska, N.; Stowe, H.B.; Crockett, C.; Liu, W.; Palma, D.; Faivre-Finn, C.; Badiyan, S.N. Stereotactic Radiation for Lung Cancer: A Practical Approach to Challenging Scenarios. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2021, 16, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.S.; Loblaw, A.; Chang, E.L.; Mayr, N.A.; Teh, B.S.; Huang, Z.; Yao, M.; Ellis, R.J.; Biswas, T.; Sohn, J.W.; et al. Emerging applications of stereotactic body radiotherapy. Future Oncol. 2014, 10, 1299–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milano, M.T.; Kong, F.S.; Movsas, B. Stereotactic body radiotherapy as salvage treatment for recurrence of non-small cell lung cancer after prior surgery or radiotherapy. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2019, 8, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Hermann, G.; Lewis, J.H.; Aerts, H.J.; Baldini, E.H.; Chen, A.B.; Colson, Y.L.; Hacker, F.L.; Killoran, J.H.; Kozono, D.E.; et al. Clinical Outcomes after Lung Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy in Patients with or without a Prior Lung Resection. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 41, 695–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prezzano, K.M.; Ma, S.J.; Hermann, G.M.; Rivers, C.I.; Gomez-Suescun, J.A.; Singh, A.K. Stereotactic body radiation therapy for non-small cell lung cancer: A review. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 10, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaskou Badra, E.; Baumgartl, M.; Fabiano, S.; Jongen, A.; Guckenberger, M. Stereotactic radiotherapy for early stage non-small cell lung cancer: Current standards and ongoing research. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 1930–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, L.; Xu, K.; Mu, F. Cryosurgery for lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2012, 4, 408–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medlej, Z.a.A.; Medlej, W.; Slaba, S.; Torrecillas, P.; Cueto, A.; Urbaneja, A.; Garrido, A.J.; Lugnani, F. Cryoablation and Immunotherapy: An Enthralling Synergy for Cancer Treatment. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 4844–4860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velez, A.; DeMaio, A.; Sterman, D. Cryoablation and immunity in non-small cell lung cancer: A new era of cryo-immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1203539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uhlschmid, G.; Kolb, E.; Largiadèr, F. Cryosurgery of pulmonary metastases. Cryobiology 1979, 16, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, M.; Liang, S.-Z.; Wang, X.-H.; Liang, Y.-Q.; Zhang, M.-J.; Niu, L.-Z.; Chen, J.-B.; Li, H.-B.; Xu, K.-C. Clinical efficacy of percutaneous cryoablation combined with allogenic NK cell immunotherapy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Immunol. Res. 2017, 65, 880–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.Y.; Jiang, Z.; Fang, W. Cryoablation combined with molecular target therapy improves the curative effect in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. J. Int. Med. Res. 2011, 39, 1736–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Huang, Y.Y.; Li, B.; Yu, X.X.; Xiao, R.H.; Yang, H.F. Comparing cryoablation and microwave ablation for the treatment of patients with stage IIIB/IV non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 1031–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokwena, M.G.; Kruger, C.A.; Ivan, M.T.; Heidi, A. A review of nanoparticle photosensitizer drug delivery uptake systems for photodynamic treatment of lung cancer. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2018, 22, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, M.S.; Cadet, J.; Di Mascio, P.; Ghogare, A.A.; Greer, A.; Hamblin, M.R.; Lorente, C.; Nunez, S.C.; Ribeiro, M.S.; Thomas, A.H.; et al. Type I and Type II Photosensitized Oxidation Reactions: Guidelines and Mechanistic Pathways. Photochem. Photobiol. 2017, 93, 912–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Q.-L.; Shen, M.-O.; Han, N.; Xu, H.-Z.; Peng, X.-C.; Li, Q.-R.; Yu, T.-T.; Li, L.-G.; Xu, X.; Liu, B.; et al. Chlorin e6 mediated photodynamic therapy triggers resistance through ATM-related DNA damage response in lung cancer cells. Photodiagnosis Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 37, 102645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Yu, B.; Pathak, J.L. An update in clinical utilization of photodynamic therapy for lung cancer. J. Cancer 2021, 12, 1154–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maziak, D.E.; Markman, B.R.; MacKay, J.A.; Evans, W.K. Photodynamic therapy in nonsmall cell lung cancer: A systematic review. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2004, 77, 1484–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafirstein, G.; Battoo, A.; Harris, K.; Baumann, H.; Gollnick, S.O.; Lindenmann, J.; Nwogu, C.E. Photodynamic Therapy of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Narrative Review and Future Directions. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crous, A.; Abrahamse, H. Photodynamic therapy of lung cancer, where are we? Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 932098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszowy, M.; Nowak-Perlak, M.; Woźniak, M. Current Strategies in Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) and Photodynamic Diagnostics (PDD) and the Future Potential of Nanotechnology in Cancer Treatment. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, P.; Rompicharla, S.V.K.; Bhatt, H.; Ghosh, B.; Biswas, S. Development of chlorin e6-conjugated poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(d,l-lactide) nanoparticles for photodynamic therapy. Nanomedicine 2019, 14, 819–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Liu, B.; Xia, F.; Duan, M.; Hong, Y.; Niu, J.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Cui, D. MnO2@Ce6-loaded mesenchymal stem cells as an “oxygen-laden guided-missile” for the enhanced photodynamic therapy on lung cancer. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 3090–3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, M.; Miyajima, K.; Kojika, M.; Kono, T.; Kato, H. Photodynamic Therapy (PDT) with Chemotherapy for Advanced Lung Cancer with Airway Stenosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 25466–25475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Yoo, J.W.; Bae, E.K.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, C.M. The effect of Radachlorin® PDT in advanced NSCLC: A pilot study. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2013, 10, 120–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, S.S.; Demmy, T.L.; Yendamuri, S.; Loewen, G.; Nwogu, C.; Cooper, M.; Henderson, B.W. A Phase I Study of Light Dose for Photodynamic Therapy Using 2-[1-Hexyloxyethyl]-2 Devinyl Pyropheophorbide-a for the Treatment of Non-Small Cell Carcinoma In Situ or Non-Small Cell Microinvasive Bronchogenic Carcinoma: A Dose Ranging Study. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2016, 11, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberg, B.D.; Allison, R.R.; Sibata, C.; Parent, T.; Downie, G. Results of combined photodynamic therapy (PDT) and high dose rate brachytherapy (HDR) in treatment of obstructive endobronchial non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Photodiagn. Photodyn Ther. 2010, 7, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonokawa, T.; Obi, N.; Usuda, J.; Sudo, Y.; Hamakubo, T. Development of a new minimally invasive phototherapy for lung cancer using antibody-toxin conjugate. Thorac. Cancer. 2023, 14, 645–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunne, M.; Regenold, M.; Allen, C. Hyperthermia can alter tumor physiology and improve chemo- and radio-therapy efficacy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2020, 163–164, 98–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oei, A.L.; Vriend, L.E.; Crezee, J.; Franken, N.A.; Krawczyk, P.M. Effects of hyperthermia on DNA repair pathways: One treatment to inhibit them all. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 10, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-H.; Xie, J.; Lai, Z.-Y.; Yang, M.-D.; Zhang, G.-H.; Li, Y.; Mu, J.-B.; Xu, J. Radiofrequency deep hyperthermia combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Chin. Med. J. 2019, 132, 922–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherukuri, P.; Glazer, E.S.; Curley, S.A. Targeted hyperthermia using metal nanoparticles. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 339–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spirou, S.V.; Basini, M.; Lascialfari, A.; Sangregorio, C.; Innocenti, C. Magnetic Hyperthermia and Radiation Therapy: Radiobiological Principles and Current Practice. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, B.; Jeon, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, H.; Kang, H.; Youn, H.; Jo, S.; Youn, B. Radiotherapy in combination with hyperthermia suppresses lung cancer progression via increased NR4A3 and KLF11 expression. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2019, 95, 1696–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Kim, S.; Choi, B.-H.; Park, M.-T.; Lee, J.; Jeong, S.-Y.; Choi, E.K.; Lim, B.-U.; Kim, C.; Park, H.J. Hyperthermia improves therapeutic efficacy of doxorubicin carried by mesoporous silica nanocontainers in human lung cancer cells. Int. J. Hyperth. 2011, 27, 698–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazan, G.; Lurie, H.; Yerushalmi, A. Sensitization of combined cis-platinum and cyclophosphamide by local hyperthermia in mice bearing the Lewis lung carcinoma. Oncology 1984, 41, 68–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, P.; Hurwitz, M.D.; Krishnan, S.; Asea, A. Combined hyperthermia and radiotherapy for the treatment of cancer. Cancers 2011, 3, 3799–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohguri, T.; Imada, H.; Yahara, K.; Moon, S.D.; Yamaguchi, S.; Yatera, K.; Mukae, H.; Hanagiri, T.; Tanaka, F.; Korogi, Y. Re-irradiation plus regional hyperthermia for recurrent non-small cell lung cancer: A potential modality for inducing long-term survival in selected patients. Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 140–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markman, J.L.; Rekechenetskiy, A.; Holler, E.; Ljubimova, J.Y. Nanomedicine therapeutic approaches to overcome cancer drug resistance. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 1866–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amreddy, N.; Babu, A.; Panneerselvam, J.; Srivastava, A.; Muralidharan, R.; Chen, A.; Zhao, Y.D.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Chemo-biologic combinatorial drug delivery using folate receptor-targeted dendrimer nanoparticles for lung cancer treatment. Nanomedicine 2018, 14, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Shambhwani, D.; Pandey, S.; Singh, J.; Lalhlenmawia, H.; Kumarasamy, M.; Singh, S.K.; Chellappan, D.K.; Gupta, G.; Prasher, P.; et al. Advances in Lung Cancer Treatment Using Nanomedicines. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 10–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutu, V.; Gupta, M.; Das, S.; Rawat, D.K.; Kharade, V.; Pasricha, R.K. Nanotechnology in Lung Cancer Therapeutics: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e34245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Hao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, R.; Huang, D.B.; Pan, Y.Y. Nanomedicine in lung cancer: Current states of overcoming drug resistance and improving cancer immunotherapy. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 13, e1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco-Esteban, E.; Domínguez-Rullán, J.A.; Barrionuevo-Castillo, P.; Pelari-Mici, L.; Leaman, O.; Sastre-Gallego, S.; López-Campos, F. Current role of nanoparticles in the treatment of lung cancer. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2021, 7, 140–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Pan, J.; Tang, Y.; Chen, J.; Fei, X.; Xue, W.; Liu, X. Advances of hafnium based nanomaterials for cancer theranostics. Front. Chem. 2023, 11, 1283924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, G.; Ni, K.; Veroneau, S.S.; Song, Y.; Lin, W. Nanoscale Metal-Organic Layers for Radiotherapy-Radiodynamic Therapy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 16971–16975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Paris, S.; Barsoumian, H.; Abana, C.O.; He, K.; Wasley, M.; Younes, A.I.; Masrorpour, F.; Chen, D.; Yang, L.; et al. Radiation Therapy Enhanced by NBTXR3 Nanoparticles Overcomes Anti-PD1 Resistance and Evokes Abscopal Effects. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2021, 111, 647–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Paris, S.; Bertolet, G.; Barsoumian, H.B.; Wang, Q.; Da Silva, J.; Patel, N.B.; Nguyen, N.; Doss, D.J.; Huang, A.; et al. NBTXR3 improves the efficacy of immunoradiotherapy combining nonfucosylated anti-CTLA4 in an anti-PD1 resistant lung cancer model. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1022011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Paris, S.; Sahoo, N.; Bertolet, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Q.; Barsoumian, H.B.; Da Silva, J.; Huang, A.; Doss, D.J.; et al. Nanoparticle-enhanced proton beam immunoradiotherapy drives immune activation and durable tumor rejection. JCI Insight 2023, 8, e167749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.; Frakes, J.; Niu, J.; Weiss, J.; Caudell, J.; Seiwert, T.; Said, P.; Guedj, M.; Tyan, P.; Vivar, O.; et al. 684 NBTXR3 activated by radiotherapy in combination with nivolumab or pembrolizumab in patients with advanced cancers: Results from an ongoing dose escalation phase I trial (Study 1100). BMJ Spec. J. 2022, 10 (Suppl. S2), A1–A1603. [Google Scholar]
- Ngema, L.M.; Adeyemi, S.A.; Marimuthu, T.; Choonara, Y.E. A review on engineered magnetic nanoparticles in Non-Small-Cell lung carcinoma targeted therapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 606, 120870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Chen, B.; Xu, L.; Feng, J.; Xia, G.; Cheng, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, F.; Wang, X. Reversal of multidrug resistance by cisplatin-loaded magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles in A549/DDP lung cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1867–1877. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, X.; Song, Y.; Song, N.; Li, J.; Yang, L.; Li, Y.; Tan, H. The preliminary study of immune superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for the detection of lung cancer in magnetic resonance imaging. Carbohydr. Res. 2016, 419, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Li, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, X. Fabrication of Hybrid Nanostructures Based on Fe3O4 Nanoclusters as Theranostic Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Drug Delivery. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2019, 14, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadhukha, T.; Wiedmann, T.S.; Panyam, J. Inhalable magnetic nanoparticles for targeted hyperthermia in lung cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5163–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Puranik, N.; Yadav, D.; Jin, J.O.; Lee, P.C.W. Lipid Nanocarrier-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Therapeutic Advances in the Treatment of Lung Cancer. Int. J. Nanomed. 2023, 18, 2659–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dristant, U.; Mukherjee, K.; Saha, S.; Maity, D. An Overview of Polymeric Nanoparticles-Based Drug Delivery System in Cancer Treatment. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2023, 22, 15330338231152083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Suita, Y.; Miriyala, S.; Dean, J.; Tapinos, N.; Shen, J. Advances in Lipid-Based Nanoparticles for Cancer Chemoimmunotherapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, K.; Zhang, W.; Yu, L.; Yu, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, X. Transferrin-Decorated Protein-Lipid Hybrid Nanoparticle Efficiently Delivers Cisplatin and Docetaxel for Targeted Lung Cancer Treatment. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2021, 15, 3475–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, J.; Mo, Z.; Huang, Y.; Ma, C.; Wang, W.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. PLGA Porous Microspheres Dry Powders for Codelivery of Afatinib-Loaded Solid Lipid Nanoparticles and Paclitaxel: Novel Therapy for EGFR Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors Resistant Nonsmall Cell Lung Cancer. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2019, 8, e1900965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Sato, T.; Endo, R.; Sasaki, S.; Takahashi, N.; Sato, Y.; Hyodo, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Harashima, H. STING agonist loaded lipid nanoparticles overcome anti-PD-1 resistance in melanoma lung metastasis via NK cell activation. J Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amreddy, N.; Babu, A.; Muralidharan, R.; Munshi, A.; Ramesh, R. Polymeric Nanoparticle-Mediated Gene Delivery for Lung Cancer Treatment. Top. Curr. Chem. 2017, 375, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezhilarasan, D.; Lakshmi, T.; Mallineni, S.K. Nano-based targeted drug delivery for lung cancer: Therapeutic avenues and challenges. Nanomedicine 2022, 17, 1855–1869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, H.; Tang, Z.; Mao, J.; Wang, L. Pursuing for the better lung cancer therapy effect: Comparison of two different kinds of hyaluronic acid and nitroimidazole co-decorated nanomedicines. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shukla, S.K.; Kulkarni, N.S.; Farrales, P.; Kanabar, D.D.; Parvathaneni, V.; Kunda, N.K.; Muth, A.; Gupta, V. Sorafenib Loaded Inhalable Polymeric Nanocarriers against Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Pharm. Res. 2020, 37, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, J.U.; Kuriakose, A.; Iyer, R.; Hernandez, E.; Gandee, L.; Zhang, S.; Takahashi, M.; Zhang, Z.; Saha, D.; Nguyen, K.T. Dual-Drug Containing Core-Shell Nanoparticles for Lung Cancer Therapy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Yang, W.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Jiang, F.; Xie, J.; Huang, X. Combining Doxorubicin-Conjugated Polymeric Nanoparticles and 5-Aminolevulinic Acid for Enhancing Radiotherapy against Lung Cancer. Bioconjug. Chem. 2022, 33, 654–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Representative Antibody | Target | Approved Indication | Refs. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nivolumab | PD-1 | Advanced NSCLC | [86] |
| Pembrolizumab | PD-1 and PD-2 | Advanced NSCLC | [87] |
| Cemiplimab | PD-1 | Advanced NSCLC | [88] |
| Atezolizumab | PD-1 and PD-L1 | NSCLC | [89,90] |
| Durvalumab | PD-L1 | Advanced NSCLC | [91] |
| Ipilimumab | CTLA-4 | Advanced NSCLC | [86] |
| Tremelimumab | CTLA-4 | Metastatic NSCLC | [92] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
La’ah, A.S.; Chiou, S.-H. Cutting-Edge Therapies for Lung Cancer. Cells 2024, 13, 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13050436
La’ah AS, Chiou S-H. Cutting-Edge Therapies for Lung Cancer. Cells. 2024; 13(5):436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13050436
Chicago/Turabian StyleLa’ah, Anita Silas, and Shih-Hwa Chiou. 2024. "Cutting-Edge Therapies for Lung Cancer" Cells 13, no. 5: 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13050436
APA StyleLa’ah, A. S., & Chiou, S.-H. (2024). Cutting-Edge Therapies for Lung Cancer. Cells, 13(5), 436. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13050436






