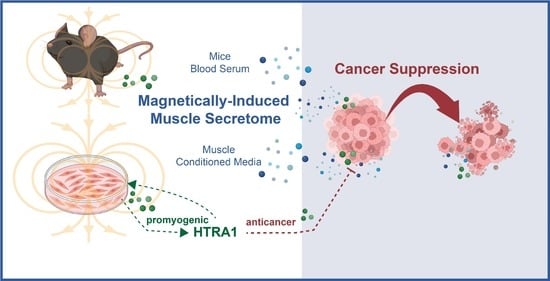
Secretome from Magnetically Stimulated Muscle Exhibits Anticancer Potency: Novel Preconditioning Methodology Highlighting HTRA1 Action
Abstract
Share and Cite
Tai, Y.K.; Iversen, J.N.; Chan, K.K.W.; Fong, C.H.H.; Abdul Razar, R.B.; Ramanan, S.; Yap, L.Y.J.; Yin, J.N.; Toh, S.J.; Wong, C.J.K.; et al. Secretome from Magnetically Stimulated Muscle Exhibits Anticancer Potency: Novel Preconditioning Methodology Highlighting HTRA1 Action. Cells 2024, 13, 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13050460
Tai YK, Iversen JN, Chan KKW, Fong CHH, Abdul Razar RB, Ramanan S, Yap LYJ, Yin JN, Toh SJ, Wong CJK, et al. Secretome from Magnetically Stimulated Muscle Exhibits Anticancer Potency: Novel Preconditioning Methodology Highlighting HTRA1 Action. Cells. 2024; 13(5):460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13050460
Chicago/Turabian StyleTai, Yee Kit, Jan Nikolas Iversen, Karen Ka Wing Chan, Charlene Hui Hua Fong, Rafhanah Banu Abdul Razar, Sharanya Ramanan, Lye Yee Jasmine Yap, Jocelyn Naixin Yin, Shi Jie Toh, Craig Jun Kit Wong, and et al. 2024. "Secretome from Magnetically Stimulated Muscle Exhibits Anticancer Potency: Novel Preconditioning Methodology Highlighting HTRA1 Action" Cells 13, no. 5: 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13050460
APA StyleTai, Y. K., Iversen, J. N., Chan, K. K. W., Fong, C. H. H., Abdul Razar, R. B., Ramanan, S., Yap, L. Y. J., Yin, J. N., Toh, S. J., Wong, C. J. K., Koh, P. F. A., Huang, R. Y. J., & Franco-Obregón, A. (2024). Secretome from Magnetically Stimulated Muscle Exhibits Anticancer Potency: Novel Preconditioning Methodology Highlighting HTRA1 Action. Cells, 13(5), 460. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells13050460