Modeling the Effect of Cannabinoid Exposure During Human Neurodevelopment Using Bidimensional and Tridimensional Cultures
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. General Properties of Cannabinoids in the Mature Nervous System
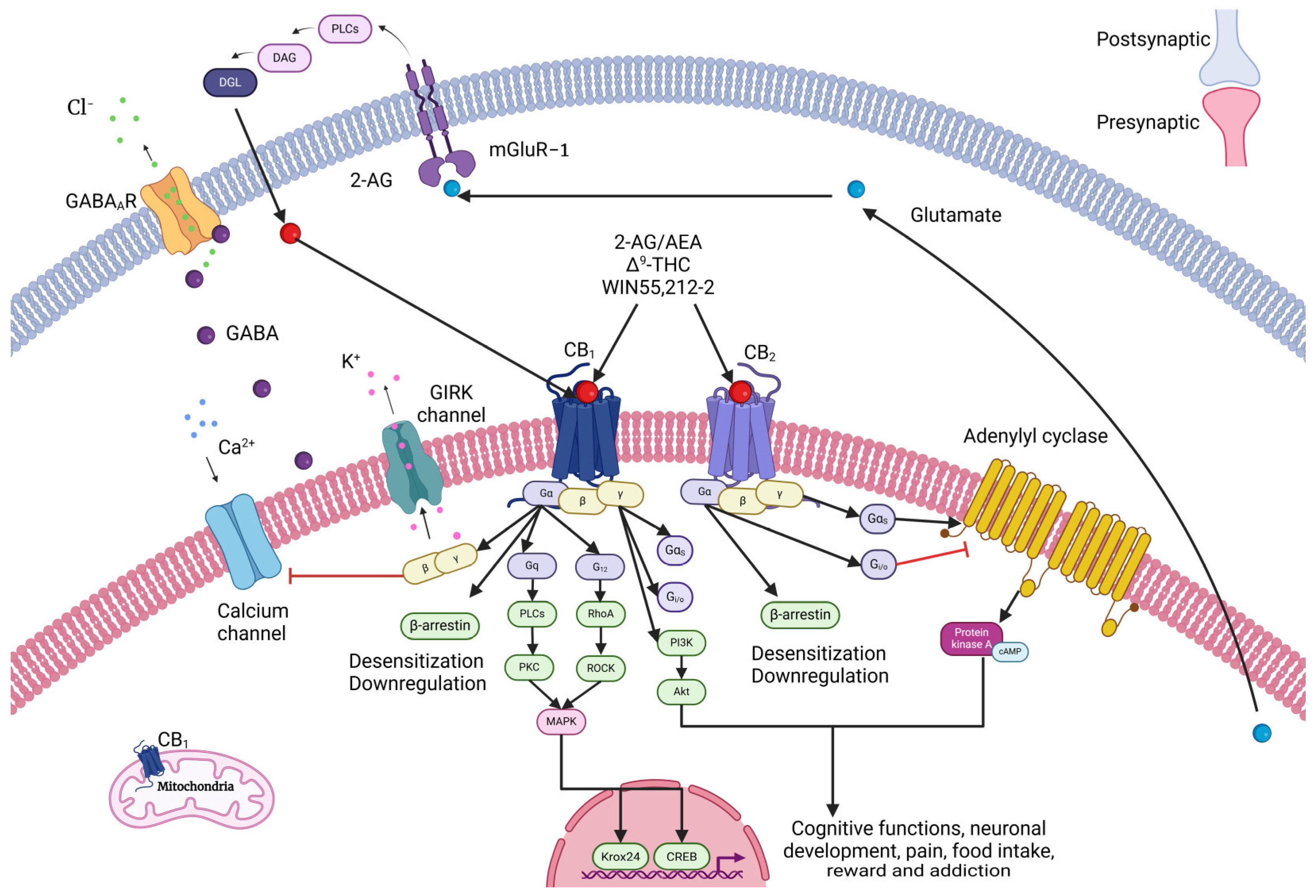
2.1. Cannabinoid Receptors
2.2. Types of Cannabinoids
3. Cannabinoid Signaling During Neurodevelopment
3.1. Endocannabinoid Signaling in Neurodevelopment
3.2. Role of Cannabinoids in Axon Elongation and Synaptogenesis
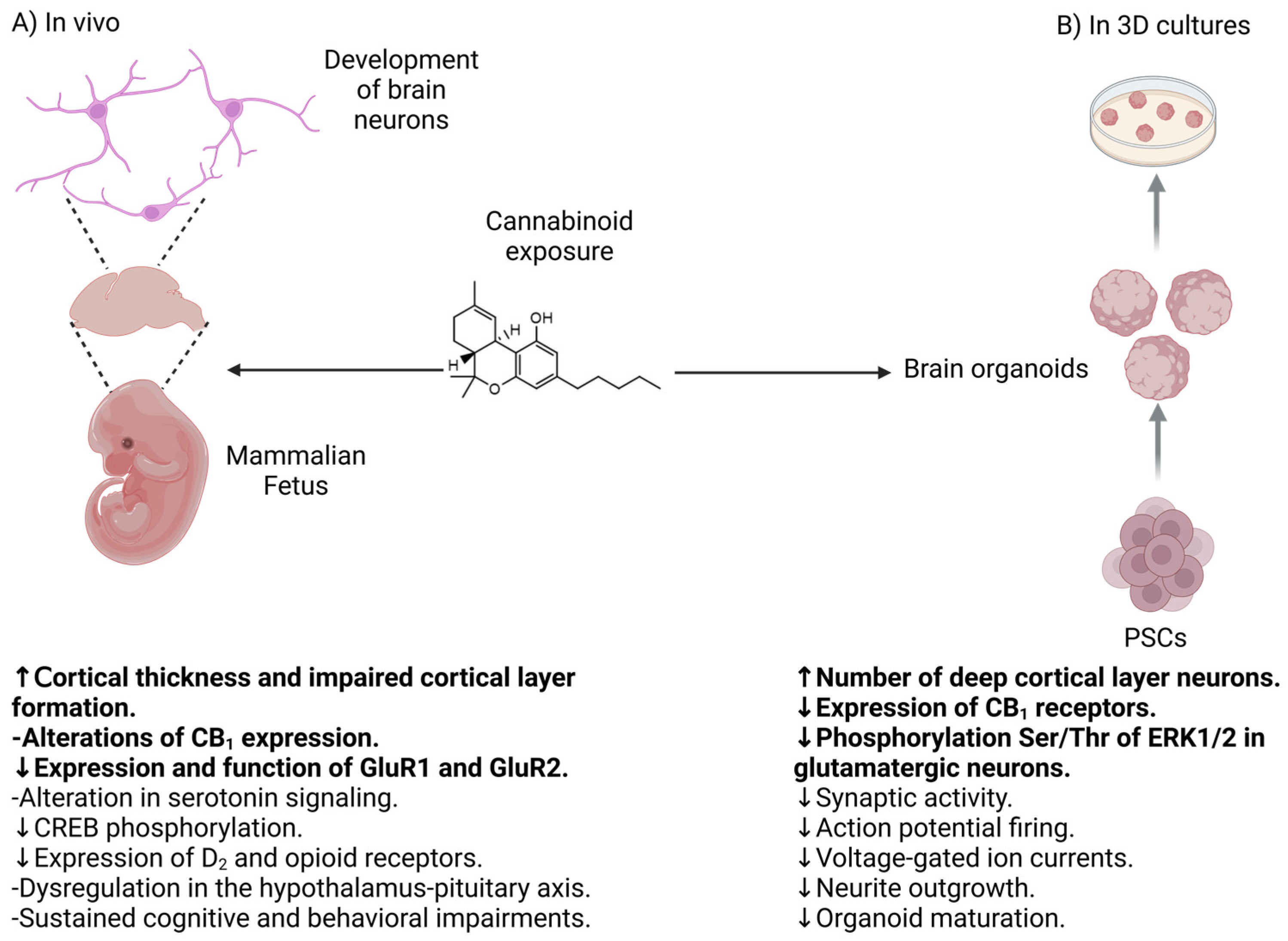
4. Clinical Evidence of the Effect of Cannabinoid Consumption During Pregnancy
4.1. Effect of Cannabinoids in the Development of Peripheral Tissues
4.2. Effect of Cannabinoids in the Development of the Nervous System
5. Bidimensional and Tridimensional Neuronal Cultures from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells and Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells for Neurodevelopmental Studies
5.1. ESCs and iPSCs for Neurodevelopmental Studies
5.2. Unpatterned and Patterned 3D Cell Cultures
5.3. Organoids for Neurodevelopmental Studies
5.4. Future Directions in 3D Cell Cultures
6. Evidence of the Effect of Cannabinoids on Human Bidimensional and Tridimensional Neuronal Cultures
6.1. Effect of Cannabinoids in PSCs
6.2. Effect of Cannabinoids in Neuronal Differentiation of Human Neurons and Brain Organoids
7. Conclusions
8. Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Young-Wolff, K.C.; Tucker, L.Y.; Alexeeff, S.; Armstrong, M.A.; Conway, A.; Weisner, C.; Goler, N. Trends in Self-Reported and Biochemically Tested Marijuana Use Among Pregnant Females in California from 2009–2016. JAMA 2017, 318, 2490–2491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Dow-Edwards, D.; Keller, E.; Hurd, Y.L. Preferential Limbic Expression of the Cannabinoid Receptor MRNA in the Human Fetal Brain. Neuroscience 2003, 118, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, S.; Del Olmo, E.; Pazos, A. Ontogenetic Development of Cannabinoid Receptor Expression and Signal Transduction Functionality in the Human Brain. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 1747–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendall, D.A.; Yudowski, G.A. Cannabinoid Receptors in the Central Nervous System: Their Signaling and Roles in Disease. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Marroun, H.; Tiemeier, H.; Franken, I.H.A.; Jaddoe, V.W.V.; van der Lugt, A.; Verhulst, F.C.; Lahey, B.B.; White, T. Prenatal Cannabis and Tobacco Exposure in Relation to Brain Morphology: A Prospective Neuroimaging Study in Young Children. Biol. Psychiatry 2016, 79, 971–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dow-Edwards, D.; Anderson, V.; Minkoff, H.; Hurd, Y.L. Discrete Opioid Gene Expression Impairment in the Human Fetal Brain Associated with Maternal Marijuana Use. Pharmacogenom. J. 2006, 6, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Dow-Edwards, D.; Anderson, V.; Minkoff, H.; Hurd, Y.L. In Utero Marijuana Exposure Associated with Abnormal Amygdala Dopamine D2 Gene Expression in the Human Fetus. Biol. Psychiatry 2004, 56, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinieri, J.A.; Wang, X.; Szutorisz, H.; Spano, S.M.; Kaur, J.; Casaccia, P.; Dow-Edwards, D.; Hurd, Y.L. Maternal Cannabis Use Alters Ventral Striatal Dopamine D2 Gene Regulation in the Offspring. Biol. Psychiatry 2011, 70, 763–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, V.L.; Gonçalves, J.L.; Aguiar, J.; Teixeira, H.M.; Câmara, J.S. The Synthetic Cannabinoids Phenomenon: From Structure to Toxicological Properties. A Review. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2020, 50, 359–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevyrin, V.A.; Morzherin, Y.Y. Cannabinoids: Structures, Effects, and Classification. Russ. Chem. Bull. 2015, 64, 1249–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Arellano, J.; Canseco-Alba, A.; Cutler, S.J.; León, F. The Polypharmacological Effects of Cannabidiol. Molecules 2023, 28, 3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.C.; Mackie, K. Review of the Endocannabinoid System. Biol. Psychiatry Cogn. Neurosci. Neuroimaging 2021, 6, 607–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basavarajappa, B.S.; Subbanna, S. Molecular Insights into Epigenetics and Cannabinoid Receptors. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herkenham, M.; Lynn, A.B.; Little, M.D.; Johnson, M.R.; Melvin, L.S.; De Costa, B.R.; Rice, K.C. Cannabinoid Receptor Localization in Brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 1932–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsou, K.; Brown, S.; Sañudo-Peña, M.C.; Mackie, K.; Walker, J.M. Immunohistochemical Distribution of Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors in the Rat Central Nervous System. Neuroscience 1998, 83, 393–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomes, T.M.; da Silva, D.D.; Carmo, H.; Carvalho, F.; Silva, J.P. Epigenetics and the Endocannabinoid System Signaling: An Intricate Interplay Modulating Neurodevelopment. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 162, 105237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechoulam, R. A Delightful Trip Along the Pathway of Cannabinoid and Endocannabinoid Chemistry and Pharmacology. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2023, 63, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Addario, C.; Di Francesco, A.; Pucci, M.; Finazzi Agrò, A.; MacCarrone, M. Epigenetic Mechanisms and Endocannabinoid Signalling. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 1905–1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayser, R.R.; Snorrason, I.; Haney, M.; Lee, F.S.; Simpson, H.B. The Endocannabinoid System: A New Treatment Target for Obsessive Compulsive Disorder? Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2019, 4, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lutz, B.; Marsicano, G.; Maldonado, R.; Hillard, C.J. The Endocannabinoid System in Guarding against Fear, Anxiety and Stress. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 705–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laprairie, R.B.; Kelly, M.E.M.; Denovan-Wright, E.M. The Dynamic Nature of Type 1 Cannabinoid Receptor (CB1) Gene Transcription. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 167, 1583–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Hempel, B.J.; Yang, H.J.; Han, X.; Bi, G.H.; Gardner, E.L.; Xi, Z.X. Dissecting the Role of CB1 and CB2 Receptors in Cannabinoid Reward versus Aversion Using Transgenic CB1- and CB2-Knockout Mice. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2021, 43, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperi, V.; Guzzo, T.; Topai, A.; Gambacorta, N.; Ciriaco, F.; Nicolotti, O.; Maccarrone, M. Recent Advances on Type-2 Cannabinoid (CB2) Receptor Agonists and Their Therapeutic Potential. Curr. Med. Chem. 2023, 30, 1420–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onaivi, E.S.; Ishiguro, H.; Gu, S.; Liu, Q.R. CNS Effects of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptors: Beyond Neuro-Immuno-Cannabinoid Activity. J. Psychopharmacol. 2012, 26, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.J.; Gao, M.; Gao, F.F.; Su, Q.X.; Wu, J. Brain Cannabinoid Receptor 2: Expression, Function and Modulation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofek, O.; Karsak, M.; Leclerc, N.; Fogel, M.; Frenkel, B.; Wright, K.; Tam, J.; Attar-Namdar, M.; Kram, V.; Shohami, E.; et al. Peripheral Cannabinoid Receptor, CB2, Regulates Bone Mass. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 696–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, S.; Sun, X.; Lima, I.V.; Tavenier, A.; de Oliveira, A.C.P.; Dey, S.K.; Danzer, S.C. Cannabinoid Receptor 1/2 Double-Knockout Mice Develop Epilepsy. Epilepsia 2017, 58, e162–e166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Alvaro, A.; Aracil-Fernández, A.; García-Gutiérrez, M.S.; Navarrete, F.; Manzanares, J. Deletion of CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor Induces Schizophrenia-Related Behaviors in Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2011, 36, 1489–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canseco-Alba, A.; Rodríguez-Manzo, G. Cannabis: Drug of Abuse and Therapeutic Agent, Two Sides of the Same Coin. Rev. Investig. Clin. 2023, 75, 105–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Marzo, V.; Stella, N.; Zimmer, A. Endocannabinoid Signalling and the Deteriorating Brain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackie, K. Endocannabinoid-Mediated Synaptic Plasticity. In Endocannabinoid Regulation of Monoamines in Psychiatric and Neurological Disorders; Van Bockstaele, E.J., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 11–24. [Google Scholar]
- Leo, L.M.; Abood, M.E. CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling and Biased Signaling. Molecules 2021, 26, 5413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher-Jones, A.; Hildick, K.L.; Evans, A.J.; Nakamura, Y.; Henley, J.M.; Wilkinson, K.A. Protein Interactors and Trafficking Pathways That Regulate the Cannabinoid Type 1 Receptor (CB1R). Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veilleux, A.; Di Marzo, V.; Silvestri, C. The Expanded Endocannabinoid System/Endocannabinoidome as a Potential Target for Treating Diabetes Mellitus. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2019, 19, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mechoulam, R.; Gaoni, Y. A total synthesis of dl-Δ1-Tetrahydrocannabinol, the active constituent of hashish. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1965, 87, 3273–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsi, D.J.; Murphy, M.S.Q.; Cook, J. The Effects of Cannabis on Female Reproductive Health Across the Life Course. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res. 2021, 6, 275–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alipour, A.; Patel, P.B.; Shabbir, Z.; Gabrielson, S. Review of the Many Faces of Synthetic Cannabinoid Toxicities. Ment. Health Clin. 2019, 9, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghuis, P.; Rajnicek, A.M.; Morozov, Y.M.; Ross, R.A.; Mulder, J.; Urbán, G.M.; Monory, K.; Marsicano, G.; Matteoli, M.; Canty, A.; et al. Hardwiring the Brain: Endocannabinoids Shape Neuronal Connectivity. Science 2007, 316, 1212–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antypa, M.; Faux, C.; Eichele, G.; Parnavelas, J.G.; Andrews, W.D. Differential Gene Expression in Migratory Streams of Cortical Interneurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 34, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kano, M.; Ohno-Shosaku, T.; Hashimotodani, Y.; Uchigashima, M.; Watanabe, M. Endocannabinoid-Mediated Control of Synaptic Transmission. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 309–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkany, T.; Mackie, K.; Doherty, P. Wiring and Firing Neuronal Networks: Endocannabinoids Take Center Stage. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2008, 18, 338–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bisogno, T.; Howell, F.; Williams, G.; Minassi, A.; Cascio, M.G.; Ligresti, A.; Matias, I.; Schiano-Moriello, A.; Paul, P.; Williams, E.J.; et al. Cloning of the First Sn1-DAG Lipases Points to the Spatial and Temporal Regulation of Endocannabinoid Signaling in the Brain. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 163, 463–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duff, G.; Argaw, A.; Cecyre, B.; Cherif, H.; Tea, N.; Zabouri, N.; Casanova, C.; Ptito, M.; Bouchard, J.F. Cannabinoid Receptor CB2 Modulates Axon Guidance. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e70849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keimpema, E.; Barabas, K.; Morozov, Y.M.; Tortoriello, G.; Torii, M.; Cameron, G.; Yanagawa, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Mackie, K.; Harkany, T. Differential Subcellular Recruitment of Monoacylglycerol Lipase Generates Spatial Specificity of 2-Arachidonoyl Glycerol Signaling during Axonal Pathfinding. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 13992–14007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keimpema, E.; Alpar, A.; Howell, F.; Malenczyk, K.; Hobbs, C.; Hurd, Y.L.; Watanabe, M.; Sakimura, K.; Kano, M.; Doherty, P.; et al. Diacylglycerol Lipase α Manipulation Reveals Developmental Roles for Intercellular Endocannabinoid Signaling. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morozov, Y.M.; Torii, M.; Rakic, P. Origin, Early Commitment, Migratory Routes, and Destination of Cannabinoid Type 1 Receptor-Containing Interneurons. Cereb. Cortex 2009, 19 (Suppl. S1), i78–i89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkany, T.; Guzmán, M.; Galve-Roperh, I.; Berghuis, P.; Devi, L.A.; Mackie, K. The Emerging Functions of Endocannabinoid Signaling during CNS Development. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2007, 28, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguado, T.; Palazuelos, J.; Monory, K.; Stella, N.; Cravatt, B.; Lutz, B.; Marsicano, G.; Kokaia, Z.; Guzmán, M.; Galve-Roperh, I. The Endocannabinoid System Promotes Astroglial Differentiation by Acting on Neural Progenitor Cells. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 1551–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, D.J.; Suetterlin, P.; Reisenberg, M.; Williams, G.; Doherty, P. Down-Regulation of Diacylglycerol Lipase-α during Neural Stem Cell Differentiation: Identification of Elements That Regulate Transcription. J. Neurosci. Res. 2010, 88, 735–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, M.B.; Suetterlin, P.; Yip, P.; Molina-Holgado, F.; Walker, D.J.; Oudin, M.J.; Zentar, M.P.; Pollard, S.; Yáñez-Muñoz, R.J.; Williams, G.; et al. A Diacylglycerol Lipase-CB2 Cannabinoid Pathway Regulates Adult Subventricular Zone Neurogenesis in an Age-Dependent Manner. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2008, 38, 526–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortoriello, G.; Morris, C.V.; Alpar, A.; Fuzik, J.; Shirran, S.L.; Calvigioni, D.; Keimpema, E.; Botting, C.H.; Reinecke, K.; Herdegen, T.; et al. Miswiring the Brain: Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol Disrupts Cortical Development by Inducing an SCG10/Stathmin-2 Degradation Pathway. EMBO J. 2014, 33, 668–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, E.J.; Walsh, F.S.; Doherty, P. The FGF Receptor Uses the Endocannabinoid Signaling System to Couple to an Axonal Growth Response. J. Cell Biol. 2003, 160, 481–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galve-Roperh, I.; Chiurchiù, V.; Díaz-Alonso, J.; Bari, M.; Guzmán, M.; Maccarrone, M. Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling in Progenitor/Stem Cell Proliferation and Differentiation. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 633–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.S.; Zhu, J.; Wager-Miller, J.; Wang, S.; O’Leary, D.; Monory, K.; Lutz, B.; MacKie, K.; Lu, H.C. Requirement of Cannabinoid CB1 Receptors in Cortical Pyramidal Neurons for Appropriate Development of Corticothalamic and Thalamocortical Projections. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2010, 32, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.C.; Gomes, I.; Nguyen, T.; Jayaram, G.; Ram, P.T.; Devi, L.A.; Iyengar, R. The G α(o/i)-Coupled Cannabinoid Receptor-Mediated Neurite Outgrowth Involves Rap Regulation of Src and Stat3. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33426–33434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goswami, C.; Schmidt, H.; Hucho, F. TRPV1 at Nerve Endings Regulates Growth Cone Morphology and Movement through Cytoskeleton Reorganization. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauckner, J.E.; Jensen, J.B.; Chen, H.Y.; Lu, H.C.; Hille, B.; Mackie, K. GPR55 Is a Cannabinoid Receptor That Increases Intracellular Calcium and Inhibits M Current. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, L.A.; Roelofs, A.J.; Anavi-Goffer, S.; Mowat, L.; Simpson, D.G.; Irving, A.J.; Rogers, M.J.; Rajnicek, A.M.; Ross, R.A. A Role for L-α-Lysophosphatidylinositol and GPR55 in the Modulation of Migration, Orientation and Polarization of Human Breast Cancer Cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2010, 160, 762–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chédotal, A.; Richards, L.J. Wiring the Brain: The Biology of Neuronal Guidance. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCormick, L.E.; Gupton, S.L. Mechanistic Advances in Axon Pathfinding. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2020, 63, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argaw, A.; Duff, G.; Zabouri, N.; Cécyre, B.; Chainé, N.; Cherif, H.; Tea, N.; Lutz, B.; Ptito, M.; Bouchard, J.F. Concerted Action of CB1 Cannabinoid Receptor and Deleted in Colorectal Cancer in Axon Guidance. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez, M.; Hernández, M.L.; Pazos, M.R.; Tolón, R.M.; Romero, J.; Fernández-Ruiz, J. Colocalization of CB1 Receptors with L1 and GAP-43 in Forebrain White Matter Regions during Fetal Rat Brain Development: Evidence for a Role of These Receptors in Axonal Growth and Guidance. Neuroscience 2008, 153, 687–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulder, J.; Aguado, T.; Keimpema, E.; Barabás, K.; Rosado, C.J.B.; Nguyen, L.; Menory, K.; Marsicano, G.; Di Marzo, V.; Hurd, Y.L.; et al. Endocannabinoid Signaling Controls Pyramidal Cell Specification and Long-Range Axon Patterning. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 8760–8765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begbie, J.; Doherty, P.; Graham, A. Cannabinoid Receptor, CB1, Expression Follows Neuronal Differentiation in the Early Chick Embryo. J. Anat. 2004, 205, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaffuri, A.L.; Ladarre, D.; Lenkei, Z. Type-1 Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling in Neuronal Development. Pharmacology 2012, 90, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina-Holgado, E.; Paniagua-Torija, B.; Arevalo-Martin, A.; Moreno-Luna, R.; Esteban, P.F.; Le, M.Q.U.; Del Cerro, M.d.M.; Garcia-Ovejero, D. Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Associates to Different Molecular Complexes during GABAergic Neuron Maturation. J. Neurochem. 2021, 158, 640–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bromberg, K.D.; Ma’ayan, A.; Neves, S.R.; Iyengar, R. Design Logic of a Cannabinoid Receptor Signaling Network That Triggers Neurite Outgrowth. Science 2008, 320, 903–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitalis, T.; Lainé, J.; Simon, A.; Roland, A.; Leterrier, C.; Lenkei, Z. The Type 1 Cannabinoid Receptor Is Highly Expressed in Embryonic Cortical Projection Neurons and Negatively Regulates Neurite Growth in Vitro. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 1705–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, R.; Lokmane, L.; Ozdemir, D.; Traoré, C.; Agesilas, A.; Hakibilen, C.; Lenkei, Z.; Zala, D. Local Glycolysis Fuels Actomyosin Contraction during Axonal Retraction. J. Cell Biol. 2023, 222, e202206133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roland, A.B.; Ricobaraza, A.; Carrel, D.; Jordan, B.M.; Rico, F.; Simon, A.; Humbert-Claude, M.; Ferrier, J.; McFadden, M.H.; Scheuring, S.; et al. Cannabinoid-Induced Actomyosin Contractility Shapes Neuronal Morphology and Growth. elife 2014, 3, e03159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, A.K.; Alecu, J.E.; Ziegler, M.; Vasilopoulou, C.G.; Merciai, F.; Jumo, H.; Afshar-Saber, W.; Sahin, M.; Ebrahimi-Fakhari, D.; Borner, G.H.H. AP-4-Mediated Axonal Transport Controls Endocannabinoid Production in Neurons. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Luo, P.; Liu, X.; Cheng, R.; Zhang, S.; Qian, X.; Liu, F. Roles of Fibroblast Growth Factors in the Axon Guidance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asimaki, O.; Leondaritis, G.; Lois, G.; Sakellaridis, N.; Mangoura, D. Cannabinoid 1 Receptor-Dependent Transactivation of Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor 1 Emanates from Lipid Rafts and Amplifies Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 Activation in Embryonic Cortical Neurons. J. Neurochem. 2011, 116, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghuis, P.; Dobszay, M.B.; Wang, X.; Spano, S.; Ledda, F.; Sousa, K.M.; Schulte, G.; Ernfors, P.; Mackie, K.; Paratcha, G.; et al. Endocannabinoids Regulate Interneuron Migration and Morphogenesis by Transactivating the TrkB Receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 19115–19120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itami, C.; Uesaka, N.; Huang, J.Y.; Lu, H.C.; Sakimura, K.; Kano, M.; Kimura, F. Endocannabinoid-Dependent Formation of Columnar Axonal Projection in the Mouse Cerebral Cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2022, 119, e2122700119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaques, S.C.; Kingsbury, A.; Henshcke, P.; Chomchai, C.; Clews, S.; Falconer, J.; Abdel-Latif, M.E.; Feller, J.M.; Oei, J.L. Cannabis, the Pregnant Woman and Her Child: Weeding out the Myths. J. Perinatol. 2014, 34, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Money, K.M.; Stanwood, G.D. Developmental Origins of Brain Disorders: Roles for Dopamine. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 7, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenney, S.P.; Kekuda, R.; Prasad, P.D.; Leibach, F.H.; Devoe, L.D.; Ganapathy, V. Cannabinoid Receptors and Their Role in the Regulation of the Serotonin Transporter in Human Placenta. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1999, 181, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conner, S.N.; Bedell, V.; Lipsey, K.; Macones, G.A.; Cahill, A.G.; Tuuli, M.G. Maternal Marijuana Use and Adverse Neonatal Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Obstetrics and gynecology. Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 128, 713–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunn, J.K.L.; Rosales, C.B.; Center, K.E.; Nuñez, A.; Gibson, S.J.; Christ, C.; Ehiri, J.E. Prenatal Exposure to Cannabis and Maternal and Child Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e009986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westfall, R.E.; Janssen, P.A.; Lucas, P.; Capler, R. Survey of Medicinal Cannabis Use among Childbearing Women: Patterns of Its Use in Pregnancy and Retroactive Self-Assessment of Its Efficacy against “Morning Sickness”. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 2006, 12, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campolongo, P.; Trezza, V.; Palmery, M.; Trabace, L.; Cuomo, V. Developmental Exposure to Cannabinoids Causes Subtle and Enduring Neurofunctional Alterations. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2009, 85, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alhowail, A.; Aldubayan, M. Mechanisms Underlying Cognitive Impairment Induced by Prenatal Cannabinoid Exposure: A Literature Review. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2023, 27, 4960–4975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayer, S.; Mandelbaum, A.D.; Watch, L.; Ryan, K.S.; Hedges, M.A.; Manuzak, J.A.; Easley, C.A.; Schust, D.J.; Lo, J.O. Cannabis and Pregnancy: A Review. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2023, 78, 411–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, N.; Yang, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C. Reduced Expression of Glutamate Receptors and Phosphorylation of CREB Are Responsible for in Vivo Δ9-THC Exposure-Impaired Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. J. Neurochem. 2010, 112, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.E.; Hatoum, A.S.; Fine, J.D.; Johnson, E.C.; Hansen, I.; Karcher, N.R.; Moreau, A.L.; Bondy, E.; Qu, Y.; Carter, E.B.; et al. Associations Between Prenatal Cannabis Exposure and Childhood Outcomes: Results From the ABCD Study. JAMA Psychiatry 2021, 78, 64–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldschmidt, L.; Richardson, G.A.; Willford, J.; Day, N.L. Prenatal Marijuana Exposure and Intelligence Test Performance at Age 6. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2008, 47, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Xie, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, H.; Bradshaw, H.B.; Dey, S.K. Endocannabinoid Signaling Directs Differentiation of Trophoblast Cell Lineages and Placentation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16887–16892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fine, J.D.; Moreau, A.L.; Karcher, N.R.; Agrawal, A.; Rogers, C.E.; Barch, D.M.; Bogdan, R. Association of Prenatal Cannabis Exposure with Psychosis Proneness Among Children in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development (ABCD) Study. JAMA Psychiatry 2019, 76, 762–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, K.S.; Conover, E.; Chambers, C.D. Update on the Developmental Consequences of Cannabis Use during Pregnancy and Lactation. Birth Defects Res. 2020, 112, 1126–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noland, J.S.; Singer, L.T.; Short, E.J.; Minnes, S.; Arendt, R.E.; Kirchner, H.L.; Bearer, C. Prenatal Drug Exposure and Selective Attention in Preschoolers. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2005, 27, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winiger, E.A.; Hewitt, J.K. Prenatal Cannabis Exposure and Sleep Outcomes in Children 9–10 Years of Age in the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development SM Study. Sleep Health 2020, 6, 787–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayatbakhsh, M.R.; Flenady, V.J.; Gibbons, K.S.; Kingsbury, A.M.; Hurrion, E.; Mamun, A.A.; Najman, J.M. Birth Outcomes Associated with Cannabis Use before and during Pregnancy. Pediatr. Res. 2012, 71, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klonoff-Cohen, H.; Lam-Kruglick, P. Maternal and Paternal Recreational Drug Use and Sudden Infant Death Syndrome. Arch. Pediatr. Adolesc. Med. 2001, 155, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Gelder, M.M.H.J.; Reefhuis, J.; Caton, A.R.; Werler, M.M.; Druschel, C.M.; Roeleveld, N. Maternal Periconceptional Illicit Drug Use and the Risk of Congenital Malformations. Epidemiology 2009, 20, 60–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.R.; Pan, C.H.; Hishimoto, A.; Li, C.Y.; Xi, Z.X.; Llorente-Berzal, A.; Viveros, M.P.; Ishiguro, H.; Arinami, T.; Onaivi, E.S.; et al. Species Differences in Cannabinoid Receptor 2 (CNR2 Gene): Identification of Novel Human and Rodent CB2 Isoforms, Differential Tissue Expression and Regulation by Cannabinoid Receptor Ligands. Genes Brain Behav. 2009, 8, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Kumar, U. Cannabinoid Receptors and the Endocannabinoid System: Signaling and Function in the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jutras-Aswad, D.; DiNieri, J.A.; Harkany, T.; Hurd, Y.L. Neurobiological Consequences of Maternal Cannabis on Human Fetal Development and Its Neuropsychiatric Outcome. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2009, 259, 395–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.P.; Yonamine, M. Bioanalytical and Methodological Challenges in the Evaluation of Fetal Cannabis Exposure. Bioanalysis 2018, 10, 713–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asher, M.J.; McMullan, H.M.; Dong, A.; Li, Y.; Thayer, S.A. A Complete Endocannabinoid Signaling System Modulates Synaptic Transmission between Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 2023, 103, 100–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, J.A.; Itskovitz-Eldor, J.; Shapiro, S.S.; Waknitz, M.A.; Swiergiel, J.J.; Marshall, V.S.; Jones, J.M. Embryonic Stem Cell Lines Derived from Human Blastocysts. Science 1998, 282, 1145–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergenreder, E.; Minotti, A.P.; Zorina, Y.; Oberst, P.; Zhao, Z.; Munguba, H.; Calder, E.L.; Baggiolini, A.; Walsh, R.M.; Liston, C.; et al. Author Correction: Combined Small-Molecule Treatment Accelerates Maturation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Neurons. Nat. Biotechnol. 2024, 42, 1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasca, A.M.; Sloan, S.A.; Clarke, L.E.; Tian, Y.; Makinson, C.D.; Huber, N.; Kim, C.H.; Park, J.Y.; O’Rourke, N.A.; Nguyen, K.D.; et al. Functional Cortical Neurons and Astrocytes from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells in 3D Culture. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Y.; Kirwan, P.; Livesey, F.J. Directed Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells to Cerebral Cortex Neurons and Neural Networks. Nat. Protoc. 2012, 7, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Renner, M.; Martin, C.A.; Wenzel, D.; Bicknell, L.S.; Hurles, M.E.; Homfray, T.; Penninger, J.M.; Jackson, A.P.; Knoblich, J.A. Cerebral Organoids Model Human Brain Development and Microcephaly. Nature 2013, 501, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takebe, T.; Wells, J.M. Organoids by Design. Science 2019, 364, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Mouse Embryonic and Adult Fibroblast Cultures by Defined Factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, K.; Tanabe, K.; Ohnuki, M.; Narita, M.; Ichisaka, T.; Tomoda, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of Pluripotent Stem Cells from Adult Human Fibroblasts by Defined Factors. Cell 2007, 131, 861–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, B.; Mazzoni, E.O. Cell Reprogramming: The Many Roads to Success. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 35, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Sances, S.; Workman, M.J.; Svendsen, C.N. Multi-Lineage Human IPSC-Derived Platforms for Disease Modeling and Drug Discovery. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 309–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Knoblich, J.A. Generation of Cerebral Organoids from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 2329–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eiraku, M.; Watanabe, K.; Matsuo-Takasaki, M.; Kawada, M.; Yonemura, S.; Matsumura, M.; Wataya, T.; Nishiyama, A.; Muguruma, K.; Sasai, Y. Self-Organized Formation of Polarized Cortical Tissues from ESCs and Its Active Manipulation by Extrinsic Signals. Cell Stem Cell 2008, 3, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danjo, T.; Eiraku, M.; Muguruma, K.; Watanabe, K.; Kawada, M.; Yanagawa, Y.; Rubenstein, J.L.R.; Sasai, Y. Subregional Specification of Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Ventral Telencephalic Tissues by Timed and Combinatory Treatment with Extrinsic Signals. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 1919–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, J.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, A.X.; Cukuroglu, E.; Tran, H.D.; Göke, J.; Tan, Z.Y.; Saw, T.Y.; Tan, C.P.; Lokman, H.; et al. Midbrain-like Organoids from Human Pluripotent Stem Cells Contain Functional Dopaminergic and Neuromelanin-Producing Neurons. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 19, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakaguchi, H.; Kadoshima, T.; Soen, M.; Narii, N.; Ishida, Y.; Ohgushi, M.; Takahashi, J.; Eiraku, M.; Sasai, Y. Generation of Functional Hippocampal Neurons from Self-Organizing Human Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Dorsomedial Telencephalic Tissue. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muguruma, K.; Nishiyama, A.; Kawakami, H.; Hashimoto, K.; Sasai, Y. Self-Organization of Polarized Cerebellar Tissue in 3D Culture of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells. Cell Rep. 2015, 10, 537–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Nguyen, H.N.; Song, M.M.; Hadiono, C.; Ogden, S.C.; Hammack, C.; Yao, B.; Hamersky, G.R.; Jacob, F.; Zhong, C.; et al. Brain-Region-Specific Organoids Using Mini-Bioreactors for Modeling ZIKV Exposure. Cell 2016, 165, 1238–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Jacob, F.; Song, M.M.; Nguyen, H.N.; Song, H.; Ming, G.L. Generation of Human Brain Region-Specific Organoids Using a Miniaturized Spinning Bioreactor. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 565–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, N.; Vaslin, C.; Barata, T.C.; Frarma, Y.; Contremoulins, V.; Baudin, X.; Nedelec, S.; Ribes, V.C. BMP4 Patterns Smad Activity and Generates Stereotyped Cell Fate Organization in Spinal Organoids. Development 2019, 146, dev175430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Song, H.; Ming, G.L. Brain Organoids: Advances, Applications and Challenges. Development 2019, 146, dev166074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lancaster, M.A.; Knoblich, J.A. Organogenesis in a Dish: Modeling Development and Disease Using Organoid Technologies. Science 2014, 345, 1247125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, J.; Simonini, M.V.; Palejev, D.; Tomasini, L.; Coppola, G.; Szekely, A.M.; Horvath, T.L.; Vaccarino, F.M. Modeling Human Cortical Development in Vitro Using Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12770–12775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Yang, J.; Xiang, Y. Modeling Human Neurodevelopmental Diseases with Brain Organoids. Cell Regen. 2022, 11, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trujillo, C.A.; Muotri, A.R. Brain Organoids and the Study of Neurodevelopment. Trends Mol. Med. 2018, 24, 982–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pas, S.P. The Rise of Three-Dimensional Human Brain Cultures. Nature 2018, 553, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Bhattacharyya, A. Human Models Are Needed for Studying Human Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 103, 829–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silbereis, J.C.; Pochareddy, S.; Zhu, Y.; Li, M.; Sestan, N. The Cellular and Molecular Landscapes of the Developing Human Central Nervous System. Neuron 2016, 89, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Fu, Y.; Williams, J.; Wood, J.A.; Pandarinathan, L.; Avraham, S.; Makriyannis, A.; Avraham, S.; Avraham, H.K. Expression and Function of Cannabinoid Receptors CB1 and CB2 and Their Cognate Cannabinoid Ligands in Murine Embryonic Stem Cells. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nones, J.; Spohr, T.C.; Furtado, D.R.; Sartore, R.C.; Paulsen, B.S.; Guimarães, M.Z.; Rehen, S.K. Cannabinoids Modulate Cell Survival in Embryoid Bodies. Cell Biol. Int. 2010, 34, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ao, Z.; Cai, H.; Havert, D.J.; Wu, Z.; Gong, Z.; Beggs, J.M.; Mackie, K.; Guo, F. One-Stop Microfluidic Assembly of Human Brain Organoids To Model Prenatal Cannabis Exposure. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 4630–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papariello, A.; Taylor, D.; Soderstrom, K.; Litwa, K. CB1 Antagonism Increases Excitatory Synaptogenesis in a Cortical Spheroid Model of Fetal Brain Development. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paraíso-Luna, J.; Aguareles, J.; Martín, R.; Ayo-Martín, A.C.; Simón-Sánchez, S.; Garcıá-Rincón, D.; Costas-Insua, C.; Garcıá-Taboada, E.; de Salas-Quiroga, A.; Dıáz-Alonso, J.; et al. Endocannabinoid Signalling in Stem Cells and Cerebral Organoids Drives Differentiation to Deep Layer Projection Neurons via CB1 Receptors. Development 2020, 147, dev192161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shum, C.; Dutan, L.; Annuario, E.; Warre-Cornish, K.; Taylor, S.E.; Taylor, R.D.; Andreae, L.C.; Buckley, N.J.; Price, J.; Bhattacharyya, S.; et al. Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol and 2-AG Decreases Neurite Outgrowth and Differentially Affects ERK1/2 and Akt Signaling in HiPSC-Derived Cortical Neurons. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2020, 103, 103463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, C.C.; Barata, T.; Vaz, S.H.; Ferreira, C.; Quintas, A.; Bekman, E.P. HiPSC-Based Model of Prenatal Exposure to Cannabinoids: Effect on Neuronal Differentiation. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanslowsky, N.; Jahn, K.; Venneri, A.; Naujock, M.; Haase, A.; Martin, U.; Frieling, H.; Wegner, F. Functional Effects of Cannabinoids during Dopaminergic Specification of Human Neural Precursors Derived from Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Addict. Biol. 2017, 22, 1329–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamanaka, S. Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells: Past, Present, and Future. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muratore, C.R.; Srikanth, P.; Callahan, D.G.; Young-Pearse, T.L. Comparison and Optimization of HiPSC Forebrain Cortical Differentiation Protocols. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Chen, X.; Dowbaj, A.M.; Sljukic, A.; Bratlie, K.; Lin, L.; Fong, E.L.S.; Balachander, G.M.; Chen, Z.; Soragni, A.; et al. Organoids. Nature reviews. Methods Primers 2022, 2, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Chen, D.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Y.; Yang, J.; Lin, C.; Dang, X.; Cen, Z.; Liang, D.; et al. A Live-Cell Image-Based Machine Learning Strategy for Reducing Variability in PSC Differentiation Systems. Cell Discov. 2023, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, Z.; Bourgeois-Tchir, N.; Lyashenko, E.; Cundiff, P.E.; Cullen, P.F.; Challa, R.; Li, K.; Zhang, X.; Casey, F.; Engle, S.J.; et al. Characterizing the Composition of IPSC Derived Cells from Bulk Transcriptomics Data with CellMap. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 17394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.H.; Haddad, G. Brain Organoid Protocols and Limitations. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1351734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavon, N.; Sun, Y.; Pak, C.H. Cell Type Specification and Diversity in Subpallial Organoids. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1440583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birtele, M.; Lancaster, M.; Quadrato, G. Modelling Human Brain Development and Disease with Organoids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2024. Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Chen, J.; Deng, Z.; Sun, T.; Luo, Q.; Gong, H.; Li, X.; Long, B. Multiscale Analysis of Cellular Composition and Morphology in Intact Cerebral Organoids. Biology 2022, 11, 1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, B. Approaches to Vascularizing Human Brain Organoids. PLoS Biol. 2023, 21, e3002141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Ju, X.C.; Li, Y.; Zeng, P.M.; Wu, J.; Zhou, Y.Y.; Shen, L.B.; Dong, J.; Chen, Y.J.; Luo, Z.G. Generation of Vascularized Brain Organoids to Study Neurovascular Interactions. elife 2022, 11, e76707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gao, L.; Zhao, L.; Zou, T.; Xu, H. Toward the next Generation of Vascularized Human Neural Organoids. Med. Res. Rev. 2023, 43, 31–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Platform Study | Drug | Biological Effects | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| hiPSC-derived neuron/astrocyte cultures | Win-2 Δ9-THC 2-AG Carbachol | hiPSC-derived neuronal cultures displayed a glutamatergic signaling network and sensitivity to synthetic cannabinoids and endocannabinoids. Additionally, these cells produced endocannabinoids, like 2-AG, in response to carbachol in a Ca2+-independent manner, while Δ9-THC acted as a partial agonist inhibiting synaptic activity. | [100] |
| Human cerebral organoids from ESCs | Δ9-THC | Prolonged exposure to Δ9-THC showed brain organoids with altered neurite outgrowth, reduced neuronal maturation, and down-regulation of CB1 expression. | [130] |
| Cortical spheroid model of neurodevelopment | CB1-selective antagonist SR141716A | CB1 receptors regulated the synaptic strength and the balance of inhibitory and excitatory signaling. Acute SR141716A treatment contributed to demonstrate the role of the endocannabinoid system in regulating neuronal connections and synaptic activity. | [131] |
| hiPSC-derived cerebral organoids | HU-210, CB1 agonist THC | CB1 receptor participated in neuronal differentiation of deep layer neurons. THC and CB1 agonist HU-210 promoted the expansion of BCL11B+ neurons, meanwhile reducing the number of SATB2+ upper layer neurons. | [132] |
| Cortical neurons derived from human hiPSCs | 2-AG Δ9-THC SR 141716A, CB1 Selective inverse agonist | Cortical neurons derived from hiPSCs expressed CB1 and responded to cannabinoids; 2AG and Δ9-THC reduced neurite outgrowth and phosphorylation of serine/threonine kinase extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (ERK1/2), while Δ9-THC reduced phosphorylation of Akt. These effects could be blocked by a CB1 receptor antagonist. | [133] |
| Neuronal cells derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) | Cannabidiol (CBD) Δ9-THC THJ-018 and EG-018, synthetic cannabinoids (SCs) | These compounds promoted alterations in neuronal development; CBD is neurotoxic, reducing cellular density in cultures of neuronal progenitor and differentiated neurons. SCs and Δ9-THC induced premature glial and neuronal differentiation and abnormal function of voltage-gated calcium channels in neurons. | [134] |
| Human cord blood-derived induced pluripotent stem cell (hCBiPSC)-derived small molecule neural precursor cells (smNPSc) | Anandamide (AEA), endogenous cannabinoid, CB1 receptor agonist Δ9-THC, exogenous cannabinoid, CB1 receptor agonist | High concentrations (10 µM) of AEA or THC during human neurogenesis reduced synaptic activity, action potential firing, and voltage-gated ion currents, affecting neuronal functionality, while low concentrations (1 µM) of AEA increased synaptic activity in neurons. | [135] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Estudillo, E.; Castillo-Arellano, J.I.; Martínez, E.; Rangel-López, E.; López-Ornelas, A.; Magaña-Maldonado, R.; Adalid-Peralta, L.; Velasco, I.; Escobedo-Ávila, I. Modeling the Effect of Cannabinoid Exposure During Human Neurodevelopment Using Bidimensional and Tridimensional Cultures. Cells 2025, 14, 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14020070
Estudillo E, Castillo-Arellano JI, Martínez E, Rangel-López E, López-Ornelas A, Magaña-Maldonado R, Adalid-Peralta L, Velasco I, Escobedo-Ávila I. Modeling the Effect of Cannabinoid Exposure During Human Neurodevelopment Using Bidimensional and Tridimensional Cultures. Cells. 2025; 14(2):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14020070
Chicago/Turabian StyleEstudillo, Enrique, Jorge Iván Castillo-Arellano, Emilio Martínez, Edgar Rangel-López, Adolfo López-Ornelas, Roxana Magaña-Maldonado, Laura Adalid-Peralta, Iván Velasco, and Itzel Escobedo-Ávila. 2025. "Modeling the Effect of Cannabinoid Exposure During Human Neurodevelopment Using Bidimensional and Tridimensional Cultures" Cells 14, no. 2: 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14020070
APA StyleEstudillo, E., Castillo-Arellano, J. I., Martínez, E., Rangel-López, E., López-Ornelas, A., Magaña-Maldonado, R., Adalid-Peralta, L., Velasco, I., & Escobedo-Ávila, I. (2025). Modeling the Effect of Cannabinoid Exposure During Human Neurodevelopment Using Bidimensional and Tridimensional Cultures. Cells, 14(2), 70. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14020070







