Gut Microbiome Modulation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Preventive Role in NAFLD/NASH Progression and Potential Applications in Immunotherapy-Based Strategies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Direct and Indirect Roles of Gut Microbiota in HCC Development
2.1. Gut Integrity in Chronic Liver Disease and HCC
2.2. Dysbiosis in Chronic Liver Disease and HCC
2.3. Microbial Metabolites in Chronic Liver Disease and HCC
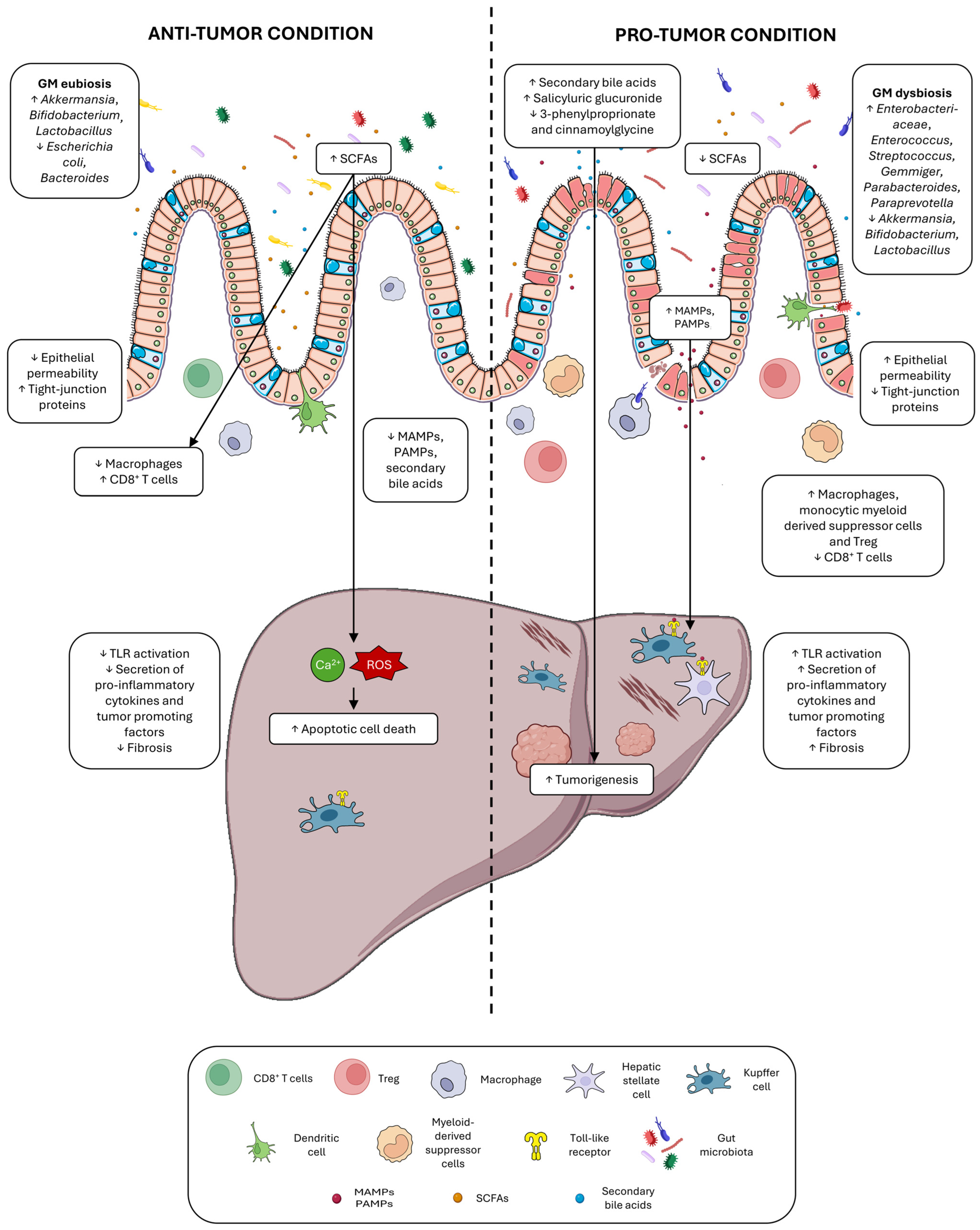
Bile Acid Changes in Chronic Liver Disease and HCC
3. NAFLD-HCC Pathogenesis
3.1. NAFLD Progression and Dysbiosis of the Gut and Liver Microbiome
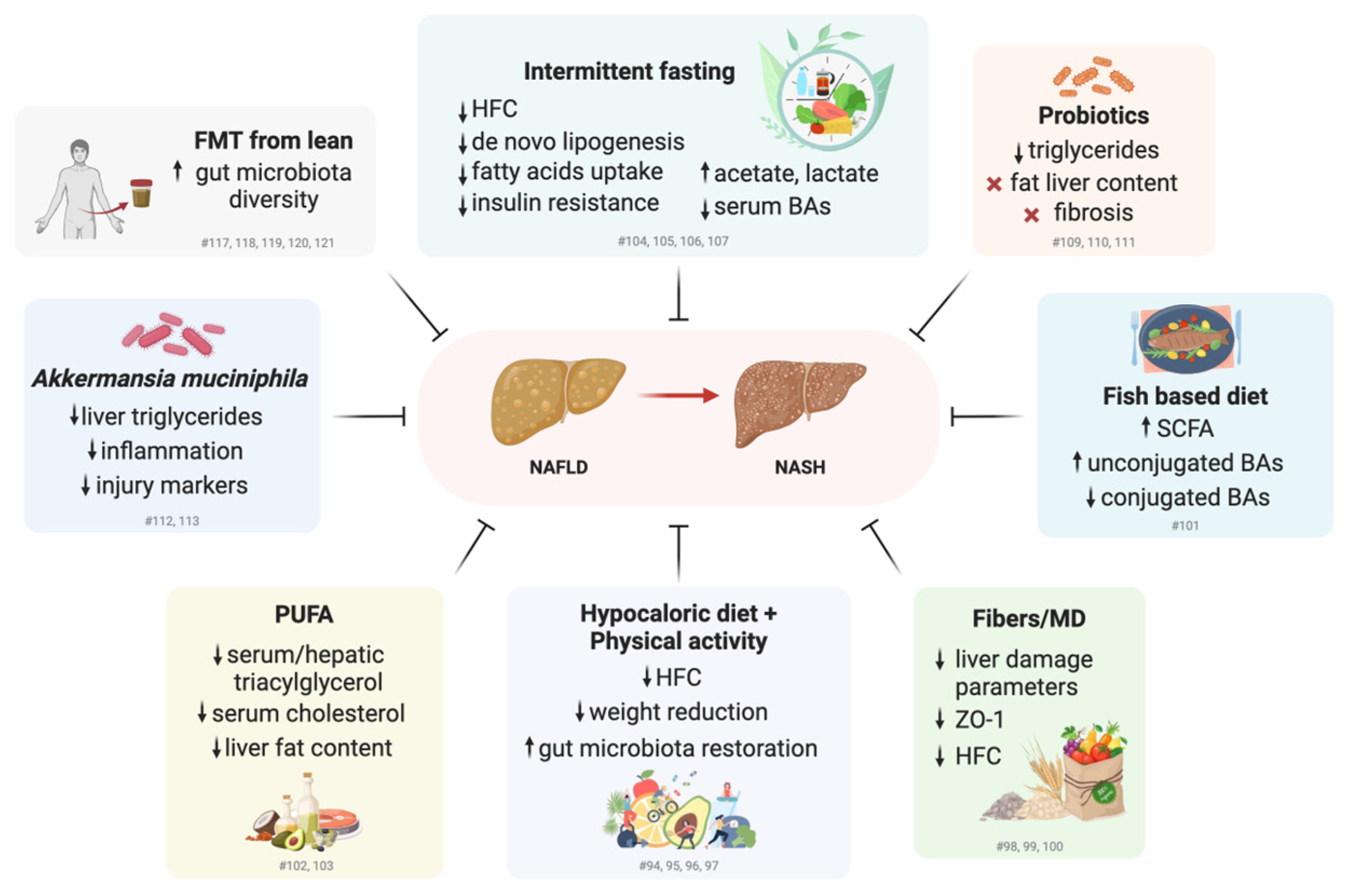
3.2. Promoting Healthy Lifestyles and Modulating Gut Microbiome Composition for the Treatment of NAFLD: Clinical and Preclinical Studies
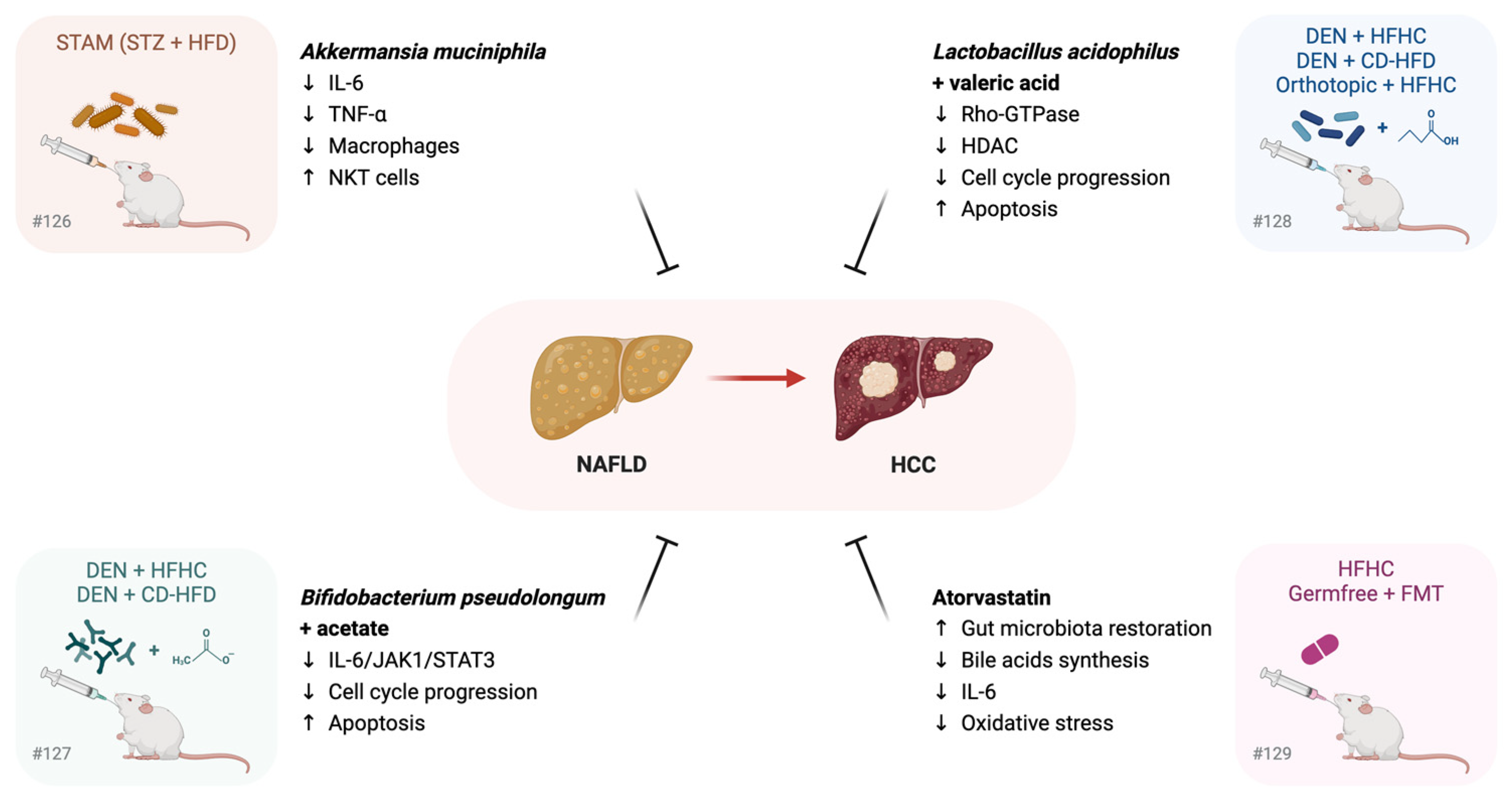
3.3. Gut Microbiome Restoration in the Prevention of NAFLD Progression to HCC: Preclinical Studies
4. Systemic Treatments for Advanced HCCs
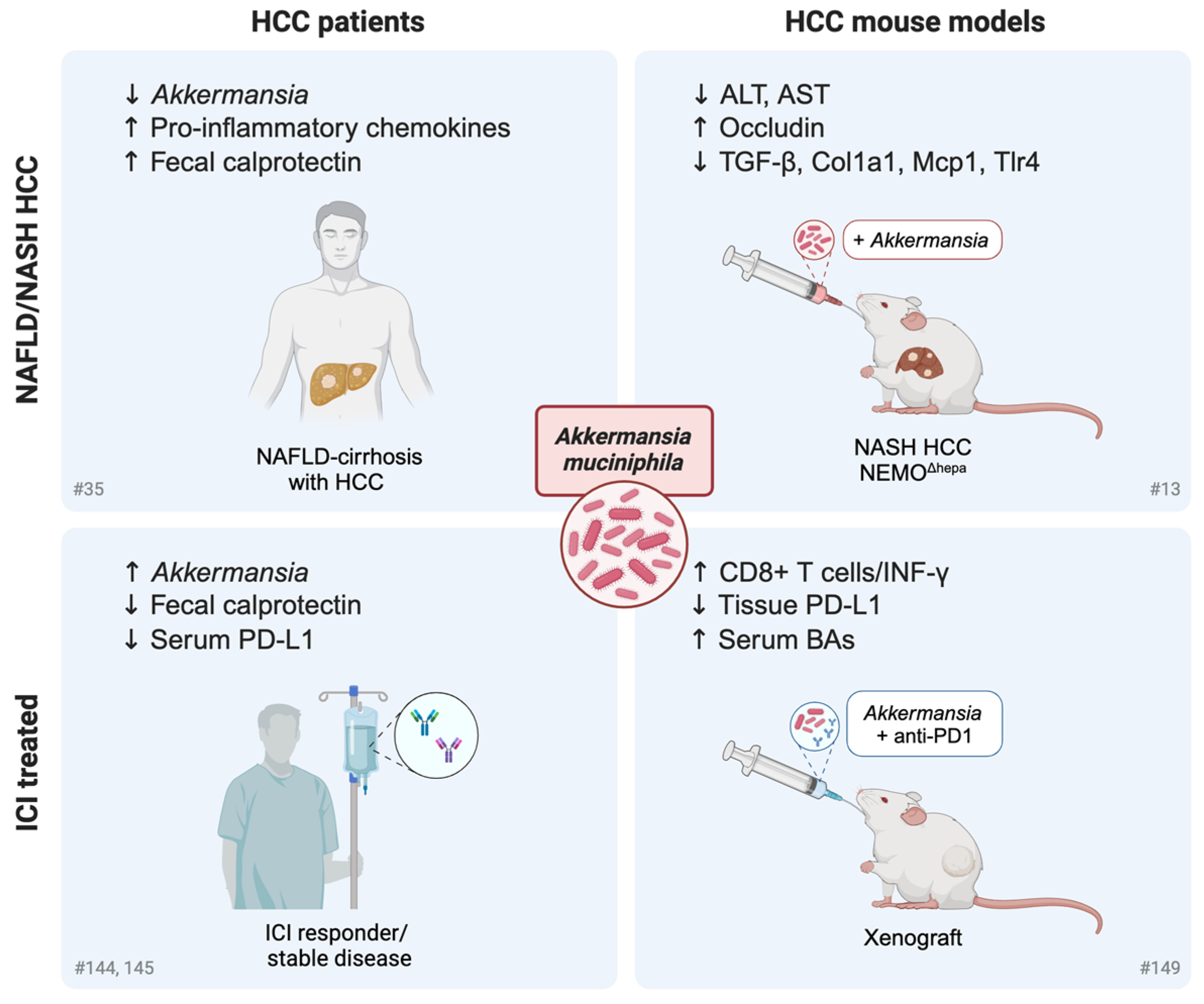
Influence of the Gut Microbiome and Its Modulation on Response to Immunotherapy in HCC
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riazi, K.; Azhari, H.; Charette, J.H.; Underwood, F.E.; King, J.A.; Afshar, E.E.; Swain, M.G.; Congly, S.E.; Kaplan, G.G.; Shaheen, A.-A. The Prevalence and Incidence of NAFLD Worldwide: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 7, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singal, A.G.; Kanwal, F.; Llovet, J.M. Global Trends in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Epidemiology: Implications for Screening, Prevention and Therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 20, 864–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estes, C.; Anstee, Q.M.; Arias-Loste, M.T.; Bantel, H.; Bellentani, S.; Caballeria, J.; Colombo, M.; Craxi, A.; Crespo, J.; Day, C.P.; et al. Modeling NAFLD Disease Burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the Period 2016–2030. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reig, M.; Forner, A.; Rimola, J.; Ferrer-Fàbrega, J.; Burrel, M.; Garcia-Criado, Á.; Kelley, R.K.; Galle, P.R.; Mazzaferro, V.; Salem, R.; et al. BCLC Strategy for Prognosis Prediction and Treatment Recommendation: The 2022 Update. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 681–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waldman, A.D.; Fritz, J.M.; Lenardo, M.J. A Guide to Cancer Immunotherapy: From T Cell Basic Science to Clinical Practice. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 651–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gordan, J.D.; Kennedy, E.B.; Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Beal, E.; Finn, R.S.; Gade, T.P.; Goff, L.; Gupta, S.; Guy, J.; Hoang, H.T.; et al. Systemic Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: ASCO Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2024, 40, 1830–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, D.; Núñez, N.G.; Pinyol, R.; Govaere, O.; Pinter, M.; Szydlowska, M.; Gupta, R.; Qiu, M.; Deczkowska, A.; Weiner, A.; et al. NASH Limits Anti-Tumour Surveillance in Immunotherapy-Treated HCC. Nature 2021, 592, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Yu, C.-H.; Li, X.-J.; Yao, J.-M.; Fang, Z.-Y.; Yoon, S.-H.; Yu, W.-Y. Gut Dysbiosis in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Therapeutic Implications. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 997018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderburg, C.; Luedde, T. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in the Development and Progression of Liver Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajapakse, J.; Khatiwada, S.; Akon, A.C.; Yu, K.L.; Shen, S.; Zekry, A. Unveiling the Complex Relationship between Gut Microbiota and Liver Cancer: Opportunities for Novel Therapeutic Interventions. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2240031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iida, N.; Mizukoshi, E.; Yamashita, T.; Yutani, M.; Seishima, J.; Wang, Z.; Arai, K.; Okada, H.; Yamashita, T.; Sakai, Y.; et al. Chronic Liver Disease Enables Gut Enterococcus Faecalis Colonization to Promote Liver Carcinogenesis. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 1039–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, K.M.; Mohs, A.; Gui, W.; Galvez, E.J.C.; Candels, L.S.; Hoenicke, L.; Muthukumarasamy, U.; Holland, C.H.; Elfers, C.; Kilic, K.; et al. Imbalanced Gut Microbiota Fuels Hepatocellular Carcinoma Development by Shaping the Hepatic Inflammatory Microenvironment. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 3964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan, V.; Helmink, B.A.; Spencer, C.N.; Reuben, A.; Wargo, J.A. The Influence of the Gut Microbiome on Cancer, Immunity, and Cancer Immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Chen, X.; Yang, X.; Zhang, B. Understanding Gut Dysbiosis for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Diagnosis and Treatment. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2024, 35, 1006–1020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilg, H.; Adolph, T.E.; Trauner, M. Gut-Liver Axis: Pathophysiological Concepts and Clinical Implications. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 1700–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.L.; Schnabl, B. The Gut–Liver Axis and Gut Microbiota in Health and Liver Disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 719–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripathi, A.; Debelius, J.; Brenner, D.A.; Karin, M.; Loomba, R.; Schnabl, B.; Knight, R. The Gut-Liver Axis and the Intersection with the Microbiome. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 397–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ijssennagger, N.; van Rooijen, K.S.; Magnúsdóttir, S.; Ramos Pittol, J.M.; Willemsen, E.C.L.; de Zoete, M.R.; Baars, M.J.D.; Stege, P.B.; Colliva, C.; Pellicciari, R.; et al. Ablation of Liver Fxr Results in an Increased Colonic Mucus Barrier in Mice. JHEP Rep. Innov. Hepatol. 2021, 3, 100344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everard, A.; Belzer, C.; Geurts, L.; Ouwerkerk, J.P.; Druart, C.; Bindels, L.B.; Guiot, Y.; Derrien, M.; Muccioli, G.G.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Cross-Talk between Akkermansia Muciniphila and Intestinal Epithelium Controls Diet-Induced Obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9066–9071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benedé-Ubieto, R.; Cubero, F.J.; Nevzorova, Y.A. Breaking the Barriers: The Role of Gut Homeostasis in Metabolic-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD). Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2331460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mouries, J.; Brescia, P.; Silvestri, A.; Spadoni, I.; Sorribas, M.; Wiest, R.; Mileti, E.; Galbiati, M.; Invernizzi, P.; Adorini, L.; et al. Microbiota-Driven Gut Vascular Barrier Disruption Is a Prerequisite for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis Development. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 1216–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwabe, R.F.; Greten, T.F. Gut Microbiome in HCC—Mechanisms, Diagnosis and Therapy. J. Hepatol. 2020, 72, 230–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapito, D.H.; Mencin, A.; Gwak, G.-Y.; Pradere, J.-P.; Jang, M.-K.; Mederacke, I.; Caviglia, J.M.; Khiabanian, H.; Adeyemi, A.; Bataller, R.; et al. Promotion of Hepatocellular Carcinoma by the Intestinal Microbiota and TLR4. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 504–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ram, A.K.; Vairappan, B.; Srinivas, B.H. Nimbolide Attenuates Gut Dysbiosis and Prevents Bacterial Translocation by Improving Intestinal Barrier Integrity and Ameliorating Inflammation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Phytother. Res. PTR 2022, 36, 2143–2160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-L.; Yu, L.-X.; Yang, W.; Tang, L.; Lin, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhai, B.; Tan, Y.-X.; Shan, L.; Liu, Q.; et al. Profound Impact of Gut Homeostasis on Chemically-Induced pro-Tumorigenic Inflammation and Hepatocarcinogenesis in Rats. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fang, Y.; Liang, W.; Cai, Y.; Wong, C.C.; Wang, J.; Wang, N.; Lau, H.C.-H.; Jiao, Y.; Zhou, X.; et al. Gut-Liver Translocation of Pathogen Klebsiella Pneumoniae Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Mice. Nat. Microbiol. 2025; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Tan, J.; Qian, W.; Zhang, L.; Hou, X. Gut Inflammation Exacerbates Hepatic Injury in the High-Fat Diet Induced NAFLD Mouse: Attention to the Gut-Vascular Barrier Dysfunction. Life Sci. 2018, 209, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-L.; Liu, C.; Yang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, L.; Guo, X.; Niu, C.; Zhang, N.-P.; Ding, J.; Wu, J. Dynamic Changes of Gut Microbiota in Mouse Models of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis and Its Transition to Hepatocellular Carcinoma. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2024, 38, e23766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orci, L.A.; Lacotte, S.; Delaune, V.; Slits, F.; Oldani, G.; Lazarevic, V.; Rossetti, C.; Rubbia-Brandt, L.; Morel, P.; Toso, C. Effects of the Gut-Liver Axis on Ischaemia-Mediated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence in the Mouse Liver. J. Hepatol. 2018, 68, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshahrani, M.Y.; Oghenemaro, E.F.; Rizaev, J.; Kyada, A.; Roopashree, R.; Kumar, S.; Taha, Z.A.; Yadav, G.; Mustafa, Y.F.; Abosaoda, M.K. Exploring the Modulation of TLR4 and Its Associated ncRNAs in Cancer Immunopathogenesis, with an Emphasis on the Therapeutic Implications and Mechanisms Underlying Drug Resistance. Hum. Immunol. 2025, 86, 111188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Croce, C.M. MicroRNA: Trends in Clinical Trials of Cancer Diagnosis and Therapy Strategies. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1314–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Li, A.; Jiang, J.; Zhou, L.; Yu, Z.; Lu, H.; Xie, H.; Chen, X.; Shao, L.; Zhang, R.; et al. Gut Microbiome Analysis as a Tool towards Targeted Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Early Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut 2019, 68, 1014–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Feng, Q.; Wong, S.H.; Zhang, D.; Liang, Q.Y.; Qin, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhao, H.; Stenvang, J.; Li, Y.; et al. Metagenomic Analysis of Faecal Microbiome as a Tool towards Targeted Non-Invasive Biomarkers for Colorectal Cancer. Gut 2017, 66, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Bhoori, S.; Castelli, C.; Putignani, L.; Rivoltini, L.; Del Chierico, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Morelli, D.; Paroni Sterbini, F.; Petito, V.; et al. Hepatocellular Carcinoma Is Associated With Gut Microbiota Profile and Inflammation in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2019, 69, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behary, J.; Amorim, N.; Jiang, X.-T.; Raposo, A.; Gong, L.; McGovern, E.; Ibrahim, R.; Chu, F.; Stephens, C.; Jebeili, H.; et al. Gut Microbiota Impact on the Peripheral Immune Response in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Effenberger, M.; Waschina, S.; Bronowski, C.; Sturm, G.; Tassiello, O.; Sommer, F.; Zollner, A.; Watschinger, C.; Grabherr, F.; Gstir, R.; et al. A Gut Bacterial Signature in Blood and Liver Tissue Characterizes Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e00182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujkovic-Cvijin, I.; Sklar, J.; Jiang, L.; Natarajan, L.; Knight, R.; Belkaid, Y. Host Variables Confound Gut Microbiota Studies of Human Disease. Nature 2020, 587, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Q.; Liang, S.; Jia, H.; Stadlmayr, A.; Tang, L.; Lan, Z.; Zhang, D.; Xia, H.; Xu, X.; Jie, Z.; et al. Gut Microbiome Development along the Colorectal Adenoma–Carcinoma Sequence. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grąt, M.; Wronka, K.M.; Krasnodębski, M.; Masior, Ł.; Lewandowski, Z.; Kosińska, I.; Grąt, K.; Stypułkowski, J.; Rejowski, S.; Wasilewicz, M.; et al. Profile of Gut Microbiota Associated With the Presence of Hepatocellular Cancer in Patients With Liver Cirrhosis. Transplant. Proc. 2016, 48, 1687–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pallozzi, M.; De Gaetano, V.; Di Tommaso, N.; Cerrito, L.; Santopaolo, F.; Stella, L.; Gasbarrini, A.; Ponziani, F.R. Role of Gut Microbial Metabolites in the Pathogenesis of Primary Liver Cancers. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfora, E.E.; Meex, R.C.R.; Venema, K.; Blaak, E.E. Gut Microbial Metabolites in Obesity, NAFLD and T2DM. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2019, 15, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caussy, C.; Hsu, C.; Lo, M.-T.; Liu, A.; Bettencourt, R.; Ajmera, V.H.; Bassirian, S.; Hooker, J.; Sy, E.; Richards, L.; et al. Link between Gut-Microbiome Derived Metabolite and Shared Gene-Effects with Hepatic Steatosis and Fibrosis in NAFLD. Hepatology 2018, 68, 918–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.I.; Fontillas, A.C.; Kwan, S.-Y.; Sanchez, C.I.; Calderone, T.L.; Lee, J.L.; Elsaiey, A.; Cleere, D.W.; Wei, P.; Vierling, J.M.; et al. Metabolomics Biomarkers of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in a Prospective Cohort of Patients with Cirrhosis. JHEP Rep. Innov. Hepatol. 2024, 6, 101119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yi, Y.; Wu, T.; Chen, N.; Gu, X.; Xiang, L.; Jiang, Z.; Li, J.; Jin, H. Integrated Microbiome and Metabolome Analysis Reveals the Interaction between Intestinal Flora and Serum Metabolites as Potential Biomarkers in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patients. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1170748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, E.R.; Lam, Y.K.; Uhlig, H.H. Short-Chain Fatty Acids: Linking Diet, the Microbiome and Immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2024, 24, 577–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Che, Y.; Chen, G.; Guo, Q.; Duan, Y.; Feng, H.; Xia, Q. Gut Microbial Metabolite Butyrate Improves Anticancer Therapy by Regulating Intracellular Calcium Homeostasis. Hepatology 2023, 78, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Xu, B.; Wang, X.; Wan, W.-H.; Lu, J.; Kong, D.; Jin, Y.; You, W.; Sun, H.; Mu, X.; et al. Gut Microbiota-Derived Short-Chain Fatty Acids Regulate Group 3 Innate Lymphoid Cells in HCC. Hepatology 2023, 77, 48–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.; Yang, L.; Liang, Y.; Liu, F.; Hu, J.; Zhang, R.; Li, Y.; Yuan, L.; Feng, F.B. Thetaiotaomicron-Derived Acetic Acid Modulate Immune Microenvironment and Tumor Growth in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2297846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Chang, W.-Y.; Gong, D.-A.; Xia, J.; Chen, W.; Huang, L.-Y.; Liu, R.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, K.; et al. High Dietary Fructose Promotes Hepatocellular Carcinoma Progression by Enhancing O-GlcNAcylation via Microbiota-Derived Acetate. Cell Metab. 2023, 35, 1961–1975.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Zang, D.; Sun, H.; Sun, Y.; Chen, J. Butyrate as a Promising Therapeutic Target in Cancer: From Pathogenesis to Clinic (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2024, 64, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlström, A.; Sayin, S.I.; Marschall, H.-U.; Bäckhed, F. Intestinal Crosstalk between Bile Acids and Microbiota and Its Impact on Host Metabolism. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, W.; Xie, G.; Jia, W. Bile Acid-Microbiota Crosstalk in Gastrointestinal Inflammation and Carcinogenesis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchs, C.D.; Simbrunner, B.; Baumgartner, M.; Campbell, C.; Reiberger, T.; Trauner, M. Bile Acid Metabolism and Signalling in Liver Disease. J. Hepatol. 2025, 82, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, S.L.; Stine, J.G.; Bisanz, J.E.; Okafor, C.D.; Patterson, A.D. Bile Acids and the Gut Microbiota: Metabolic Interactions and Impacts on Disease. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2023, 21, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Lau, H.C.; Zhang, X.; Yu, J. Bile Acids, Gut Microbiota, and Therapeutic Insights in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Biol. Med. 2023, 21, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smirnova, E.; Muthiah, M.D.; Narayan, N.; Siddiqui, M.S.; Puri, P.; Luketic, V.A.; Contos, M.J.; Idowu, M.; Chuang, J.-C.; Billin, A.N.; et al. Metabolic Reprogramming of the Intestinal Microbiome with Functional Bile Acid Changes Underlie the Development of NAFLD. Hepatology 2022, 76, 1811–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, S.; Loo, T.M.; Atarashi, K.; Kanda, H.; Sato, S.; Oyadomari, S.; Iwakura, Y.; Oshima, K.; Morita, H.; Hattori, M.; et al. Obesity-Induced Gut Microbial Metabolite Promotes Liver Cancer through Senescence Secretome. Nature 2013, 499, 97–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, S.; Takashina, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Nagamine, R.; Saito, Y.; Kamada, N.; Saito, H. Bile Acid Metabolism Regulated by the Gut Microbiota Promotes Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Mice. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 9925–9939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Han, M.; Heinrich, B.; Fu, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Sandhu, M.; Agdashian, D.; Terabe, M.; Berzofsky, J.A.; Fako, V.; et al. Gut Microbiome-Mediated Bile Acid Metabolism Regulates Liver Cancer via NKT Cells. Science 2018, 360, eaan5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conde de la Rosa, L.; Garcia-Ruiz, C.; Vallejo, C.; Baulies, A.; Nuñez, S.; Monte, M.J.; Marin, J.J.G.; Baila-Rueda, L.; Cenarro, A.; Civeira, F.; et al. STARD1 Promotes NASH-Driven HCC by Sustaining the Generation of Bile Acids through the Alternative Mitochondrial Pathway. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1429–1441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larabi, A.B.; Masson, H.L.P.; Bäumler, A.J. Bile Acids as Modulators of Gut Microbiota Composition and Function. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2172671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Anstee, Q.M.; Marietti, M.; Hardy, T.; Henry, L.; Eslam, M.; George, J.; Bugianesi, E. Global Burden of NAFLD and NASH: Trends, Predictions, Risk Factors and Prevention. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 15, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michelotti, G.A.; Machado, M.V.; Diehl, A.M. NAFLD, NASH and Liver Cancer. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilg, H.; Moschen, A.R.; Roden, M. NAFLD and Diabetes Mellitus. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J.; Sanyal, A.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.; Tiribelli, C.; Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.; Bugianesi, E.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; et al. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Golabi, P.; Paik, J.M.; Henry, A.; Van Dongen, C.; Henry, L. The Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH): A Systematic Review. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1335–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, L.A.; Lymp, J.F.; St Sauver, J.; Sanderson, S.O.; Lindor, K.D.; Feldstein, A.; Angulo, P. The Natural History of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Population-Based Cohort Study. Gastroenterology 2005, 129, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buzzetti, E.; Pinzani, M.; Tsochatzis, E.A. The Multiple-Hit Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016, 65, 1038–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McPherson, S.; Hardy, T.; Henderson, E.; Burt, A.D.; Day, C.P.; Anstee, Q.M. Evidence of NAFLD Progression from Steatosis to Fibrosing-Steatohepatitis Using Paired Biopsies: Implications for Prognosis and Clinical Management. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekstedt, M.; Hagström, H.; Nasr, P.; Fredrikson, M.; Stål, P.; Kechagias, S.; Hultcrantz, R. Fibrosis Stage Is the Strongest Predictor for Disease-Specific Mortality in NAFLD after up to 33 Years of Follow-Up. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1547–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, D.L.; Kanwal, F.; El-Serag, H.B. Association between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Risk for Hepatocellular Cancer, Based on Systematic Review. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2012, 10, 1342–1359.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.R.; Mapakshi, S.; Natarajan, Y.; Chayanupatkul, M.; Richardson, P.A.; Li, L.; Desiderio, R.; Thrift, A.P.; Asch, S.M.; et al. Risk of Hepatocellular Cancer in Patients With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1828–1837.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanwal, F.; Kramer, J.R.; Li, L.; Dai, J.; Natarajan, Y.; Yu, X.; Asch, S.M.; El-Serag, H.B. Effect of Metabolic Traits on the Risk of Cirrhosis and Hepatocellular Cancer in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2020, 71, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piscaglia, F.; Svegliati-Baroni, G.; Barchetti, A.; Pecorelli, A.; Marinelli, S.; Tiribelli, C.; Bellentani, S.; HCC-NAFLD Italian Study Group. Clinical Patterns of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Multicenter Prospective Study. Hepatology 2016, 63, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motta, B.M.; Masarone, M.; Torre, P.; Persico, M. From Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) to Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC): Epidemiology, Incidence, Predictions, Risk Factors, and Prevention. Cancers 2023, 15, 5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Kikuta, J.; Matsui, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Fujii, K.; Okuzaki, D.; Liu, Y.-C.; Yoshioka, T.; Seno, S.; Motooka, D.; et al. Periportal Macrophages Protect against Commensal-Driven Liver Inflammation. Nature 2024, 629, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stols-Gonçalves, D.; Mak, A.L.; Madsen, M.S.; van der Vossen, E.W.J.; Bruinstroop, E.; Henneman, P.; Mol, F.; Scheithauer, T.P.M.; Smits, L.; Witjes, J.; et al. Faecal Microbiota Transplantation Affects Liver DNA Methylation in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Multi-Omics Approach. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2223330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirola, C.J.; Salatino, A.; Quintanilla, M.F.; Castaño, G.O.; Garaycoechea, M.; Sookoian, S. The Influence of Host Genetics on Liver Microbiome Composition in Patients with NAFLD. EBioMedicine 2022, 76, 103858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juárez-Fernández, M.; Goikoetxea-Usandizaga, N.; Porras, D.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Bravo, M.; Serrano-Maciá, M.; Simón, J.; Delgado, T.C.; Lachiondo-Ortega, S.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; et al. Enhanced Mitochondrial Activity Reshapes a Gut Microbiota Profile That Delays NASH Progression. Hepatology 2023, 77, 1654–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Lyu, B.; Xie, F.; Li, F.; Xing, Y.; Han, Z.; Lai, J.; Ma, J.; Zou, Y.; Zeng, H.; et al. From Gut to Liver: Unveiling the Differences of Intestinal Microbiota in NAFL and NASH Patients. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1366744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senghor, B.; Sokhna, C.; Ruimy, R.; Lagier, J.-C. Gut Microbiota Diversity According to Dietary Habits and Geographical Provenance. Hum. Microbiome J. 2018, 7–8, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Wu, W.; Zheng, H.-M.; Li, P.; McDonald, D.; Sheng, H.-F.; Chen, M.-X.; Chen, Z.-H.; Ji, G.-Y.; Zheng, Z.-D.-X.; et al. Regional Variation Limits Applications of Healthy Gut Microbiome Reference Ranges and Disease Models. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1532–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, E.K.; Stagaman, K.; Dethlefsen, L.; Bohannan, B.J.M.; Relman, D.A. The Application of Ecological Theory toward an Understanding of the Human Microbiome. Science 2012, 336, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Astbury, S.; Atallah, E.; Vijay, A.; Aithal, G.P.; Grove, J.I.; Valdes, A.M. Lower Gut Microbiome Diversity and Higher Abundance of Proinflammatory Genus Collinsella Are Associated with Biopsy-Proven Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saga, K.; Iwashita, Y.; Hidano, S.; Aso, Y.; Isaka, K.; Kido, Y.; Tada, K.; Takayama, H.; Masuda, T.; Hirashita, T.; et al. Secondary Unconjugated Bile Acids Induce Hepatic Stellate Cell Activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, T.; Castro, R.E.; Pinto, S.N.; Coutinho, A.; Lucas, S.D.; Moreira, R.; Rodrigues, C.M.P.; Prieto, M.; Fernandes, F. Deoxycholic Acid Modulates Cell Death Signaling through Changes in Mitochondrial Membrane Properties. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 2158–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenneally, S.; Sier, J.H.; Moore, J.B. Efficacy of Dietary and Physical Activity Intervention in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2017, 4, e000139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazidi, M.; Kengne, A.P. Higher Adherence to Plant-Based Diets Are Associated with Lower Likelihood of Fatty Liver. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2019, 38, 1672–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Taub, R.; Neff, G.W.; Lucas, K.J.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Alkhouri, N.; Bashir, M.R. Resmetirom for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2919–2928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, S.A.; Bedossa, P.; Guy, C.D.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Loomba, R.; Taub, R.; Labriola, D.; Moussa, S.E.; Neff, G.W.; Rinella, M.E.; et al. A Phase 3, Randomized, Controlled Trial of Resmetirom in NASH with Liver Fibrosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; Lavine, J.E.; Diehl, A.M.; Brunt, E.M.; Cusi, K.; Charlton, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; American Gastroenterological Association; American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases; et al. The Diagnosis and Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Practice Guideline by the American Gastroenterological Association, American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases, and American College of Gastroenterology. Gastroenterology 2012, 142, 1592–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL–EASD–EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Management of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 1121–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Promrat, K.; Kleiner, D.E.; Niemeier, H.M.; Jackvony, E.; Kearns, M.; Wands, J.R.; Fava, J.L.; Wing, R.R. Randomized Controlled Trial Testing the Effects of Weight Loss on Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2010, 51, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Ge, J.; Zhao, C.; Le, S.; Yang, Y.; Ke, D.; Wu, N.; Tan, X.; Zhang, X.; Du, X.; et al. Effect of Aerobic Exercise and Diet on Liver Fat in Pre-Diabetic Patients with Non-Alcoholic-Fatty-Liver-Disease: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, R.; Wang, L.; Le, S.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, X.; Yang, X.; Xu, T.; Xu, L.; Wiklund, P.; et al. A Randomized Controlled Trial for Response of Microbiome Network to Exercise and Diet Intervention in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, F.M.; Disciglio, V.; Franco, I.; Sorino, P.; Bonfiglio, C.; Bianco, A.; Campanella, A.; Lippolis, T.; Pesole, P.L.; Polignano, M.; et al. A Low Glycemic Index Mediterranean Diet Combined with Aerobic Physical Activity Rearranges the Gut Microbiota Signature in NAFLD Patients. Nutrients 2022, 14, 1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, M.; Maciejewska, D.; Ryterska, K.; Czerwińka-Rogowska, M.; Jamioł-Milc, D.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K.; Milkiewicz, P.; Raszeja-Wyszomirska, J.; Stachowska, E. Gut Permeability Might Be Improved by Dietary Fiber in Individuals with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) Undergoing Weight Reduction. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogianni, M.D.; Tileli, N.; Margariti, A.; Georgoulis, M.; Deutsch, M.; Tiniakos, D.; Fragopoulou, E.; Zafiropoulou, R.; Manios, Y.; Papatheodoridis, G. Adherence to the Mediterranean Diet Is Associated with the Severity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Clin. Nutr. Edinb. Scotl. 2014, 33, 678–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stachowska, E.; Portincasa, P.; Jamioł-Milc, D.; Maciejewska-Markiewicz, D.; Skonieczna-Żydecka, K. The Relationship between Prebiotic Supplementation and Anthropometric and Biochemical Parameters in Patients with NAFLD-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, K.; Guo, L.-L.; Tang, H.; Peng, X.; Li, J.; Feng, S.; Bie, C.; Chen, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; et al. A Freshwater Fish-Based Diet Alleviates Liver Steatosis by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites: A Clinical Randomized Controlled Trial in Chinese Participants With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 117, 1621–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šmíd, V.; Dvořák, K.; Stehnová, K.; Strnad, H.; Rubert, J.; Stříteský, J.; Staňková, B.; Stránská, M.; Hajšlová, J.; Brůha, R.; et al. The Ameliorating Effects of N-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids on Liver Steatosis Induced by a High-Fat Methionine Choline-Deficient Diet in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, H.M.; Johnson, N.A.; Burdon, C.A.; Cohn, J.S.; O’Connor, H.T.; George, J. Omega-3 Supplementation and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Yang, W.; Feng, W.; Huang, X.; Cen, M.; Peng, G.; Wu, W.; Wang, Z.; Jing, Y.; Long, T.; et al. Time-Restricted Feeding Ameliorates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease through Modulating Hepatic Nicotinamide Metabolism via Gut Microbiota Remodeling. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2390164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, J.; Guo, W.; Hu, M.; Jin, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Qiu, H.; Wang, K.; Zhuge, A.; Li, S.; et al. Resynchronized Rhythmic Oscillations of Gut Microbiota Drive Time-Restricted Feeding Induced Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Alleviation. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2221450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Xie, C.; Lu, S.; Nichols, R.G.; Tian, Y.; Li, L.; Patel, D.; Ma, Y.; Brocker, C.N.; Yan, T.; et al. Intermittent Fasting Promotes White Adipose Browning and Decreases Obesity by Shaping the Gut Microbiota. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 672–685.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, X.; Zhu, X.; Xin, Y.; Zhang, P.; Xiao, Y.; He, T.; Guo, H. Intermittent Fasting Alleviates Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis by Regulating Bile Acid Metabolism and Promoting Fecal Bile Acid Excretion in High-Fat and High-Cholesterol Diet Fed Mice. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2023, 67, e2200595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minciuna, I.; Gallage, S.; Heikenwalder, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Dufour, J.-F. Intermittent Fasting-the Future Treatment in NASH Patients? Hepatology 2023, 78, 1290–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.B.; Jun, D.W.; Kang, B.-K.; Lim, J.H.; Lim, S.; Chung, M.-J. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of a Multispecies Probiotic Mixture in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorletti, E.; Afolabi, P.R.; Miles, E.A.; Smith, D.E.; Almehmadi, A.; Alshathry, A.; Childs, C.E.; Del Fabbro, S.; Bilson, J.; Moyses, H.E.; et al. Synbiotics Alter Fecal Microbiomes, But Not Liver Fat or Fibrosis, in a Randomized Trial of Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1597–1610.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musazadeh, V.; Assadian, K.; Rajabi, F.; Faghfouri, A.H.; Soleymani, Y.; Kavyani, Z.; Najafiyan, B. The Effect of Synbiotics on Liver Enzymes, Obesity Indices, Blood Pressure, Lipid Profile, and Inflammation in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 208, 107398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Li, C.; Guo, S.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Hu, Y.; Song, B.; Jiang, Z.; Ge, Z.; et al. Gut Akkermansia Muciniphila Ameliorates Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease by Regulating the Metabolism of L-Aspartate via Gut-Liver Axis. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plovier, H.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Depommier, C.; Van Hul, M.; Geurts, L.; Chilloux, J.; Ottman, N.; Duparc, T.; Lichtenstein, L.; et al. A Purified Membrane Protein from Akkermansia Muciniphila or the Pasteurized Bacterium Improves Metabolism in Obese and Diabetic Mice. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Depommier, C.; Everard, A.; Druart, C.; Plovier, H.; Van Hul, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Falony, G.; Raes, J.; Maiter, D.; Delzenne, N.M.; et al. Supplementation with Akkermansia Muciniphila in Overweight and Obese Human Volunteers: A Proof-of-Concept Exploratory Study. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EFSA Panel on Nutrition, Novel Foods and Food Allergens (NDA); Turck, D.; Bohn, T.; Castenmiller, J.; De Henauw, S.; Hirsch-Ernst, K.I.; Maciuk, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; McArdle, H.J.; Naska, A.; et al. Safety of Pasteurised Akkermansia Muciniphila as a Novel Food Pursuant to Regulation (EU) 2015/2283. EFSA J. Eur. Food Saf. Auth. 2021, 19, e06780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijangos-Trejo, A.; Nuño-Lambarri, N.; Barbero-Becerra, V.; Uribe-Esquivel, M.; Vidal-Cevallos, P.; Chávez-Tapia, N. Prebiotics and Probiotics: Therapeutic Tools for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 14918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yadegar, A.; Bar-Yoseph, H.; Monaghan, T.M.; Pakpour, S.; Severino, A.; Kuijper, E.J.; Smits, W.K.; Terveer, E.M.; Neupane, S.; Nabavi-Rad, A.; et al. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation: Current Challenges and Future Landscapes. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2024, 37, e0006022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Lezana, T.; Raurell, I.; Bravo, M.; Torres-Arauz, M.; Salcedo, M.T.; Santiago, A.; Schoenenberger, A.; Manichanh, C.; Genescà, J.; Martell, M.; et al. Restoration of a Healthy Intestinal Microbiota Normalizes Portal Hypertension in a Rat Model of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2018, 67, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, D.; Pan, Q.; Shen, F.; Cao, H.; Ding, W.; Chen, Y.; Fan, J. Total Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Alleviates High-Fat Diet-Induced Steatohepatitis in Mice via Beneficial Regulation of Gut Microbiota. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Deng, Z.; Luo, W.; He, X.; Chen, Y. Effect of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 759306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witjes, J.J.; Smits, L.P.; Pekmez, C.T.; Prodan, A.; Meijnikman, A.S.; Troelstra, M.A.; Bouter, K.E.C.; Herrema, H.; Levin, E.; Holleboom, A.G.; et al. Donor Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Alters Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Obese Individuals With Steatohepatitis. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Nood, E.; Vrieze, A.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Fuentes, S.; Zoetendal, E.G.; De Vos, W.M.; Visser, C.E.; Kuijper, E.J.; Bartelsman, J.F.W.M.; Tijssen, J.G.P.; et al. Duodenal Infusion of Donor Feces for Recurrent Clostridium Difficile. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, C.R.; Kim, A.M.; Laine, L.; Wu, G.D. The AGA’s Fecal Microbiota Transplantation National Registry: An Important Step Toward Understanding Risks and Benefits of Microbiota Therapeutics. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 681–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Marchesini, G.; Pinto-Cortez, H.; Petta, S. Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Implications for Liver Transplantation. Transplantation 2019, 103, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Lin, X.; Shen, B.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Zhi, F. Akkermansia Muciniphila Suppressing Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis Associated Tumorigenesis through CXCR6+ Natural Killer T Cells. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1047570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sung, C.Y.J.; Lee, N.; Ni, Y.; Pihlajamäki, J.; Panagiotou, G.; El-Nezami, H. Probiotics Modulated Gut Microbiota Suppresses Hepatocellular Carcinoma Growth in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1306–E1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Wei, H.; Liang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, Y.; Ji, F.; Ho-Kwan Cheung, A.; Wong, N.; et al. Bifidobacterium Pseudolongum-Generated Acetate Suppresses Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1352–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, H.C.-H.; Zhang, X.; Ji, F.; Lin, Y.; Liang, W.; Li, Q.; Chen, D.; Fong, W.; Kang, X.; Liu, W.; et al. Lactobacillus Acidophilus Suppresses Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma through Producing Valeric Acid. EBioMedicine 2024, 100, 104952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Coker, O.O.; Chu, E.S.; Fu, K.; Lau, H.C.H.; Wang, Y.-X.; Chan, A.W.H.; Wei, H.; Yang, X.; Sung, J.J.Y.; et al. Dietary Cholesterol Drives Fatty Liver-Associated Liver Cancer by Modulating Gut Microbiota and Metabolites. Gut 2021, 70, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llovet, J.M.; Montal, R.; Sia, D.; Finn, R.S. Molecular Therapies and Precision Medicine for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 599–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.S.; Qin, S.; Ikeda, M.; Galle, P.R.; Ducreux, M.; Kim, T.-Y.; Kudo, M.; Breder, V.; Merle, P.; Kaseb, A.O.; et al. Atezolizumab plus Bevacizumab in Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 1894–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abou-Alfa, G.K.; Chan, S.L.; Kudo, M.; Lau, G.; Kelley, R.K.; Furuse, J.; Sukeepaisarnjaroen, W.; Kang, Y.-K.; Dao, T.V.; De Toni, E.N.; et al. Phase 3 Randomized, Open-Label, Multicenter Study of Tremelimumab (T) and Durvalumab (D) as First-Line Therapy in Patients (Pts) with Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma (uHCC): HIMALAYA. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhu, X.; Wu, Z.; Wei, Q.; Cai, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Hu, X.; Hu, H.; Zhang, X.; Pan, H.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of PD-1 Inhibitor Combined with Antiangiogenic Therapy for Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Multicenter Retrospective Study. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 3612–3622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz de Galarreta, M.; Bresnahan, E.; Molina-Sánchez, P.; Lindblad, K.E.; Maier, B.; Sia, D.; Puigvehi, M.; Miguela, V.; Casanova-Acebes, M.; Dhainaut, M.; et al. β-Catenin Activation Promotes Immune Escape and Resistance to Anti-PD-1 Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1124–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loo, T.M.; Kamachi, F.; Watanabe, Y.; Yoshimoto, S.; Kanda, H.; Arai, Y.; Nakajima-Takagi, Y.; Iwama, A.; Koga, T.; Sugimoto, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiota Promotes Obesity-Associated Liver Cancer through PGE2-Mediated Suppression of Antitumor Immunity. Cancer Discov. 2017, 7, 522–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foerster, F.; Gairing, S.J.; Ilyas, S.I.; Galle, P.R. Emerging Immunotherapy for HCC: A Guide for Hepatologists. Hepatology 2022, 75, 1604–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Routy, B.; Le Chatelier, E.; Derosa, L.; Duong, C.P.M.; Alou, M.T.; Daillère, R.; Fluckiger, A.; Messaoudene, M.; Rauber, C.; Roberti, M.P.; et al. Gut Microbiome Influences Efficacy of PD-1-Based Immunotherapy against Epithelial Tumors. Science 2018, 359, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Tu, J.; Pan, H.; Zhong, X.; Han, W.; Yao, J. Concomitant Medications Alter Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Advanced Digestive Tract Cancer Receiving PD-1 Checkpoint Inhibitors Combined with Antiangiogenetic Agents. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2024, 55, 1388–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, K.S.; Lam, L.K.; Seto, W.K.; Leung, W.K. Use of Antibiotics during Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Treatment Is Associated with Lower Survival in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2021, 10, 606–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fessas, P.; Naeem, M.; Pinter, M.; Marron, T.U.; Szafron, D.; Balcar, L.; Saeed, A.; Jun, T.; Dharmapuri, S.; Gampa, A.; et al. Early Antibiotic Exposure Is Not Detrimental to Therapeutic Effect from Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Liver Cancer 2021, 10, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinato, D.J.; Li, X.; Mishra-Kalyani, P.; D’Alessio, A.; Fulgenzi, C.A.M.; Scheiner, B.; Pinter, M.; Wei, G.; Schneider, J.; Rivera, D.R.; et al. Association between Antibiotics and Adverse Oncological Outcomes in Patients Receiving Targeted or Immune-Based Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. JHEP Rep. Innov. Hepatol. 2023, 5, 100747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, J.; Wang, D.; Long, J.; Yang, X.; Lin, J.; Song, Y.; Xie, F.; Xun, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiome Is Associated with the Clinical Response to Anti-PD-1 Based Immunotherapy in Hepatobiliary Cancers. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e003334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.-C.; Wu, C.-J.; Hung, Y.-W.; Lee, C.J.; Chi, C.-T.; Lee, I.-C.; Yu-Lun, K.; Chou, S.-H.; Luo, J.-C.; Hou, M.-C.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Metabolites Associate with Outcomes of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Treated Unresectable Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2022, 10, e004779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Wang, T.; Tu, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Tan, D.; Jiang, W.; Cai, S.; Zhao, P.; Song, R.; et al. Gut Microbiome Affects the Response to Anti-PD-1 Immunotherapy in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2019, 7, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponziani, F.R.; De Luca, A.; Picca, A.; Marzetti, E.; Petito, V.; Del Chierico, F.; Reddel, S.; Paroni Sterbini, F.; Sanguinetti, M.; Putignani, L.; et al. Gut Dysbiosis and Fecal Calprotectin Predict Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 1492–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, C.; Wang, S.; Xun, Z.; Zhang, D.; Lan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Chao, J.; Liang, Y.; Pu, Z.; et al. Characterizations of Multi-Kingdom Gut Microbiota in Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor-Treated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2024, 12, e008686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Zheng, X.; Pan, T.; Yang, X.; Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Peng, L.; Xie, C. Dynamic Microbiome and Metabolome Analyses Reveal the Interaction between Gut Microbiota and Anti-PD-1 Based Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 1321–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakatsu, G. Toward a Postbiotic Era of Microbiome Science: Opportunities to Advance Immunotherapies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 37, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, X.; Ma, J.; Huang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Hu, Y. Akkermansia Muciniphila Might Improve Anti-PD-1 Therapy against HCC by Changing Host Bile Acid Metabolism. J. Gene Med. 2024, 26, e3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poyet, M.; Groussin, M.; Gibbons, S.M.; Avila-Pacheco, J.; Jiang, X.; Kearney, S.M.; Perrotta, A.R.; Berdy, B.; Zhao, S.; Lieberman, T.D.; et al. A Library of Human Gut Bacterial Isolates Paired with Longitudinal Multiomics Data Enables Mechanistic Microbiome Research. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1442–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Zilberman-Schapira, G.; Mor, U.; Dori-Bachash, M.; Bashiardes, S.; Zur, M.; Regev-Lehavi, D.; Ben-Zeev Brik, R.; Federici, S.; et al. Post-Antibiotic Gut Mucosal Microbiome Reconstitution Is Impaired by Probiotics and Improved by Autologous FMT. Cell 2018, 174, 1406–1423.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porcari, S.; Fusco, W.; Spivak, I.; Fiorani, M.; Gasbarrini, A.; Elinav, E.; Cammarota, G.; Ianiro, G. Fine-Tuning the Gut Ecosystem: The Current Landscape and Outlook of Artificial Microbiome Therapeutics. Lancet Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 9, 460–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wieërs, G.; Belkhir, L.; Enaud, R.; Leclercq, S.; Philippart de Foy, J.-M.; Dequenne, I.; de Timary, P.; Cani, P.D. How Probiotics Affect the Microbiota. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 9, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Q.; Zhao, F.; Liu, W.; Lv, R.; Khine, W.W.T.; Han, J.; Sun, Z.; Lee, Y.-K.; Zhang, H. Probiotic-Directed Modulation of Gut Microbiota Is Basal Microbiome Dependent. Gut Microbes 2020, 12, 1736974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Comparison | HCC Etiology | Dysregulated Microbiome | Methodology | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| eHCC vs. cirrhosis | HBV infection | Actinobacteria phylum ↑, Gemmiger ↑, Parabacteroides ↑, Paraprevotella ↑ | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing | [33] |
| NAFLD-HCC vs. NAFLD-cirrhosis | NAFLD | Enterococcus ↑, Streptococcus ↑, Akkermansia ↓, Bifidobacterium ↓ | 16S rRNA amplicon sequencing | [35] |
| NAFLD-HCC vs. NAFLD-cirrhosis | NAFLD | Bacteroides caecimuris ↑, Veillonella parvula ↑, Clostridium bolteae ↑, Ruminococcus gnavus ↑, Enterobacteriaceae ↑ | Shotgun metagenomic sequencing | [36] |
| HCC vs. NAFLD | AFLD, NAFLD, HBV/HCV infection, PBC, PSC, AIH | Blautia ↓, Agathobacter ↓, Ruminococcaceae ↑, Bacteroidaceae ↑ | 16S rRNA sequencing | [37] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Monti, E.; Vianello, C.; Leoni, I.; Galvani, G.; Lippolis, A.; D’Amico, F.; Roggiani, S.; Stefanelli, C.; Turroni, S.; Fornari, F. Gut Microbiome Modulation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Preventive Role in NAFLD/NASH Progression and Potential Applications in Immunotherapy-Based Strategies. Cells 2025, 14, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14020084
Monti E, Vianello C, Leoni I, Galvani G, Lippolis A, D’Amico F, Roggiani S, Stefanelli C, Turroni S, Fornari F. Gut Microbiome Modulation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Preventive Role in NAFLD/NASH Progression and Potential Applications in Immunotherapy-Based Strategies. Cells. 2025; 14(2):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14020084
Chicago/Turabian StyleMonti, Elisa, Clara Vianello, Ilaria Leoni, Giuseppe Galvani, Annalisa Lippolis, Federica D’Amico, Sara Roggiani, Claudio Stefanelli, Silvia Turroni, and Francesca Fornari. 2025. "Gut Microbiome Modulation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Preventive Role in NAFLD/NASH Progression and Potential Applications in Immunotherapy-Based Strategies" Cells 14, no. 2: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14020084
APA StyleMonti, E., Vianello, C., Leoni, I., Galvani, G., Lippolis, A., D’Amico, F., Roggiani, S., Stefanelli, C., Turroni, S., & Fornari, F. (2025). Gut Microbiome Modulation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Preventive Role in NAFLD/NASH Progression and Potential Applications in Immunotherapy-Based Strategies. Cells, 14(2), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14020084







