Analysis of Ferric Protoporphyrin IX Effects on Human Platelets: Hematin Is a More Potent Agonist than Hemin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Approval
2.2. Reagents and Working Buffers
2.3. Human Platelets Preparation
2.4. Hematin and Hemin Preparation
2.5. Analysis of Hematin- and Hemin-Induced Activation, Aggregation, and Disaggregation Using the Laser Diffraction Method
2.6. Analysis of Platelet Ca2+ Mobilization
2.7. Flow Cytometry Analysis
2.7.1. Analysis of Platelet aIIbβ3 Integrin Activation
2.7.2. Analysis of Alpha and Dense Granule Secretion
Alpha Granule Secretion (CD62P/P-Selectin)
Dense Granule Secretion
2.7.3. Analysis of Phosphatidylserine Surface Exposure
2.7.4. Analysis of Platelet Viability
2.8. Confocal Microscopy
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
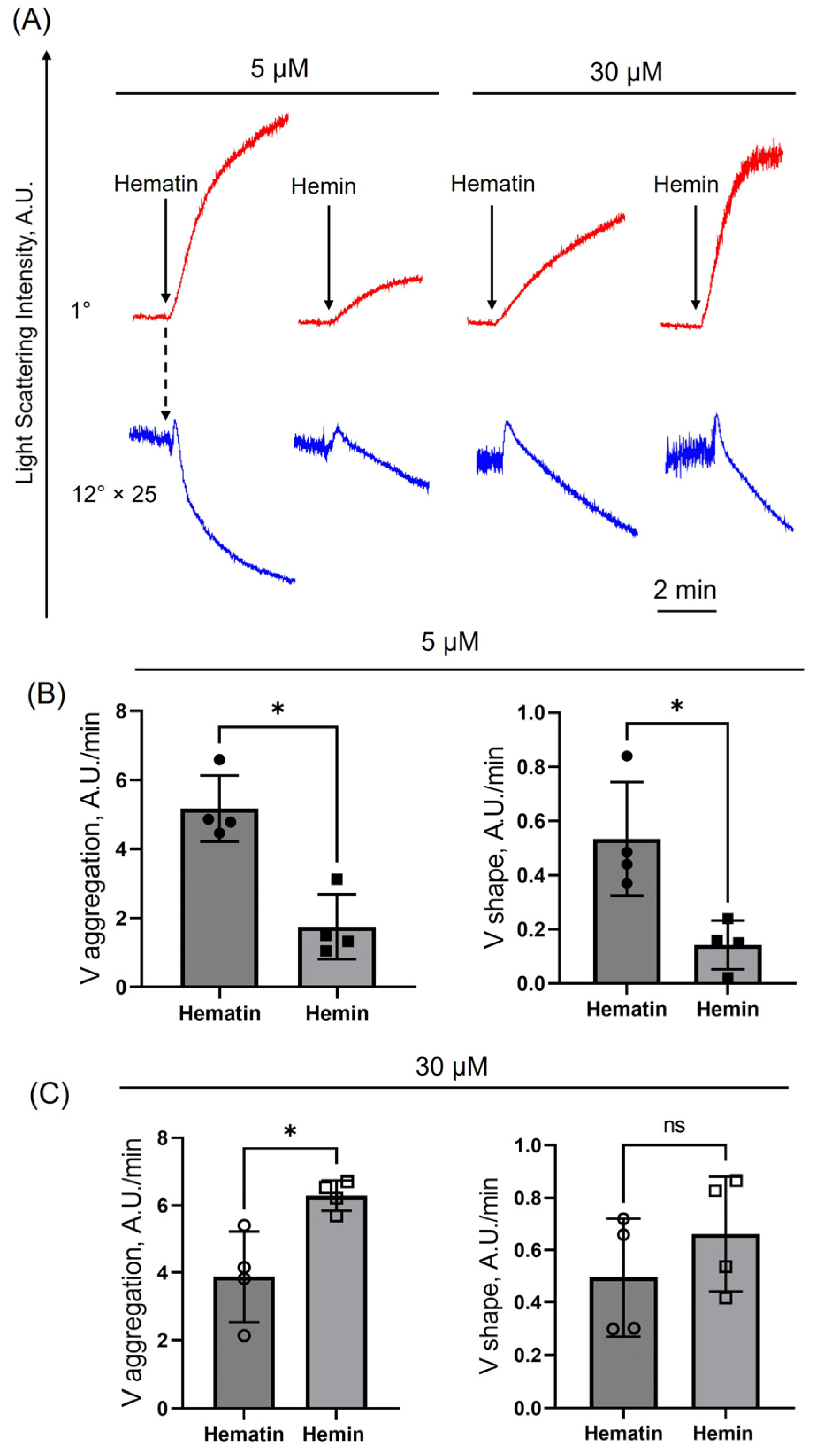
3.1. Hematin-Induced Platelet Activation Is More Pronounced than That of Hemin
3.2. Hematin at Low Concentrations Induces Reversible Intracellular Calcium Increase
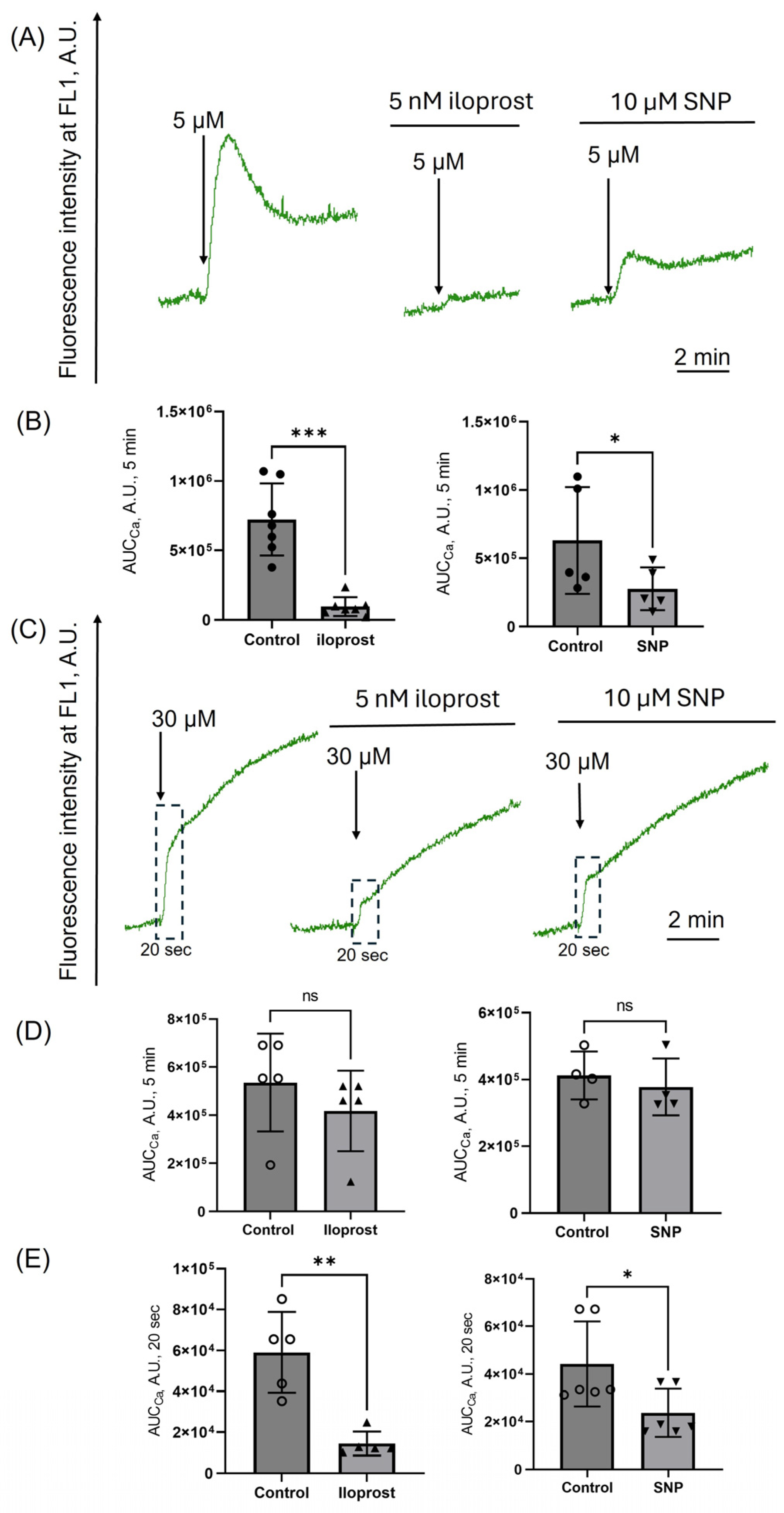
3.3. Platelet Aggregation Induced by Low Doses of Hematin Is Inhibited by cAMP/PKA and cGMP/PKG Signaling Pathways Activation
3.4. Activation of PKA/PKG Inhibits Calcium Increase Induced Only by Low Doses of Hematin
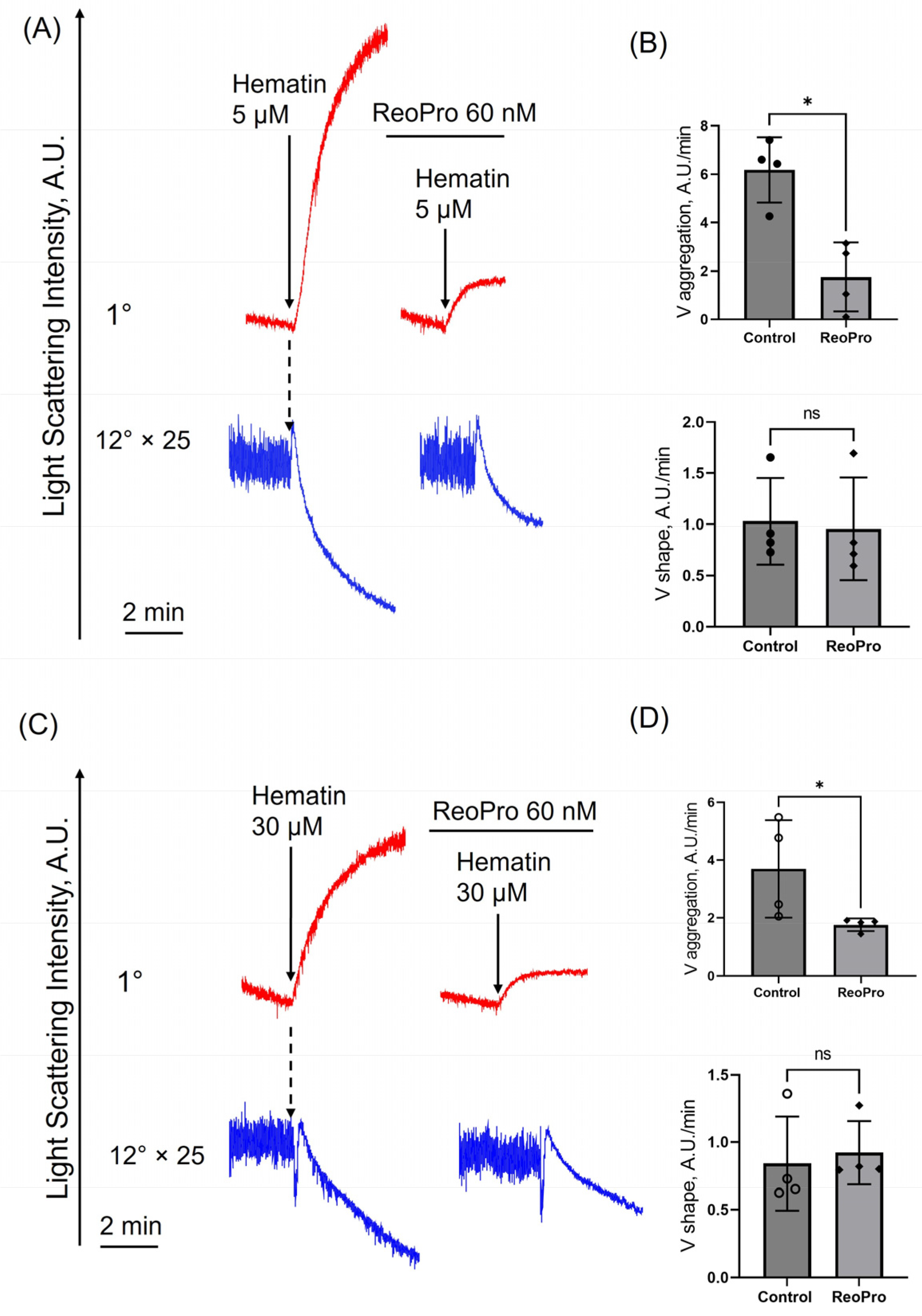
3.5. Hematin at Both Low and High Doses Induces Platelet Aggregation but Not Agglutination
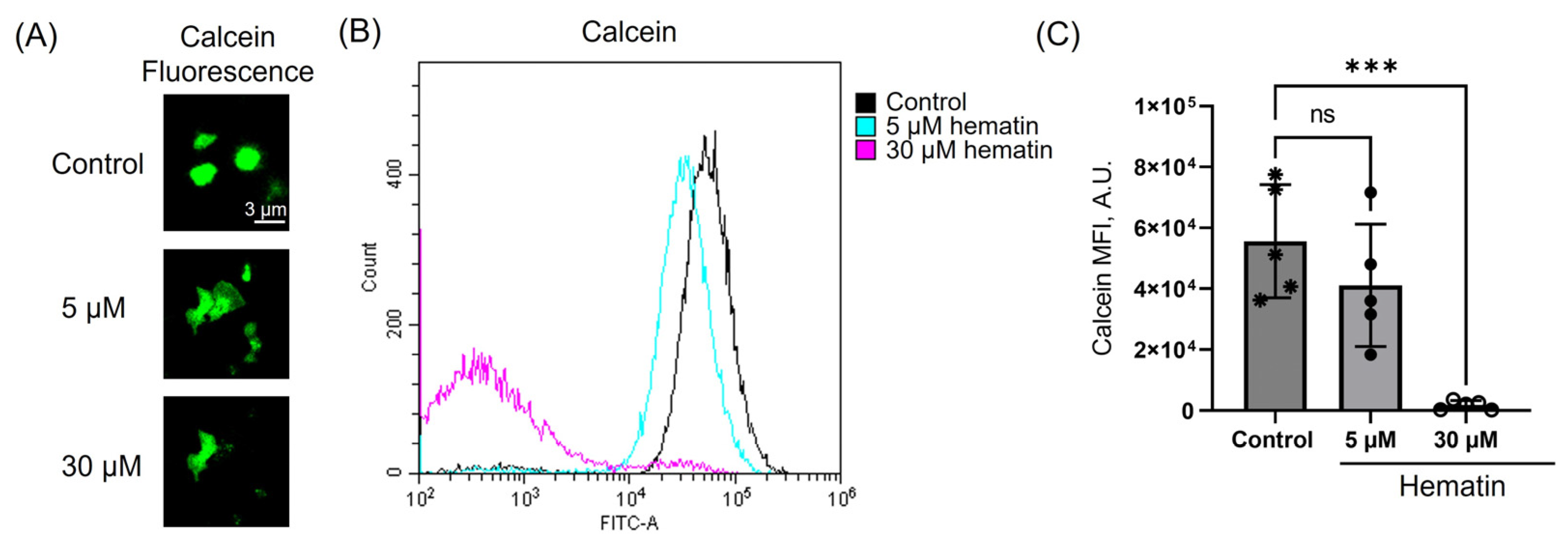
3.6. Hematin Decreases Platelet Viability Only at High Concentrations
3.7. Hematin Triggers Phosphatidylserine Exposure Only at High Concentrations
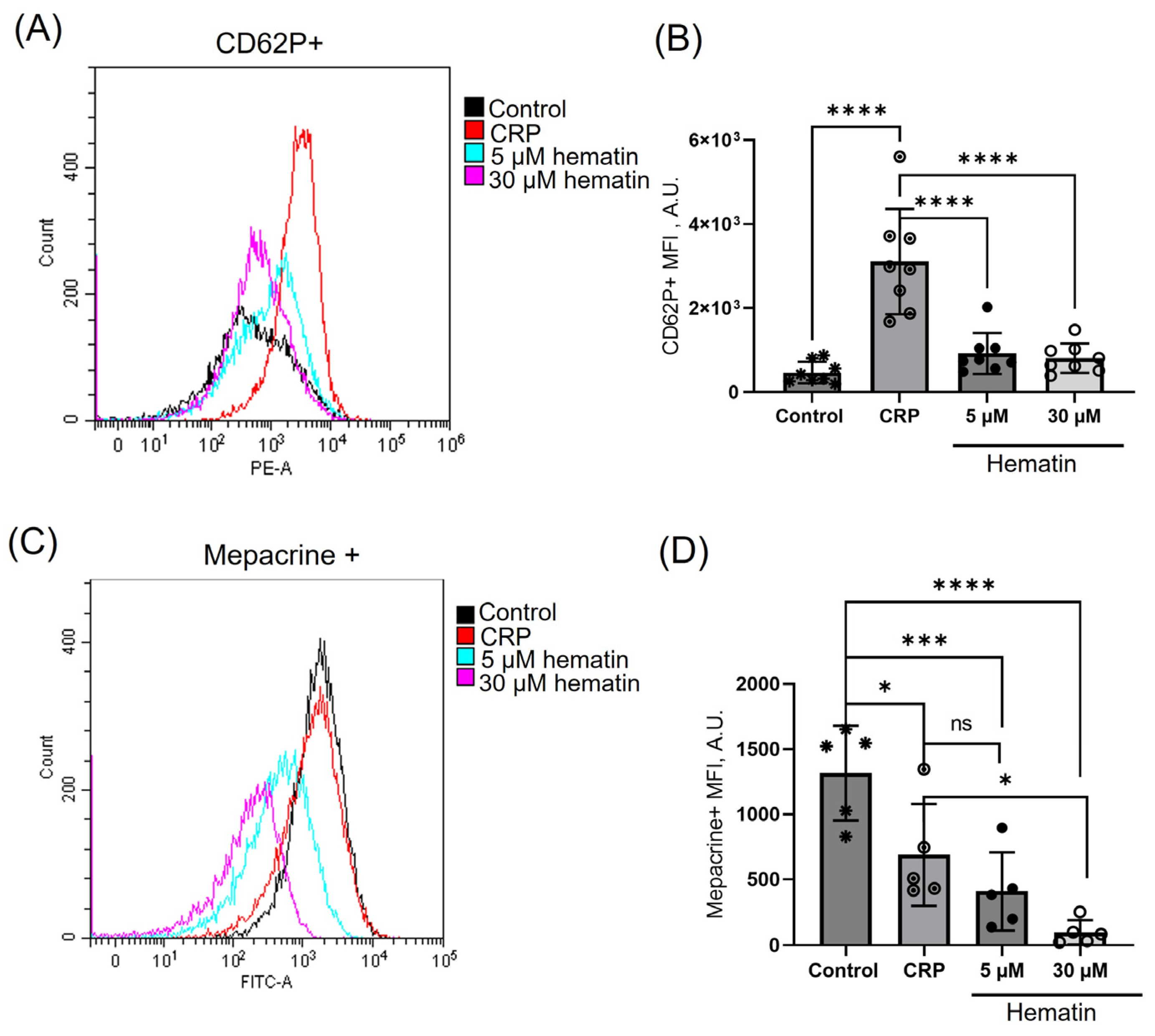
3.8. Hematin Induces Dense but Not Alpha Granule Secretion
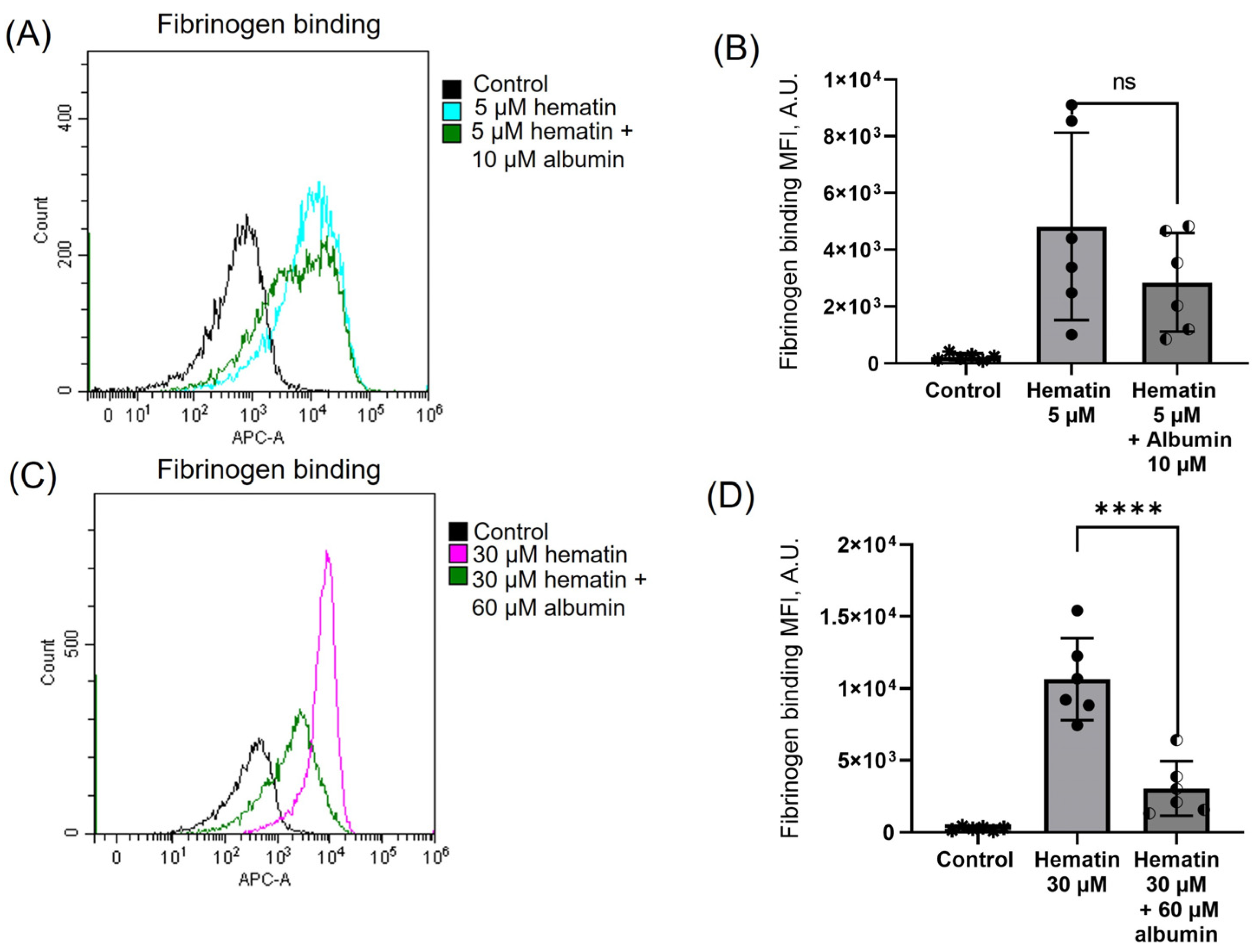
3.9. Albumin Moderates Hematin-Induced Platelet Activation
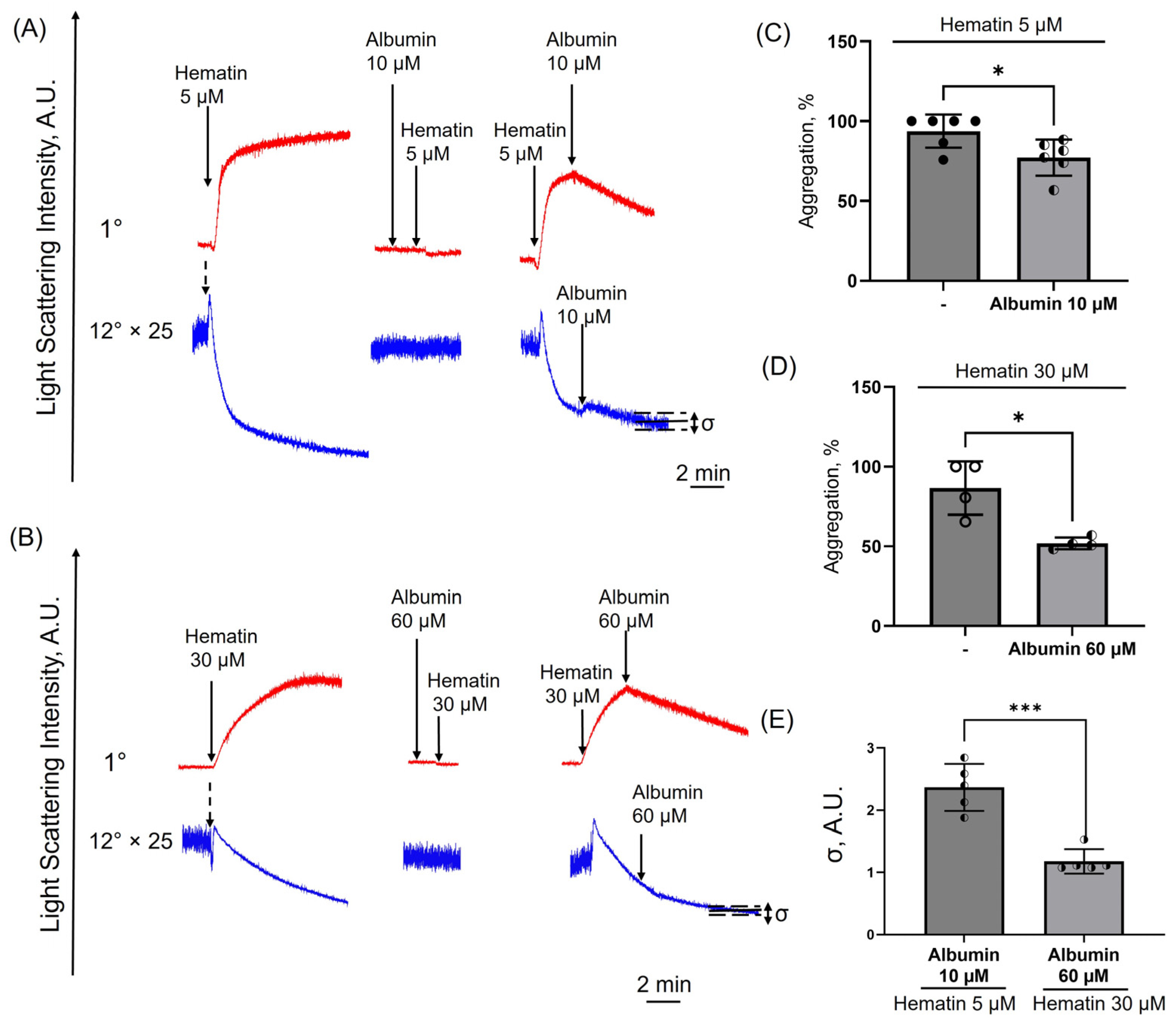
3.10. Albumin Induces Disaggregation in Hematin-Treated Platelets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Limitations of the Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Belcher, J.D.; Chen, C.; Nguyen, J.; Milbauer, L.; Abdulla, F.; Alayash, A.I.; Smith, A.; Nath, K.A.; Hebbel, R.P.; Vercellotti, G.M. Heme triggers TLR4 signaling leading to endothelial cell activation and vaso-occlusion in murine sickle cell disease. Blood 2014, 123, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frimat, M.; Tabarin, F.; Dimitrov, J.D.; Poitou, C.; Halbwachs-Mecarelli, L.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Roumenina, L.T. Complement activation by heme as a secondary hit for atypical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 2013, 122, 282–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.; Maier, J.; Gorki, A.D.; Huber, K.V.; Sharif, O.; Starkl, P.; Saluzzo, S.; Quattrone, F.; Gawish, R.; Lakovits, K.; et al. Heme drives hemolysis-induced susceptibility to infection via disruption of phagocyte functions. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 1361–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayan, V.; Greite, R.; Schott, S.; Doricic, J.; Madyaningrana, K.; Pradhan, P.; Martens, J.; Blasczyk, R.; Janciauskiene, S.; Immenschuh, S. Determination of free heme in stored red blood cells with an apo-horseradish peroxidase-based assay. Biol. Chem. 2022, 403, 1091–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, J.; Holbert, K.; Czysz, K.; George, J.; Fernandes, C.; Fraidenburg, D.R. Hemin-Induced Endothelial Dysfunction and Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition in the Pathogenesis of Pulmonary Hypertension Due to Chronic Hemolysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, J.E. Molecular Regulation of Platelet-Dependent Thrombosis. Circulation 2005, 112, 2725–2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grenoble, D.C.; Drickamer, H.G. The effect of pressure on the oxidation state of iron. 3. Hemin and hematin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1968, 61, 1177–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Bandyopadhyay, U. Free heme toxicity and its detoxification systems in human. Toxicol. Lett. 2005, 157, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller-Eberhard, U.; Javid, J.; Liem, H.H.; Hanstein, A.; Hanna, M. Plasma concentrations of hemopexin, haptoglobin and heme in patients with various hemolytic diseases. Blood 1968, 32, 811–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatidis, S.; Föller, M.; Lang, F. Hemin-Induced suicidal erythrocyte death. Ann. Hematol. 2009, 88, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laspa, Z.; Dicenta-Baunach, V.; Schaale, D.; Sigle, M.; Hochuli, R.; Castor, T.; Bayrak, A.; Harm, T.; Müller, K.A.L.; Pillaiyar, T.; et al. Hemin-Induced platelet activation is regulated by the ACKR3 chemokine surface receptor and has implications for passivation of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques. FEBS J. 2024, 291, 5420–5434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, S.R.; Dang, T.N.; Dringen, R.; Bishop, G.M. Hemin toxicity: A preventable source of brain damage following hemorrhagic stroke. Redox Rep. Commun. Free Radic. Res. 2009, 14, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mubeen, S.; Domingo-Fernández, D.; Díaz Del Ser, S.; Solanki, D.M.; Kodamullil, A.T.; Hofmann-Apitius, M.; Hopp, M.T.; Imhof, D. Exploring the Complex Network of Heme-Triggered Effects on the Blood Coagulation System. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopp, M.-T.; Imhof, D. Linking Labile Heme with Thrombosis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolodgie, F.D.; Gold, H.K.; Burke, A.P.; Fowler, D.R.; Kruth, H.S.; Weber, D.K.; Farb, A.; Guerrero, L.J.; Hayase, M.; Kutys, R.; et al. Intraplaque hemorrhage and progression of coronary atheroma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 349, 2316–2325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourne, J.H.; Colicchia, M.; Di, Y.; Martin, E.; Slater, A.; Roumenina, L.T.; Dimitrov, J.D.; Watson, S.P.; Rayes, J. Heme induces human and mouse platelet activation through C-type-lectin-like receptor-2. Haematologica 2021, 106, 626–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, D.; Luo, M.; Liu, B. The Role of CLEC-2 and Its Ligands in Thromboinflammation. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 688643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Peng, D.; Li, Y.; He, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, S.; Ma, P.; Lv, L.; Wang, X.; et al. Hemin regulates platelet clearance in hemolytic disease by binding to GPIbα. Platelets 2024, 35, 2383642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NaveenKumar, S.K.; SharathBabu, B.N.; Hemshekhar, M.; Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S.; Mugesh, G. The Role of Reactive Oxygen Species and Ferroptosis in Heme-Mediated Activation of Human Platelets. ACS Chem. Biol. 2018, 13, 1996–2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NaveenKumar, S.K.; Hemshekhar, M.; Kemparaju, K.; Girish, K.S. Hemin-Induced platelet activation and ferroptosis is mediated through ROS-driven proteasomal activity and inflammasome activation: Protection by Melatonin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2019, 1865, 2303–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaale, D.; Laspa, Z.; Balmes, A.; Sigle, M.; Dicenta-Baunach, V.; Hochuli, R.; Fu, X.; Serafimov, K.; Castor, T.; Harm, T.; et al. Hemin promotes platelet activation and plasma membrane disintegration regulated by the subtilisin-like proprotein convertase furin. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e70155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wichaiyo, S.; Koonyosying, P.; Morales, N.P. Functional Roles of Furin in Cardio-Cerebrovascular Diseases. ACS Pharmacol. Transl. Sci. 2024, 7, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrides, P.E. Therapy Follows Diagnosis: Old and New Approaches for the Treatment of Acute Porphyrias, What We Know and What We Should Know. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azouzi, S.; El Kirat, K.; Morandat, S. Hematin loses its membranotropic activity upon oligomerization into malaria pigment. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Biomembr. 2015, 1848, 2952–2959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambaryan, S.; Kobsar, A.; Rukoyatkina, N.; Herterich, S.; Geiger, J.; Smolenski, A.; Lohmann, S.M.; Walter, U. Thrombin and collagen induce a feedback inhibitory signaling pathway in platelets involving dissociation of the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A from an NFkappaB-IkappaB complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 18352–18363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlova, E.; Chernysh, A.; Moroz, V.; Gudkova, O.; Sergunova, V.; Kuzovlev, A. Transformation of membrane nanosurface of red blood cells under hemin action. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mikhailova, D.M.; Skverchinskaya, E.; Sudnitsyna, J.; Butov, K.R.; Koltsova, E.M.; Mindukshev, I.V.; Gambaryan, S. Hematin- and Hemin-Induced Spherization and Hemolysis of Human Erythrocytes Are Independent of Extracellular Calcium Concentration. Cells 2024, 13, 554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindukshev, I.; Gambaryan, S.; Kehrer, L.; Schuetz, C.; Kobsar, A.; Rukoyatkina, N.; Nikolaev, V.O.; Krivchenko, A.; Watson, S.P.; Walter, U.; et al. Low angle light scattering analysis: A novel quantitative method for functional characterization of human and murine platelet receptors. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2012, 50, 1253–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mindukshev, I.; Fock, E.; Dobrylko, I.; Sudnitsyna, J.; Gambaryan, S.; Panteleev, M.A. Platelet Hemostasis Reactions at Different Temperatures Correlate with Intracellular Calcium Concentration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponomareva, A.A.; Nevzorova, T.A.; Mordakhanova, E.R.; Andrianova, I.A.; Rauova, L.; Litvinov, R.I.; Weisel, J.W. Intracellular origin and ultrastructure of platelet-derived microparticles. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1655–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khourssaji, M.; Bareille, M.; Alberio, L.; Borgel, D.; Fouassier, M.; Béné, M.C.; Lecompte, T.; Mullier, F. Mepacrine Flow Cytometry Assay for the Diagnosis of Platelet δ-granule Defects: Literature Review on Methods-Towards a Shared Detailed Protocol. Thromb. Haemost. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolenski, A. Novel roles of cAMP/cGMP-dependent signaling in platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2012, 10, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambaryan, S. The Role of NO/sGC/cGMP/PKG Signaling Pathway in Regulation of Platelet Function. Cells 2022, 11, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohlfing, A.K.; Kremser, M.; Schaale, D.; Dicenta-Baunach, V.; Laspa, Z.; Fu, X.; Zizmare, L.; Sigle, M.; Harm, T.; Münzer, P.; et al. cGMP modulates hemin-mediated platelet death. Thromb. Res. 2024, 234, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.H.; Chiang, T.B.; Wang, W.J. A critical role for the regulation of Syk from agglutination to aggregation in human platelets. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 443, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huffman, L.J.; Miles, P.R.; Shi, X.; Bowman, L. Hemoglobin potentiates the production of reactive oxygen species by alveolar macrophages. Exp. Lung Res. 2000, 26, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, H.W.; Takatsu, H. Phosphatidylserine exposure in living cells. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2020, 55, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golebiewska, E.M.; Poole, A.W. Platelet secretion: From haemostasis to wound healing and beyond. Blood Rev. 2015, 29, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dicenta, V.; Pelzer, A.; Laspa, Z.; Castor, T.; Gawaz, M.P.; Rohlfing, A.K. The subtilisin-like protease furin regulates hemin-induced CD63 surface expression on platelets. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2024, 701, 149629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fink, A.; Rohlfing, A.K.; Dicenta, V.; Schaale, D.; Kremser, M.; Laspa, Z.; Sigle, M.; Fu, X.; Pelzer, A.; Fischer, M.; et al. The Subtilisin-Like Protease Furin Regulates Hemin-Dependent Ectodomain Shedding of Glycoprotein VI. Thromb. Haemost. 2023, 123, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, G.; Varricchio, R.; Ruberto, T.F.; di Masi, A.; Ascenzi, P. Heme Scavenging and Delivery: The Role of Human Serum Albumin. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaklai, N.; Shviro, Y.; Rabizadeh, E.; Kirschner-Zilber, I. Accumulation and drainage of hemin in the red cell membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1985, 821, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhart, W.H.; Piety, N.Z.; Deuel, J.W.; Makhro, A.; Schulzki, T.; Bogdanov, N.; Goede, J.S.; Bogdanova, A.; Abidi, R.; Shevkoplyas, S.S. Washing stored red blood cells in an albumin solution improves their morphologic and hemorheologic properties. Transfusion 2015, 55, 1872–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaer, D.J.; Buehler, P.W.; Alayash, A.I.; Belcher, J.D.; Vercellotti, G.M. Hemolysis and free hemoglobin revisited: Exploring hemoglobin and hemin scavengers as a novel class of therapeutic proteins. Blood 2013, 121, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga-Szabo, D.; Braun, A.; Nieswandt, B. Calcium signaling in platelets. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 7, 1057–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Hua, Y.; Keep, R.F.; Feng, H.; Xi, G. Deferoxamine therapy reduces brain hemin accumulation after intracerebral hemorrhage in piglets. Exp. Neurol. 2019, 318, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levitt, D.G.; Levitt, M.D. Human serum albumin homeostasis: A new look at the roles of synthesis, catabolism, renal and gastrointestinal excretion, and the clinical value of serum albumin measurements. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2016, 9, 229–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallelian, F.; Buehler, P.W.; Schaer, D.J. Hemolysis, free hemoglobin toxicity, and scavenger protein therapeutics. Blood 2022, 140, 1837–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mikhailova, D.M.; Sudnitsyna, J.; Kovgan, P.; Naida, L.; Kharazova, A.; Mindukshev, I.; Gambaryan, S. Analysis of Ferric Protoporphyrin IX Effects on Human Platelets: Hematin Is a More Potent Agonist than Hemin. Cells 2025, 14, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040255
Mikhailova DM, Sudnitsyna J, Kovgan P, Naida L, Kharazova A, Mindukshev I, Gambaryan S. Analysis of Ferric Protoporphyrin IX Effects on Human Platelets: Hematin Is a More Potent Agonist than Hemin. Cells. 2025; 14(4):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040255
Chicago/Turabian StyleMikhailova, Diana M., Julia Sudnitsyna, Polina Kovgan, Lidia Naida, Alexandra Kharazova, Igor Mindukshev, and Stepan Gambaryan. 2025. "Analysis of Ferric Protoporphyrin IX Effects on Human Platelets: Hematin Is a More Potent Agonist than Hemin" Cells 14, no. 4: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040255
APA StyleMikhailova, D. M., Sudnitsyna, J., Kovgan, P., Naida, L., Kharazova, A., Mindukshev, I., & Gambaryan, S. (2025). Analysis of Ferric Protoporphyrin IX Effects on Human Platelets: Hematin Is a More Potent Agonist than Hemin. Cells, 14(4), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040255









