Circular RNA ZNF277 Sponges miR-378d to Inhibit the Intracellular Survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Upregulating Rab10
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Cell Culture
2.2. Cell Infection with Mtb
2.3. Generate Stable Cell Lines and Cell Transfection
2.4. Dual Luciferase Reporter Assays
2.5. Ribonuclease R Digestion Assay
2.6. Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
2.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
2.8. Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) and Nucleocytoplasmic Isolation
2.9. Pathway Inhibition Assay
2.10. Western-Blot Analysis
2.11. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
2.12. Colony-Forming Units (CFU) Count
2.13. Prediction Analysis of circRNAs Targeting miR-378d
2.14. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
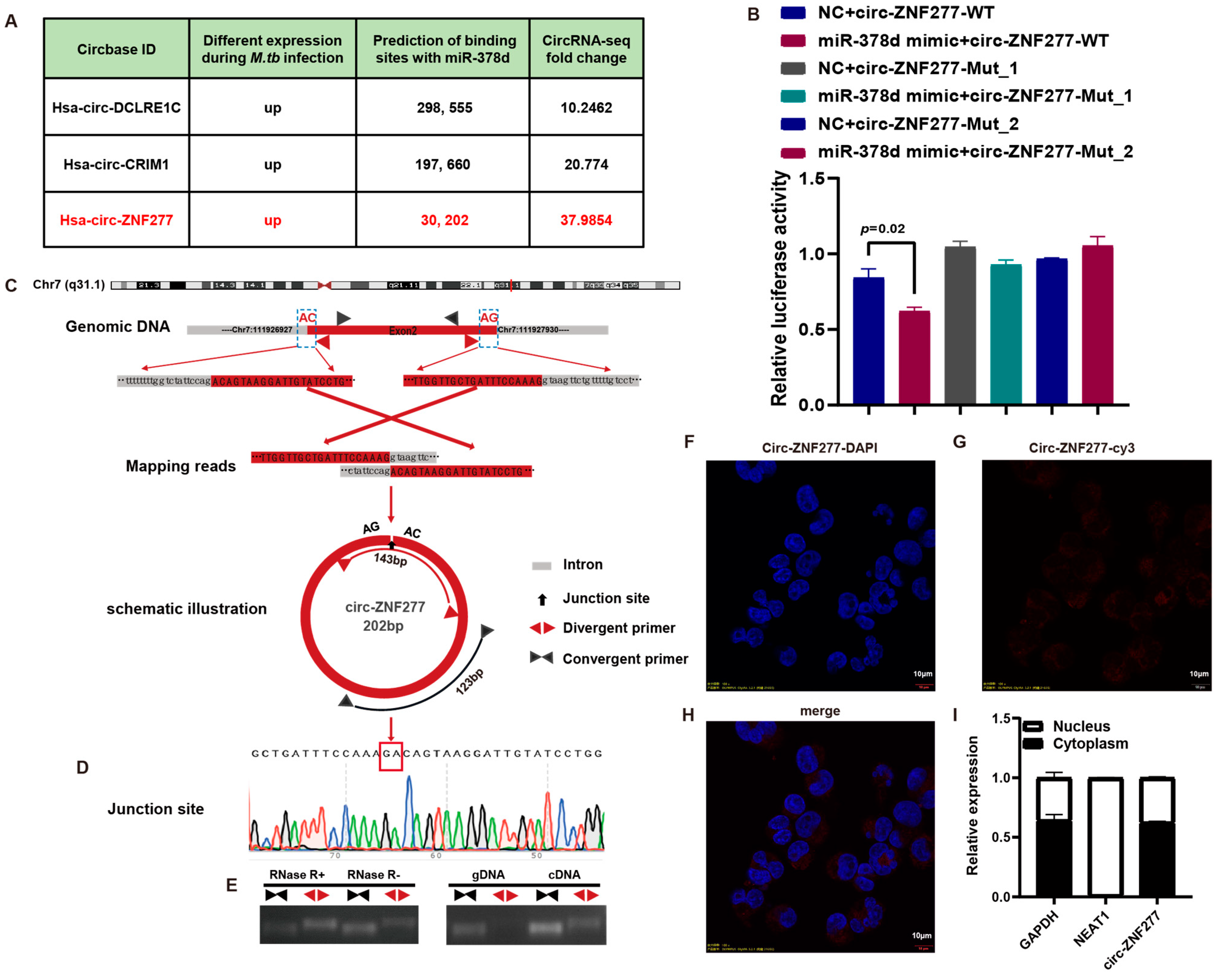
3.1. Circ-ZNF277 Exists in the THP-1 Cells and It Interacts with miR-378d In Vivo
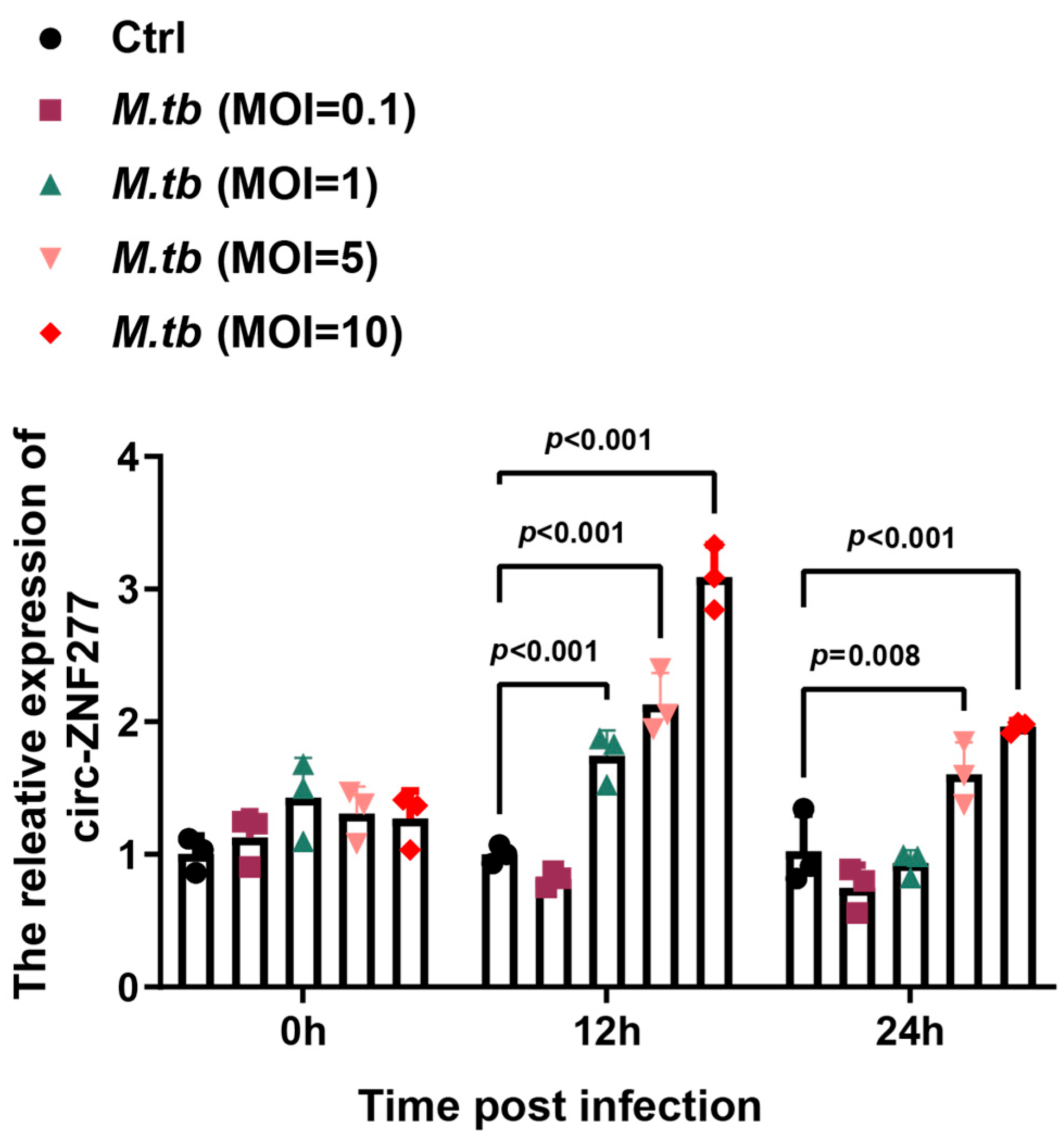
3.2. Circ-ZNF277 Responses to Mtb Infection in THP-1 Cells
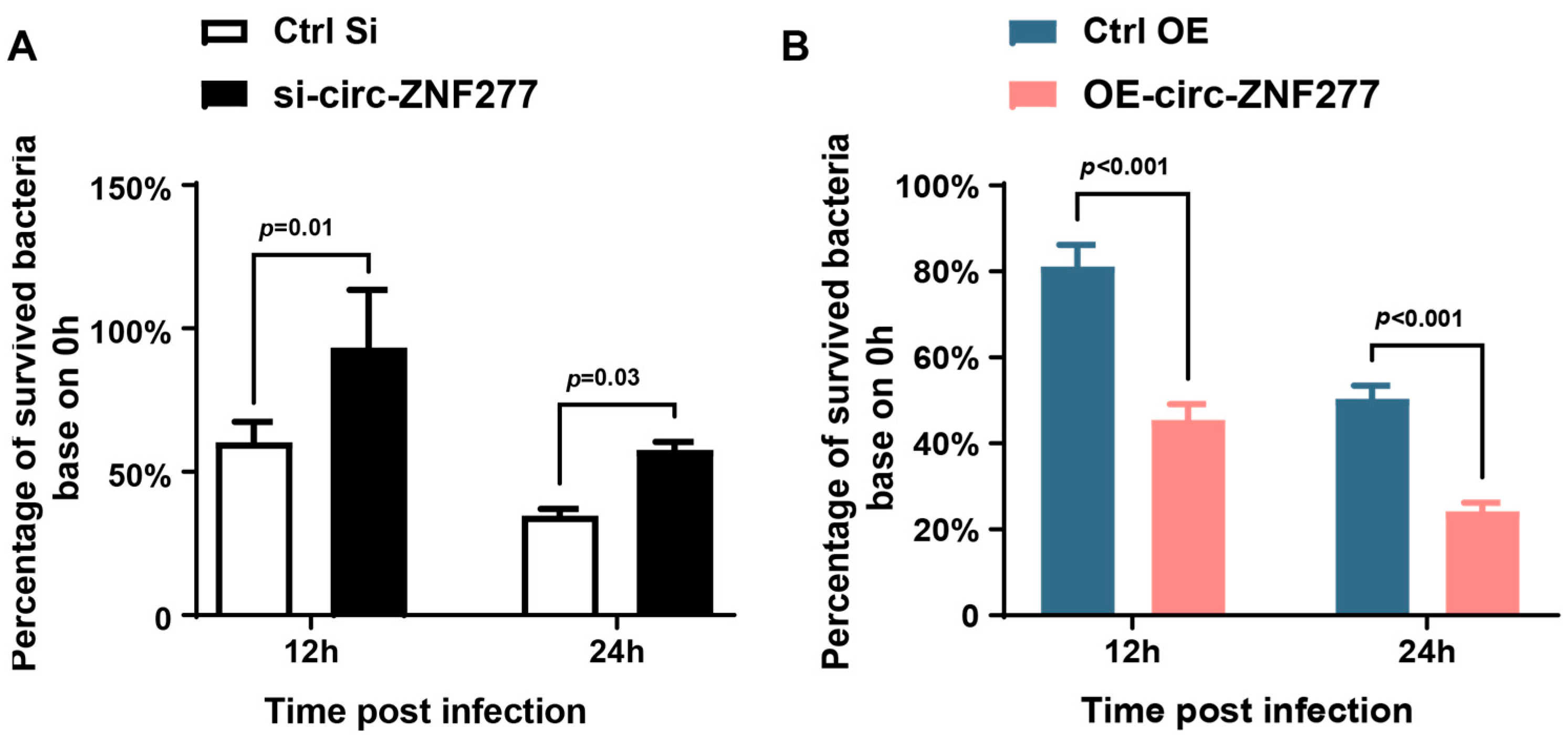
3.3. Overexpression of Circ-ZNF277 Inhibits Survival of Mtb in the THP-1 Cells
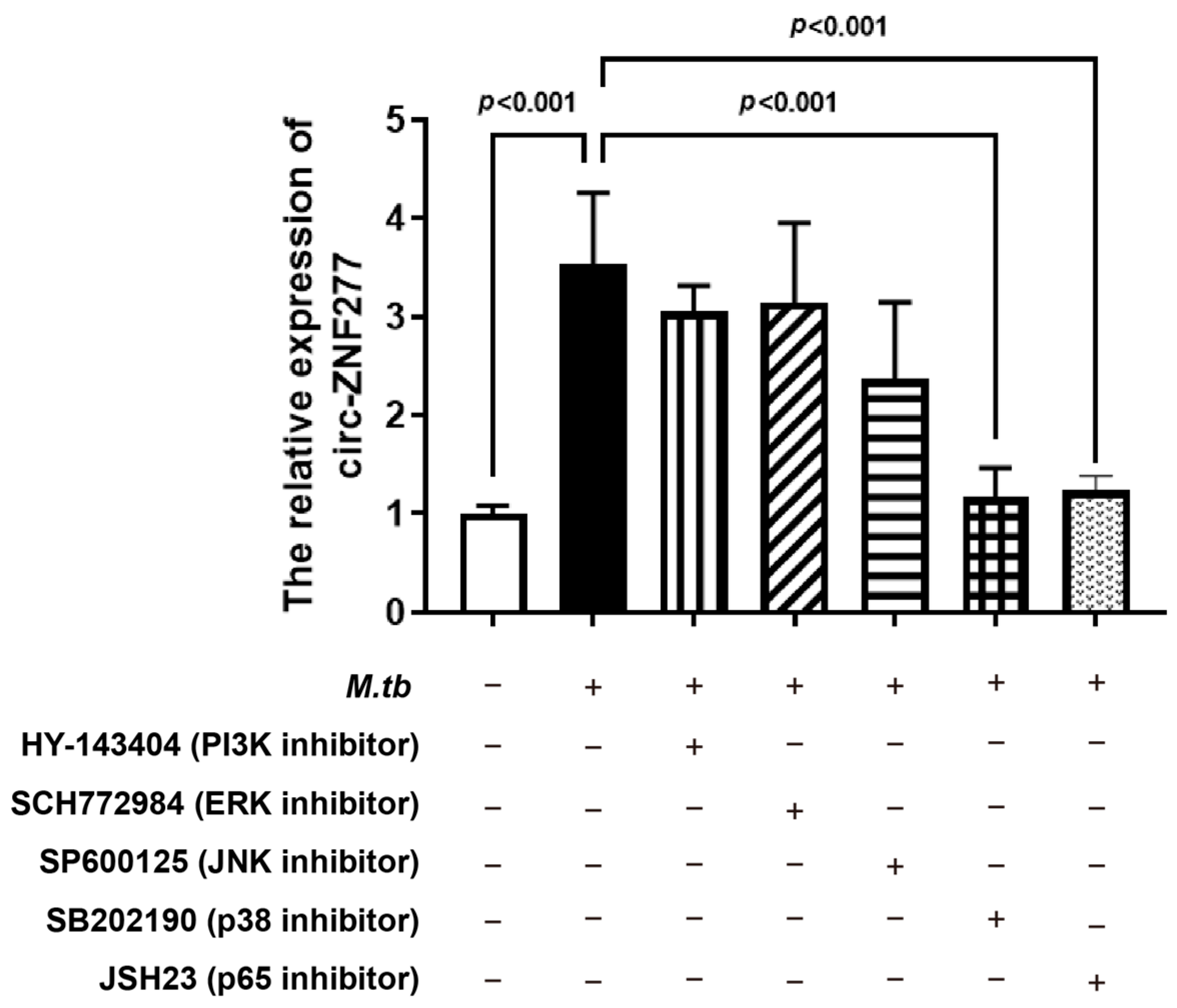
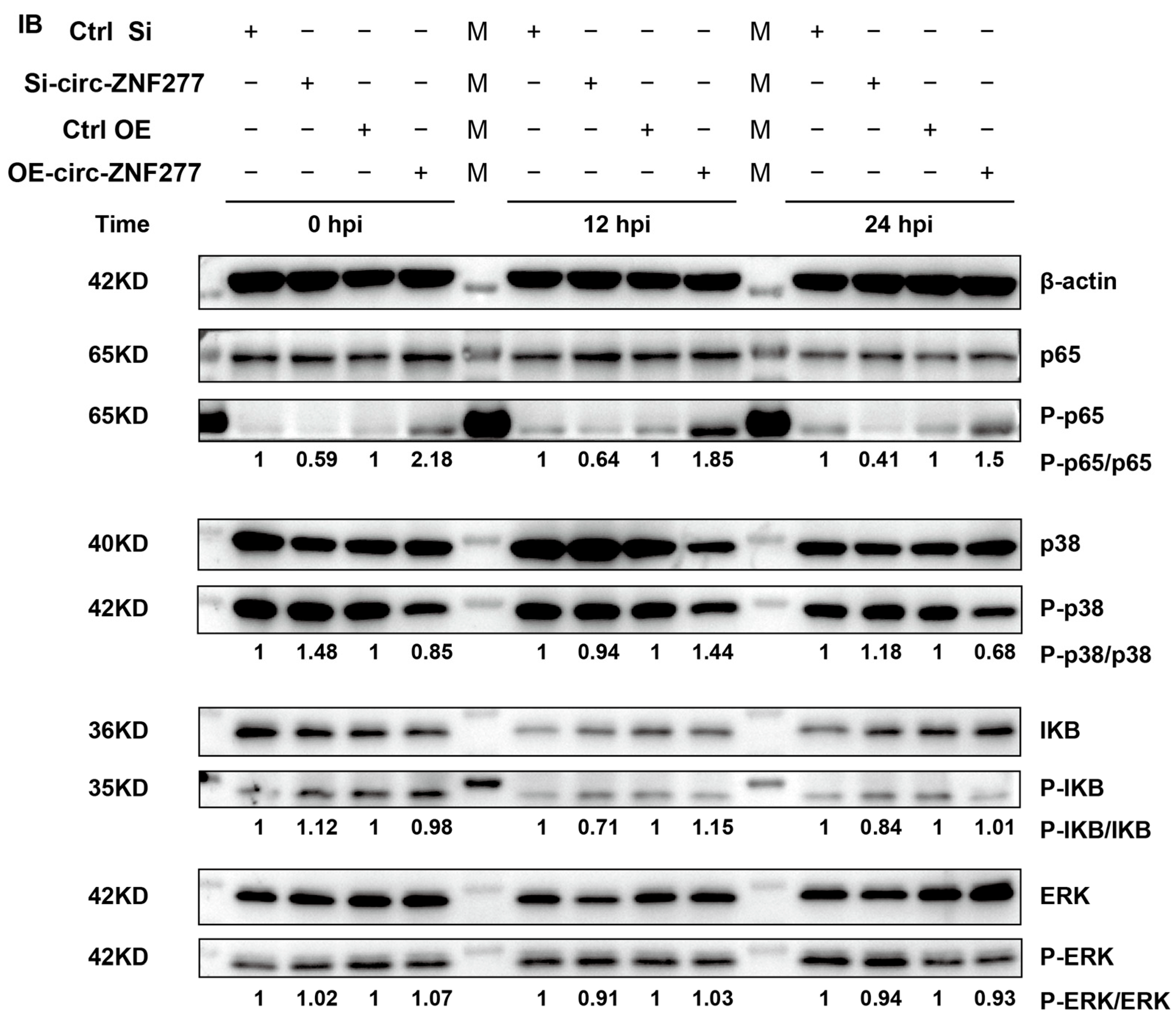
3.4. The Expression Level of Circ-ZNF277 Affects NF-κB Signaling Pathway in the THP-1 Cells During Mtb Infection
3.5. The Increased Expression Level of Circ-ZNF277 Promotes the Secretion of Inflammatory Factors in Mtb-Infected THP-1 Cells
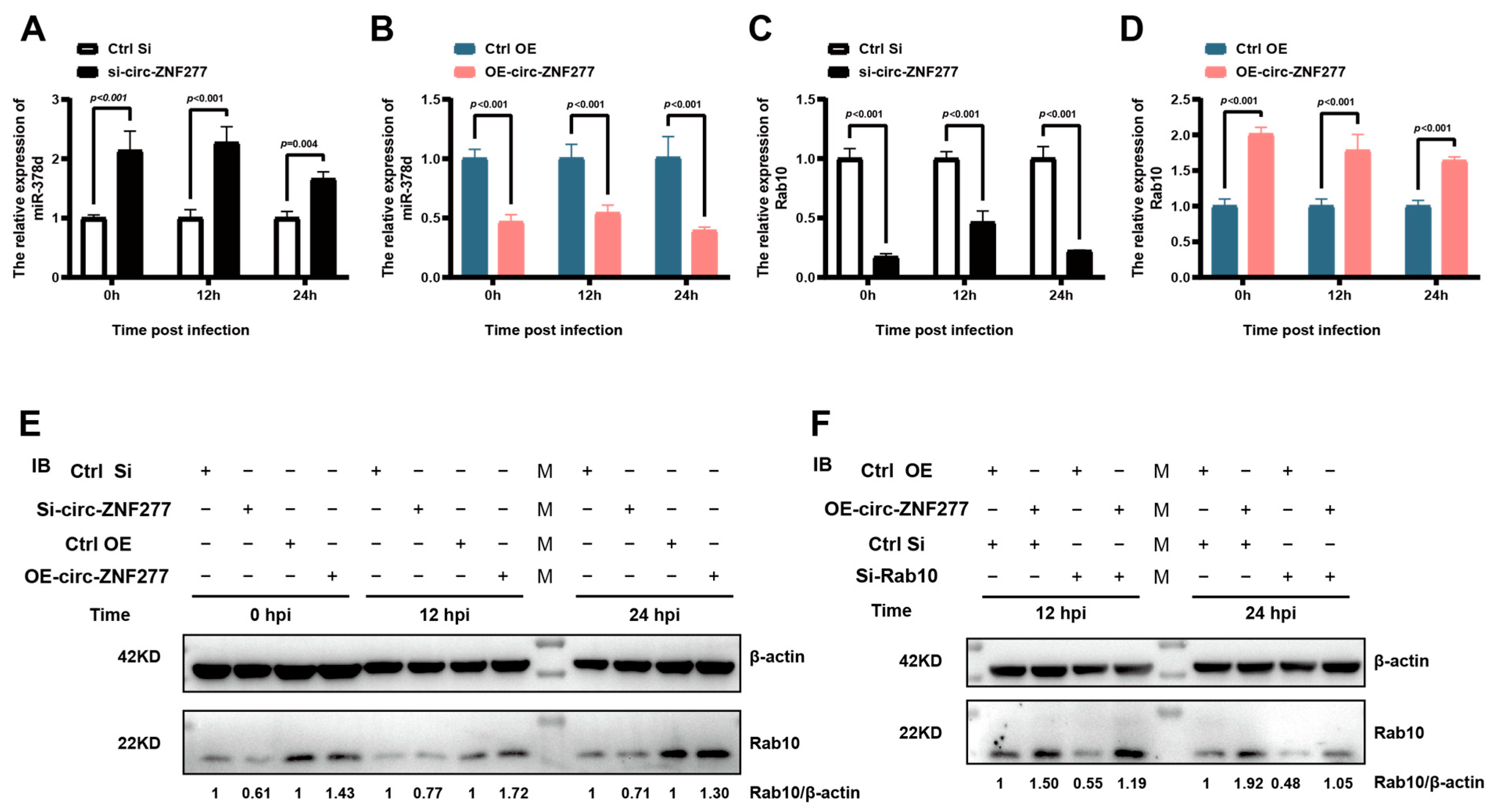
3.6. Circ-ZNF277 Specifically Targets miR-378d to Promote the Expression of Rab10
3.7. Circ-ZNF277 Promotes the Secretion of Inflammatory Cytokines to Inhibit the Survival of Mtb in THP-1 Cells via Circ-ZNF277/miR-378d/Rab10 Axis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. Global Tuberculosis Report 2024; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Schwander, S.; Dheda, K. Human lung immunity against Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Insights into pathogenesis and protection. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2011, 183, 696–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, A.; Pahuja, I.; Singh, S.P.; Verma, A.; Bhattacharya, D.; Bhaskar, A.; Dwivedi, V.P.; Das, G. Revisiting the role of mesenchymal stem cells in tuberculosis and other infectious diseases. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, W.; Wu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.; Liu, Z. The immune escape mechanisms of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandra, P.; Grigsby, S.J.; Philips, J.A. Immune evasion and provocation by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 750–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, J.L. Mechanisms of pH Homeostasis and Cytochrome C Maturation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Weill Medical College of Cornell University: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Shankar, G.; Akhter, Y. Stealing Survival: Iron Acquisition Strategies of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Biochimie 2024, 227, 37–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hmama, Z.; Peña-Díaz, S.; Joseph, S.; Av-Gay, Y. Immunoevasion and immunosuppression of the macrophage by M ycobacterium tuberculosis. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 264, 220–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maphasa, R.E.; Meyer, M.; Dube, A. The macrophage response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis and opportunities for autophagy inducing nanomedicines for tuberculosis therapy. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 10, 618414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visser, J.G. Manipulation of Macrophage Phagocytosis-Development of an Endogenous Delivery System. Ph.D. Thesis, Stellenbosch University, Stellenbosch, South Africa, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Bo, H.; Moure, U.A.E.; Yang, Y.; Pan, J.; Li, L.; Wang, M.; Ke, X.; Cui, H. Mycobacterium tuberculosis-macrophage interaction: Molecular updates. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1062963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landes, M.B.; Rajaram, M.V.; Nguyen, H.; Schlesinger, L.S. Role for NOD2 in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced iNOS expression and NO production in human macrophages. J. Leucoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 1111–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Singh, V.K.; Hunter, R.L.; Jagannath, C. Macrophage heterogeneity and plasticity in tuberculosis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2019, 106, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, D.; Podell, B.K.; Chambers, M.; Basaraba, R.J. Host-directed therapy targeting the Mycobacterium tuberculosis granuloma: A review. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 167–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, M.; Bailey, C.; Cahatol, I.; Dodge, L.; Yim, J.; Kassissa, C.; Luong, J.; Kasko, S.; Pandya, S.; Venketaraman, V. Mechanisms of control of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by NK cells: Role of glutathione. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.G.; Kaviratne, M.; Rothfuchs, A.G.; Cheever, A.; Hieny, S.; Young, H.A.; Wynn, T.A.; Sher, A. NK cell-derived IFN-γ differentially regulates innate resistance and neutrophil response in T cell-deficient hosts infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 7086–7093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weeratunga, P.; Moller, D.R.; Ho, L.-P. Immune mechanisms of granuloma formation in sarcoidosis and tuberculosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e175264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awuh, J.A.; Flo, T.H. Molecular basis of mycobacterial survival in macrophages. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 1625–1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergne, I.; Gilleron, M.; Nigou, J. Manipulation of the endocytic pathway and phagocyte functions by Mycobacterium tuberculosis lipoarabinomannan. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2015, 4, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Ge, P.; Qiang, L.; Tian, F.; Zhao, D.; Chai, Q.; Zhu, M.; Zhou, R.; Meng, G.; Iwakura, Y. The mycobacterial phosphatase PtpA regulates the expression of host genes and promotes cell proliferation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, P.; Lei, Z.; Yu, Y.; Lu, Z.; Qiang, L.; Chai, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, D.; Li, B.; Pang, Y.; et al. M. tuberculosis PknG manipulates host autophagy flux to promote pathogen intracellular survival. Autophagy 2022, 18, 576–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zulauf, K.E.; Sullivan, J.T.; Braunstein, M. The SecA2 pathway of Mycobacterium tuberculosis exports effectors that work in concert to arrest phagosome and autophagosome maturation. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1007011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, B.X.; Ge, P.P.; Li, J.; Wang, Q.; Gao, G.F.; Qiu, X.B.; Liu, C.H. Mycobacterium tuberculosis suppresses innate immunity by coopting the host ubiquitin system. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 237–245. [Google Scholar]
- Bach, H.; Papavinasasundaram, K.G.; Wong, D.; Hmama, Z.; Av-Gay, Y. Mycobacterium tuberculosis virulence is mediated by PtpA dephosphorylation of human vacuolar protein sorting 33B. Cell Host Microbe 2008, 3, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, D.; Bach, H.; Sun, J.; Hmama, Z.; Av-Gay, Y. Mycobacterium tuberculosis protein tyrosine phosphatase (PtpA) excludes host vacuolar-H+–ATPase to inhibit phagosome acidification. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 19371–19376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xander, C.; Rajagopalan, S.; Jacobs William, R.; Braunstein, M. The SapM phosphatase can arrest phagosome maturation in an ESX-1 independent manner in Mycobacterium tuberculosis and BCG. Infect. Immun. 2024, 92, e00217-24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Dong, C.; Xiong, S. Mycobacterial SapM hampers host autophagy initiation for intracellular bacillary survival via dephosphorylating Raptor. iScience 2024, 27, 109671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Liu, K.; Jia, Q.; Zhang, H.; Bie, Q.; Zhang, B. The Roles of Host Noncoding RNAs in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 664787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Wei, Z.; Jia, Y.; Wu, Y.; Qi, X.; Li, Y.; Gao, X. The role of non-coding RNA on macrophage modification in tuberculosis infection. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etna, M.P.; Sinigaglia, A.; Grassi, A.; Giacomini, E.; Romagnoli, A.; Pardini, M.; Severa, M.; Cruciani, M.; Rizzo, F.; Anastasiadou, E.; et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis-induced miR-155 subverts autophagy by targeting ATG3 in human dendritic cells. PLoS Pathog. 2018, 14, e1006790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, T.; Ge, B. miRNAs in immune responses to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Cancer Lett. 2018, 431, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saaoud, F.; Drummer, I.V.C.; Shao, Y.; Sun, Y.; Lu, Y.; Xu, K.; Ni, D.; Jiang, X.; Wang, H.; Yang, X. Circular RNAs are a novel type of non-coding RNAs in ROS regulation, cardiovascular metabolic inflammations and cancers. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 220, 107715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verduci, L.; Tarcitano, E.; Strano, S.; Yarden, Y.; Blandino, G. CircRNAs: Role in human diseases and potential use as biomarkers. Cell Death Dis. 2021, 12, 468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, X.; Chen, Z.; Han, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, M.; Lv, J.; Xie, X.; Zhai, Y.; Li, L.; Du, H. Profile analysis of circRNAs in human THP-1 derived macrophages infected with intracellular Staphylococcus aureus. Microb. Pathog. 2022, 165, 105466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, H.; Liu, F.; Long, J.; Duan, G.; Yang, H. A review on circular RNAs and bacterial infections. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Wang, M.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, M.; Chen, Z.; Han, M.; Zhao, C.; Xie, Z.; Dong, Q.; Zhang, H. Intracellular Staphylococcus aureus infection in human osteoblasts: circRNA expression analysis. Heliyon 2024, 10, e28461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasankhani, A.; Bahrami, A.; Mackie, S.; Maghsoodi, S.; Alawamleh, H.S.K.; Sheybani, N.; Safarpoor Dehkordi, F.; Rajabi, F.; Javanmard, G.; Khadem, H. In-depth systems biological evaluation of bovine alveolar macrophages suggests novel insights into molecular mechanisms underlying Mycobacterium bovis infection. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 1041314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhu, X.; Huang, S. Clinical applications of extracellular vesicle long RNAs. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2020, 57, 508–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.H.; Liu, Z.-B.; Zhang, S. Down-regulation of hsa_circ_0045474 induces macrophage autophagy in tuberculosis via miR-582-5p/TNKS2 axis. Innate Immun. 2021, 28, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.L.; Pi, J.; Zhang, J.A.; Yang, E.Z.; Xu, H.; Luo, H.; Shen, L.; Peng, Y.; Liu, G.B.; Song, C.M.; et al. Circular RNA TRAPPC6B inhibits intracellular Mycobacterium tuberculosis growth while inducing autophagy in macrophages by targeting microRNA-874-3p. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2021, 10, e1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Zhou, H.; Xiao, H.-X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, T. MiR-378 is an independent prognostic factor and inhibits cell growth and invasion in colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.; Shi, S.; Yu, J.; Liu, J.; Wei, H.; Song, H.; Wang, S.; Li, Z.; He, S.; Li, L. miR-378d suppresses malignant phenotype of ESCC cells through AKT signaling. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, J.; Wang, S.; Kim, J.; Rao, K.M.; Park, S.Y.; Chung, I.; Ha, C.-S.; Kim, S.-W.; Yun, Y.H.; Jung, Y. MicroRNA-378 limits activation of hepatic stellate cells and liver fibrosis by suppressing Gli3 expression. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 10993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, M.; Zhu, L.; Li, L.; Kang, C. miR-378 suppresses the proliferation, migration and invasion of colon cancer cells by inhibiting SDAD1. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2017, 22, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almudimeegh, S. Modulation of LRRK2 Mediated Signaling in Immune Cells. Ph.D. Thesis, UCL (University College London), London, UK, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, S.; Cao, B.; Xuan, G.; Xu, S.; An, Z.; Zhu, C.; Li, L.; Tang, C. Function and regulation of Rab GTPases in cancers. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2024, 40, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuo, J.; Han, J.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, R.; Shen, C.; Li, H.; Dai, L.; Sheng, A.; Yao, H.; Yang, X. RAB10 promotes breast cancer proliferation migration and invasion predicting a poor prognosis for breast cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 15252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavana, J.P.; Rosene, M.; Jensen, N.O.; Ridge, P.G.; Kauwe, J.S.; Karch, C.M. RAB10: An Alzheimer’s disease resilience locus and potential drug target. Clin. Interv. Aging 2019, 14, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Kong, D.; Liu, H.; Chen, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, T.; Peng, Y.; Zhai, W.; Hu, C. Down-regulation of miR-378d increased Rab10 expression to help clearance of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in macrophages. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Sahu, S.K.; Kumar, R.; Subuddhi, A.; Maji, R.K.; Jana, K.; Gupta, P.; Raffetseder, J.; Lerm, M.; Ghosh, Z.; et al. MicroRNA let-7 modulates the immune response to Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection via control of A20, an inhibitor of the NF-kappaB pathway. Cell Host Microbe 2015, 17, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Kong, D.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Tang, T.; Peng, Y.; Hu, C.; Chao, J.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; et al. Identification of Differential Circular RNA Expression Profiles and Functional Networks in Human Macrophages Induced by Virulent and Avirulent Mycobacterium tuberculosis Strains. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 17561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaei, S.; Zarrabi, A.; Hashemi, F.; Zabolian, A.; Saleki, H.; Ranjbar, A.; Saleh, S.H.S.; Bagherian, M.; omid Sharifzadeh, S.; Hushmandi, K. Regulation of Nuclear Factor-KappaB (NF-κB) signaling pathway by non-coding RNAs in cancer: Inhibiting or promoting carcinogenesis? Cancer Lett. 2021, 509, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-X.; Chen, Z.-H.; Chen, D.-L.; Tian, X.-P.; Wang, C.-Y.; Zhou, Z.-W.; Gao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, Z.-S. RETRACTED ARTICLE: LINC01410-miR-532-NCF2-NF-kB feedback loop promotes gastric cancer angiogenesis and metastasis. Oncogene 2018, 37, 2660–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chojnacka, K.; Lewandowska, U. Inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion by polyphenol-rich extracts in macrophages via NF-κB pathway. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 5459–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Shi, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Lv, J.; Xie, X.; Bai, Y.; et al. Potential Diagnostic Power of Blood Circular RNA Expression in Active Pulmonary Tuberculosis. EBioMedicine 2018, 27, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Q.; Wang, J.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y. CircAGFG1modulates autophagy and apoptosis of macrophages infected by Mycobacterium tuberculosis via the Notch signaling pathway. Ann. Transl. Med. 2020, 8, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemati, Z.; Neamati, F.; Khaledi, M.; Gheibihayat, S.M.; Jafarzadeh, L.; Momen-Heravi, M.; Haddadi, M.H.; Sameni, F.; Fathizadeh, H. Circular RNAs and tuberculosis infection. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 226, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Chen, X.L.; Sun, Q. microRNA-579 upregulation mediates death of human macrophages with mycobacterium tuberculosis infection. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 518, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Yao, F.; Liu, J.; Xu, J.; Guo, Y.; Su, R.; Luo, Q.; Li, J. Up-regulation of circRNA-0003528 promotes mycobacterium tuberculosis associated macrophage polarization via down-regulating miR-224-5p, miR-324-5p and miR-488-5p and up-regulating CTLA4. Aging 2020, 12, 25658–25672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Yang, D.; Zuo, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, W. Emerging roles of circular RNAs in tuberculosis. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 995701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Wu, X.J.; Ji, X.J.; Huang, G.X.; Wu, T.; Liu, X.; Yang, R.; Pi, J.; Shen, H.B.; Wang, F.F.; et al. Circular RNA circTRAPPC6B Enhances IL-6 and IL-1β Expression and Repolarizes Mycobacteria Induced Macrophages from M2- to M1-Like Phenotype by Targeting miR-892c-3p. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2023, 43, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno-Corona, N.C.; de León-Bautista, M.P.; León-Juárez, M.; Hernández-Flores, A.; Barragán-Gálvez, J.C.; López-Ortega, O. Rab GTPases, Active Members in Antigen-Presenting Cells, and T Lymphocytes. Traffic 2024, 25, e12950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, C.; Finsel, I.; Otto, A.; Pfaffinger, G.; Rothmeier, E.; Hecker, M.; Becher, D.; Hilbi, H. Functional analysis of novel Rab GTPases identified in the proteome of purified Legionella-containing vacuoles from macrophages. Cell. Microbiol. 2014, 16, 1034–1052. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Lou, J.; Ouyang, C.; Chen, W.; Liu, Y.; Liu, X.; Cao, X.; Wang, J.; Lu, L. Ras-related protein Rab10 facilitates TLR4 signaling by promoting replenishment of TLR4 onto the plasma membrane. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 13806–13811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, C.M.; Jordao, L.; Vieira, O.V. Rab10 regulates phagosome maturation and its overexpression rescues Mycobacterium-containing phagosomes maturation. Traffic 2010, 11, 221–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, X.; Yu, X.; Li, Z. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0001658 regulates apoptosis and autophagy in gastric cancer through microRNA-182/Ras-related protein Rab-10 signaling axis. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 2387–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Dang, X.; Liu, J.; Feng, H.; Sun, J.; Peng, Z. Circtdrd9 contributes to sepsis-induced acute lung injury by enhancing the expression of rab10 via directly binding to mir-223-3p. Shock 2023, 60, 206–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poladian, N.; Orujyan, D.; Narinyan, W.; Oganyan, A.K.; Navasardyan, I.; Velpuri, P.; Chorbajian, A.; Venketaraman, V. Role of NF-κB during Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Gao, Y.; Mu, D.-G.; Fu, E.-Q. MiR-23a-5p modulates mycobacterial survival and autophagy during mycobacterium tuberculosis infection through TLR2/MyD88/NF-κB pathway by targeting TLR2. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 354, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Liu, H.; Su, L.; Xiong, X.; Wang, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Peng, Y.; Dawood, A.; Hu, C. MicroRNA-18b-5p downregulation favors Mycobacterium tuberculosis clearance in macrophages via HIF-1α by promoting an inflammatory response. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 800–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, T.; Chen, Y.; Lu, L.; Liu, H.; Kong, D.; Peng, Y.; Chen, X.; et al. Circular RNA ZNF277 Sponges miR-378d to Inhibit the Intracellular Survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Upregulating Rab10. Cells 2025, 14, 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040262
Zhu Y, Zhang L, Wang Z, Li T, Chen Y, Lu L, Liu H, Kong D, Peng Y, Chen X, et al. Circular RNA ZNF277 Sponges miR-378d to Inhibit the Intracellular Survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Upregulating Rab10. Cells. 2025; 14(4):262. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040262
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yifan, Lei Zhang, Zijian Wang, Ting Li, Yingyu Chen, Lu Lu, Han Liu, Delai Kong, Yongchong Peng, Xi Chen, and et al. 2025. "Circular RNA ZNF277 Sponges miR-378d to Inhibit the Intracellular Survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Upregulating Rab10" Cells 14, no. 4: 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040262
APA StyleZhu, Y., Zhang, L., Wang, Z., Li, T., Chen, Y., Lu, L., Liu, H., Kong, D., Peng, Y., Chen, X., Hu, C., Chen, H., & Guo, A. (2025). Circular RNA ZNF277 Sponges miR-378d to Inhibit the Intracellular Survival of Mycobacterium tuberculosis by Upregulating Rab10. Cells, 14(4), 262. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells14040262






