The NF-κB Pathway and Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
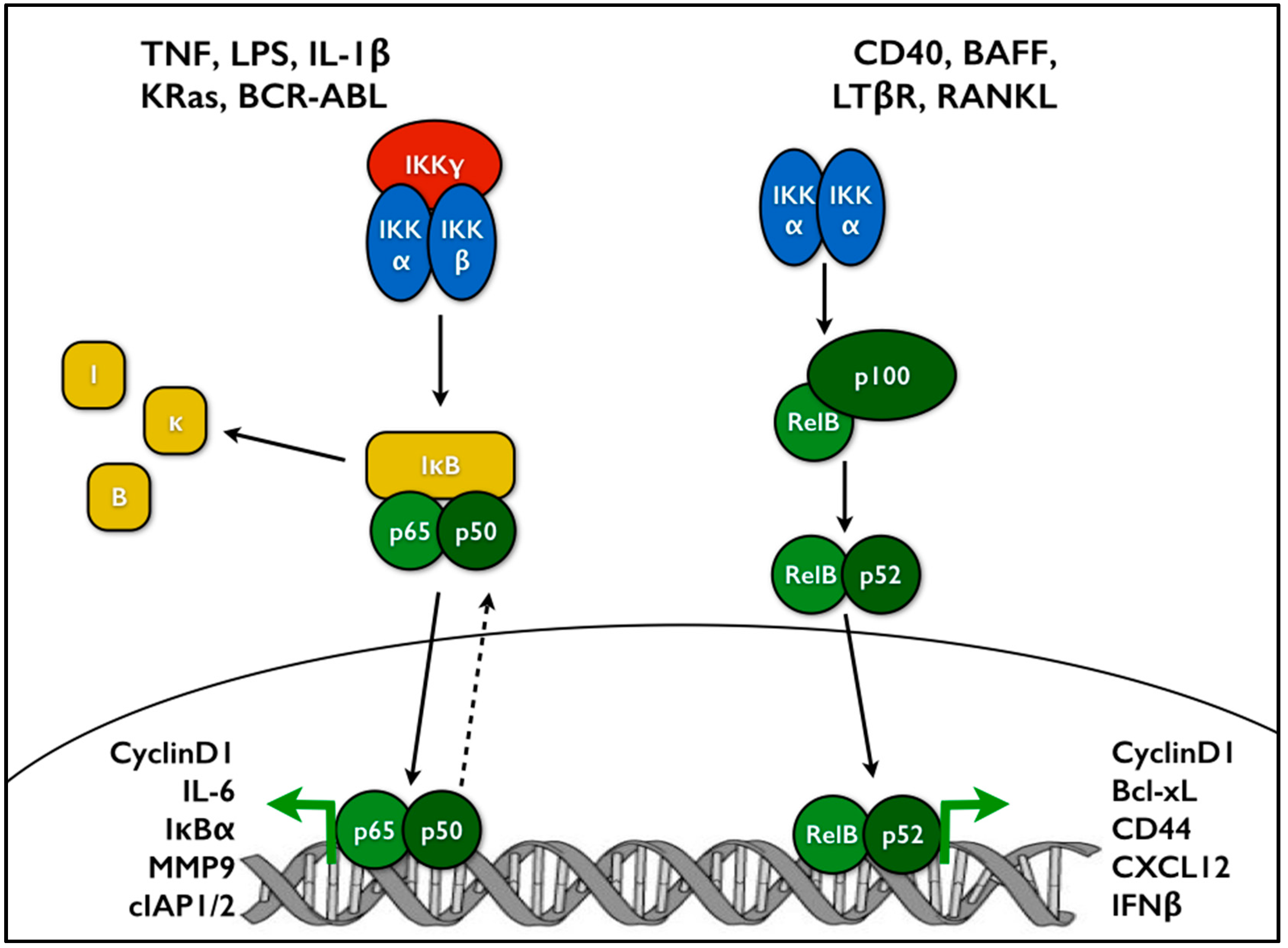
:1. Introduction to NF-κB Signaling
2. NF-κB in Cancer
2.1. NF-κB Activation in Cancer
2.2. Chronic Inflammation as a Precursor to Cancer
3. Cancer Stem Cells
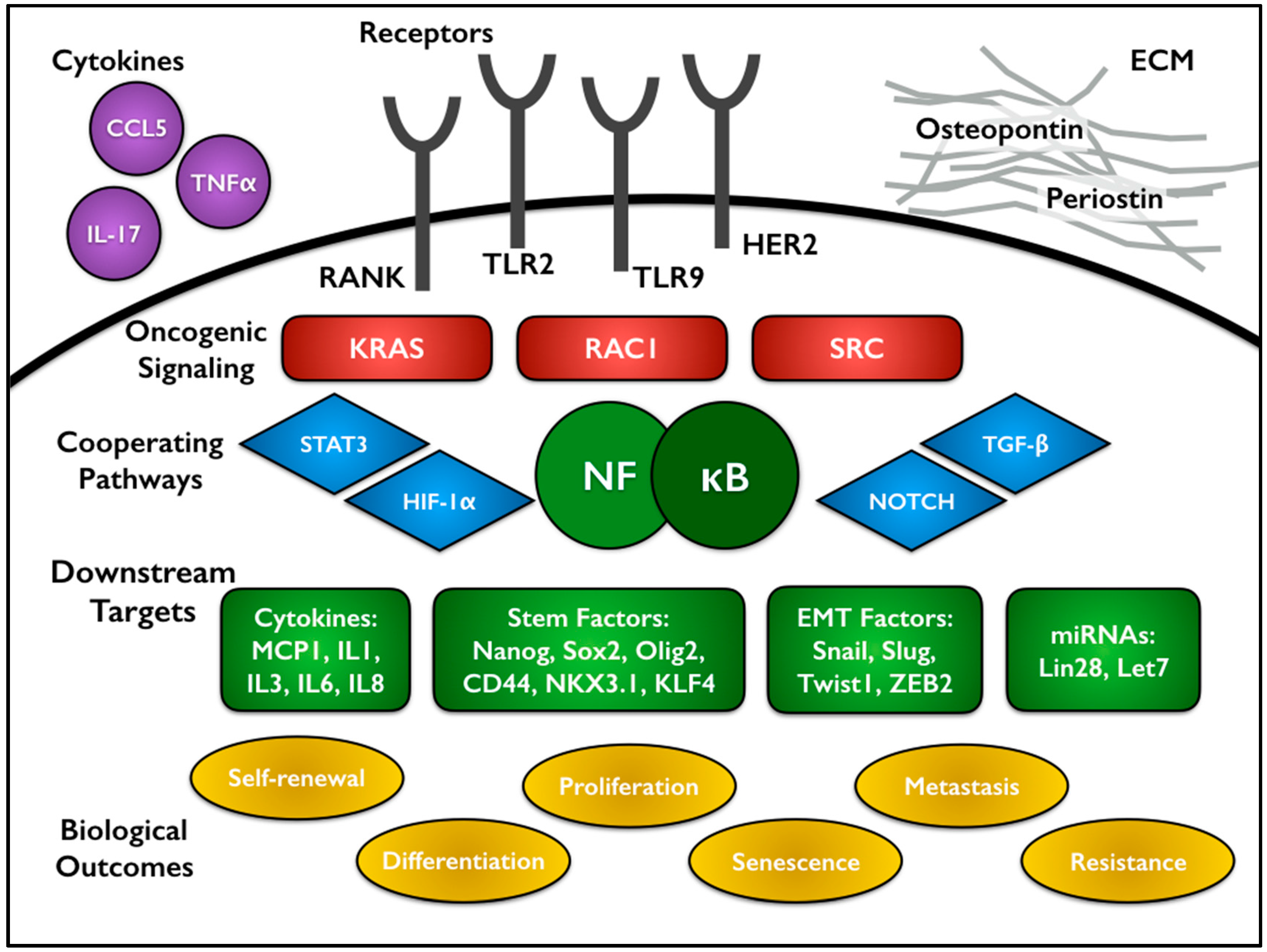
3.1. NF-κB Activation in CSCs
3.2. Connections between NF-κB Signaling, Cytokines, and CSCs
3.3. Interactions between NF-κB and the Tumor Microenvironment
3.4. Contributions by the NF-κB Pathway to Invasion and Metastasis
4. NF-κB as a Therapeutic Target
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AML | acute myeloid leukemia |
| APC | adenomatous polyposis coli |
| CML | chronic myeloid leukemia |
| CSC | cancer stem cells |
| DEN | diethylnitrosamine |
| DLBCL | diffuse large B cell lymphoma |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| HSC | hematopoietic stem cell |
| IκBα | nuclear factor of κ light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-Cells inhibitor, α |
| IKK | inhibitor of κB kinase |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| NBD | NEMO binding domain |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor of κ light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-Cells |
| NIK | NF-κB-inducing kinase |
| POSTN | periostin |
| RANK | receptor activator of NF-κB |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
References
- Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Shared Principles in NF-κB Signaling. Cell 2008, 132, 344–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, C.; Van Antwerp, D.; Hope, T.J. An N-terminal nuclear export signal is required for the nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of IκBα. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 6682–6693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.T.; Kudo, N.; Yoshida, M.; Miyamoto, S. A nuclear export signal in the N-terminal regulatory domain of IκBα controls cytoplasmic localization of inactive NF-κB/IκBα complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 1014–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlotti, F.; Dower, S.K.; Qwarnstrom, E.E. Dynamic Shuttling of Nuclear Factor-κB between the Nucleus and Cytoplasm as a Consequence of Inhibitor Dissociation. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 41028–41034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birbach, A.; Gold, P.; Binder, B.R.; Hofer, E.; De Martin, R.; Schmid, J.A. Signaling Molecules of the NF-κB Pathway Shuttle Constitutively between Cytoplasm and Nucleus. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 10842–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S.; Hayden, M.S. Celebrating 25 years of NF-κB research. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, J.W.; Baldwin, A.S. IKK/Nuclear Factor-κB and Oncogenesis. Adv. Cancer Res. 2014, 121, 125–145. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weih, F.; Carrasco, D.; Durham, S.K.; Barton, D.S.; Rizzo, C.A.; Ryseck, R.P.; Lira, S.A.; Bravo, R. Multiorgan inflammation and hematopoietic abnormalities in mice with a targeted disruption of RelB, a member of the NF-κ B/Rel family. Cell 1995, 80, 331–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossmann, M.; Metcalf, D.; Merryfull, J.; Beg, A.; Baltimore, D.; Gerondakis, S. The combined absence of the transcription factors Rel and RelA leads to multiple hemopoietic cell defects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 11848–11853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, S.J.; Baldwin, A.S. Deletion of the NF-kappaB subunit p65/RelA in the hematopoietic compartment leads to defects in hematopoietic stem cell function. Blood 2013, 121, 5015–5024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Xiu, Y.; Ashton, J.; Xing, L.; Morita, Y.; Jordan, C.T.; Boyce, B.F. Noncanonical NF-κB Signaling Regulates Hematopoietic Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Microenvironment Interactions. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 709–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.L.; Rao, D.S.; O’Connell, R.M.; Garcia-Flores, Y.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNA-146a acts as a guardian of the quality and longevity of hematopoietic stem cells in mice. Elife 2013, 2, e00537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.L.; Ma, C.; O’Connell, R.M.; Mehta, A.; DiLoreto, R.; Heath, J.R.; Baltimore, D. Conversion of Danger Signals into Cytokine Signals by Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells for Regulation of Stress-Induced Hematopoiesis. Cell Stem Cell 2014, 14, 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, L.; Hughes, O.; Yung, S.; Hyslop, L.; Stewart, R.; Wappler, I.; Peters, H.; Walter, T.; Stojkovic, P.; Evans, J.; et al. The role of PI3K/AKT, MAPK/ERK and NFκB signalling in the maintenance of human embryonic stem cell pluripotency and viability highlighted by transcriptional profiling and functional analysis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 1894–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, P.; Zhou, C.; Alvarez, R.; Hong, C.; Wang, C.-Y. Inhibition of IKK/NF-κB Signaling Enhances Differentiation of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Human Embryonic Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lüningschrör, P.; Stöcker, B.; Kaltschmidt, B.; Kaltschmidt, C. miR-290 Cluster Modulates Pluripotency by Repressing Canonical NF-κB Signaling. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 655–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttridge, D.C.; Albanese, C.; Reuther, J.Y.; Pestell, R.G.; Baldwin, A.S. NF-κB controls cell growth and differentiation through transcriptional regulation of cyclin D1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 5785–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canicio, J.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; Carrasco, M.; Palacin, M.; Chien, K.; Zorzano, A.; Kaliman, P. Nuclear factor κB-inducing kinase and IκB kinase-α signal skeletal muscle cell differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 20228–20233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakkar, N.; Wang, J.; Ladner, K.J.; Wang, H.; Dahlman, J.M.; Carathers, M.; Acharyya, S.; Rudnicki, M.A.; Hollenbach, A.D.; Guttridge, D.C. IKK/NF-κB regulates skeletal myogenesis via a signaling switch to inhibit differentiation and promote mitochondrial biogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 787–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelmsen, K.C.; Eggleton, K.; Temin, H.M. Nucleic acid sequences of the oncogene v-rel in reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T and its cellular homolog, the proto-oncogene c-rel. J. Virol. 1984, 52, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kieran, M.; Blank, V.; Logeat, F.; Vandekerckhove, J.; Lottspeich, F.; Le Bail, O.; Urban, M.B.; Kourilsky, P.; Baeuerle, P.A.; Israel, A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-κB is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell 1990, 62, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finco, T.S.; Westwick, J.K.; Norris, J.L.; Beg, A.A.; Der, C.J.; Baldwin, A.S. Oncogenic Ha-Ras-induced signaling activates NF-κB transcriptional activity, which is required for cellular transformation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 24113–24116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuther, J.Y.; Reuther, G.W.; Cortez, D.; Pendergast, A.M.; Baldwin, A.S. A requirement for NF-κB activation in Bcr-Abl-mediated transformation. Genes Dev. 1998, 12, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stein, S.J.; Baldwin, A.S. NF-κB suppresses ROS levels in BCR-ABL(+) cells to prevent activation of JNK and cell death. Oncogene 2011, 45, 4557–4566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, M.W.; Wang, C.Y.; Cogswell, P.C.; Rogers-Graham, K.S.; Lowe, S.W.; Der, C.J.; Baldwin, A.S. Requirement of NF-κB activation to suppress p53-independent apoptosis induced by oncogenic Ras. Science 1997, 278, 1812–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisz, L.; Damalas, A.; Liontos, M.; Karakaidos, P.; Fontemaggi, G.; Maor-Aloni, R.; Kalis, M.; Levrero, M.; Strano, S.; Gorgoulis, V.G.; et al. Mutant p53 Enhances Nuclear Factor-κB Activation by Tumor Necrosis Factor α in Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2396–2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooks, T.; Pateras, I.S.; Tarcic, O.; Solomon, H.; Schetter, A.J.; Wilder, S.; Lozano, G.; Pikarsky, E.; Forshew, T.; Rozenfeld, N.; et al. Mutant p53 Prolongs NF-κB Activation and Promotes Chronic Inflammation and Inflammation-Associated Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 634–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Minin, G.; Bellazzo, A.; Dal Ferro, M.; Chiaruttini, G.; Nuzzo, S.; Bicciato, S.; Piazza, S.; Rami, D.; Bulla, R.; Sommaggio, R.; et al. Mutant p53 Reprograms TNF Signaling in Cancer Cells through Interaction with the Tumor Suppressor DAB2IP. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 617–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, H.; Ohh, M. The von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor protein sensitizes renal cell carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-induced cytotoxicity by suppressing the nuclear factor-κB-dependent antiapoptotic pathway. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7076–7080. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Fisher, M.; Rettig, M.B. VHL expression in renal cell carcinoma sensitizes to bortezomib (PS-341) through an NF-κB-dependent mechanism. Oncogene 2004, 24, 1563–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, J.; Rettig, M.B. Mechanism of von Hippel-Lindau Protein-Mediated Suppression of Nuclear Factor κB Activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 7546–7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gustin, J.A.; Maehama, T.; Dixon, J.E.; Donner, D.B. The PTEN Tumor Suppressor Protein Inhibits Tumor Necrosis Factor-induced Nuclear Factor-κB Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 27740–27744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asano, T.; Yao, Y.; Zhu, J.; Li, D.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Reddy, S.A.G. The PI 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway is activated due to aberrant Pten expression and targets transcription factors NF-κB and c-Myc in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 8571–8580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, H.; Elpek, K.G.; Vinjamoori, A.; Zimmerman, S.M.; Chu, G.C.; Yan, H.; Fletcher-Sananikone, E.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; et al. PTEN Is a Major Tumor Suppressor in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma and Regulates an NF-κB-Cytokine Network. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 158–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Belguise, K.; Kersual, N.; Kirsch, K.H.; Mineva, N.D.; Galtier, F.; Chalbos, D.; Sonenshein, G.E. Oestrogen signalling inhibits invasive phenotype by repressing RelB and its target BCL2. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Josson, S.; Fang, F.; Oberley, T.D.; St Clair, D.K.; Wan, X.S.; Sun, Y.; Bakthavatchalu, V.; Muthuswamy, A.; St Clair, W.H. RelB Enhances Prostate Cancer Growth: Implications for the Role of the Nuclear Factor-kappaB Alternative Pathway in Tumorigenicity. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 3267–3271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wharry, C.E.; Haines, K.M.; Carroll, R.G.; May, M.J. Constitutive noncanonical NFκB signaling in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 8, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thu, Y.M.; Su, Y.; Yang, J.; Splittgerber, R.; Na, S.; Boyd, A.; Mosse, C.; Simons, C.; Richmond, A. NF-κB inducing kinase (NIK) modulates melanoma tumorigenesis by regulating expression of pro-survival factors through the β-catenin pathway. Oncogene 2011, 31, 2580–2592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Ramakrishnan, D.; Valenta, J.; Parney, I.F.; Bayless, K.J.; Sitcheran, R. The NF-κB RelB Protein Is an Oncogenic Driver of Mesenchymal Glioma. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uno, M.; Saitoh, Y.; Mochida, K.; Tsuruyama, E.; Kiyono, T.; Imoto, I.; Inazawa, J.; Yuasa, Y.; Kubota, T.; Yamaoka, S. NF-κB Inducing Kinase, a Central Signaling Component of the Non-Canonical Pathway of NF-κB, Contributes to Ovarian Cancer Progression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.-L.; Sun, W.; Chandrasekharan, P.; Cheng, H.S.; Ying, Z.; Lakshmanan, M.; Raju, A.; Tenen, D.G.; Cheng, S.-Y.; et al. Non-canonical NF-κB signalling and ETS1/2 cooperatively drive C250T mutant TERT promoter activation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meylan, E.; Dooley, A.L.; Feldser, D.M.; Shen, L.; Turk, E.; Ouyang, C.; Jacks, T. Requirement for NF-κB signalling in a mouse model of lung adenocarcinoma. Nature 2009, 461, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassères, D.S.; Ebbs, A.; Levantini, E.; Baldwin, A.S. Requirement of the NF-κB subunit p65/RelA for K-Ras-induced lung tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 3537–3546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Splittgerber, R.; Yull, F.E.; Kantrow, S.; Ayers, G.D.; Karin, M.; Richmond, A. Conditional ablation of Ikkb inhibits melanoma tumor development in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 2010, 120, 2563–2574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of Cancer: The Next Generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, A.S. Regulation of cell death and autophagy by IKK and NF-κB: Critical mechanisms in immune function and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 327–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.L.; McKinsey, T.A.; Liu, L.; Gentry, J.J.; Malim, M.H.; Ballard, D.W. Suppression of tumor necrosis factor-induced cell death by inhibitor of apoptosis c-IAP2 is under NF-κB control. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 10057–10062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Mayo, M.W.; Korneluk, R.G.; Goeddel, D.V.; Baldwin, A.S. NF-κB antiapoptosis: Induction of TRAF1 and TRAF2 and c-IAP1 and c-IAP2 to suppress caspase-8 activation. Science 1998, 281, 1680–1683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, P.; Kahn, D.A.; Baltimore, D. Anti-apoptotic effect of hyperglycemia can allow survival of potentially autoreactive T cells. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 18, 690–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassères, D.S.; Baldwin, A.S. Nuclear factor-κB and inhibitor of κB kinase pathways in oncogenic initiation and progression. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6817–6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beroukhim, R.; Mermel, C.H.; Porter, D.; Wei, G.; Raychaudhuri, S.; Donovan, J.; Barretina, J.; Boehm, J.S.; Dobson, J.; Urashima, M.; et al. The landscape of somatic copy-number alteration across human cancers. Nature 2010, 463, 899–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boehm, J.S.; Zhao, J.J.; Yao, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Firestein, R.; Dunn, I.F.; Sjostrom, S.K.; Garraway, L.A.; Weremowicz, S.; Richardson, A.L.; et al. Integrative Genomic Approaches Identify IKBKE as a Breast Cancer Oncogene. Cell 2007, 129, 1065–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlowski, R.Z.; Baldwin, A.S. NF-κB as a therapeutic target in cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neri, A.; Chang, C.C.; Lombardi, L.; Salina, M.; Corradini, P.; Maiolo, A.T.; Chaganti, R.S.; Dalla-Favera, R. B cell lymphoma-associated chromosomal translocation involves candidate oncogene lyt-10, homologous to NF-κB p50. Cell 1991, 67, 1075–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, M.; Mohankumar, K.M.; Punchihewa, C.; Weinlich, R.; Dalton, J.D.; Li, Y.; Lee, R.; Tatevossian, R.G.; Phoenix, T.N.; Thiruvenkatam, R.; et al. C11orf95–RELA fusions drive oncogenic NF-κB signalling in ependymoma. Nature 2014, 506, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bredel, M.; Scholtens, D.M.; Yadav, A.K.; Alvarez, A.A.; Renfrow, J.J.; Chandler, J.P.; Yu, I.L.Y.; Carro, M.S.; Dai, F.; Tagge, M.J.; et al. NFKBIA Deletion in Glioblastomas. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 627–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.-H.; Yang, Y.; Staudt, L.M. Pathogenetic importance and therapeutic implications of NF-κB in lymphoid malignancies. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 359–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkhofer, E.C.; Cogswell, P.; Baldwin, A.S. Her2 activates NF-κB and induces invasion through the canonical pathway involving IKKα. Oncogene 2010, 29, 1238–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.; Babic, I.; Nathanson, D.; Akhavan, D.; Guo, D.; Gini, B.; Dang, J.; Zhu, S.; Yang, H.; De Jesus, J.; et al. Oncogenic EGFR Signaling Activates an mTORC2-NF-κB Pathway That Promotes Chemotherapy Resistance. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 524–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, H.C.; Adli, M.; Baldwin, A.S. Regulation of Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Activity in PTEN-Inactive Prostate Cancer Cells by IκB Kinase α. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6263–6269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, H.C.; Cooper, M.J.; Cogswell, P.C.; Duncan, J.A.; Ting, J.P.Y.; Baldwin, A.S. Akt-dependent regulation of NF-κB is controlled by mTOR and Raptor in association with IKK. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1490–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Lai, E.; Liu, J.; Lin, J.; Yang, C.; Jia, C.; Li, Y.; Bai, X.; Li, M. IKK interacts with rictor and regulates mTORC2. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 2239–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, H.C.; Ebbs, A.; Pasparakis, M.; Van Dyke, T.; Bassères, D.S.; Baldwin, A.S. Akt-dependent Activation of mTORC1 Complex Involves Phosphorylation of mTOR (Mammalian Target of Rapamycin) by IκB Kinase α (IKKα). J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 25227–25240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Tan, W.; Wu, X.; Poustovoitov, M.; Strasner, A.; Li, W.; Borcherding, N.; Ghassemian, M.; Karin, M. A NIK-IKKα Module Expands ErbB2-Induced Tumor-Initiating Cells by Stimulating Nuclear Export of p27/Kip1. Cancer Cell 2013, 23, 647–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, Y.; Padre, R.C.; De Mendoza, T.H.; Bottero, V.; Tergaonkar, V.B.; Verma, I.M. Phosphorylation of p53 by IκB kinase 2 promotes its degradation by beta-TrCP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 2629–2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greten, F.R.; Eckmann, L.; Greten, T.F.; Park, J.M.; Li, Z.-W.; Egan, L.J.; Kagnoff, M.F.; Karin, M. IKKβ Links Inflammation and Tumorigenesis in a Mouse Model of Colitis-Associated Cancer. Cell 2004, 118, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, S.; Kamata, H.; Luo, J.-L.; Leffert, H.; Karin, M. IKKβ Couples Hepatocyte Death to Cytokine-Driven Compensatory Proliferation that Promotes Chemical Hepatocarcinogenesis. Cell 2005, 121, 977–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakurai, T.; Maeda, S.; Chang, L.; Karin, M. Loss of hepatic NF-κB activity enhances chemical hepatocarcinogenesis through sustained c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1 activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10544–10551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiDonato, J.A.; Mercurio, F.; Karin, M. NF-κB and the link between inflammation and cancer. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 379–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erez, N.; Truitt, M.; Olson, P.; Hanahan, D. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Are Activated in Incipient Neoplasia to Orchestrate Tumor-Promoting Inflammation in an NF-κB-Dependent Manner. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 135–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliaraki, V.; Pasparakis, M.; Kollias, G. IKKbeta in intestinal mesenchymal cells promotes initiation of colitis-associated cancer. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 205, 331. [Google Scholar]
- Pallangyo, C.K.; Ziegler, P.K.; Greten, F.R. IKKbeta acts as a tumor suppressor in cancer-associated fibroblasts during intestinal tumorigenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 223, 162. [Google Scholar]
- Saccani, A.; Schioppa, T.; Porta, C.; Biswas, S.K.; Nebuloni, M.; Vago, L.; Bottazzi, B.; Colombo, M.P.; Mantovani, A.; Sica, A. p50 Nuclear Factor-κB Overexpression in Tumor-Associated Macrophages Inhibits M1 Inflammatory Responses and Antitumor Resistance. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11432–11440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagemann, T.; Lawrence, T.; McNeish, I.; Charles, K.A.; Kulbe, H.; Thompson, R.G.; Robinson, S.C.; Balkwill, F.R. “Re-educating” tumor-associated macrophages by targeting NF-κB. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, D.; Dick, J.E. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat. Med. 1997, 3, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Clarke, I.D.; Terasaki, M.; Bonn, V.E.; Hawkins, C.; Squire, J.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of a cancer stem cell in human brain tumors. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 5821–5828. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Hawkins, C.; Clarke, I.D.; Squire, J.A.; Bayani, J.; Hide, T.; Henkelman, R.M.; Cusimano, M.D.; Dirks, P.B. Identification of human brain tumour initiating cells. Nature 2004, 432, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hajj, M.; Wicha, M.S.; Benito-Hernandez, A.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F. Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 3983–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, A.T. Prospective Identification of Tumorigenic Prostate Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 10946–10951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci-Vitiani, L.; Lombardi, D.G.; Pilozzi, E.; Biffoni, M.; Todaro, M.; Peschle, C.; De Maria, R. Identification and expansion of human colon-cancer-initiating cells. Nature 2006, 445, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Heidt, D.G.; Dalerba, P.; Burant, C.F.; Zhang, L.; Adsay, V.; Wicha, M.; Clarke, M.F.; Simeone, D.M. Identification of Pancreatic Cancer Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reya, T.; Morrison, S.J.; Clarke, M.F.; Weissman, I.L. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells. Nature 2001, 414, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Nishimura, M.C.; Bumbaca, S.M.; Kharbanda, S.; Forrest, W.F.; Kasman, I.M.; Greve, J.M.; Soriano, R.H.; Gilmour, L.L.; Rivers, C.S.; et al. A Hierarchy of Self-Renewing Tumor-Initiating Cell Types in Glioblastoma. Cancer Cell 2010, 17, 362–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruce, W.R.; van der Gaag, H. A Quantitative Assay for the Number of Murine Lymphoma Cells Capable of Proliferation in vivo. Nature 1963, 199, 79–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, B.A.; Weiss, S. Generation of neurons and astrocytes from isolated cells of the adult mammalian central nervous system. Science 1992, 255, 1707–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemmati, H.D.; Nakano, I.; Lazareff, J.A.; Masterman-Smith, M.; Geschwind, D.H.; Bronner-Fraser, M.; Kornblum, H.I. Cancerous stem cells can arise from pediatric brain tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15178–15183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, L.V.; Vanner, R.; Dirks, P.; Eaves, C.J. Cancer stem cells: An evolving concept. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalerba, P.; Dylla, S.J.; Park, I.-K.; Liu, R.; Wang, X.; Cho, R.W.; Hoey, T.; Gurney, A.; Huang, E.H.; Simeone, D.M. Phenotypic characterization of human colorectal cancer stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 10158–10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sales, K.M.; Winslet, M.C.; Seifalian, A.M. Stem Cells and Cancer: An Overview. Stem Cell Rev. 2007, 3, 249–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, M.L.; Neering, S.J.; Upchurch, D.; Grimes, B.; Howard, D.S.; Rizzieri, D.A.; Luger, S.M.; Jordan, C.T. Nuclear factor-κB is constitutively activated in primitive human acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood 2001, 98, 2301–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekhar, V.K.; Studer, L.; Gerald, W.; Socci, N.D.; Scher, H.I. Tumour-initiating stem-like cells in human prostate cancer exhibit increased NF-κB signalling. Nat. Commun. 2011, 2, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garner, J.M.; Fan, M.; Yang, C.H.; Du, Z.; Sims, M.; Davidoff, A.M.; Pfeffer, L.M. Constitutive Activation of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 3 (STAT3) and Nuclear Factor-κB Signaling in Glioblastoma Cancer Stem Cells Regulates the Notch Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 26167–26176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Liu, L.; Wu, Z.; Li, Y.; Ying, Z.; Lin, C.; Wu, J.; Hu, B.; Cheng, S.-Y.; Li, M.; Li, J. TGF-β induces miR-182 to sustain NF-κB activation in glioma subsets. J. Clin. Invest. 2012, 122, 3563–3578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tafani, M.; Di Vito, M.; Frati, A.; Pellegrini, L.; De Santis, E.; Sette, G.; Eramo, A.; Sale, P.; Mari, E.; Santoro, A.; et al. Pro-inflammatory gene expression in solid glioblastoma microenvironment and in hypoxic stem cells from human glioblastoma. J. Neuroinflamm. 2011, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murohashi, M.; Hinohara, K.; Kuroda, M.; Isagawa, T.; Tsuji, S.; Kobayashi, S.; Umezawa, K.; Tojo, A.; Aburatani, H.; Gotoh, N. Gene set enrichment analysis provides insight into novel signalling pathways in breast cancer stem cells. Br. J. Cancer 2009, 102, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, G.Y.; Dalerba, P.; Gurney, A.; Hoey, T.; Sherlock, G.; Lewicki, J.; Shedden, K.; Clarke, M.F. The prognostic role of a gene signature from tumorigenic breast-cancer cells. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnie, R.; Bryce, S.D.; Roome, C.; Dussupt, V.; Droop, A.; Lang, S.H.; Berry, P.A.; Hyde, C.F.; Lewis, J.L.; Stower, M.J.; et al. Gene expression profiling of human prostate cancer stem cells reveals a pro-inflammatory phenotype and the importance of extracellular matrix interactions. Genome Biol. 2008, 9, R83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leizer, A.L.; Alvero, A.B.; Fu, H.H.; Holmberg, J.C.; Cheng, Y.-C.; Silasi, D.-A.; Rutherford, T.; Mor, G. Regulation of Inflammation by the NF-κB Pathway in Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 65, 438–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korkaya, H.; Liu, S.; Wicha, M.S. Regulation of Cancer Stem Cells by Cytokine Networks: Attacking Cancer’s Inflammatory Roots. Clin. Can. Res. 2011, 17, 6125–6129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratt, M.A.C.; Tibbo, E.; Robertson, S.J.; Jansson, D.; Hurst, K.; Perez-Iratxeta, C.; Lau, R.; Niu, M.Y. The canonical NF-κB pathway is required for formation of luminal mammary neoplasias and is activated in the mammary progenitor population. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2710–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Sakamaki, T.; Casimiro, M.C.; Willmarth, N.E.; Quong, A.A.; Ju, X.; Ojeifo, J.; Jiao, X.; Yeow, W.-S.; Katiyar, S.; et al. The canonical NF-κB pathway governs mammary tumorigenesis in transgenic mice and tumor stem cell expansion. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 10464–10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Luo, J.-L.; Karin, M. IκB kinase α kinase activity is required for self-renewal of ErbB2/Her2-transformed mammary tumor-initiating cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 15852–15857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myant, K.B.; Cammareri, P.; McGhee, E.J.; Ridgway, R.A.; Huels, D.J.; Cordero, J.B.; Schwitalla, S.; Kalna, G.; Ogg, E.-L.; Athineos, D.; et al. ROS Production and NF-κB Activation Triggered by RAC1 Facilitate WNT-Driven Intestinal Stem Cell Proliferation and Colorectal Cancer Initiation. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 12, 761–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chefetz, I.; Alvero, A.; Holmberg, J.; Lebowitz, N.; Craveiro, V.; Yang-Hartwich, Y.; Yin, G.; Squillace, L.; Gurrea Soteras, M.; Aldo, P.; et al. TLR2 enhances ovarian cancer stem cell self-renewal and promotes tumor repair and recurrence. Cell Cycle 2014, 12, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, D.; Zhang, Q.; Hossain, D.M.S.; Nechaev, S.; Li, H.; Kowolik, C.M.; D’Apuzzo, M.; Forman, S.; Jones, J.; Pal, S.K.; et al. TLR9 signaling through NF-κB/RELA and STAT3 promotes tumor-propagating potential of prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17302–17313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallipoli, P.; Pellicano, F.; Morrison, H.; Laidlaw, K.; Allan, E.K.; Bhatia, R.; Copland, M.; Jørgensen, H.G.; Holyoake, T.L. Autocrine TNF-α production supports CML stem and progenitor cell survival and enhances their proliferation. Blood 2013, 122, 3335–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagoya, Y.; Yoshimi, A.; Kataoka, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Kumano, K.; Arai, S.; Kobayashi, H.; Saito, T.; Iwakura, Y.; Kurokawa, M. Positive feedback between NF-κB and TNF-α promotes leukemia-initiating cell capacity. J. Clin. Invest. 2014, 124, 528–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Storci, G.; Sansone, P.; Mari, S.; D’Uva, G.; Tavolari, S.; Guarnieri, T.; Taffurelli, M.; Ceccarelli, C.; Santini, D.; Chieco, P.; et al. TNFα up-regulates SLUG via the NF-κB/HIF1α axis, which imparts breast cancer cells with a stem cell-like phenotype. J. Cell. Physiol. 2010, 225, 682–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Fu, L.; Sun, H.; Guo, L.; DuBois, R.N. Prostaglandin E2 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Stem Cell Expansion and Metastasis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2015, 149, 1884–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parajuli, P.; Anand, R.; Mandalaparty, C.; Suryadevara, R.; Sriranga, P.U.; Michelhaugh, S.K.; Cazacu, S.; Finniss, S.; Thakur, A.; Lum, L.G.; et al. Preferential expression of functional IL-17R in glioma stem cells: Potential role in self-renewal. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 6121–6135. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Hirsch, H.A.; Struhl, K. An epigenetic switch involving NF-κB, Lin28, Let-7 MicroRNA, and IL6 links inflammation to cell transformation. Cell 2009, 139, 693–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iliopoulos, D.; Hirsch, H.A.; Wang, G.; Struhl, K. Inducible formation of breast cancer stem cells and their dynamic equilibrium with non-stem cancer cells via IL6 secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 1397–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Sun, X.; Qin, S.; Wang, H.; Zheng, Z.; Xu, S.; Luo, G.; Liu, P.; Liu, J.; Du, N.; et al. Let-7a regulates mammosphere formation capacity through Ras/NF-κB and Ras/MAPK/ERK pathway in breast cancer stem cells. Cell Cycle 2015, 14, 1686–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynaud, D.; Pietras, E.; Barry-Holson, K.; Mir, A.; Binnewies, M.; Jeanne, M.; Sala-Torra, O.; Radich, J.P.; Passegué, E. IL-6 controls leukemic multipotent progenitor cell fate and contributes to chronic myelogenous leukemia development. Cancer Cell 2011, 20, 661–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Lathia, J.D.; Wu, Q.; Wang, J.; Li, Z.; Heddleston, J.M.; Eyler, C.E.; Elderbroom, J.; Gallagher, J.; et al. Targeting Interleukin 6 Signaling Suppresses Glioma Stem Cell Survival and Tumor Growth. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2393–2404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, C.; Poppleton, H.; Kocak, M.; Hogg, T.L.; Fuller, C.; Hamner, B.; Oh, E.Y.; Gaber, M.W.; Finklestein, D.; Allen, M.; et al. A Perivascular Niche for Brain Tumor Stem Cells. Cancer Cell 2007, 11, 69–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charles, N.; Ozawa, T.; Squatrito, M.; Bleau, A.-M.; Brennan, C.W.; Hambardzumyan, D.; Holland, E.C. Perivascular nitric oxide activates notch signaling and promotes stem-like character in PDGF-induced glioma cells. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, T.; Long, H.; He, L.; Han, X.; Lin, K.; Liang, Z.; Zhuo, W.; Xie, R.; Zhu, B. Interleukin-17 produced by tumor microenvironment promotes self-renewal of CD133+ cancer stem-like cells in ovarian cancer. Oncogene 2013, 34, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvero, A.B.; Fu, H.H.; Holmberg, J.; Visintin, I.; Mor, L.; Marquina, C.C.; Oidtman, J.; Silasi, D.-A.; Mor, G. Stem-Like Ovarian Cancer Cells Can Serve as Tumor Vascular Progenitors. Stem Cells 2009, 27, 2405–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Chadalavada, K.; Wilshire, J.; Kowalik, U.; Hovinga, K.E.; Geber, A.; Fligelman, B.; Leversha, M.; Brennan, C.; Tabar, V. Glioblastoma stem-like cells give rise to tumour endothelium. Nature 2010, 468, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soda, Y.; Marumoto, T.; Friedmann-Morvinski, D.; Soda, M.; Liu, F.; Michiue, H.; Pastorino, S.; Yang, M.; Hoffman, R.M.; Kesari, S.; Verma, I.M. Transdifferentiation of glioblastoma cells into vascular endothelial cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4274–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Fan, X.; Jing, W.; Liang, Y.; Chen, R.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, M.; Jia, R.; Wang, H.; Zhang, X.; et al. Osteopontin promotes a cancer stem cell-like phenotype in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via an integrin-NF-κB-HIF-1α pathway. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 6627–6640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malanchi, I.; Santamaria-Martínez, A.; Susanto, E.; Peng, H.; Lehr, H.-A.; Delaloye, J.-F.; Huelsken, J. Interactions between cancer stem cells and their niche govern metastatic colonization. Nature 2011, 481, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambert, A.W.; Wong, C.K.; Ozturk, S.; Papageorgis, P.; Raghunathan, R.; Alekseyev, Y.; Gower, A.C.; Reinhard, B.M.; Abdolmaleky, H.M.; Thiagalingam, S. Tumor Cell-Derived Periostin Regulates Cytokines That Maintain Breast Cancer Stem Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramek, D.; Leibbrandt, A.; Sigl, V.; Kenner, L.; Pospisilik, J.A.; Lee, H.J.; Hanada, R.; Joshi, P.A.; Aliprantis, A.; Glimcher, L.; et al. Osteoclast differentiation factor RANKL controls development of progestin-driven mammary cancer. Nature 2010, 468, 98–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mani, S.A.; Guo, W.; Liao, M.-J.; Eaton, E.N.; Ayyanan, A.; Zhou, A.Y.; Brooks, M.; Reinhard, F.; Zhang, C.C.; Shipitsin, M.; et al. The Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Generates Cells with Properties of Stem Cells. Cell 2008, 133, 704–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barberà, M.J.; Puig, I.; Domínguez, D.; Julien-Grille, S.; Guaita-Esteruelas, S.; Peiró, S.; Baulida, J.; Francí, C.; Dedhar, S.; Larue, L.; et al. Regulation of Snail transcription during epithelial to mesenchymal transition of tumor cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 7345–7354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.J.; Litzenburger, B.C.; Cui, X.; Delgado, D.A.; Grabiner, B.C.; Lin, X.; Lewis, M.T.; Gottardis, M.M.; Wong, T.W.; Attar, R.M.; et al. Constitutively Active Type I Insulin-Like Growth Factor Receptor Causes Transformation and Xenograft Growth of Immortalized Mammary Epithelial Cells and Is Accompanied by an Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Mediated by NF-κB and Snail. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 3165–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belguise, K.; Guo, S.; Yang, S.; Rogers, A.E.; Seldin, D.C.; Sherr, D.H.; Sonenshein, G.E. Green Tea Polyphenols Reverse Cooperation between c-Rel and CK2 that Induces the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor, Slug, and an Invasive Phenotype. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11742–11750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Allison, D.F.; Baranova, N.N.; Wamsley, J.J.; Katz, A.J.; Bekiranov, S.; Jones, D.R.; Mayo, M.W. NF-κB Regulates Mesenchymal Transition for the Induction of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Initiating Cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e68597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chua, H.L.; Bhat-Nakshatri, P.; Clare, S.E.; Morimiya, A.; Badve, S.; Nakshatri, H. NF-κB represses E-cadherin expression and enhances epithelial to mesenchymal transition of mammary epithelial cells: Potential involvement of ZEB-1 and ZEB-2. Oncogene 2006, 26, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.M.; Coljee, V.W.; Pignolo, R.J.; Rotenberg, M.O.; Cristofalo, V.J.; Sierra, F. Cloning of the human twist gene: Its expression is retained in adult mesodermally-derived tissues. Gene 1997, 187, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanegae, Y.; Tavares, A.T.; Izpisúa Belmonte, J.C.; Verma, I.M. Role of Rel/NF-κB transcription factors during the outgrowth of the vertebrate limb. Nature 1998, 392, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takeda, K.; Takeuchi, O.; Tsujimura, T.; Itami, S.; Adachi, O.; Kawai, T.; Sanjo, H.; Yoshikawa, K.; Terada, N.; Akira, S. Limb and skin abnormalities in mice lacking IKKα. Science 1999, 284, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Šošić, D.; Richardson, J.A.; Yu, K.; Ornitz, D.M.; Olson, E.N. Twist regulates cytokine gene expression through a negative feedback loop that represses NF-κB activity. Cell 2003, 112, 169–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, C.G.; Bubici, C.; Zazzeroni, F.; Knabb, J.R.; Papa, S.; Kuntzen, C.; Franzoso, G. Upregulation of Twist-1 by NF-κB Blocks Cytotoxicity Induced by Chemotherapeutic Drugs. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 3920–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, C.; Eddy, S.F.; Sherr, D.H.; Sonenshein, G.E. NF-κB and epithelial to mesenchymal transition of cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Deng, J.; Rychahou, P.G.; Qiu, S.; Evers, B.M.; Zhou, B.P. Stabilization of Snail by NF-κB Is Required for Inflammation-Induced Cell Migration and Invasion. Cancer Cell 2009, 15, 416–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.W.; Xia, W.; Huo, L.; Lim, S.O.; Wu, Y.; Hsu, J.L.; Chao, C.H.; Yamaguchi, H.; Yang, N.K.; Ding, Q.; et al. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Induced by TNF-α Requires NF-κB-Mediated Transcriptional Upregulation of Twist1. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 1290–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, M.A.; Azoitei, N.; Baumann, B.; Grünert, S.; Sommer, A.; Pehamberger, H.; Kraut, N.; Beug, H.; Wirth, T. NF-κB is essential for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis in a model of breast cancer progression. J. Clin. Invest. 2004, 114, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palafox, M.; Ferrer, I.; Pellegrini, P.; Vila, S.; Hernandez-Ortega, S.; Urruticoechea, A.; Climent, F.; Soler, M.T.; Munoz, P.; Vinals, F.; et al. RANK Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness in Human Mammary Epithelial Cells and Promotes Tumorigenesis and Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 2879–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asiedu, M.K.; Beauchamp-Perez, F.D.; Ingle, J.N.; Behrens, M.D.; Radisky, D.C.; Knutson, K.L. AXL induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and regulates the function of breast cancer stem cells. Oncogene 2013, 33, 1316–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wamsley, J.J.; Kumar, M.; Allison, D.F.; Clift, S.H.; Holzknecht, C.M.; Szymura, S.J.; Hoang, S.A.; Xu, X.; Moskaluk, C.A.; Jones, D.R.; et al. Activin Upregulation by NF-κB Is Required to Maintain Mesenchymal Features of Cancer Stem-like Cells in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancer Res. 2015, 75, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Es-haghi, M.; Soltanian, S.; Dehghani, H. Perspective: Cooperation of Nanog, NF-κB, and CXCR4 in a regulatory network for directed migration of cancer stem cells. Tumor Biol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.P.; Arora, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Srivastava, S.K.; Kadakia, M.P.; Wang, B.; Grizzle, W.E.; Owen, L.B.; Singh, S. CXCL12/CXCR4 Protein Signaling Axis Induces Sonic Hedgehog Expression in Pancreatic Cancer Cells via Extracellular Regulated Kinase- and Akt Kinase-mediated Activation of Nuclear Factor-κB: Implications for Bidirectional Tumor-Stromal Interactions. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 39115–39124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helbig, G.; Christopherson, K.W.; Bhat-Nakshatri, P.; Kumar, S.; Kishimoto, H.; Miller, K.D.; Broxmeyer, H.E.; Nakshatri, H. NF-κB Promotes Breast Cancer Cell Migration and Metastasis by Inducing the Expression of the Chemokine Receptor CXCR4. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 21631–21638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, Y.; Duan, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yin, X.; Guan, G.; Zhang, H.; Dong, Q.; Yang, K. NF-κB signaling pathway confers neuroblastoma cells migration and invasion ability via the regulation of CXCR4. Med. Sci. Monit. 2014, 20, 2746–2752. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Himelstein, B.P.; Lee, E.J.; Sato, H.; Seiki, M.; Muschel, R.J. Transcriptional activation of the matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene in an H-ras and v-myc transformed rat embryo cell line. Oncogene 1997, 14, 1995–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farina, A.R.; Tacconelli, A.; Vacca, A.; Maroder, M.; Gulino, A.; Mackay, A.R. Transcriptional up-regulation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression during spontaneous epithelial to neuroblast phenotype conversion by SK-N-SH neuroblastoma cells, involved in enhanced invasivity, depends upon GT-box and nuclear factor κB elements. Cell Growth Differ. 1999, 10, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ricca, A.; Biroccio, A.; Del Bufalo, D.; Mackay, A.R.; Santoni, A.; Cippitelli, M. BCL-2 over-expression enhances NF-κB activity and induces mmp-9 transcription in human MCF7(ADR) breast-cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 86, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.P.; Tuan, T.L.; Wu, H.; Hughes, M.; Garner, W.L. TNF-α stimulates activation of pro-MMP2 in human skin through NF-κB mediated induction of MT1-MMP. J. Cell. Sci. 2001, 114, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Philip, S.; Bulbule, A.; Kundu, G.C. Osteopontin stimulates tumor growth and activation of promatrix metalloproteinase-2 through nuclear factor-κB-mediated induction of membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase in murine melanoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 44926–44935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Connelly, L.; Robinson-Benion, C.; Chont, M.; Saint-Jean, L.; Li, H.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Blackwell, T.S.; Yull, F.E. A transgenic model reveals important roles for the NF-κB alternative pathway (p100/p52) in mammary development and links to tumorigenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10028–10035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, H.; Xie, R.; Xiang, T.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, S.; Liang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Zhu, B. Autocrine CCL5 Signaling Promotes Invasion and Migration of CD133+ Ovarian Cancer Stem-Like Cells via NF-κB-Mediated MMP-9 Upregulation. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 2309–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Robinson, J.B.; Deguzman, A.; Bucana, C.D.; Fidler, I.J. Blockade of nuclear factor-κB signaling inhibits angiogenesis and tumorigenicity of human ovarian cancer cells by suppressing expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and interleukin 8. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 5334–5339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, M.; Taguchi, Y.; Ito-Kureha, T.; Semba, K.; Yamaguchi, N.; Inoue, J.-I. NF-κB non-cell-autonomously regulates cancer stem cell populations in the basal-like breast cancer subtype. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohtsu, N.; Nakatani, Y.; Yamashita, D.; Ohue, S.; Ohnishi, T.; Kondo, T. Eva1 Maintains the Stem-like Character of Glioblastoma-Initiating Cells by Activating the Noncanonical NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, M.L.; Swiderski, C.F.; Howard, D.S.; Grimes, B.A.; Rossi, R.M.; Szilvassy, S.J.; Jordan, C.T. Preferential induction of apoptosis for primary human leukemic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16220–16225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzman, M.L.; Rossi, R.M.; Karnischky, L.; Li, X.; Peterson, D.R.; Howard, D.S.; Jordan, C.T. The sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide induces apoptosis of human acute myelogenous leukemia stem and progenitor cells. Blood 2005, 105, 4163–4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassane, D.C.; Guzman, M.L.; Corbett, C.; Li, X.; Abboud, R.; Young, F.; Liesveld, J.L.; Carroll, M.; Jordan, C.T. Discovery of agents that eradicate leukemia stem cells using an in silico screen of public gene expression data. Blood 2008, 111, 5654–5662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, H.; Gu, P.; Bai, J.; Margolick, J.B.; Zhang, Y. NF-κB pathway inhibitors preferentially inhibit breast cancer stem-like cells. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2007, 111, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Ren, X.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, X.; Allen, J.E.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, Y.; Huang, S.-Y.; Yang, W.; Berg, A.; et al. The NFκB inhibitor, SN50, induces differentiation of glioma stem cells and suppresses their oncogenic phenotype. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2014, 15, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nogueira, L.; Ruiz-Ontañon, P.; Vazquez-Barquero, A.; Lafarga, M.; Berciano, M.T.; Aldaz, B.; Grande, L.; Casafont, I.; Segura, V.; Robles, E.F.; et al. Blockade of the NFκB pathway drives differentiating glioblastoma-initiating cells into senescence both in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 2011, 30, 3537–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jazirehi, A.R.; Huerta-Yepez, S.; Cheng, G.; Bonavida, B. Rituximab (chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody) inhibits the constitutive nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma B-cell lines: Role in sensitization to chemotherapeutic drug-induced apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 264–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akinleye, A.; Chen, Y.; Mukhi, N.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. Ibrutinib and novel BTK inhibitors in clinical development. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2013, 6, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, W.; Meylan, E.; Oliver, T.G.; Feldser, D.M.; Winslow, M.M.; Bronson, R.; Jacks, T. Response and Resistance to NF-κB Inhibitors in Mouse Models of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Discov. 2011, 1, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassères, D.S.; Ebbs, A.; Cogswell, P.C.; Baldwin, A.S. IKK is a therapeutic target in KRAS-Induced lung cancer with disrupted p53 activity. Genes Cancer 2014, 5, 41–55. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Friedmann-Morvinski, D.; Narasimamurthy, R.; Xia, Y.; Myskiw, C.; Soda, Y.; Verma, I.M. Targeting NF-κB in glioblastoma: A therapeutic approach. Science Advances 2016, 2, e1501292–e1501292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habineza Ndikuyeze, G.; Gaurnier-Hausser, A.; Patel, R.; Baldwin, A.S.; May, M.J.; Flood, P.; Krick, E.; Propert, K.J.; Mason, N.J. A Phase I Clinical Trial of Systemically Delivered NEMO Binding Domain Peptide in Dogs with Spontaneous Activated B-Cell like Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95404. [Google Scholar]
- Gaurnier-Hausser, A.; Patel, R.; Baldwin, A.S.; May, M.J.; Mason, N.J. NEMO-Binding Domain Peptide Inhibits Constitutive NF-κB Activity and Reduces Tumor Burden in a Canine Model of Relapsed, Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Clin. Can. Res. 2011, 17, 4661–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Mayo, M.W.; Baldwin, A.S. TNF- and cancer therapy-induced apoptosis: Potentiation by inhibition of NF-κB. Science 1996, 274, 784–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.Y.; Cusack, J.C.; Liu, R.; Baldwin, A.S. Control of inducible chemoresistance: Enhanced anti-tumor therapy through increased apoptosis by inhibition of NF-κB. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 412–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cusack, J.C.; Liu, R.; Houston, M.; Abendroth, K.; Elliott, P.J.; Adams, J.; Baldwin, A.S. Enhanced chemosensitivity to CPT-11 with proteasome inhibitor PS-341: Implications for systemic nuclear factor-κB inhibition. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 3535–3540. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, T.; Kawaguchi, M.; Yorita, K.; Tanaka, H.; Takeshima, H.; Umezawa, K.; Kataoka, H. Antitumor effect of dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin, a small molecule inhibitor of nuclear factor-κB, on glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2011, 14, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brassesco, M.S.; Roberto, G.M.; Morales, A.G.; Oliveira, J.C.; Delsin, L.E.A.; Pezuk, J.A.; Valera, E.T.; Carlotti, C.G.; Rego, E.M.; de Oliveira, H.F.; et al. Inhibition of NF-κB by Dehydroxymethylepoxyquinomicin Suppresses Invasion and Synergistically Potentiates Temozolomide and γ-Radiation Cytotoxicity in Glioblastoma Cells. Chemother. Res. Pract. 2013, 2013, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, S.; Pia Patric, I.R.; Thinagararjan, S.; Srinivasan, S.; Mondal, B.; Hegde, A.S.; Chandramouli, B.A.; Santosh, V.; Arivazhagan, A.; Somasundaram, K. The NPTX2-PTEN-NFκB nexus is an essential component of a prognostic DNA methylation signature of glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 6563–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, G.; Hayes, E.; Lewis, R.; Ichi, S.; Mania-Farnell, B.; Shim, K.; Takao, T.; Allender, E.; Mayanil, C.S.; Tomita, T. CD133 and DNA-PK regulate MDR1 via the PI3K- or Akt-NF-κB pathway in multidrug-resistant glioblastoma cells in vitro. Oncogene 2015, 35, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seguin, L.; Kato, S.; Franovic, A.; Camargo, M.F.; Lesperance, J.; Elliott, K.C.; Yebra, M.; Mielgo, A.; Lowy, A.M.; Husain, H.; et al. An integrin β3-KRAS-RalB complex drives tumour stemness and resistance to EGFR inhibition. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wee, Z.N.; Yatim, S.M.J.M.; Kohlbauer, V.K.; Feng, M.; Goh, J.Y.; Yi, B.; Lee, P.L.; Zhang, S.; Wang, P.P.; Lim, E.; et al. IRAK1 is a therapeutic target that drives breast cancer metastasis and resistance to paclitaxel. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2016 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons by Attribution (CC-BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rinkenbaugh, A.L.; Baldwin, A.S. The NF-κB Pathway and Cancer Stem Cells. Cells 2016, 5, 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells5020016
Rinkenbaugh AL, Baldwin AS. The NF-κB Pathway and Cancer Stem Cells. Cells. 2016; 5(2):16. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells5020016
Chicago/Turabian StyleRinkenbaugh, Amanda L., and Albert S. Baldwin. 2016. "The NF-κB Pathway and Cancer Stem Cells" Cells 5, no. 2: 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells5020016
APA StyleRinkenbaugh, A. L., & Baldwin, A. S. (2016). The NF-κB Pathway and Cancer Stem Cells. Cells, 5(2), 16. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells5020016




