Lamin B Receptor: Interplay between Structure, Function and Localization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. LBR Targeting to the Nuclear Envelope
3. Regulation of LBR by Post-Translational Modifications
4. The Intricate Roles of LBR at the Nuclear Envelope
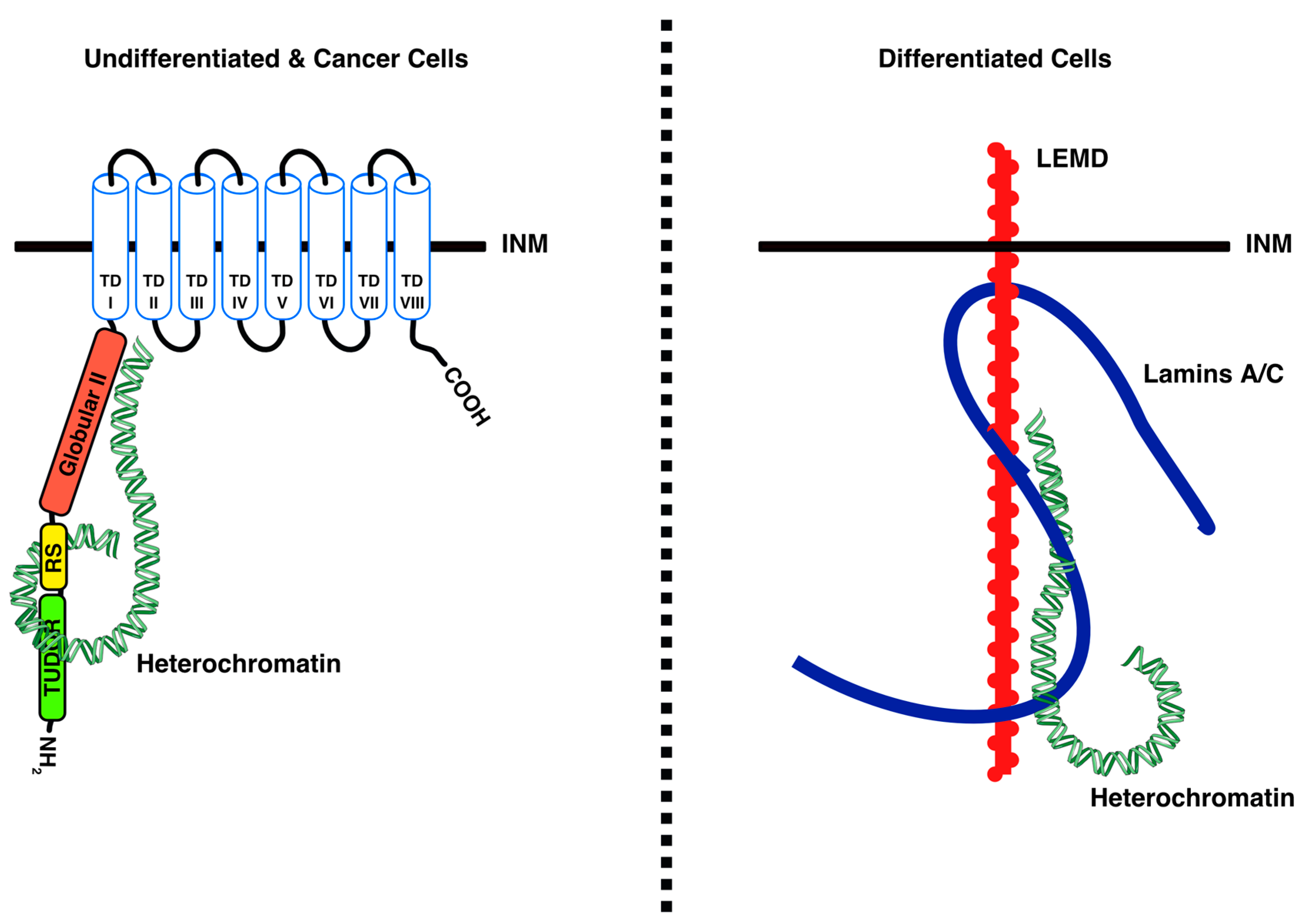
4.1. LBR Tethers Heterochromatin to the INM in Undifferentiated Cells
4.2. LBR–Chromatin Interactions and Functional Consequences
4.3. LBR C14 Sterol Reductase Activity
4.4. Disease-Associated Mutations in the LBR Gene
5. Our Current View and Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kind, J.; van Steensel, B. Genome-Nuclear lamina interactions and gene regulation. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 320–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuleger, N.; Boyle, S.; Kelly, D.A.; de las Heras, J.I.; Lazou, V.; Korfali, N.; Batrakou, D.G.; Randles, K.N.; Morris, G.E.; Harrison, D.J.; et al. Specific nuclear envelope transmembrane proteins can promote the location of chromosomes to and from the nuclear periphery. Genome Biol. 2013, 14, R14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mattout, A.; Cabianca, D.S.; Gasser, S.M. Chromatin states and nuclear organization in development-a view from the nuclear lamina. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovei, I.; Wang, A.S.; Thanisch, K.; Schmidt, C.S.; Krebs, S.; Zwerger, M.; Cohen, T.V.; Devys, D.; Foisner, R.; Peichl, L.; et al. LBR and Lamin A/C sequentially tether peripheral heterochromatin and inversely regulate differentiation. Cell 2013, 152, 584–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirmer, E.C.; Florens, L.; Guan, T.; Yates, J.R., 3rd; Gerace, L. Nuclear membrane proteins with potential disease links found by subtractive proteomics. Science 2003, 301, 1380–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olins, A.L.; Rhodes, G.; Welch, D.B.; Zwerger, M.; Olins, D.E. Lamin B receptor: Multi-tasking at the nuclear envelope. Nucleus 2010, 1, 53–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinke, P.; Nguyen, T.D.; Wehnert, M.S. The LINC complex and human disease. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1693–1697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brachner, A.; Foisner, R. Lamina-associated polypeptide (LAP) 2α and other LEM proteins in cancer biology. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 773, 143–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cartwright, S.; Karakesisoglou, I. Nesprins in health and disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 29, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, L.J.; Soshnev, A.A.; Geyer, P.K. Networking in the nucleus: A spotlight on LEM-domain proteins. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 34, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukášová, E.; Kovařík, A.; Bačíková, A.; Falk, M.; Kozubek, S. Loss of lamin B receptor is necessary to induce cellular senescence. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 281–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, P.L.; Zhao, C.; Turner, E.; Schlieker, C. The Lamin B receptor is essential for cholesterol synthesis and perturbed by disease-causing mutations. Elife 2016, 5, e16011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.; Blobel, G. The first membrane spanning region of the lamin B receptor is sufficient for sorting to the inner nuclear membrane. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 120, 631–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soullam, B.; Worman, H.J. The amino-terminal domain of the lamin B receptor is a nuclear envelope targeting signal. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 120, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellenberg, J.; Siggia, E.D.; Moreira, J.E.; Smith, C.L.; Presley, J.F.; Worman, H.J.; Lippincott-Schwartz, J. Nuclear membrane dynamics and reassembly in living cells: Targeting of an inner nuclear membrane protein in interphase and mitosis. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 138, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungricht, R.; Klann, M.; Horvath, P.; Kutay, U. Diffusion and retention are major determinants of protein targeting to the inner nuclear membrane. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 209, 687–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boni, A.; Politi, A.Z.; Strnad, P.; Xiang, W.; Hossain, M.J.; Ellenberg, J. Live imaging and modeling of inner nuclear membrane targeting reveals its molecular requirements in mammalian cells. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 209, 705–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katta, S.S.; Smoyer, C.J.; Jaspersen, S.L. Destination: Inner nuclear membrane. Trends Cell Biol. 2014, 24, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busayavalasa, K.; Chen, X.; Farrants, A.K.; Wagner, N.; Sabri, N. The Nup155-mediated organisation of inner nuclear membrane proteins is independent of Nup155 anchoring to the metazoan nuclear pore complex. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 4214–4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Shi, Y.; Lu, Q.; Ma, Y.; Luo, J.; Wang, Q.; Ji, J.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, C. Requirement for lamin B receptor and its regulation by importin β and phosphorylation in nuclear envelope assembly during mitotic exit. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 33281–33293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannios, I.; Chatzantonaki, E.; Georgatos, S. Dynamics and Structure-function relationships of the Lamin B Receptor (LBR). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makatsori, D.; Kourmouli, N.; Polioudaki, H.; Shultz, L.D.; McLean, K.; Theodoropoulos, P.A.; Singh, P.B.; Georgatos, S.D. The inner nuclear membrane protein lamin B receptor forms distinct microdomains and links epigenetically marked chromatin to the nuclear envelope. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25567–25573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolakaki, E.; Simos, G.; Georgatos, S.D.; Giannakouros, T. A nuclear envelope-associated kinase phosphorylates arginine-serine motifs and modulates interactions between the lamin B receptor and other nuclear proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 8365–8372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papoutsopoulou, S.; Nikolakaki, E.; Giannakouros, T. SRPK1 and LBR protein kinases show identical substrate specificities. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 255, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takano, M.; Koyama, Y.; Ito, H.; Hoshino, S.; Onogi, H.; Hagiwara, M.; Furukawa, K.; Horigome, T. Regulation of binding of lamin B receptor to chromatin by SR protein kinase and cdc2 kinase in Xenopus egg extracts. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 13265–13271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sellis, D.; Drosou, V.; Vlachakis, D.; Voukkalis, N.; Giannakouros, T.; Vlassi, M. Phosphorylation of the arginine/serine repeats of lamin B receptor by SRPK1-insights from molecular dynamics simulations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voukkalis, N.; Koutroumani, M.; Zarkadas, C.; Nikolakaki, E.; Vlassi, M.; Giannakouros, T. SRPK1 and Akt protein kinases phosphorylate the RS domain of Lamin B Receptor with distinct specificity: A combined biochemical and in silico approach. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaffe, M.B.; Leparc, G.G.; Lai, J.; Obata, T.; Volinia, S.; Cantley, L.C. A motif-based profile scanning approach for genome-wide prediction of signaling pathways. Nat. Biotechnol. 2001, 19, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giannakouros, T.; Nikolakaki, E.; Mylonis, I.; Georgatsou, E. Serine-arginine protein kinases: A small protein kinase family with a large cellular presence. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 570–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Fu, X.D. Regulation of splicing by SR proteins and SR protein-specific kinases. Chromosoma 2013, 122, 191–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolakaki, E.; Drosou, V.; Sanidas, I.; Peidis, P.; Papamarcaki, T.; Iakoucheva, L.M.; Giannakouros, T. RNA association or phosphorylation of the RS domain prevents aggregation of RS domain-containing proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1780, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, Y.; Hizume, K.; Kimura, H.; Takeyasu, K.; Haraguchi, T.; Hiraoka, Y. Lamin B receptor recognizes specific modifications of histone H4 in heterochromatin formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 42654–42663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clever, M.; Funakoshi, T.; Mimura, Y.; Takagi, M.; Imamoto, N. The nucleoporin ELYS/Mel28 regulates nuclear envelope subdomain formation in HeLa cells. Nucleus 2012, 3, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamelberg, D.; Shen, T.; McCammon, J.A. A proposed signaling motif for nuclear import in mRNA processing via the formation of arginine claw. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14947–14951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimura, Y.; Takagi, M.; Clever, M.; Imamoto, N. ELYS regulates the localization of LBR by modulating its phosphorylation state. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 4200–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuhara, T.; Hosoya, T.; Shimizu, S.; Sumi, K.; Oshiro, T.; Yoshinaka, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Yamamoto, N.; Herzenberg, L.A.; Herzenberg, L.A.; et al. Utilization of host SR protein kinases and RNA-splicing machinery during viral replication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 11329–11333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, J.H.; Zhong, X.Y.; Hagopian, J.C.; Cruz, M.M.; Ghosh, G.; Feramisco, J.; Adams, J.A.; Fu, X.D. Regulated cellular partitioning of SR protein-specific kinases in mammalian cells. Mol. Biol. Cell 2006, 17, 876–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.Y.; Ding, J.H.; Adams, J.A.; Ghosh, G.; Fu, X.D. Regulation of SR protein phosphorylation and alternative splicing by modulating kinetic interactions of SRPK1 with molecular chaperones. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 482–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fayard, E.; Xue, G.; Parcellier, A.; Bozulic, L.; Hemmings, B.A. Protein kinase B (PKB/Akt), a key mediator of the PI3K signaling pathway. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2010, 346, 31–56. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Qiu, J.; Liu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Plocinik, R.M.; Li, H.; Hu, Q.; Ghosh, G.; Adams, J.A.; Rosenfeld, M.G.; et al. The Akt-SRPK-SR axis constitutes a major pathway in transducing EGF signaling to regulate alternative splicing in the nucleus. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 422–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gui, J.F.; Lane, W.S.; Fu, X.D. A serine kinase regulates intracellular localization of splicing factors in the cell cycle. Nature 1994, 369, 678–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolakaki, E.; Meier, J.; Simos, G.; Georgatos, S.D.; Giannakouros, T. Mitotic phosphorylation of the lamin B receptor by a serine/arginine kinase and p34(cdc2). J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 6208–6213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, L.C.; Chen, R.H. Temporal control of nuclear envelope assembly by phosphorylation of lamin B receptor. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 3306–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wells, L.; Vosseller, K.; Cole, R.N.; Cronshaw, J.M.; Matunis, M.J.; Hart, G.W. Mapping sites of O-GlcNAc modification using affinity tags for serine and threonine post-translational modifications. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2002, 10, 791–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremer, T.; Cremer, M. Chromosome territories. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a003889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumova, N.; Dekker, J. Integrating one-dimensional and three-dimensional maps of genomes. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1979–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovei, I.; Thanisch, K.; Feodorova, Y. How to rule the nucleus: Divide et impera. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2016, 40, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Worman, H.J. Primary structure analysis and lamin B and DNA binding of human LBR, an integral protein of the nuclear envelope inner membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 11306–11311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duband-Goulet, I.; Courvalin, J.C. Inner nuclear membrane protein LBR preferentially interacts with DNA secondary structures and nucleosomal linker. Biochemistry 2000, 39, 6483–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worman, H.J.; Schirmer, E.C. Nuclear membrane diversity: Underlying tissue-specific pathologies in disease? Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2015, 34, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thanisch, K.; Song, C.; Engelkamp, D.; Koch, J.; Wang, A.; Hallberg, E.; Foisner, R.; Leonhardt, H.; Stewart, C.L.; Joffe, B.; et al. Nuclear envelope localization of LEMD2 is developmentally dynamic and lamin A/C dependent yet insufficient for heterochromatin tethering. Differentiation 2017, 94, 58–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solovei, I.; Kreysing, M.; Lanctôt, C.; Kösem, S.; Peichl, L.; Cremer, T.; Guck, J.; Joffe, B. Nuclear architecture of rod photoreceptor cells adapts to vision in mammalian evolution. Cell 2009, 137, 356–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clowney, E.J.; LeGros, M.A.; Mosley, C.P.; Clowney, F.G.; Markenskoff-Papadimitriou, E.C.; Myllys, M.; Barnea, G.; Larabell, C.A.; Lomvardas, S. Nuclear aggregation of olfactory receptor genes governs their monogenic expression. Cell 2012, 151, 724–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilinc, S.; Meredith, D.T.; Lane, R.P. Sequestration within nuclear chromocenters is not a requirement for silencing olfactory receptor transcription in a placode-derived cell line. Nucleus 2014, 5, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olins, A.L.; Zwerger, M.; Herrmann, H.; Zentgraf, H.; Simon, A.J.; Monestier, M.; Olins, D.E. The human granulocyte nucleus: Unusual nuclear envelope and heterochromatin composition. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 87, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olins, A.L.; Ernst, A.; Zwerger, M.; Herrmann, H.; Olins, D.E. An in vitro model for Pelger-Huët anomaly: Stable knockdown of lamin B receptor in HL-60 cells. Nucleus 2010, 1, 506–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Gong, K.; Denholtz, M.; Chandra, V.; Kamps, M.P.; Alber, F.; Murre, C. Comprehensive characterization of neutrophil genome topology. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowat, A.C.; Jaalouk, D.E.; Zwerger, M.; Ung, W.L.; Eydelnant, I.A.; Olins, D.E.; Olins, A.L.; Herrmann, H.; Weitz, D.A.; Lammerding, J. Nuclear envelope composition determines the ability of neutrophil-type cells to passage through micron-scale constrictions. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 8610–8618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, K.; Dreger, K.; Olins, A.L.; Olins, D.E.; Shultz, L.D.; Lucke, B.; Karl, H.; Kaps, R.; Müller, D.; Vayá, A.; et al. Mutations in the gene encoding the lamin B receptor produce an altered nuclear morphology in granulocytes (Pelger-Huët anomaly). Nat. Genet. 2002, 31, 410–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldowitz, D.; Mullen, R.J. Granule cell as a site of gene action in the weaver mouse cerebellum: Evidence from heterozygous mutant chimeras. J. Neurosci. 1982, 2, 1474–1485. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shultz, L.D.; Lyons, B.L.; Burzenski, L.M.; Gott, B.; Samuels, R.; Schweitzer, P.A.; Dreger, C.; Herrmann, H.; Kalscheuer, V.; Olins, A.L.; et al. Mutations at the mouse ichthyosis locus are within the lamin b receptor gene: A single gene model for human Pelger-Huët anomaly. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2003, 12, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sola Carvajal, A.; McKenna, T.; Wallén Arzt, E.; Eriksson, M. Overexpression of Lamin B Receptor results in impaired skin differentiation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zink, D.; Fischer, A.H.; Nickerson, J.A. Nuclear structure in cancer cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Las Heras, J.I.; Batrakou, D.G.; Schirmer, E.C. Cancer biology and the nuclear envelope: A convoluted relationship. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013, 23, 125–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenain, C.; Gusyatiner, O.; Douma, S.; van den Broek, B.; Peeper, D.S. Autophagy-mediated degradation of nuclear envelope proteins during oncogene-induced senescence. Carcinogenesis 2015, 36, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, R.; En, A.; Ukekawa, R.; Miki, K.; Fujii, M.; Ayusawa, D. Aberrant localization of lamin B receptor (LBR) in cellular senescence in human cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 1078–1083. [Google Scholar]
- McHugh, C.A.; Chen, C.K.; Chow, A.; Surka, C.F.; Tran, C.; McDonel, P.; Pandya-Jones, A.; Blanco, M.; Burghard, C.; Moradian, A.; et al. The Xist lncRNA interacts directly with SHARP to silence transcription through HDAC3. Nature 2015, 521, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.K.; Blanco, M.; Jackson, C.; Aznauryan, E.; Ollikainen, N.; Surka, C.; Chow, A.; Cerase, A.; McDonel, P.; Guttman, M. Xist recruits the X chromosome to the nuclear lamina to enable chromosome-wide silencing. Science 2016, 354, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liokatis, S.; Edlich, C.; Soupsana, K.; Giannios, I.; Panagiotidou, P.; Tripsianes, K.; Sattler, M.; Georgatos, S.D.; Politou, A.S. Solution structure and molecular interactions of lamin B receptor Tudor domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Koyama, Y.; Takano, M.; Ishii, K.; Maeno, M.; Furukawa, K.; Horigome, T. Nuclear envelope precursor vesicle targeting to chromatin is stimulated by protein phosphatase 1 in Xenopus egg extracts. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 1897–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrulis, E.D.; Neiman, A.M.; Zappulla, D.C.; Sternglanz, R. Perinuclear localization of chromatin facilitates transcriptional silencing. Nature 1998, 394, 592–595. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ye, Q.; Worman, H.J. Interaction between an integral protein of the nuclear envelope inner membrane and human chromodomain proteins homologous to Drosophila HP1. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 14653–14656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechner, M.S.; Schultz, D.C.; Negorev, D.; Maul, G.G.; Rauscher, F.J., 3rd. The mammalian heterochromatin protein 1 binds diverse nuclear proteins through a common motif that targets the chromoshadow domain. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 929–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guarda, A.; Bolognese, F.; Bonapace, I.M.; Badaracco, G. Interaction between the inner nuclear membrane lamin B receptor and the heterochromatic methyl binding protein, MeCP2. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 1895–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polioudaki, H.; Kourmouli, N.; Drosou, V.; Bakou, A.; Theodoropoulos, P.A.; Singh, P.B.; Giannakouros, T.; Georgatos, S.D. Histones H3/H4 form a tight complex with the inner nuclear membrane protein LBR and heterochromatin protein 1. EMBO Rep. 2001, 2, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Worman, H.J.; Yuan, J.; Blobel, G.; Georgatos, S.D. A lamin B receptor in the nuclear envelope. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 8531–8534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appelbaum, J.; Blobel, G.; Georgatos, S.D. In vivo phosphorylation of the lamin b receptor. Binding of lamin b to its nuclear membrane receptor is affected by phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 4181–4184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rada-Iglesias, A.; Enroth, S.; Ameur, A.; Koch, C.M.; Clelland, G.K.; Respuela-Alonso, P.; Wilcox, S.; Dovey, O.M.; Ellis, P.D.; Langford, C.F.; et al. Butyrate mediates decrease of histone acetylation centered on transcription start sites and down-regulation of associated genes. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 708–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mylonis, I.; Drosou, V.; Brancorsini, S.; Nikolakaki, E.; Sassone-Corsi, P.; Giannakouros, T. Temporal association of protamine 1 with the inner nuclear membrane protein lamin B receptor during spermiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 11626–11631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmer, L.; Pezhman, A.; Worman, H.J. The human lamin b receptor/sterol reductase multigene family. Genomics 1998, 54, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silve, S.; Dupuy, P.H.; Ferrara, P.; Loison, G. Human lamin b receptor exhibits sterol c14-reductase activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1392, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, A.; Sengupta, S.; Aparna, K.; Kasbekar, D.P. The erg-3 (sterol delta14, 15-reductase) gene of Neurospora crassa: Generation of null mutants by repeat-induced point mutation and complementation by proteins chimeric for human lamin b receptor sequences. Microbiology 1999, 145, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennati, A.M.; Castelli, M.; Della Fazia, M.A.; Beccari, T.; Caruso, D.; Servillo, G.; Roberti, R. Sterol dependent regulation of human TM7SF2 gene expression: Role of the encoded 3β-hydroxysterol Δ14-reductase in human cholesterol biosynthesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1761, 677–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennati, A.M.; Schiavoni, G.; Franken, S.; Piobbico, D.; Della Fazia, M.A.; Caruso, D.; De Fabiani, E.; Benedetti, L.; Cusella De Angelis, M.G.; Gieselmann, V.; et al. Disruption of the gene encoding 3beta-hydroxysterol Delta-reductase (Tm7sf2) in mice does not impair cholesterol biosynthesis. FEBS J. 2008, 275, 5034–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Roberti, R.; Blobel, G. Structure of an integral membrane sterol reductase from Methylomicrobium alcaliphilum. Nature 2015, 517, 104–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, G.; Chaudhury, P.; Malu, K.; Fowler, S.; Manmode, R.; Gotur, D.; Zwerger, M.; Ryan, D.; Roberti, R.; Gaines, P. Lamin B receptor regulates the growth and maturation of myeloid progenitors via its sterol reductase domain: Implications for cholesterol biosynthesis in regulating myelopoiesis. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 85–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, P.; Fischer, B.; Mann, A.; Mansour, S.; Rossier, E.; Veen, M.; Lang, C.; Baasanjav, S.; Kieslich, M.; Brossuleit, K.; et al. Mutations causing Greenberg dysplasia but not Pelger anomaly uncouple enzymatic from structural functions of a nuclear membrane protein. Nucleus 2010, 1, 354–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wassif, C.A.; Brownson, K.E.; Sterner, A.L.; Forlino, A.; Zerfas, P.M.; Wilson, W.K.; Starost, M.F.; Porter, F.D. HEM dysplasia and ichthyosis are likely laminopathies and not due to 3beta-hydroxysterol Delta14-reductase deficiency. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 1176–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waterham, H.R.; Koster, J.; Mooyer, P.; van Noort, G.; Kelley, R.I.; Wilcox, W.R.; Wanders, R.J.; Hennekam, R.C.; Oosterwijk, J.C.; Raoul Hennekam, C.M. Autosomal recessive HEM/Greenberg skeletal dysplasia is caused by 3β-hydroxysterol Δ14-reductase deficiency due to mutations in the lamin B receptor gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 72, 1013–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borovik, L.; Modaff, P.; Waterham, H.R.; Krentz, A.D.; Pauli, R.M. Pelger-huet anomaly and a mild skeletal phenotype secondary to mutations in LBR. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2013, 161A, 2066–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, E.M.; Schlieker, C. Pelger-Huët anomaly and Greenberg skeletal dysplasia: LBR-associated diseases of cholesterol metabolism. Rare Dis. 2016, 4, e1241363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstantinidou, A.; Karadimas, C.; Waterham, H.R.; Superti-Furga, A.; Kaminopetros, P.; Grigoriadou, M.; Kokotas, H.; Agrogiannis, G.; Giannoulia-Karantana, A.; Patsouris, E.; et al. Pathologic, radiographic and molecular findings in three fetuses diagnosed with HEM/Greenberg skeletal dysplasia. Prenat Diagn. 2008, 28, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickmore, W.A.; van Steensel, B. Genome architecture: Domain organization of interphase chromosomes. Cell 2013, 152, 1270–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibcus, J.H.; Dekker, J. The hierarchy of the 3D genome. Mol. Cell 2013, 49, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouwman, B.A.; de Laat, W. Architectural hallmarks of the pluripotent genome. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 2905–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sexton, T.; Cavalli, G. The role of chromosome domains in shaping the functional genome. Cell 2015, 160, 1049–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonev, B.; Cavalli, G. Organization and function of the 3D genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 661–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshorer, E.; Misteli, T. Chromatin in pluripotent embryonic stem cells and differentiation. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 7, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finlan, L.E.; Sproul, D.; Thomson, I.; Boyle, S.; Kerr, E.; Perry, P.; Ylstra, B.; Chubb, J.R.; Bickmore, W.A. Recruitment to the nuclear periphery can alter expression of genes in human cells. PLoS Genet. 2008, 4, e1000039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reddy, K.L.; Zullo, J.M.; Bertolino, E.; Singh, H. Transcriptional repression mediated by repositioning of genes to the nuclear lamina. Nature 2008, 452, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumaran, R.I.; Spector, D.L. A genetic locus targeted to the nuclear periphery in living cells maintains its transcriptional competence. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 180, 51–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almassalha, L.M.; Tiwari, A.; Ruhoff, P.T.; Stypula-Cyrus, Y.; Cherkezyan, L.; Matsuda, H.; Dela Cruz, M.A.; Chandler, J.E.; White, C.; Maneval, C.; et al. The global relationship between chromatin physical topology, fractal structure, and gene expression. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 41061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, N.; Oltean, S. The many faces of SRPK1. J. Pathol. 2017, 241, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czubaty, A.; Piekiełko-Witkowska, A. Protein kinases that phosphorylate splicing factors: Roles in cancer development, progression and possible therapeutic options. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 17, 1357–2725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivanco, I.; Sawyers, C.L. The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carone, D.M.; Lawrence, J.B. Heterochromatin instability in cancer: From the Barr body to satellites and the nuclear periphery. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013, 23, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherkezyan, L.; Stypula-Cyrus, Y.; Subramanian, H.; White, C.; Dela Cruz, M.; Wali, R.K.; Goldberg, M.J.; Bianchi, L.K.; Roy, H.K.; Backman, V. Nanoscale changes in chromatin organization represent the initial steps of tumorigenesis: A transmission electron microscopy study. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezgin, E.; Levental, I.; Mayor, S.; Eggeling, C. The mystery of membrane organization: Composition, regulation and roles of lipid rafts. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascianelli, G.; Villani, M.; Tosti, M.; Marini, F.; Bartoccini, E.; Magni, M.V.; Albi, E. Lipid microdomains in cell nucleus. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 5289–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codini, M.; Cataldi, S.; Lazzarini, A.; Tasegian, A.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Floridi, A.; Lazzarini, R.; Ambesi-Impiombato, F.S.; Curcio, F.; Beccari, T.; et al. Why high cholesterol levels help hematological malignancies: Role of nuclear lipid microdomains. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, I.T.G.; Fernandes, V.; Souza, C.; Treptow, W.; Santos, G.M. Biophysical studies of cholesterol effects on chromatin. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 934–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nikolakaki, E.; Mylonis, I.; Giannakouros, T. Lamin B Receptor: Interplay between Structure, Function and Localization. Cells 2017, 6, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells6030028
Nikolakaki E, Mylonis I, Giannakouros T. Lamin B Receptor: Interplay between Structure, Function and Localization. Cells. 2017; 6(3):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells6030028
Chicago/Turabian StyleNikolakaki, Eleni, Ilias Mylonis, and Thomas Giannakouros. 2017. "Lamin B Receptor: Interplay between Structure, Function and Localization" Cells 6, no. 3: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells6030028
APA StyleNikolakaki, E., Mylonis, I., & Giannakouros, T. (2017). Lamin B Receptor: Interplay between Structure, Function and Localization. Cells, 6(3), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells6030028





