Samp1 Mislocalization in Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Cultures and Treatments
2.2. Muscle Biopsies
2.3. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.4. Proximity Ligation Assay (PLA)
2.5. Statistical Analysis
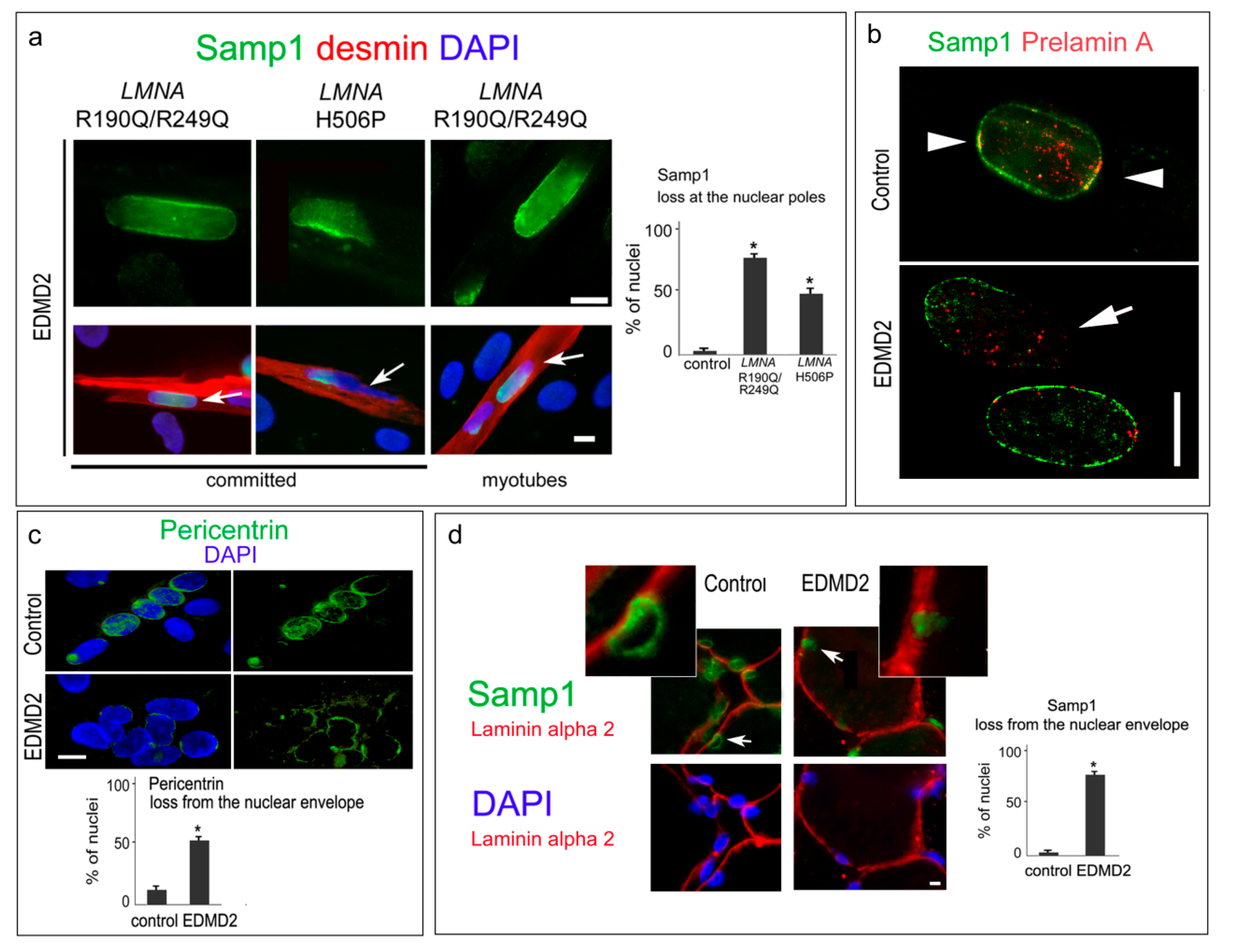
3. Results
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Burke, B.; Stewart, C.L. The nuclear lamins: Flexibility in function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.; Worman, H.J.; Gundersen, G.G. Accessorizing and anchoring the linc complex for multifunctionality. J. Cell Biol. 2015, 208, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, C.; Fischer, M.; Mamchaoui, K.; Bigot, A.; Lok, T.; Verdier, C.; Duperray, A.; Michel, R.; Holt, I.; Voit, T.; et al. Lamins and nesprin-1 mediate inside-out mechanical coupling in muscle cell precursors through fhod1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.L.; Burke, B. Linc complexes and nuclear positioning. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 82, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Lei, K.; Yuan, X.; Wu, X.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, T.; Xu, R.; Han, M. Sun1/2 and syne/nesprin-1/2 complexes connect centrosome to the nucleus during neurogenesis and neuronal migration in mice. Neuron 2009, 64, 173–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roman, W.; Gomes, E.R. Nuclear positioning in skeletal muscle. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 82, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, K.L.; Berk, J.M. The nuclear envelope at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2010, 123, 1973–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gomes, E.R.; Jani, S.; Gundersen, G.G. Nuclear movement regulated by cdc42, mrck, myosin, and actin flow establishes mtoc polarization in migrating cells. Cell 2005, 121, 451–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espigat-Georger, A.; Dyachuk, V.; Chemin, C.; Emorine, L.; Merdes, A. Nuclear alignment in myotubes requires centrosome proteins recruited by nesprin-1. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 4227–4237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chang, W.; Folker, E.S.; Worman, H.J.; Gundersen, G.G. Emerin organizes actin flow for nuclear movement and centrosome orientation in migrating fibroblasts. Mol. Biol. Cell 2013, 24, 3869–3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gnocchi, V.F.; Scharner, J.; Huang, Z.; Brady, K.; Lee, J.S.; White, R.B.; Morgan, J.E.; Sun, Y.B.; Ellis, J.A.; Zammit, P.S. Uncoordinated transcription and compromised muscle function in the Lmna-null mouse model of Emery- Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folker, E.S.; Ostlund, C.; Luxton, G.W.; Worman, H.J.; Gundersen, G.G. Lamin A variants that cause striated muscle disease are defective in anchoring transmembrane actin-associated nuclear lines for nuclear movement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gimpel, P.; Lee, Y.L.; Sobota, R.M.; Calvi, A.; Koullourou, V.; Patel, R.; Mamchaoui, K.; Nedelec, F.; Shackleton, S.; Schmoranzer, J.; et al. Nesprin-1alpha-dependent microtubule nucleation from the nuclear envelope via akap450 is necessary for nuclear positioning in muscle cells. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, 2999–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, W.; Antoku, S.; Ostlund, C.; Worman, H.J.; Gundersen, G.G. Linker of nucleoskeleton and cytoskeleton (LINC) complex-mediated actin-dependent nuclear positioning orients centrosomes in migrating myoblasts. Nucleus 2015, 6, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mattioli, E.; Columbaro, M.; Capanni, C.; Maraldi, N.M.; Cenni, V.; Scotlandi, K.; Marino, M.T.; Merlini, L.; Squarzoni, S.; Lattanzi, G. Prelamin A-mediated recruitment of sun1 to the nuclear envelope directs nuclear positioning in human muscle. Cell Death Differ. 2011, 18, 1305–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roncarati, R.; Viviani Anselmi, C.; Krawitz, P.; Lattanzi, G.; von Kodolitsch, Y.; Perrot, A.; di Pasquale, E.; Papa, L.; Portararo, P.; Columbaro, M.; et al. Doubly heterozygous LMNA and TTN mutations revealed by exome sequencing in a severe form of dilated cardiomyopathy. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2013, 21, 1105–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Meinke, P.; Mattioli, E.; Haque, F.; Antoku, S.; Columbaro, M.; Straatman, K.R.; Worman, H.J.; Gundersen, G.G.; Lattanzi, G.; Wehnert, M.; et al. Muscular dystrophy-associated SUN1 and SUN2 variants disrupt nuclear-cytoskeletal connections and myonuclear organization. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.; Zhang, X.; Ding, X.; Guo, X.; Chen, M.; Zhu, B.; Xu, T.; Zhuang, Y.; Xu, R.; Han, M. SUN1 and SUN2 play critical but partially redundant roles in anchoring nuclei in skeletal muscle cells in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2009, 106, 10207–10212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mejat, A.; Decostre, V.; Li, J.; Renou, L.; Kesari, A.; Hantai, D.; Stewart, C.L.; Xiao, X.; Hoffman, E.; Bonne, G.; et al. Lamin A/C-mediated neuromuscular junction defects in emery-dreifuss muscular dystrophy. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 184, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puckelwartz, M.J.; Kessler, E.; Zhang, Y.; Hodzic, D.; Randles, K.N.; Morris, G.; Earley, J.U.; Hadhazy, M.; Holaska, J.M.; Mewborn, S.K.; et al. Disruption of nesprin-1 produces an emery dreifuss muscular dystrophy-like phenotype in mice. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buch, C.; Lindberg, R.; Figueroa, R.; Gudise, S.; Onischenko, E.; Hallberg, E. An integral protein of the inner nuclear membrane localizes to the mitotic spindle in mammalian cells. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 2100–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsson, V.J.; Jafferali, M.H.; Vijayaraghavan, B.; Figueroa, R.A.; Hallberg, E. Mitotic spindle assembly and gamma-tubulin localisation depend on the integral nuclear membrane protein samp1. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs211664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudise, S.; Figueroa, R.A.; Lindberg, R.; Larsson, V.; Hallberg, E. Samp1 is functionally associated with the linc complex and a-type lamina networks. J. Cell Sci. 2011, 124, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafferali, M.H.; Vijayaraghavan, B.; Figueroa, R.A.; Crafoord, E.; Gudise, S.; Larsson, V.J.; Hallberg, E. Mclip, an effective method to detect interactions of transmembrane proteins of the nuclear envelope in live cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 2399–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vijayaraghavan, B.; Figueroa, R.A.; Bergqvist, C.; Gupta, A.J.; Sousa, P.; Hallberg, E. RanGTPase regulates the interaction between the inner nuclear membrane proteins, samp1 and emerin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2018, 1860, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borrego-Pinto, J.; Jegou, T.; Osorio, D.S.; Aurade, F.; Gorjanacz, M.; Koch, B.; Mattaj, I.W.; Gomes, E.R. Samp1 is a component of tan lines and is required for nuclear movement. J. Cell Sci. 2012, 125, 1099–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafferali, M.H.; Figueroa, R.A.; Hasan, M.; Hallberg, E. Spindle associated membrane protein 1 (Samp1) is required for the differentiation of muscle cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergqvist, C.; Jafferali, M.H.; Gudise, S.; Markus, R.; Hallberg, E. An inner nuclear membrane protein induces rapid differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cell Res. 2017, 23, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernasconi, P.; Carboni, N.; Ricci, G.; Siciliano, G.; Politano, L.; Maggi, L.; Mongini, T.; Vercelli, L.; Rodolico, C.; Biagini, E.; et al. Elevated TGF beta2 serum levels in emery-dreifuss muscular dystrophy: Implications for myocyte and tenocyte differentiation and fibrogenic processes. Nucleus 2018, 9, 292–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Thanh, P.; Meinke, P.; Korfali, N.; Srsen, V.; Robson, M.I.; Wehnert, M.; Schoser, B.; Sewry, C.A.; Schirmer, E.C. Immunohistochemistry on a panel of Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy samples reveals nuclear envelope proteins as inconsistent markers for pathology. Neuromuscul. Disord. 2017, 27, 338–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenni, V.; Sabatelli, P.; Mattioli, E.; Marmiroli, S.; Capanni, C.; Ognibene, A.; Squarzoni, S.; Maraldi, N.M.; Bonne, G.; Columbaro, M.; et al. Lamin a n-terminal phosphorylation is associated with myoblast activation: Impairment in Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angori, S.; Capanni, C.; Faulkner, G.; Bean, C.; Boriani, G.; Lattanzi, G.; Cenni, V. Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy-associated mutant forms of lamin a recruit the stress responsive protein Ankrd2 into the nucleus, affecting the cellular response to oxidative stress. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 169–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srsen, V.; Fant, X.; Heald, R.; Rabouille, C.; Merdes, A. Centrosome proteins form an insoluble perinuclear matrix during muscle cell differentiation. BMC Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janin, A.; Bauer, D.; Ratti, F.; Millat, G.; Mejat, A. Nuclear envelopathies: a complex linc between nuclear envelope and pathology. Orphanet J. Rare Dis. 2017, 12, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapman, M.A.; Zhang, J.; Banerjee, I.; Guo, L.T.; Zhang, Z.; Shelton, G.D.; Ouyang, K.; Lieber, R.L.; Chen, J. Disruption of both nesprin 1 and desmin results in nuclear anchorage defects and fibrosis in skeletal muscle. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 22, 5879–5892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadot, B.; Gache, V.; Gomes, E.R. Moving and positioning the nucleus in skeletal muscle-one step at a time. Nucleus 2015, 6, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salpingidou, G.; Smertenko, A.; Hausmanowa-Petrucewicz, I.; Hussey, P.J.; Hutchison, C.J. A novel role for the nuclear membrane protein emerin in association of the centrosome to the outer nuclear membrane. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 178, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wheeler, M.A.; Davies, J.D.; Zhang, Q.; Emerson, L.J.; Hunt, J.; Shanahan, C.M.; Ellis, J.A. Distinct functional domains in nesprin-1alpha and nesprin-2beta bind directly to emerin and both interactions are disrupted in x-linked Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 2845–2857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stroud, M.J.; Feng, W.; Zhang, J.; Veevers, J.; Fang, X.; Gerace, L.; Chen, J. Nesprin 1alpha2 is essential for mouse postnatal viability and nuclear positioning in skeletal muscle. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 1915–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capanni, C.; Del Coco, R.; Squarzoni, S.; Columbaro, M.; Mattioli, E.; Camozzi, D.; Rocchi, A.; Scotlandi, K.; Maraldi, N.; Foisner, R.; et al. Prelamin A is involved in early steps of muscle differentiation. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 3628–3637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gesson, K.; Vidak, S.; Foisner, R. Lamina-associated polypeptide (LAP)2alpha and nucleoplasmic lamins in adult stem cell regulation and disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 29, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pilat, U.; Dechat, T.; Bertrand, A.T.; Woisetschlager, N.; Gotic, I.; Spilka, R.; Biadasiewicz, K.; Bonne, G.; Foisner, R. The muscle dystrophy-causing deltak32 lamin A/C mutant does not impair the functions of the nucleoplasmic lamin-A/C-LAP2alpha complex in mice. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 1753–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertrand, A.T.; Renou, L.; Papadopoulos, A.; Beuvin, M.; Lacene, E.; Massart, C.; Ottolenghi, C.; Decostre, V.; Maron, S.; Schlossarek, S.; et al. Delk32-lamin A/C has abnormal location and induces incomplete tissue maturation and severe metabolic defects leading to premature death. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capanni, C.; Cenni, V.; Mattioli, E.; Sabatelli, P.; Ognibene, A.; Columbaro, M.; Parnaik, V.K.; Wehnert, M.; Maraldi, N.M.; Squarzoni, S.; et al. Failure of lamin A/C to functionally assemble in R482L mutated familial partial lipodystrophy fibroblasts: Altered intermolecular interaction with emerin and implications for gene transcription. Exp. Cell Res 2003, 291, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muchir, A.; Medioni, J.; Laluc, M.; Massart, C.; Arimura, T.; van der Kooi, A.J.; Desguerre, I.; Mayer, M.; Ferrer, X.; Briault, S.; et al. Nuclear envelope alterations in fibroblasts from patients with muscular dystrophy, cardiomyopathy, and partial lipodystrophy carrying lamin A/C gene mutations. Muscle Nerve 2004, 30, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taimen, P.; Pfleghaar, K.; Shimi, T.; Moller, D.; Ben-Harush, K.; Erdos, M.R.; Adam, S.A.; Herrmann, H.; Medalia, O.; Collins, F.S.; et al. A progeria mutation reveals functions for lamin A in nuclear assembly, architecture, and chromosome organization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20788–20793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shimi, T.; Pfleghaar, K.; Kojima, S.; Pack, C.G.; Solovei, I.; Goldman, A.E.; Adam, S.A.; Shumaker, D.K.; Kinjo, M.; Cremer, T.; et al. The A- and B-type nuclear lamin networks: Microdomains involved in chromatin organization and transcription. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 3409–3421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mattioli, E.; Columbaro, M.; Jafferali, M.H.; Schena, E.; Hallberg, E.; Lattanzi, G. Samp1 Mislocalization in Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy. Cells 2018, 7, 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100170
Mattioli E, Columbaro M, Jafferali MH, Schena E, Hallberg E, Lattanzi G. Samp1 Mislocalization in Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy. Cells. 2018; 7(10):170. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100170
Chicago/Turabian StyleMattioli, Elisabetta, Marta Columbaro, Mohammed Hakim Jafferali, Elisa Schena, Einar Hallberg, and Giovanna Lattanzi. 2018. "Samp1 Mislocalization in Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy" Cells 7, no. 10: 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100170
APA StyleMattioli, E., Columbaro, M., Jafferali, M. H., Schena, E., Hallberg, E., & Lattanzi, G. (2018). Samp1 Mislocalization in Emery-Dreifuss Muscular Dystrophy. Cells, 7(10), 170. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100170





