Inhibitory-κB Kinase (IKK) α and Nuclear Factor-κB (NFκB)-Inducing Kinase (NIK) as Anti-Cancer Drug Targets
Abstract
:1. Introduction and Background
1.1. Nuclear Factor Kappa-B (NF-κB) Proteins
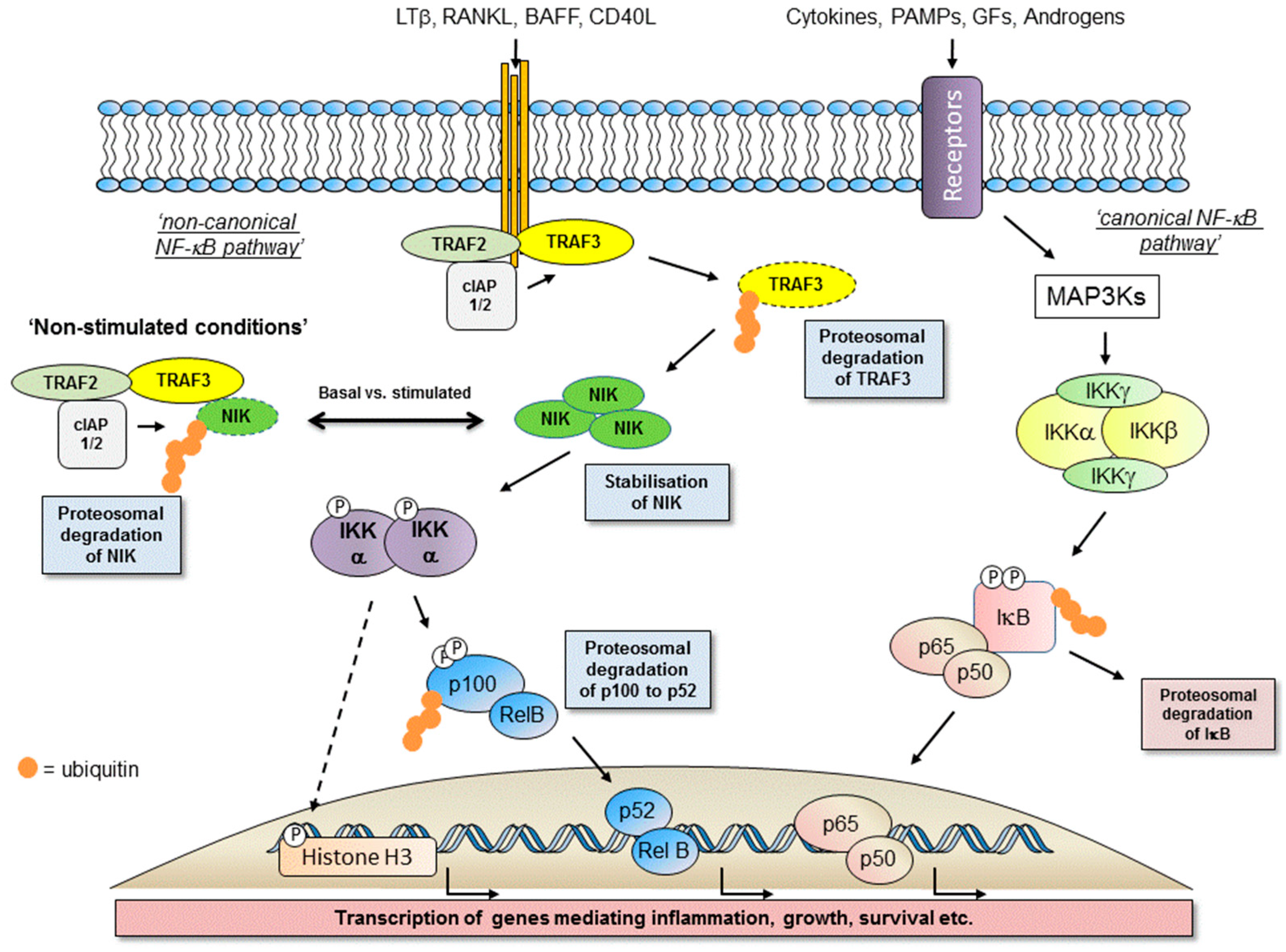
1.2. Activation of the Non-Canonical NF-κB Pathway
1.3. Major Components of The Receptor Activated Non-Canonical NF-κB Pathway
1.4. IKKα-Dependent, NF-κB-Independent Signalling Integrates with IKKα-Dependent Non-Canonical NF-κB Signalling to Contribute to Global Cellular Transcription
1.5. Signalling Complexities
2. IKKα in Solid Tumours
IKKα Signalling Independent of NF-κB Pathways in Solid Tumours
3. IKKα Association with Hallmarks of Cancer in Human Tumours
4. NF-κB in Haematological Malignancies
5. Targeting the IKKα and NIK Protein Kinases with Small Molecule Inhibitors
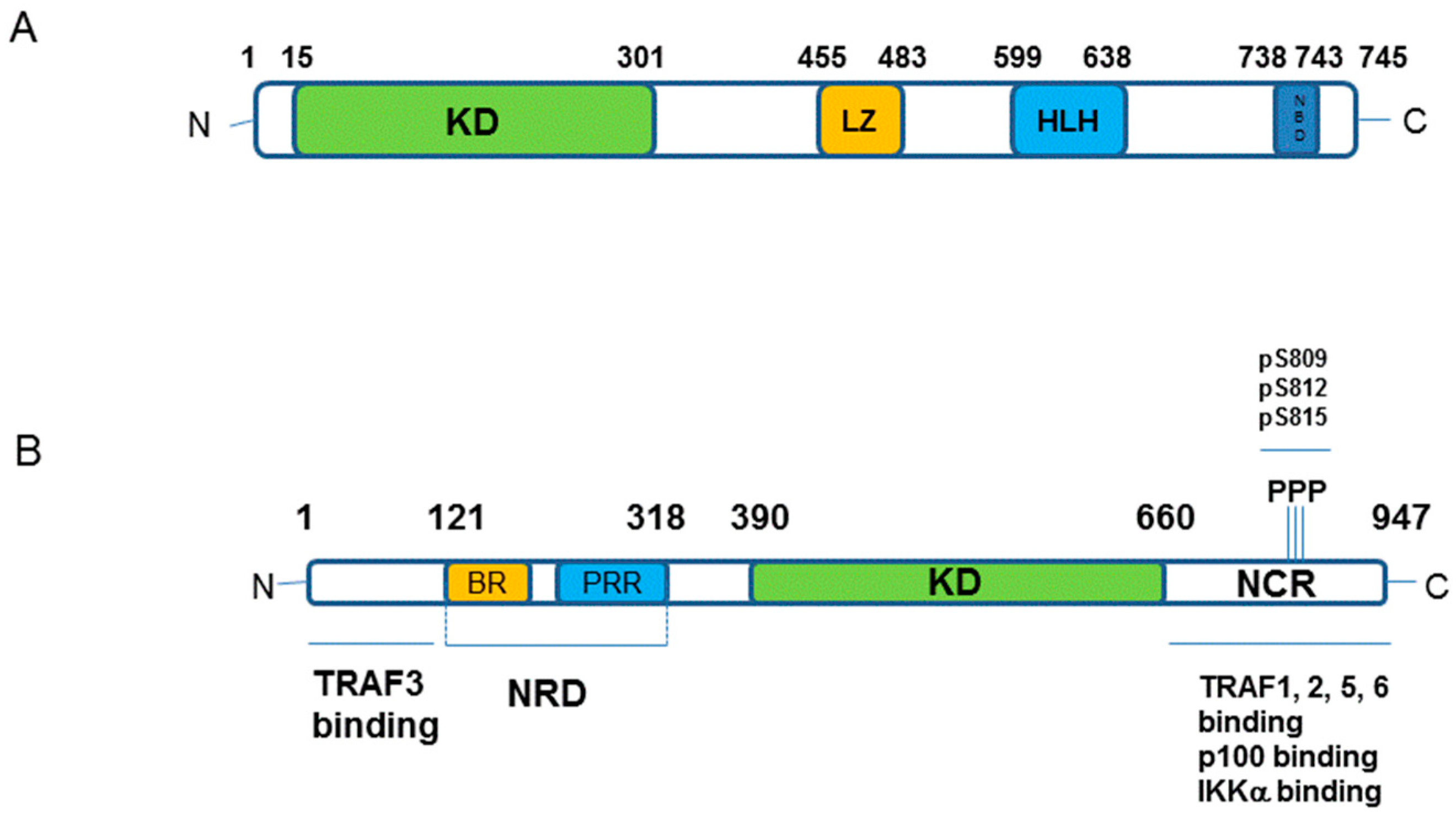
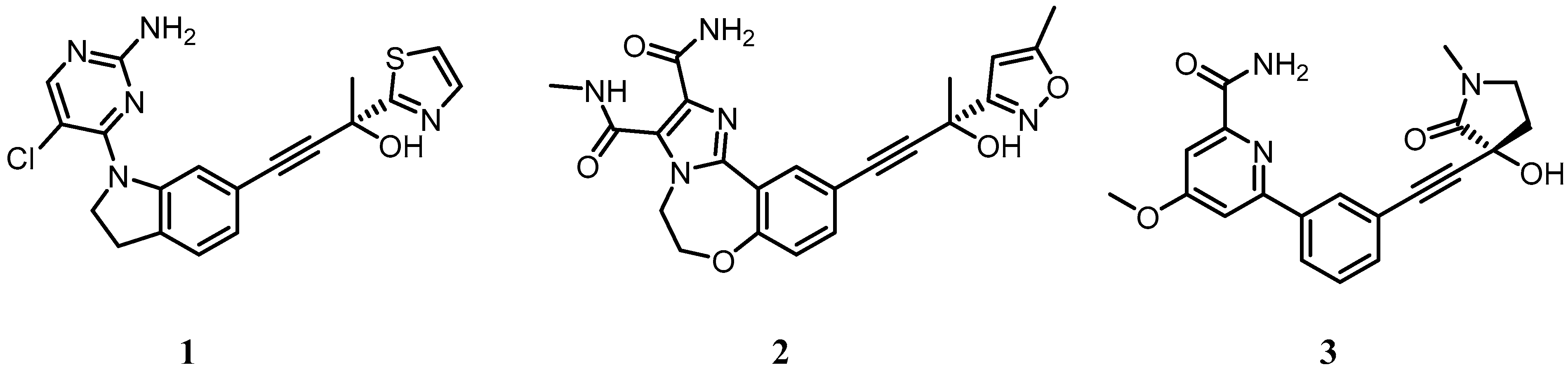
5.1. Development of Small Molecule Inhibitors of IKKα and NIK
5.2. Structure of IKKα and IKKβ from a Small Molecule Design Perspective
5.3. IKKα/β Non-Selective Inhibitors
6. Future Perspectives
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| List of chemical names for compounds 1–19 | |
| 1 | (R)-4-(1-(2-amino-5-chloropyrimidin-4-yl)indolin-6-yl)-2-(thiazol-2-yl)but-3-yn-2-ol |
| 2 | (R)-10-(3-hydroxy-3-(5-methylisoxazol-3-yl)but-1-yn-1-yl)-N3-methyl-5,6-dihydrobenzo[f]imidazo[1,2-d][1,4]oxazepine-2,3-dicarboxamide |
| 3 | (R)-6-(3-((3-hydroxy-1-methyl-2-oxopyrrolidin-3-yl)ethynyl)phenyl)-4-methoxypicolinamide |
| 4 | 1-(3-(8-methyl-5-(methylamino)imidazo[1,2-a]thieno[3,2-e]pyrazin-2-yl)phenethyl)urea |
| 5 | N-((8-methyl-5-(methylamino)imidazo[1,2-a]thieno[3,2-e]pyrazin-2-yl)methyl)aminosulfonamide |
| 6 | N-(1,8-dimethylimidazo[1,2-a]quinoxalin-4-yl)ethane-1,2-diamine |
| 7 | 2-amino-5-(pyridin-4-yl)-4’-sulfamoyl-[1,1’-biphenyl]-3-carboxamide |
| 8 | N-(2-aminoethyl)-4-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide |
| 9 | N-(azetidin-3-yl)-4-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide |
| 10 | N-(1,1-dioxidotetrahydro-2H-thiopyran-4-yl)-4-(2-methyl-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide |
| 11 | 4-((4-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)benzoic acid |
| 12 | 4-((4-(benzo[b]thiophen-2-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenyl)(4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl)methanone |
| 13 | 4-((4-(5-(3-amino-3-methylbutyl)thiophen-2-yl)pyrimidin-2-yl)amino)phenyl)(4-(pyrrolidin-1-yl)piperidin-1-yl)methanone |
| 14 | (1R,2S,3R,4S)-4-(6-amino-9H-purin-9-yl)cyclopentane-1,2,3-triol (NAM) |
| 15 | 4-(3-cyano-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-5-yl)benzenesulfonamide |
| 16 | 5-(1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridin-4-yl)-1H-indazol-3-amine |
| 17 | 5-(1H-pyrazolo[3,4-b]pyridin-4-yl)-1H-indazol-3-amine |
| 18 | 5,7-dihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-4H-chromen-4-one (apigenin) |
| 19 | 4-(2-amino-5-cyano-7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidin-4-yl)benzenesulfonamide (SU909) |
References
- Sun, S.C. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling pathway. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razani, B.; Reichardt, A.D.; Cheng, G. Non-canonical NF-κB signaling activation and regulation: principles and perspectives. Immunol. Rev. 2011, 244, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cildir, G.; Low, K.C.; Tergaonkar, V. Noncanonical NF-κB Signaling in Health and Disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2016, 22, 414–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.C. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xia, L.; Tan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, J.; Wang, H.; Oyang, L.; Tian, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, M.; Wang, H.; et al. Role of the NFκB-signaling pathway in cancer. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 2063–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perkins, N.D. Integrating cell-signalling pathways with NF-kappaB and IKK function. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 8, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, C.; McIntosh, K.; Scott, R.; Ho, K.H.; Plevin, R.; Paul, A. Inhibitory kappa B Kinases as targets for pharmacological regulation. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 802–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyawaki, S.; Nakamura, Y.; Suzuka, H.; Koba, M.; Yasumizu, R.; Ikehara, S.; Shibata, Y. A new mutation, aly, that induces a generalized lack of lymph nodes accompanied by immunodeficiency in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1994, 24, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, R.; Nishimura, T.; Yasumizu, R.; Tanaka, H.; Hataba, Y.; Hataba, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Miyawaki, S.; Miyasaka, M. The splenic marginal zone is absent in alymphoplastic aly mutant mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1996, 26, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkura, R.; Matsuda, F.; Sakiyama, T.; Tsubata, T.; Hiai, H.; Paumen, M.; Miyawaki, S.; Honjo, T. Defects of somatic hypermutation and class switching in alymphoplasia (aly) mutant mice. Int. Immunol. 1996, 8, 1067–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shinkura, R.; Kitada, K.; Matsuda, F.; Tashiro, K.; Ikuta, K.; Suzuki, M.; Kogishi, K.; Serikawa, T.; Honjo, T. Alymphoplasia is caused by a point mutation in the mouse gene encoding Nf-kappa b-inducing kinase. Nat. Genet. 1999, 22, 74–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, L.; Wu, L.; Wesche, H.; Arthur, C.D.; White, J.M.; Goeddel, D.V.; Schreiber, R.D. Defective lymphotoxin-beta receptor-induced NF-kappaB transcriptional activity in NIK-deficient mice. Science 2001, 16, 2162–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fütterer, A.; Mink, K.; Luz, A.; Kosco-Vilbois, M.H.; Pfeffer, K. The lymphotoxin beta receptor controls organogenesis and affinity maturation in peripheral lymphoid tissues. Immunity 1998, 9, 59–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Takeuchi, O.; Tsujimura, T.; Itami, S.; Adachi, O.; Kawai, T.; Sanjo, H.; Yoshikawa, K.; Terada, N.; Akira, S. Limb and skin abnormalities in mice lacking IKKalpha. Science 1999, 284, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Baud, V.; Delhase, M.; Zhang, P.; Deerinck, T.; Ellisman, M.; Johnson, R.; Karin, M. Abnormal morphogenesis but intact IKK activation in mice lacking the IKKalpha subunit of IkappaB kinase. Science 1999, 284, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, G.; Zhang, M.; Harhaj, E.W.; Sun, S.C. Regulation of the NF-kappaB-inducing kinase by tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 3-induced degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 26243–26250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallabhapurapu, S.; Matsuzawa, A.; Zhang, W.; Tseng, P.H.; Keats, J.J.; Wang, H.; Vignali, D.A.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Karin, M. Nonredundant and complementary functions of TRAF2 and TRAF3 in a ubiquitination cascade that activates NIK-dependent alternative NF-kappaB signaling. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1364–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vince, J.E.; Wong, W.W.; Khan, N.; Feltham, R.; Chau, D.; Ahmed, A.U.; Benetatos, C.A.; Chunduru, S.K.; Condon, S.M.; McKinlay, M.; et al. IAP antagonists target cIAP1 to induce TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 2007, 131, 682–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varfolomeev, E.; Blankenship, J.W.; Wayson, S.M.; Fedorova, A.V.; Kayagaki, N.; Garg, P.; Zobel, K.; Dynek, J.N.; Elliott, L.O.; Wallweber, H.J.; et al. IAP antagonists induce autoubiquitination of c-IAPs, NF-kappaB activation, and TNFalpha-dependent apoptosis. Cell 2007, 131, 669–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarnegar, B.J.; Wang, Y.; Mahoney, D.J.; Dempsey, P.W.; Cheung, H.H.; He, J.; Shiba, T.; Yang, X.; Yeh, W.C.; Mak, T.W.; et al. Noncanonical NF-kappaB activation requires coordinated assembly of a regulatory complex of the adaptors cIAP1, cIAP2, TRAF2 and TRAF3 and the kinase NIK. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 1371–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardam, S.; Turner, V.M.; Anderton, H.; Limaye, S.; Basten, A.; Koentgen, F.; Vaux, D.L.; Silke, J.; Brink, R. Deletion of cIAP1 and cIAP2 in murine B lymphocytes constitutively activates cell survival pathways and inactivates the germinal center response. Blood 2011, 117, 4041–4051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, G.; Fong, A.; Sun, S.C. Induction of p100 processing by NF-kappaB-inducing kinase involves docking IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKalpha) to p100 and IKKalpha-mediated phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30099–30105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Harhaj, E.W.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB-inducing kinase regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 p100. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.; Zhang, M.; Sun, S.C. beta-TrCP binding and processing of NF-kappaB2/p100 involve its phosphorylation at serines 866 and 870. Cell. Signal. 2006, 18, 1309–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senftleben, U.; Cao, Y.; Xiao, G.; Greten, F.R.; Krähn, G.; Bonizzi, G.; Chen, Y.; Hu, Y.; Fong, A.; Sun, S.C.; et al. Activation by IKKalpha of a second, evolutionary conserved, NF-kappa B signaling pathway. Science 2001, 293, 1495–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claudio, E.; Brown, K.; Park, S.; Wang, H.; Siebenlist, U. BAFF-induced NEMO-independent processing of NF-kappa B2 in maturing B cells. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 958–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejardin, E.; Droin, N.M.; Delhase, M.; Haas, E.; Cao, Y.; Makris, C.; Li, Z.W.; Karin, M.; Ware, C.F.; Green, D.R. The lymphotoxin-beta receptor induces different patterns of gene expression via two NF-kappaB pathways. Immunity 2002, 17, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anthony, N.G.; Baiget, J.; Berretta, G.; Boyd, M.; Breen, D.; Edwards, J.; Gamble, C.; Gray, A.I.; Harvey, A.L.; Hatziieremia, S.; et al. Inhibitory Kappa B Kinase α (IKKα) Inhibitors That Recapitulate Their Selectivity in Cells against Isoform-Related Biomarkers. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 7043–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, R.P.; Zhang, M.; Li, Y.; Diao, F.C.; Chen, D.; Zhai, Z.; Shu, H.B. Differential regulation of IKK alpha-mediated activation of IRF3/7 by NIK. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 1926–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, Z.; Prajapati, S.; Park, K.J.; Kelly, N.J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Gaynor, R.B. IKK alpha regulates estrogen-induced cell cycle progression by modulating E2F1 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 6699–6706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammirante, M.; Kuraishy, A.I.; Shalapour, S.; Strasner, A.; Ramirez-Sanchez, C.; Zhang, W.; Shabaik, A.; Karin, M. An IKKα-E2F1-BMI1 cascade activated by infiltrating B cells controls prostate regeneration and tumor recurrence. Genes Dev. 2013, 27, 1435–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamberti, C.; Lin, K.M.; Yamamoto, Y.; Verma, U.; Verma, I.M.; Byers, S.; Gaynor, R.B. Regulation of beta-catenin function by the IkappaB kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42276–42286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.C.; Ju, T.K.; Hung, M.C.; Chen, C.C. Phosphorylation of CBP by IKKalpha promotes cell growth by switching the binding preference of CBP from p53 to NF-kappaB. Mol. Cell 2007, 26, 75–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoberg, J.E.; Popko, A.E.; Ramsey, C.S.; Mayo, M.W. IkappaB kinase alpha-mediated derepression of SMRT potentiates acetylation of RelA/p65 by p300. Mol. Cell Biol. 2006, 26, 457–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, Y.T.; Li, R.; Becerra, C.R.; Tripathy, D.; Frenkel, E.P.; Verma, U.N. IkappaB kinase alpha regulates subcellular distribution and turnover of cyclin D1 by phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 33945–33952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Yang, Y.; Chernishof, V.; Loo, R.R.; Jang, H.; Tahk, S.; Yang, R.; Mink, S.; Shultz, D.; Bellone, C.J.; et al. Proinflammatory stimuli induce IKKalpha-mediated phosphorylation of PIAS1 to restrict inflammation and immunity. Cell 2007, 129, 903–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.J.; Krishnan, V.; O’Malley, B.W.; Yamamoto, Y.; Gaynor, R.B. Formation of an IKKalpha-dependent transcription complex is required for estrogen receptor-mediated gene activation. Mol. Cell 2005, 18, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, G.; Voogdt, C.; Tobias, A.; Spindler, K.D.; Möller, P.; Cronauer, M.V.; Marienfeld, R.B. IκB kinases modulate the activity of the androgen receptor in prostate carcinoma cell lines. Neoplasia 2012, 14, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.C.; Qin, J.; Hashimoto, Y.; Wong, J.; Xu, J.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; O’Malley, B.W. Regulation of SRC-3 (pCIP/ACTR/AIB-1/RAC-3/TRAM-1) Coactivator activity by I kappa B kinase. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 22, 3549–3561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.C.; Qin, J.; Yi, P.; Wong, J.; Tsai, S.Y.; Tsai, M.J.; O’Malley, B.W. Selective phosphorylations of the SRC-3/AIB1 coactivator integrate genomic reponses to multiple cellular signaling pathways. Mol. Cell 2004, 15, 937–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prajapati, S.; Tu, Z.; Yamamoto, Y.; Gaynor, R.B. IKKalpha regulates the mitotic phase of the cell cycle by modulating Aurora A phosphorylation. Cell Cycle 2006, 5, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irelan, J.T.; Murphy, T.J.; DeJesus, P.D.; Teo, H.; Xu, D.; Gomez-Ferreria, M.A.; Zhou, Y.; Miraglia, L.J.; Rines, D.R.; Verma, I.M.; et al. A role for IkappaB kinase 2 in bipolar spindle assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16940–16945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schumm, K.; Rocha, S.; Caamano, J.; Perkins, N.D. Regulation of p53 tumour suppressor target gene expression by the p52 NF-kappaB subunit. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 4820–4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iannetti, A.; Ledoux, A.C.; Tudhope, S.J.; Sellier, H.; Zhao, B.; Mowla, S.; Moore, A.; Hummerich, H.; Gewurz, B.E.; Cockell, S.J.; et al. Regulation of p53 and Rb links the alternative NF-κB pathway to EZH2 expression and cell senescence. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledoux, A.C.; Sellier, H.; Gillies, K.; Iannetti, A.; James, J.; Perkins, N.D. NFκB regulates expression of Polo-like kinase 4. Cell Cycle 2013, 12, 3052–3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 2000, 100, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Massa, P.E.; Hanidu, A.; Peet, G.W.; Aro, P.; Savitt, A.; Mische, S.; Li, J.; Marcu, K.B. IKKalpha, IKKbeta, and NEMO/IKKgamma are each required for the NF-kappa B-mediated inflammatory response program. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 45129–45140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massa, P.E.; Li, X.; Hanidu, A.; Siamas, J.; Pariali, M.; Pareja, J.; Savitt, A.G.; Catron, K.M.; Li, J.; Marcu, K.B. Gene expression profiling in conjunction with physiological rescues of IKKalpha-null cells with wild type or mutant IKKalpha reveals distinct classes of IKKalpha/NF-kappaB-dependent genes. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 14057–14069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadiminty, N.; Dutt, S.; Tepper, C.; Gao, A.C. Microarray analysis reveals potential target genes of NF-kappaB2/p52 in LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2010, 70, 276–287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wharry, C.E.; Haines, K.M.; Carroll, R.G.; May, M.J. Constitutive non-canonical NFkappaB signaling in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2009, 8, 1567–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammirante, M.; Shalapour, S.; Kang, Y.; Jamieson, C.A.; Karin, M. Tissue injury and hypoxia promote malignant progression of prostate cancer by inducing CXCL13 expression in tumor myofibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 14776–14781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ammirante, M.; Luo, J.L.; Grivennikov, S.; Nedospasov, S.; Karin, M. B-cell-derived lymphotoxin promotes castration-resistant prostate cancer. Nature 2010, 464, 302–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, Q.L.; Sun, W.; Chandrasekharan, P.; Cheng, H.S.; Ying, Z.; Lakshmanan, M.; Raju, A.; Tenen, D.G.; Cheng, S.Y.; et al. Non-canonical NF-κB signalling and ETS1/2 cooperatively drive C250T mutant TERT promoter activation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2015, 17, 1327–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Margalef, P.; Fernández-Majada, V.; Villanueva, A.; Garcia-Carbonell, R.; Iglesias, M.; López, L.; Martínez-Iniesta, M.; Villà-Freixa, J.; Mulero, M.C.; Andreu, M.; et al. A truncated form of IKKα is responsible for specific nuclear IKK activity in colorectal cancer. Cell Rep. 2012, 2, 840–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margalef, P.; Colomer, C.; Villanueva, A.; Montagut, C.; Iglesias, M.; Bellosillo, B.; Salazar, R.; Martínez-Iniesta, M.; Bigas, A.; Espinosa, L. BRAF-induced tumorigenesis is IKKα-dependent but NF-κB-independent. Sci. Signal 2015, 8, ra38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, C.L.; Lee, D.W.; Jung, J.U.; Ravi, S.; Pogue, C.B.; Toussaint, L.G.; Bayless, K.J.; Sitcheran, R. NIK regulates MT1-MMP activity and promotes glioma cell invasion independently of the canonical NF-κB pathway. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherry, E.; Lee, D.; Jung, J.; Sitcheran, R. Non-canonical NF-kB signaling drives the aggressive invasiveness of glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, v2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lessard, L.; Bégin, L.R.; Gleave, M.E.; Mes-Masson, A.M.; Saad, F. Nuclear localisation of nuclear factor-kappaB transcription factors in prostate cancer: an immunohistochemical study. Br. J. Cancer 2005, 93, 1019–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lessard, L.; Saad, F.; Le Page, C.; Diallo, J.S.; Péant, B.; Delvoye, N.; Mes-Masson, A.M. NF-kappaB2 processing and p52 nuclear accumulation after androgenic stimulation of LNCaP prostate cancer cells. Cell Signal 2007, 19, 1093–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döppler, H.; Liou, G.Y.; Storz, P. Downregulation of TRAF2 mediates NIK-induced pancreatic cancer cell proliferation and tumorigenicity. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishina, T.; Yamaguchi, N.; Gohda, J.; Semba, K.; Inoue, J. NIK is involved in constitutive activation of the alternative NF-kappaB pathway and proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 388, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, N.M.; Canete, J.J.; Callery, M.P. Increased expression of NF-kappa B subunits in human pancreatic cancer cells. J. Surg. Res. 2004, 118, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, H.; Akedo, I.; Suzuki, T.; Narahara, H.; Otani, T. Adverse effects of sulindac used for prevention of colorectal cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1997, 89, 1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lua, J.; Qayyum, T.; Edwards, J.; Roseweir, A.K. The Prognostic Role of the Non-Canonical Nuclear Factor-Kappa B Pathway in Renal Cell Carcinoma Patients. Urol. Int. 2018, 101, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamieson, S.; Fuller, P.J. Characterization of the inhibitor of kappaB kinase (IKK) complex in granulosa cell tumors of the ovary and granulosa cell tumor-derived cell lines. Horm. Cancer 2013, 4, 277–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, P.; Xu, J.; Tang, Z.; Ma, H.; Guo, F. Prognostic significance of RelB overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer patients. Thorac. Cancer 2016, 7, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, M.; Duan, X.; Zhou, P.; Zhou, W.; Wu, X.; Xu, S.; Chen, Y.; Tao, Z. Lymphotoxin β receptor activation promotes bladder cancer in a nuclear factor-κB-dependent manner. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 783–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sovak, M.A.; Bellas, R.E.; Kim, D.W.; Zanieski, G.J.; Rogers, A.E.; Traish, A.M.; Sonenshein, G.E. Aberrant nuclear factor-kappaB/Rel expression and the pathogenesis of breast cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2952–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennett, L.; Quinn, J.; McCall, P.; Mallon, E.A.; Horgan, P.G.; McMillan, D.C.; Paul, A.; Edwards, J. High IKKα expression is associated with reduced time to recurrence and cancer specific survival in oestrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2017, 140, 1633–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cao, Y.; Bonizzi, G.; Seagroves, T.N.; Greten, F.R.; Johnson, R.; Schmidt, E.V.; Karin, M. IKKalpha provides an essential link between RANK signaling and cyclin D1 expression during mammary gland development. Cell 2001, 107, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, X.L.; Bai, R.; Liu, W.Y.; Li, X.; Liu, M.; Tang, H. miR-23a promotes IKKα expression but suppresses ST7L expression to contribute to the malignancy of epithelial ovarian cancer cells. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 115, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connelly, L.; Robinson-Benion, C.; Chont, M.; Saint-Jean, L.; Li, H.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Blackwell, T.S.; Yull, F.E. A transgenic model reveals important roles for the NF-kappa B alternative pathway (p100/p52) in mammary development and links to tumorigenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 10028–10035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Bonnizi, G.; Cao, Y. NF-kB: A factor that provides a link between stress, inflammation and cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, S116. [Google Scholar]
- Karin, M.; Cao, Y.X.; Greten, F.R.; Li, Z.W. NF-kappa B in cancer: From innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Lin, A. NF-kappa B at the crossroads of life and death. Nat. Immunol. 2002, 3, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogswell, P.C.; Guttridge, D.C.; Funkhouser, W.K.; Baldwin, A.S., Jr. Selective activation of NF-kappa B subunits in human breast cancer: potential roles for NF-kappa B2/p52 and for Bcl-3. Oncogene 2000, 19, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, H.C.; Antonia, R.J.; Baldwin, A.S. PI3K/Akt promotes feedforward mTORC2 activation through IKK alpha. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 21064–21075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa, L.; Margalef, P.; Bigas, A. Non-conventional functions for NF-kappa B members: the dark side of NF-kappa B. Oncogene 2015, 34, 2279–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzo, P.; Miao, H.; D’Souza, G.; Osipo, C.; Song, L.L.; Yun, J.; Zhao, H.; Mascarenhas, J.; Wyatt, D.; Antico, G.; et al. Cross-talk between notch and the estrogen receptor in breast cancer suggests novel therapeutic approaches. Cancer Res. 2008, 68, 5226–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.; Rizzo, P.; Osipo, C.; Pannuti, A.; Wyatt, D.; Cheung, L.W.; Sonenshein, G.; Osborne, B.A.; Miele, L. Notch-1 activates estrogen receptor-alpha-dependent transcription via IKKalpha in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2010, 29, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roseweir, A.K.; Bennett, L.; Dickson, A.; Cheng, K.; Quintayo, M.A.; Bayani, J.; McMillan, D.C.; Horgan, P.G.; van de Velde, C.J.H.; Seynaeve, C.; et al. Predictive Biomarkers for Endocrine Therapy: Retrospective Study in Tamoxifen and Exemestane Adjuvant Multinational (TEAM) Trial. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2018, 110, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merga, Y.J.; O’Hara, A.; Burkitt, M.D.; Duckworth, C.A.; Probert, C.S.; Campbell, B.J.; Pritchard, D.M. Importance of the alternative NF-κB activation pathway in inflammation-associated gastrointestinal carcinogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2016, 310, G1081–G1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, L.; Vu, T.; Yuan, G.; Datta, P.K. STRAP Promotes Stemness of Human Colorectal Cancer via Epigenetic Regulation of the NOTCH Pathway. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5464–5478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leopizzi, M.; Cocchiola, R.; Milanetti, E.; Raimondo, D.; Politi, L.; Giordano, C.; Scandurra, R.; Scotto d’Abusco, A. IKKα inibition by a glucosamine derivative enhances Maspin expression in osteosarcoma cell line. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 262, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.K.W.; Bennett, L.; Edwards, J. Identification of a novel biomarker of IKK alpha-dependent NF-kappa B signalling in oestrogen receptor (ER)-positive breast cancer. Scot. Med. J. 2016, 61, 55. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, J.L.; Tan, W.; Ricono, J.M.; Korchynskyi, O.; Zhang, M.; Gonias, S.L.; Cheresh, D.A.; Karin, M. Nuclear cytokine-activated IKKalpha controls prostate cancer metastasis by repressing Maspin. Nature 2007, 446, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammirante, M.; De Laurenzi, V.; Graziano, V.; Turco, M.C.; Rosati, A. BAG3 is required for IKKα nuclear translocation and emergence of castration resistant prostate cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2011, 2, e139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizel, L.; Safieh, C.; Shalev, S.A.; Mezer, E.; Jabaly-Habib, H.; Ben-Neriah, Z.; Chervinsky, E.; Briscoe, D.; Ben-Yosef, T. Novel mutations of MYO7A and USH1G in Israeli Arab families with Usher syndrome type 1. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 3548–3555. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ben-Neriah, Y.; Karin, M. Inflammation meets cancer, with NF-kappa B as the matchmaker. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karin, M.; Greten, F.R. NF kappa B: Linking inflammation and immunity to cancer development and progression. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2005, 5, 749–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepulveda, A.; Soriano, H.; Espino, A. Gastrointestinal tract involvement in Klippel-Trénaunay syndrome. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018, 3, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, J.; Shi, Y.; Yan, B.; Xiao, D.; Lai, W.; Pan, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Chen, L.; Mao, C.; Zhou, J.; et al. LGR5 expression is controled by IKKα in basal cell carcinoma through activating STAT3 signaling pathway. Oncotarget. 2016, 7, 27280–28294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manna, S.; Singha, B.; Phyo, S.A.; Gatla, H.R.; Chang, T.P.; Sanacora, S.; Ramaswami, S.; Vancurova, I. Proteasome inhibition by bortezomib increases IL-8 expression in androgen-independent prostate cancer cells: the role of IKKα. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 2837–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, S.; Dong, H.; Song, J.; Thiruppathi, M.; Prabhakar, B.S.; Qiu, Q.; Lin, Z.; Chini, E.; Zhang, B.; Fang, D. Deleted in Breast Cancer 1 Suppresses B Cell Activation through RelB and Is Regulated by IKKα Phosphorylation. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3685–3693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qu, L.L.; He, L.; Zhao, X.; Xu, W. Downregulation of miR-518a-3p activates the NIK-dependent NF-kappa B pathway in colorectal cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015, 35, 1266–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frelin, C.; Imbert, V.; Griessinger, E.; Peyron, A.C.; Rochet, N.; Philip, P.; Dageville, C.; Sirvent, A.; Hummelsberger, M.; Bérard, E.; et al. Targeting NF-kappaB activation via pharmacologic inhibition of IKK2-induced apoptosis of human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Blood 2005, 105, 804–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hehner, S.P.; Hofmann, T.G.; Dröge, W.; Schmitz, M.L. The antiinflammatory sesquiterpene lactone parthenolide inhibits NF-kappa B by targeting the I kappa B kinase complex. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 5617–5623. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hideshima, T.; Chauhan, D.; Kiziltepe, T.; Ikeda, H.; Okawa, Y.; Podar, K.; Raje, N.; Protopopov, A.; Munshi, N.C.; Richardson, P.G.; et al. Biologic sequelae of I{kappa}B kinase (IKK) inhibition in multiple myeloma: therapeutic implications. Blood 2009, 113, 5228–5236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coope, H.J.; Atkinson, P.G.; Huhse, B.; Belich, M.; Janzen, J.; Holman, M.J.; Klaus, G.G.; Johnston, L.H.; Ley, S.C. CD40 regulates the processing of NF-kappaB2 p100 to p52. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 5375–5385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kayagaki, N.; Yan, M.; Seshasayee, D.; Wang, H.; Lee, W.; French, D.M.; Grewal, I.S.; Cochran, A.G.; Gordon, N.C.; Yin, J.; et al. BAFF/BLyS receptor 3 binds the B cell survival factor BAFF ligand through a discrete surface loop and promotes processing of NF-kappaB2. Immunity 2002, 17, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novack, D.V.; Yin, L.; Hagen-Stapleton, A.; Schreiber, R.D.; Goeddel, D.V.; Ross, F.P.; Teitelbaum, S.L. The IkappaB function of NF-kappaB2 p100 controls stimulated osteoclastogenesis. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.C. The non-canonical NF-κB pathway. Immunol. Rev. 2012, 246, 125–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarfò, L.; Ferreri, A.J.; Ghia, P. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 104, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuní, S.; Pérez-Aciego, P.; Pérez-Chacón, G.; Vargas, J.A.; Sánchez, A.; Martín-Saavedra, F.M.; Ballester, S.; García-Marco, J.; Jordá, J.; Durántez, A. A sustained activation of PI3K/NF-κB pathway is critical for the survival of chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells. Leukemia 2004, 18, 1391–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hewamana, S.; Alghazal, S.; Lin, T.T.; Clement, M.; Jenkins, C.; Guzman, M.L.; Jordan, C.T.; Neelakantan, S.; Crooks, P.A.; Burnett, A.K.; et al. The NF-kappaB subunit Rel A is associated with in vitro survival and clinical disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and represents a promising therapeutic target. Blood 2008, 111, 4681–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mansouri, L.; Sutton, L.A.; Ljungström, V.; Bondza, S.; Arngården, L.; Bhoi, S.; Larsson, J.; Cortese, D.; Kalushkova, A.; Plevova, K.; et al. Functional loss of IκBε leads to NF-κB deregulation in aggressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fabbri, G.; Rasi, S.; Rossi, D.; Trifonov, V.; Khiabanian, H.; Ma, J.; Grunn, A.; Fangazio, M.; Capello, D.; Monti, S.; et al. Analysis of the chronic lymphocytic leukemia coding genome: role of NOTCH1 mutational activation. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1389–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosati, E.; Sabatini, R.; Rampino, G.; Tabilio, A.; Di Ianni, M.; Fettucciari, K.; Bartoli, A.; Coaccioli, S.; Screpanti, I.; Marconi, P. Constitutively activated Notch signaling is involved in survival and apoptosis resistance of B-CLL cells. Blood 2009, 113, 856–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliakas, P.; Hadzidimitriou, A.; Sutton, L.A.; Rossi, D.; Minga, E.; Villamor, N.; Larrayoz, M.; Kminkova, J.; Agathangelidis, A.; Davis, Z.; et al. Recurrent mutations refine prognosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. European Research Initiative on CLL (ERIC). Leukemia 2015, 29, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiaretti, S.; Marinelli, M.; Del Giudice, I.; Bonina, S.; Piciocchi, A.; Messina, M.; Vignetti, M.; Rossi, D.; Di Maio, V.; Mauro, F.R.; et al. NOTCH1, SF3B1, BIRC3 and TP53 mutations in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia undergoing first-line treatment: correlation with biological parameters and response to treatment. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2014, 55, 2785–2792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejardin, E. The alternative NF-kappaB pathway from biochemistry to biology: pitfalls and promises for future drug development. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 72, 1161–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, D.; Rasi, S.; Fabbri, G.; Spina, V.; Fangazio, M.; Forconi, F.; Marasca, R.; Laurenti, L.; Bruscaggin, A.; Cerri, M.; et al. Mutations of NOTCH1 are an independent predictor of survival in chronic lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puente, X.S.; Pinyol, M.; Quesada, V.; Conde, L.; Ordóñez, G.R.; Villamor, N.; Escaramis, G.; Jares, P.; Beà, S.; González-Díaz, M.; et al. Whole-genome sequencing identifies recurrent mutations in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nature 2011, 475, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herishanu, Y.; Pérez-Galán, P.; Liu, D.; Biancotto, A.; Pittaluga, S.; Vire, B.; Gibellini, F.; Njuguna, N.; Lee, E.; Stennett, L.; et al. The lymph node microenvironment promotes B-cell receptor signaling, NF-kappaB activation, and tumor proliferation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2011, 117, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosén, A.; Murray, F.; Evaldsson, C.; Rosenquist, R. Antigens in chronic lymphocytic leukemia—Implications for cell origin and leukemogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2010, 20, 400–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wodarz, D.; Garg, N.; Komarova, N.L.; Benjamini, O.; Keating, M.J.; Wierda, W.G.; Kantarjian, H.; James, D.; O’Brien, S.; Burger, J.A. Kinetics of CLL cells in tissues and blood during therapy with the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib. Blood 2014, 123, 4132–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lucas, P.C.; Kuffa, P.; Gu, S.; Kohrt, D.; Kim, D.S.; Siu, K.; Jin, X.; Swenson, J.; McAllister-Lucas, L.M. A dual role for the API2 moiety in API2-MALT1-dependent NF-kappaB activation: heterotypic oligomerization and TRAF2 recruitment. Oncogene 2007, 26, 5643–5654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosebeck, S.; Madden, L.; Jin, X.; Gu, S.; Apel, I.J.; Appert, A.; Hamoudi, R.A.; Noels, H.; Sagaert, X.; Van Loo, P.; et al. Cleavage of NIK by the API2-MALT1 fusion oncoprotein leads to noncanonical NF-kappaB activation. Science 2011, 331, 468–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spina, V.; Rossi, D. NF-κB deregulation in splenic marginal zone lymphoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2016, 39, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thu, Y.M.; Richmond, A. NF-κB inducing kinase: A key regulator in the immune system and in cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010, 21, 213–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, R.E.; Brown, K.D.; Siebenlist, U.; Staudt, L.M. Constitutive nuclear factor κB activity is required for survival of activated B cell-like diffuse large B cell lymphoma cells. J. Exp. Med. 2001, 194, 1861–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenz, G.; Davis, R.E.; Ngo, V.N.; Lam, L.; George, T.C.; Wright, G.W.; Dave, S.S.; Zhao, H.; Xu, W.; Rosenwald, A.; et al. Oncogenic CARD11 mutations in human diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Science 2008, 319, 1676–1679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, V.N.; Young, R.M.; Schmitz, R.; Jhavar, S.; Xiao, W.; Lim, K.H.; Kohlhammer, H.; Xu, W.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, H.; et al. Oncogenically active MYD88 mutations in human lymphoma. Nature 2011, 470, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Calado, D.P.; Wang, Z.; Fröhler, S.; Köchert, K.; Qian, Y.; Koralov, S.B.; Schmidt-Supprian, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Unitt, C.; et al. An oncogenic role for alternative NF-κB signaling in DLBCL revealed upon deregulated BCL6 expression. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annunziata, C.M.; Davis, R.E.; Demchenko, Y.; Bellamy, W.; Gabrea, A.; Zhan, F.; Lenz, G.; Hanamura, I.; Wright, G.; Xiao, W.; et al. Frequent engagement of the classical and alternative NF-kappaB pathways by diverse genetic abnormalities in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keats, J.J.; Fonseca, R.; Chesi, M.; Schop, R.; Baker, A.; Chng, W.J.; Van Wier, S.; Tiedemann, R.; Shi, C.X.; Sebag, M.; et al. Promiscuous mutations activate the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway in multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demchenko, Y.N.; Glebov, O.K.; Zingone, A.; Keats, J.J.; Bergsagel, P.L.; Kuehl, W.M. Classical and/or alternative NF-kappaB pathway activation in multiple myeloma. Blood 2010, 115, 3541–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hauer, J.; Püschner, S.; Ramakrishnan, P.; Simon, U.; Bongers, M.; Federle, C.; Engelmann, H. TNF receptor (TNFR)-associated factor (TRAF) 3 serves as an inhibitor of TRAF2/5-mediated activation of the noncanonical NF-kappaB pathway by TRAF-binding TNFRs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2874–2879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Andres, M.; Almeida, J.; Martin-Ayuso, M.; De Las Heras, N.; Moro, M.J.; Martin-Nuñez, G.; Galende, J.; Cuello, R.; Abuín, I.; Moreno, I.; et al. Soluble and membrane levels of molecules involved in the interaction between clonal plasma cells and the immunological microenvironment in multiple myeloma and their association with the characteristics of the disease. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 124, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richardson, P.; Schlossman, R.; Jagannath, S.; Alsina, M.; Desikan, R.; Blood, E.; Weller, E.; Mitsiades, C.; Hideshima, T.; Davies, F.; et al. Thalidomide for patients with relapsed multiple myeloma after high-dose chemotherapy and stem cell transplantation: results of an open-label multicenter phase 2 study of efficacy, toxicity, and biological activity. Mayo. Clin. Proc. 2004, 79, 875–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMillin, D.W.; Negri, J.M.; Mitsiades, C.S. The role of tumour-stromal interactions in modifying drug response: challenges and opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, D.; Uchiyama, H.; Akbarali, Y.; Urashima, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Libermann, T.A.; Anderson, K.C. Multiple myeloma cell adhesion-induced interleukin-6 expression in bone marrow stromal cells involves activation of NF-kappa B. Blood 1996, 87, 1104–1112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bommert, K.; Bargou, R.C.; Stühmer, T. Signalling and survival pathways in multiple myeloma. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 1574–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sezer, O.; Heider, U.; Jakob, C.; Zavrski, I.; Eucker, J.; Possinger, K.; Sers, C.; Krenn, V. Immunocytochemistry reveals RANKL expression of myeloma cells. Blood 2002, 99, 4646–4647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boyce, B.F.; Xiu, Y.; Li, J.; Xing, L.; Yao, Z. NF-κB-Mediated Regulation of Osteoclastogenesis. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 30, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, R.; Anderson, G.; Xiao, G.; Elliott, G.; Leoni, L.; Mapara, M.Y.; Roodman, G.D.; Lentzsch, S. SDX-308, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent, inhibits NF-kappaB activity, resulting in strong inhibition of osteoclast formation/activity and multiple myeloma cell growth. Blood 2007, 109, 2130–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Connor, B.P.; Raman, V.S.; Erickson, L.D.; Cook, W.J.; Weaver, L.K.; Ahonen, C.; Lin, L.L.; Mantchev, G.T.; Bram, R.J.; Noelle, R.J. BCMA is essential for the survival of long-lived bone marrow plasma cells. J. Exp. Med. 2004, 199, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreaux, J.; Cremer, F.W.; Reme, T.; Raab, M.; Mahtouk, K.; Kaukel, P.; Pantesco, V.; De Vos, J.; Jourdan, E.; Jauch, A.; et al. The level of TACI gene expression in myeloma cells is associated with a signature of microenvironment dependence versus a plasmablastic signature. Blood 2005, 106, 1021–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bentires-Alj, M.; Barbu, V.; Fillet, M.; Chariot, A.; Relic, B.; Jacobs, N.; Gielen, J.; Merville, M.P.; Bours, V. NF-kappaB transcription factor induces drug resistance through MDR1 expression in cancer cells. Oncogene 2003, 22, 90–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brinkmann, U.; Eichelbaum, M. Polymorphisms in the ABC drug transporter gene MDR1. Pharmacogenomics J. 2001, 1, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catz, S.D.; Johnson, J.L. Transcriptional regulation of bcl-2 by nuclear factor kappa B and its significance in prostate cancer. Oncogene 2001, 20, 7342–7351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glasgow, J.N.; Qiu, J.; Rassin, D.; Grafe, M.; Wood, T.; Perez-Pol, J.R. Transcriptional regulation of the BCL-X gene by NF-kappaB is an element of hypoxic responses in the rat brain. Neurochem. Res. 2001, 26, 647–659. [Google Scholar]
- Zong, W.X.; Edelstein, L.C.; Chen, C.; Bash, J.; Gélinas, C. The prosurvival Bcl-2 homolog Bfl-1/A1 is a direct transcriptional target of NF-kappaB that blocks TNFalpha-induced apoptosis. Genes. Dev. 1999, 13, 382–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreuz, S.; Siegmund, D.; Scheurich, P.; Wajant, H. NF-kappaB inducers upregulate cFLIP, a cycloheximide-sensitive inhibitor of death receptor signaling. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 3964–3973. [Google Scholar]
- Traxler, P.; Furet, P. Strategies toward the Design of Novel and Selective Protein Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors. Pharmacol. Ther. 1999, 82, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The Protein Kinase Complement of the Human Genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, L.N.; Lowe, E.D.; Noble, M.E.M.; Owen, D.J. The structural basis for substrate recognition and control by protein kinases. FEBS Lett. 1998, 430, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gray, N.S. Rational design of inhibitors that bind to inactive kinase conformations. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghose, A.K.; Herbertz, T.; Pippin, D.A.; Salvino, J.M.; Mallamo, J.P. Knowledge based prediction of ligand binding modes and rational inhibitor design for kinase drug discovery. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 5149–5171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yang, P.L.; Gray, N.S. Targeting cancer with small molecule kinase inhibitors. Nauret. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohren, J.F.; Chen, H.; Pavlovsky, A.; Whitehead, C.; Zhang, E.; Kuffa, P.; Yan, C.; McConnell, P.; Spessard, C.; Banotai, C.; et al. Structures of human MAP kinase kinase 1 (MEK1) and MEK2 describe novel noncompetitive kinase inhibition. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2004, 11, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, M.S.; Zhang, C.; Shokat, K.M.; Taunton, J. Structural Bioinformatics-Based Design of Selective, Irreversible Kinase Inhibitors. Science 2005, 308, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Llona-Minguez, S.; Baiget, J.; Mackay, S.P. Small-molecule inhibitors of IκB kinase (IKK) and IKK-related kinases. Pharm. Pat. Anal. 2013, 2, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wullaert, A.; Bonnet, M.C.; Pasparakis, M. NF-κB in the Regulation of Epithelial Homeostasis and Inflammation. Cell Res. 2011, 21, 146–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustapha, S.; Kirshner, A.; De Moissac, D.; Kirshenbaum, L.A. A Direct Requirement of Nuclear Factor-Kappa B for Suppression of Apoptosis in Ventricular Myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2000, 27, H939–H945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baud, V.; Karin, M. Is NF-kappaB a Good Target for Cancer Therapy? Hopes and Pitfalls. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beg, A.A.; Sha, W.C.; Bronson, R.T.; Ghosh, S.; Baltimore, D. Embryonic Lethality and Liver Degeneration in Mice Lacking the RelA Component of NF-Kappa, B. Nature 1995, 376, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pannicke, U.; Baumann, B.; Fuchs, S.; Henneke, P.; Rensing-Ehl, A.; Rizzi, M.; Janda, A.; Hese, K.; Schlesier, M.; Holzmann, K.; et al. Deficiency of Innate and Acquired Immunity Caused by an IKBKB Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 369, 2504–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; O’Rahilly, S. Insulin Resistance; Kumar, S., O’Rahilly, S., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Viatour, P.; Merville, M.P.; Bours, V.; Chariot, A. Phosphorylation of NF-kB and IkB Proteins: Implications in Cancer and Inflammation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2005, 30, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adli, M.; Merkhofer, E.; Cogswell, P.; Baldwin, A.S. IKKα and IKKβ Each Function to Regulate NF-κB Activation in the TNF-Induced/canonical Pathway. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Leon-Boenig, G.; Bowman, K.K.; Feng, J.A.; Crawford, T.; Everett, C.; Franke, Y.; Oh, A.; Stanley, M.; Staben, S.T.; Starovasnik, M.A.; et al. The crystal structure of the catalytic domain of the NF-κB inducing kinase reveals a narrow but flexible active site. Structure 2012, 20, 1704–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Z.; Ghosh, G. Understanding NIK regulation from its structure. Structure 2012, 20, 1615–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castanedo, G.M.; Blaquiere, N.; Beresini, M.; Bravo, B.; Brightbill, H.; Chen, J.; Cui, H.F.; Eigenbrot, C.; Everett, C.; Feng, J.; et al. Structure-Based Design of Tricyclic NF-κB Inducing Kinase (NIK) Inhibitors That Have High Selectivity over Phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K). J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 627–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaquiere, N.; Castanedo, G.M.; Burch, J.D.; Berezhkovskiy, L.M.; Brightbill, H.; Brown, S.; Chan, C.; Chiang, P.C.; Crawford, J.J.; Dong, T.; et al. Scaffold-Hopping Approach to Discover Potent, Selective, and Efficacious Inhibitors of NF-κB Inducing Kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 61, 6801–6813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwak, Y.T.; Guo, J.; Shen, J.; Gaynor, R.B. Analysis of domains in the IKK alpha and IKK beta proteins that regulate their kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 14752–14759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, H.; Ghosh, S.; Luesch, H.; Ghosh, A.; Wong, E.T.; Malik, N.; Orth, A.; de Jesus, P.; Perry, A.S.; Oliver, J.D.; et al. Telomere-independent Rap1 is an IKK adaptor and regulates NF-κB-dependent gene expression. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 758–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polley, S.; Passos, D.O.; Huang, D.B.; Mulero, M.C.; Mazumder, A.; Biswas, T.; Verma, I.M.; Lyumkis, D.; Ghosh, G. Structural Basis for the Activation of IKK1/α. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 1907–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, Y.C.; Chung, J.Y.; Rich, R.L.; Myszka, D.G.; Wu, H. High-affinity interaction between IKKbeta and NEMO. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 3109–3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Lo, Y.-C.; Li, Q.; Napolitano, G.; Wu, X.; Jiang, X.; Dreano, M.; Karin, M.; Wu, H. Crystal structure of inhibitor of κB kinase beta. Nature 2011, 472, 325–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polley, S.; Huang, D.B.; Hauenstein, A.V.; Fusco, A.J.; Zhong, X.; Vu, D.; Schröfelbauer, B.; Kim, Y.; Hoffmann, A.; Verma, I.M.; et al. A structural basis for IκB kinase 2 activation via oligomerization-dependent trans auto-phosphorylation. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Misquitta, Y.R.; Olland, A.; Johnson, M.A.; Kelleher, K.S.; Kriz, R.; Lin, L.L.; Stahl, M.; Mosyak, L. Crystal structure of a human IκB kinase β asymmetric dimer. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 22758–22767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, Q.K.; Boddupalli, H.; Rouw, S.A.; Koboldt, C.M.; Hall, T.; Sommers, C.; Hauser, S.D.; Pierce, J.L.; Combs, R.G.; Reitz, B.A.; et al. Characterization of the recombinant IKK1/IKK2 heterodimer. Mechanisms regulating kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 25883–25891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mercurio, F.; Murray, B.W.; Shevchenko, A.; Bennett, B.L.; Young, D.B.; Li, J.W.; Pascual, G.; Motiwala, A.; Zhu, H.; Mann, M.; et al. IkappaB kinase (IKK)-associated protein 1, a common component of the heterogeneous IKK complex. Mol. Cell Biol. 1999, 19, 1526–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mbalaviele, G.; Sommers, C.D.; Bonar, S.L.; Mathialagan, S.; Schindler, J.F.; Guzova, J.A.; Shaffer, A.F.; Melton, M.A.; Christine, L.J.; Tripp, C.S.; et al. A novel, highly selective, tight binding IkappaB kinase-2 (IKK-2) inhibitor: a tool to correlate IKK-2 activity to the fate and functions of the components of the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway in arthritis-relevant cells and animal models. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2009, 329, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, E.R.R. IKK as a Therapeutic Intervention Point for Diseases Related to Inflammation in Anti-Inflammatory Drug Discovery; Levin, J.I., Laufer, S., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2012; pp. 255–296. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, M.J.; Yamamoto, Y.; Gaynor, R.B. The anti-inflammatory agents aspirin and salicylate inhibit the activity of I(kappa)B kinase-beta. Nature 1998, 396, 77–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avila, C.M.; Romeiro, N.C.; Sant’Anna, C.M.; Barreiro, E.J.; Fraga, C.A. Structural insights into IKKbeta inhibition by natural products staurosporine and quercetin. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 6907–6910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folmer, F.; Jaspars, M.; Dicato, M.; Diederich, M. Marine natural products as targeted modulators of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 603–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, B.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Seo, J.H.; Lee, H.Y.; Ryu, S.Y.; Ahn, B.W.; Lee, C.K.; Hwang, B.Y.; Han, S.B.; Kim, Y. Artemisolide is a typical inhibitor of IkappaB kinase beta targeting cysteine-179 residue and down-regulates NF-kappaB-dependent TNF-alpha expression in LPS-activated macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 361, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, A.K.; Wan, C.K.; Shen, X.L.; Yang, M.; Fong, W.F. Honokiol inhibits TNF-alpha-stimulated NF-kappaB activation and NF-kappaB-regulated gene expression through suppression of IKK activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2005, 70, 1443–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobori, M.; Yang, Z.; Gong, D.; Heissmeyer, V.; Zhu, H.; Jung, Y.K.; Gakidis, M.A.; Rao, A.; Sekine, T.; Ikegami, F.; et al. Wedelolactone suppresses LPS-induced caspase-11 expression by directly inhibiting the IKK complex. Cell Death Differ. 2004, 11, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crèvecoeur, J.; Merville, M.P.; Piette, J.; Gloire, G. Geldanamycin inhibits tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent NF-kappaB activation. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 2183–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belema, M.; Bunker, A.; Nguyen, V.N.; Beaulieu, F.; Ouellet, C.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Martel, A.; Burke, J.R.; McIntyre, K.W.; et al. Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of imidazo(1,2-a)thieno(3,2-e)pyrazines as IKK-beta inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 4284–4289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, J.R.; Pattoli, M.A.; Gregor, K.R.; Brassil, P.J.; MacMaster, J.F.; McIntyre, K.W.; Yang, X.; Iotzova, V.S.; Clarke, W.; Strnad, J.; et al. BMS-345541 is a highly selective inhibitor of I kappa B kinase that binds at an allosteric site of the enzyme and blocks NF-kappa B-dependent transcription in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 1450–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christopher, J.A.; Avitabile, B.G.; Bamborough, P.; Champigny, A.C.; Cutler, G.J.; Dyos, S.L.; Grace, K.G.; Kerns, J.K.; Kitson, J.D.; Mellor, G.W.; et al. The discovery of 2-amino-3,5-diarylbenzamide inhibitors of IKK-alpha and IKK-beta kinases. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2007, 17, 3972–3977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smithkline Beecham Corporation. O-Hydroxy-and O-Amino Benzamide Derivatives as Ikk2 Inhibitors. International Publication No. WO2007025575A1, 8 March 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Liddle, J.; Bamborough, P.; Barker, M.D.; Campos, S.; Cousins, R.P.; Cutler, G.J.; Hobbs, H.; Holmes, D.S.; Ioannou, C.; Mellor, G.W.; et al. 4-Phenyl-7-azaindoles as potent and selective IKK2 inhibitors. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19, 2504–2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waelchli, R.; Bollbuck, B.; Bruns, C.; Buhl, T.; Eder, J.; Feifel, R.; Hersperger, R.; Janser, P.; Revesz, L.; Zerwes, H.G.; et al. Design and preparation of 2-benzamido-pyrimidines as inhibitors of IKK. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asamitsu, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Nakata, K.; Hibi, Y.; Victoriano, A.F.; Imai, K.; Onozaki, K.; Kitade, Y.; Okamoto, T. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by blocking IkappaB kinase with noraristeromycin. J. Biochem. 2008, 144, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaxo Group Limited; Smithkline Beecham Corporation. Pyrrolo-Pyridine Derivatives for The Treatment of Disorders Associated with Inappropriate Ikk1 Activity. International Publication No. WO2008110508A1, 18 September 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Glaxo Group Limited; Smithkline Beecham Corporation. Lh-Indazole-3-Amine Compounds as Ikk1 Inhibitors. International Publication No. WO2008132121A1, 6 November 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Shukla, S.; Kanwal, R.; Shankar, E.; Datt, M.; Chance, M.R.; Fu, P.; MacLennan, G.T.; Gupta, S. Apigenin blocks IKKα activation and suppresses prostate cancer progression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31216–31232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shukla, S.; Shankar, E.; Fu, P.; MacLennan, G.T.; Gupta, S. Suppression of NF-κB and NF-κB-Regulated Gene Expression by Apigenin through IκBα and IKK Pathway in TRAMP Mice. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0138710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paul, A.; Edwards, J.; Pepper, C.; Mackay, S. Inhibitory-κB Kinase (IKK) α and Nuclear Factor-κB (NFκB)-Inducing Kinase (NIK) as Anti-Cancer Drug Targets. Cells 2018, 7, 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100176
Paul A, Edwards J, Pepper C, Mackay S. Inhibitory-κB Kinase (IKK) α and Nuclear Factor-κB (NFκB)-Inducing Kinase (NIK) as Anti-Cancer Drug Targets. Cells. 2018; 7(10):176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100176
Chicago/Turabian StylePaul, Andrew, Joanne Edwards, Christopher Pepper, and Simon Mackay. 2018. "Inhibitory-κB Kinase (IKK) α and Nuclear Factor-κB (NFκB)-Inducing Kinase (NIK) as Anti-Cancer Drug Targets" Cells 7, no. 10: 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100176
APA StylePaul, A., Edwards, J., Pepper, C., & Mackay, S. (2018). Inhibitory-κB Kinase (IKK) α and Nuclear Factor-κB (NFκB)-Inducing Kinase (NIK) as Anti-Cancer Drug Targets. Cells, 7(10), 176. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells7100176





