Adhesion Deregulation in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
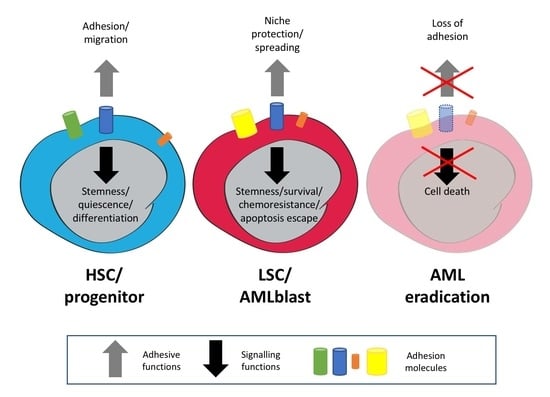
2. Expression of Adhesion Molecules on Haematopoietic/Leukaemic Stem Cells
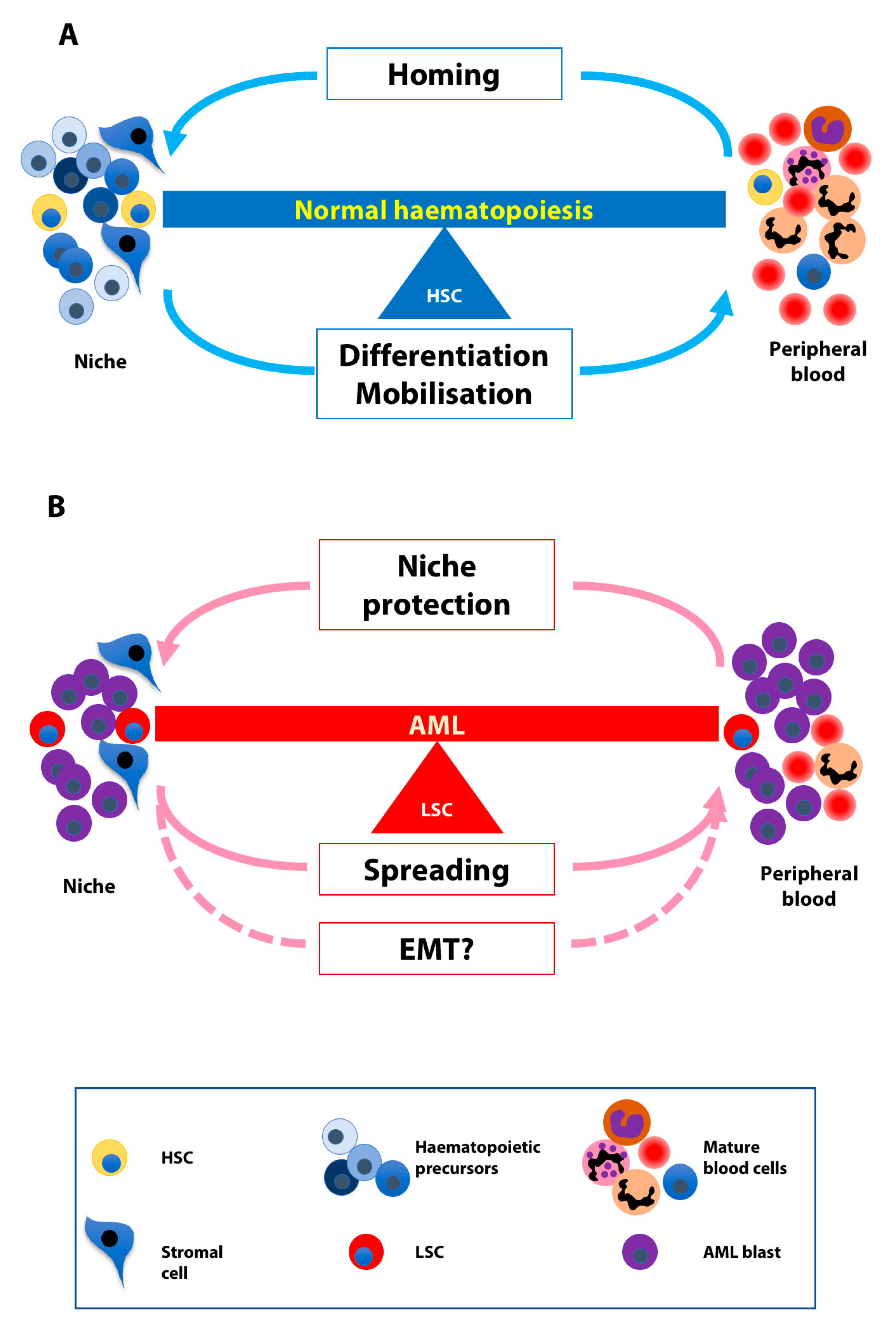
3. Normal and Leukaemic Niche
4. The Balance between Homing and Migration in Normal and Leukaemic Cells
5. Involvement of AMs in AML Signaling
6. EMT-Like Programme Activation in AML
7. Clinical Implications
7.1. Prognosis
7.2. Targeted Therapies
8. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of interest
References
- Barczyk, M.; Carracedo, S.; Gullberg, D. Integrins. Cell Tissue Res. 2010, 339, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coombe, D.R.; Dye, D.E. Feature, structure, and classification of adhesion molecules: An overview. In Adhesion Molecules; Preedy, V.R., Ed.; Science Publisher: Enfield, NH, USA, 2010; pp. 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Kupsa, T.; Horacek, J.M.; Jebavy, L. The role of adhesion molecules in acute myeloid leukemia and (hemato)oncology: A systematic review. Biomed. Pap. 2015, 159, 001–011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levesque, J.-P.; Winkler, I.G. Cell Adhesion Molecules in Normal and Malignant Hematopoiesis: From Bench to Bedside. Curr. Stem Cell Rep. 2016, 2, 356–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipkins, D.A.; Wei, X.; Wu, J.W.; Runnels, J.M.; Cote, D.; Means, T.K.; Luster, A.D.; Scadden, D.T.; Lin, C.P. In vivo imaging of specialized bone marrow endothelial microdomains for tumour engraftment. Nature 2005, 435, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Juliano, R.L. Signal transduction by cell adhesion receptors and the cytoskeleton: Functions of integrins, cadherins, selectins, and immunoglobulin-superfamily members. Ann. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2002, 42, 283–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barclay, A.N. Membrane proteins with immunoglobulin-like domains-a master superfamily of interaction molecules. Semin. Immunol. 2003, 15, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszka, A.M.; Valli, D.; Alcalay, M. Understanding the molecular basis of acute myeloid leukemias: Where are we now? Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 6, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohner, H.; Estey, E.H.; Amadori, S.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Buchner, T.; Burnett, A.K.; Dombret, H.; Fenaux, P.; Grimwade, D.; Larson, R.A.; et al. Diagnosis and management of acute myeloid leukemia in adults: Recommendations from an international expert panel, on behalf of the European LeukemiaNet. Blood 2010, 115, 453–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kode, A.; Manavalan, J.S.; Mosialou, I.; Bhagat, G.; Rathinam, C.V.; Luo, N.; Khiabanian, H.; Lee, A.; Murty, V.V.; Friedman, R.; et al. Leukaemogenesis induced by an activating β-catenin mutation in osteoblasts. Nature 2014, 506, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raaijmakers, M.H.G.P.; Mukherjee, S.; Guo, S.; Zhang, S.; Kobayashi, T.; Schoonmaker, J.A.; Ebert, B.L.; Al-Shahrour, F.; Hasserjian, R.P.; Scadden, E.O.; et al. Bone progenitor dysfunction induces myelodysplasia and secondary leukaemia. Nature 2010, 464, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinisch, A.; Chan, S.M.; Thomas, D.; Majeti, R. Biology and Clinical Relevance of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. Semin. Hematol. 2015, 52, 150–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, D.; Majeti, R. Biology and relevance of human acute myeloid leukemia stem cells. Blood 2017, 129, 1577–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuss-Borst, M.A.; Bhüring, H.J.; Klein, G.; Müller, C.A. Adhesion molecules on CD34+ hematopoietic cells in normal human bone marrow and leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 1992, 65, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corbel, C.; Salaun, J. AlphaIIb integrin expression during development of the murine hemopoietic system. Dev. Biol. 2002, 243, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umemoto, T.; Yamato, M.; Shiratsuchi, Y.; Terasawa, M.; Yang, J.; Nishida, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Okano, T. Expression of Integrin beta3 is correlated to the properties of quiescent hemopoietic stem cells possessing the side population phenotype. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 7733–7739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansas, G.S.; Muirhead, M.J.; Dailey, M.O. Expression of the CD11/CD18, leukocyte adhesion molecule 1, and CD44 adhesion molecules during normal myeloid and erythroid differentiation in humans. Blood 1990, 76, 2483–2492. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Puch, S.; Armeanu, S.; Kibler, C.; Johnson, K.R.; Mller, C.A.; Wheelock, M.J.; Klein, G. N-cadherin is developmentally regulated and functionally involved in early hematopoietic cell differentiation. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Turel, K.R.; Rao, S.G. Expression of the cell adhesion molecule E-cadherin by the human bone marrow stromal cells and its probable role in CD34(+) stem cell adhesion. Cell Biol. Int. 1998, 22, 641–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peled, A.; Petit, I.; Kollet, O.; Magid, M.; Ponomaryov, T.; Byk, T.; Nagler, A.; Ben-Hur, H.; Many, A.; Shultz, L.; et al. Dependence of human stem cell engraftment and repopulation of NOD/SCID mice on CXCR4. Science (New York) 1999, 283, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simmons, P.J.; Levesque, J.P.; Zannettino, A.C. Adhesion molecules in haemopoiesis. Bailliere’s Clin. Haematol. 1997, 10, 485–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewinsohn, D.M.; Nagler, A.; Ginzton, N.; Greenberg, P.; Butcher, E.C. Hematopoietic progenitor cell expression of the H-CAM (CD44) homing-associated adhesion molecule. Blood 1990, 75, 589–595. [Google Scholar]
- McDermott, S.P.; Ranheim, E.A.; Leatherberry, V.S.; Khwaja, S.S.; Klos, K.S.; Alexander, C.M. Juvenile syndecan-1 null mice are protected from carcinogen-induced tumor development. Oncogene 2007, 26, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitroff, C.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Fuhlbrigge, R.C.; Sackstein, R. A distinct glycoform of CD44 is an L-selectin ligand on human hematopoietic cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13841–13846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Möhle, R.; Bautz, F.; Rafii, S.; Moore, M.A.; Brugger, W.; Kanz, L. The chemokine receptor CXCR-4 is expressed on CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors and leukemic cells and mediates transendothelial migration induced by stromal cell-derived factor-1. Blood 1998, 91, 4523–4530. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zou, Y.R.; Kottmann, A.H.; Kuroda, M.; Taniuchi, I.; Littman, D.R. Function of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 in haematopoiesis and in cerebellar development. Nature 1998, 393, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrobel, T.; Pogrzeba, J.; Stefanko, E.; Wojtowicz, M.; Jazwiec, B.; Dzietczenia, J.; Mazur, G.; Kuliczkowski, K. Expression of Eph A4, Eph B2 and Eph B4 receptors in AML. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2014, 20, 901–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirabayashi, Y.; Yoon, B.I.; Tsuboi, I.; Huo, Y.; Kodama, Y.; Kanno, J.; Ott, T.; Trosko, J.E.; Inoue, T. Protective role of connexin 32 in steady-state hematopoiesis, regeneration state, and leukemogenesis. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2007, 232, 700–712. [Google Scholar]
- Krenacs, T.; Rosendaal, M. Connexin43 gap junctions in normal, regenerating, and cultured mouse bone marrow and in human leukemias: Their possible involvement in blood formation. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 152, 993–1004. [Google Scholar]
- Reuss-Borst, M.A.; Klein, G.; Waller, H.D.; Müller, C.A. Differential expression of adhesion molecules in acute leukemia. Leukemia 1995, 9, 869–874. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj, J.; Konuma, T.; Lytle, N.K.; Kwon, H.Y.; Ablack, J.N.; Cantor, J.M.; Rizzieri, D.; Chuah, C.; Oehler, V.G.; Broome, E.H.; et al. CD98-Mediated Adhesive Signaling Enables the Establishment and Propagation of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 792–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gallay, N.; Anani, L.; Lopez, A.; Colombat, P.; Binet, C.; Domenech, J.; Weksler, B.B.; Malavasi, F.; Herault, O. The Role of Platelet/Endothelial Cell Adhesion Molecule-1 (CD31) and CD38 Antigens in Marrow Microenvironmental Retention of Acute Myelogenous Leukemia Cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 16, 8624–8656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinyuk, M.; Alvarado, A.G.; Nesmiyanov, P.; Shaw, J.; Mulkearns-Hubert, E.E.; Eurich, J.T.; Hale, J.S.; Bogdanova, A.; Hitomi, M.; Maciejewski, J.; et al. Cx25 contributes to leukemia cell communication and chemosensitivity. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31508–31521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulais, P.E.; Frenette, P.S. Making sense of hematopoietic stem cell niches. Blood 2015, 125, 2621–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richter, R.; Forssmann, W.; Henschler, R. Current Developments in Mobilization of Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells and Their Interaction with Niches in Bone Marrow. Transfus. Med. Hemother. Offizielles Organ Deutschen Ges. Transfusionsmed. Immunhamatol. 2017, 44, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Niu, C.; Ye, L.; Huang, H.; He, X.; Tong, W.-G.; Ross, J.; Haug, J.; Johnson, T.; Feng, J.Q.; et al. Identification of the haematopoietic stem cell niche and control of the niche size. Nature 2003, 425, 836–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van der Loo, J.C.; Xiao, X.; McMillin, D.; Hashino, K.; Kato, I.; Williams, D.A. VLA-5 is expressed by mouse and human long-term repopulating hematopoietic cells and mediates adhesion to extracellular matrix protein fibronectin. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 102, 1051–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermeulen, M.; Le Pesteur, F.; Gagnerault, M.C.; Mary, J.Y.; Sainteny, F.; Lepault, F. Role of adhesion molecules in the homing and mobilization of murine hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Blood 1998, 92, 894–900. [Google Scholar]
- Boyerinas, B.; Zafrir, M.; Yesilkanal, A.E.; Price, T.T.; Hyjek, E.M.; Sipkins, D.A. Adhesion to osteopontin in the bone marrow niche regulates lymphoblastic leukemia cell dormancy. Blood 2013, 121, 4821–4831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mirzaei, A.; Mohammadi, S.; Ghaffari, S.H.; Nikbakht, M.; Bashash, D.; Alimoghaddam, K.; Ghavamzadeh, A. Osteopontin b and c isoforms: Molecular Candidates Associated with Leukemic Stem Cell Chemoresistance in Acute Myeloid. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cogle, C.R.; Bosse, R.C.; Brewer, T.; Migdady, Y.; Shirzad, R.; Kampen, K.R.; Saki, N. Acute myeloid leukemia in the vascular niche. Cancer Lett. 2016, 380, 552–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacamo, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, W.; Zhang, M.; Spaeth, E.L.; Wang, Y.; Battula, V.L.; Mak, P.Y.; Schallmoser, K.; et al. Reciprocal leukemia-stroma VCAM-1/VLA-4-dependent activation of NF-$\kappa$B mediates chemoresistance. Blood 2014, 123, 2691–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsunaga, T.; Takemoto, N.; Sato, T.; Takimoto, R.; Tanaka, I.; Fujimi, A.; Akiyama, T.; Kuroda, H.; Kawano, Y.; Kobune, M.; et al. Interaction between leukemic-cell VLA-4 and stromal fibronectin is a decisive factor for minimal residual disease of acute myelogenous leukemia. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 1158–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cogle, C.R.; Goldman, D.C.; Madlambayan, G.J.; Leon, R.P.; Masri, A.A.; Clark, H.A.; Asbaghi, S.A.; Tyner, J.W.; Dunlap, J.; Fan, G.; et al. Functional integration of acute myeloid leukemia into the vascular niche. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1978–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Winkler, I.G.; Barbier, V.; Pattabiraman, D.R.; Gonda, T.J.; Magnani, J.L.; Levesque, J.-P. Vascular Niche E-Selectin Protects Acute Myeloid Leukaemia Stem Cells from Chemotherapy. Blood 2014, 124, 620. [Google Scholar]
- Karpova, D.; Bonig, H. Concise Review: CXCR4/CXCL12 Signaling in Immature Hematopoiesis-Lessons From Pharmacological and Genetic Models. Stem Cells 2015, 33, 2391–2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Becker, P.S. Dependence of Acute Myeloid Leukemia on Adhesion within the Bone Marrow Microenvironment. Sci. World J. 2012, 2012, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, J.A.; Spoo, A.; Dwenger, A.; Burger, M.; Behringer, D. CXCR4 chemokine receptors (CD184) and alpha4beta1 integrins mediate spontaneous migration of human CD34+ progenitors and acute myeloid leukaemia cells beneath marrow stromal cells (pseudoemperipolesis). Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 122, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sison, E.A.R.; McIntyre, E.; Magoon, D.; Brown, P. Dynamic Chemotherapy-Induced Upregulation of CXCR4 Expression: A Mechanism of Therapeutic Resistance in Pediatric AML. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Macanas-Pirard, P.; Quezada, T.; Navarrete, L.; Broekhuizen, R.; Leisewitz, A.; Nervi, B.; Ramrez, P.A. The CCL2/CCR2 Axis Affects Transmigration and Proliferation but Not Resistance to Chemotherapy of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0168888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, K.; Pietras, E.M.; Reynaud, D.; Flach, J.; Binnewies, M.; Garg, T.; Wagers, A.J.; Hsiao, E.C.; Passegue, E. Myeloproliferative neoplasia remodels the endosteal bone marrow niche into a self-reinforcing leukemic niche. Cell Stem Cell 2013, 13, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.-C.; Link, D.C. Concise Review: The Malignant Hematopoietic Stem Cell Niche. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, B.; Garcia, M.; Weng, L.; Jung, X.; Murakami, J.L.; Hu, X.; McDonald, T.; Lin, A.; Kumar, A.R.; DiGiusto, D.L.; et al. Acute myeloid leukemia transforms the bone marrow niche into a leukemia-permissive microenvironment through exosome secretion. Leukemia 2018, 32, 575–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalinkovich, A.; Tavor, S.; Avigdor, A.; Kahn, J.; Brill, A.; Petit, I.; Goichberg, P.; Tesio, M.; Netzer, N.; Naparstek, E.; et al. Functional CXCR4-expressing microparticles and SDF-1 correlate with circulating acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11013–11020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvorakova, M.; Karafiat, V.; Pajer, P.; Kluzakova, E.; Jarkovska, K.; Pekova, S.; Krutilkova, L.; Dvorak, M. DNA released by leukemic cells contributes to the disruption of the bone marrow microenvironment. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5201–5209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Souhibani, N.; Al-Ghamdi, M.; Al-Ahmadi, W.; Khabar, K.S.A. Posttranscriptional control of the chemokine receptor CXCR4 expression in cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 1983–1992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sachdev, R.; George, T.I.; Schwartz, E.J.; Sundram, U.N. Discordant immunophenotypic profiles of adhesion molecules and cytokines in acute myeloid leukemia involving bone marrow and skin. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 138, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raspadori, D.; Lauria, F.; Ventura, M.A.; Rondelli, D.; Tura, S. Expression of adhesion molecules on acute leukemic blast cells and sensitivity to normal LAK activity. Ann. Hematol. 1993, 67, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meads, M.B.; Gatenby, R.A.; Dalton, W.S. Environment-mediated drug resistance: A major contributor to minimal residual disease. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, P.; Carrillo, E.; Velez, C.; Hita-Contreras, F.; Martinez-Amat, A.; Rodriguez-Serrano, F.; Boulaiz, H.; Ortiz, R.; Melguizo, C.; Prados, J.; et al. Regulatory systems in bone marrow for hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells mobilization and homing. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 312656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thankamony, S.P.; Sackstein, R. Enforced hematopoietic cell E- and L-selectin ligand (HCELL) expression primes transendothelial migration of human mesenchymal stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2258–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caocci, G.; Greco, M.; La Nasa, G. Bone Marrow Homing and Engraftment Defects of Human Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cells. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2017, 9, e2017032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pillozzi, S.; Brizzi, M.F.; Bernabei, P.A.; Bartolozzi, B.; Caporale, R.; Basile, V.; Boddi, V.; Pegoraro, L.; Becchetti, A.; Arcangeli, A. VEGFR-1 (FLT-1), beta1 integrin, and hERG K+ channel for a macromolecular signaling complex in acute myeloid leukemia: Role in cell migration and clinical outcome. Blood 2007, 110, 1238–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelbaset-Ismail, A.; Borkowska-Rzeszotek, S.; Kubis, E.; Bujko, K.; Brzeniakiewicz-Janus, K.; Bolkun, L.; Kloczko, J.; Moniuszko, M.; Basak, G.W.; Wiktor-Jedrzejczak, W.; et al. Activation of the complement cascade enhances motility of leukemic cells by downregulating expression of HO-1. Leukemia 2017, 31, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hynes, R.O. Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 2002, 110, 673–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannigan, G.; Troussard, A.A.; Dedhar, S. Integrin-linked kinase: A cancer therapeutic target unique among its ILK. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2005, 5, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amico, M.; Hulit, J.; Amanatullah, D.F.; Zafonte, B.T.; Albanese, C.; Bouzahzah, B.; Fu, M.; Augenlicht, L.H.; Donehower, L.A.; Takemaru, K.; et al. The integrin-linked kinase regulates the cyclin D1 gene through glycogen synthase kinase 3beta and cAMP-responsive element-binding protein-dependent pathways. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 32649–32657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sykes, S.M.; Lane, S.W.; Bullinger, L.; Kalaitzidis, D.; Yusuf, R.; Saez, B.; Ferraro, F.; Mercier, F.; Singh, H.; Brumme, K.M.; et al. AKT/FOXO signaling enforces reversible differentiation blockade in myeloid leukemias. Cell 2011, 146, 697–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peifer, M.; Polakis, P. Wnt signaling in oncogenesis and embryogenesis-a look outside the nucleus. Science 2000, 287, 1606–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oellerich, T.; Oellerich, M.F.; Engelke, M.; Munch, S.; Mohr, S.; Nimz, M.; Hsiao, H.H.; Corso, J.; Zhang, J.; Bohnenberger, H.; et al. β2 integrin-derived signals induce cell survival and proliferation of AML blasts by activating a Syk/STAT signaling axis. Blood 2013, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, P.G.; Al-Shahrour, F.; Hartwell, K.A.; Chu, L.P.; Jaras, M.; Puram, R.V.; Puissant, A.; Callahan, K.P.; Ashton, J.; McConkey, M.E.; et al. In Vivo RNAi screening identifies a leukemia-specific dependence on integrin beta 3 signaling. Cancer Cell 2013, 24, 45–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansen, S.; Brenner, A.K.; Bartaula-Brevik, S.; Reikvam, H.; Bruserud, O. The Possible Importance of beta3 Integrins for Leukemogenesis and Chemoresistance in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Zeng, D.; Shen, Z.; Liao, J.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Kong, P. Integrin alphavbeta3 enhances beta-catenin signaling in acute myeloid leukemia harboring Fms-like tyrosine kinase-3 internal tandem duplication mutations: Implications for microenvironment influence on sorafenib sensitivity. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 40387–40397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, S.; Haq, S.U.; Pawlus, M.; Moon, R.T.; Estey, E.H.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Othus, M.; Magnani, J.L. Adhesion Of Acute Myeloid Leukemia Blasts To E-Selectin In The Vascular Niche Enhances Their Survival By Mechanisms Such As Wnt Activation. Blood 2013, 122, 61. [Google Scholar]
- Sadot, E.; Simcha, I.; Shtutman, M.; Ben-Ze’ev, A.; Geiger, B. Inhibition of beta-catenin-mediated transactivation by cadherin derivatives. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15339–15344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kam, Y.; Quaranta, V. Cadherin-bound beta-catenin feeds into the Wnt pathway upon adherens junctions dissociation: Evidence for an intersection between beta-catenin pools. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orlichenko, L.S.; Radisky, D.C. Matrix metalloproteinases stimulate epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor development. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2008, 25, 593–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saia, M.; Termanini, A.; Rizzi, N.; Mazza, M.; Barbieri, E.; Valli, D.; Ciana, P.; Gruszka, A.M.; Alcalay, M. AML1/ETO accelerates cell migration and impairs cell-to-cell adhesion and homing of hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Weinberg, R.A. Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition: At the Crossroads of Development and Tumor Metastasis. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 818–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sato, R.; Semba, T.; Saya, H.; Arima, Y. Concise Review: Stem Cells and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer: Biological Implications and Therapeutic Targets. Stem Cells 2016, 34, 1997–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rao, Q.; Wang, J.Y.; Meng, J.; Tang, K.; Wang, Y.; Wang, M.; Xing, H.; Tian, Z.; Wang, J. Low-expression of E-cadherin in leukaemia cells causes loss of homophilic adhesion and promotes cell growth. Cell Biol. Int. 2011, 35, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, S.; Haigh, J.J. The Role of EMT Modulators in Hematopoiesis and Leukemic Transformation. In Hematology—Science and Practice; Lawrie, C., Ed.; InTech: London, UK, 2012; pp. 101–120. [Google Scholar]
- Stavropoulou, V.; Kaspar, S.; Brault, L.; Sanders, M.A.; Juge, S.; Morettini, S.; Tzankov, A.; Iacovino, M.; Lau, I.J.; Milne, T.A.; et al. MLL-AF9 Expression in Hematopoietic Stem Cells Drives a Highly Invasive AML Expressing EMT-Related Genes Linked to Poor Outcome. Cancer Cell 2016, 30, 43–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, S.; Janzen, V.; Bartunkova, S.; Yokomizo, T.; Drogat, B.; Crisan, M.; Haigh, K.; Seuntjens, E.; Umans, L.; Riedt, T.; et al. The EMT regulator Zeb2/Sip1 is essential for murine embryonic hematopoietic stem/progenitor cell differentiation and mobilization. Blood 2011, 117, 5620–5630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Riedt, T.; Goossens, S.; Carrillo Garcia, C.; Szczepanski, S.; Brandes, M.; Pieters, T.; Dobrosch, L.; Gutgemann, I.; Farla, N.; et al. The EMT transcription factor Zeb2 controls adult murine hematopoietic differentiation by regulating cytokine signaling. Blood 2017, 129, 460–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caudell, D.; Harper, D.P.; Novak, R.L.; Pierce, R.M.; Slape, C.; Wolff, L.; Aplan, P.D. Retroviral insertional mutagenesis identifies Zeb2 activation as a novel leukemogenic collaborating event in CALM-AF10 transgenic mice. Blood 2010, 115, 1194–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Mar, B.G.; Zhang, H.; Puram, R.V.; Vazquez, F.; Weir, B.A.; Hahn, W.C.; Ebert, B.; Pellman, D. The EMT regulator ZEB2 is a novel dependency of human and murine acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2017, 129, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melki, J.R.; Vincent, P.C.; Brown, R.D.; Clark, S.J. Hypermethylation of E-cadherin in leukemia. Blood 2000, 95, 3208–3213. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Konoplev, S.; Rassidakis, G.Z.; Estey, E.; Kantarjian, H.; Liakou, C.I.; Huang, X.; Xiao, L.; Andreeff, M.; Konopleva, M.; Medeiros, L.J. Overexpression of CXCR4 predicts adverse overall and event-free survival in patients with unmutatedFLT3 acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. Cancer 2007, 109, 1152–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rombouts, E.J.C.; Pavic, B.; Lwenberg, B.; Ploemacher, R.E. Relation between CXCR-4 expression, Flt3 mutations, and unfavorable prognosis of adult acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2004, 104, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Spoo, A.C.; Lubbert, M.; Wierda, W.G.; Burger, J.A. CXCR4 is a prognostic marker in acute myelogenous leukemia. Blood 2007, 109, 786–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tavernier-Tardy, E.; Cornillon, J.; Campos, L.; Flandrin, P.; Duval, A.; Nadal, N.; Guyotat, D. Prognostic value of CXCR4 and FAK expression in acute myelogenous leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2009, 33, 764–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walter, R.B.; Alonzo, T.A.; Gerbing, R.B.; Ho, P.A.; Smith, F.O.; Raimondi, S.C.; Hirsch, B.A.; Gamis, A.S.; Franklin, J.L.; Hurwitz, C.A.; et al. High Expression of the Very Late Antigen-4 Integrin Independently Predicts Reduced Risk of Relapse and Improved Outcome in Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia: A Report From the Children’s Oncology Group. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 2831–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becker, P.S.; Kopecky, K.J.; Wilks, A.N.; Chien, S.; Harlan, J.M.; Willman, C.L.; Petersdorf, S.H.; Stirewalt, D.L.; Papayannopoulou, T.; Appelbaum, F.R. Very late antigen-4 function of myeloblasts correlates with improved overall survival for patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2009, 113, 866–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.H.; Oh, S.-H.; Park, C.-J.; Lee, B.-R.; Kim, Y.J.; Cho, Y.-U.; Jang, S.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, N.; Park, S.H.; et al. VLA-4 and CXCR4 expression levels show contrasting prognostic impact (favorable and unfavorable, respectively) in acute myeloid leukemia. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 1631–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brault, L.; Rovo, A.; Decker, S.; Dierks, C.; Tzankov, A.; Schwaller, J. CXCR4-SERINE339 regulates cellular adhesion, retention and mobilization, and is a marker for poor prognosis in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2014, 28, 566–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recher, C.; Ysebaert, L.; Beyne-Rauzy, O.; Mansat-De Mas, V.; Ruidavets, J.B.; Cariven, P.; Demur, C.; Payrastre, B.; Laurent, G.; Racaud-Sultan, C. Expression of focal adhesion kinase in acute myeloid leukemia is associated with enhanced blast migration, increased cellularity, and poor prognosis. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 3191–3197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Li, D.; Li, T.; Zhao, B.O.; Chen, X. Prognostic value of the expression of phosphatase and tensin homolog and CD44 in elderly patients with refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Larsen, A.M.; Leinoe, E.B.; Johansson, P.I.; Birgens, H.; Ostrowski, S.R. High syndecan-1 levels in acute myeloid leukemia are associated with bleeding, thrombocytopathy, endothelial cell damage, and leukocytosis. Leuk. Res. 2013, 37, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.; Du, Y.; Beckford, J.; Alachkar, H. Upregulation of the EMT marker vimentin is associated with poor clinical outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.-J.; Zhou, J.-D.; Ma, J.-C.; Deng, Z.-Q.; Qian, Z.; Yao, D.-M.; Yang, J.; Li, X.-X.; Lin, J.; Qian, J. CDH1 (E-cadherin) expression independently affects clinical outcome in acute myeloid leukemia with normal cytogenetics. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2017, 55, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, P.; Vachhani, P.; Cortes, J.E. Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2017, 18, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombret, H.; Gardin, C. An update of current treatments for adult acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2016, 127, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazlehurst, L.A.; Dalton, W.S. Mechanisms associated with cell adhesion mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR) in hematopoietic malignancies. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2001, 20, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashidi, A.; DiPersio, J.F. Targeting the leukemia-stroma interaction in acute myeloid leukemia: Rationale and latest evidence. Ther. Adv. Hematol. 2016, 7, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, A.; Zhong, H. Roles of the bone marrow niche in hematopoiesis, leukemogenesis, and chemotherapy resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Hematology (Amsterdam) 2018, 23, 729–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Layani-Bazar, A.; Skornick, I.; Berrebi, A.; Pauker, M.H.; Noy, E.; Silberman, A.; Albeck, M.; Longo, D.L.; Kalechman, Y.; Sredni, B. Redox modulation of adjacent thiols in VLA-4 by AS101 converts myeloid leukemia cells from a drug-resistant to drug-sensitive state. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 3092–3103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- US Clinical Trial NCT01010373—Application of AS101 in Combination With Chemotherapy for Elderly Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) and Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS)—Ironsift. Available online: https://ironsift.com/record/display/US-clinical-trial-NCT01010373 (accessed on 5 November 2018).
- Matsunaga, T.; Fukai, F.; Miura, S.; Nakane, Y.; Owaki, T.; Kodama, H.; Tanaka, M.; Nagaya, T.; Takimoto, R.; Takayama, T.; et al. Combination therapy of an anticancer drug with the FNIII14 peptide of fibronectin effectively overcomes cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance of acute myelogenous leukemia. Leukemia 2008, 22, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloomgren, G.; Richman, S.; Hotermans, C.; Subramanyam, M.; Goelz, S.; Natarajan, A.; Lee, S.; Plavina, T.; Scanlon, J.V.; Sandrock, A.; et al. Risk of Natalizumab-Associated Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 1870–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devata, S.; Sood, S.L.; Hemmer, M.V.; Flanner, H.; Kramer, W.; Nietubicz, C.; Hawley, A.; Angelini, D.E.; Myers, D.D.; Blackburn, S.; et al. First in Human Phase 1 Single Dose Escalation Studies of the E-Selectin Antagonist GMI-1271 Show a Favorable Safety, Pharmacokinetic, and Biomarker Profile. Blood 2015, 126, 1004. [Google Scholar]
- Peled, A.; Tavor, S. Role of CXCR4 in the pathogenesis of acute myeloid leukemia. Theranostics 2013, 3, 34–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreeff, M.; Konoplev, S.; Wang, R.-Y.; Zeng, Z.; McQueen, T.; Shi, Y.-X.; Medeiros, L.J.; Estey, E.; McCarty, J.M.; Elkins, S.; et al. Massive Mobilization of AML Cells into Circulation by Disruption of Leukemia/Stroma Cell Interactions Using CXCR4 Antagonist AMD3100: First Evidence in Patients and Potential for Abolishing Bone Marrow Microenvironment-Mediated Resistance. Blood 2006, 108, 568. [Google Scholar]
- Liesveld, J.L.; Bechelli, J.; Rosell, K.; Lu, C.; Bridger, G.; Phillips, G.; Abboud, C.N. Effects of AMD3100 on transmigration and survival of acute myelogenous leukemia cells. Leuk. Res. 2007, 31, 1553–1563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shen, Z.-H.; Zeng, D.-F.; Kong, P.-Y.; Ma, Y.-y.; Zhang, X. AMD3100 and G-CSF disrupt the cross-talk between leukemia cells and the endosteal niche and enhance their sensitivity to chemotherapeutic drugs in biomimetic polystyrene scaffolds. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2016, 59, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugiyama, T.; Kohara, H.; Noda, M.; Nagasawa, T. Maintenance of the Hematopoietic Stem Cell Pool by CXCL12-CXCR4 Chemokine Signaling in Bone Marrow Stromal Cell Niches. Immunity 2006, 25, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tavor, S.; Eisenbach, M.; Jacob-Hirsch, J.; Golan, T.; Petit, I.; BenZion, K.; Kay, S.; Baron, S.; Amariglio, N.; Deutsch, V.; et al. The CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 impairs survival of human AML cells and induces their differentiation. Leukemia 2008, 22, 2151–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, Z.; Shi, Y.X.; Samudio, I.J.; Wang, R.Y.; Ling, X.; Frolova, O.; Levis, M.; Rubin, J.B.; Negrin, R.R.; Estey, E.H.; et al. Targeting the leukemia microenvironment by CXCR4 inhibition overcomes resistance to kinase inhibitors and chemotherapy in AML. Blood 2009, 113, 6215–6224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreeff, M.; Zeng, Z.; Kelly, M.A.; Wang, R.-y.; McQueen, T.; Duvvuri, S.; Nowshad, G.; Borthakur, G.; Burger, J.A.; Kadia, T.M.; et al. Mobilization and Elimination of FLT3-ITD+ Acute Myelogenous Leukemia (AML) Stem/Progenitor Cells by Plerixafor/G-CSF/Sorafenib: Results From a Phase I Trial in Relapsed/Refractory AML Patients. Blood 2012, 120, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scandura, J.M.; Ritchie, E.; Dault, Y.; Lam, L.; Xie, W.; Hsu, H.-T.; Marshall, D.; Christos, P.J.; Ippoliti, C.; Feldman, E.J.; et al. Combining Decitabine With Plerixafor Yields a High Response Rate In Newly Diagnosed Older Patients With AML. Blood 2013, 122, 621. [Google Scholar]
- Uy, G.L.; Rettig, M.P.; Motabi, I.H.; McFarland, K.; Trinkaus, K.M.; Hladnik, L.M.; Kulkarni, S.; Abboud, C.N.; Cashen, A.F.; Stockerl-Goldstein, K.E.; et al. A phase 1/2 study of chemosensitization with the CXCR4 antagonist plerixafor in relapsed or refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2012, 119, 3917–3924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, P.S.; Foran, J.M.; Altman, J.K.; Yacoub, A.; Castro, J.E.; Sabbatini, P.; Dilea, C.; Wade, M.; Xing, G.; Gutierrez, A.; et al. Targeting the CXCR4 Pathway: Safety, Tolerability and Clinical Activity of Ulocuplumab (BMS-936564), an Anti-CXCR4 Antibody, in Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2014, 124, 386. [Google Scholar]
- Kuhne, M.R.; Mulvey, T.; Belanger, B.; Chen, S.; Pan, C.; Chong, C.; Cao, F.; Niekro, W.; Kempe, T.; Henning, K.A.; et al. BMS-936564/MDX-1338: A Fully Human Anti-CXCR4 Antibody Induces Apoptosis In Vitro and Shows Antitumor Activity In Vivo in Hematologic Malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borthakur, G.; Nagler, A.; Ofran, Y.; Rowe, J.M.; Altman, J.K.; Frankfurt, O.; Tallman, M.S.; Avivi, I.; Peled, A.; Pereg, Y.; et al. BL-8040, a Peptidic CXCR4 Antagonist, Induces Leukemia Cell Death and Specific Leukemia Cell Mobilization in Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patients in an Ongoing Phase IIa Clinical Trial. Blood 2014, 124, 950. [Google Scholar]
- Borthakur, G.; Tallman, M.S.; Ofran, Y.; Foran, J.M.; Uy, G.L.; DiPersio, J.F.; Nagler, A.; Rowe, J.M.; Showel, M.M.; Altman, J.; et al. The Selective Anti Leukemic Effect of BL-8040, a Peptidic CXCR4 Antagonist, Is Mediated By Induction of Leukemic Blast Mobilization, Differentiation and Apoptosis: Results of Correlative Studies from a Ph2a Trial in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2016, 128, 2745. [Google Scholar]
- Boddu, P.; Borthakur, G.; Koneru, M.; Huang, X.; Naqvi, K.; Wierda, W.; Bose, P.; Jabbour, E.; Estrov, Z.; Burger, J.; et al. Initial Report of a Phase I Study of LY2510924, Idarubicin, and Cytarabine in Relapsed/Refractory Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacsovics, T.J.; Mims, A.; Salama, M.E.; Pantin, J.M.; Deininger, M.W.; Kennedy, T.P.; Bavisotto, L.M.; Boucher, K.M.; Marcus, S.G.; Shami, P.J. Preliminary Evidence That ODSH (2-O, 3-O Desulfated Heparin) Is Safe and Enhances Count Recovery in Patients Treated with Intensive Therapy for Acute Myeloid Leukemia—Results of a Pilot Study. Blood 2014, 124, 5297. [Google Scholar]
- Kovacsovics, T.J.; Mims, A.S.; Salama, M.E.; Pantin, J.M.; Kosak, K.M.; Rao, N.; Ahorukomeye, P.; Glenn, M.; Deininger, M.W.; Boucher, K.M.; et al. CX-01, a Low Anticoagulant Heparin, May Enhance Count Recovery and Treatment Efficacy in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Blood 2016, 128, 5220. [Google Scholar]
- Hoellenriegel, J.; Zboralski, D.; Maasch, C.; Rosin, N.Y.; Wierda, W.G.; Keating, M.J.; Kruschinski, A.; Burger, J.A. The Spiegelmer NOX-A12, a novel CXCL12 inhibitor, interferes with chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell motility and causes chemosensitization. Blood 2014, 123, 1032–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vater, A.; Sahlmann, J.; Krger, N.; Zllner, S.; Lioznov, M.; Maasch, C.; Buchner, K.; Vossmeyer, D.; Schwoebel, F.; Purschke, W.G.; et al. Hematopoietic Stem and Progenitor Cell Mobilization in Mice and Humans by a First-in-Class Mirror-Image Oligonucleotide Inhibitor of CXCL12. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 94, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, B.-S.; Kim, H.-J.; Konopleva, M. Targeting the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis in acute myeloid leukemia: From bench to bedside. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koike, T.; Kimura, N.; Miyazaki, K.; Yabuta, T.; Kumamoto, K.; Takenoshita, S.; Chen, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Hosokawa, M.; Taniguchi, A.; et al. Hypoxia induces adhesion molecules on cancer cells: A missing link between Warburg effect and induction of selectin-ligand carbohydrates. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 8132–8137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fiegl, M.; Samudio, I.; Clise-Dwyer, K.; Burks, J.K.; Mnjoyan, Z.; Andreeff, M. CXCR4 expression and biologic activity in acute myeloid leukemia are dependent on oxygen partial pressure. Blood 2008, 113, 1504–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jensen, P.O.; Mortensen, B.T.; Hodgkiss, R.J.; Iversen, P.O.; Christensen, I.J.; Helledie, N.; Larsen, J.K. Increased cellular hypoxia and reduced proliferation of both normal and leukaemic cells during progression of acute myeloid leukaemia in rats. Cell Prolif. 2000, 33, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Portwood, S.; Lal, D.; Hsu, Y.-C.; Vargas, R.; Johnson, M.K.; Wetzler, M.; Hart, C.P.; Wang, E.S. Activity of the hypoxia-activated prodrug, TH-302, in preclinical human acute myeloid leukemia models. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 6506–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badar, T.; Handisides, D.R.; Benito, J.M.; Richie, M.A.; Borthakur, G.; Jabbour, E.; Harutyunyan, K.; Konoplev, S.; Faderl, S.; Kroll, S.; et al. Phase I study of evofosfamide, an investigational hypoxia-activated prodrug, in patients with advanced leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Leech, A.O.; Cruz, R.G.; Hill, A.D.; Hopkins, A.M. Paradigms lost-an emerging role for over-expression of tight junction adhesion proteins in cancer pathogenesis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2015, 3, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, A.R. The origins of the molecular era of adhesion research. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 805–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mikkilineni, L.; Kochenderfer, J.N. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapies for multiple myeloma. Blood 2017, 130, 2594–2602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.L.; Hsu, E.C.; Chou, C.C.; Chuang, H.C.; Bai, L.Y.; Kulp, S.K.; Chen, C.S. Identification and characterization of a novel integrin-linked kinase inhibitor. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 6364–6374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

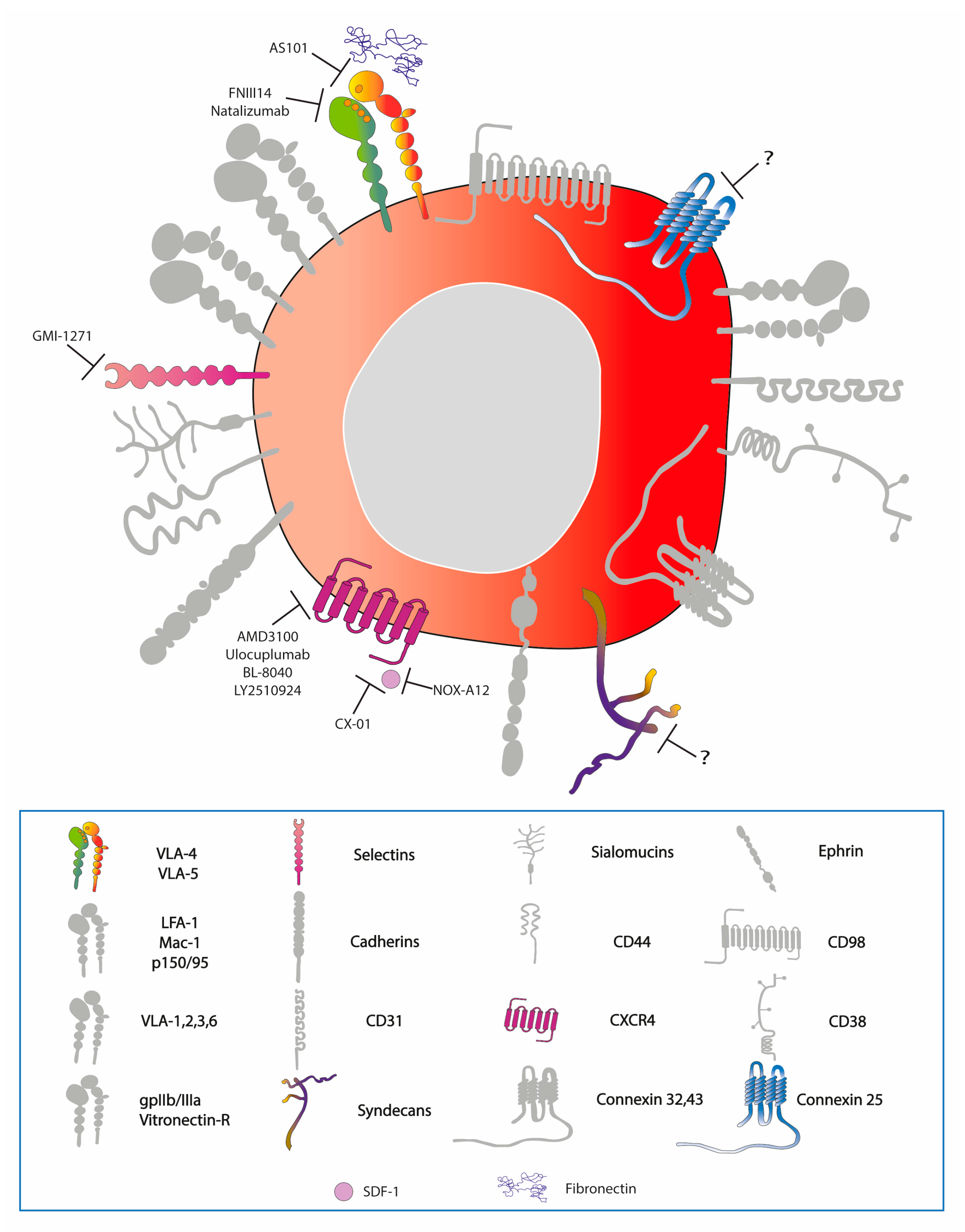
| Classification of Cell Adhesion Molecules and Other Adhesion-Modulating Proteins Relevant to AML | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Family | Adhesion Molecule | Distribution | Extracellular Ligands |
| Integrin | VLA-1, VLA-2 | LSC | Collagen, Laminin |
| VLA-3 | LSC | Collagen, Laminin, Fibronectin | |
| VLA-4 | HSC/Progenitors/LSC | Fibronectin, VCAM-1, ICAM-2 | |
| VLA-5 | HSC/Progenitors/LSC | Fibronectin, Invasin | |
| VLA-6 | LSC | Laminin, Merosin, Kalinin, Invasin | |
| LFA-1 | HSC/LSC | ICAM-1, ICAM-2, ICAM-3 | |
| MAC-1 | C3b, ICAM-1, Factor X, Fibrinogen | ||
| p150/95 | C3b, Fibrinogen | ||
| gpIIb/IIIa Vitronectin-R | HSC/LSC | Fibronectin, Fibrinogen, von Willenbrand factor, Vitronectin | |
| Selectin | L-selectin | HSC/LSC | ICAM-1, Sialomucins |
| E-selectin | Stromal cells | Sialomucins, CLA-1 | |
| P-selectin | HSC/LSC/Stromal cells | Mucin-like molecules | |
| IgSF | VCAM-1 | Stromal cells | VLA-4 |
| ICAM-1 | Stromal cells | LFA-1, MAC-1 | |
| CD31 | HSC/LSC/Stromal cells | Vitronectin-R | |
| Cadherin | E,N-cadherin | CD34+ progenitors/ Stromal cells | Other cadherins |
| VE-cadherin | Stromal cells | ||
| Sialomucin | CD34, CD45R, CD43, CD162, CD164 | HSC/LSC | Selectins |
| Other adhesion molecules | CD44, HCELL | HSC/LSC/Stromal cells | Hyaluronan, Osteopontin |
| Syndecans | Integrins, FGFs, VEGFs, PDGFs | ||
| Connexins | Connexins | ||
| Adhesion-modulating proteins | Ephrin receptors | HSC/Progenitors | Ephrins |
| CD98 | HSC/LSC | Integrins | |
| CD38 | HSC/LSC | CD31 | |
| Chemokine receptors | CXCR4 | HSC/LSC | SDF-1 |
| Signal transducers | FAK, PYK2, ILK | HSC/LSC | Integrins |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gruszka, A.M.; Valli, D.; Restelli, C.; Alcalay, M. Adhesion Deregulation in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Cells 2019, 8, 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010066
Gruszka AM, Valli D, Restelli C, Alcalay M. Adhesion Deregulation in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Cells. 2019; 8(1):66. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010066
Chicago/Turabian StyleGruszka, Alicja M., Debora Valli, Cecilia Restelli, and Myriam Alcalay. 2019. "Adhesion Deregulation in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia" Cells 8, no. 1: 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010066
APA StyleGruszka, A. M., Valli, D., Restelli, C., & Alcalay, M. (2019). Adhesion Deregulation in Acute Myeloid Leukaemia. Cells, 8(1), 66. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8010066