The Role of miRNAs in Immune Cell Development, Immune Cell Activation, and Tumor Immunity: With a Focus on Macrophages and Natural Killer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
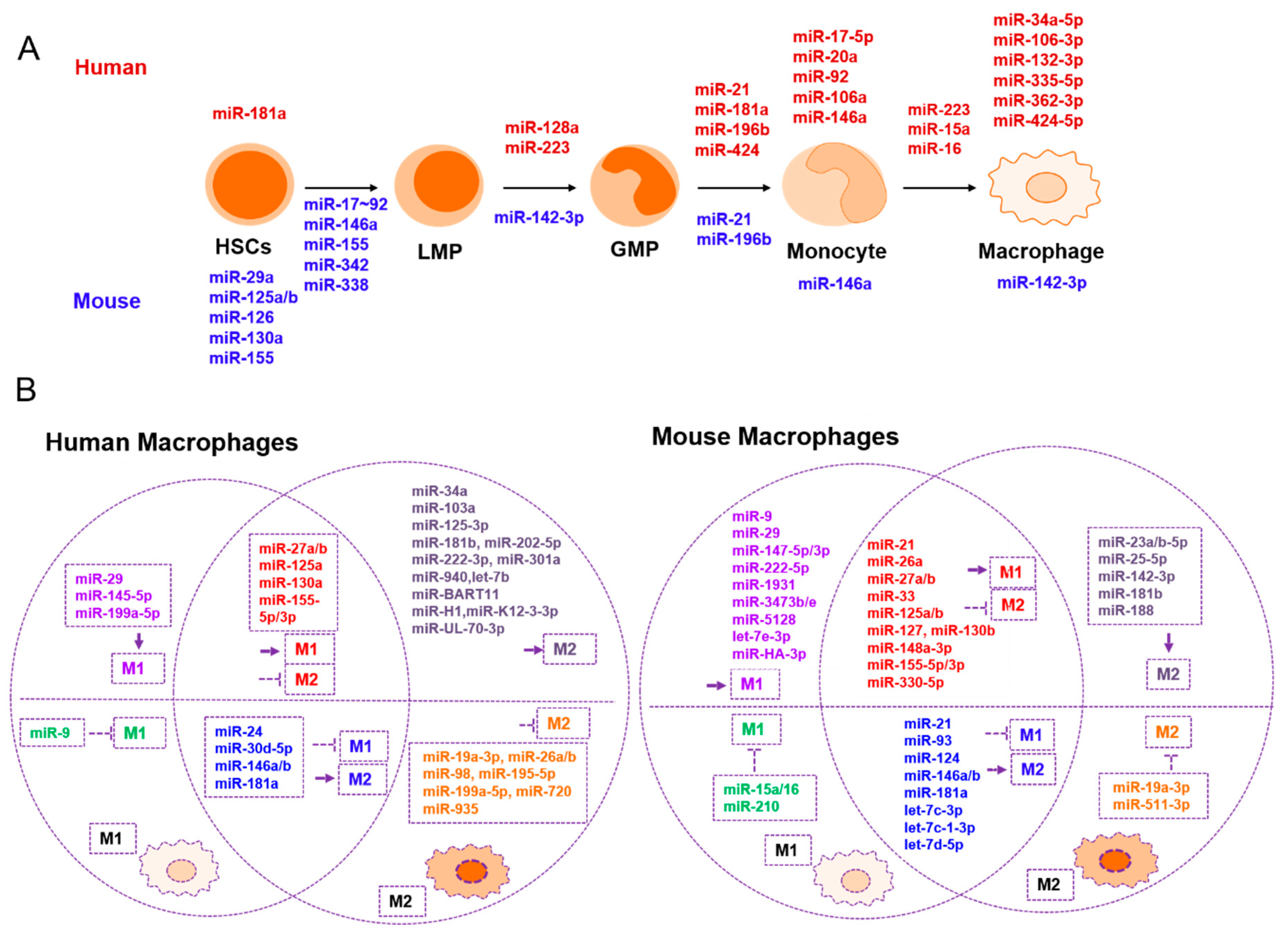
2. The Role of miRNAs in Macrophages
| Development and Maturation | Promotes M1 | Suppresses M1 | Promotes M2 | Suppresses M2 | Related to Tumor Immunity |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mmu-miR-29a [17](+) | hsa-miR-155 [39,40] mmu-miR-155-3p/5p [31] | mmu-miR-124 [41] | hsa-miR-27a [40] mmu-miR-27a-5p [31] | hsa-miR-130a [42] mmu-miR-130b [43] | hsa-miR-3570 [37](–) |
| mmu-miR-126 [19](+) | hsa-miR-125a/b-5p [40] mmu-miR-125a-3p [31,44] mmu- miR-125b [45] | hsa-miR-181a [46] mmu-miR-181a [46] | mmu-miR-23a/b-5p [31] | hsa-miR-27b [47] mmu-miR-27a [48] | hsa-miR-3614-5p [49](–) |
| mmu-miR-130a [17](+) | hsa-miR-29b [40] mmu-miR-29b-1-5p [31] | hsa-miR-9 [50] | mmu-miR-188 [31] | mmu-miR-21 [51] | hsa-miR-29 [52](+) |
| mmu-miR-155 [17,20](+) | hsa-miR-145-5p [28] mmu-miR-145-5p [31] | mmu-let-7c [53] mmu-let-7d-5p [54] | mmu-let-7c-1-3p [31] mmu-let-7c [53] mmu-let-7d-5p [54] | mmu-miR-23a [55] | mmu-let-7d-5p [54](–) |
| mmu-miR-125a/b [17,18](+) | mmu-miR-147-5p/3p [31] | mmu-miR-210 [56] | hsa-miR-26a [40] | hsa-miR-155 [57,58] | mmu-miR-155 [33](+) |
| mmu-miR-146a [20](+) hsa/mmu-miR-146a [59](+) | mmu-miR-9-5p/3p [31] | mmu-miR-93 [60] | hsa-miR-146a/b [40] mmu-miR-146b [61] | hsa-miR-720 [62] | mmu-miR-223 [63](+) |
| mmu-miR-342 [20](+) | mmu-miR-21 [51] | hsa-miR-146b [64] mmu-miR-146b [61] | hsa-miR-222-3p [40] | mmu-miR-125a-3p [31,44] mmu- miR-125b [45] | hsa-miR-23a-3p [65](–) |
| mmu-miR-338 [20](+) | mmu-miR-33 [66] | mmu-miR-15a/16 [67] | mmu-miR-127 [68] | mmu-miR-26a [69] hsa-miR-26a/b [70,71] | hsa-miR-146a [59](+) |
| mmu-miR-17-92 cluster [21] (–) hsa-miR-17-5p-20a-106a-92 [27](–) | mmu-miR-330-5p [72] | hsa-miR-30d-5p [73] | hsa-miR-181a [46] mmu-miR-181a [46] | hsa-miR-19a-3p [74] mmu-miR-19a-3p [74] | hsa-miR-17/20a/106a [75](+) |
| hsa-miR-223 [22](+) | mmu-let-7e-3p [31] | hsa-miR-24 [76] | hsa-miR-145-3p [77] | mmu-miR-33 [66] | mmu-miR-142-3p [32](+) |
| hsa-miR-424 [23](+) | mmu-miR-1931 [31] | mmu-miR-223 [78] | mmu-miR-223 [78] | mmu-miR-330-5p [72] | hsa-miR-34a [79](–) |
| hsa/mmu-miR-21 [24](+) | mmu-miR-3473e [31] | mmu-miR-21 [80,81] | hsa-miR-181b [82] mmu-miR-181b [82] | mmu-miR-127 [68] | hsa-miR-195-5p [83](+) |
| hsa/mmu-miR-196b [24](+) | mmu-miR-5128 [31] | hsa-miR-103a [84] | hsa-miR-935 [85] | hsa-miR-301a [86](–) | |
| hsa-miR-128a [25](–) | mmu-miR-222-5p [31] | hsa-miR-30d-5p [73] | mmu-miR-148a-3p [87] | hsa-miR-375 [88](+) | |
| mmu-miR-3473b [31] | mmu-miR-124 [89] | mmu-miR-511-3p [90] | miR-HA-3p [38](+) | ||
| mmu-miR-142-3p [32](–) | hsa-miR-199a-5p [91] | mmu-miR-142-3p [32] | mmu-miR-378-3p [92] | BART miRNA [34](–) | |
| mmu-miR-127 [68] | hsa-miR-940 [93] | hsa-miR-98 [94] | ebv-miR-BART11 [36](–) | ||
| hsa-miR-106-3p [28](+) | mmu-miR-148a-3p [87] | hsa-miR-24 [76] | hsa-miR-195-5p [83] | ||
| hsa-miR-132-3p [28](+) | hsa-miR-130a [42] mmu-miR-130b [43] | hsa-miR-202-5p [95] | hsa-miR-199a-5p [91] | ||
| hsa-miR-335-5p [28](+) | hsa-miR-27b [47] mmu-miR-27a [48] | hsa-let-7b [96] | |||
| hsa-miR-34a-5p [28](+) | mmu-miR-26a [69] | hsa-miR-34a [79] | |||
| hsa-miR-362-3p [28](+) | miR-HA-3p [38] | hsa-miR-301a [86] | |||
| hsa-miR-424-5p [28](+) | mmu-miR-21 [80,81] | ||||
| hsa-miR-223/15a/16 [97](–) | BART miRNAs [34] | ||||
| miR-H1 [34] | |||||
| miR-K12-3-3p [34] | |||||
| miR-UL-70-3p [34] | |||||
| ebv-miR-BART11 [36] |
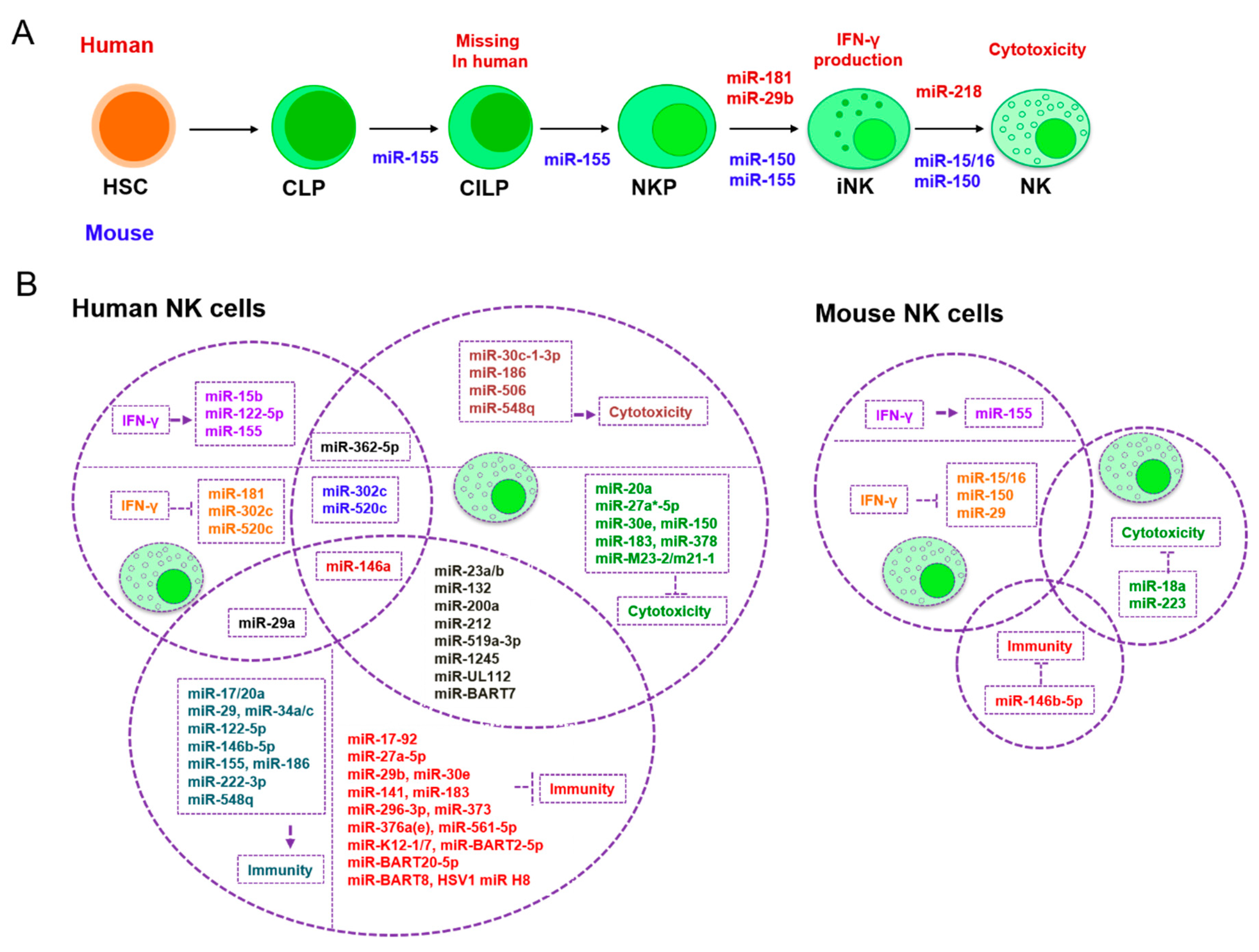
3. The Role of miRNAs in NK Cells
| Development and Maturation | Classical Activation | NK Cell-Related Tumor Immunity Escape | |
|---|---|---|---|
| IFN-γ Production | Cytotoxicity | ||
| mmu-miR-155 [127](+) | hsa-miR-155 [115,116,117](+) | hsa-miR-1245 [123](–) | hsa-miR-155 [117](–) |
| mmu-miR-150 [111](+) | hsa-miR-146a [125](-) | hsa-miR-183 [124](–) | hsa-miR-1245 [123](+) |
| hsa-miR-181 [110](+) | hsa-miR-122/15b [128](+) | hsa-miR-519a-3p [126](–) | hsa-miR-183 [124](+) |
| mmu-miR-15/16 [112](+) | mmu-miR-155 [127](+) | mmu-miR-223 [119](–) | hsa-miR-519a-3p [126](+) |
| hsa-miR-29b [129](–) | mmu-miR-15/16 [113](-) | hsa-miR-150 [120](–) | hsa/mmu-miR-146b-5p [130](–) |
| hsa-miR-218 [131](–) | mmu-miR-150 [111](–) | hsa-miR-27a*-5p [121](–) | hsa-miR-296-3p [132](+) |
| hsa-miR-181 [110](–) | hsa-miR-378 [122](–) | hsa-miR-146a [133](+) | |
| mmu-miR-29 [114](–) hsa-miR-29a [134](–) | hsa-miR-30e [122](–) | hsa-miR-376a(e) [135](+) | |
| hsa-miR-362-5p [136](+) | hsa-miR-20a [137](–) | hsa-miR-186 [138](–) | |
| hsa-miR-302c/520c [139](–) | hsa-miR-362-5p [136](+) | hsa-miR-122-5p [138](–) | |
| hsa-miR-122-5p [140](+) | hsa-miR-30c-1-3p [141](+) | hsa-miR-222-3p [138](–) | |
| hsa-miR-132 [142](–) hsa-miR-212 [142](–) hsa-miR-200a [142](–) | hsa-miR-146a [133](–) | hsa-miR-29b [129](+) hsa-miR-29 [143](–) mmu-miR-29b [144](+) | |
| hsa-miR-302c/520c [139](–) | hsa-miR-519a-3p [126](+) | ||
| hsa-miR-186 [138](+) | hsa-miR-141 [145](+) | ||
| hsa-miR-519a-3p [126](–) | hsa-miR-548q [146](–) | ||
| hsa-miR-23a [147](–) | hsa-miR-23a [147](+) | ||
| hsa-miR-10b [148](–) | hsa-miR-17-92 [149](+) hsa-miR17/20a [150](–) | ||
| hsa-miR-506 [151](+) | hsa-miR-373 [152](+) | ||
| hsa-miR-548q [146](+) | hsa-miR-23b [148](+) | ||
| hsa-miR-152 [153](+) | hsa-miR-27a-5p [154](+) | ||
| mmu-miR-18a [155](–) | hsa-miR-561-5p [156](+) | ||
| hsa-miR-132/212/200a [142](–) | hsa-miR-132/212/200a [142](+) | ||
| ebv-miR-BART7 [157](–) | hsa-miR-34a/c [158](–) | ||
| miR-M23-2 [159](–) miR-m21-1 [159](–) | hsa-miR-30e [160](+) | ||
| miR-UL112 [161](–) | miR-J1-3p [162](–) | ||
| miR-J1-3p [162](+) | hcmv-miR-UL112 [163](+) | ||
| hcmv-miR-UL112 [163](–) | miR-K12-7 [164](+) miR-BART2-5p [164](+) | ||
| EBV-miR-BART20-5p [165](+) EBV-miR-BART8 [165](+) | |||
| HSV1-miR-H8 [166](+) | |||
| ebv-miR-BART7 [157](+) | |||
| kshv-miR-K12-1 [167](+) | |||
4. Conclusions and Further Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joyce, J.A.; Pollard, J.W. Microenvironmental regulation of metastasis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivashkiv, L.B.; Donlin, L.T. Regulation of type I interferon responses. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 36–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivier, E.; Tomasello, E.; Baratin, M.; Walzer, T.; Ugolini, S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, W.; Cheng, W.; Wu, W. MicroRNAs Reprogram Tumor Immune Response. MicroRNA Cancer 2018, 1699, 67–74. [Google Scholar]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNA Target Recognition and Regulatory Functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, H.; Remark, R.; Gnjatic, S.; Merad, M. Host tissue determinants of tumour immunity. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2019, 19, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovchinnikov, D.A. Macrophages in the embryo and beyond: Much more than just giant phagocytes. Genesis 2008, 46, 447–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baltimore, D.; Boldin, M.P.; O’Connell, R.M.; Rao, D.S.; Taganov, K.D. MicroRNAs: new regulators of immune cell development and function. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 839–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terry, R.L.; Miller, S.D. Molecular control of monocyte development. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 291, 16–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perdiguero, E.G.; Klapproth, K.; Schulz, C.; Busch, K.; Azzoni, E.; Crozet, L.; Garner, H.; Trouillet, C.; de Bruijn, M.F.; Geissmann, F.; et al. Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolk-sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. Nature 2015, 518, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdiguero, E.G. Tissue-resident macrophages originate from yolk sac-derived erythro-myeloid progenitors. Immunology 2014, 143, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jiang, T.; Li, M.-Q.; Zheng, X.-L.; Zhao, G.-J. Transcriptional Regulation of Macrophages Polarization by MicroRNAs. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, S.K.; Mantovani, A. Macrophage plasticity and interaction with lymphocyte subsets: cancer as a paradigm. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 889–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mantovani, A.; Sica, A.; Sozzani, S.; Allavena, P.; Vecchi, A.; Locati, M. The chemokine system in diverse forms of macrophage activation and polarization. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanmee, T.; Ontong, P.; Konno, K.; Itano, N. Tumor-Associated Macrophages as Major Players in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2014, 6, 1670–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Connell, R.M.; Chaudhuri, A.A.; Rao, D.S.; Gibson, W.S.J.; Balazs, A.B.; Baltimore, D. MicroRNAs enriched in hematopoietic stem cells differentially regulate long-term hematopoietic output. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14235–14240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, S.; Lu, J.; Schlanger, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.Y.; Fox, M.C.; Purton, L.E.; Fleming, H.H.; Cobb, B.; Merkenschlager, M.; et al. MicroRNA miR-125a controls hematopoietic stem cell number. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 14229–14234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechman, E.R.; Gentner, B.; Van Galen, P.; Giustacchini, A.; Saini, M.; Boccalatte, F.E.; Hiramatsu, H.; Restuccia, U.; Bachi, A.; Voisin, V.; et al. Attenuation of miR-126 Activity Expands HSC In Vivo without Exhaustion. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 11, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghani, S.; Riemke, P.; Schönheit, J.; Lenze, D.; Stumm, J.; Hoogenkamp, M.; Lagendijk, A.; Heinz, S.; Bonifer, C.; Bakkers, J.; et al. Macrophage development from HSCs requires PU.1-coordinated microRNA expression. Blood 2011, 118, 2275–2284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pospisil, V.; Vargova, K.; Kokavec, J.; Rybarova, J.; Savvulidi, F.; Jonasova, A.; Nečas, E.; Zavadil, J.; Laslo, P.; Stopka, T. Epigenetic silencing of the oncogenic miR-17-92 cluster during PU.1-directed macrophage differentiation. EMBO J. 2011, 30, 4450–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazi, F.; Rosa, A.; Fatica, A.; Gelmetti, V.; De Marchis, M.L.; Nervi, C.; Bozzoni, I. A minicircuitry comprised of MicroRNA-223 and transcription factors NFI-A and C/EBPα regulates human granulopoiesis. Cell 2005, 123, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, A.; Ballarino, M.; Sorrentino, A.; Sthandier, O.; De Angelis, F.G.; Marchioni, M.; Masella, B.; Guarini, A.; Fatica, A.; Peschle, C.; et al. The interplay between the master transcription factor PU.1 and miR-424 regulates human monocyte/macrophage differentiation. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19849–19854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velu, C.S.; Baktula, A.M.; Grimes, H.L. Gfi1 regulates miR-21 and miR-196b to control myelopoiesis. Blood 2009, 113, 4720–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, L.; Trino, S.; Laurenzana, I.; Tagliaferri, D.; Falco, G.; Grieco, V.; Bianchino, G.; Nozza, F.; Campia, V.; D’Alessio, F.; et al. Knockdown of miR-128a induces Lin28a expression and reverts myeloid differentiation blockage in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Lin, H.S.; Zhang, X.H.; Yin, X.L.; Ning, H.M.; Liu, B.; Zhai, P.F.; Gong, J.N.; Shen, C.; Song, L.; et al. MiR-181 family: regulators of myeloid differentiation and acute myeloid leukemia as well as potential therapeutic targets. Oncogene 2015, 34, 3226–3239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, L.; Pelosi, E.; Greco, P.; Racanicchi, S.; Testa, U.; Liuzzi, F.; Croce, C.M.; Brunetti, E.; Grignani, F.; Peschle, C. MicroRNAs 17-5p-20a-106a control monocytopoiesis through AML1 targeting and M-CSF receptor upregulation. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 775–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, V.C.; Bradley, E.J.; Willemsen, A.M.; Van Kampen, A.H.C.; Baas, F.; Kootstra, N.A. Next-generation sequencing of microRNAs uncovers expression signatures in polarized macrophages. Physiol. Genom. 2014, 46, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murray, P.J. Macrophage Polarization. Annu. Review Physiol. 2017, 79, 541–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtale, G. MiRNAs at the Crossroads between Innate Immunity and Cancer: Focus on Macrophages. Cells 2018, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, L.; McCurdy, S.; Huang, S.; Zhu, X.; Peplowska, K.; Tiirikainen, M.; Boisvert, W.A.; Garmire, L.X. Time Series miRNA-mRNA integrated analysis reveals critical miRNAs and targets in macrophage polarization. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonda, N.; Simonato, F.; Peranzoni, E.; Cali, B.; Bortoluzzi, S.; Bisognin, A.; Wang, E.; Marincola, F.M.; Naldini, L.; Gentner, B.; et al. miR-142-3p prevents macrophage differentiation during cancer-induced myelopoiesis. Immunity 2013, 38, 1236–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonari, E.; Pucci, F.; Saini, M.; Mazzieri, R.; Politi, L.S.; Gentner, B.; Naldini, L. A role for miR-155 in enabling tumor-infiltrating innate immune cells to mount effective antitumor responses in mice. Blood 2013, 122, 243–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higuchi, H.; Yamakawa, N.; Imadome, K.-I.; Yahata, T.; Kotaki, R.; Ogata, J.; Kakizaki, M.; Fujita, K.; Lu, J.; Yokoyama, K.; et al. Role of exosomes as a proinflammatory mediator in the development of EBV-associated lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2552–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Naqvi, A.R.; Shango, J.; Seal, A.; Shukla, D.; Nares, S. Viral miRNAs alter host cell miRNA profiles and modulate innate immune responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Zeng, Z.; Li, Q.; Gong, Z.; Liao, Q.; Li, X.; Chen, P.; Xiang, B.; Zhang, W.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus encoded miR-BART11 promotes inflammation-induced carcinogenesis by targeting FOXP1. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 36783–36799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Chu, Q.; Cui, J.; Bi, D. Inducible microRNA-3570 feedback inhibits the RIG-I-dependent innate immune response to rhabdovirus in teleost fish by targeting MAVS/IPS-1. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Fu, Z.; Liang, H.; Wang, Y.; Qi, X.; Ding, M.; Sun, X.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Gu, H.; et al. H5N1 influenza virus-specific miRNA-like small RNA increases cytokine production and mouse mortality via targeting poly(rC)-binding protein 2. Cell Res. 2018, 28, 157–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, M.; Xu, Z.; Ding, T.; Kuang, D.-M.; Zheng, L. MicroRNA-155 Regulates Inflammatory Cytokine Production in Tumor-associated Macrophages via Targeting C/EBPβ. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2009, 6, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff, J.W.; Dickson, A.M.; Clay, G.; McCaffrey, A.P.; Wilson, M.E. Identifying Functional MicroRNAs in Macrophages with Polarized Phenotypes. J. Boil. Chem. 2012, 287, 21816–21825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, A.; Zhang, T.; Duan, H.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, X.; Yang, G.; Wang, J.; Deng, Y.; Yang, Z. MiR-124 contributes to M2 polarization of microglia and confers brain inflammatory protection via the C/EBP-alpha pathway in intracerebral hemorrhage. Immunol. Lett. 2017, 182, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Lin, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, B.; Hao, X.; Shi, Y. miR-130a regulates macrophage polarization and is associated with non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 3088–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, S. MiR-130b promotes obesity associated adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in diabetes mice through alleviating M2 macrophage polarization via repression of PPAR-γ. Immunol. Lett. 2016, 180, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.-L.; Huang, F.; He, F.; Gao, C.-C.; Liang, S.-Q.; Ma, P.-F.; Dong, G.-Y.; Han, H.; Qin, H.-Y. Forced Activation of Notch in Macrophages Represses Tumor Growth by Upregulating miR-125a and Disabling Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1403–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhuri, A.A.; So, A.Y.-L.; Sinha, N.; Gibson, W.S.J.; Taganov, K.D.; O’Connell, R.M.; Baltimore, D. MiR-125b potentiates macrophage activation1. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 5062–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Zeng, X.; Zhao, L.; Wei, Q.; Yu, L.; Wang, X.; Yu, Z.; Cao, Y.; Shan, F.; Wei, M. miR-181a Induces Macrophage Polarized to M2 Phenotype and Promotes M2 Macrophage-mediated Tumor Cell Metastasis by Targeting KLF6 and C/EBPalpha. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jennewein, C.; Von Knethen, A.; Schmid, T.; Brüne, B. MicroRNA-27b Contributes to Lipopolysaccharide-mediated Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptor γ (PPARγ) mRNA Destabilization. J. Boil. Chem. 2010, 285, 11846–11853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, F.; Yu, Y.; Feng, L.; Li, J.; Zhang, M.; Lan, X.; Yan, X.; Liu, Y.; Guan, F.; Zhang, M.; et al. Adipogenic miR-27a in adipose tissue upregulates macrophage activation via inhibiting PPARγ of insulin resistance induced by high-fat diet-associated obesity. Exp. Cell Res. 2017, 355, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diosa-Toro, M.; Echavarría-Consuegra, L.; Flipse, J.; Fernandez, G.J.; Kluiver, J.; Berg, A.V.D.; Urcuqui-Inchima, S.; Smit, J.M. MicroRNA profiling of human primary macrophages exposed to dengue virus identifies miRNA-3614-5p as antiviral and regulator of ADAR1 expression. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2017, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thulin, P.; Wei, T.; Werngren, O.; Cheung, L.; Fisher, R.M.; Grander, D.; Corcoran, M.; Ehrenborg, E. MicroRNA-9 regulates the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ in human monocytes during the inflammatory response. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Brandt, S.; Medeiros, A.; Wang, S.; Wu, H.; Dent, A.; Serezani, C.H. MicroRNA 21 Is a Homeostatic Regulator of Macrophage Polarization and Prevents Prostaglandin E2-Mediated M2 Generation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Zhou, L.; Ma, T.-C.; Song, L.; Wu, J.-G.; Li, J.-L.; Ho, W.-Z. Toll-like receptor 3-activated macrophages confer anti-HCV activity to hepatocytes through exosomes. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 4132–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, S.; Xie, N.; Cui, H.; Tan, Z.; Yang, S.; Icyuz, M.; Abraham, E.; Liu, G. microRNA let-7c regulates macrophage polarization. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 6542–6549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baer, C.; Squadrito, M.L.; Laoui, D.; Thompson, D.; Hansen, S.K.; Kiialainen, A.; Hoves, S.; Ries, C.H.; Ooi, C.H.; De Palma, M. Suppression of microRNA activity amplifies IFN-gamma-induced macrophage activation and promotes anti-tumour immunity. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016, 18, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.S.; Liu, M.; Xu, Z.B.; Li, Y.S.; Guo, H.; Ge, Y.H.; Liu, Y.X.; Zheng, D.X.; Shi, J. A double feedback loop mediated by microRNA-23a/27a/24-2 regulates M1 versus M2 macrophage polarization and thus regulates cancer progression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 13502–13519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, S.; Zhao, W.; Gao, C. microRNA-210 negatively regulates LPS-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines by targeting NF-κB1 in murine macrophages. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Nunez, R.T.; Louafi, F.; Sanchez-Elsner, T. The Interleukin 13 (IL-13) Pathway in Human Macrophages Is Modulated by MicroRNA-155 via Direct Targeting of Interleukin 13 Receptor alpha 1 (IL13R alpha 1). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, M.Y.; Li, X.Q.; Tang, Z.S.; Wang, X.M.; Zhong, M.; Suo, Q.F.; Zhang, Y.; Lv, K. Silencing MicroRNA-155 Attenuates Cardiac Injury and Dysfunction in Viral Myocarditis via Promotion of M2 Phenotype Polarization of Macrophages. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etzrodt, M.; Cortez-Retamozo, V.; Newton, A.; Zhao, J.; Ng, A.; Wildgruber, M.; Romero, P.; Wurdinger, T.; Xavier, R.; Geissmann, F.; et al. Regulation of monocyte functional heterogeneity by miR-146a and Relb. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganta, V.C.; Choi, M.H.; Kutateladze, A.; Fox, T.E.; Farber, C.R.; Annex, B.H. A MicroRNA93-Interferon Regulatory Factor-9-Immunoresponsive Gene-1-Itaconic Acid Pathway Modulates M2-Like Macrophage Polarization to Revascularize Ischemic Muscle. Circulation 2017, 135, 2403–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Zhang, H.; Hao, Y.; Xu, F.; Yang, J.; Zhang, R.; Lu, G.; Zheng, Z.; Cui, M.; Qi, C.-F.; et al. Reprogramming macrophage orientation by microRNA 146b targeting transcription factor IRF5. EBioMedicine 2016, 14, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhong, Y.; Yi, C. MicroRNA-720 suppresses M2 macrophage polarization by targeting GATA3. Biosci. Rep. 2016, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Song, Y.; He, L.; Wan, X.; Lai, L.; Dai, F.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Q. MicroRNA-223 Promotes Type I Interferon Production in Antiviral Innate Immunity by Targeting Forkhead Box Protein O3 (FOXO3). J. Boil. Chem. 2016, 291, 14706–14716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, L.; Dai, Y.-M.; Ji, C.-B.; Yang, L.; Shi, C.-M.; Xu, G.-F.; Pang, L.-X.; Huang, F.-Y.; Zhang, C.-M.; Guo, X.-R. MiR-146b is a regulator of human visceral preadipocyte proliferation and differentiation and its expression is altered in human obesity. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 393, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Fan, L.; Yu, H.; Zhang, J.; He, Y.; Feng, D.; Wang, F.; Li, X.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; et al. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Causes Liver Cancer Cells to Release Exosomal miR-23a-3p and Up-regulate Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression in Macrophages. Hepatology 2019, 70, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouimet, M.; Ediriweera, H.N.; Gundra, U.M.; Sheedy, F.J.; Ramkhelawon, B.; Hutchison, S.B.; Rinehold, K.; Van Solingen, C.; Fullerton, M.D.; Cecchini, K.; et al. MicroRNA-33–dependent regulation of macrophage metabolism directs immune cell polarization in atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 4334–4348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.Q.; Hu, X.Y.; Han, S.; Miao, X.; Liu, H.; Li, X.M.; Lin, Z.J.; Wang, Z.B.; Gong, W.J. Increased M1 macrophages in young miR-15a/16(−/−) mice with tumour grafts or dextran sulphate sodium-induced colitis. Scand. J. Immunol. 2018, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, H.; Kang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhao, D.; Xia, J.; Lu, Z.; Wang, H.; Xu, F.; Shi, L. MiR-127 modulates macrophage polarization and promotes lung inflammation and injury by activating the JNK pathway. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, S.K.; Kumar, M.; Chakraborty, S.; Banerjee, S.K.; Kumar, R.; Gupta, P.; Jana, K.; Gupta, U.D.; Ghosh, Z.; Kundu, M.; et al. MicroRNA 26a (miR-26a)/KLF4 and CREB-C/EBP beta regulate innate immune signaling, the polarization of macrophages and the trafficking of Mycobacterium tuberculosis to lysosomes during infection. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pello, O.M.; De Pizzol, M.; Mirolo, M.; Soucek, L.; Zammataro, L.; Amabile, A.; Doni, A.; Nebuloni, M.; Swigart, L.B.; Evan, G.I.; et al. Role of c-MYC in alternative activation of human macrophages and tumor-associated macrophage biology. Blood 2012, 119, 411–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Liang, Y.; Lv, H.; Meng, H.; Xiong, G.; Guan, X.; Chen, X.; Bai, Y.; Wang, K. miR-26a and miR-26b inhibit esophageal squamous cancer cell proliferation through suppression of c-MYC pathway. Gene 2017, 625, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Huang, Q.; Li, S.; Meng, F.; Li, X.; Gong, X. miR-330-5p/Tim-3 axis regulates macrophage M2 polarization and insulin resistance in diabetes mice. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 95, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Wang, H.; Jin, M.; Yang, X.; Ji, H.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wu, F.; Wu, G.; Lai, X.; et al. Exosomes from MiR-30d-5p-ADSCs Reverse Acute Ischemic Stroke-Induced, Autophagy-Mediated Brain Injury by Promoting M2 Microglial/Macrophage Polarization. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 864–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, C.; Liu, Y.; Si, Q.; Chuang, T.H.; Li, N.; Gomez-Cabrero, A.; Reisfeld, R.A.; Xiang, R.; et al. MicroRNA-19a-3p inhibits breast cancer progression and metastasis by inducing macrophage polarization through downregulated expression of Fra-1 proto-oncogene. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3014–3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Pan, C.; Li, L.; Bian, Z.; Lv, Z.; Shi, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, D.; Gu, H.; Zhang, C.-Y.; et al. MicroRNA-17/20a/106a modulate macrophage inflammatory responses through targeting signal-regulatory protein α. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013, 132, 426–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Zhang, N.; Wu, W.; Guo, Q.H.; Wang, W.J.; Wang, P.; Wang, X.P. MicroRNA-24 Modulates Staphylococcus aureus-Induced Macrophage Polarization by Suppressing CHI3L1. Inflammation 2017, 40, 995–1005. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Du, K.L.; Guo, P.Y.; Zhao, R.M.; Wang, B.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, C.Q. IL-16 regulates macrophage polarization as a target gene of mir-145-3p. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 107, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, G.Q.; Meng, C.; Guo, X.; Cheruku, P.S.; Shi, L.; Xu, H.; Li, H.G.; Wang, G.; Evans, A.R.; Safe, S.; et al. A Novel Regulator of Macrophage Activation miR-223 in Obesity-Associated Adipose Tissue Inflammation. Circulation 2012, 125, 2892–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, Y.S.; Tseng, H.Y.; Chen, Y.A.; Shen, P.C.; Al Haq, A.T.; Chen, L.M.; Tung, Y.C.; Hsu, H.L. MCT-1/miR-34a/IL-6/IL-6R signaling axis promotes EMT progression, cancer stemness and M2 macrophage polarization in triple-negative breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.X.; Munitz, A.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA-21 is up-regulated in allergic airway inflammation and regulates IL-12p35 expression1. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4994–5002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caescu, C.I.; Guo, X.; Tesfa, L.; Bhagat, T.D.; Verma, A.; Zheng, D.; Stanley, E.R. Colony stimulating factor-1 receptor signaling networks inhibit mouse macrophage inflammatory responses by induction of microRNA-21. Blood 2015, 125, e1–e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, T.H.; He, Q.W.; Xia, Y.P.; Chen, S.C.; Baral, S.; Mao, L.; Jin, H.J.; Li, Y.N.; Wang, M.D.; Chen, J.G.; et al. MiR-181b Antagonizes Atherosclerotic Plaque Vulnerability Through Modulating Macrophage Polarization by Directly Targeting Notch1. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6329–6341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.B.; Wang, S.Y.; Sun, M.; Zhang, C.X.; Wei, C.; Yang, C.G.; Dou, R.Z.; Liu, Q.; Xiong, B. miR-195-5p/NOTCH2-mediated EMT modulates IL-4 secretion in colorectal cancer to affect M2-like TAM polarization. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Hung, F.Y.; Chang, W.A.; Jian, S.F.; Lin, Y.S.; Pan, Y.C.; Wu, C.Y.; Kuo, P.L. Hypoxic Lung-Cancer-Derived Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNA-103a Increases the Oncogenic Effects of Macrophages by Targeting PTEN. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 568–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.K.; Du, Y.; He, Y.Q.; Liu, Y.W.; Zhang, G.L.; Yang, C.X.; Gao, F. INT-HA induces M2-like macrophage differentiation of human monocytes via TLR4-miR-935 pathway. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2019, 68, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, G.; Zhang, K.; Cao, J.; Huang, C.; Jiang, T.; Liu, B.; Su, L.; Qiu, Z. Hypoxic Tumor-Derived Exosomal miR-301a Mediates M2 Macrophage Polarization via PTEN/PI3Kγ to Promote Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4586–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Zhao, J.L.; Wang, L.; Gao, C.C.; Liang, S.Q.; An, D.J.; Bai, J.; Chen, Y.; Han, H.; Qin, H.Y. miR-148a-3p Mediates notch signaling to Promote the Differentiation and M1 activation of Macrophages. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frank, A.-C.; Ebersberger, S.; Fink, A.F.; Lampe, S.; Weigert, A.; Schmid, T.; Ebersberger, I.; Syed, S.N.; Brüne, B. Apoptotic tumor cell-derived microRNA-375 uses CD36 to alter the tumor-associated macrophage phenotype. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taj, S.H.; Kho, W.; Riou, A.; Wiedermann, D.; Hoehn, M. MiRNA-124 induces neuroprotection and functional improvement after focal cerebral ischemia. Biomaterials 2016, 91, 151–165. [Google Scholar]
- Squadrito, M.L.; Pucci, F.; Magri, L.; Moi, D.; Gilfillan, G.D.; Ranghetti, A.; Casazza, A.; Mazzone, M.; Lyle, R.; Naldini, L.; et al. miR-511-3p Modulates Genetic Programs of Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Cell Rep. 2012, 1, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Xue, M.; Zhang, S.; Hu, F.; Li, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zou, M.; Li, S.; Wang, L.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles from Albumin-Induced Tubular Epithelial Cells Promote the M1 Macrophage Phenotype by Targeting Klotho. Mol. Ther. 2019, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruckerl, D.; Jenkins, S.J.; Laqtom, N.N.; Gallagher, I.J.; Sutherland, T.E.; Duncan, S.; Buck, A.H.; Allen, J.E. Induction of IL-4Rα–dependent microRNAs identifies PI3K/Akt signaling as essential for IL-4–driven murine macrophage proliferation in vivo. Blood 2012, 120, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ying, X.; Zhu, Q.; Chen, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, X. Exosomes derived from hypoxic epithelial ovarian cancer deliver microRNA-940 to induce macrophage M2 polarization. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 522–528. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Li, L.; Sun, P.F.; Zhang, C.S.; Li, Z.C.; Zhou, W.Y. MiR-98 suppresses the effects of tumor-associated macrophages on promoting migration and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by regulating IL-10. Biochimie 2018, 150, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, X.Y.; Song, X.C.; Dong, L.; Liu, D.W. MiR-202-5p Promotes M2 Polarization in Allergic Rhinitis by Targeting MATN2. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2019, 178, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.G.; Xu, L.; Hu, Y.Y.; Huang, Y.Q.; Zhang, Y.J.; Zheng, X.F.; Wang, S.S.; Wang, Y.F.; Yu, Y.R.; Zhang, M.; et al. miRNA let-7b modulates macrophage polarization and enhances tumor-associated macrophages to promote angiogenesis and mobility in prostate cancer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Morgan, M.J.; Choksi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Kim, Y.S.; Liu, Z.G. MicroRNAs modulate the noncanonical transcription factor NF-kappaB pathway by regulating expression of the kinase IKKalpha during macrophage differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 799–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivier, E.; Raulet, D.H.; Moretta, A.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Zitvogel, L.; Lanier, L.L.; Yokoyama, W.M.; Ugolini, S. Innate or adaptive immunity? The example of natural killer cells. Science 2011, 331, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesce, S.; Squillario, M.; Greppi, M.; Loiacono, F.; Moretta, L.; Moretta, A.; Sivori, S.; Castagnola, P.; Barla, A.; Candiani, S.; et al. New miRNA signature heralds human NK cell subsets at different maturation steps: Involvement of miR-146a-5p in the regulation of KIR expression. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, A.; Bottino, C.; Vitale, M.; Pende, D.; Cantoni, C.; Mingari, M.C.; Biassoni, R.; Moretta, L. Activating receptors and coreceptors involved in human natural killer cell-mediated cytolysis. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2001, 19, 197–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moretta, A.; Bottino, C.; Vitale, M.; Pende, D.; Biassoni, R.; Mingari, M.C.; Moretta, L. Receptors for HLA class-I molecules in human natural killer cells. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1996, 14, 619–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cooper, M.A.; Fehniger, T.A.; Caligiuri, M.A. The biology of human natural killer-cell subsets. Trends Immunol. 2001, 22, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freud, A.G.; Caligiuri, M.A. Human natural killer cell development. Immunol. Rev. 2006, 214, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.C.; Lanier, L.L. NK cell development, homeostasis and function: parallels with CD8(+) T cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 645–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, J.W.; Wagner, J.A.; Ireland, A.R.; Fehniger, T.A. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of NK cell development and function. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 177, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezman, N.A.; Cedars, E.; Steiner, D.F.; Blelloch, R.; Hesslein, D.G.; Lanier, L.L. Distinct requirements of microRNAs in NK cell activation, survival, and function. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3835–3846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, J.W.; Sullivan, R.P.; Fehniger, T.A. Natural Killer Cell Regulation by MicroRNAs in Health and Disease. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Q.; Yan, J.; Huang, J.; Zhu, S.; Yu, J. Identification of microRNA transcriptome involved in human natural killer cell activation. Immunol. Lett. 2012, 143, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaulieu, A.M.; Bezman, N.A.; Lee, J.E.; Matloubian, M.; Sun, J.C.; Lanier, L.L. MicroRNA function in NK-cell biology. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 253, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cichocki, F.; Felices, M.; McCullar, V.; Presnell, S.R.; Al-Attar, A.; Lutz, C.T.; Miller, J.S. Cutting Edge: MicroRNA-181 Promotes Human NK Cell Development by Regulating Notch Signaling. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 6171–6175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bezman, N.A.; Chakraborty, T.; Bender, T.; Lanier, L.L. miR-150 regulates the development of NK and iNKT cells. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 2717–2731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.P.; Leong, J.W.; Schneider, S.E.; Ireland, A.R.; Berrien-Elliott, M.M.; Singh, A.; Schappe, T.; Jewell, B.A.; Sexl, V.; Fehniger, T.A. MicroRNA-15/16 antagonizes Myb to control natural killer cell maturation. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 2806–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.P.; Leong, J.W.; Schneider, S.E.; Keppel, C.R.; Germino, E.; French, A.R.; Fehniger, T.A. MicroRNA Deficient NK Cells Exhibit Decreased Survival but Enhanced Function. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3019–3030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Xu, S.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, X.; Liu, M.; Hua, M.; Li, N.; Yao, H.; Cao, X. The microRNA miR-29 controls innate and adaptive immune responses to intracellular bacterial infection by targeting interferon-γ. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 861–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, R.P.; Fogel, L.A.; Leong, J.W.; Schneider, S.E.; Wong, R.; Romee, R.; Thai, T.-H.; Sexl, V.; Matkovich, S.J.; Dorn, G.W.; et al. miR-155 tunes both the threshold and extent of NK cell activation via targeting of multiple signaling pathways. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 5904–5913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, R.; Chen, L.; Ciarlariello, D.; Josyula, S.; Mao, C.; Costinean, S.; Yu, L.; Butchar, J.P.; Tridandapani, S.; Croce, C.M.; et al. miR-155 regulates IFN-γ production in natural killer cells. Blood 2012, 119, 3478–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.Q.; Ren, J.P.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J.M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.Y.; Moorman, J.P.; Yao, Z.Q. MicroRNA-155 regulates interferon-gamma production in natural killer cells via Tim-3 signalling in chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Immunology 2015, 145, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, A.; Tagawa, H.; Yamashita, J.; Teshima, K.; Nara, M.; Iwamoto, K.; Kume, M.; Kameoka, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Nakagawa, T.; et al. The role of microRNA-150 as a tumor suppressor in malignant lymphoma. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fehniger, T.A.; Wylie, T.; Germino, E.; Leong, J.W.; Magrini, V.J.; Koul, S.; Keppel, C.R.; Schneider, S.E.; Koboldt, D.C.; Sullivan, R.P.; et al. Next-generation sequencing identifies the natural killer cell microRNA transcriptome. Genome Res. 2010, 20, 1590–1604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.; Kim, M.; Yun, S.; Doh, J.; Greenberg, P.D.; Kim, T.-D.; Choi, I. MicroRNA-150 regulates the cytotoxicity of natural killers by targeting perforin-1. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-D.; Lee, S.U.; Yun, S.; Sun, H.-N.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, H.M.; Park, S.-K.; Lee, C.W.; Yoon, S.R.; et al. Human microRNA-27a* targets Prf1 and GzmB expression to regulate NK-cell cytotoxicity. Blood 2011, 118, 5476–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Han, Y.; Hou, J.; Lin, L.; Wu, C.; Bao, Y.; Su, X.; Jiang, M.; et al. Identification of Resting and Type I IFN-Activated Human NK Cell miRNomes Reveals MicroRNA-378 and MicroRNA-30e as Negative Regulators of NK Cell Cytotoxicity. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Espinoza, J.L.; Takami, A.; Yoshioka, K.; Nakata, K.; Sato, T.; Kasahara, Y.; Nakao, S. Human microRNA-1245 down-regulates the NKG2D receptor in natural killer cells and impairs NKG2D-mediated functions. Haematologica 2012, 97, 1295–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Donatelli, S.S.; Zhou, J.M.; Gilvary, D.L.; Eksioglu, E.A.; Chen, X.; Cress, W.D.; Haura, E.B.; Schabath, M.B.; Coppola, D.; Wei, S.; et al. TGF-beta-inducible microRNA-183 silences tumor-associated natural killer cells. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 4203–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Cui, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, J.; Tun, N.; Peng, Y.; Yu, J. Regulation of Human Natural Killer Cell IFN-gamma Production by MicroRNA-146a via Targeting the NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breunig, C.; Pahl, J.; Kublbeck, M.; Miller, M.; Antonelli, D.; Erdem, N.; Wirth, C.; Will, R.; Bott, A.; Cerwenka, A.; et al. MicroRNA-519a-3p mediates apoptosis resistance in breast cancer cells and their escape from recognition by natural killer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotta, R.; Chen, L.; Costinean, S.; Josyula, S.; Mundy-Bosse, B.L.; Ciarlariello, D.; Mao, C.; Briercheck, E.L.; McConnell, K.K.; Mishra, A.; et al. Overexpression of miR-155 causes expansion, arrest in terminal differentiation and functional activation of mouse natural killer cells. Blood 2013, 121, 3126–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Chu, J.H.; Wu, L.C.; Mao, H.Y.; Peng, Y.; Alvarez-Breckenridge, C.A.; Hughes, T.; Wei, M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Yuan, S.Z.; et al. MicroRNAs activate natural killer cells through Toll-like receptor signaling. Blood 2013, 121, 4663–4671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scoville, S.D.; Nalin, A.; Chen, L.X.; Chen, L.; McConnell, K.; Casas, S.B.; Al-Rahman, A.; Hashi, N.; Zhang, M.; Saultz, J.; et al. The aryl hydrocarbon receptor directly regulates microRNA-29b to inhibit human natural killer cell development and function in acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Res. 2018, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Su, W.; Kang, Q.; Xing, Z.; Lin, X.; Wu, Z. Natural killer cells inhibit oxaliplatin-resistant colorectal cancer by repressing WBSCR22 via upregulating microRNA-146b-5p. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 824–834. [Google Scholar]
- Victor, A.R.; Weigel, C.; Scoville, S.D.; Chan, W.K.; Chatman, K.; Nemer, M.M.; Mao, C.; Young, K.A.; Zhang, J.; Yu, J.; et al. Epigenetic and Posttranscriptional Regulation of CD16 Expression during Human NK Cell Development. J. Immunol. 2018, 200, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Q.; Yan, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, C.; Chen, C.; Zhao, X.; Xu, M.; Sun, Q.; Deng, R.; et al. MiRNA-296-3p-ICAM-1 axis promotes metastasis of prostate cancer by possible enhancing survival of natural killer cell-resistant circulating tumour cells. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.Q.; Han, Q.J.; Hou, Z.H.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J. miR-146a negatively regulates NK cell functions via STAT1 signaling. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2017, 14, 712–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikulak, J.; Bozzo, L.; Roberto, A.; Pontarini, E.; Tentorio, P.; Hudspeth, K.; Lugli, E.; Mavilio, D. Dopamine Inhibits the Effector Functions of Activated NK Cells via the Upregulation of the D5 Receptor. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 2792–2800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nachmani, D.; Zimmermann, A.; Djian, E.O.; Weisblum, Y.; Livneh, Y.; Le, V.T.K.; Galun, E.; Horejsi, V.; Isakov, O.; Shomron, N.; et al. MicroRNA Editing Facilitates Immune Elimination of HCMV Infected Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, F.; Guo, C.; Sun, R.; Fu, B.Q.; Yang, Y.; Wu, L.L.; Ren, S.T.; Tian, Z.G.; Wei, H.M. MicroRNA transcriptomes of distinct human NK cell populations identify miR-362-5p as an essential regulator of NK cell function. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Liu, M.; Li, Y.; Nie, Y.; Mi, Q.; Zhao, S. Ovarian tumor-associated microRNA-20a decreases natural killer cell cytotoxicity by downregulating MICA/B expression. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 495–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neviani, P.; Wise, P.M.; Murtadha, M.; Liu, C.W.; Wu, C.H.; Jong, A.Y.; Seeger, R.C.; Fabbri, M. Natural Killer-Derived Exosomal miR-186 Inhibits Neuroblastoma Growth and Immune Escape Mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, D.; Lv, X.-B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, B.; Meng, W.; Yu, F.; Hu, H. Downregulation of miR-302c and miR-520c by 1,25(OH)2D3 treatment enhances the susceptibility of tumour cells to natural killer cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Br. J. Cancer 2013, 109, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stelma, F.; van der Ree, M.H.; Sinnige, M.J.; Brown, A.; Swadling, L.; de Vree, J.M.L.; Willemse, S.B.; van der Valk, M.; Grint, P.; Neben, S.; et al. Immune Phenotype and Function of Natural Killer and T Cells in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients Who Received a Single Dose of Anti-MicroRNA-122, RG-101. Hepatology 2017, 66, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, J.; Liu, R.; Zhuang, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fang, L.; Xu, Z.; Jin, L.; Wang, T.; Song, C.; Yang, K.; et al. miR-30c-1* promotes natural killer cell cytotoxicity against human hepatoma cells by targeting the transcription factor HMBOX1. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hou, L.; Zhang, M.; Dayton, A.I. MicroRNA regulation of STAT4 protein expression: Rapid and sensitive modulation of IL-12 signaling in human natural killer cells. Blood 2011, 118, 6793–6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Cheung, I.Y.; Guo, H.-F.; Cheung, N.-K.V. MicroRNA miR-29 modulates expression of immunoinhibitory molecule B7-H3: Potential implications for immune based therapy of human solid tumors. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6275–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mundy-Bosse, B.L.; Scoville, S.D.; Chen, L.; McConnell, K.; Mao, H.C.; Ahmed, E.H.; Zorko, N.; Harvey, S.; Cole, J.; Zhang, X.; et al. MicroRNA-29b mediates altered innate immune development in acute leukemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 4404–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Feng, L.; Ma, H.; Chang, L.; Zhou, X.; Wang, N.; Zhao, L.; Zuo, J.; Wang, Y.; Han, J.; Wang, G. Role of microRNA-141 in colorectal cancer with lymph node metastasis. Exp. Ther. Med. 2016, 12, 3405–3410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jasinski-Bergner, S.; Reches, A.; Stoehr, C.; Massa, C.; Gonschorek, E.; Huettelmaier, S.; Braun, J.; Wach, S.; Wullich, B.; Spath, V.; et al. Identification of novel microRNAs regulating HLA-G expression and investigating their clinical relevance in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 26866–26878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berchem, G.; Noman, M.Z.; Bosseler, M.; Paggetti, J.; Baconnais, S.; Le Cam, E.; Nanbakhsh, A.; Moussay, E.; Mami-Chouaib, F.; Janji, B.; et al. Hypoxic tumor-derived microvesicles negatively regulate NK cell function by a mechanism involving TGF- and miR23a transfer. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukerman, P.; Stern-Ginossar, N.; Gur, C.; Glasner, A.; Nachmani, D.; Bauman, Y.; Yamin, R.; Vitenshtein, A.; Stanietsky, N.; Bar-Mag, T.; et al. MiR-10b Downregulates the Stress-Induced Cell Surface Molecule MICB, a Critical Ligand for Cancer Cell Recognition by Natural Killer Cells. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 5463–5472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Lan, P.; Hou, Z.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, W.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, C. Histone deacetylase inhibitor SAHA epigenetically regulates miR-17-92 cluster and MCM7 to upregulate MICA expression in hepatoma. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 112, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Wang, P.; Li, X.; Wang, Q.; Deng, Z.-B.; Zhuang, X.; Mu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Yan, J.; et al. Restoration of MiR-17/20a in Solid Tumor Cells Enhances the Natural Killer Cell Antitumor Activity by Targeting Mekk2. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 789–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Ye, X.; Shang, L. MiR-506 Promotes Natural Killer Cell Cytotoxicity against Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells by Targeting STAT3. Yonsei Med. J. 2019, 60, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.M.; Zhang, X.J.; Shi, K.Q.; Chen, Y.P.; Ren, Y.F.; Song, Y.J.; Li, G.L.; Xue, Y.F.; Fang, Y.X.; Deng, Z.J.; et al. Hepatitis B surface antigen inhibits MICA and MICB expression via induction of cellular miRNAs in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.-M.; Han, T.; Wang, X.-H.; Li, Y.-H.; Yang, H.-G.; Luo, Y.-N.; Yin, G.-W.; Yao, Y.-Q. Overexpression of miR-152 leads to reduced expression of human leukocyte antigen-G and increased natural killer cell mediated cytolysis in JEG-3 cells. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 202, e1–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regis, S.; Caliendo, F.; Dondero, A.; Casu, B.; Romano, F.; LoIacono, F.; Moretta, A.; Bottino, C.; Castriconi, R. TGF-β1 Downregulates the Expression of CX3CR1 by Inducing miR-27a-5p in Primary Human NK Cells. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Han, X.; Hu, X.; Jin, F.; Gao, Z.; Yin, L.; Qin, J.; Yin, F.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. IDO1 impairs NK cell cytotoxicity by decreasing NKG2D/NKG2DLs via promoting miR-18a. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 103, 144–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.B.; Zhou, Z.J.; Xiao, K.; Zhu, G.Q.; Yang, Y.; Wang, B.; Zhou, S.L.; Chen, Q.; Yin, D.; Wang, Z.; et al. The miR-561-5p/CX3CL1 Signaling Axis Regulates Pulmonary Metastasis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Involving CX3CR1(+) Natural Killer Cells Infiltration. Theranostics 2019, 9, 4779–4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.; Chen, S.; Zhang, M.; Chan, J.Y.; Gao, W. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNA BART7 downregulates major histocompatibility complex class I chain-related peptide A and reduces the cytotoxicity of natural killer cells to nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 2887–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, A.; Zhao, F.; Pechlivanis, S.; Eberle, J.; Steinle, A.; Diederichs, S.; Schadendorf, D.; Paschen, A. Tumor suppressive microRNAs miR-34a/c control cancer cell expression of ULBP2, a stress-induced ligand of the natural killer cell receptor NKG2D. Cancer Res. 2012, 72, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dölken, L.; Krmpotić, A.; Kothe, S.; Tuddenham, L.; Tanguy, M.; Marcinowski, L.; Ruzsics, Z.; Elefant, N.; Altuvia, Y.; Margalit, H.; et al. Cytomegalovirus microRNAs Facilitate Persistent Virus Infection in Salivary Glands. PLoS Pathog. 2010, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Ding, J.; Gong, M.; Wei, M.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, J. Effect of miR-30e regulating NK cell activities on immune tolerance of maternal-fetal interface by targeting PRF1. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 109, 1478–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Pelsmaeker, S.; Romero, N.; Vitale, M.; Favoreel, H.W. Herpesvirus Evasion of Natural Killer Cells. J. Virol. 2018, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bauman, Y.; Nachmani, D.; Vitenshtein, A.; Tsukerman, P.; Drayman, N.; Stern-Ginossar, N.; Lankry, D.; Gruda, R.; Mandelboim, O. An Identical miRNA of the Human JC and BK Polyoma Viruses Targets the Stress-Induced Ligand ULBP3 to Escape Immune Elimination. Cell Host Microbe 2011, 9, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stern-Ginossar, N.; Elefant, N.; Zimmermann, A.; Wolf, D.G.; Saleh, N.; Biton, M.; Horwitz, E.; Prokocimer, Z.; Prichard, M.; Hahn, G.; et al. Host immune system gene targeting by a viral miRNA. Science 2007, 317, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachmani, D.; Stern-Ginossar, N.; Sarid, R.; Mandelboim, O. Diverse Herpesvirus MicroRNAs Target the Stress-Induced Immune Ligand MICB to Escape Recognition by Natural Killer Cells. Cell Host Microbe 2009, 5, 376–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, W.-T.; Lin, C.-W. EBV-Encoded miR-BART20-5p and miR-BART8 Inhibit the IFN-γ–STAT1 Pathway Associated with Disease Progression in Nasal NK-Cell Lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enk, J.; Levi, A.; Weisblum, Y.; Yamin, R.; Charpak-Amikam, Y.; Wolf, D.G.; Mandelboim, O. HSV1 MicroRNA Modulation of GPI Anchoring and Downstream Immune Evasion. Cell Rep. 2016, 17, 949–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piedade, D.; Azevedo-Pereira, J.M. The Role of microRNAs in the Pathogenesis of Herpesvirus Infection. Viruses 2016, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leong, J.W.; Sullivan, R.P.; Fehniger, T.A. microRNA management of NK-cell developmental and functional programs. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 2862–2868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xu, S.J.; Hu, H.T.; Li, H.L.; Chang, S. The Role of miRNAs in Immune Cell Development, Immune Cell Activation, and Tumor Immunity: With a Focus on Macrophages and Natural Killer Cells. Cells 2019, 8, 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101140
Xu SJ, Hu HT, Li HL, Chang S. The Role of miRNAs in Immune Cell Development, Immune Cell Activation, and Tumor Immunity: With a Focus on Macrophages and Natural Killer Cells. Cells. 2019; 8(10):1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101140
Chicago/Turabian StyleXu, Shi Jun, Hong Tao Hu, Hai Liang Li, and Suhwan Chang. 2019. "The Role of miRNAs in Immune Cell Development, Immune Cell Activation, and Tumor Immunity: With a Focus on Macrophages and Natural Killer Cells" Cells 8, no. 10: 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101140
APA StyleXu, S. J., Hu, H. T., Li, H. L., & Chang, S. (2019). The Role of miRNAs in Immune Cell Development, Immune Cell Activation, and Tumor Immunity: With a Focus on Macrophages and Natural Killer Cells. Cells, 8(10), 1140. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101140






