The Major Histocompatibility Complex of Old World Camels—A Synopsis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Analysis of Selected Non-Antigen Presenting MHC Genes
2.2. New Annotation of the MHC Region and Phylogenetic Analyses
3. Results
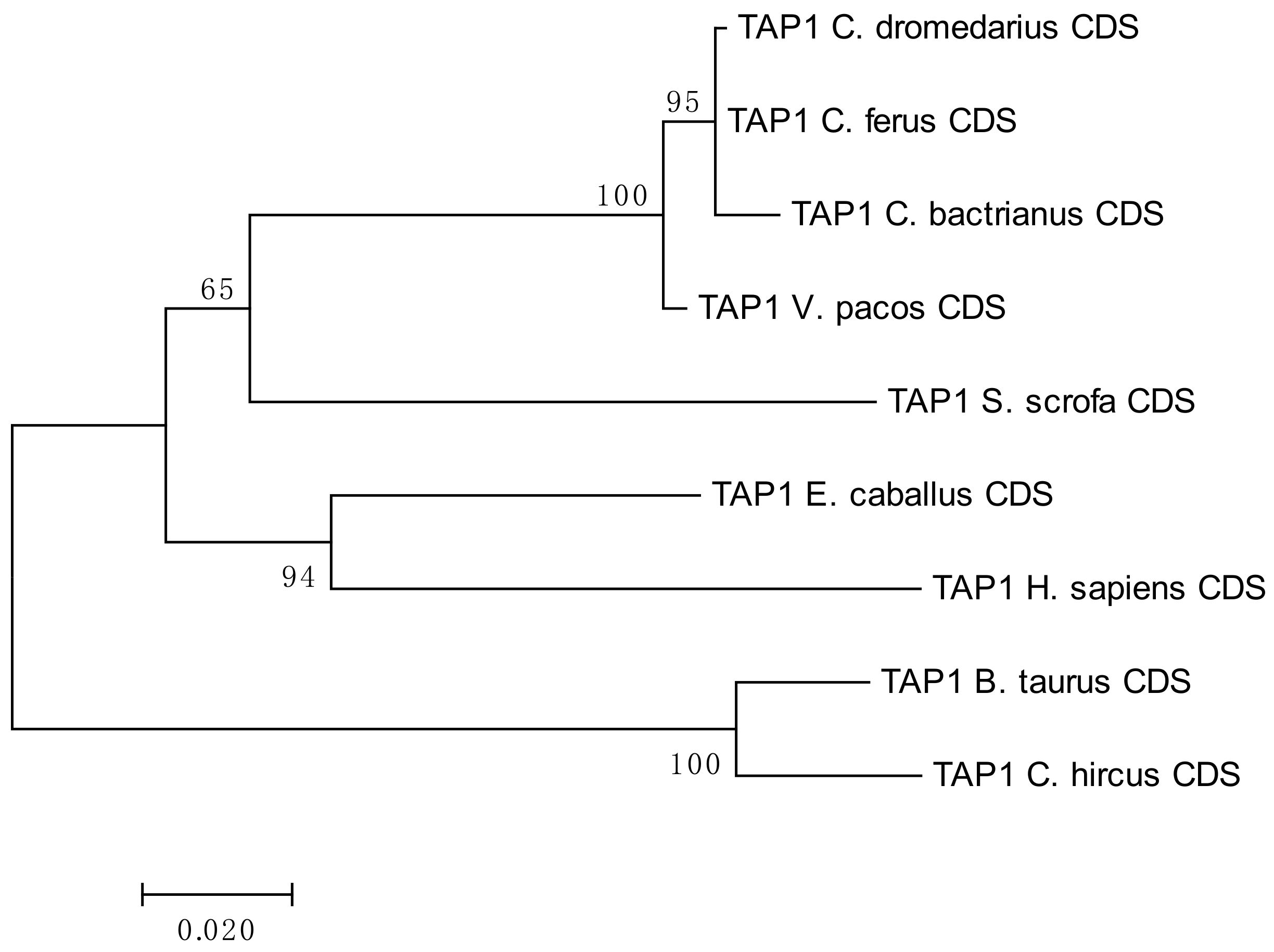
3.1. The MHC Class II Gene TAP 1
3.2. MHC Class III Genes
3.2.1. The TNFA Gene
3.2.2. The LY6G6 Gene Family
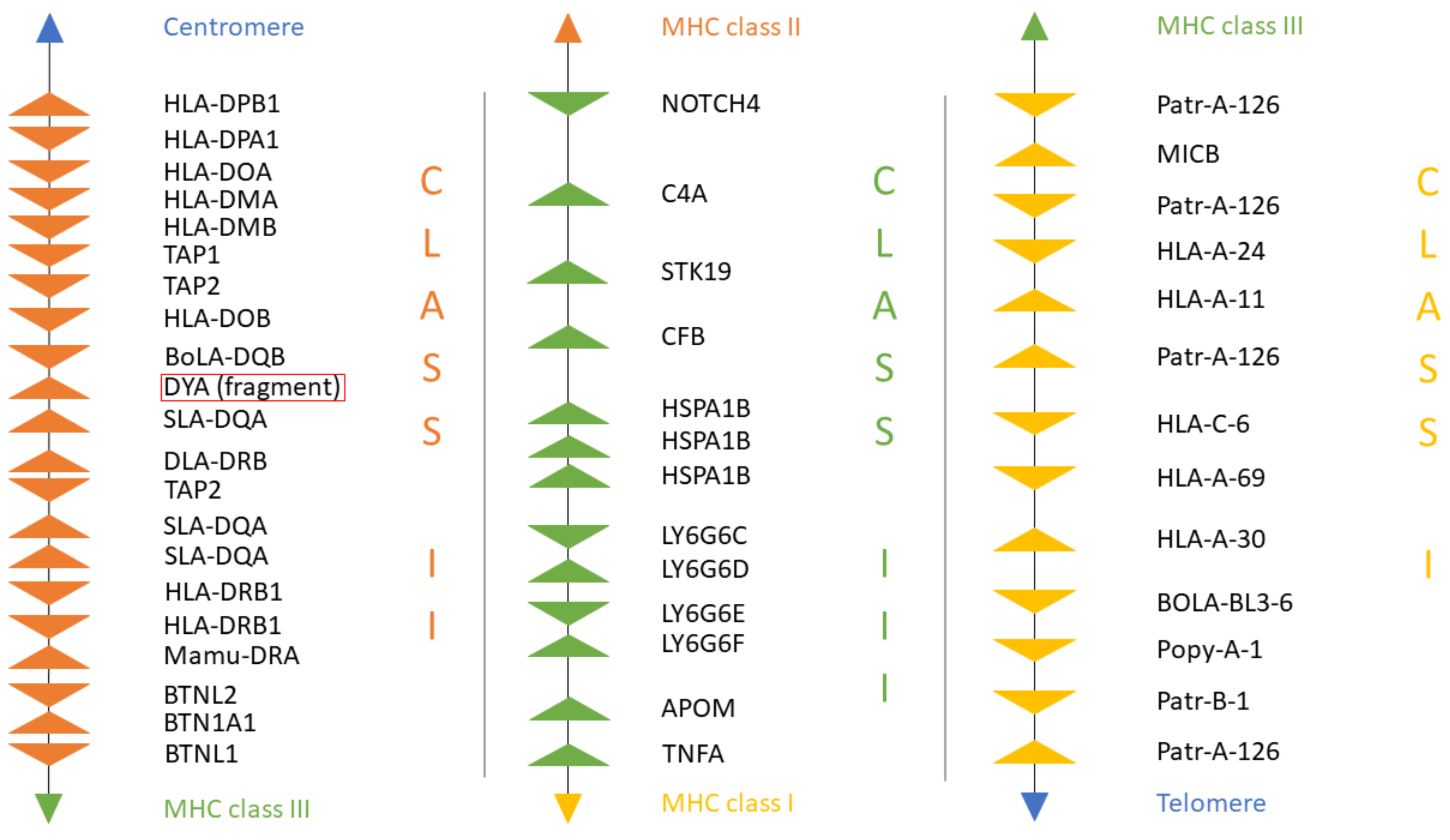
3.3. New Annotation of the MHC Region in the Dromedary
4. Discussion
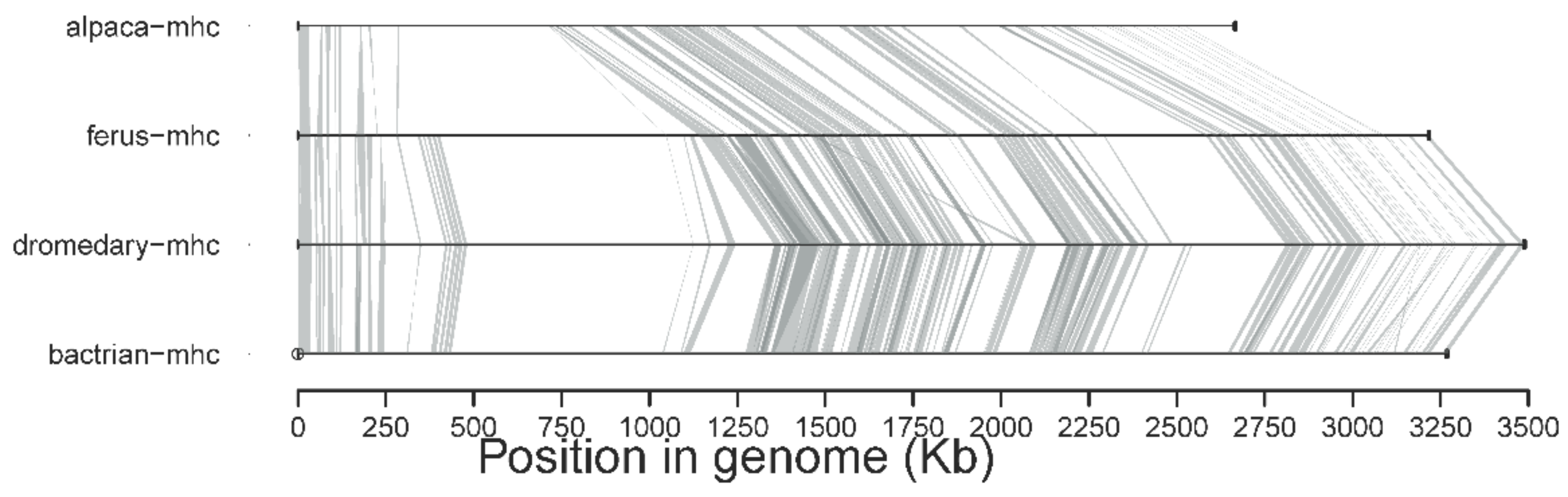
4.1. MHC Region Organization and Diversity in Old World Camels
4.2. Cross-Species Comparisons with New World Camelids and Other Mammals
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Janeway, C.A.; Travers, P.; Walport, M.; Shlomchik, M.J. Immunobiology: The Immune System in Health and Disease, 6th ed.; Taylor & Francis Group, Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick, P.W.; Whittam, T.S.; Parham, P. Heterozygosity at individual amino acid sites: Extremely high levels for HLA-A and-B genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 5897–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumánovics, A.; Takada, T.; Lindahl, K.F. Genomic organization of the mammalian MHC. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 21, 629–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winternitz, J.C.; Minchey, S.G.; Garamszegi, L.Z.; Huang, S.; Stephens, P.R.; Altizer, S. Sexual selection explains more functional variation in the mammalian major histocompatibility complex than parasitism. Proc. Biol. Sci. 2013, 280, 20131605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, R.G.; Magalhães, V.; López-Bao, J.V.; van der Loo, W.; Llaneza, L.; Alvares, F.; Esteves, P.J.; Godinho, R. Alternated selection mechanisms maintain adaptive diversity in different demographic scenarios of a large carnivore. BMC Evol. Biol. 2019, 19, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, A.; Roemer, G.; Debenham, S.; Binns, M.; Garcelon, D.; Wayne, R.K. High MHC diversity maintained by balancing selection in an otherwise genetically monomorphic mammal. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 3490–3494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikko, S.; Røed, K.; Schmutz, S.; Andersson, L. Monomorphism and polymorphism at Mhc DRB loci in domestic and wild ruminants. Immunol. Rev. 1999, 167, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doxiadis, G.G.; Otting, N.; de Groot, N.G.; Bontrop, R.E. Differential evolutionary MHC class II strategies in humans and rhesus macaques: Relevance for biomedical studies. Immunol. Rev. 2001, 183, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernatchez, L.; Landry, C. MHC studies in nonmodel vertebrates: What have we learned about natural selection in 15 years? J. Evol. Biol. 2003, 16, 363–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, P.A.; Ciani, E.; Faye, B. Old World camels in a modern world—A balancing act between conservation and genetic improvement. Anim. Genet. 2019, in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Guang, X.; Al-Fageeh, M.B.; Cao, J.; Pan, S.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, L.; Abutarboush, M.H.; Xing, Y.; Xie, Z. Camelid genomes reveal evolution and adaptation to desert environments. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Cui, P.; Ding, F.; Geng, J.; Gao, H.; Zhang, H.; Yu, J.; Hu, S.; Meng, H. Monophyletic origin of domestic bactrian camel (Camelus bactrianus) and its evolutionary relationship with the extant wild camel (Camelus bactrianus ferus). Anim. Genet. 2009, 40, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silbermayr, K.; Orozco-terWengel, P.; Charruau, P.; Enkhbileg, D.; Walzer, C.; Vogl, C.; Schwarzenberger, F.; Kaczensky, P.; Burger, P.A. High mitochondrial differentiation levels between wild and domestic Bactrian camels: A basis for rapid detection of maternal hybridization. Anim. Genet. 2010, 41, 315–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sequencing, T.B.C.G.; Analysis Consortium. Genome sequences of wild and domestic bactrian camels. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burger, P.A. The history of Old World camelids in the light of molecular genetics. Trop. Anim. Health Pro. 2016, 48, 905–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernery, U.; Kinne, J. Foot and mouth disease and similar virus infections in camelids: A review. Rev. Sci. Tech. Oie 2012, 31, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirie, M.F.; Abdurahman, O. Observations on little known diseases of camels (Camelus dromedarius) in the Horn of Africa. Rev. Sci. Tech. Oie 2003, 22, 1043–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Kanhal, H.A. Compositional, technological and nutritional aspects of dromedary camel milk. Int. Dairy J. 2010, 20, 811–821. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Baby, B.; Vijayan, R. Camel Genome-from Desert to Medicine. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muyldermans, S. Single domain camel antibodies: Current status. Rev. Mol. Biotech. 2001, 74, 277–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarese, S.M.; Burger, P.; Ciani, E.; Castelli, V.; Linguiti, G.; Plasil, M.; Massari, S.; Horin, P.; Antonacci, R. The camel adaptive immune receptors repertoire as a singular example of structural and functional genomics. Front. Genet. 2019. Under review. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antczak, D. Major histocompatibility complex genes of the dromedary camel. In Proceedings of the Qatar Foundation Annual Research Conference, Doha, Qatar, 24–25, November, 2013; Hamad bin Khalifa University Press (HBKU Press): Doha, Qatar, 2013; p. BIOP015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avila, F.; Baily, M.P.; Perelman, P.; Das, P.J.; Pontius, J.; Chowdhary, R.; Owens, E.; Johnson, W.E.; Merriwether, D.A.; Raudsepp, T. A comprehensive whole-genome integrated cytogenetic map for the alpaca (Lama pacos). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2014, 144, 196–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plasil, M.; Mohandesan, E.; Fitak, R.R.; Musilova, P.; Kubickova, S.; Burger, P.A.; Horin, P. The major histocompatibility complex in Old World camelids and low polymorphism of its class II genes. BMC Genomics 2016, 17, 167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plasil, M.; Wijkmark, S.; Elbers, J.P.; Oppelt, J.; Burger, P.; Horin, P. The major histocompatibility complex of Old World camelids: Class I and class I-related genes. HLA 2019, 93, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lado, S.; Elbers, J.P.; Rogers, M.F.; Perelman, P.L.; Proskuryakova, A.A.; Serdyukova, N.A.; Johnson, W.E.; Horin, P.; Corander, J.; Murphy, D.; et al. Reference-guided assembly of two Old World camel genomes and genomic diversity of Old World camelid immune response genes. Manuscript in preparation.
- Elbers, J.P.; Rogers, M.F.; Perelman, P.L.; Proskuryakova, A.A.; Serdyukova, N.A.; Johnson, W.E.; Horin, P.; Corander, J.; Murphy, D.; Burger, P.A. Improving Illumina assemblies with Hi-C and long reads: An example with the North African dromedary. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 19, 1015–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitak, R.R.; Mohandesan, E.; Corander, J.; Burger, P.A. The de novo genome assembly and annotation of a female domestic dromedary of North African origin. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2016, 16, 314–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putnam, N.H.; O’Connell, B.L.; Stites, J.C.; Rice, B.J.; Blanchette, M.; Calef, R.; Troll, C.J.; Fields, A.; Hartley, P.D.; Sugnet, C.W. Chromosome-scale shotgun assembly using an in vitro method for long-range linkage. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, A.C.; Richards, S.; Han, Y.; Wang, M.; Vee, V.; Qu, J.; Qin, X.; Muzny, D.M.; Reid, J.G.; Worley, K.C. Mind the gap: Upgrading genomes with Pacific Biosciences RS long-read sequencing technology. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, B.J.; Abeel, T.; Shea, T.; Priest, M.; Abouelliel, A.; Sakthikumar, S.; Cuomo, C.A.; Zeng, Q.; Wortman, J.; Young, S.K. Pilon: An integrated tool for comprehensive microbial variant detection and genome assembly improvement. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarasov, A.; Vilella, A.J.; Cuppen, E.; Nijman, I.J.; Prins, P. Sambamba: Fast processing of NGS alignment formats. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 2032–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackman, S.D.; Vandervalk, B.P.; Mohamadi, H.; Chu, J.; Yeo, S.; Hammond, S.A.; Jahesh, G.; Khan, H.; Coombe, L.; Warren, R.L. ABySS 2.0: Resource-efficient assembly of large genomes using a Bloom filter. Genome Res. 2017, 27, 768–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 7.0 for bigger datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K. Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions when there are strong transition-transversion and G+ C-content biases. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1992, 9, 678–687. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jukes, T.H.; Cantor, C.R. Evolution of protein molecules. Mammal. Prot. Metab. 1969, 3, 132. [Google Scholar]
- Kimura, M. A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol. Evol. 1980, 16, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plasil, M. Comparative genomics of the major histocompatibility complex MHC. Ph.D. Thesis, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic, 26 October 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cantarel, B.L.; Korf, I.; Robb, S.M.; Parra, G.; Ross, E.; Moore, B.; Holt, C.; Alvarado, A.S.; Yandell, M. MAKER: An easy-to-use annotation pipeline designed for emerging model organism genomes. Genome Res. 2008, 18, 188–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, C.; Yandell, M. MAKER2: An annotation pipeline and genome-database management tool for second-generation genome projects. BMC Bioinformatics 2011, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrer, R.A. Synima: A Synteny imaging tool for annotated genome assemblies. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, W.M. Tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Lett. 2013, 328, 222–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, S.; An, P.; Zhang, R.; He, X.; Yin, G.; Min, W. Etk/Bmx as a tumor necrosis factor receptor type 2-specific kinase: Role in endothelial cell migration and angiogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 7512–7523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odbileg, R.; Konnai, S.; Ohashi, K.; Onuma, M. Molecular cloning and phylogenetic analysis of inflammatory cytokines of Camelidae (llama and camel). J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2005, 67, 921–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ranjan, S.; Bhushan, B.; Panigrahi, M.; Kumar, A.; Deb, R.; Kumar, P.; Sharma, D. Association and expression analysis of single nucleotide polymorphisms of partial tumor necrosis factor alpha gene with mastitis in crossbred cattle. Anim. Biotechnol. 2015, 26, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lendez, P.A.; Passucci, J.A.; Poli, M.A.; Gutierrez, S.E.; Dolcini, G.L.; Ceriani, M.C. Association of TNF-α gene promoter region polymorphisms in bovine leukemia virus (BLV)-infected cattle with different proviral loads. Arch. Virol. 2015, 160, 2001–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Aoki, Y.; Magata, F.; Miyamoto, A.; Kawashima, C.; Hojo, T.; Okuda, K.; Shirasuna, K.; Shimizu, T. The effect of single nucleotide polymorphisms in the tumor necrosis factor-α gene on reproductive performance and immune function in dairy cattle. J. Reprod. Develop. 2014, 60, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitzer, U.; Gerdes, J.; Müller-Quernheim, J. Genotyping in the MHC locus: Potential for defining predictive markers in sarcoidosis. Resp. Res. 2001, 3, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallya, M.; Campbell, R.D.; Aguado, B. Characterization of the five novel Ly-6 superfamily members encoded in the MHC, and detection of cells expressing their potential ligands. Protein. Sci. 2006, 15, 2244–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trowsdale, J.; Hanson, I.; Mockridge, I.; Beck, S.; Townsendt, A.; Kelly, A. Sequences encoded in the class II region of the MHC related to the ’ABC’ superfamily of transporters. Nature 1990, 348, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, J. Co-evolution with chicken class I genes. Immunol. Rev. 2015, 267, 56–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Praest, P.; Luteijn, R.D.; Brak-Boer, I.G.J.; Lanfermeijer, J.; Hoelen, H.; Ijgosse, L.; Costa, A.I.; Gorham, R.D.; Lebbink, R.J.; Wiertz, E. The influence of TAP1 and TAP2 gene polymorphisms on TAP function and its inhibition by viral immune evasion proteins. Mol. Immunol. 2018, 101, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulski, J.K.; Shiina, T.; Anzai, T.; Kohara, S.; Inoko, H. Comparative genomic analysis of the MHC: The evolution of class I duplication blocks, diversity and complexity from shark to man. Immunol. Rev. 2002, 190, 95–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viļuma, A.; Mikko, S.; Hahn, D.; Skow, L.; Andersson, G.; Bergström, T.F. Genomic structure of the horse major histocompatibility complex class II region resolved using PacBio long-read sequencing technology. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijacki, J.; (Department of Animal Morphology, Physiology and Genetics, Mendel University, Brno, Czech Republic). Personal communication, 2019.
- Wang, Q.; Yang, C. The phylogeny of the Cetartiodactyla based on complete mitochondrial genomes. Int. J. Biol. 2013, 5, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Mallya, M.; Campbell, R.D.; Aguado, B. Transcriptional analysis of a novel cluster of LY-6 family members in the human and mouse major histocompatibility complex: Five genes with many splice forms. Genomics 2002, 80, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birch, J.; Sanjuan, C.D.J.; Guzman, E.; Ellis, S.A. Genomic location and characterisation of MIC genes in cattle. Immunogenetics 2008, 60, 477–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renard, C.; Vaiman, M.; Chiannilkulchai, N.; Cattolico, L.; Robert, C.; Chardon, P. Sequence of the pig major histocompatibility region containing the classical class I genes. Immunogenetics 2001, 53, 490–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Futas, J.; Oppelt, J.; Jelinek, A.; Elbers, J.P.; Wijacki, J.; Knoll, A.; Burger, P.A.; Horin, P. Natural killer cell receptor genes in camels: Another mammalian model. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






| Locus | Camelus bactrianus (n) | Camelus dromedarius (n) |
|---|---|---|
| TNFA | 21 | 22 |
| TAP1 | 10 | 8 |
| Ly6G6C | 10 | 10 |
| Ly6G6D | 10 | 10 |
| Ly6G6E | 10 | 10 |
| Ly6G6F | 10 | 10 |
| Name | Sequence 5’ → 3’ | Locus | Tm (°C) | Product Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TAP1-1-F | CATTACCCCAGTGTGGACTTCT | TAP1 | 64.4 | 8268 |
| TAP1-1-R | GCAACCAAAGGAAATTGAAAAC | |||
| LY6G6C-1-F | GGAGGGACCGTTGGAATTAT | LY6G6C | 68.0 | 3491 |
| LY6G6C-1-R | GGCGGCTTTTCTGTCAATAG | |||
| LY6G6D-1-F | CCTCCCCTTTTATTGCCCTA | LY6G6D | 68.0 | 2479 |
| LY6G6D-1-R | CCCCATATCACTCCTTCAGC | |||
| LY6G6E-1-F | CACAAGTGGTCACGGTCTCT | LY6G6E | 68.0 | 4703 |
| LY6G6E-1-R | GAGTGCTACTTCCCAGTCCAG | |||
| LY6G6F-1-F | GCGTTTATCTGGGCTCTGTT | LY6G6F | 65.0 | 3854 |
| LY6G6F-1-R | CCACCCTGTCACTGGCTACT | |||
| TNF-1-F | TGCCTGAGTGTCTGAAAGTCC | TNFA | 66.0 | 3667 |
| TNF-1-R | CCCACATACACAGCAGGAACT |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Plasil, M.; Wijkmark, S.; Elbers, J.P.; Oppelt, J.; Burger, P.A.; Horin, P. The Major Histocompatibility Complex of Old World Camels—A Synopsis. Cells 2019, 8, 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101200
Plasil M, Wijkmark S, Elbers JP, Oppelt J, Burger PA, Horin P. The Major Histocompatibility Complex of Old World Camels—A Synopsis. Cells. 2019; 8(10):1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101200
Chicago/Turabian StylePlasil, Martin, Sofia Wijkmark, Jean Pierre Elbers, Jan Oppelt, Pamela Anna Burger, and Petr Horin. 2019. "The Major Histocompatibility Complex of Old World Camels—A Synopsis" Cells 8, no. 10: 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101200
APA StylePlasil, M., Wijkmark, S., Elbers, J. P., Oppelt, J., Burger, P. A., & Horin, P. (2019). The Major Histocompatibility Complex of Old World Camels—A Synopsis. Cells, 8(10), 1200. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101200






