C9orf72 Proteins Regulate Autophagy and Undergo Autophagosomal or Proteasomal Degradation in a Cell Type-Dependent Manner
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. shRNA and cDNA Constructs
2.2. Secondary Cell Culture, Transfection, and Treatments
2.3. Immunofluorescence Studies
2.4. Primary Mouse Cortical Cell Culture, Virus Vector Transduction and Treatments
2.5. Protein Extraction from Cells and Western Blotting
2.6. Proteasomal Activity Measurement
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
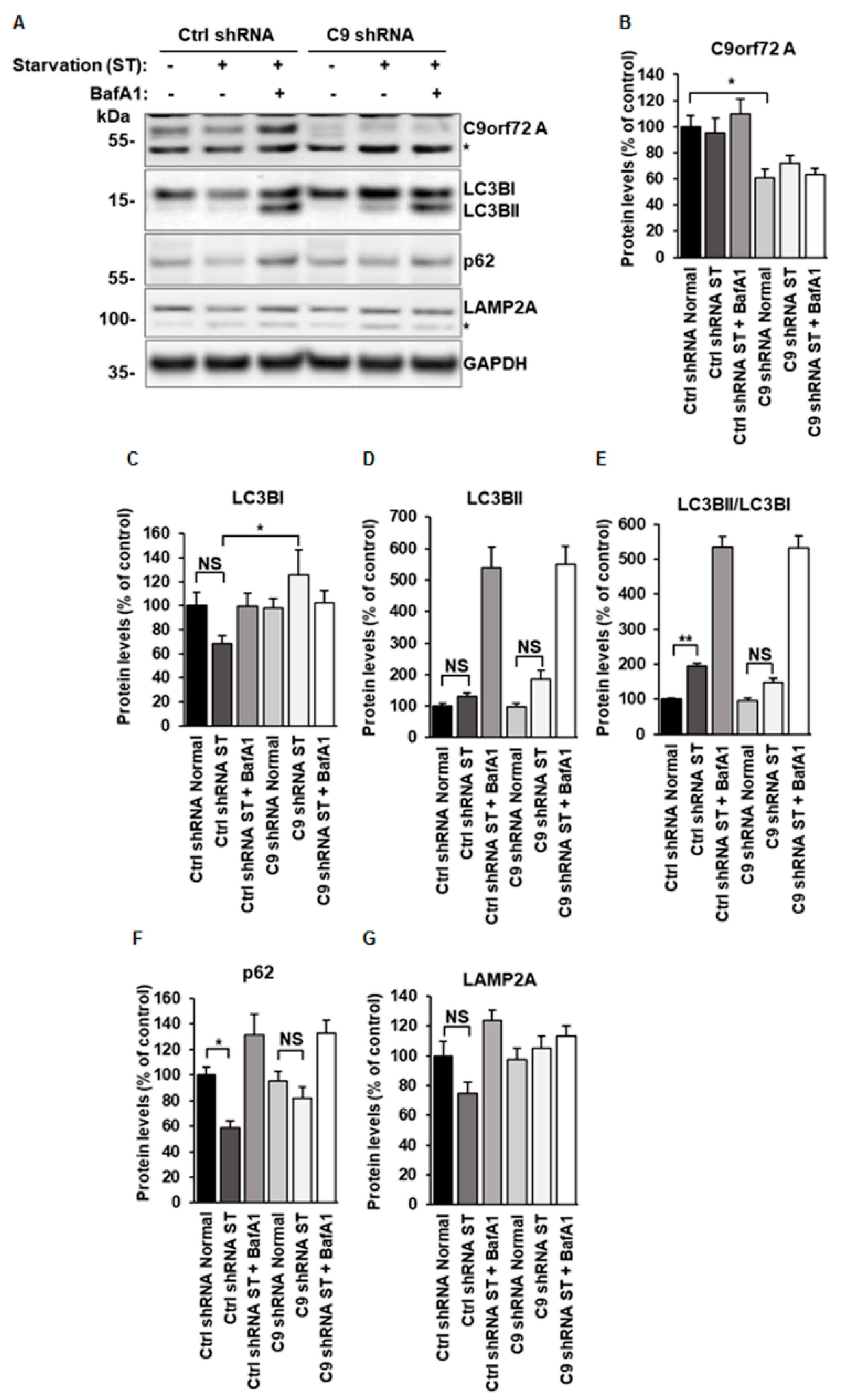
3.1. C9orf72 Knockdown Leads to Decreased Autophagy Induction in N2a Cells
3.2. Overexpression of C9orf72 Isoform A Does Not Affect Autophagy, But Its Levels are Decreased after Induction of Autophagy in N2a Cells
3.3. C9orf72 Protein Isoform A Levels Are Increased after Proteasomal Inhibition in N2a Cells and Primary Neurons
3.4. Decreased C9orf72 Protein Isoform A Levels in Serum-Starved N2a Cells Are Restored by Proteasomal Inhibition
3.5. Proteasomal Activity Is Slightly Decreased in N2a Cells Upon C9orf72 Knockdown but Not Changed After C9orf72 Protein Isoform A Overexpression
3.6. C9orf72 Protein Isoform A Levels Are Unchanged After BafA1 Treatment in N2a Cells, but Decreased in Mouse Primary Cortical Neurons
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALS | Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| BafA1 | Bafilomycin A1 |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| C9FTD/ALS | Concomitant FTD/ALS caused by C9orf72 hexanucleotide repeat expansion |
| C9orf72 | Chromosome 9 open reading frame 72 gene |
| C9orf72 | C9orf72 protein coded by C9orf72 |
| DENN | Differentially expressed in normal and neoplastic cells |
| DPR | Dipeptide repeat |
| FTD | Frontotemporal dementia |
| FTLD | Frontotemporal lobar degeneration |
| GEF | Guanosine exchange factor |
| HRE | Hexanucleotide repeat expansion |
| LC3B | Microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| p62/SQSTMI | Sequestosome 1 |
| PE | Phosphatidylethanolamine |
| SMCR8 | Smith-Magenis syndrome chromosome region candidate 8 |
| TDP-43 | TAR DNA-binding protein 43 |
| UPS | Ubiquitin-proteasome system |
| WDR41 | WD repeat-containing protein 41 |
References
- Vieira, R.T.; Caixeta, L.; Machado, S.; Silva, A.C.; Nardi, A.E.; Arias-Carrión, O.; Carta, M.G. Epidemiology of Early-Onset Dementia: A Review of the Literature. Clin. Pract. Epidemiol. Ment. Health 2013, 9, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, J.; Spina, S.; Miller, B.L. Frontotemporal Dementia. Lancet 2015, 386, 1672–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swinnen, B.; Robberecht, W. The Phenotypic Variability of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2014, 10, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renton, A.E.; Majounie, E.; Waite, A.; Simón-Sánchez, J.; Rollinson, S.; Gibbs, J.R.; Schymick, J.C.; Laaksovirta, H.; van Swieten, J.C.; Myllykangas, L.; et al. A Hexanucleotide Repeat Expansion in C9ORF72 Is the Cause of Chromosome 9p21-Linked ALS-FTD. Neuron 2011, 72, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeJesus-Hernandez, M.; Mackenzie, I.R.; Boeve, B.F.; Boxer, A.L.; Baker, M.; Rutherford, N.J.; Nicholson, A.M.; Finch, N.A.; Flynn, H.; Adamson, J.; et al. Expanded GGGGCC Hexanucleotide Repeat in Noncoding Region of C9ORF72 Causes Chromosome 9p-Linked FTD and ALS. Neuron 2011, 72, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majounie, E.; Renton, A.E.; Mok, K.; Dopper, E.G.; Waite, A.; Rollinson, S.; Chiò, A.; Restagno, G.; Nicolaou, N.; Simon-Sanchez, J.; et al. Frequency of the C9orf72 Hexanucleotide Repeat Expansion in Patients with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia: A Cross-Sectional Study. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, K.; Weng, S.-M.; Arzberger, T.; May, S.; Rentzsch, K.; Kremmer, E.; Schmid, B.; Kretzschmar, H.A.; Cruts, M.; Van Broeckhoven, C.; et al. The C9orf72 GGGGCC Repeat Is Translated into Aggregating Dipeptide-Repeat Proteins in FTLD/ALS. Science 2013, 339, 1335–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, T.F.; Bieniek, K.F.; Zhang, Y.-J.; Jansen-West, K.; Ash, P.E.A.; Caulfield, T.; Daughrity, L.; Dunmore, J.H.; Castanedes-Casey, M.; Chew, J.; et al. Antisense Transcripts of the Expanded C9ORF72 Hexanucleotide Repeat Form Nuclear RNA Foci and Undergo Repeat-Associated Non-ATG Translation in C9FTD/ALS. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 829–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waite, A.J.; Bäumer, D.; East, S.; Neal, J.; Morris, H.R.; Ansorge, O.; Blake, D.J. Reduced C9orf72 Protein Levels in Frontal Cortex of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Degeneration Brain with the C9ORF72 Hexanucleotide Repeat Expansion. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 1779.e5–1779.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frick, P.; Sellier, C.; Mackenzie, I.R.A.; Cheng, C.-Y.; Tahraoui-Bories, J.; Martinat, C.; Pasterkamp, R.J.; Prudlo, J.; Edbauer, D.; Oulad-Abdelghani, M.; et al. Novel Antibodies Reveal Presynaptic Localization of C9orf72 Protein and Reduced Protein Levels in C9orf72 Mutation Carriers. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balendra, R.; Isaacs, A.M. C9orf72-Mediated ALS and FTD: Multiple Pathways to Disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2018, 14, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; MacNair, L.; McGoldrick, P.; McKeever, P.M.; McLean, J.R.; Zhang, M.; Keith, J.; Zinman, L.; Rogaeva, E.; Robertson, J. Isoform-Specific Antibodies Reveal Distinct Subcellular Localizations of C9orf72 in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2015, 78, 568–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, T.P.; Daniels, R.D.; Gatta, A.T.; Wong, L.H.; Hayes, M.J. The Product of C9orf72, a Gene Strongly Implicated in Neurodegeneration, Is Structurally Related to DENN Rab-GEFs. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marat, A.L.; Dokainish, H.; McPherson, P.S. DENN Domain Proteins: Regulators of Rab GTPases. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 13791–13800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farg, M.A.; Sundaramoorthy, V.; Sultana, J.M.; Yang, S.; Atkinson, R.A.K.; Levina, V.; Halloran, M.A.; Gleeson, P.A.; Blair, I.P.; Soo, K.Y.; et al. C9ORF72, Implicated in Amytrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia, Regulates Endosomal Trafficking. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 3579–3595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellier, C.; Campanari, M.-L.; Julie Corbier, C.; Gaucherot, A.; Kolb-Cheynel, I.; Oulad-Abdelghani, M.; Ruffenach, F.; Page, A.; Ciura, S.; Kabashi, E.; et al. Loss of C9ORF72 Impairs Autophagy and Synergizes with PolyQ Ataxin-2 to Induce Motor Neuron Dysfunction and Cell Death. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 1276–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.P.; Smith, E.F.; Bauer, C.S.; Moller, A.; Hautbergue, G.M.; Ferraiuolo, L.; Myszczynska, M.A.; Higginbottom, A.; Walsh, M.J.; Whitworth, A.J.; et al. The C9orf72 Protein Interacts with Rab1a and the ULK1 Complex to Regulate Initiation of Autophagy. EMBO J. 2016, 35, 1656–1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Chen, L.; Swaminathan, K.; Herrlinger, S.; Lai, F.; Shiekhattar, R.; Chen, J.F. A C9ORF72/SMCR8-Containing Complex Regulates ULK1 and Plays a Dual Role in Autophagy. Sci. Adv. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoki, Y.; Manzano, R.; Lee, Y.; Dafinca, R.; Aoki, M.; Douglas, A.G.L.; Varela, M.A.; Sathyaprakash, C.; Scaber, J.; Barbagallo, P.; et al. C9orf72 and RAB7L1 Regulate Vesicle Trafficking in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Frontotemporal Dementia. Brain 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wandinger-Ness, A.; Zerial, M. Rab Proteins and the Compartmentalization of the Endosomal System. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Iyer, L.M.; He, F.; Aravind, L. Discovery of Novel DENN Proteins: Implications for the Evolution of Eukaryotic Intracellular Membrane Structures and Human Disease. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yerbury, J.J.; Ooi, L.; Dillin, A.; Saunders, D.N.; Hatters, D.M.; Beart, P.M.; Cashman, N.R.; Wilson, M.R.; Ecroyd, H. Walking the Tightrope: Proteostasis and Neurodegenerative Disease. J. Neurochem. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lilienbaum, A. Relationship between the Proteasomal System and Autophagy. Int. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2013, 4, 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, H.O.; Yadav, R.K.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. ER Stress: Autophagy Induction, Inhibition and Selection. Autophagy 2015, 11, 1956–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klionsky, D.J.; Abdelmohsen, K.; Abe, A.; Abedin, M.J.; Abeliovich, H.; Arozena, A.A.; Adachi, H.; Adams, C.M.; Adams, P.D.; Adeli, K.; et al. Guidelines for the Use and Interpretation of Assays for Monitoring Autophagy (3rd Edition). Autophagy 2016, 12, 1–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizushima, N.; Komatsu, M. Autophagy: Renovation of Cells and Tissues. Cell 2011, 147, 728–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, C.H.; Kwon, Y.T. Crosstalk and Interplay between the Ubiquitin-Proteasome System and Autophagy. Mol. Cells 2017, 40, 441–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Lan, M.; Mojsilovic-Petrovic, J.; Choi, W.H.; Safren, N.; Barmada, S.; Lee, M.J.; Kalb, R. The Proline/Arginine Dipeptide from Hexanucleotide Repeat Expanded C9ORF72 Inhibits the Proteasome. Eneuro 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Q.; Lehmer, C.; Martínez-Sánchez, A.; Rudack, T.; Beck, F.; Hartmann, H.; Pérez-Berlanga, M.; Frottin, F.; Hipp, M.S.; Hartl, F.U.; et al. In Situ Structure of Neuronal C9orf72 Poly-GA Aggregates Reveals Proteasome Recruitment. Cell 2018, 172, 696–705.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webster, C.P.; Smith, E.F.; Grierson, A.J.; De Vos, K.J. C9orf72 Plays a Central Role in Rab GTPase-Dependent Regulation of Autophagy. Small GTPases 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, P.M.; Zhou, X.; Robins, A.M.; Paushter, D.H.; Kim, D.; Smolka, M.B.; Hu, F. The ALS/FTLD Associated Protein C9orf72 Associates with SMCR8 and WDR41 to Regulate the Autophagy-Lysosome Pathway. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2016, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugolino, J.; Ji, Y.J.; Conchina, K.; Chu, J.; Nirujogi, R.S.; Pandey, A.; Brady, N.R.; Hamacher-Brady, A.; Wang, J. Loss of C9orf72 Enhances Autophagic Activity via Deregulated MTOR and TFEB Signaling. PLoS Genet. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amick, J.; Roczniak-Ferguson, A.; Ferguson, S.M. C9orf72 Binds SMCR8, Localizes to Lysosomes, and Regulates MTORC1 Signaling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leskelä, S.; Takalo, M.; Marttinen, M.; Huber, N.; Paananen, J.; Mitra, V.; Rauramaa, T.; Mäkinen, P.; Leinonen, V.; Soininen, H.; et al. Interrelationship between the Levels of C9orf72 and Amyloid-β Protein Precursor and Amyloid-β in Human Cells and Brain Samples. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 62, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natunen, T.; Takalo, M.; Kemppainen, S.; Leskelä, S.; Marttinen, M.; Kurkinen, K.M.A.; Pursiheimo, J.-P.; Sarajärvi, T.; Viswanathan, J.; Gabbouj, S.; et al. Relationship between Ubiquilin-1 and BACE1 in Human Alzheimer’s Disease and APdE9 Transgenic Mouse Brain and Cell-Based Models. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 85, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martiskainen, H.; Paldanius, K.M.A.; Natunen, T.; Takalo, M.; Marttinen, M.; Leskelä, S.; Huber, N.; Mäkinen, P.; Bertling, E.; Dhungana, H.; et al. DHCR24 Exerts Neuroprotection upon Inflammation-Induced Neuronal Death. J. Neuroinflam. 2017, 14, 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotthibundhu, A.; McDonagh, K.; von Kriegsheim, A.; Garcia-Munoz, A.; Klawiter, A.; Thompson, K.; Chauhan, K.D.; Krawczyk, J.; McInerney, V.; Dockery, P.; et al. Rapamycin Regulates Autophagy and Cell Adhesion in Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2016, 7, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshii, S.R.; Mizushima, N. Monitoring and Measuring Autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Rourke, J.G.; Bogdanik, L.; Yáñez, A.; Lall, D.; Wolf, A.J.; Muhammad, A.K.M.G.; Ho, R.; Carmona, S.; Vit, J.P.; Zarrow, J.; et al. C9orf72 Is Required for Proper Macrophage and Microglial Function in Mice. Science 2016, 351, 1324–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, W.Y.; Tai, Y.K.; Chang, J.-C.; Liang, J.; Tyan, S.-H.; Chen, S.; Guan, J.-L.; Zhou, H.; Shen, H.-M.; Koo, E.; et al. The ALS-FTD-Linked Gene Product, C9orf72, Regulates Neuronal Morphogenesis via Autophagy. Autophagy 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Lin, S.; Staats, K.A.; Li, Y.; Chang, W.-H.; Hung, S.-T.; Hendricks, E.; Linares, G.R.; Wang, Y.; Son, E.Y.; et al. Haploinsufficiency Leads to Neurodegeneration in C9ORF72 ALS/FTD Human Induced Motor Neurons. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 313–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leskelä, S.; Huber, N.; Rostalski, H.; Natunen, T.; Remes, A.M.; Takalo, M.; Hiltunen, M.; Haapasalo, A. C9orf72 Proteins Regulate Autophagy and Undergo Autophagosomal or Proteasomal Degradation in a Cell Type-Dependent Manner. Cells 2019, 8, 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101233
Leskelä S, Huber N, Rostalski H, Natunen T, Remes AM, Takalo M, Hiltunen M, Haapasalo A. C9orf72 Proteins Regulate Autophagy and Undergo Autophagosomal or Proteasomal Degradation in a Cell Type-Dependent Manner. Cells. 2019; 8(10):1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101233
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeskelä, Stina, Nadine Huber, Hannah Rostalski, Teemu Natunen, Anne M. Remes, Mari Takalo, Mikko Hiltunen, and Annakaisa Haapasalo. 2019. "C9orf72 Proteins Regulate Autophagy and Undergo Autophagosomal or Proteasomal Degradation in a Cell Type-Dependent Manner" Cells 8, no. 10: 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101233
APA StyleLeskelä, S., Huber, N., Rostalski, H., Natunen, T., Remes, A. M., Takalo, M., Hiltunen, M., & Haapasalo, A. (2019). C9orf72 Proteins Regulate Autophagy and Undergo Autophagosomal or Proteasomal Degradation in a Cell Type-Dependent Manner. Cells, 8(10), 1233. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8101233





