Associations between Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4–A Proinflammatory Adipokine and Insulin Resistance, Gestational and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4
3. Relationship between FABP4 and PPARγ
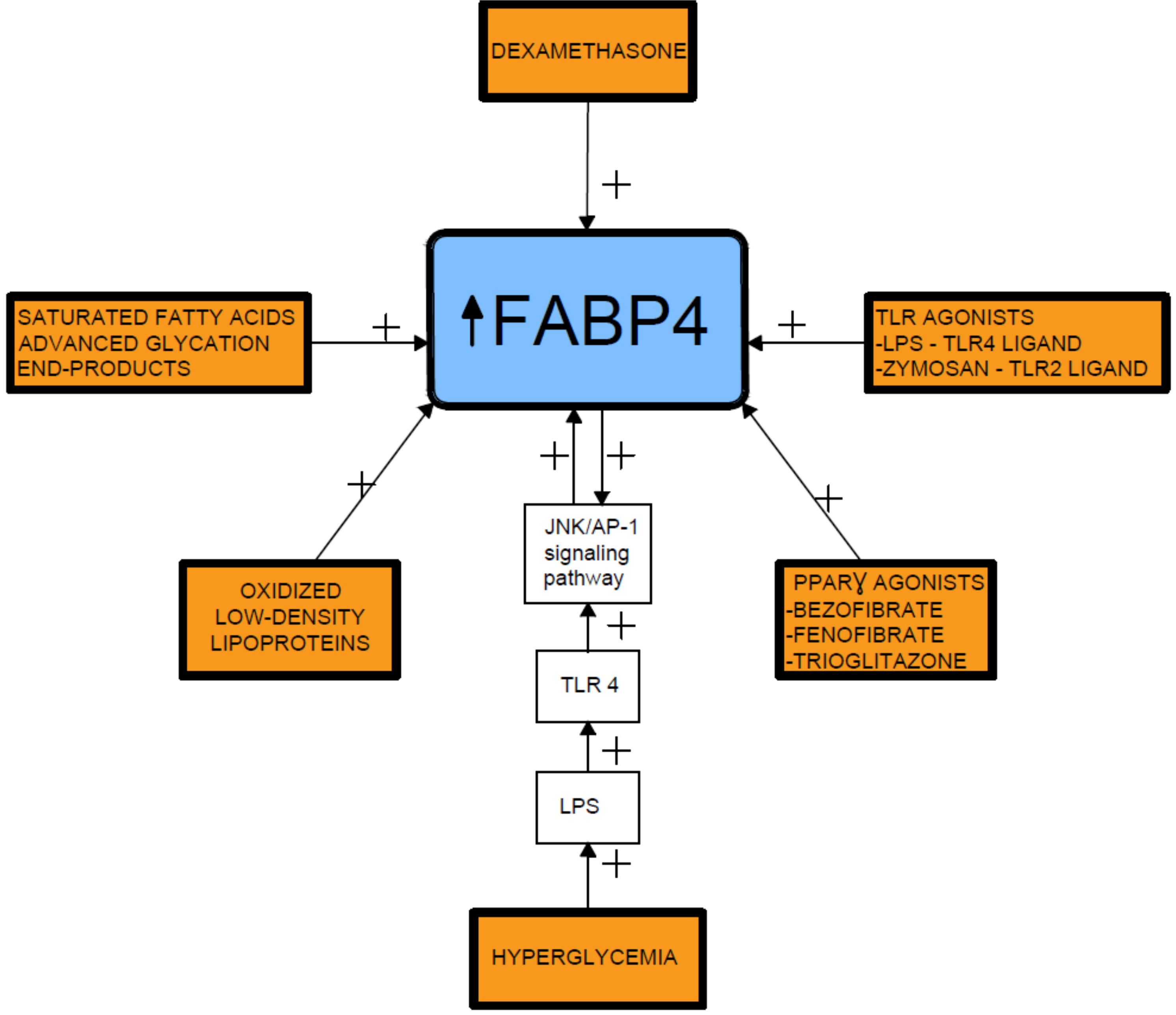
4. Relationship between FABP4 and Diseases of Civilization
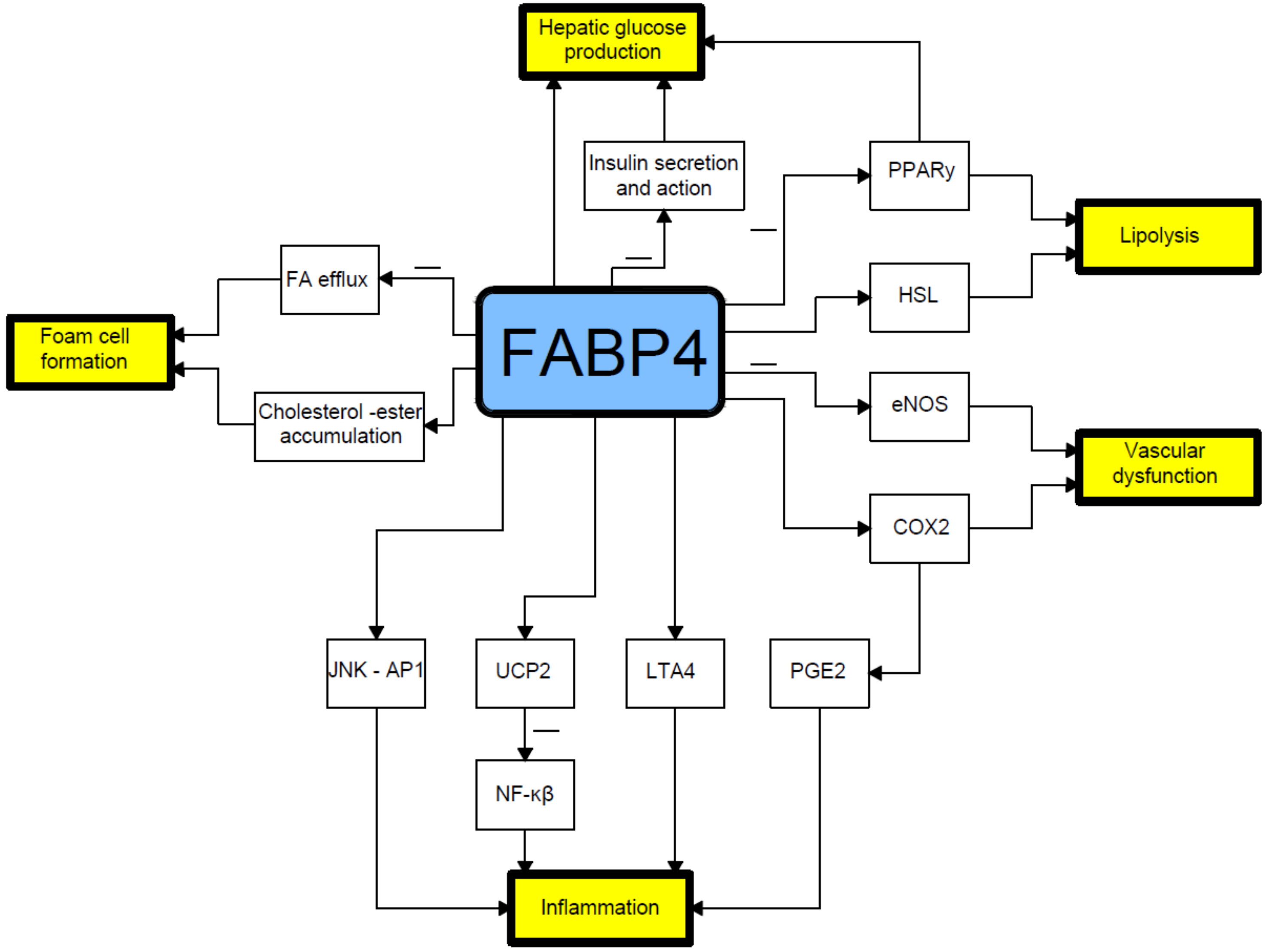
5. Associations of FABP4 with Adipogenesis and Inflammation
6. Relationship between FABP4 and Insulin Resistance
7. Relationship between FABP4 and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
8. Relationship between FABP4 and T2DM and its Complications
9. Relationship between FABP4 and Diabetic Retinopathy
10. Relationship between FABP4 and Diabetic Nephropathy
11. Relationship between FABP4 and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Blumberg, J.; Ballares, V.; Durbin, J.L. Ethnic variations on gestational diabetes mellitus and evidence-based first-line interventions. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 31, 2641–2647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Patro-Małysza, J.; Trojnar, M.; Skórzyńska-Dziduszko, K.E.; Bartosiewicz, J.; Oleszczuk, J.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4-An "Inauspicious" Adipokine-In Serum and Urine of Post-Partum Women with Excessive Gestational Weight Gain and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. J. Clin. Med. 2018, 7, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolic, D.; Al-Rasadi, K.; Al Busaidi, N.; Al-Waili, K.; Banerjee, Y.; Al-Hashmi, K.; Montalto, G.; Rizvi, A.A.; Rizzo, M.; Al-Dughaishi, T. Incretins, Pregnancy, and Gestational Diabetes. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 597–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skórzyńska-Dziduszko, K.E.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Patro-Małysza, J.; Olszewska, A.; Zaborowski, T.; Małecka-Massalska, T. An Interplay between obesity and inflammation in gestational diabetes mellitus. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2016, 17, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marciniak, A.; Patro-Małysza, J.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Marciniak, B.; Oleszczuk, J.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B. Fetal programming of the metabolic syndrome. Taiwan. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 56, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Y.; Kapoor, D.; Josyula, L.K.; Praveen, D.; Naheed, A.; Desai, A.K.; Pathmeswaran, A.; de Silva, H.A.; Lombard, C.B.; Shamsul Alam, D.; et al. A lifestyle intervention programme for the prevention of Type 2 diabetes mellitus among South Asian women with gestational diabetes mellitus [LIVING study]: protocol for a randomized trial. Diabet. Med. 2019, 36, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellamy, L.; Casas, J.; Hingorani, A.; Williams, D. Type 2 diabetes mellitus after gestational diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2009, 373, 1773–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huopio, H.; Hakkarainen, H.; Pääkkönen, M.; Kuulasmaa, T.; Voutilainen, R.; Heinonen, S.; Cederberg, H. Long-Term changes in glucose metabolism after gestational diabetes: A double cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2014, 14, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiefari, E.; Arcidiacono, B.; Foti, D.; Brunetti, A. Gestational diabetes mellitus: an updated overview. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2017, 40, 899–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Z.; Tu, W.J.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Q.; Liu, Q.; Sun, L.; Yu, L. Circulating Serum Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 Levels Predict the Development of Diabetic Retinopathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 187, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, H.; Tao, H.; Weng, Z.; Zhao, X. Plasma fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4) as a novel biomarker to predict gestational diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 2016, 53, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Calvo, R.; Girona, J.; Alegret, J.M.; Bosquet, A.; Ibarretxe, D.; Masana, L. Role of the fatty acid-binding protein 4 in heart failure and cardiovascular disease. J. Endocrinol. 2017, 233, R173–R184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, M.; Furuhashi, M.; Okazaki, Y.; Mita, T.; Fuseya, T.; Ohno, K.; Ishimura, S.; Yoshida, H.; Miura, T. Ectopic expression of fatty acid-binding protein 4 in the glomerulus is associated with proteinuria and renal dysfunction. Nephron. Clin. Pract. 2014, 128, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, M.; Ishimura, S.; Ota, H.; Miura, T. Lipid chaperones and metabolic inflammation. Int. J. Inflam. 2011, 2011, 642612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kucharski, M.; Kaczor, U. Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 (FABP4) and the Body Lipid Balance. Folia Biologica (Kraków) 2017, 65, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, Y.; Furuhashi, M.; Tanaka, M.; Mita, T.; Fuseya, T.; Ishimura, S.; Watanabe, Y.; Hoshina, K.; Akasaka, H.; Ohnishi, H.; et al. Urinary excretion of fatty acid-binding protein 4 is associated with albuminuria and renal dysfunction. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, M.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Fatty acid-binding proteins: role in metabolic diseases and potential as drug targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, J.S.; Dyckes, D.F.; Bernlohr, D.A.; Murphy, R.C. Fatty acid binding proteins stabilize leukotriene A4: Competition with arachidonic acid but not other lipoxygenase products. J. Lipid Res. 2004, 45, 2138–2144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.J.; Wise, L.S.; Berkowitz, R.; Wan, C.; Rubin, C.S. Insulin-like growth factor-I is an essential regulator of the differentiation of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 9402–9408. [Google Scholar]
- Makowski, L.; Brittingham, K.C.; Reynolds, J.M.; Suttles, J.; Hotamisligil, G.S. The fatty acid-binding protein, aP2, coordinates macrophage cholesterol trafficking and inflammatory activity. Macrophage expression of aP2 impacts peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and IkappaB kinase activities. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 12888–12895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashkin, P.N.; Jain, N.; Miller, Y.I.; Rissing, B.A.; Huo, Y.; Keller, S.R.; Vandenhoff, G.E.; Nadler, J.L.; McIntyre, T.M. Insulin and glucose play a role in foam cell formation and function. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2006, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Siersbaek, R.; Nielsen, R.; Mandrup, S. PPARgamma in adipocyte differentiation and metabolism—novel insights from genome-wide studies. FEBS Lett. 2010, 584, 3242–3249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.; Ma, C.; Chen, L.; Luo, D.; Chen, R.; Liang, F. Mechanistic Insights Into the Interaction Between Transcription Factors and Epigenetic Modifications and the Contribution to the Development of Obesity. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2018, 9, 370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizukami, H.; Takahashi, K.; Inaba, W.; Tsuboi, K.; Osonoi, S.; Yoshida, T.; Yagihashi, S. Involvement of oxidative stress-induced DNA damage, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and autophagy deficits in the decline of β-cell mass in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2014, 37, 1966–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehrke, M.; Lazar, M.A. The many faces of PPARg. Cell 2005, 123, 993–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.J.; Liang, Y.; Hong, R.; Patel, S.; Natu, V.; Sridhar, K.; Jenkins, A.; Bernlohr, D.A.; Kraemer, F.B. Characterization of the functional interaction of adipocyte lipid-binding protein with hormone-sensitive lipase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 49443–49448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 in Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prentice, K.J.; Saksi, J.; Hotamisligil, G.S. Adipokine FABP4 integrates energy stores and counter regulatory metabolic responses. J. Lipid Res. 2019, pii: jlr.S091793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M.; Saitoh, S.; Shimamoto, K.; Miura, T. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 (FABP4): Pathophysiological Insights and Potent Clinical Biomarker of Metabolic and Cardiovascular Diseases. Clin. Med. Insights Cardiol. 2015, 8, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.Y.; Xiao, R.; Li, C.P.; Huangfu, J.; Mao, J.F. Increased plasma levels of FABP4 and PTEN is associated with more severe insulin resistance in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Med. Sci. Monit. 2015, 21, 426–431. [Google Scholar]
- Tso, A.W.; Xu, A.; Sham, P.C.; Wat, N.M.; Wang, Y.; Fong, C.H.; Cheung, B.M.; Janus, E.D.; Lam, K.S. Serum adipocyte fatty acid binding protein as a new biomarker predicting the development of type 2 diabetes: A 10-year prospective study in a Chinese cohort. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2667–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Lee, S.J.; Kook, S.Y.; Ahn, T.G.; Lee, J.Y.; Hwang, J.Y. Serum from pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus increases the expression of FABP4 mRNA in primary subcutaneous human pre-adipocytes. Obstet. Gynecol. Sci. 2017, 60, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Micaelo, N.; Rodríguez-Calvo, R.; Guaita-Esteruelas, S.; Heras, M.; Girona, J.; Masana, L. Extracellular FABP4 uptake by endothelial cells is dependent on cytokeratin 1 expression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Biol. Lipids 2018, 1864, 234–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabia, B.; Andrade, S.; Carreira, M.C.; Casanueva, F.F.; Crujeiras, A.B. A role for novel adipose tissue-secreted factors in obesity-related carcinogenesis. Obes. Rev. 2016, 17, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garin-Shkolnik, T.; Rudich, A.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Rubinstein, M. FABP4 attenuates PPARγ and adipogenesis and is inversely correlated with PPARγ in adipose tissues. Diabetes 2014, 63, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, J.M.; Moore, L.B.; Smith-Oliver, T.A.; Wilkison, W.O.; Kliewer, S.A. An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 12953–12956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odegaard, J.I.; Ricardo-Gonzalez, R.R.; Goforth, M.H.; Morel, C.R.; Subramanian, V.; Mukundan, L.; Red Eagle, A.; Vats, D.; Brombacher, F.; Ferrante, A.W.; et al. Macrophage-specific PPARgamma controls alternative activation and improves insulin resistance. Nature 2007, 447, 1116–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chawla, A.; Boisvert, W.A.; Lee, C.H.; Laffitte, B.A.; Barak, Y.; Joseph, S.B.; Liao, D.; Nagy, L.; Edwards, P.A.; Curtiss, L.K.; et al. A PPAR gamma-LXR-ABCA1 pathway in macrophages is involved in cholesterol efflux and atherogenesis. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 161–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralisch, S.; Fasshauer, M. Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein: a novel adipokine involved in the pathogenesis of metabolic and vascular disease? Diabetologia 2013, 56, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Wang, Y.; Xu, J.Y.; Stejskal, D.; Tam, S.; Zhang, J.; Wat, N.M.; Wong, W.K.; Lam, K.S. Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein is a plasma biomarker closely associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 405–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, A.; Tso, A.W.; Cheung, B.M.; Wang, Y.; Wat, N.M.; Fong, C.H.; Yeung, D.C.; Janus, E.D.; Sham, P.C.; Lam, K.S. Circulating adipocyte-fatty acid binding protein levels predict the development of the metabolic syndrome: a 5-year prospective study. Circulation 2007, 115, 1537–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Bi, P.; Zhao, W.; Lian, Y.; Zhu, H.; Xu, D.; Ding, J.; Wang, Q.; Yin, C. Prognostic Utility of Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Acute Ischemic Stroke. Neurotox. Res. 2018, 33, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stejskal, D.; Karpisek, M. Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein in a Caucasian population: A new marker of metabolic syndrome? Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2006, 36, 621–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabré, A.; Lázaro, I.; Girona, J.; Manzanares, J.M.; Marimón, F.; Plana, N.; Heras, M.; Masana, L. Fatty acid binding protein 4 is increased in metabolic syndrome and with thiazolidinedione treatment in diabetic patients. Atherosclerosis 2007, 195, e150–e158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, R.; Okura, T.; Fujioka, Y.; Sumi, K.; Matsuzawa, K.; Izawa, S.; Ueta, E.; Kato, M.; Taniguchi, S.I.; Yamamoto, K. Serum fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4) concentration is associated with insulin resistance in peripheral tissues, A clinical study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0179737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Rizk, S.; Bernard, C.; Lai, M.P.; Kam, D.; Storch, J.; Stark, R.E. Protocols and pitfalls in obtaining fatty acid-binding proteins for biophysical studies of ligand-protein and protein-protein interactions. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2017, 10, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.A.; Sun, X.M.; Yan, C.Y.; Liu, L.; Hao, M.W.; Liu, Q.; Jiao, X.Y.; Liang, Y.M. Hyperglycemia-induced PATZ1 negatively modulates endothelial vasculogenesis via repression of FABP4 signaling. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 477, 548–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjes, U.; Bridges, E.; McIntyre, A.; Fielding, B.A.; Harris, A.L. Fatty acid-binding protein 4, a point of convergence for angiogenic and metabolic signaling pathways in endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 23168–23176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Ren, P.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.L.; Chen, L.; Shen, Y.H. Metformin reduces lipid accumulation in macrophages by inhibiting FOXO1-mediated transcription of fatty acid-binding protein 4. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 393, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.J.; Guo, M.; Shi, X.D.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Fu, C.W. First-Trimester Serum Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 and Subsequent Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 130, 1011–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coe, N.R.; Bernlohr, D.A. Physiological properties and functions of intracellular fatty acid-binding proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1391, 287–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, K.; Cao, H.; Kono, K.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Furuhashi, M.; Uysal, K.T.; Cao, Q.; Atsumi, G.; Malone, H.; Krishnan, B.; et al. Adipocyte/macrophage fatty acid binding proteins control integrated metabolic responses in obesity and diabetes. Cell. Metab. 2005, 1, 107–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kralisch, S.; Klöting, N.; Ebert, T.; Kern, M.; Hoffmann, A.; Krause, K.; Jessnitzer, B.; Lossner, U.; Sommerer, I.; Stumvoll, M.; et al. Circulating adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein induces insulin resistance in mice in vivo. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2015, 23, 1007–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, M.; Tuncman, G.; Görgün, C.Z.; Makowski, L.; Atsumi, G.; Vaillancourt, E.; Kono, K.; Babaev, V.R.; Fazio, S.; Linton, M.F.; et al. Treatment of diabetes and atherosclerosis by inhibiting fatty-acid-binding protein aP2. Nature 2007, 447, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erbay, E.; Babaev, V.R.; Mayers, J.R.; Makowski, L.; Charles, K.N.; Snitow, M.E.; Fazio, S.; Wiest, M.M.; Watkins, S.M.; Linton, M.F.; et al. Reducing endoplasmic reticulum stress through a macrophage lipid chaperone alleviates atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, Z.; Lam, K.S.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, D.; Ding, K.; Wang, Y.; Vanhoutte, P.M.; Xu, A. Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein modulates inflammatory responses in macrophages through a positive feedback loop involving c-Jun NH2-terminal kinases and activator protein-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10273–10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hotamisligil, G.S.; Bernlohr, D.A. Metabolic functions of FABPs--mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2015, 11, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, A.J.; Thompson, B.R.; Sanders, M.A.; Bernlohr, D.A. Interaction of the adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein with the hormone-sensitive lipase: regulation by fatty acids and phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 32424–32432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, B.R.; Mazurkiewicz-Muñoz, A.M.; Suttles, J.; Carter-Su, C.; Bernlohr, D.A. Interaction of adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein (AFABP) and JAK2: AFABP/aP2 as a regulator of JAK2 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 13473–13480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Luo, H.Y.; Liu, Q.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, L.; Zhong, F.; Huang, G.; Xu, J.M.; Xu, A.M.; Zhou, Z.G.; et al. Intermittent High Glucose Exacerbates A-FABP Activation and Inflammatory Response through TLR4-JNK Signaling in THP-1 Cells. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 1319272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Luo, N.; Lopes-Virella, M.F.; Garvey, W.T. The adipocyte lipid binding protein (ALBP/aP2) gene facilitates foam cell formation in human THP-1 macrophages. Atherosclerosis 2002, 165, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazemi, M.R.; McDonald, C.M.; Shigenaga, J.K.; Grunfeld, C.; Feingold, K.R. Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein expression and lipid accumulation are increased during activation of murine macrophages by toll-like receptor agonists. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1220–1224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelton, P.D.; Zhou, L.; Demarest, K.T.; Burris, T.P. PPARgamma activation induces the expression of the adipocyte fatty acid binding protein gene in human monocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 261, 456–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, F.; Li, Z.; Ehara, T.; Yang, L.; Wang, D.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, K.; Shi, Y.; Duan, H.; et al. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 mediates apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress in mesangial cells of diabetic nephropathy. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 411, 232–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.H.; Lu, J.H.; Zheng, S.Y.; Long, T.; Li, Y.T.; Wu, W.Z.; Wang, F. Changes in serum adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein in women with gestational diabetes mellitus and normal pregnant women during mid- and late pregnancy. J. Diabetes Investig. 2016, 7, 797–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Yi, Z.; Sinha, S.; Madan, M.; Bowen, B.P.; Langlais, P.; Ma, D.; Mandarino, L.; Meyer, C. Proteomics analyses of subcutaneous adipocytes reveal novel abnormalities in human insulin resistance. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2016, 24, 1506–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourani, M.R.; Owada, Y.; Kitanaka, N.; Sakagami, H.; Hoshi, H.; Iwasa, H.; Spener, F.; Kondo, H. Occurrence of immunoreactivity for adipocyte-type fatty acid binding protein in degenerating granulosa cells in atretic antral follicles of mouse ovary. J. Mol. Histol. 2005, 36, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, W.C.; Okeke, E.; Cheung, S.; Keenan, H.; Tsui, T.; Cheng, K.; King, G.L. A cross-sectional characterization of insulin resistance by phenotype and insulin clamp in East Asian Americans with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, H.; Furuhashi, M.; Ishimura, S.; Koyama, M.; Okazaki, Y.; Mita, T.; Fuseya, T.; Yamashita, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yoshida, H.; et al. Elevation of fatty acid-binding protein 4 is predisposed by family history of hypertension and contributes to blood pressure elevation. Am. J. Hypertens. 2012, 25, 1124–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.E.; Samocha-Bonet, D.; Whitworth, P.T.; Fazakerley, D.J.; Turner, N.; Biden, T.J.; James, D.E.; Cantley, J. Identification of fatty acid binding protein 4 as an adipokine that regulates insulin secretion during obesity. Mol. Metab. 2014, 3, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greco, E.A.; Francomano, D.; Fornari, R.; Marocco, C.; Lubrano, C.; Papa, V.; Wannenes, F.; di Luigi, L.; Donini, L.M.; Lenzi, A.; et al. Negative association between trunk fat, insulin resistance and skeleton in obese women. World J. Diabetes 2013, 4, 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasshauer, M.; Blüher, M.; Stumvoll, M. Adipokines in gestational diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2014, 2, 488–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralisch, S.; Stepan, H.; Kratzsch, J.; Verlohren, M.; Verlohren, H.J.; Drynda, K.; Lössner, U.; Blüher, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Fasshauer, M. Serum levels of adipocyte fatty acid binding protein are increased in gestational diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2009, 160, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega-Senovilla, H.; Schaefer-Graf, U.; Meitzner, K.; Abou-Dakn, M.; Graf, K.; Kintscher, U.; Herrera, E. Gestational diabetes mellitus causes changes in the concentrations of adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein and other adipocytokines in cord blood. Diabetes Care 2011, 34, 2061–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zhu, Q.; Peng, H.; Du, M.; Dong, M.; Wang, H. Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 in Endometrial Epithelium Is Involved in Embryonic Implantation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 41, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Yang, H.; Zhang, W.; Shi, Y.; Qin, S.; Wei, Y.; He, Y.; Yang, W.; Jiang, S.; Jin, H. Fatty acid-binding protein 4 predicts gestational hypertension and preeclampsia in women with gestational diabetes mellitus. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wotherspoon, A.C.; Young, I.S.; McCance, D.R.; Patterson, C.C.; Maresh, M.J.; Pearson, D.W.; Walker, J.D.; Holmes, V.A. Diabetes and Pre-eclampsia Intervention Trial (DAPIT) Study Group. Serum Fatty Acid Binding Protein 4 (FABP4) Predicts Pre-eclampsia in Women With Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1827–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, H.; Wetterling, L.; Andersson-Hall, U.; Jennische, E.; Edén, S.; Holmäng, A.; Lönn, M. Adipose tissue and body composition in women six years after gestational diabetes: Factors associated with development of type 2 diabetes. Adipocyte 2018, 7, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joussen, A.M.; Poulaki, V.; Le, M.L.; Koizumi, K.; Esser, C.; Janicki, H.; Schraermeyer, U.; Kociok, N.; Fauser, S.; Kirchhof, B.; et al. A central role for inflammation in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. FASEB J. 2004, 18, 1450–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Kaur, I.; Kotwani, A. Implication of oxidative stress in progression of diabetic retinopathy. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2016, 61, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragonès, G.; Ferré, R.; Lázaro, I.; Cabré, A.; Plana, N.; Merino, J.; Heras, M.; Girona, J.; Masana, L. Fatty acid-binding protein 4 is associated with endothelial dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Atherosclerosis 2010, 213, 329–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragonès, G.; Saavedra, P.; Heras, M.; Cabré, A.; Girona, J.; Masana, L. Fatty acid-binding protein 4 impairs the insulin-dependent nitric oxide pathway in vascular endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2012, 11, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabré, A.; Lázaro, I.; Girona, J.; Manzanares, J.M.; Marimón, F.; Plana, N.; Heras, M.; Masana, L. Plasma fatty acid binding protein 4 is associated with atherogenic dyslipidemia in diabetes. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1746–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamounier-Zepter, V.; Look, C.; Alvarez, J.; Christ, T.; Ravens, U.; Schunck, W.H.; Ehrhart-Bornstein, M.; Bornstein, S.R.; Morano, I. Adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein suppresses cardiomyocyte contraction: a new link between obesity and heart disease. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 326–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peeters, W.; de Kleijn, D.P.; Vink, A.; van de Weg, S.; Schoneveld, A.H.; Sze, S.K.; van der Spek, P.J.; de Vries, J.P.; Moll, F.L.; Pasterkamp, G. Adipocyte fatty acid binding protein in atherosclerotic plaques is associated with local vulnerability and is predictive for the occurrence of adverse cardiovascular events. Eur. Heart J. 2011, 32, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agardh, H.E.; Folkersen, L.; Ekstrand, J.; Marcus, D.; Swedenborg, J.; Hedin, U.; Gabrielsen, A.; Paulsson-Berne, G. Expression of fatty acid-binding protein 4/aP2 is correlated with plaque instability in carotid atherosclerosis. J. Intern. Med. 2011, 269, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holm, S.; Ueland, T.; Dahl, T.B.; Michelsen, A.E.; Skjelland, M.; Russell, D.; Nymo, S.H.; Krohg-Sørensen, K.; Clausen, O.P.; Atar, D.; et al. Fatty Acid binding protein 4 is associated with carotid atherosclerosis and outcome in patients with acute ischemic stroke. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e28785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Ding, M.; Chiuve, S.E.; Rimm, E.B.; Franks, P.W.; Meigs, J.B.; Hu, F.B.; Sun, Q. Plasma Levels of Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4, Retinol-Binding Protein 4, High-Molecular-Weight Adiponectin, and Cardiovascular Mortality Among Men With Type 2 Diabetes: A 22-Year Prospective Study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 2259–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowski, L.; Boord, J.B.; Maeda, K.; Babaev, V.R.; Uysal, K.T.; Morgan, M.A.; Parker, R.A.; Suttles, J.; Fazio, S.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; et al. Lack of macrophage fatty-acid-binding protein aP2 protects mice deficient in apolipoprotein E against atherosclerosis. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parvanova, A.I.; Trevisan, R.; Iliev, I.P.; Dimitrov, B.D.; Vedovato, M.; Tiengo, A.; Remuzzi, G.; Ruggenenti, P. Insulin resistance and microalbuminuria: a cross-sectional, case-control study of 158 patients with type 2 diabetes and different degrees of urinary albumin excretion. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1456–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Chavez, G.; Hernandez-Ramırez, E.; Osorio-Paz, I.; Hernandez-Espinosa, C.; Salceda, R. Potential role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 1098–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, X.; Gu, Y.; Yu, H.; Wang, S.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Yuan, X.; Jia, W. Serum Adipocyte Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 Levels Are Independently Associated with Radioisotope Glomerular Filtration Rate in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Early Diabetic Nephropathy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 4578140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toruner, F.; Altinova, A.E.; Akturk, M.; Kaya, M.; Arslan, E.; Bukan, N.; Kan, E.; Yetkin, I.; Arslan, M. The relationship between adipocyte fatty acid binding protein-4, retinol binding protein-4 levels and early diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2011, 91, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeung, D.C.; Xu, A.; Tso, A.W.; Chow, W.S.; Wat, N.M.; Fong, C.H.; Tam, S.; Sham, P.C.; Lam, K.S. Circulating levels of adipocyte and epidermal fatty acid-binding proteins in relation to nephropathy staging and macrovascular complications in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 132–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Ma, X.; Luo, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiong, Q.; Pan, X.; Bao, Y.; Jia, W. Contribution of serum adipocyte fatty acid-binding protein levels to the presence of microalbuminuria in a Chinese hyperglycemic population. J. Diabetes Investig. 2017, 8, 582–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalera, A.; Tarantino, G. Could metabolic syndrome lead to hepatocarcinoma via non-alcoholic fatty liver disease? World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 9217–9228. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, K.J.; Austin, R.G.; Nazari, S.S.; Gersin, K.S.; Iannitti, D.A.; McKillop, I.H. Altered fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4) expression and function in human and animal models of hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, W.J.; Zeng, X.W.; Deng, A.; Zhao, S.J.; Luo, D.Z.; Ma, G.Z.; Wang, H.; Liu, Q. Circulating FABP4 (Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4) Is a Novel Prognostic Biomarker in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke 2017, 48, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellos, I.; Fitrou, G.; Pergialiotis, V.; Perrea, D.N.; Daskalakis, G. Serum levels of adipokines in gestational diabetes: A systematic review. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trojnar, M.; Patro-Małysza, J.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B.; Mosiewicz, J. Associations between Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4–A Proinflammatory Adipokine and Insulin Resistance, Gestational and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cells 2019, 8, 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030227
Trojnar M, Patro-Małysza J, Kimber-Trojnar Ż, Leszczyńska-Gorzelak B, Mosiewicz J. Associations between Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4–A Proinflammatory Adipokine and Insulin Resistance, Gestational and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cells. 2019; 8(3):227. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030227
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrojnar, Marcin, Jolanta Patro-Małysza, Żaneta Kimber-Trojnar, Bożena Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, and Jerzy Mosiewicz. 2019. "Associations between Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4–A Proinflammatory Adipokine and Insulin Resistance, Gestational and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus" Cells 8, no. 3: 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030227
APA StyleTrojnar, M., Patro-Małysza, J., Kimber-Trojnar, Ż., Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, B., & Mosiewicz, J. (2019). Associations between Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4–A Proinflammatory Adipokine and Insulin Resistance, Gestational and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cells, 8(3), 227. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8030227






