RAC1 Takes the Lead in Solid Tumors
Abstract
:1. Prologue
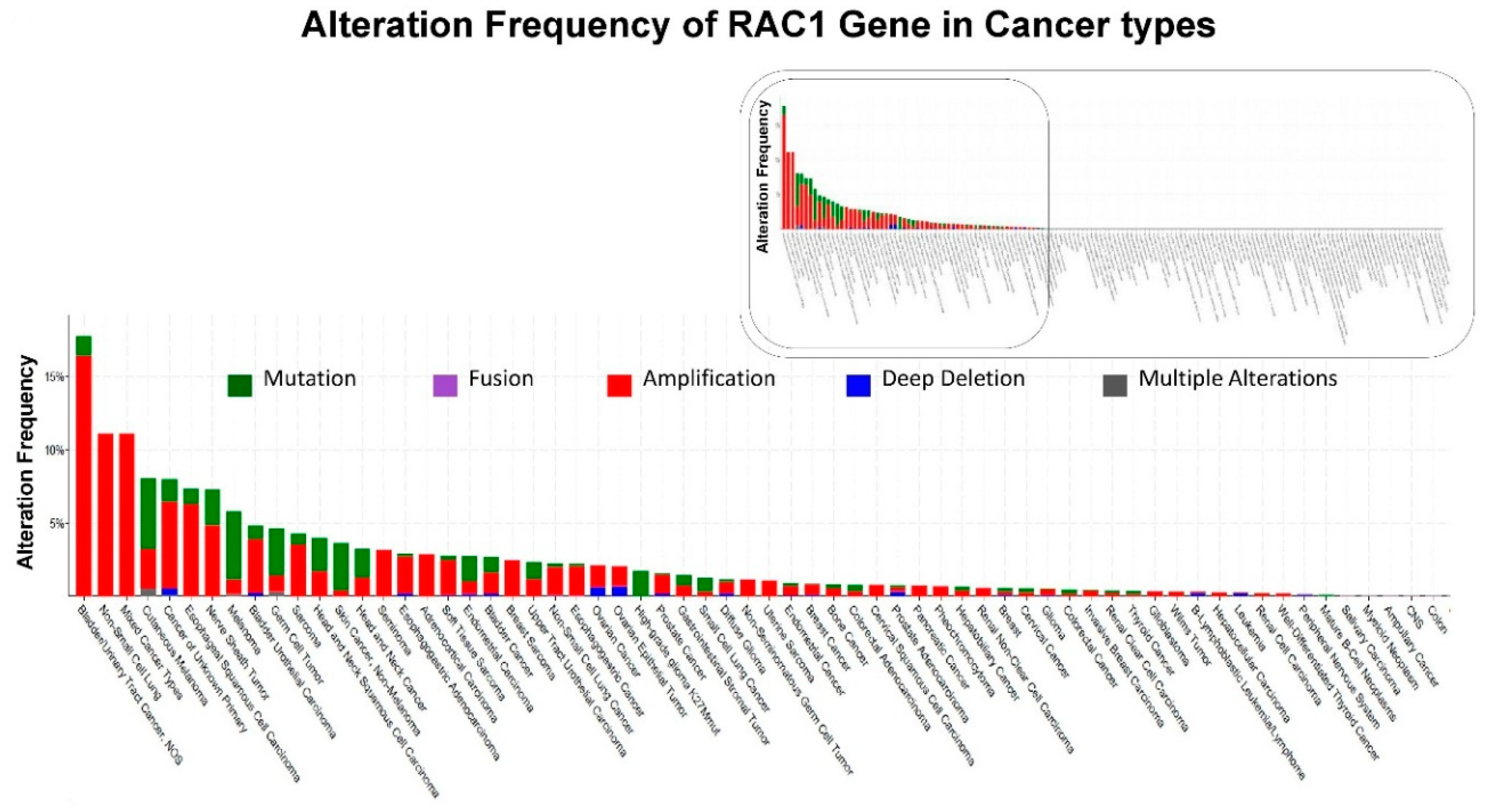
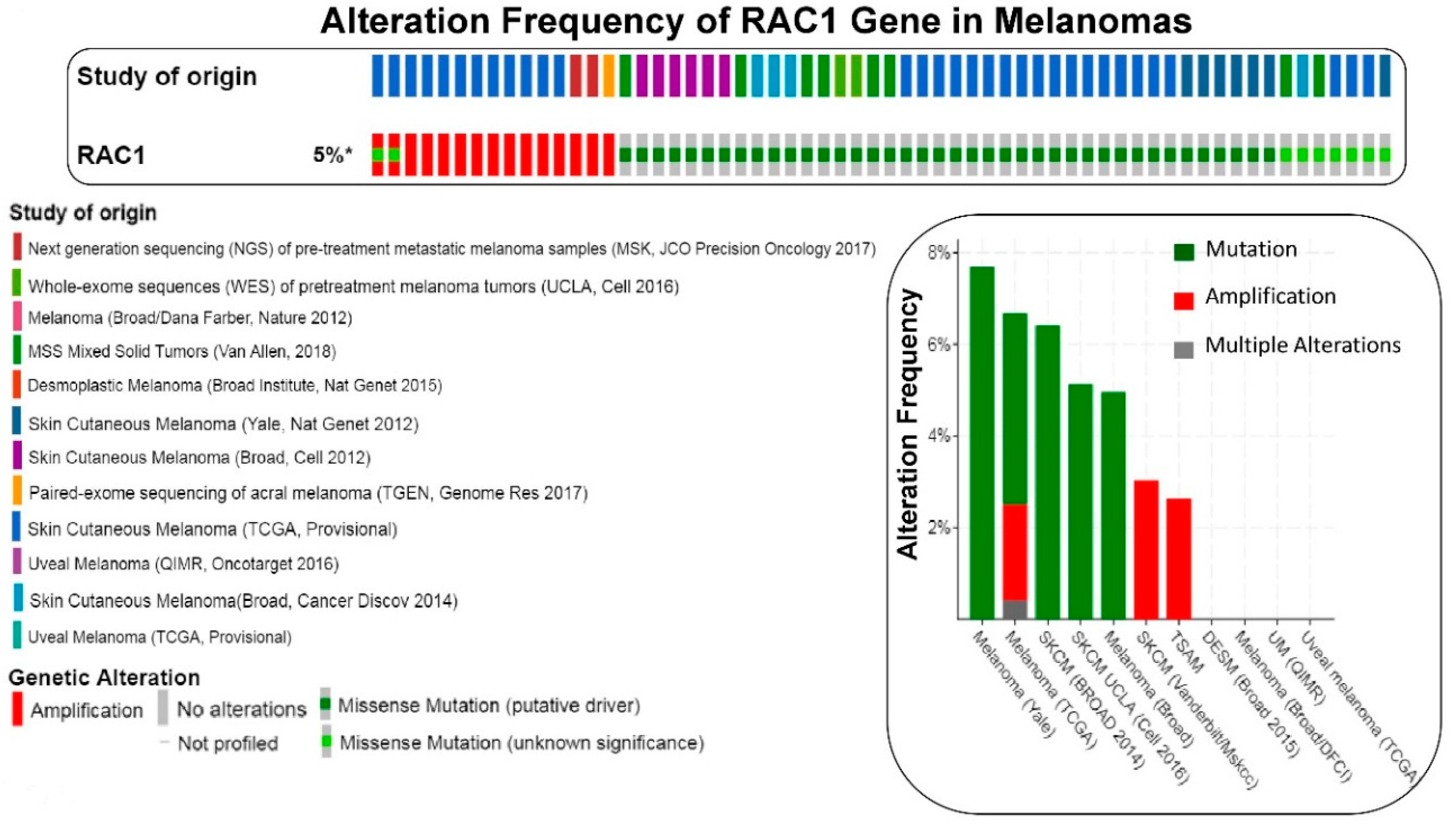
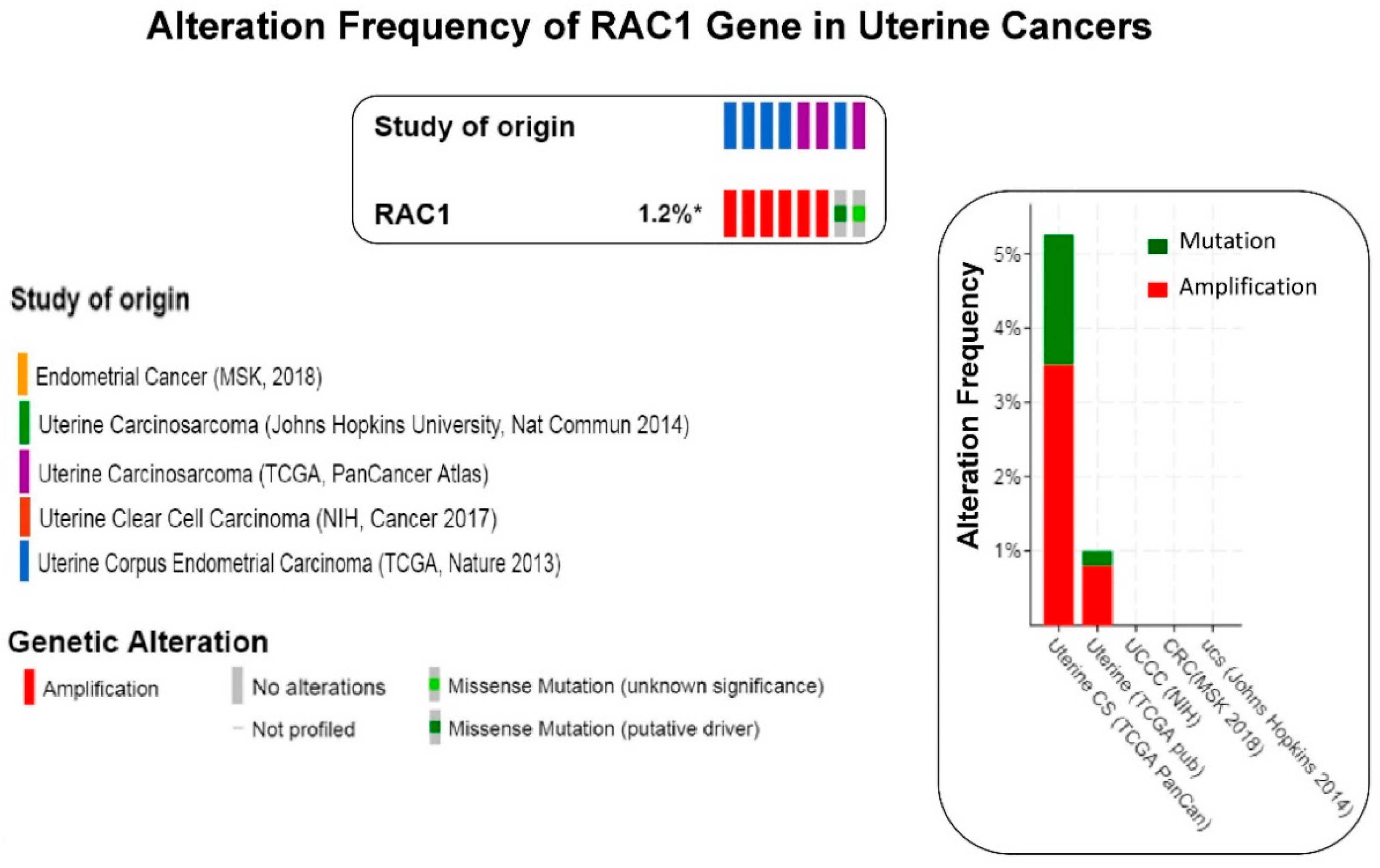
2. RAC1 and Solid Tumors
3. Sub-Cellular Location-Based Activation and Regulation of RAC1 Functions in Tumor Cells
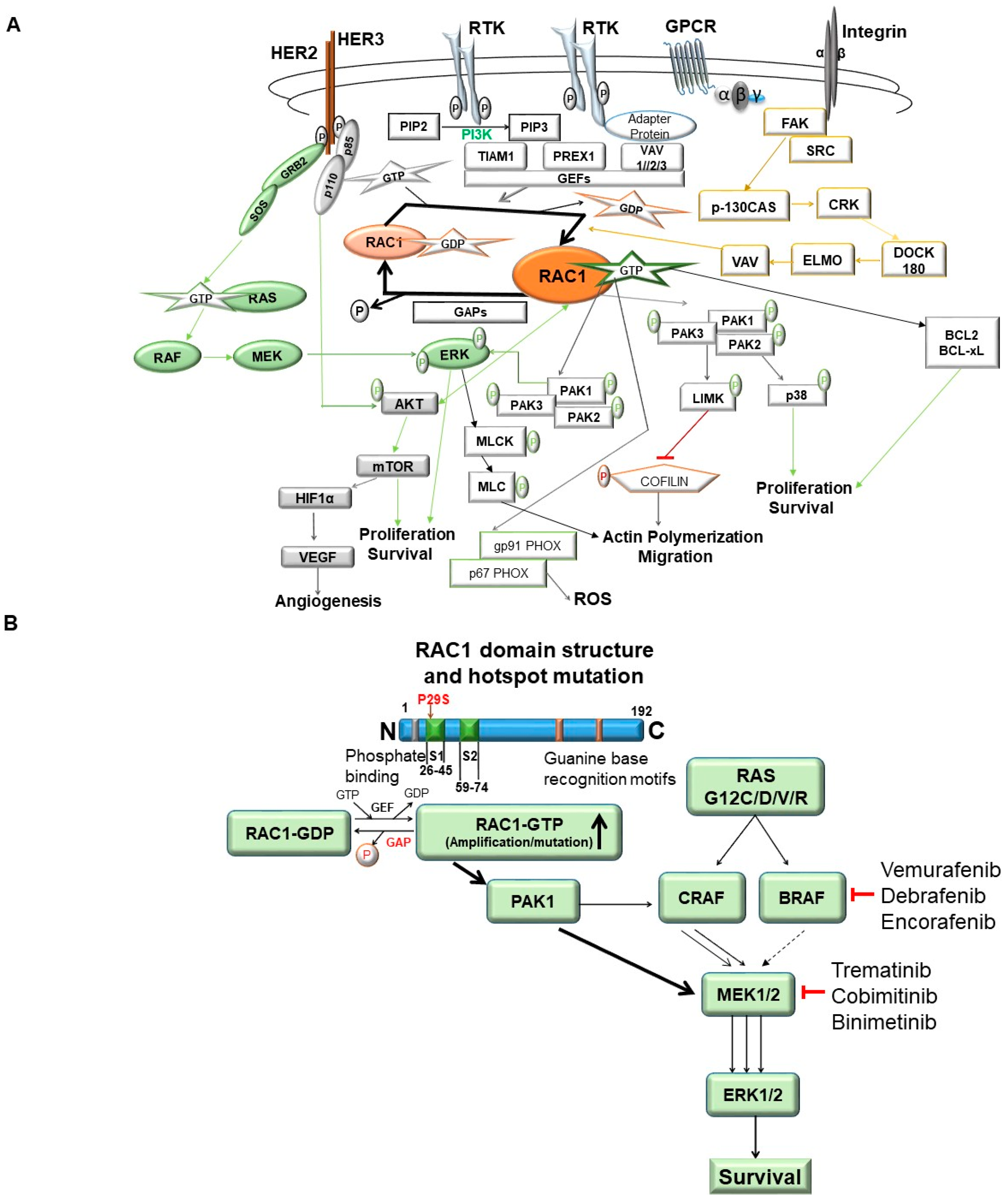
4. Cellular Signaling of RAC1 in Solid Tumors
5. RAC1 Signaling in Tumor Cell Proliferation
6. RAC1 Signaling in Tumor Cells Migration
7. RAC1 Signaling in Tumor Angiogenesis and Resistance
8. Epilogue
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yamauchi, A.; Marchal, C.C.; Molitoris, J.; Pech, N.; Knaus, U.; Towe, J.; Aktinson, S.J.; Dinauer, M.C. Rac GTPase isoform-specific regulation of NADPH oxidase and chemotaxis in murine neutrophils in vivo. Role of the C-terminal polybasic domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 953–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.W.; Kim, C.; Zhen, L.; Lowe, J.B.; Kapur, R.; Petryniak, B.; Spaetti, A.; Pollock, J.D.; Borneo, J.B.; Bradford, G.B.; et al. Deficiency of the hematopoietic cell-specific Rho family GTPase Rac2 is characterized by abnormalities in neutrophil function and host defense. Immunity 1999, 10, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, D.E.; Agaisse, H. A role for the small GTPase Rac1 in vaccinia actin-based motility. Small GTPases 2014, 5, e29038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, X.; Herbst-Robinson, K.J.; Zhang, J. Visualizing dynamic activities of signaling enzymes using genetically encodable FRET-based biosensors from designs to applications. Methods Enzymol. 2012, 504, 317–340. [Google Scholar]
- Matos, P.; Skaug, J.; Marques, B.; Beck, S.; Verissimo, F.; Gespach, C.; Boavida, M.G.; Scherer, S.W.; Jordan, P. Small GTPase Rac1: Structure, localization, and expression of the human gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 277, 741–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jordan, P.; Brazao, R.; Boavida, M.G.; Gespach, C.; Chastre, E. Cloning of a novel human Rac1b splice variant with increased expression in colorectal tumors. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6835–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sugihara, K.; Nakatsuji, N.; Nakamura, K.; Nakao, K.; Hashimoto, R.; Otani, H.; Sakagami, H.; Kondo, H.; Nozama, S.; Aiba, A.; et al. Rac1 is required for the formation of three germ layers during gastrulation. Oncogene 1998, 17, 3427–3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, I.R.; Li, L.; Cabeceiras, P.K.; Mahdavi, M.; Gutschner, T.; Genovese, G.; Wang, G.; Fang, Z.; Tepper, J.M.; Stemke-Hale, K.Y.; et al. The RAC1 P29S hotspot mutation in melanoma confers resistance to pharmacological inhibition of RAF. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4845–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, R.B.; Ridley, A.J. Rho GTPases: Regulation and roles in cancer cell biology. Small GTPases 2016, 7, 207–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, S.; Gosens, R.; Wieland, T.; Schmidt, M. Paving the Rho in cancer metastasis: Rho GTPases and beyond. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 183, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawson, C.D.; Ridley, A.J. Rho GTPase signaling complexes in cell migration and invasion. J. Cell Biol. 2018, 217, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, L.G.; Gillette, J.M.; Kang, H.; Rivera, M.R.; Wandinger-Ness, A. Ovarian Tumor Microenvironment Signaling: Convergence on the Rac1 GTPase. Cancers 2018, 10, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maldonado, M.D.M.; Dharmawardhane, S. Targeting Rac and Cdc42 GTPases in Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3101–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krauthammer, M.; Kong, Y.; Ha, B.H.; Evans, P.; Bacchiocchi, A.; McCusker, J.P.; Cheng, E.; Damis, M.J.; Goh, G.; Choi, M.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies recurrent somatic RAC1 mutations in melanoma. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1006–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hodis, E.; Watson, I.R.; Kryukov, G.V.; Arold, S.T.; Imielinski, M.; Theurillat, J.P.; Nickerson, E.; Auclair, D.; Li, L.; Place, C.; et al. A landscape of driver mutations in melanoma. Cell 2012, 150, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Machesky, L.M. Rac1 cycling fast in melanoma with P29S. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2013, 26, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.J.; Ha, B.H.; Holman, E.C.; Halaban, R.; Schlessinger, J.; Boggon, T.J. RAC1P29S is a spontaneously activating cancer-associated GTPase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 912–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawazu, M.; Ueno, T.; Kontani, K.; Ogita, Y.; Ando, M.; Fukumura, K.; Yamato, A.; Soda, M.; Takeuchi, K.; Miki, Y.; et al. Transforming mutations of RAC guanosine triphosphatases in human cancers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3029–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zehir, A.; Benayed, R.; Shah, R.H.; Syed, A.; Middha, S.; Kim, H.R.; Srinivasan, P.; Gao, J.; Chakravarty, D.; Devlin, S.M.; et al. Mutational landscape of metastatic cancer revealed from prospective clinical sequencing of 10,000 patients. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 703–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerami, E.; Gao, J.; Dogrusoz, U.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Aksoy, B.A.; Jacobsen, A.; Byrne, C.J.; Heuer, M.L.; Larsson, E.; et al. The cBio cancer genomics portal: An open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, J.X.; Luo, J.H.; Wu, S.; Yuan, G.J.; Ma, N.F.; Feng, Y.; Cai, M.Y.; Chen, R.X.; Lu, J.; et al. CSTF2-Induced Shortening of the RAC1 3’UTR Promotes the Pathogenesis of Urothelial Carcinoma of the Bladder. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 5848–5862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payapilly, A.; Malliri, A. Compartmentalisation of RAC1 signalling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2018, 54, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, E.E.; Mulloy, J.C.; Zheng, Y. Rac1 GTPase: A “Rac” of all trades. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2009, 66, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridley, A.J.; Paterson, H.F.; Johnston, C.L.; Diekmann, D.; Hall, A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell 1992, 70, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nobes, C.D.; Hall, A. Rho, rac, and cdc42 GTPases regulate the assembly of multimolecular focal complexes associated with actin stress fibers, lamellipodia, and filopodia. Cell 1995, 81, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga, V.M.; Machesky, L.M.; Hall, A.; Hotchin, N.A. The small GTPases Rho and Rac are required for the establishment of cadherin-dependent cell-cell contacts. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 137, 1421–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, W.D.; Inoue, T.; Park, W.S.; Kim, M.L.; Park, B.O.; Wandless, T.J.; Meyer, T. PI(3,4,5)P3 and PI(4,5)P2 lipids target proteins with polybasic clusters to the plasma membrane. Science 2006, 314, 1458–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Yin, T.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Wu, Y.I.; Yu, J. Single-molecule tracking of small GTPase Rac1 uncovers spatial regulation of membrane translocation and mechanism for polarized signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E267–E276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finkielstein, C.V.; Overduin, M.; Capelluto, D.G. Cell migration and signaling specificity is determined by the phosphatidylserine recognition motif of Rac1. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 27317–27326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, R.D.; Pertz, O. The dynamics of spatio-temporal Rho GTPase signaling: Formation of signaling patterns. F1000Research 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmon, K.S.; Gong, X.; Yi, J.; Wu, L.; Thomas, A.; Moore, C.M.; Masuho, I.; Timson, D.J.; Martemyanov, K.A.; Liu, Q.J. LGR5 receptor promotes cell-cell adhesion in stem cells and colon cancer cells via the IQGAP1-Rac1 pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 14989–15001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Lerida, I.; Sanchez-Perales, S.; Calvo, M.; Rentero, C.; Zheng, Y.; Enrich, C.; Del Pozo, M.A. A palmitoylation switch mechanism regulates Rac1 function and membrane organization. Embo J. 2012, 31, 534–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remorino, A.; De Beco, S.; Cayrac, F.; Di Federico, F.; Cornilleau, G.; Gautreau, A.; Parrini, M.C.; Masson, J.B.; Dahan, M.; Coppey, M. Gradients of Rac1 Nanoclusters Support Spatial Patterns of Rac1 Signaling. Cell Rep. 2017, 21, 1922–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, K.N.; Zhou, Y.; Hancock, J.F. Clustering of Rac1: Selective Lipid Sorting Drives Signaling. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 75–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, J.; Li, L.; Ballermann, B.; Wang, Z. Phosphorylation of Rac1 T108 by extracellular signal-regulated kinase in response to epidermal growth factor: A novel mechanism to regulate Rac1 function. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2013, 33, 4538–4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelson, D.; Abidi, W.; Guardavaccaro, D.; Zhou, M.; Ahearn, I.; Pagano, M.; Phillips, M.R. Rac1 accumulates in the nucleus during the G2 phase of the cell cycle and promotes cell division. J. Cell Biol. 2008, 181, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- May, M.; Schelle, I.; Brakebusch, C.; Rottner, K.; Genth, H. Rac1-dependent recruitment of PAK2 to G2 phase centrosomes and their roles in the regulation of mitotic entry. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 2211–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodcock, S.A.; Rushton, H.J.; Castaneda-Saucedo, E.; Myant, K.; White, G.R.; Blyth, K.; Sansom, O.J.; Malliri, A. Tiam1-Rac signaling counteracts Eg5 during bipolar spindle assembly to facilitate chromosome congression. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justilien, V.; Ali, S.A.; Jamieson, L.; Yin, N.; Cox, A.D.; Der, C.J.; Murray, N.R.; Fields, A.P. Ect2-Dependent rRNA Synthesis Is Required for KRAS-TRP53-Driven Lung Adenocarcinoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diamantopoulou, Z.; White, G.; Fadlullah, M.Z.H.; Dreger, M.; Pickering, K.; Maltas, J.; Ashton, G.; MacLeod, R.; Baillie, G.S.; Kouskoff, V.; et al. TIAM1 Antagonizes TAZ/YAP Both in the Destruction Complex in the Cytoplasm and in the Nucleus to Inhibit Invasion of Intestinal Epithelial Cells. Cancer Cell 2017, 31, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamieson, C.; Lui, C.; Brocardo, M.G.; Martino-Echarri, E.; Henderson, B.R. Rac1 augments Wnt signaling by stimulating beta-catenin-lymphoid enhancer factor-1 complex assembly independent of beta-catenin nuclear import. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 3933–3946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Lerida, I.; Pellinen, T.; Sanchez, S.A.; Guadamillas, M.C.; Wang, Y.; Mirtti, T.; Calvo, E.; DelPozo, M.A. Rac1 nucleocytoplasmic shuttling drives nuclear shape changes and tumor invasion. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 318–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Disanza, A.; Scita, G. Nuclear and cellular plasticity: Nuclear RAC1 takes center stage. Dev. Cell 2015, 32, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Velaithan, R.; Kang, J.; Hirpara, J.L.; Loh, T.; Goh, B.C.; Le Bras, M.; Brenner, C.; Clement, M.V.; Pervaiz, S. The small GTPase Rac1 is a novel binding partner of Bcl-2 and stabilizes its antiapoptotic activity. Blood 2011, 117, 6214–6226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pradip, D.; Bouzyk, M.; Dey, N.; Leyland-Jones, B. Dissecting GRB7-mediated signals for proliferation and migration in HER2 overexpressing breast tumor cells: GTP-ase rules. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 3, 173–195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wertheimer, E.; Gutierrez-Uzquiza, A.; Rosemblit, C.; Lopez-Haber, C.; Sosa, M.S.; Kazanietz, M.G. Rac signaling in breast cancer: A tale of GEFs and GAPs. Cell. Signal. 2012, 24, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, P.; Carlson, J.H.; Jepperson, T.; Willis, S.; Leyland-Jones, B.; Dey, N. RAC1 GTP-ase signals Wnt-beta-catenin pathway mediated integrin-directed metastasis-associated tumor cell phenotypes in triple negative breast cancers. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 3072–3103. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dummler, B.; Ohshiro, K.; Kumar, R.; Field, J. Pak protein kinases and their role in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2009, 28, 51–63. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Shrestha, Y.; Schafer, E.J.; Boehm, J.S.; Thomas, S.R.; He, F.; Du, J.; Wang, S.; Barretina, J.; Weir, B.A.; Zhao, J.J.; et al. PAK1 is a breast cancer oncogene that coordinately activates MAPK and MET signaling. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokoch, G.M. Regulation of cell function by Rho family GTPases. Immunol. Res. 2000, 21, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, D.C.; Sanders, L.C.; Bokoch, G.M.; Gill, G.N. Activation of LIM-kinase by Pak1 couples Rac/Cdc42 GTPase signalling to actin cytoskeletal dynamics. Nat. Cell Biol. 1999, 1, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadlamudi, R.K.; Li, F.; Barnes, C.J.; Bagheri-Yarmand, R.; Kumar, R. p41-Arc subunit of human Arp2/3 complex is a p21-activated kinase-1-interacting substrate. Embo Rep. 2004, 5, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hein, A.L.; Post, C.M.; Sheinin, Y.M.; Lakshmanan, I.; Natarajan, A.; Enke, C.A.; Bartra, S.K.; Ouellete, M.M.; Yan, Y. RAC1 GTPase promotes the survival of breast cancer cells in response to hyper-fractionated radiation treatment. Oncogene 2016, 35, 6319–6329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morrison Joly, M.; Williams, M.M.; Hicks, D.J.; Jones, B.; Sanchez, V.; Young, C.D.; Sarbassov, D.D.; Muller, W.J.; Brantely-Sieders, D.; Cook, R.S. Two distinct mTORC2-dependent pathways converge on Rac1 to drive breast cancer metastasis. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2017, 19, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goncalves, M.D.; Hopkins, B.D.; Cantley, L.C. Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase, Growth Disorders, and Cancer. New Engl. J. Med. 2018, 379, 2052–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzav, S. Vav1: A Dr. Jekyll and Mr. Hyde protein--good for the hematopoietic system, bad for cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 28731–28742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Luby-Phelps, K.; Das, B.; Shu, X.; Xia, Y.; Mosteller, R.D.; Krisna, U.M.; Falck, J.R.; White, M.A.; Broek, D. Role of substrates and products of PI 3-kinase in regulating activation of Rac-related guanosine triphosphatases by Vav. Science 1998, 279, 558–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalom, B.; Farago, M.; Pikarsky, E.; Katzav, S. Vav1 mutations identified in human cancers give rise to different oncogenic phenotypes. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vega, F.M.; Ridley, A.J. Rho GTPases in cancer cell biology. Febs Lett. 2008, 582, 2093–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rayala, S.K.; Molli, P.R.; Kumar, R. Nuclear p21-activated kinase 1 in breast cancer packs off tamoxifen sensitivity. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5985–5988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, E.E.; Nakai, Y.; Hennigan, R.F.; Ratner, N.; Zheng, Y. NF2-deficient cells depend on the Rac1-canonical Wnt signaling pathway to promote the loss of contact inhibition of proliferation. Oncogene 2010, 29, 2540–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lozano, E.; Betson, M.; Braga, V.M. Tumor progression: Small GTPases and loss of cell-cell adhesion. Bioessays 2003, 25, 452–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Villasana, V.; Fuentes-Mattei, E.; Ivan, C.; Dalton, H.J.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Fernandez-de Thomas, R.J.; Aslan, B.; Cel, C.; Monroig, P.; Velazquez-Torres, G.; et al. Rac1/Pak1/p38/MMP-2 Axis Regulates Angiogenesis in Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, K.; Wu, Y.I.; Liu, Y.; Geiger, J.; Tam, E.; Overall, C.; Stack, M.S.; Friedl, P. Multi-step pericellular proteolysis controls the transition from individual to collective cancer cell invasion. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 893–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, N.; Young, B.; Abramovitz, M.; Bouzyk, M.; Barwick, B.; De, P.; Leyland-Jones, B. Differential activation of Wnt-beta-catenin pathway in triple negative breast cancer increases MMP7 in a PTEN dependent manner. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e77425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Increased Rac1b expression sustains colorectal tumor cell survival. Mol. Cancer Res. 2008, 6, 1178–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Karnoub, A.E.; Palmby, T.R.; Lengyel, E.; Sondek, J.; Der, C.J. Rac1b, a tumor associated, constitutively active Rac1 splice variant, promotes cellular transformation. Oncogene 2004, 23, 9369–9380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matos, P.; Jordan, P. Rac1, but not Rac1B, stimulates RelB-mediated gene transcription in colorectal cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 13724–13732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radisky, D.C.; Levy, D.D.; Littlepage, L.E.; Liu, H.; Nelson, C.M.; Fata, J.E.; Leake, D.; Godden, E.L.; Albertson, D.G.; Nieto, M.A.; et al. Rac1b and reactive oxygen species mediate MMP-3-induced EMT and genomic instability. Nature 2005, 436, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esufali, S.; Charames, G.S.; Pethe, V.V.; Buongiorno, P.; Bapat, B. Activation of tumor-specific splice variant Rac1b by dishevelled promotes canonical Wnt signaling and decreased adhesion of colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 2469–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissil, J.L.; Walmsley, M.J.; Hanlon, L.; Haigis, K.M.; Bender Kim, C.F.; Sweet-Cordero, A.; Eckman, M.S.; Tuveson, D.A.; Capobianco, A.J.; Tybulewicz, V.; et al. Requirement for Rac1 in a K-ras induced lung cancer in the mouse. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 8089–8094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malliri, A.; van der Kammen, R.A.; Clark, K.; van der Valk, M.; Michiels, F.; Collard, J.G. Mice deficient in the Rac activator Tiam1 are resistant to Ras-induced skin tumours. Nature 2002, 417, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradip, D.; Peng, X.; Durden, D.L. Rac2 specificity in macrophage integrin signaling: Potential role for Syk kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 41661–41669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, N.; Howell, B.W.; De, P.K.; Durden, D.L. CSK negatively regulates nerve growth factor induced neural differentiation and augments AKT kinase activity. Exp. Cell Res. 2005, 307, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dey, N.; De, P.K.; Wang, M.; Zhang, H.; Dobrota, E.A.; Robertson, K.A.; Drudern, D.L. CSK controls retinoic acid receptor (RAR) signaling: A RAR-c-SRC signaling axis is required for neuritogenic differentiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 4179–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eden, S.; Rohatgi, R.; Podtelejnikov, A.V.; Mann, M.; Kirschner, M.W. Mechanism of regulation of WAVE1-induced actin nucleation by Rac1 and Nck. Nature 2002, 418, 790–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Borek, D.; Padrick, S.B.; Gomez, T.S.; Metlagel, Z.; Ismail, A.M.; Umetani, J.; Billadeau, D.D.; Otwinowski, Z.; Rosen, M.K. Structure and control of the actin regulatory WAVE complex. Nature 2010, 468, 533–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Katoh, H.; Negishi, M. RhoG activates Rac1 by direct interaction with the Dock180-binding protein Elmo. Nature 2003, 424, 461–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orgaz, J.L.; Herraiz, C.; Sanz-Moreno, V. Rho GTPases modulate malignant transformation of tumor cells. Small GTPases 2014, 5, e29019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, C.; Cho, S.J.; Chang, K.K.; Park, D.J.; Ryeom, S.W.; Yoon, S.S. Role of Rac1 Pathway in Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Cancer Stem-like Cell Phenotypes in Gastric Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2017, 15, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonelli, M.A.; Cavazzoni, A.; Saccani, F.; Alfieri, R.R.; Quaini, F.; La Monica, S.; Galetti, M.; Cretella, D.; Caffarra, C.; Madeddu, D.; et al. Inhibition of PI3K Pathway Reduces Invasiveness and Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Squamous Lung Cancer Cell Lines Harboring PIK3CA Gene Alterations. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 1916–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavazzoni, A.; La Monica, S.; Alfieri, R.; Ravelli, A.; Van Der Steen, N.; Sciarrillo, R.; Madeddu, D.; Lagrasta, C.A.M.; Quaini, F.; Bonelli, M.; et al. Enhanced efficacy of AKT and FAK kinase combined inhibition in squamous cell lung carcinomas with stable reduction in PTEN. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53068–53083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, K.; Rao, J.; Zhou, Z.H.; Yao, X.H.; Wu, F.; Yang, J.; Yang, L.; Zhang, X.; Cui, Y.H.; Bian, X.W.; et al. RAC1-GTP promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of colorectal cancer by activation of STAT3. Lab Invest 2018, 98, 989–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bid, H.K.; Roberts, R.D.; Manchanda, P.K.; Houghton, P.J. RAC1: An emerging therapeutic option for targeting cancer angiogenesis and metastasis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1925–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nohata, N.; Uchida, Y.; Stratman, A.N.; Adams, R.H.; Zheng, Y.; Weinstein, B.M.; Mukouyama, Y.S.; Gutkind, J.S. Temporal-specific roles of Rac1 during vascular development and retinal angiogenesis. Dev. Biol. 2016, 411, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan Moya, E.M.; Le Guelte, A.; Gavard, J. PAKing up to the endothelium. Cell. Signal. 2009, 21, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Abraham, S.; Scarcia, M.; Bagshaw, R.D.; McMahon, K.; Grant, G.; Harvey, T.; Yeo, M.; Estevens, F.O.; Thygesen, H.H.; Jones, P.F.; et al. A Rac/Cdc42 exchange factor complex promotes formation of lateral filopodia and blood vessel lumen morphogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fryer, B.H.; Field, J. Rho, Rac, Pak and angiogenesis: Old roles and newly identified responsibilities in endothelial cells. Cancer Lett. 2005, 229, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Y.; Bi, F.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Y.; Liu, N.; Zheng, Y.; Fan, D. Inhibition of endothelial cell proliferation by targeting Rac1 GTPase with small interference RNA in tumor cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 320, 1309–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, P.; Peng, Q.; Traktuev, D.O.; Li, W.; Yoder, M.C.; March, K.L.; Durden, D.L. Expression of RAC2 in endothelial cells is required for the postnatal neovascular response. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 248–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Van Allen, E.M.; Wagle, N.; Sucker, A.; Treacy, D.J.; Johannessen, C.M.; Goetz, E.M.; Place, C.S.; Taylor-Weiner, A.; Whittaker, S.; Kryukov, G.V.; et al. The genetic landscape of clinical resistance to RAF inhibition in metastatic melanoma. Cancer Discov. 2014, 4, 94–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.; Ma, Y.; Jin, M.; Mason, S.; Mort, R.L.; Blyth, K.; Larue, L.; Sansom, O.J.; Machesky, L.M. Activated mutant NRas(Q61K) drives aberrant melanocyte signaling, survival, and invasiveness via a Rac1-dependent mechanism. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2610–2621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardama, G.A.; Alonso, D.F.; Gonzalez, N.; Maggio, J.; Gomez, D.E.; Rolfo, C.; Menna, P.L. Relevance of small GTPase Rac1 pathway in drug and radio-resistance mechanisms: Opportunities in cancer therapeutics. Crit. Rev. Oncol./Hematol. 2018, 124, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofbauer, S.W.; Krenn, P.W.; Ganghammer, S.; Asslaber, D.; Pichler, U.; Oberascher, K.; Henschler, R.; Wallner, M.; Kerschbaum, H.; Greil, R.; et al. Tiam1/Rac1 signals contribute to the proliferation and chemoresistance, but not motility, of chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Blood 2014, 123, 2181–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ikram, M.; Lim, Y.; Baek, S.Y.; Jin, S.; Jeong, Y.H.; Kwak, J.Y.; Yoon, S. Co-targeting of Tiam1/Rac1 and Notch ameliorates chemoresistance against doxorubicin in a biomimetic 3D lymphoma model. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 2058–2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bright, M.D.; Clarke, P.A.; Workman, P.; Davies, F.E. Oncogenic RAC1 and NRAS drive resistance to endoplasmic reticulum stress through MEK/ERK signalling. Cell. Signal. 2018, 44, 127–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodakoski, C.; Hopkins, B.D.; Zhang, G.; Su, T.; Cheng, Z.; Morris, R.; Rhee, K.Y.; Gonclaves, M.D.; Cantley, L.C. Rac-Mediated Macropinocytosis of Extracellular Protein Promotes Glucose Independence in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, H.L.; Rosenbaum, S.; Purwin, T.J.; Davies, M.A.; Aplin, A.E. RAC1 P29S regulates PD-L1 expression in melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2015, 28, 590–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araiza-Olivera, D.; Feng, Y.; Semenova, G.; Prudnikova, T.Y.; Rhodes, J.; Chernoff, J. Suppression of RAC1-driven malignant melanoma by group A PAK inhibitors. Oncogene 2018, 37, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manser, E.; Leung, T.; Salihuddin, H.; Zhao, Z.S.; Lim, L. A brain serine/threonine protein kinase activated by Cdc42 and Rac1. Nature 1994, 367, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marei, H.; Malliri, A. Rac1 in human diseases: The therapeutic potential of targeting Rac1 signaling regulatory mechanisms. Small GTPases 2017, 8, 139–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De, P.; Aske, J.C.; Dey, N. RAC1 Takes the Lead in Solid Tumors. Cells 2019, 8, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050382
De P, Aske JC, Dey N. RAC1 Takes the Lead in Solid Tumors. Cells. 2019; 8(5):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050382
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe, Pradip, Jennifer Carlson Aske, and Nandini Dey. 2019. "RAC1 Takes the Lead in Solid Tumors" Cells 8, no. 5: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050382
APA StyleDe, P., Aske, J. C., & Dey, N. (2019). RAC1 Takes the Lead in Solid Tumors. Cells, 8(5), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050382




