Delivery of microRNAs by Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infections: Could the News be Packaged?
Abstract
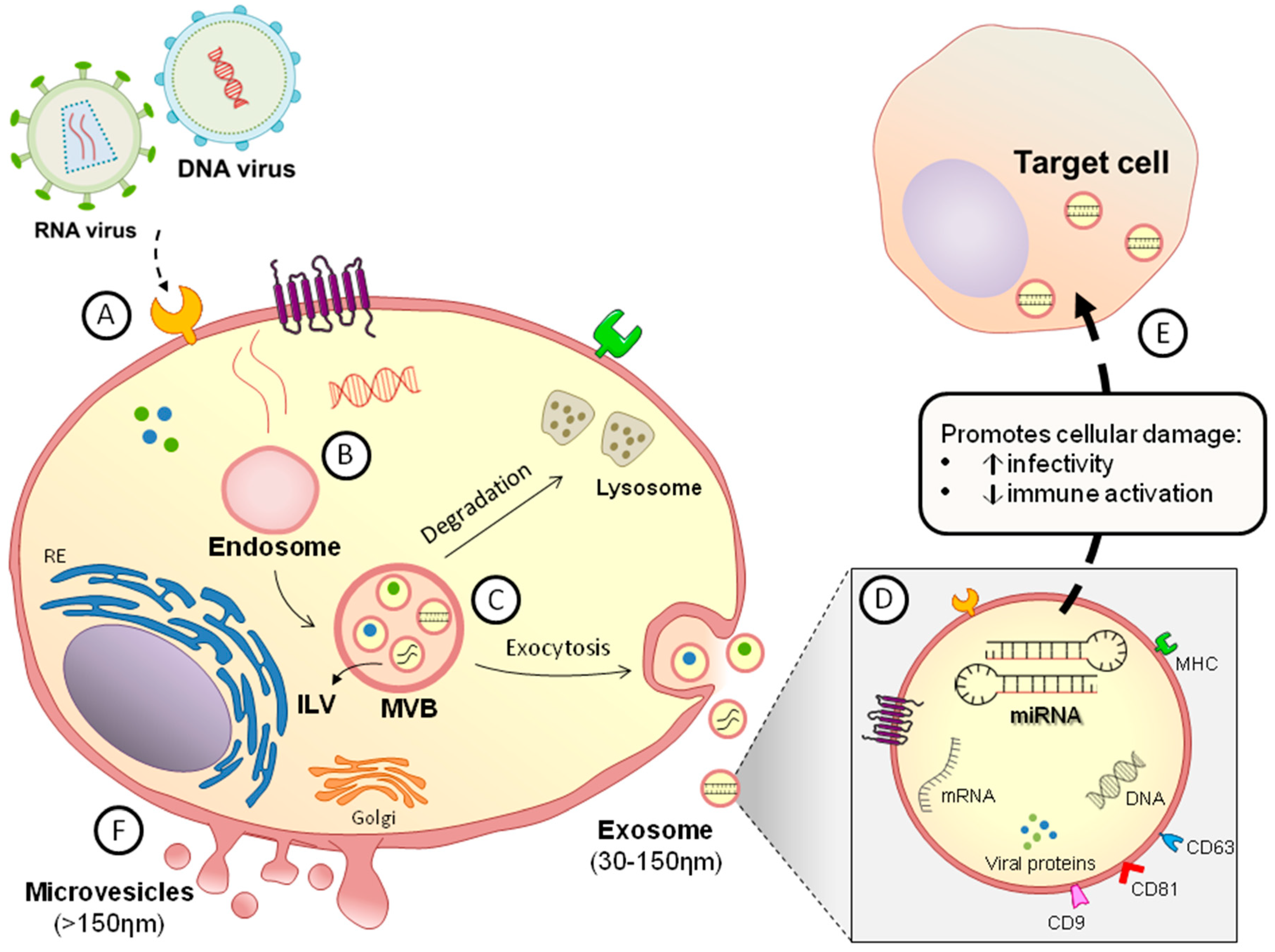
:1. Introduction
2. General Features of Extracellular Vesicles
3. DNA Viruses
3.1. Epstein–Barr Virus
3.2. Human Papillomaviruses
3.3. Polyomaviruses
4. RNA Viruses
4.1. Respiratory Viruses
4.2. HIV
4.3. Hepatitis C Virus
4.4. Japanese Encephalitis Virus
5. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowal, J.; Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Biogenesis and secretion of exosomes. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carpintero-Fernández, P.; Fafián-Labora, J.; O’Loghlen, A. Technical Advances to Study Extracellular Vesicles. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shenoda, B.B.; Ajit, S.K. Modulation of Immune Responses by Exosomes Derived from Antigen-Presenting Cells. Clin. Med. Insights Pathol. 2016, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, R.; Gröger, M.; Rauscher, S.; Fendl, B.; Eichhorn, T.; Fischer, M.B.; Spittler, A.; Weber, V. Differential Interaction of Platelet-Derived Extracellular Vesicles with Leukocyte Subsets in Human Whole Blood. Sci. Rep. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tung, S.L.; Boardman, D.A.; Sen, M.; Letizia, M.; Peng, Q.; Cianci, N.; Dioni, L.; Carlin, L.M.; Lechler, R.; Bollati, V.; et al. Regulatory T cell-derived extracellular vesicles modify dendritic cell function. Sci. Rep. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willms, E.; Cabañas, C.; Mäger, I.; Wood, M.J.A.; Vader, P. Extracellular Vesicle Heterogeneity: Subpopulations, Isolation Techniques, and Diverse Functions in Cancer Progression. Front. Immunol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada, I.; Gabrielli, M.; Turola, E.; Iorio, A.; D’Arrigo, G.; Parolisi, R.; De Luca, M.; Pacifici, M.; Bastoni, M.; Lombardi, M.; et al. Glia-to-neuron transfer of miRNAs via extracellular vesicles: A new mechanism underlying inflammation-induced synaptic alterations. Acta Neuropathol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, S.J.; Booth, A.M.; Hildreth, J.E. The Trojan exosome hypothesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10592–10597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nolte, E.; Cremer, T.; Gallo, R.C.; Margolis, L.B. Extracellular vesicles and viruses: Are they close relatives? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 9155–9161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Théry, C.; Witwer, K.W.; Aikawa, E.; Alcaraz, M.J.; Anderson, J.D.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Antoniou, A.; Arab, T.; Archer, F.; Atkin-Smith, G.K.; et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergenreider, E.; Heydt, S.; Tréguer, K.; Boettger, T.; Horrevoets, A.J.; Zeiher, A.M.; Scheffer, M.P.; Frangakis, A.S.; Yin, X.; Mayr, M.; et al. Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoorvogel, W.; Kleijmeer, M.J.; Geuze, H.J.; Raposo, G. The biogenesis and functions of exosomes. Traffic 2002, 3, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cocucci, E.; Meldolesi, J. Ectosomes and exosomes: Shedding the confusion between extracellular vesicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niel, G.; Porto-Carreiro, I.; Simoes, S.; Raposo, G. Exosomes: A common pathway for a specialized function. J. Biochem. 2006, 140, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, H.L.; Francis, S.E.; Dower, S.K.; Crossman, D.C. Secretion of intracellular IL-1 receptor antagonist (type 1) is dependent on P2X7 receptor activation. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 1202–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obregon, C.; Rothen-Rutishauser, B.; Gitahi, S.K.; Gehr, P.; Nicod, L.P. Exovesicles from human activated dendritic cells fuse with resting dendritic cells, allowing them to present alloantigens. Am. J. Pathol. 2006, 169, 2127–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldolesi, J. Exosomes and Ectosomes in Intercellular Communication. Curr. Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Properzi, F.; Logozzi, M.; Fais, S. Exosomes: The future of biomarkers in medicine. Biomark. Med. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Kang, M.H.; Jeyaraj, M.; Qasim, M.; Kim, J.H. Review of the Isolation, Characterization, Biological Function, and Multifarious Therapeutic Approaches of Exosomes. Cells 2019, 8, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeppesen, D.K.; Fenix, A.M.; Franklin, J.L.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Zhang, Q.; Zimmerman, L.J.; Liebler, D.C.; Ping, J.; Liu, Q.; Evans, R.; et al. Reassessment of Exosome Composition. Cell 2019, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dongen, H.M.; Masoumi, N.; Witwer, K.W.; Pegtel, D.M. Extracellular Vesicles Exploit Viral Entry Routes for Cargo Delivery. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2016, 80, 369–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Greenhill, C. Hepatitis: New route of HCV transmission. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Z.; Hensley, L.; McKnight, K.L.; Hu, F.; Madden, V.; Ping, L.; Jeong, S.H.; Walker, C.; Lanford, R.E.; Lemon, S.M. A pathogenic picornavirus acquires an envelope by hijacking cellular membranes. Nature 2013, 496, 367–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ota, M.; Serada, S.; Naka, T.; Mori, Y. MHC class I molecules are incorporated into human herpesvirus-6 viral particles and released into the extracellular environment. Microbiol. Immunol. 2014, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Izquierdo-Useros, N.; Lorizate, M.; Puertas, M.C.; Rodriguez-Plata, M.T.; Zangger, N.; Erikson, E.; Pino, M.; Erkizia, I.; Glass, B.; Clotet, B.; et al. Siglec-1 is a novel dendritic cell receptor that mediates HIV-1 trans-infection through recognition of viral membrane gangliosides. PLoS Biol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Croce, C.M. Causes and consequences of microRNA dysregulation in cancer. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eacker, S.M.; Dawson, T.M.; Dawson, V.L. Understanding microRNAs in neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raab-Traub, N.; Dittmer, D.P. Viral effects on the content and function of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2017, 15, 559–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valadi, H.; Ekström, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjöstrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lötvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shurtleff, M.J.; Temoche-Diaz, M.M.; Karfilis, K.V.; Ri, S.; Schekman, R. Y-box protein 1 is required to sort microRNAs into exosomes in cells and in a cell-free reaction. eLife 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, D.J.; Franklin, J.L.; Dou, Y.; Liu, Q.; Higginbotham, J.N.; Demory Beckler, M.; Weaver, A.M.; Vickers, K.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.; et al. KRAS-dependent sorting of miRNA to exosomes. eLife 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouillet, J.F.; Ouyang, Y.; Bayer, A.; Coyne, C.B.; Sadovsky, Y. The role of trophoblastic microRNAs in placental viral infection. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delorme-Axford, E.; Donker, R.B.; Mouillet, J.F.; Chu, T.; Bayer, A.; Ouyang, Y.; Wang, T.; Stolz, D.B.; Sarkar, S.N.; Morelli, A.E.; et al. Human placental trophoblasts confer viral resistance to recipient cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12048–12053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kimura, H.; Kwong, Y.L. EBV Viral Loads in Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Response Assessment. Front. Oncol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forte, E.; Luftig, M.A. The role of microRNAs in Epstein-Barr virus latency and lytic reactivation. Microbes Infect. 2011, 13, 1156–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pegtel, D.M.; Cosmopoulos, K.; Thorley-Lawson, D.A.; van Eijndhoven, M.A.; Hopmans, E.S.; Lindenberg, J.L.; de Gruijl, T.D.; Würdinger, T.; Middeldorp, J.M. Functional delivery of viral miRNAs via exosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canitano, A.; Venturi, G.; Borghi, M.; Ammendolia, M.G.; Fais, S. Exosomes released in vitro from Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-infected cells contain EBV-encoded latent phase mRNAs. Cancer Lett. 2013, 337, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meckes, D.G.; Gunawardena, H.P.; Dekroon, R.M.; Heaton, P.R.; Edwards, R.H.; Ozgur, S.; Griffith, J.D.; Damania, B.; Raab-Traub, N. Modulation of B-cell exosome proteins by gamma herpesvirus infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, C.; Kim, J.; Park, G.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.; Hur, D.Y.; Kim, B.; Kim, Y.S. Delivery of miR-155 to retinal pigment epithelial cells mediated by Burkitt’s lymphoma exosomes. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Swan, K.; Zhang, X.; Cao, S.; Brett, Z.; Drury, S.; Strong, M.J.; Fewell, C.; Puetter, A.; Wang, X.; et al. Secreted Oral Epithelial Cell Membrane Vesicles Induce Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation in Latently Infected B Cells. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3469–3479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoshina, S.; Sekizuka, T.; Kataoka, M.; Hasegawa, H.; Hamada, H.; Kuroda, M.; Katano, H. Profile of Exosomal and Intracellular microRNA in Gamma-Herpesvirus-Infected Lymphoma Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meckes, D.G.; Shair, K.H.; Marquitz, A.R.; Kung, C.P.; Edwards, R.H.; Raab-Traub, N. Human tumor virus utilizes exosomes for intercellular communication. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gourzones, C.; Gelin, A.; Bombik, I.; Klibi, J.; Vérillaud, B.; Guigay, J.; Lang, P.; Témam, S.; Schneider, V.; Amiel, C.; et al. Extra-cellular release and blood diffusion of BART viral micro-RNAs produced by EBV-infected nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Virol. J. 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourzones, C.; Ferrand, F.R.; Amiel, C.; Vérillaud, B.; Barat, A.; Guérin, M.; Gattolliat, C.H.; Gelin, A.; Klibi, J.; Chaaben, A.B.; et al. Consistent high concentration of the viral microRNA BART17 in plasma samples from nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients--evidence of non-exosomal transport. Virol. J. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Vella, S.; Miele, M.; Timoneri, F.; Di Bella, M.; Bosi, S.; Sciveres, M.; Conaldi, P.G. Global profiling of viral and cellular non-coding RNAs in Epstein-Barr virus-induced lymphoblastoid cell lines and released exosome cargos. Cancer Lett. 2017, 388, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komabayashi, Y.; Kishibe, K.; Nagato, T.; Ueda, S.; Takahara, M.; Harabuchi, Y. Circulating Epstein-Barr virus-encoded micro-RNAs as potential biomarkers for nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramayanti, O.; Verkuijlen, S.A.W.M.; Novianti, P.; Scheepbouwer, C.; Misovic, B.; Koppers-Lalic, D.; van Weering, J.; Beckers, L.; Adham, M.; Martorelli, D.; et al. Vesicle-bound EBV-BART13-3p miRNA in circulation distinguishes nasopharyngeal from other head and neck cancer and asymptomatic EBV-infections. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toussirot, E.; Roudier, J. Epstein-Barr virus in autoimmune diseases. Best Pract Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 22, 883–896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallo, A.; Jang, S.I.; Ong, H.L.; Perez, P.; Tandon, M.; Ambudkar, I.; Illei, G.; Alevizos, I. Targeting the Ca(2+) Sensor STIM1 by Exosomal Transfer of Ebv-miR-BART13-3p is Associated with Sjögren’s Syndrome. EBioMedicine 2016, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y. Involvement of Human Papillomaviruses in Cervical Cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yim, E.K.; Park, J.S. The role of HPV E6 and E7 oncoproteins in HPV-associated cervical carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. Treat. 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishodia, G.; Verma, G.; Das, B.C.; Bharti, A.C. miRNA as viral transcription tuners in HPV-mediated cervical carcinogenesis. Front. Biosci. 2018, 10, 21–47. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Chiantore, M.V.; Mangino, G.; Iuliano, M.; Zangrillo, M.S.; De Lillis, I.; Vaccari, G.; Accardi, R.; Tommasino, M.; Columba Cabezas, S.; Federico, M.; et al. Human papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoproteins affect the expression of cancer-related microRNAs: Additional evidence in HPV-induced tumorigenesis. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 142, 1751–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honegger, A.; Schilling, D.; Bastian, S.; Sponagel, J.; Kuryshev, V.; Sültmann, H.; Scheffner, M.; Hoppe-Seyler, K.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. Dependence of intracellular and exosomal microRNAs on viral E6/E7 oncogene expression in HPV-positive tumor cells. PLoS Pathog 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harden, M.E.; Munger, K. Human papillomavirus 16 E6 and E7 oncoprotein expression alters microRNA expression in extracellular vesicles. Virology 2017, 508, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peacock, B.; Rigby, A.; Bradford, J.; Pink, R.; Hunter, K.; Lambert, D.; Hunt, S. Extracellular vesicle microRNA cargo is correlated with HPV status in oropharyngeal carcinoma. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2018, 47, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cokarić Brdovčak, M.; Zubković, A.; Jurak, I. Herpes Simplex Virus 1 Deregulation of Host MicroRNAs. Noncoding RNA 2018, 4, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalamvoki, M.; Du, T.; Roizman, B. Cells infected with herpes simplex virus 1 export to uninfected cells exosomes containing STING, viral mRNAs, and microRNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elphick, G.F.; Querbes, W.; Jordan, J.A.; Gee, G.V.; Eash, S.; Manley, K.; Dugan, A.; Stanifer, M.; Bhatnagar, A.; Kroeze, W.K.; et al. The human polyomavirus, JCV, uses serotonin receptors to infect cells. Science 2004, 306, 1380–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagatie, O.; Tritsmans, L.; Stuyver, L.J. The miRNA world of polyomaviruses. Virol. J. 2013, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giovannelli, I.; Clausi, V.; Nukuzuma, S.; Della Malva, N.; Nosi, D.; Giannecchini, S. Polyomavirus JC microRNA expression after infection in vitro. Virus Res. 2016, 213, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakfetrat, M.; Yaghobi, R.; Salmanpoor, Z.; Roozbeh, J.; Torabinezhad, S.; Kadkhodaei, S. Frequency of Polyomavirus BK Infection in Kidney Transplant Patients Suspected to Nephropathy. Int. J. Organ. Transplant. Med. 2015, 6, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Seo, J.W.; Moon, H.; Kim, J.S.; Kim, Y.G.; Jeong, K.H.; Moon, J.Y.; Lee, T.W.; Ihm, C.G.; et al. Urinary exosomal viral microRNA as a marker of BK virus nephropathy in kidney transplant recipients. PLoS ONE 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Ree, M.H.; Jansen, L.; Kruize, Z.; van Nuenen, A.C.; van Dort, K.A.; Takkenberg, R.B.; Reesink, H.W.; Kootstra, N.A. Plasma MicroRNA Levels Are Associated With Hepatitis B e Antigen Status and Treatment Response in Chronic Hepatitis B Patients. J. Infect. Dis. 2017, 215, 1421–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enomoto, Y.; Takagi, R.; Naito, Y.; Kiniwa, T.; Tanaka, Y.; Hamada-Tsutsumi, S.; Kawano, M.; Matsushita, S.; Ochiya, T.; Miyajima, A. Identification of the novel 3′UTR sequences of human IL-21 mRNA as potential targets of miRNAs. Sci Rep. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chahar, H.S.; Bao, X.; Casola, A. Exosomes and Their Role in the Life Cycle and Pathogenesis of RNA Viruses. Viruses 2015, 7, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, M.J.; Gomez, J.L.; Perez, G.F.; Pancham, K.; Val, S.; Pillai, D.K.; Giri, M.; Ferrante, S.; Freishtat, R.; Rose, M.C.; et al. Airway Secretory microRNAome Changes during Rhinovirus Infection in Early Childhood. PLoS ONE 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Fukushima, Y.; Kouwaki, T.; Daito, T.; Kohara, M.; Kida, H.; Oshiumi, H. MicroRNA-451a in extracellular, blood-resident vesicles attenuates macrophage and dendritic cell responses to influenza whole-virus vaccine. J. Biol. Chem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheller, N.; Herold, S.; Kellner, R.; Bertrams, W.; Jung, A.L.; Janga, H.; Greulich, T.; Schulte, L.N.; Vogelmeier, C.F.; Lohmeyer, J.; et al. Proviral MicroRNAs Detected in Extracellular Vesicles from Bronchoalveolar Lavage Fluid of Patients With Influenza Virus-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome. J. Infect. Dis. 2019, 219, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellwanger, J.H.; Veit, T.D.; Chies, J.A.B. Exosomes in HIV infection: A review and critical look. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2017, 53, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, W.W.; Huang, M.B.; Addae Konadu, K.; Powell, M.D.; Bond, V.C. Micro RNA in Exosomes from HIV-Infected Macrophages. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubert, A.; Subra, C.; Jenabian, M.A.; Tremblay Labrecque, P.F.; Tremblay, C.; Laffont, B.; Provost, P.; Routy, J.P.; Gilbert, C. Elevated Abundance, Size, and MicroRNA Content of Plasma Extracellular Vesicles in Viremic HIV-1+ Patients: Correlations with Known Markers of Disease Progression. J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2015, 70, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; Muth, D.C.; Eitan, E.; Travers, M.; Learman, L.N.; Lehrmann, E.; Witwer, K.W. Serum extracellular vesicle depletion processes affect release and infectivity of HIV-1 in culture. Sci. Rep. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, R.P.; Costantini, L.M.; Myers, T.A.; Schouest, B.; Maness, N.J.; Griffith, J.D.; Damania, B.A.; MacLean, A.G.; Dittmer, D.P. Nef Secretion into Extracellular Vesicles or Exosomes Is Conserved across Human and Simian Immunodeficiency Viruses. mBio 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stumptner-Cuvelette, P.; Jouve, M.; Helft, J.; Dugast, M.; Glouzman, A.S.; Jooss, K.; Raposo, G.; Benaroch, P. Human immunodeficiency virus-1 Nef expression induces intracellular accumulation of multivesicular bodies and major histocompatibility complex class II complexes: Potential role of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Mol. Biol. Cell 2003, 14, 4857–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqil, M.; Naqvi, A.R.; Mallik, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Maulik, U.; Jameel, S. The HIV Nef protein modulates cellular and exosomal miRNA profiles in human monocytic cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqil, M.; Mallik, S.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Maulik, U.; Jameel, S. Transcriptomic Analysis of mRNAs in Human Monocytic Cells Expressing the HIV-1 Nef Protein and Their Exosomes. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aqil, M.; Naqvi, A.R.; Bano, A.S.; Jameel, S. The HIV-1 Nef protein binds argonaute-2 and functions as a viral suppressor of RNA interference. PLoS ONE 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazleton, J.E.; Berman, J.W.; Eugenin, E.A. Novel mechanisms of central nervous system damage in HIV infection. HIV AIDS 2010, 2, 39–49. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Niu, F.; Yao, H.; Liao, K.; Chen, X.; Kook, Y.; Ma, R.; Hu, G.; Buch, S. Exosomal miR-9 Released from HIV Tat Stimulated Astrocytes Mediates Microglial Migration. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 330–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yelamanchili, S.V.; Lamberty, B.G.; Rennard, D.A.; Morsey, B.M.; Hochfelder, C.G.; Meays, B.M.; Levy, E.; Fox, H.S. MiR-21 in Extracellular Vesicles Leads to Neurotoxicity via TLR7 Signaling in SIV Neurological Disease. PLoS Pathog 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Yao, H.; Chaudhuri, A.D.; Duan, M.; Yelamanchili, S.V.; Wen, H.; Cheney, P.D.; Fox, H.S.; Buch, S. Exosome-mediated shuttling of microRNA-29 regulates HIV Tat and morphine-mediated neuronal dysfunction. Cell Death Dis. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, H.; Chinnappan, M.; Agarwal, S.; Dalvi, P.; Gunewardena, S.; O’Brien-Ladner, A.; Dhillon, N.K. Macrophage-derived extracellular vesicles mediate smooth muscle hyperplasia: Role of altered miRNA cargo in response to HIV infection and substance abuse. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 5174–5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biyani, S.; Garg, R.K.; Jain, A.; Malhotra, H.S.; Kumar, R.; Prakash, S.; Verma, R.; Sharma, P.K. Toll-like receptor-3 gene polymorphism in patients with Japanese encephalitis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2015, 286, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klase, Z.; Kale, P.; Winograd, R.; Gupta, M.V.; Heydarian, M.; Berro, R.; McCaffrey, T.; Kashanchi, F. HIV-1 TAR element is processed by Dicer to yield a viral micro-RNA involved in chromatin remodeling of the viral LTR. BMC Mol. Biol. 2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narayanan, A.; Iordanskiy, S.; Das, R.; Van Duyne, R.; Santos, S.; Jaworski, E.; Guendel, I.; Sampey, G.; Dalby, E.; Iglesias-Ussel, M.; et al. Exosomes derived from HIV-1-infected cells contain trans-activation response element RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20014–20033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, C.; Narayanan, S.; Hahn, Y.S. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells: The dark knight or the joker in viral infections? Immunol. Rev. 2013, 255, 210–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampey, G.C.; Saifuddin, M.; Schwab, A.; Barclay, R.; Punya, S.; Chung, M.C.; Hakami, R.M.; Zadeh, M.A.; Lepene, B.; Klase, Z.A.; et al. Exosomes from HIV-1-infected Cells Stimulate Production of Pro-inflammatory Cytokines through Trans-activating Response (TAR) RNA. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1251–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramakrishnaiah, V.; Thumann, C.; Fofana, I.; Habersetzer, F.; Pan, Q.; de Ruiter, P.E.; Willemsen, R.; Demmers, J.A.; Stalin Raj, V.; Jenster, G.; et al. Exosome-mediated transmission of hepatitis C virus between human hepatoma Huh7.5 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13109–13113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bukong, T.N.; Momen-Heravi, F.; Kodys, K.; Bala, S.; Szabo, G. Exosomes from hepatitis C infected patients transmit HCV infection and contain replication competent viral RNA in complex with Ago2-miR122-HSP90. PLoS Pathog 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devhare, P.B.; Sasaki, R.; Shrivastava, S.; Di Bisceglie, A.M.; Ray, R.; Ray, R.B. Exosome-Mediated Intercellular Communication between Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Hepatocytes and Hepatic Stellate Cells. J. Virol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lambrecht, J.; Jan Poortmans, P.; Verhulst, S.; Reynaert, H.; Mannaerts, I.; van Grunsven, L.A. Circulating ECV-Associated miRNAs as Potential Clinical Biomarkers in Early Stage HBV and HCV Induced Liver Fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tellapuri, S.; Sutphin, P.D.; Beg, M.S.; Singal, A.G.; Kalva, S.P. Staging systems of hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 37, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.H.; Ren, L.N.; Wang, X.; Wang, T.; Zhang, N.; Gao, Y.; Luo, H.; Navarro-Alvarez, N.; Tang, L.J. Combination of exosomes and circulating microRNAs may serve as a promising tumor marker complementary to alpha-fetoprotein for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis in rats. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; He, P.; Li, Y.; Si, M.; Jiao, X. Circulating microRNAs as a biomarker to predict therapy efficacy in hepatitis C patients with different genotypes. Microb. Pathog. 2017, 112, 320–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, X.; Fan, Z.; Chen, H.; He, P.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ke, C. Serum and exosomal miR-122 and miR-199a as a biomarker to predict therapeutic efficacy of hepatitis C patients. J. Med. Virol 2017, 89, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santangelo, L.; Bordoni, V.; Montaldo, C.; Cimini, E.; Zingoni, A.; Battistelli, C.; D’Offizi, G.; Capobianchi, M.R.; Santoni, A.; Tripodi, M.; et al. Hepatitis C virus direct-acting antivirals therapy impacts on extracellular vesicles microRNAs content and on their immunomodulating properties. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 1741–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wang, X.; Sun, L.; Zhou, L.; Ma, T.C.; Song, L.; Wu, J.G.; Li, J.L.; Ho, W.Z. Toll-like receptor 3-activated macrophages confer anti-HCV activity to hepatocytes through exosomes. FASEB J. 2016, 30, 4132–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Xu, C.; Fang, S.; Zhao, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Yuan, W.; Qi, Z. Exosomal MicroRNAs Derived from Umbilical Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit Hepatitis C Virus Infection. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2016, 5, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, N.; Lomash, V.; Rao, P.V. Expression profile of Japanese encephalitis virus induced neuroinflammation and its implication in disease severity. J. Clin. Virol. 2010, 49, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, M.; Srivastava, N.; Singh, S.K. Exploitation of microRNAs by Japanese Encephalitis virus in human microglial cells. J. Med. Virol. 2018, 90, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Akbar, I.; Kumari, B.; Vrati, S.; Basu, A.; Banerjee, A. Japanese Encephalitis Virus-induced let-7a/b interacted with the NOTCH-TLR7 pathway in microglia and facilitated neuronal death via caspase activation. J. Neurochem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germano, J.F.; Sawaged, S.; Saadaeijahromi, H.; Andres, A.M.; Feuer, R.; Gottlieb, R.A.; Sin, J. Coxsackievirus B infection induces the extracellular release of miR-590-5p, a proviral microRNA. Virology 2019, 529, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoshikawa, F.S.Y.; Teixeira, F.M.E.; Sato, M.N.; Oliveira, L.M.d.S. Delivery of microRNAs by Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infections: Could the News be Packaged? Cells 2019, 8, 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060611
Yoshikawa FSY, Teixeira FME, Sato MN, Oliveira LMdS. Delivery of microRNAs by Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infections: Could the News be Packaged? Cells. 2019; 8(6):611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060611
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoshikawa, Fabio Seiti Yamada, Franciane Mouradian Emidio Teixeira, Maria Notomi Sato, and Luanda Mara da Silva Oliveira. 2019. "Delivery of microRNAs by Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infections: Could the News be Packaged?" Cells 8, no. 6: 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060611
APA StyleYoshikawa, F. S. Y., Teixeira, F. M. E., Sato, M. N., & Oliveira, L. M. d. S. (2019). Delivery of microRNAs by Extracellular Vesicles in Viral Infections: Could the News be Packaged? Cells, 8(6), 611. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8060611





