MicroRNA-34a and MicroRNA-181a Mediate Visfatin-Induced Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress via NF-κB Pathway in Human Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chondrocyte Cultures
2.2. Treatment of Chondrocyte Cultures
2.3. Transfection of Chondrocytes
2.4. Detection of Apoptosis
2.5. RNA Isolation and Quantitative Real-Time PCR
2.6. Mitochondrial Superoxide Anion (•O2−) Production
2.7. Western Blot
2.8. Immunofluorescence Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
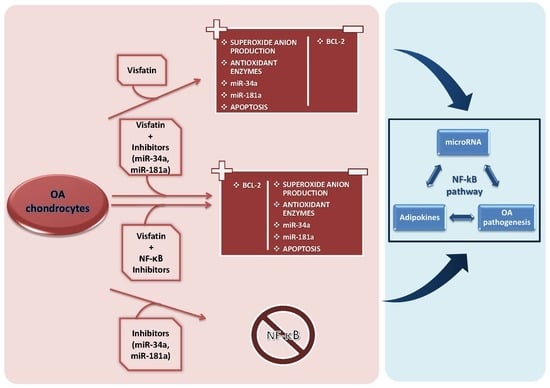
3. Results
3.1. Visfatin Regulates Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress Processes
3.2. MiRNA Specific Inhibitors Block Visfatin Effect on Mir-34a and Mir-181a Gene Expression
3.3. MiR-34a and Mir-181a Specific Inhibitors Prevent Chondrocyte Apoptosis Induced by Visfatin by Regulating BCL2
3.4. MiR-34a and MiR-181a Specific Inhibitors Regulate Oxidative Stress Induced by Visfatin
3.5. NF-κB Pathway Mediates Visfatin Effects
3.6. MiR-34a and MiR-181a Regulate NF-κB Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malemud, C.J. MicroRNAs and Osteoarthritis. Cells 2018, 7, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Prado, S.; Cicione, C.; Muiños-López, E.; Hermida-Gómez, T.; Oreiro, N.; Fernández-López, C.; Blanco, F.J. Characterization of microRNA expression profiles in normal and osteoarthritic human chondrocytes. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2012, 13, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Palma, A.; Cheleschi, S.; Pascarelli, N.A.; Tenti, S.; Galeazzi, M.; Fioravanti, A. Do MicroRNAs have a key epigenetic role in osteoarthritis and in mechanotransduction? Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cheleschi, S.; De Palma, A.; Pascarelli, N.A.; Giordano, N.; Galeazzi, M.; Tenti, S.; Fioravanti, A. Could Oxidative Stress Regulate the Expression of MicroRNA-146a and MicroRNA-34a in Human Osteoarthritic Chondrocyte Cultures? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, H.; Wedel, S.; Cavinato, M.; Jansen-Dürr, P. MicroRNA Regulation of Oxidative Stress-Induced Cellular Senescence. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumann, E.; Junker, S.; Schett, G.; Frommer, K.; Müller-Ladner, U. Adipokines in bone disease. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 296–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, V.; Pérez, T.; Pino, J.; López, V.; Franco, E.; Alonso, A.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Mera, A.; Lago, F.; Gómez, R.; et al. Biomechanics, obesity, and osteoarthritis. The role of adipokines: When the levee breaks. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 36, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenti, S.; Palmitesta, P.; Giordano, N.; Galeazzi, M.; Fioravanti, A. Increased serum leptin and visfatin levels in patients with diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis: A comparative study. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2017, 46, 156–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioravanti, A.; Cheleschi, S.; De Palma, A.; Addimanda, O.; Mancarella, L.; Pignotti, E.; Pulsatelli, L.; Galeazzi, M.; Meliconi, R. Can adipokines serum levels be used as biomarkers of hand osteoarthritis? Biomarkers 2018, 23, 265–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, V.; Ruiz-Fernández, C.; Pino, J.; Mera, A.; Gonzalez-Gay, M.A.; Gómez, R.; Lago, F.; Mobasheri, A.; Gualillo, O. Adipokines: Linking metabolic syndrome, the immune system, and arthritic diseases. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 165, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fioravanti, A.; Giannitti, C.; Cheleschi, S.; Simpatico, A.; Pascarelli, N.A.; Galeazzi, M. Circulating levels of adiponectin, resistin, and visfatin after mud-bath therapy in patients with bilateral knee osteoarthritis. Int. J. Biometeorol. 2015, 59, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, M.-H.; Tsai, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-L.; Fong, Y.-C.; Tang, C.-H. Visfatin Promotes IL-6 and TNF-α Production in Human Synovial Fibroblasts by Repressing miR-199a-5p through ERK, p38 and JNK Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheleschi, S.; Giordano, N.; Volpi, N.; Tenti, S.; Gallo, I.; Di Meglio, M.; Giannotti, S.; Fioravanti, A. A Complex Relationship between Visfatin and Resistin and microRNA: An In Vitro Study on Human Chondrocyte Cultures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurizi, G.; Babini, L.; Della Guardia, L. Potential role of microRNAs in the regulation of adipocytes liposecretion and adipose tissue physiology. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 9077–9086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altman, R.; Alarcon, G.; Appelrouth, D.; Bloch, D.; Borenstein, D.; Brandt, K.; Brown, C.; Cooke, T.D.; Daniel, W.; Feldman, D.; et al. The American College of Rheumatology criteria for the classification and reporting of osteoarthritis of the hip. Arthritis Rheum. 1991, 34, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mankin, H.J.; Dorfman, H.; Lippiello, L.; Zarins, A. Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. II. Correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data. J. Bone Jt. Surgery-American Vol. 1971, 53, 523–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francin, P.-J.; Guillaume, C.; Humbert, A.-C.; Pottie, P.; Netter, P.; Mainard, D.; Presle, N. Association between the chondrocyte phenotype and the expression of adipokines and their receptors: Evidence for a role of leptin but not adiponectin in the expression of cartilage-specific markers. J. Cell. Physiol. 2011, 226, 2790–2797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gosset, M.; Berenbaum, F.; Salvat, C.; Sautet, A.; Pigenet, A.; Tahiri, K.; Jacques, C. Crucial role of visfatin/pre–B cell colony-enhancing factor in matrix degradation and prostaglandin E2 synthesis in chondrocytes: Possible influence on osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 1399–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheleschi, S.; De Palma, A.; Pecorelli, A.; Pascarelli, N.A.; Valacchi, G.; Belmonte, G.; Carta, S.; Galeazzi, M.; Fioravanti, A. Hydrostatic Pressure Regulates MicroRNA Expression Levels in Osteoarthritic Chondrocyte Cultures via the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobasheri, A.; Rayman, M.P.; Gualillo, O.; Sellam, J.; Van Der Kraan, P.; Fearon, U. The role of metabolism in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deiuliis, J.A. MicroRNAs as regulators of metabolic disease: Pathophysiologic significance and emerging role as biomarkers and therapeutics. Int. J. Obes. 2016, 40, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, L.; Zhou, C.; Yang, X.; Li, L. Down-regulation of microRNA-375 regulates adipokines and inhibits inflammatory cytokines by targeting AdipoR2 in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 45, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasinski-Bergner, S.; Kielstein, H. Adipokines Regulate the Expression of Tumor-Relevant MicroRNAs. Obes. Facts 2019, 12, 211–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musumeci, G.; Castrogiovanni, P.; Trovato, F.M.; Weinberg, A.M.; Al-Wasiyah, M.K.; Alqahtani, M.H.; Mobasheri, A. Biomarkers of Chondrocyte Apoptosis and Autophagy in Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 20560–20575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Chen, S.; Gao, H.; Ren, L.; Song, G. Visfatin induces the apoptosis of endothelial progenitor cells via the induction of pro-inflammatory mediators through the NF-κB pathway. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 637–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wang, M.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, Y.; Qiu, X.; Ma, B.; Fan, Q. MicroRNA-34a affects chondrocyte apoptosis and proliferation by targeting the SIRT1/p53 signaling pathway during the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 38, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouheif, M.M.; Nakasa, T.; Shibuya, H.; Niimoto, T.; Kongcharoensombat, W.; Ochi, M. Silencing microRNA-34a inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis in a rat osteoarthritis model in vitro. Rheumatology 2010, 49, 2054–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P.; Chen, C.-Z.; Li, L.; Lodish, H.F. MicroRNAs Modulate Hematopoietic Lineage Differentiation. Science 2004, 303, 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Okuhara, A.; Nakasa, T.; Shibuya, H.; Niimoto, T.; Adachi, N.; Deie, M.; Ochi, M. Changes in microRNA expression in peripheral mononuclear cells according to the progression of osteoarthritis. Mod. Rheumatol. 2012, 22, 446–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Rampersaud, Y.R.; Sharma, A.; Lewis, S.J.; Wu, B.; Datta, P.; Sundararajan, K.; Endisha, H.; Rossomacha, E.; Rockel, J.S.; et al. Identification of microRNA-181a-5p and microRNA-4454 as mediators of facet cartilage degeneration. JCI Insight 2016, 1, 86820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Palma, A.; Cheleschi, S.; Pascarelli, N.A.; Giannotti, S.; Galeazzi, M.; Fioravanti, A. Hydrostatic pressure as epigenetic modulator in chondrocyte cultures: A study on miRNA-155, miRNA-181a and miRNA-223 expression levels. J. Biomech. 2018, 66, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, H.; Liu, J.; Tycksen, E.; Nunley, R.; McAlinden, A. MicroRNA-181a/b-1 over-expression enhances osteogenesis by modulating PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling and mitochondrial metabolism. Bone 2019, 123, 92–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, X.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Hou, D.; Zhu, A. Role of miR-181a in the process of apoptosis of multiple malignant tumors: A literature review. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 27, 263–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, A.; Rampersaud, Y.R.; Nakamura, S.; Sharma, A.M.; Zeng, F.; Rossomacha, E.; Ali, S.A.; Krawetz, R.; Haroon, N.; Perruccio, A.V.; et al. microRNA-181a-5p antisense oligonucleotides attenuate osteoarthritis in facet and knee joints. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.; Song, J.; Kim, S.; Chun, C.-H.; Jin, E.-J. MicroRNA-34a regulates migration of chondroblast and IL-1β-induced degeneration of chondrocytes by targeting EphA5. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 415, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisch, K.M.; Akagi, R.; Alvarez-Garcia, O.; Teramura, T.; Muramatsu, Y.; Saito, M.; Duffy, S.; Grogan, S.; Sasho, T.; D’Lima, D.; et al. Integrative omics profiling reveals dysregulated novel pathways mediated by microRNAs and DNA methylation in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, S829–S830. [Google Scholar]
- Ouyang, Y.B.; Lu, Y.; Yue, S.; Giffard, R.G. miR-181 targets multiple Bcl-2 family members and influences apoptosis and mitochondrial function in astrocytes. Mitochondrion 2012, 12, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Adamo, S.; Cetrullo, S.; Guidotti, S.; Borzì, R.M.; Flamigni, F.; D’Adamo, S. Hydroxytyrosol modulates the levels of microRNA-9 and its target sirtuin-1 thereby counteracting oxidative stress-induced chondrocyte death. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2017, 25, 600–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, C.M.; Guilak, F.; Weinberg, J.B.; Fermor, B. Reactive nitrogen and oxygen species in interleukin-1-mediated DNA damage associated with osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 624–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, T.M.; Resende, A.C.; Bezerra, F.F.; Da Costa, D.C.; O Soulage, C.; Daleprane, J.B. Activation of Nrf2-Antioxidant Signaling by 1,25-Dihydroxycholecalciferol Prevents Leptin-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Human Endothelial Cells. J. Nutr. 2017, 147, 506–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.M.; Ahmad, I.; Haqqi, T.M. Nrf2/ARE pathway attenuates oxidative and apoptotic response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes by activating ERK1/2/ELK1-P70S6K-P90RSK signaling axis. Free. Radic. Boil. Med. 2018, 116, 159–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathy-Hartert, M.; Hogge, L.; Sanchez, C.; Deby-Dupont, G.; Crielaard, J.; Henrotin, Y. Interleukin-1β and interleukin-6 disturb the antioxidant enzyme system in bovine chondrocytes: a possible explanation for oxidative stress generation. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2008, 16, 756–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.L.-H.; Chiang, S.; Kalinowski, D.S.; Bae, D.-H.; Sahni, S.; Richardson, D.R. The Role of the Antioxidant Response in Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Degenerative Diseases: Cross-Talk between Antioxidant Defense, Autophagy, and Apoptosis. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McMahon, M.; Thomas, N.; Itoh, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Hayes, J.D. Redox-regulated Turnover of Nrf2 Is Determined by at Least Two Separate Protein Domains, the Redox-sensitive Neh2 Degron and the Redox-insensitive Neh6 Degron*. J. Boil. Chem. 2004, 279, 31556–31567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchev, A.S.; Dimitrova, P.A.; Burns, A.J.; Kostov, R.V.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Georgiev, M.I. Oxidative stress and chronic inflammation in osteoarthritis: can NRF2 counteract these partners in crime? Ann. New York Acad. Sci. 2017, 1401, 114–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, H.; Fan, Y.; Kong, B.; Hu, H.; Hu, K.; Guo, J.; Mei, Y.; Liu, W.-L. Effects of Downregulation of MicroRNA-181a on H2O2-Induced H9c2 Cell Apoptosis via the Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2014, 2014, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.R.; Vuppusetty, C.; Colley, T.; Papaioannou, A.I.; Fenwick, P.; Donnelly, L.; Ito, K.; Barnes, P.J. Oxidative stress dependent microRNA-34a activation via PI3Kα reduces the expression of sirtuin-1 and sirtuin-6 in epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 35871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.L.; Fu, Y.Y.; Shi, M.Y.; Li, H.X. Down-regulation of miR-181a can reduce heat stress damage in PBMCs of Holstein cows. In Vitro Cell Dev. Biol. Anim. 2016, 52, 864–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, X.; Li, P.; Li, J.; He, R.; Cheng, G.; Li, Y. Downregulation of microRNA-34a inhibits oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigoglou, S.; Papavassiliou, A.G. The NF-κB signalling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Boil. 2013, 45, 2580–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Lenardo, M.J.; Baltimore, D. 30 years of NF-κB: a blossoming of relevance to human pathobiology. Cell 2017, 168, 37–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romacho, T.; Azcutia, V.; Vázquez-Bella, M.; Matesanz, N.; Cercas, E.; Nevado, J.; Carraro, R.; Rodriguez-Mañas, L.; Sánchez-Ferrer, C.F.; Peiro, C. Extracellular PBEF/NAMPT/visfatin activates pro-inflammatory signalling in human vascular smooth muscle cells through nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase activity. Diabetologia 2009, 52, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, J.; Qiao, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, S.; Zhao, W.; Gao, C. microRNA-210 negatively regulates LPS-induced production of proinflammatory cytokines by targeting NF-κB1 in murine macrophages. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 1201–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, F.; Yang, Y.; Jin, D.; Sun, J.; Yu, X.; Yang, Z. MiRNA-145 is involved in the development of resistin-induced insulin resistance in HepG2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 445, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Zhou, B.; Li, H. miR-27 inhibits the NF-κB signaling pathway by targeting leptin in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 40, 523–530. [Google Scholar]







| miRNA Genes | Cat. No. (Qiagen) |
| miR-34a | MS00003318 |
| miR-181a | MS00006692 |
| SNORD-25 | MS00014007 |
| Target Genes | Cat. No. (Qiagen) |
| BCL2 | QT00000721 |
| SOD-2 | QT01008693 |
| CAT | QT00079674 |
| NRF2 | QT00027384 |
| ACTB | QT00095431 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheleschi, S.; Tenti, S.; Mondanelli, N.; Corallo, C.; Barbarino, M.; Giannotti, S.; Gallo, I.; Giordano, A.; Fioravanti, A. MicroRNA-34a and MicroRNA-181a Mediate Visfatin-Induced Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress via NF-κB Pathway in Human Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes. Cells 2019, 8, 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080874
Cheleschi S, Tenti S, Mondanelli N, Corallo C, Barbarino M, Giannotti S, Gallo I, Giordano A, Fioravanti A. MicroRNA-34a and MicroRNA-181a Mediate Visfatin-Induced Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress via NF-κB Pathway in Human Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes. Cells. 2019; 8(8):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080874
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheleschi, Sara, Sara Tenti, Nicola Mondanelli, Claudio Corallo, Marcella Barbarino, Stefano Giannotti, Ines Gallo, Antonio Giordano, and Antonella Fioravanti. 2019. "MicroRNA-34a and MicroRNA-181a Mediate Visfatin-Induced Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress via NF-κB Pathway in Human Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes" Cells 8, no. 8: 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080874
APA StyleCheleschi, S., Tenti, S., Mondanelli, N., Corallo, C., Barbarino, M., Giannotti, S., Gallo, I., Giordano, A., & Fioravanti, A. (2019). MicroRNA-34a and MicroRNA-181a Mediate Visfatin-Induced Apoptosis and Oxidative Stress via NF-κB Pathway in Human Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes. Cells, 8(8), 874. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8080874