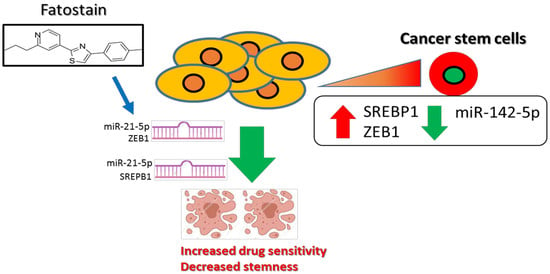
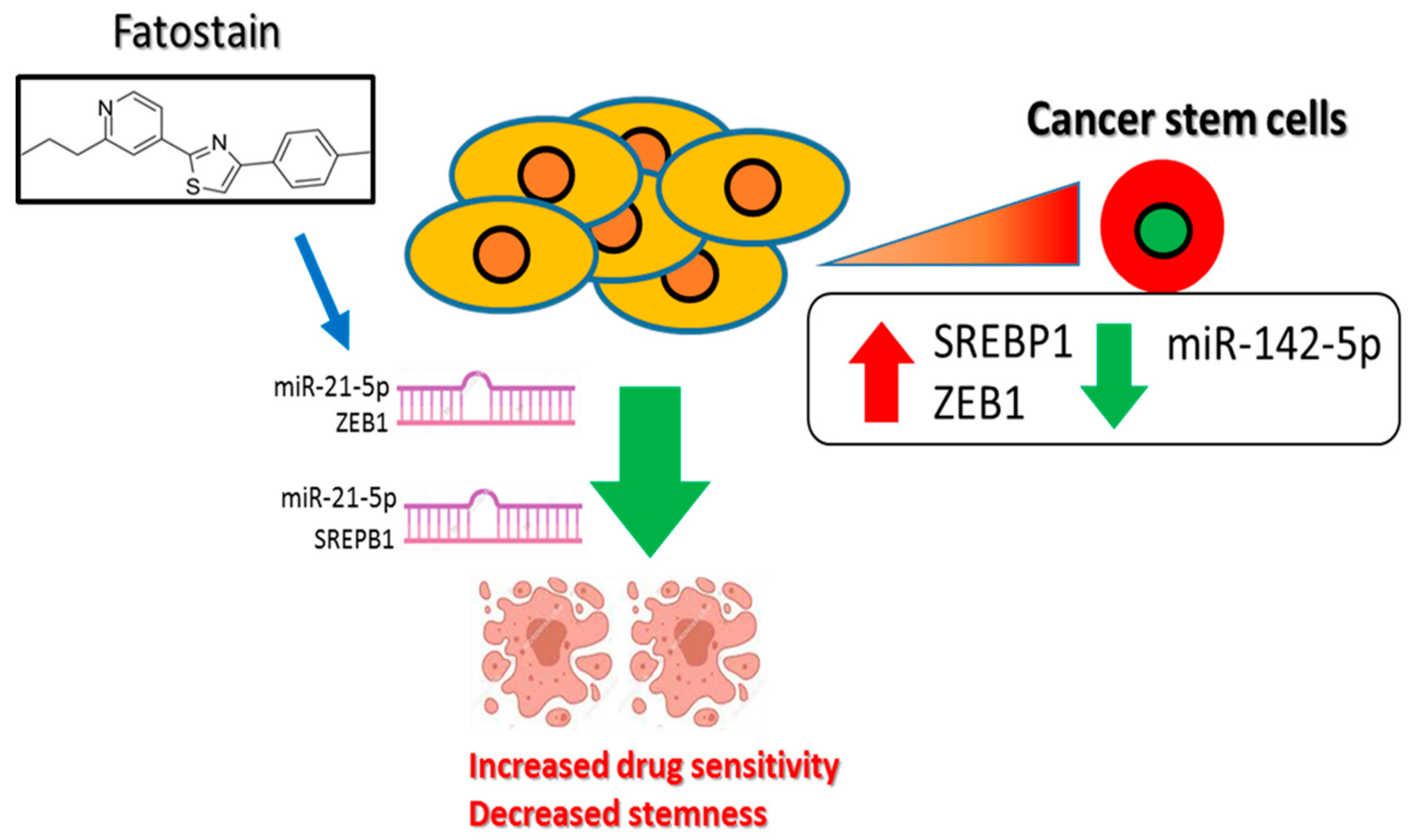
Disruption of Cancer Metabolic SREBP1/miR-142-5p Suppresses Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness in Esophageal Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.3. Gene-Silencing Experiments
2.4. Colony Formation Assay
2.5. Tumor Sphere Formation Assay
2.6. Real-Time PCR
2.7. SDS-PAGE and Western Blots
2.8. Flow Cytometric Analysis
2.9. In Vitro Migration and Invasion Assays
2.10. Animal Experiments
2.11. Immunohistochemistry
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. SREBP1 Expression Was Elevated in ESCC Tissues and Cell Lines
3.2. SREBP1 Expression Is Closely Associated with EMT and Metastatic Potential of ESCC
3.3. Tumor Suppressor miR-142-5p Targets both SREBP1 and ZEB1
3.4. SREBP1 Inhibitor, Fatostatin, Suppressed ESCC Tumorigenesis, and Stemness
3.5. In Vivo Validation of the Antineoplastic Function of Fatostatin
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abnet, C.C.; Arnold, M.; Wei, W.Q. Epidemiology of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2018, 154, 360–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, S. World Cancer Report 2014. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization, International Agency for Research on Cancer, WHO Press, 2015. Adv. Nutr. 2015, 7, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hou, H.; Meng, Z.; Zhao, X.; Ding, G.; Sun, M.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Survival of Esophageal Cancer in China: A Pooled Analysis on Hospital-Based Studies From 2000 to 2018. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Deng, F.; Liu, Q.; Ma, Y. Prognostic significance of lymph node metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2017, 213, 842–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordonez-Moran, P.; Huelsken, J. Complex metastatic niches: Already a target for therapy? Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2014, 31, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeone, P.; Trerotola, M.; Franck, J.; Cardon, T.; Marchisio, M.; Fournier, I.; Salzet, M.; Maffia, M.; Vergara, D. The multiverse nature of epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 58, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dongre, A.; Weinberg, R.A. New insights into the mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 20, 69–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saini, S.; Sripada, L.; Tulla, K.; Kumar, P.; Yue, F.; Kunda, N.; Maker, A.V.; Prabhakar, B.S. Loss of MADD expression inhibits cellular growth and metastasis in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, R.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, L.; Dai, D.; Wu, D.; Mi, L.; Mao, C.; Chen, D. Lin28/microRNA-let-7a promotes metastasis under circumstances of hyperactive Wnt signaling in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5265–5271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Li, W.; Liu, S.; Su, Y.; Han, G.; Xu, C.; Liu, H.; Zheng, T.; Zhou, Y.; Mao, C. Interleukin-23 promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of oesophageal carcinoma cells via the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, H.; Yang, X.; Guo, Y.; Shui, L.; Li, S.; Bai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, M.; Xia, J. HERG1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis through TXNDC5 by activating the PI3K/AKT pathway. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, R.; Ding, F.; Cao, X.; Lin, D.; Liu, Z. OTUB1 promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma metastasis through modulating Snail stability. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3356–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Chikina, M.; Deshpande, R.; Menk, A.V.; Wang, T.; Tabib, T.; Brunazzi, E.A.; Vignali, K.M.; Sun, M.; Stolz, D.B.; et al. Treg Cells Promote the SREBP1-Dependent Metabolic Fitness of Tumor-Promoting Macrophages via Repression of CD8(+) T Cell-Derived Interferon-gamma. Immunity 2019, 51, 381–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, L.; Li, Q.; Li, S.; He, J.; Cao, W.; Lan, J.; Sun, B.; Zou, H.; Wang, C.; Liu, R.; et al. Membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma: Observations from clinical and in vitro analyses. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kaufhold, S.; Bonavida, B. Central role of Snail1 in the regulation of EMT and resistance in cancer: A target for therapeutic intervention. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Wei, L.; Huang, X.; Zheng, J.; Shao, M.; Feng, T.; Li, J.; Han, Y.; Tan, W.; Tan, W.; et al. Solute Carrier Family 39 Member 6 Gene Promotes Aggressiveness of Esophageal Carcinoma Cells by Increasing Intracellular Levels of Zinc, Activating Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase Signaling, and Up-regulating Genes That Regulate Metastasis. Gastroenterology 2017, 152, 1985–1997.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hasan, M.R.; Sharma, R.; Saraya, A.; Chattopadhyay, T.K.; DattaGupta, S.; Walfish, P.G.; Chauhan, S.S.; Ralhan, R. Slug is a predictor of poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma patients. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Harada, H.; Hosoda, K.; Moriya, H.; Mieno, H.; Ema, A.; Washio, M.; Kikuchi, M.; Kosaka, Y.; Watanabe, M.; Yamashita, K. Carcinosarcoma of the esophagus: A report of 6 cases associated with zinc finger E-box-binding homeobox 1 expression. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 578–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakazawa, T.; Nobusawa, S.; Ikota, H.; Kuwano, H.; Takeyoshi, I.; Yokoo, H. Wide expression of ZEB1 in sarcomatous component of spindle cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Pathol. Int. 2015, 65, 635–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Qian, W.; Ma, J.; Cheng, L.; Jiang, Z.; Yan, B.; Li, J.; Duan, W.; Sun, L.; Cao, J.; et al. Resveratrol enhances the chemotherapeutic response and reverses the stemness induced by gemcitabine in pancreatic cancer cells via targeting SREBP1. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nie, L.Y.; Lu, Q.T.; Li, W.H.; Yang, N.; Dongol, S.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, J. Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 is required for ovarian tumor growth. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 30, 1346–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheng, C.; Ru, P.; Geng, F.; Liu, J.; Yoo, J.Y.; Wu, X.; Cheng, X.; Euthine, V.; Hu, P.; Guo, J.Y.; et al. Glucose-Mediated N-glycosylation of SCAP Is Essential for SREBP-1 Activation and Tumor Growth. Cancer Cell 2015, 28, 569–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Griffiths, B.; Lewis, C.A.; Bensaad, K.; Ros, S.; Zhang, Q.; Ferber, E.C.; Konisti, S.; Peck, B.; Miess, H.; East, P.; et al. Sterol regulatory element binding protein-dependent regulation of lipid synthesis supports cell survival and tumor growth. Cancer Metab. 2013, 1, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Singh, K.B.; Hahm, E.R.; Pore, S.K.; Singh, S.V. Leelamine is a Novel Lipogenesis Inhibitor in Prostate Cancer Cells In Vitro and In Vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2019, 18, 1800–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, Y.; Nan, X.; Shi, X.; Mu, X.; Liu, B.; Zhu, H.; Yao, B.; Liu, X.; Yang, T.; Hu, Y.; et al. SREBP1 promotes the invasion of colorectal cancer accompanied upregulation of MMP7 expression and NF-kappaB pathway activation. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perone, Y.; Farrugia, A.J.; Meira, A.R.; Gyorffy, B.; Ion, C.; Uggetti, A.; Chronopoulos, A.; Marrazzo, P.; Faronato, M.; Shousha, S.; et al. SREBP1 drives Keratin-80-dependent cytoskeletal changes and invasive behavior in endocrine-resistant ERalpha breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, N.; Clifford, R.J.; Yang, H.H.; Wang, C.; Goldstein, A.M.; Ding, T.; Taylor, P.R.; Lee, M.P. Genome wide analysis of DNA copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity (CNNLOH) and its relation to gene expression in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, H.; Hu, N.; Yang, H.H.; Wang, C.; Takikita, M.; Wang, Q.H.; Giffen, C.; Clifford, R.; Hewitt, S.M.; Shou, J.Z.; et al. Global gene expression profiling and validation in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and its association with clinical phenotypes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2955–2966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gao, S.; Shi, Z.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, J. Fatostatin suppresses growth and enhances apoptosis by blocking SREBP-regulated metabolic pathways in endometrial carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1919–1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siqingaowa; Sekar, S.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Taghibiglou, C. Sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 inhibitors decrease pancreatic cancer cell viability and proliferation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 488, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillet-Deniau, I.; Pichard, A.L.; Kone, A.; Esnous, C.; Nieruchalski, M.; Girard, J.; Prip-Buus, C. Glucose induces de novo lipogenesis in rat muscle satellite cells through a sterol-regulatory-element-binding-protein-1c-dependent pathway. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Koizume, S.; Takahashi, T.; Yoshihara, M.; Nakamura, Y.; Ruf, W.; Takenaka, K.; Miyagi, E.; Miyagi, Y. Cholesterol Starvation and Hypoxia Activate the FVII Gene via the SREBP1-GILZ Pathway in Ovarian Cancer Cells to Produce Procoagulant Microvesicles. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 119, 1058–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, A.K.; Lung, R.W.; Dawson, C.W.; Young, L.S.; Ko, C.W.; Yeung, W.W.; Kang, W.; To, K.F.; Lo, K.W. Activation of sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1)-mediated lipogenesis by the Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) promotes cell proliferation and progression of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2018, 246, 180–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, N.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Y.; Su, P.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Sun, M.; Chen, B.; Zhao, W.; Wang, L.; et al. SREBP1, targeted by miR-18a-5p, modulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition in breast cancer via forming a co-repressor complex with Snail and HDAC1/2. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 843–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giudetti, A.M.; De Domenico, S.; Ragusa, A.; Lunetti, P.; Gaballo, A.; Franck, J.; Simeone, P.; Nicolardi, G.; De Nuccio, F.; Santino, A.; et al. A specific lipid metabolic profile is associated with the epithelial mesenchymal transition program. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta. Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2019, 1864, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Qian, W.; Li, J.; Ma, J.; Chen, X.; Jiang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Duan, W.; Wang, Z.; Wu, Z.; et al. High glucose microenvironment accelerates tumor growth via SREBP1-autophagy axis in pancreatic cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, D.; Li, J.; Zhang, L.; Hu, L. miR-142-5p suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis of human osteosarcoma cell line, HOS, by targeting PLA2G16 through the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 17, 1363–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, X.; Chen, W.; Jin, Y.; Xue, R.; Su, J.; Mu, Z.; Li, J.; Jiang, S. miR-142-5p enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in ovarian cancer cells by targeting multiple anti-apoptotic genes. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 161, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, Z.; Xie, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Hu, X.; Na, Q.; Zhang, X.; Wei, G.; Xu, S.; Liu, Y.; et al. miR-142-5p in Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes Osteoporosis Involving Targeting Adhesion Molecule VCAM-1 and Inhibiting Cell Migration. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 3274641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Trissal, M.C.; Wong, T.N.; Yao, J.C.; Ramaswamy, R.; Kuo, I.; Baty, J.; Sun, Y.; Jih, G.; Parikh, N.; Berrien-Elliott, M.M.; et al. MIR142 Loss-of-Function Mutations Derepress ASH1L to Increase HOXA Gene Expression and Promote Leukemogenesis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 3510–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Yan, H.; Zhao, L.; Jia, W.; Yang, H.; Liu, L.; Zhou, X.; Miao, P.; Sun, X.; Song, S.; et al. Inhibition of SREBP increases gefitinib sensitivity in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 52392–52403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Due, S.L.; Watson, D.I.; Bastian, I.; Ding, G.Q.; Sukocheva, O.A.; Astill, D.S.; Vat, L.; Hussey, D.J. Tamoxifen enhances the cytotoxicity of conventional chemotherapy in esophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 25, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukocheva, O.A.; Li, B.; Due, S.L.; Hussey, D.J.; Watson, D.I. Androgens and esophageal cancer: What do we know? World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 6146–6156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukocheva, O.A.; Wee, C.; Ansar, A.; Hussey, D.J.; Watson, D.I. Effect of estrogen on growth and apoptosis in esophageal adenocarcinoma cells. Dis. Esophagus Off. J. Int. Soc. Dis. Esophagus 2013, 26, 628–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Settleman, J. EMT, cancer stem cells and drug resistance: An emerging axis of evil in the war on cancer. Oncogene 2010, 29, 4741–4751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brovkovych, V.; Izhar, Y.; Danes, J.M.; Dubrovskyi, O.; Sakallioglu, I.T.; Morrow, L.M.; Atilla-Gokcumen, G.E.; Frasor, J. Fatostatin induces pro- and anti-apoptotic lipid accumulation in breast cancer. Oncogenesis 2018, 7, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebi, A.; Dehairs, J.; Rambow, F.; Rogiers, A.; Nittner, D.; Derua, R.; Vanderhoydonc, F.; Duarte, J.A.G.; Bosisio, F.; Van den Eynde, K.; et al. Sustained SREBP-1-dependent lipogenesis as a key mediator of resistance to BRAF-targeted therapy. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.R.; Xing, F.; Sharma, S.; Watabe, M.; Pai, S.K.; Iiizumi-Gairani, M.; Fukuda, K.; Hirota, S.; Mo, Y.Y.; Watabe, K. Elevated lipogenesis in epithelial stem-like cell confers survival advantage in ductal carcinoma in situ of breast cancer. Oncogene 2013, 32, 5111–5122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Al-Khyatt, W.; Tufarelli, C.; Khan, R.; Iftikhar, S.Y. Selective oestrogen receptor antagonists inhibit oesophageal cancer cell proliferation in vitro. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Choi, I.; Delage-Mourroux, R.; Ediger, T.R.; Martini, P.G.; Montano, M.; Sun, J.; Weis, K.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A. Molecular mechanisms of estrogen action: Selective ligands and receptor pharmacology. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2000, 74, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Gene | Forward sequence | Reverse sequence |
|---|---|---|
| SREBP1 | CGGCGCTGCTGACCGACATC | CCCTGCCCCACTCCCAGCAT |
| GAPDH | AGCCACATCGCTCAGACAC | GCCCAATACGACCAAATCC |
| miR-142-5p | AACTCCAGCTGGTCCTTAG | TCTTGAACCCTCATCCTGT |
| U6 | GCTTCGGCAGCACATATACTAAAAT | CGCTTCACGAATTTGCGT |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, C.-M.; Huang, C.-S.; Hsu, T.-N.; Huang, M.-S.; Fong, I.-H.; Lee, W.-H.; Liu, S.-C. Disruption of Cancer Metabolic SREBP1/miR-142-5p Suppresses Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness in Esophageal Carcinoma. Cells 2020, 9, 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010007
Huang C-M, Huang C-S, Hsu T-N, Huang M-S, Fong I-H, Lee W-H, Liu S-C. Disruption of Cancer Metabolic SREBP1/miR-142-5p Suppresses Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness in Esophageal Carcinoma. Cells. 2020; 9(1):7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010007
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Chih-Ming, Chin-Sheng Huang, Tung-Nien Hsu, Mao-Suan Huang, Iat-Hang Fong, Wei-Hwa Lee, and Shao-Cheng Liu. 2020. "Disruption of Cancer Metabolic SREBP1/miR-142-5p Suppresses Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness in Esophageal Carcinoma" Cells 9, no. 1: 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010007
APA StyleHuang, C.-M., Huang, C.-S., Hsu, T.-N., Huang, M.-S., Fong, I.-H., Lee, W.-H., & Liu, S.-C. (2020). Disruption of Cancer Metabolic SREBP1/miR-142-5p Suppresses Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness in Esophageal Carcinoma. Cells, 9(1), 7. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9010007