Neurological Disturbances of Ciguatera Poisoning: Clinical Features and Pathophysiological Basis
Abstract
:1. Ciguatera: An Underreported and Misdiagnosed Disease Lacking Effective Prevention and Treatment
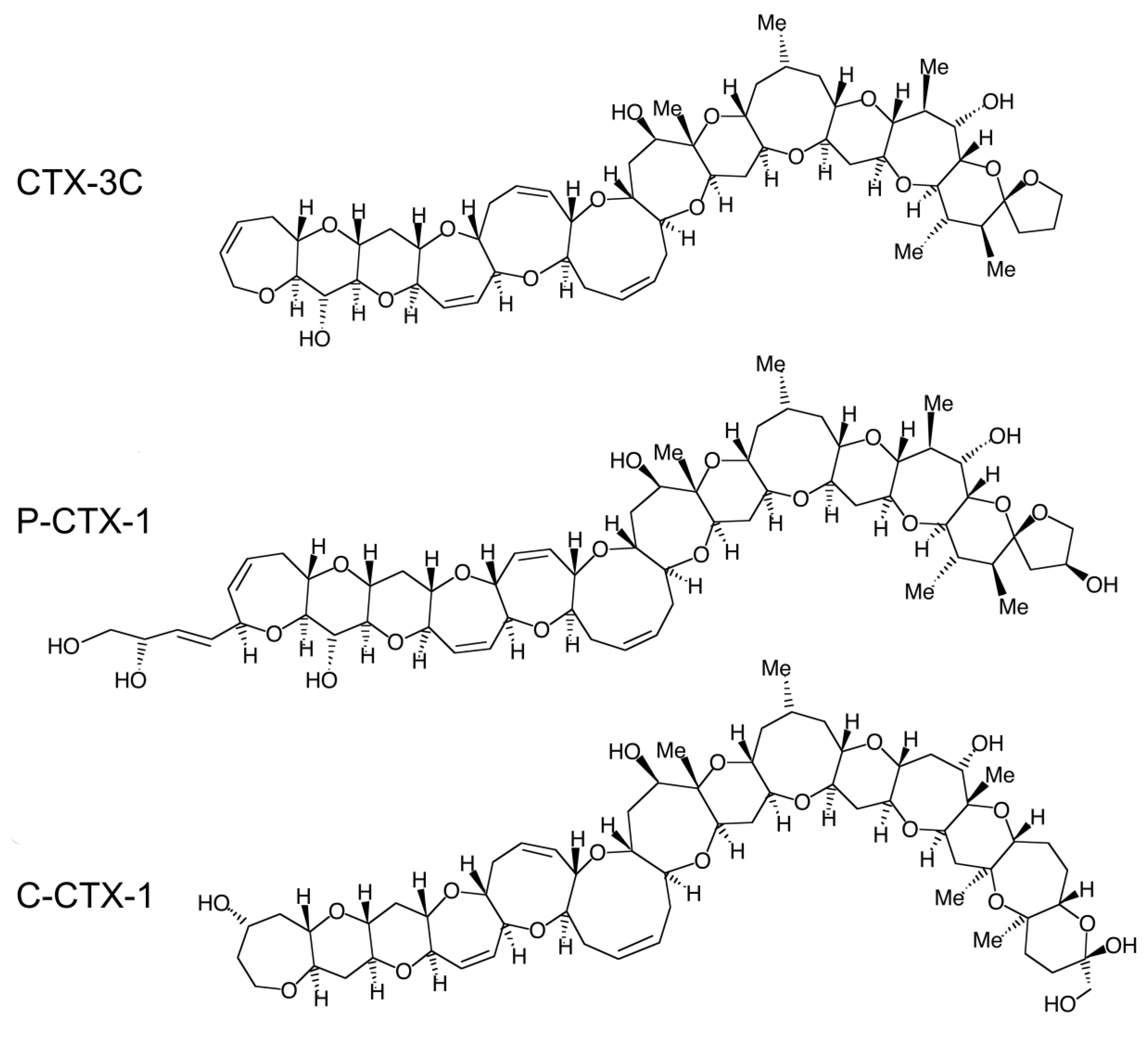
2. Clinical Features of Ciguatera
2.1. Clinical Features of Acute CFP: A Variety of Neurological Signs with Pathognomonic Sensory Disturbances
2.1.1. Paresthesia
2.1.2. Cold Dysesthesia
2.1.3. Pruritus
2.2. Cardiovascular and central Neurological Disorders in the Most Severe Cases
2.3. Persistent and Relapsing Symptoms for Weeks, Months or Years
2.4. Factors Underlying the Variability in Ciguatera Symptomatology
3. Pathophysiological Basis of Ciguatera Neurological Disturbances
3.1. Neuronal Molecular Targets of CTXs Resulting in Membrane Hyperexcitability
3.1.1. Voltage-Gated Sodium Channels (Nav) As the Main Primary Targets
3.1.2. Blockage of Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels (Kv)
3.2. Neurocellular Effects of CTXs
3.2.1. Cell Swelling
3.2.2. Neuromediator Release Linked to Autonomic Dysfunctions and Sensory Disturbances
- Acetylcholine (ACh) release:
- Release of noradrenaline (NAd) and other catecholamines:
- Neuropeptide release and role of peptidergic neurons in sensory disturbances:
- Modulation of central neurotransmitter release:
3.2.3. Increase in Intracellular Calcium Concentration in Excitable Cells by Multiple Mechanisms
- Calcium influx through the Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX):
- Calcium mobilization from intracellular stores:
- Calcium influx through transient receptor potential (TRP) channels:
- Calcium influx through voltage-gated calcium channels (Cav):
3.2.4. Modulation of Gene Expression
3.3. Neurophysiological and Nerve Histological Studies
3.4. Unsolved Issues: Prevalence and Persistence of Sensory Disturbances
4. Treatment of Ciguatera Poisoning
- -
- -
- to prevent and reverse the P-CTX-1-induced increase in nodal membrane excitability and swelling of frog myelinated axons [216];
- -
- -
- Low dose of the tricyclic antidepressant amitriptyline during the first few days have shown a variable beneficial effect on some long-lasting neurological disturbances (paresthesia, myalgia, pruritus, headache) and bradycardia, and no effect on cold dysesthesia [223,224,225,226,227]. Experimentally, amitriptyline was ineffective in reducing cold allodynia induced in rats after intraplantar exposure to P-CTX-1 [72].
- -
- Lidocaine is a local anesthetic that inhibits Nav channels. In frog myelinated axons, lidocaine reversed the membrane hyperexcitability and axonal swelling induced by P-CTX-1 [12,216]. In vivo, it countered some cardiovascular effects and some peripheral nerve disturbances elicited by ciguatoxic extracts in cats [228] and in rats [229], respectively. In humans, beneficial effects on the persistent neurological signs were obtained in 3 patients by using the orally effective local anesthetic tocainide [225].
- -
- -
- Nifedipine, a calcium channel antagonist, has successfully improved headache with no effect on myalgia, pruritus or cold dysesthesia [224]. It partially inhibited the P-CTX-1-induced calcium response in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells but failed to alter the cold allodynia induced by P-CTX-1 in rats [72].
5. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chinain, M.; Germain, M.; Deparis, X.; Pauillac, S.; Legrand, A.-M. Seasonal abundance and toxicity of the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus spp. (Dinophyceae), the causative agent of ciguatera in Tahiti, French Polynesia. Mar. Biol. 1999, 135, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Litaker, R.W.; Vandersea, M.W.; Faust, M.A.; Kibler, S.R.; Nau, A.W.; Holland, W.C.; Chinain, M.; Holmes, M.J.; Tester, P.A. Global distribution of ciguatera causing dinoflagellates in the genus Gambierdiscus. Toxicon 2010, 56, 711–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, P.T.Y.; Yan, M.; Lam, V.T.T.; Yiu, S.K.F.; Chen, C.-Y.; Murray, J.S.; Harwood, D.T.; Rhodes, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S.; Wai, T.-C. Phylogeny, morphology and toxicity of benthic dinoflagellates of the genus Fukuyoa (Goniodomataceae, Dinophyceae) from a subtropical reef ecosystem in the South China Sea. Harmful Algae 2018, 74, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Legrand, A.M.; Yasumoto, T. Isolation and structure of ciguatoxin-4A, a new ciguatoxin precursor, from cultures of dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus and Parrotfish Scarus gibbus. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1997, 60, 2103–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yogi, K.; Sakugawa, S.; Oshiro, N.; Ikehara, T.; Sugiyama, K.; Yasumoto, T. Determination of toxins involved in ciguatera fish poisoning in the Pacific by LC/MS. J. AOAC Int. 2014, 97, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, M.; Legrand, A.M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Fukui, M.; Yasumoto, T. Structures and configurations of ciguatoxin from the Moray Eel Gymnothorax javanicus and its likely precursor from the dinoglagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 4380–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satake, M.; Murata, M.; Yasumoto, T. The structure of CTX3C, a ciguatoxin congener isolated from cultured Gambierdiscus toxicus. Tetrahedron Lett. 1993, 34, 1979–1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yogi, K.; Oshiro, N.; Inafuku, Y.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T. Detailed LC-MS/MS analysis of ciguatoxins revealing distinct regional and species characteristics in fish and causative alga from the Pacific. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 8886–8891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soliño, L.; Costa, P.R. Global impact of ciguatoxins and ciguatera fish poisoning on fish, fisheries and consumers. Environ. Res. 2020, 182, 109111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Holmes, M.J. Origin and transfer of toxins involved in ciguatera. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part C Comp. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1993, 106, 615–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Sellin, M.; Poli, M.A.; Norton, R.S.; MacLeod, J.K.; Sheil, M.M. Purification and characterization of ciguatoxins from moray eel (Lycodontis javanicus, Muraenidae). Toxicon 1991, 29, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, E.; Legrand, A.-M. Gambiertoxin-induced modifications of the membrane potential of myelinated nerve fibres. Mem. Qld. Mus. 1994, 34, 461–464. [Google Scholar]
- Pawlowiez, R.; Darius, H.T.; Cruchet, P.; Rossi, F.; Caillaud, A.; Laurent, D.; Chinain, M. Evaluation of seafood toxicity in the Australes archipelago (French Polynesia) using the neuroblastoma cell-based assay. Food Addit. Contam. Part A Chem. Anal. Control Expo. Risk Assess. 2013, 30, 567–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roue, M.; Darius, H.T.; Picot, S.; Ung, A.; Viallon, J.; Gaertner-Mazouni, N.; Sibat, M.; Amzil, Z.; Chinain, M. Evidence of the bioaccumulation of ciguatoxins in giant clams (Tridacna maxima) exposed to Gambierdiscus spp. cells. Harmful Algae 2016, 57, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- FAO; WHO. Report of the Expert Meeting on Ciguatera Poisoning: Rome, 19–23 November 2018; Food Safety and Quality Series; FAO and WHO: Rome, Italy, 2020; ISBN 978-92-5-132518-6. [Google Scholar]
- Lehane, L.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatera: Recent advances but the risk remains. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 61, 91–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossen, V.; Solino, L.; Leroy, P.; David, E.; Velge, P.; Dragacci, S.; Krys, S.; Flores Quintana, H.; Diogene, J. Contribution to the risk characterization of ciguatoxins: LOAEL estimated from eight ciguatera fish poisoning events in Guadeloupe (French West Indies). Environ. Res 2015, 143, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Luan, W.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Luo, X. Ultrasensitive and accelerated detection of ciguatoxin by capillary electrophoresis via on-line sandwich immunoassay with rotating magnetic field and nanoparticles signal enhancement. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 888, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Sato, T.; Hirama, M.; Fujii, I. Highly Sensitive and Practical Fluorescent Sandwich ELISA for Ciguatoxins. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7318–7324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsumuraya, T.; Hirama, M. Rationally Designed Synthetic Haptens to Generate Anti-Ciguatoxin Monoclonal Antibodies, and Development of a Practical Sandwich ELISA to Detect Ciguatoxins. Toxins 2019, 11, 533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pasinszki, T.; Lako, J.; Dennis, T.E. Advances in Detecting Ciguatoxins in Fish. Toxins 2020, 12, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graber, N.; Stavinsky, F.; Hoffman, R.; Button, J.; Clark, N.; Martin, S.; Robertson, A.; Hustedt, J. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) Ciguatera fish poisoning—New York City, 2010–2011. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2013, 62, 61–65. [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton, B.; Whittle, N.; Shaw, G.; Eaglesham, G.; Moore, M.R.; Lewis, R.J. Human fatality associated with Pacific ciguatoxin contaminated fish. Toxicon 2010, 56, 668–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottier, I.; Vernoux, J.P.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Analysis of toxin profiles in three different fish species causing ciguatera fish poisoning in Guadeloupe, French West Indies. Food Addit. Contam. 2002, 19, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.-K.; Hung, P.; Lo, J.Y.C. Ciguatera fish poisoning in Hong Kong—A 10-year perspective on the class of ciguatoxins. Toxicon 2014, 86, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardison, D.R.; Holland, W.C.; McCall, J.R.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Baden, D.G.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Tester, P.A.; Shea, D.; Flores Quintana, H.A.; et al. Fluorescent Receptor Binding Assay for Detecting Ciguatoxins in Fish. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estevez, P.; Sibat, M.; Leão-Martins, J.M.; Reis Costa, P.; Gago-Martínez, A.; Hess, P. Liquid Chromatography Coupled to High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry for the Confirmation of Caribbean Ciguatoxin-1 as the Main Toxin Responsible for Ciguatera Poisoning Caused by Fish from European Atlantic Coasts. Toxins 2020, 12, 267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bottein Dechraoui, M.Y.; Wang, Z.; Turquet, J.; Chinain, M.; Darius, T.; Cruchet, P.; Radwan, F.F.; Dickey, R.W.; Ramsdell, J.S. Biomonitoring of ciguatoxin exposure in mice using blood collection cards. Toxicon 2005, 46, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dechraoui Bottein, M.-Y.; Wang, Z.; Ramsdell, J.S. Toxicokinetics of the ciguatoxin P-CTX-1 in rats after intraperitoneal or oral administration. Toxicology 2011, 284, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matta, J.; Navas, J.; Milad, M.; Manger, R.; Hupka, A.; Frazer, T. A pilot study for the detection of acute ciguatera intoxication in human blood. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 49–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernoux, J.P.; Lewis, R.J. Isolation and characterisation of Caribbean ciguatoxins from the horse-eye jack (Caranx latus). Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 1997, 35, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnis, R.; Kuberski, T.; Laugier, S. Clinical observations on 3009 cases of ciguatera (fish poisoning) in the South Pacific. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1979, 28, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshiro, N.; Yogi, K.; Asato, S.; Sasaki, T.; Tamanaha, K.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Inafuku, Y. Ciguatera incidence and fish toxicity in Okinawa, Japan. Toxicon 2010, 56, 656–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.; Hung, P.; Lee, K.L.; Mok, T.; Chung, T.; Kam, K.M. Features of ciguatera fish poisoning cases in Hong Kong 2004–2007. Biomed. Environ. Sci. 2008, 21, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, I.; Vernoux, J.P.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatera fish poisoning in the Caribbean islands and Western Atlantic. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Ware, G.W., Nigg, H.N., Eds.; Springer: Tuscon, Arizona, 2001; pp. 99–141. [Google Scholar]
- Quod, J.P.; Turquet, J. Ciguatera in Réunion Island (SW Indian Ocean): Epidemiology and clinical patterns. Toxicon 1996, 34, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Jones, A. Characterization of ciguatoxins and ciguatoxin congeners present in ciguateric fish by gradient reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Toxicon 1997, 35, 159–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pottier, I.; Hamilton, B.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J.; Vernoux, J.P. Identification of slow and fast-acting toxins in a highly ciguatoxic barracuda (Sphyraena barracuda) by HPLC/MS and radiolabelled ligand binding. Toxicon 2003, 42, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pottier, I.; Vernoux, J.-P.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Characterisation of multiple Caribbean ciguatoxins and congeners in individual specimens of horse-eye jack (Caranx latus) by high-performance liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Toxicon 2002, 40, 929–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, B.; Hurbungs, M.; Vernoux, J.-P.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Isolation and characterisation of Indian Ocean ciguatoxin. Toxicon 2002, 40, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, B.; Hurbungs, M.; Jones, A.; Lewis, R.J. Multiple ciguatoxins present in Indian Ocean reef fish. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1347–1353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, L.E.; Baden, D.G.; Bean, J.A.; Weisman, R.; Blythe, D.G. Marine Seafood Toxin Diseases: Issues in Epidemiology and Community Outreach. In Harmful Algae, Proceedings of the VIII International Conference on Harmful Algae, Vigo, Spain, 25–29 June 1997; Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Galicia, Spain, 1998; pp. 245–248. [Google Scholar]
- Ansdell, V.E. Food Poisoning from Marine Toxins. In CDC Yellow Book 2018: Health Information for International Travel; Oxford University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 77–81. ISBN 978-0-19-062861-1. [Google Scholar]
- Bagnis, R. Clinical aspects of ciguatera (fish poisoning) in French Polynesia. Hawaii Med. J. 1968, 28, 25–28. [Google Scholar]
- Rongo, T.; Van Woesik, R. Ciguatera poisoning in Rarotonga, southern Cook Islands. Harmful Algae 2011, 10, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skinner, M.P.; Brewer, T.D.; Johnstone, R.; Fleming, L.E.; Lewis, R.J. Ciguatera fish poisoning in the Pacific Islands (1998 to 2008). PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2011, 5, e1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, D.B.; Fleming, L.E.; Tamer, R.; Weisman, R.; Blythe, D. Physician diagnosis and reporting of ciguatera fish poisoning in an endemic area. In Harmful Algal Blooms 2000; Hallegraeff, G.M., Blackburn, S.I., Bolch, C.J., Lewis, R.J., Eds.; Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 451–453. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, W.R.; Snyder, F.R.; Fudala, P.J. Travel and Ciguatera Fish Poisoning. Arch. Intern. Med. 1992, 152, 2049–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Haro, L.; Pommier, P.; Valli, M. Emergence of imported ciguatera in Europe: Report of 18 cases at the Poison Control Centre of Marseille. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 2003, 41, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glaizal, M.; Tichadou, L.; Drouet, G.; Hayek-Lanthois, M.; De Haro, L. Ciguatera contracted by French tourists in Mauritius recurs in Senegal. Clin. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattei, C.; Vetter, I.; Eisenblätter, A.; Krock, B.; Ebbecke, M.; Desel, H.; Zimmermann, K. Ciguatera fish poisoning: A first epidemic in Germany highlights an increasing risk for European countries. Toxicon 2014, 91, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tester, P.A.; Feldman, R.L.; Nau, A.W.; Kibler, S.R.; Wayne Litaker, R. Ciguatera fish poisoning and sea surface temperatures in the Caribbean Sea and the West Indies. Toxicon 2010, 56, 698–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingold, D.B.; Strickland, M.J.; Hess, J.J. Ciguatera fish poisoning and climate change: Analysis of National Poison Center Data in the United States, 2001–2011. Environ. Health Perspect. 2014, 122, 580–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, L.L.; Smith, K.F.; Murray, J.S.; Nishimura, T.; Finch, S.C. Ciguatera Fish Poisoning: The Risk from an Aotearoa/New Zealand Perspective. Toxins 2020, 12, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez, F.; Fraga, S.; Ramilo, I.; Rial, P.; Figueroa, R.I.; Riobo, P.; Bravo, I. Canary Islands (NE Atlantic) as a biodiversity “hotspot” of Gambierdiscus: Implications for future trends of ciguatera in the area. Harmful Algae 2017, 67, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruff, T.A.; Lewis, R.J. Clinical aspects of ciguatera: An overview. Mem. Qld. Mus. 1994, 34, 609–619. [Google Scholar]
- Russell, F.E. Ciguatera poisoning: A report of 35 cases. Toxicon 1975, 13, 383–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, J.G.; Lewin, P.; Hargrett, N.T.; Smith, C.W.; Blake, P.A.; Schneider, R. Clinical features of ciguatera fish poisoning: A study of the disease in the US Virgin Islands. Arch. Intern. Med. 1982, 142, 1090–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allsop, J.L.; Martini, L.; Lebris, H.; Pollard, J.; Walsh, J.; Hodgkinson, S. Neurologic manifestations of ciguatera. 3 cases with a neurophysiologic study and examination of one nerve biopsy. Rev. Neurol. 1986, 142, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bagnis, R.A.; Legrand, A.-M.; Cameron, J. Clinical features on 12,890 cases of ciguatera (fish poisoning) in French Polynesia. In Progress in Venom and Toxin Research, Proceedings of the First Asia-Pacific Congress on Animal, Plant and Microbial Toxins, Singapore, 24–27 June 1987; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Tan, C.K., Eds.; Faculty of Medicine, National University of Singapore: Singapore, 1987; pp. 372–384. ISBN 978-9971-62-152-0. [Google Scholar]
- Kodama, A.M.; Hokama, Y. Variations in symptomatology of ciguatera poisoning. Toxicon 1989, 27, 593–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geller, R.J.; Olson, K.R.; Senécal, P.E. Ciguatera fish poisoning in San Francisco, California, caused by imported barracuda. West. J. Med. 1991, 155, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, K.; Eisenblätter, A.; Vetter, I.; Ebbecke, M.; Friedemann, M.; Desel, H. Vergiftung durch Tropenfisch: Ciguatera-Epidemie in Deutschland. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2015, 140, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gillespie, N.C.; Lewis, R.J.; Pearn, J.H.; Bourke, A.T.; Holmes, M.J.; Bourke, J.B.; Shields, W.J. Ciguatera in Australia. Occurrence, clinical features, pathophysiology and management. Med. J. Aust. 1986, 145, 584–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T. Large Outbreaks of Ciguatera after Consumption of Brown Marbled Grouper. Toxins 2014, 6, 2041–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.Y.K. Lengthy persistence of ciguatoxin in the body. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1998, 92, 662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, A.R.; Terrell-Perica, S.; Sasaki, D.M. Ciguatera on Kauai: Investigation of factors associated with severity of illness. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 1993, 49, 448–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.A.; Fernandez, M.; Backer, L.C.; Dickey, R.W.; Bernstein, J.; Schrank, K.; Kibler, S.; Stephan, W.; Gribble, M.O.; Bienfang, P.; et al. An Updated Review of Ciguatera Fish Poisoning: Clinical, Epidemiological, Environmental, and Public Health Management. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, J.; Capra, M.F. The basis of the paradoxical disturbance of temperature perception in ciguatera poisoning. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1993, 31, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, M.; Lombardi, R.; Salvalaggio, A.; Campagnolo, M.; Castellani, F.; Rondinone, R.; Lauria, G.; Briani, C. A case of Ciguatera poisoning with paradoxical dysaesthesia and degenerative features at skin biopsy. J. Neurol. Sci. 2019, 403, 112–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.D.; Pope, G.E. Noxious cold evokes multiple sensations with distinct time courses. Pain 2002, 98, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, K.; Deuis, J.R.; Inserra, M.C.; Collins, L.S.; Namer, B.; Cabot, P.J.; Reeh, P.W.; Lewis, R.J.; Vetter, I. Analgesic treatment of ciguatoxin-induced cold allodynia. Pain 2013, 154, 1999–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eisenblatter, A.; Lewis, R.; Dorfler, A.; Forster, C.; Zimmermann, K. Brain mechanisms of abnormal temperature perception in cold allodynia induced by ciguatoxin. Ann. Neurol. 2017, 81, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vernoux, J. La ciguatera dans l’île de Saint-Barthélémy: Aspects épidémiologiques, toxicologiques et préventifs. Oceanol. Acta 1988, 11, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Banner, A.H.; Shaw, S.W.; Alender, C.B.; Helfrich, P. Fish Intoxication; Notes on Ciguatera, Its Mode of Action and a Suggested Therapy; Technical Paper; South Pacific Commission: Noumea, New Caledonia, 1963. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, A.M.; Fraser, I.M.; Todd, E.C. Ciguatera poisoning: A report of three cases. Ann. Emerg. Med. 1986, 15, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, D.N.; Enriquez, M.B.; Lumish, R.M.; Maceo, A. Ciguatera fish poisoning in Miami. JAMA 1980, 244, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juranovic, L.R.; Park, D.L. Foodborne Toxins of Marine Origin: Ciguatera. In Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology: Continuation of Residue Reviews; Ware, G.W., Ed.; Reviews of Environmental Contamination and Toxicology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1991; pp. 51–94. ISBN 978-1-4612-3054-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ting, J.Y.; Brown, A.F. Ciguatera Poisoning: A Global Issue with Common Management Problems. Eur. J. Emerg. Med. 2001, 8, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Achaibar, K.C.; Moore, S.; Bain, P.G. Ciguatera poisoning. Pract. Neurol. 2007, 7, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnis, R. Concerning a fatal case of ciguatera poisoning in the Tuamotu Islands. Clin. Toxicol. 1970, 3, 579–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Defusco, D.J.; O’Dowd, P.; Hokama, Y.; Ott, B.R. Coma due to ciguatera poisoning in Rhode Island. Am. J. Med. 1993, 95, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gatti, C.; Oelher, E.; Legrand, A.M. Severe seafood poisoning in French Polynesia: A retrospective analysis of 129 medical files. Toxicon 2008, 51, 746–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.-Y.; Kim, D.-H.; Seo, M.-W.; Shin, B.-S. Reversible cerebellar dysfunction associated with ciguatera fish poisoning. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 43, 674–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, T.Y.K. Characteristic Features and Contributory Factors in Fatal Ciguatera Fish Poisoning—Implications for Prevention and Public Education. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 704–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vernoux, J.P.; Lahlou, N.; Abbad el Andaloussi, S.; Riyeche, N.; Magras, L.P. A study of the distribution of ciguatoxin in individual Caribbean fish. Acta Trop. 1985, 42, 225–233. [Google Scholar]
- Frenette, C.; MacLean, J.D.; Gyorkos, T.W. A large common-source outbreak of ciguatera fish poisoning. J. Infect. Dis. 1988, 158, 1128–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearn, J. Chronic Ciguatera: One Organic Cause of the Chronic Fatigue Syndrome. J. Chronic Fatigue Syndr. 1996, 2, 29–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pearn, J. Neurology of ciguatera. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2001, 70, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baumann, F.; Bourrat, M.-B.; Pauillac, S. Prevalence, symptoms and chronicity of ciguatera in New Caledonia: Results from an adult population survey conducted in Noumea during 2005. Toxicon 2010, 56, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vucic, S.; Kiernan, M.C. Normal axonal ion channel function in large peripheral nerve fibers following chronic ciguatera sensitization. Muscle Nerve 2008, 37, 403–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stommel, E.W.; Parsonnet, J.; Jenkyn, L.R. Polymyositis after ciguatera toxin exposure. Arch. Neurol. 1991, 48, 874–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stommel, E.W.; Jenkyn, L.R.; Parsonnet, J. Another case of polymyositis after ciguatera toxin exposure. Arch. Neurol. 1993, 50, 571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohta, R.; Shimabukuro, A.; Kinjo, M. Rheumatoid arthritis following ciguatera poisoning: A case report. J. Rural Med. 2017, 12, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shoemaker, R.C.; House, D.; Ryan, J.C. Defining the neurotoxin derived illness chronic ciguatera using markers of chronic systemic inflammatory disturbances: A case/control study. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2010, 32, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryan, J.C.; Wu, Q.; Shoemaker, R.C. Transcriptomic signatures in whole blood of patients who acquire a chronic inflammatory response syndrome (CIRS) following an exposure to the marine toxin ciguatoxin. BMC Med. Genom. 2015, 8, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pierre, O.; Misery, L.; Talagas, M.; Le Garrec, R. Immune effects of the neurotoxins ciguatoxins and brevetoxins. Toxicon 2018, 149, 6–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipkin, K.M. Ciguatera Poisoning Presenting as Psychiatric Disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1989, 46, 384–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arena, P.; Levin, B.; Fleming, L.E.; Friedman, M.A.; Blythe, D. A pilot study of the cognitive and psychological correlates of chronic ciguatera poisoning. Harmful Algae 2004, 3, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.A.; Arena, P.; Levin, B.; Fleming, L.; Fernandez, M.; Weisman, R.; Bernstein, J.; Schrank, K.; Blythe, D.; Backer, L.; et al. Neuropsychological study of ciguatera fish poisoning: A longitudinal case-control study. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2007, 22, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Cao, B.; Yang, X.; Wu, J.; Chan, L.L.; Li, Y. Chronic ciguatoxin poisoning causes emotional and cognitive dysfunctions in rats. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 6, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bidard, J.N.; Vijverberg, H.P.; Frelin, C.; Chungue, E.; Legrand, A.M.; Bagnis, R.; Lazdunski, M. Ciguatoxin is a novel type of Na+ channel toxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1984, 259, 8353–8357. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, E.; Legrand, A.M.; Dubois, J.M. Effects of ciguatoxin on current and voltage clamped frog myelinated nerve fibre. Toxicon 1986, 24, 357–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, E.; Juzans, P.; Legrand, A.M.; Molgo, J. Nodal swelling produced by ciguatoxin-induced selective activation of sodium channels in myelinated nerve fibers. Neuroscience 1996, 71, 1121–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Endean, R. Direct and indirect effects of ciguatoxin on guinea-pig atria and papillary muscles. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1986, 334, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molgo, J.; Comella, J.X.; Legrand, A.M. Ciguatoxin enhances quantal transmitter release from frog motor nerve terminals. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1990, 99, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamblin, P.A.; McLachlan, E.M.; Lewis, R.J. Sub-nanomolar concentrations of ciguatoxin-1 excite preganglionic terminals in guinea pig sympathetic ganglia. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Arch. Pharmacol. 1995, 352, 236–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, R.C.; Lewis, R.J.; Adams, D.J. Ciguatoxin-induced oscillations in membrane potential and action potential firing in rat parasympathetic neurons. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2002, 16, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogg, R.C.; Lewis, R.J.; Adams, D.J. Ciguatoxin (CTX-1) modulates single tetrodotoxin-sensitive sodium channels in rat parasympathetic neurones. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 252, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo, J.; Liberona, J.L.; Molgó, J.; Jaimovich, E. Pacific ciguatoxin-1b effect over Na+ and K+ currents, inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate content and intracellular Ca2+ signals in cultured rat myotubes. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2002, 137, 1055–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vetter, I.; Touska, F.; Hess, A.; Hinsbey, R.; Sattler, S.; Lampert, A.; Sergejeva, M.; Sharov, A.; Collins, L.S.; Eberhardt, M.; et al. Ciguatoxins activate specific cold pain pathways to elicit burning pain from cooling. EMBO J. 2012, 31, 3795–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Inserra, M.C.; Israel, M.R.; Caldwell, A.; Castro, J.; Deuis, J.R.; Harrington, A.M.; Keramidas, A.; Garcia-Caraballo, S.; Maddern, J.; Erickson, A.; et al. Multiple sodium channel isoforms mediate the pathological effects of Pacific ciguatoxin-1. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Birinyi-Strachan, L.C.; Gunning, S.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Nicholson, G.M. Block of voltage-gated potassium channels by Pacific ciguatoxin-1 contributes to increased neuronal excitability in rat sensory neurons. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2005, 204, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin, V.; Vale, C.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Roel, M.; Hirama, M.; Yamashita, S.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Chronic ciguatoxin treatment induces synaptic scaling through voltage gated sodium channels in cortical neurons. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1109–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, C.; Benoit, E.; Juzans, P.; Legrand, A.M.; Molgó, J. Gambiertoxin (CTX-4B), purified from wild Gambierdiscus toxicus dinoflagellates, induces Na(+)-dependent swelling of single frog myelinated axons and motor nerve terminals in situ. Neurosci. Lett. 1997, 234, 75–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, C.; Molgó, J.; Marquais, M.; Vernoux, J.; Benoit, E. Hyperosmolar D-mannitol reverses the increased membrane excitability and the nodal swelling caused by Caribbean ciguatoxin-1 in single frog myelinated axons. Brain Res. 1999, 847, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattei, C.; Molgó, J.; Benoit, E. Involvement of both sodium influx and potassium efflux in ciguatoxin-induced nodal swelling of frog myelinated axons. Neuropharmacology 2014, 85, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birinyi-Strachan, L.C.; Davies, M.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Nicholson, G.M. Neuroprotectant effects of iso-osmolar D-mannitol to prevent Pacific ciguatoxin-1 induced alterations in neuronal excitability: A comparison with other osmotic agents and free radical scavengers. Neuropharmacology 2005, 49, 669–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Molgo, J.; Comella, J.X.; Shimahara, T.; Legrand, A.M. Tetrodotoxin-sensitive ciguatoxin effects on quantal release, synaptic vesicle depletion, and calcium mobilization. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1991, 635, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattei, C.; Marquais, M.; Schlumberger, S.; Molgó, J.; Vernoux, J.-P.; Lewis, R.J.; Benoit, E. Analysis of Caribbean ciguatoxin-1 effects on frog myelinated axons and the neuromuscular junction. Toxicon 2010, 56, 759–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sozzi, G.; Marotta, P.; Aldeghi, D.; Tredici, G.; Calvi, L. Polyneuropathy secondary to ciguatoxin poisoning. Ital. J. Neuro. Sci. 1988, 9, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, C.-K.; Lo, Y.-K.; Li, J.-Y.; Lai, P.-H. Reversible corpus callosum lesion in ciguatera poisoning. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2009, 80, 587–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yalachkov, Y.; Hildner, M.; Polomac, N.; Jahnke, K.; Wagner, M.; Baudrexel, S. Cytotoxic edema affecting distinct fiber tracts in ciguatera fish poisoning. Neurology 2019, 92, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terao, K. Ciguatera Toxins: Toxinology. In Seafood and Freshwater Toxins: Pharmacology, Physiology, and Detection; Botana, L.M., Ed.; Food Science and Technology; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 449–472. ISBN 978-0-8247-8956-5. [Google Scholar]
- Terao, K.; Ito, E.; Oarada, M.; Ishibashi, Y.; Legrand, A.-M.; Yasumoto, T. Light and electron microscopic studies of pathologic changes induced in mice by ciguatoxin poisoning. Toxicon 1991, 29, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boydron, R.; Laurent, D.; Sauviat, M.P. Un test biologique destiné à identifier les principes actifs des plantes utilisées comme remèdes traditionnels contre l’intoxication ciguatérique en Nouvelle-Calédonie. In Explorer, Exploiter les Toxines et Maîtriser les Organismes Producteurs (Collection Rencontres en Toxinologie); Bon, C., Goudey-Perrière, F., Poulain, B., Puiseux-Dao, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Paris, France, 2001; pp. 63–66. ISBN 978-2-84299-359-7. [Google Scholar]
- Sauviat, M.-P.; Boydron-Le Garrec, R.; Masson, J.-B.; Lewis, R.L.; Vernoux, J.-P.; Molgó, J.; Laurent, D.; Benoit, E. Mechanisms involved in the swelling of erythrocytes caused by Pacific and Caribbean ciguatoxins. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2006, 36, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terao, K.; Ito, E.; Yasumoto, T. Light and electron microscopic studies of the murine heart after repeated administrations of ciguatoxin or ciguatoxin-4c. Nat. Toxins 1992, 1, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legrand, A.M.; Galonnier, M.; Bagnis, R. Studies on the mode of action of ciguateric toxins. Toxicon 1982, 20, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Endean, R. Mode of action of ciguatoxin from the Spanish Mackerel, Scomberomorus commersoni, on the guinea-pig ileum and vas deferens. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1984, 228, 756–760. [Google Scholar]
- Tatsumi, M.; Kajiwara, A.; Yasumoto, T.; Ohizumi, Y. Potent excitatory effect of scaritoxin on the guinea-pig vas deferens, taenia caeci and ileum. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1985, 235, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.J.; Wong Hoy, A.W. Comparative action of three major ciguatoxins on guinea-pig atria and ilea. Toxicon 1993, 31, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauviat, M.-P.; Marquais, M.; Vernoux, J.-P. Muscarinic effects of the Caribbean ciguatoxin C-CTX-1 on frog atrial heart muscle. Toxicon 2002, 40, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molgó, J.; Gaudry-Talarmain, Y.M.; Legrand, A.M.; Moulian, N. Ciguatoxin extracted from poisonous moray eels Gymnothorax javanicus triggers acetylcholine release from Torpedo cholinergic synaptosomes via reversed Na+-Ca2+ exchange. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 160, 65–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyahara, J.T.; Oyama, M.M.; Hokama, Y. Mechanism of norepinephrine release by ciguatoxin. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Coral Reef Congress: Symposia and Seminars, Tahiti, France, 27 May–1 June 1985; Gabrie, C., Salvat, B., Eds.; Antenne Museum-EPHE: French Polynesia, France, 1985; Volume 4, pp. 467–474. [Google Scholar]
- Lewis, R.J. Negative inotropic and arrhythmic effects of high doses of ciguatoxin on guinea-pig atria and papillary muscles. Toxicon 1988, 26, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J.; Wong Hoy, A.W.; McGiffin, D.C. Action of ciguatoxin on human atrial trabeculae. Toxicon 1992, 30, 907–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohizumi, Y.; Shibata, S.; Tachibana, K. Mode of the excitatory and inhibitory actions of ciguatoxin in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1981, 217, 475–480. [Google Scholar]
- Brock, J.A.; McLachlan, E.M.; Jobling, P.; Lewis, R.J. Electrical activity in rat tail artery during asynchronous activation of postganglionic nerve terminals by ciguatoxin-1. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1995, 116, 2213–2220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brock, J.A.; McLachlan, E.M.; Rayner, S.E. Contribution of alpha-adrenoceptors to depolarization and contraction evoked by continuous asynchronous sympathetic nerve activity in rat tail artery. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1997, 120, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattei, C.; Wen, P.J.; Nguyen-Huu, T.D.; Alvarez, M.; Benoit, E.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Baden, D.G.; Molgó, J.; Meunier, F.A. Brevenal inhibits pacific ciguatoxin-1B-induced neurosecretion from bovine chromaffin cells. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen-Huu, T.D.; Mattei, C.; Wen, P.J.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Lewis, R.J.; Benoit, E.; Baden, D.G.; Molgó, J.; Meunier, F.A. Ciguatoxin-induced catecholamine secretion in bovine chromaffin cells: Mechanism of action and reversible inhibition by brevenal. Toxicon 2010, 56, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, V.; Vale, C.; Hirama, M.; Yamashita, S.; Rubiolo, J.A.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Synthetic ciguatoxin CTX 3C induces a rapid imbalance in neuronal excitability. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1095–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touska, F.; Sattler, S.; Malsch, P.; Lewis, R.J.; Reeh, P.W.; Zimmermann, K. Ciguatoxins Evoke Potent CGRP Release by Activation of Voltage-Gated Sodium Channel Subtypes NaV1.9, NaV1.7 and NaV1.1. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Le Garrec, R.; L’herondelle, K.; Le Gall-Ianotto, C.; Lebonvallet, N.; Leschiera, R.; Buhe, V.; Talagas, M.; Vetter, I.; Lewis, R.J.; Misery, L. Release of neuropeptides from a neuro-cutaneous co-culture model: A novel in vitro model for studying sensory effects of ciguatoxins. Toxicon 2016, 116, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- L’Herondelle, K.; Pierre, O.; Fouyet, S.; Leschiera, R.; Le Gall-Ianotto, C.; Philippe, R.; Buscaglia, P.; Mignen, O.; Talagas, M.; Lewis, R.J.; et al. PAR2, keratinocytes and cathepsin S mediate the sensory effects of ciguatoxins responsible for ciguatera poisoning. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaudry-Talarmain, Y.M.; Molgo, J.; Meunier, F.A.; Moulian, N.; Legrand, A.M. Reversed mode Na(+)-Ca2+ exchange activated by ciguatoxin (CTX-1b) enhances acetylcholine release from Torpedo cholinergic synaptosomes. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1996, 779, 404–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molgó, J.; Shimahara, T.; Legrand, A.M. Ciguatoxin, extracted from poisonous morays eels, causes sodium-dependent calcium mobilization in NG108-15 neuroblastoma × glioma hybrid cells. Neurosci. Lett. 1993, 158, 147–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar-Roiné, S.; Matsui, M.; Chinain, M.; Laurent, D.; Pauillac, S. Modulation of inducible nitric oxide synthase gene expression in RAW 264.7 murine macrophages by Pacific ciguatoxin. Nitric Oxide 2008, 19, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsui, M.; Kumar-Roine, S.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Laurent, D.; Pauillac, S. Pacific ciguatoxin 1B-induced modulation of inflammatory mediators in a murine macrophage cell line. Toxicon 2010, 56, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rubiolo, J.A.; Vale, C.; Boente-Juncal, A.; Hirama, M.; Yamashita, S.; Camina, M.; Vieytes, M.R.; Botana, L.M. Transcriptomic Analysis of Ciguatoxin-Induced Changes in Gene Expression in Primary Cultures of Mice Cortical Neurons. Toxins 2018, 10, 192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryan, J.C.; Bottein Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Morey, J.S.; Rezvani, A.; Levin, E.D.; Gordon, C.J.; Ramsdell, J.S.; Van Dolah, F.M. Transcriptional profiling of whole blood and serum protein analysis of mice exposed to the neurotoxin Pacific Ciguatoxin-1. Neurotoxicology 2007, 28, 1099–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, J.C.; Morey, J.S.; Bottein, M.-Y.D.; Ramsdell, J.S.; Van Dolah, F.M. Gene expression profiling in brain of mice exposed to the marine neurotoxin ciguatoxin reveals an acute anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective response. BMC Neurosci. 2010, 11, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morey, J.S.; Ryan, J.C.; Bottein Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Rezvani, A.H.; Levin, E.D.; Gordon, C.J.; Ramsdell, J.S.; Van Dolah, F.M. Liver genomic responses to ciguatoxin: Evidence for activation of phase I and phase II detoxification pathways following an acute hypothermic response in mice. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 103, 298–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, K.-M. Ciguatera Fish Poison: A Cholinesterase Inhibitor. Science 1965, 147, 1580–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kew, C.K.; Ming, L.K.; Hang, Q.M.Y. The mechanism of respiratory failure in ciguatera poisoning. J. Pathol. 1969, 97, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setliff, J.A.; Rayner, M.D.; Ki Hong, S. Effect of Ciguatoxin on sodium transport across the frog skin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharm. 1971, 18, 676–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombet, A.; Bidard, J.-N.; Lazdunski, M. Ciguatoxin and brevetoxins share a common receptor site on the neuronal voltage-dependent Na+ channel. FEBS Lett. 1987, 219, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dechraoui, M.-Y.; Naar, J.; Pauillac, S.; Legrand, A.-M. Ciguatoxins and brevetoxins, neurotoxic polyether compounds active on sodium channels. Toxicon 1999, 37, 125–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cestèle, S.; Catterall, W.A. Molecular mechanisms of neurotoxin action on voltage-gated sodium channels. Biochimie 2000, 82, 883–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seino, A.; Kobayashi, M.; Momose, K.; Yasumoto, T.; Ohizumi, Y. The mode of inotropic action of ciguatoxin on guinea-pig cardiac muscle. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1988, 95, 876–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strachan, L.C.; Lewis, R.J.; Nicholson, G.M. Differential actions of pacific ciguatoxin-1 on sodium channel subtypes in mammalian sensory neurons. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1999, 288, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cummins, T.R.; Sheets, P.L.; Waxman, S.G. The roles of sodium channels in nociception: Implications for mechanisms of pain. Pain 2007, 131, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, R.; Brice, N.L.; Lewis, R.J.; Dickenson, A.H. Ionic mechanisms of spinal neuronal cold hypersensitivity in ciguatera. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2015, 42, 3004–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Cummins, T.R.; Black, J.A.; Waxman, S.G. Sodium channels in normal and pathological pain. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 33, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zimmermann, K.; Leffler, A.; Babes, A.; Cendan, C.M.; Carr, R.W.; Kobayashi, J.; Nau, C.; Wood, J.N.; Reeh, P.W. Sensory neuron sodium channel Nav1.8 is essential for pain at low temperatures. Nature 2007, 447, 855–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H.; Park, C.-K.; Chen, G.; Han, Q.; Xie, R.-G.; Liu, T.; Ji, R.-R.; Lee, S.-Y. A monoclonal antibody that targets a NaV1.7 channel voltage sensor for pain and itch relief. Cell 2014, 157, 1393–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devigili, G.; Eleopra, R.; Pierro, T.; Lombardi, R.; Rinaldo, S.; Lettieri, C.; Faber, C.G.; Merkies, I.S.J.; Waxman, S.G.; Lauria, G. Paroxysmal itch caused by gain-of-function Nav1.7 mutation. Pain 2014, 155, 1702–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvatierra, J.; Diaz-Bustamante, M.; Meixiong, J.; Tierney, E.; Dong, X.; Bosmans, F. A disease mutation reveals a role for NaV1.9 in acute itch. J. Clin. Investig. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, S.D.; Deng, L.; Reese, R.M.; Dourado, M.; Tao, J.; Foreman, O.; Chang, J.H.; Hackos, D.H. Insensitivity to Pain upon Adult-Onset Deletion of Nav1.7 or Its Blockade with Selective Inhibitors. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 10180–10201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kühn, H.; Kappes, L.; Wolf, K.; Gebhardt, L.; Neurath, M.F.; Reeh, P.; Fischer, M.J.M.; Kremer, A.E. Complementary roles of murine NaV1.7, NaV1.8 and NaV1.9 in acute itch signalling. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Minett, M.S.; Nassar, M.A.; Clark, A.K.; Passmore, G.; Dickenson, A.H.; Wang, F.; Malcangio, M.; Wood, J.N. Distinct Nav1.7-dependent pain sensations require different sets of sensory and sympathetic neurons. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Black, J.A.; Waxman, S.G. NaV1.9: A sodium channel linked to human pain. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2015, 16, 511–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaya, F.; Decosterd, I.; Samad, T.A.; Plumpton, C.; Tate, S.; Mannion, R.J.; Costigan, M.; Woolf, C.J. Diversity of expression of the sensory neuron-specific TTX-resistant voltage-gated sodium ion channels SNS and SNS2. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2000, 15, 331–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlumberger, S.; Mattei, C.; Molgó, J.; Benoit, E. Dual action of a dinoflagellate-derived precursor of Pacific ciguatoxins (P-CTX-4B) on voltage-dependent K+ and Na+ channels of single myelinated axons. Toxicon 2010, 56, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghiaroni, V.; Sasaki, M.; Fuwa, H.; Rossini, G.P.; Scalera, G.; Yasumoto, T.; Pietra, P.; Bigiani, A. Inhibition of voltage-gated potassium currents by gambierol in mouse taste cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2005, 85, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuypers, E.; Abdel-Mottaleb, Y.; Kopljar, I.; Rainier, J.D.; Raes, A.L.; Snyders, D.J.; Tytgat, J. Gambierol, a toxin produced by the dinoflagellate Gambierdiscus toxicus, is a potent blocker of voltage-gated potassium channels. Toxicon 2008, 51, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghiaroni, V.; Fuwa, H.; Inoue, M.; Sasaki, M.; Miyazaki, K.; Hirama, M.; Yasumoto, T.; Rossini, G.P.; Scalera, G.; Bigiani, A. Effect of ciguatoxin 3C on voltage-gated Na+ and K+ currents in mouse taste cells. Chem. Senses 2006, 31, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoit, E.; Mattei, C.; Brown, S.; Molgó, J. Confocal microscopy and passive staining with the styryl dye FM1-43: A convenient method to evaluate morphometric changes in nodes of Ranvier of single living myelinated axons. In Microscopy and Imaging Science Practical Approaches to Applied Research and Education; Méndez-Vilas, A., Ed.; Microscopy Book Series; Formatex Research Center: Badajoz, Espagne, 2017; pp. 73–80. ISBN 978-84-942134-9-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, P.A.; Granade, H.R.; McMillan, J.P. The mouse ciguatoxin bioassay: A dose-response curve and symptomatology analysis. Toxicon 1983, 21, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, R.J. Detection of Ciguatoxins and related Benthic Dinoflagellate Toxins: In vivo and in vitro Methods. In Manual on Harmful Marine Microalgae; IOC Manuals and Guides No. 33; Hallegraeff, G., Anderson, D., Cembella, A., Eds.; UNESCO: Paris, France, 1995; pp. 135–161. [Google Scholar]
- Geller, R.J.; Benowitz, N.L. Orthostatic hypotension in ciguatera fish poisoning. Arch. Intern. Med. 1992, 152, 2131–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armstrong, P.; Murray, P.; Nesdale, A.; Peckler, B. Ciguatera fish poisoning. NZMJ 2016, 129, 113–117. [Google Scholar]
- Coombe, I.F.; Capra, M.F.; Flowers, A.E.; Cameron, J. Pathological changes in the mammalian gut following administration of ciguatoxin. In Progress in Venom and Toxin Research, Proceedings of the First Asia-Pacific Congress on Animal, Plant and Microbial Toxins, Singapore, 24–27 June 1987; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Tan, C.K., Eds.; Faculty of Medicine, National University of Singapore: Singapore, 1987; pp. 405–410. ISBN 978-9971-62-152-0. [Google Scholar]
- Ito, E.; Yasumoto, T.; Terao, K. Morphological observations of diarrhea in mice caused by experimental ciguatoxicosis. Toxicon 1996, 34, 111–122. [Google Scholar]
- Glatte, P.; Buchmann, S.J.; Hijazi, M.M.; Illigens, B.M.-W.; Siepmann, T. Architecture of the Cutaneous Autonomic Nervous System. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohizumi, Y.; Ishida, Y.; Shibata, S. Mode of the ciguatoxin-induced supersensitivity in the guinea-pig vas deferens. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 1982, 221, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zegarska, B.; Lelińska, A.; Tyrakowski, T. Clinical and experimental aspects of cutaneous neurogenic inflammation. Pharmacol. Rep. 2006, 58, 13–21. [Google Scholar]
- McCoy, E.S.; Taylor-Blake, B.; Street, S.E.; Pribisko, A.L.; Zheng, J.; Zylka, M.J. Peptidergic CGRPα primary sensory neurons encode heat and itch and tonically suppress sensitivity to cold. Neuron 2013, 78, 138–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rogoz, K.; Andersen, H.H.; Lagerström, M.C.; Kullander, K. Multimodal use of calcitonin gene-related peptide and substance P in itch and acute pain uncovered by the elimination of vesicular glutamate transporter 2 from transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 neurons. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 14055–14068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stinn, J.F.; De Sylva, D.P.; Fleming, L.E.; Hack, E. Geographical information systems and ciguatera fish poisoning in the tropical Western Atlantic region. In Proceedings of the 1998 Geographic Information Systems in Public Health Conference, Third National Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 18–20 August 2000; pp. 223–233. [Google Scholar]
- Steinhoff, M.; Vergnolle, N.; Young, S.H.; Tognetto, M.; Amadesi, S.; Ennes, H.S.; Trevisani, M.; Hollenberg, M.D.; Wallace, J.L.; Caughey, G.H.; et al. Agonists of proteinase-activated receptor 2 induce inflammation by a neurogenic mechanism. Nat. Med. 2000, 6, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergnolle, N.; Bunnett, N.W.; Sharkey, K.A.; Brussee, V.; Compton, S.J.; Grady, E.F.; Cirino, G.; Gerard, N.; Basbaum, A.I.; Andrade-Gordon, P.; et al. Proteinase-activated receptor-2 and hyperalgesia: A novel pain pathway. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 821–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinhoff, M.; Neisius, U.; Ikoma, A.; Fartasch, M.; Heyer, G.; Skov, P.S.; Luger, T.A.; Schmelz, M. Proteinase-activated receptor-2 mediates itch: A novel pathway for pruritus in human skin. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 6176–6180. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Barr, T.P.; Hou, Q.; Dib-Hajj, S.D.; Black, J.A.; Albrecht, P.J.; Petersen, K.; Eisenberg, E.; Wymer, J.P.; Rice, F.L.; et al. Voltage-gated sodium channel expression in rat and human epidermal keratinocytes: Evidence for a role in pain. Pain 2008, 139, 90–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, S.R.; Thé, L.; Batia, L.M.; Beattie, K.; Katibah, G.E.; McClain, S.P.; Pellegrino, M.; Estandian, D.M.; Bautista, D.M. The epithelial cell-derived atopic dermatitis cytokine TSLP activates neurons to induce itch. Cell 2013, 155, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pang, Z.; Sakamoto, T.; Tiwari, V.; Kim, Y.-S.; Yang, F.; Dong, X.; Güler, A.D.; Guan, Y.; Caterina, M.J. Selective keratinocyte stimulation is sufficient to evoke nociception in mice. Pain 2015, 156, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumbauer, K.M.; DeBerry, J.J.; Adelman, P.C.; Miller, R.H.; Hachisuka, J.; Lee, K.H.; Ross, S.E.; Koerber, H.R.; Davis, B.M.; Albers, K.M. Keratinocytes can modulate and directly initiate nociceptive responses. Elife Sci. 2015, 4, e09674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moehring, F.; Cowie, A.M.; Menzel, A.D.; Weyer, A.D.; Grzybowski, M.; Arzua, T.; Geurts, A.M.; Palygin, O.; Stucky, C.L. Keratinocytes mediate innocuous and noxious touch via ATP-P2 × 4 signaling. Elife 2018, 7, e31684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talagas, M.; Lebonvallet, N.; Leschiera, R.; Marcorelles, P.; Misery, L. What about physical contacts between epidermal keratinocytes and sensory neurons? Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumar, G.; Au, N.P.B.; Lei, E.N.Y.; Mak, Y.L.; Chan, L.L.H.; Lam, M.H.W.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S.; Ma, C.H.E. Acute Exposure to Pacific Ciguatoxin Reduces Electroencephalogram Activity and Disrupts Neurotransmitter Metabolic Pathways in Motor Cortex. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 5590–5603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patapoutian, A.; Tate, S.; Woolf, C.J. Transient receptor potential channels: Targeting pain at the source. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Martin-Yken, H.; Gironde, C.; Derick, S.; Darius, H.T.; Furger, C.; Laurent, D.; Chinain, M. Ciguatoxins activate the Calcineurin signalling pathway in yeasts: Potential for development of an alternative detection tool? Environ. Res. 2018, 162, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oehler, E.; Gatti, C.; Legrand, A.M.; Ghawche, F. Ciguatera and acute polyradiculoneuritis. Description of two cases in French Polynesia: Immunoallergic hypothesis? Med. Trop. 2009, 69, 75–77. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, J.; Flowers, A.E.; Capra, M.F. Effects of ciguatoxin on nerve excitability in rats (Part I). J. Neurol. Sci. 1991, 101, 87–92. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, J.; Flowers, A.E.; Capra, M.F. Electrophysiological studies on ciguatera poisoning in man (Part II). J. Neurol. Sci. 1991, 101, 93–97. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Butera, R.; Prockop, L.D.; Buonocore, M.; Locatelli, C.; Gandini, C.; Manzo, L. Mild ciguatera poisoning: Case reports with neurophysiological evaluations. Muscle Nerve 2000, 23, 1598–1603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Andrade, J.M.; Herrera, M.B.; Ghilardi, J.R.; Vardanyan, M.; Melemedjian, O.K.; Mantyh, P.W. Vascularization of the dorsal root ganglia and peripheral nerve of the mouse: Implications for chemical-induced peripheral sensory neuropathies. Mol. Pain 2008, 4, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Au, N.P.B.; Kumar, G.; Asthana, P.; Tin, C.; Mak, Y.L.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S.; Ma, C.H.E. Ciguatoxin reduces regenerative capacity of axotomized peripheral neurons and delays functional recovery in pre-exposed mice after peripheral nerve injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Cao, B.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Tung, V.O.V.; Lam, P.K.S.; Chan, L.L.; Li, Y. Neurotoxicity and Reactive Astrogliosis in the Anterior Cingulate Cortex in Acute Ciguatera Poisoning. Neuromol. Med. 2013, 15, 310–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asthana, P.; Zhang, N.; Kumar, G.; Chine, V.B.; Singh, K.K.; Mak, Y.L.; Chan, L.L.; Lam, P.K.S.; Ma, C.H.E. Pacific Ciguatoxin Induces Excitotoxicity and Neurodegeneration in the Motor Cortex Via Caspase 3 Activation: Implication for Irreversible Motor Deficit. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 6769–6787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourdy, G.; Cabalion, P.; Amade, P.; Laurent, D. Traditional remedies used in the Western Pacific for the treatment of ciguatera poisoning. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1992, 36, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar-Roiné, S.; Darius, H.T.; Matsui, M.; Fabre, N.; Haddad, M.; Chinain, M.; Pauillac, S.; Laurent, D. A review of traditional remedies of ciguatera fish poisoning in the Pacific. Phytother. Res. 2011, 25, 947–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amade, P.; Laurent, D. Screening of Traditional Remedies Used in Ciguatera Fish Poisoning Treatment. In Recent Advances in Toxinology Research; Gopalakrishnakone, P., Tan, C.K., Eds.; Venom & Toxin Research Group, National University of Singapore: Singapore, 1992; pp. 503–508. ISBN 978-9971-62-283-1. [Google Scholar]
- Laurent, D.; Amade, P. Remèdes Traditionnels Contre la Ciguatera en Nouvelle Calédonie; ORSTOM: Nouméa, New Caledonia, 1992; p. 84. [Google Scholar]
- Benoit, E.; Laurent, D.; Mattei, C.; Legrand, A.-M.; Molgo, J. Reversal of Pacific ciguatoxin-1B effects on myelinated axons by agents used in ciguatera treatment. Cybium 2000, 24, 33–40. [Google Scholar]
- Boydron-Le Garrec, R.; Benoit, E.; Sauviat, M.-P.; Lewis, R.J.; Molgó, J.; Laurent, D. Ability of some plant extracts, traditionally used to treat ciguatera fish poisoning, to prevent the in vitro neurotoxicity produced by sodium channel activators. Toxicon 2005, 46, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar Roiné, S.; Matsui, M.; Reybier, K.; Darius, H.T.; Chinain, M.; Pauillac, S.; Laurent, D. Ability of certain plant extracts traditionally used to treat ciguatera fish poisoning to inhibit nitric oxide production in RAW 264.7 macrophages. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 123, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsui, M.; Kumar-Roine, S.; Taina Darius, H.; Chinain, M.; Laurent, D.; Pauillac, S. Characterisation of the anti-inflammatory potential of Vitex trifolia L. (Labiatae), a multipurpose plant of the Pacific traditionnal medicine. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 427–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadahide, N.; Ryuta, T.; Yoropiy, A. Ciguatera fish poisoning in Ulithi Atoll, Yap State, Micronesia. In Occasional Papers No. 39; Kagoshima University Research Center for the Pacific Islands: Kagoshima, Japan, 2003; pp. 83–86. [Google Scholar]
- Rossi, F.; Jullian, V.; Pawlowiez, R.; Kumar-Roine, S.; Haddad, M.; Darius, H.T.; Gaertner-Mazouni, N.; Chinain, M.; Laurent, D. Protective effect of Heliotropium foertherianum (Boraginaceae) folk remedy and its active compound, rosmarinic acid, against a Pacific ciguatoxin. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 143, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braidy, N.; Matin, A.; Rossi, F.; Chinain, M.; Laurent, D.; Guillemin, G.J. Neuroprotective Effects of Rosmarinic Acid on Ciguatoxin in Primary Human Neurons. Neurotox. Res. 2014, 25, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, R.T.; Villar, L.A. Symptomatic improvement with amitriptyline in ciguatera fish poisoning. N. Engl. J. Med. 1986, 315, 65. [Google Scholar]
- Calvert, G.M.; Hryhorczuk, D.O.; Leikin, J.B. Treatment of ciguatera fish poisoning with amitriptyline and nifedipine. J. Toxicol. Clin. Toxicol. 1987, 25, 423–428. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, W.R.; Kreider, S.D.; Hattwick, M.; Hobbs, J. Potential benefit of tocainide in the treatment of ciguatera: Report of three cases. Am. J. Med. 1988, 84, 1087–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crump, J.A.; McLay, C.L.; Chambers, S.T. Ciguatera fish poisoning. Postgrad. Med. J. 1999, 75, 678–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derouiche, F.; Cohen, E.; Rodier, G.; Boulay, C.; Courtois, S. Ciguatera and peripheral neuropathy: A case report. Rev. Neurol. 2000, 156, 514–516. [Google Scholar]
- Legrand, A.-M.; Lotte, C.; Bagnis, R. Respiratory and cardio-vascular effects of ciguatoxin in cats; antagonistic action of Hexamethonium, Atropine, Propranolol, Phentolamine, Yohimbine, Prazosin, Verapamil, Calcium and Lidocaine. In Proceedings of the Fifth International Coral Reef Conference, Tahiti, France, 27 May–1 June 1985; Gabrie, C., Salvat, B., Eds.; Antenne Museum-EPHE: Moorea, French Polynesia, 1985; pp. 463–466. [Google Scholar]
- Cameron, J.; Flowers, A.E.; Capra, M.F. Modification of the peripheral nerve disturbance in ciguatera poisoning in rats with lidocaine. Muscle Nerve 1993, 16, 782–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez, C.M.; Vasquez, P.A.; Perret, C.F. Treatment of ciguatera poisoning with gabapentin. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 692–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brett, J.; Murnion, B. Pregabalin to treat ciguatera fish poisoning. Clin Toxicol. 2015, 53, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdelais, A.J.; Campbell, S.; Jacocks, H.; Naar, J.; Wright, J.L.C.; Carsi, J.; Baden, D.G. Brevenal Is a Natural Inhibitor of Brevetoxin Action in Sodium Channel Receptor Binding Assays. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2004, 24, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gold, E.P.; Jacocks, H.M.; Bourdelais, A.J.; Baden, D.G. Brevenal, a brevetoxin antagonist from Karenia brevis, binds to a previously unreported site on mammalian sodium channels. Harmful Algae 2013, 26, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Inoue, M.; Lee, N.; Tsumuraya, T.; Fujii, I.; Hirama, M. Use of monoclonal antibodies as an effective strategy for treatment of ciguatera poisoning. Toxicon 2009, 53, 802–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palafox, N.A.; Jain, L.G.; Pinano, A.Z.; Gulick, T.M.; Williams, R.K.; Schatz, I.J. Successful treatment of ciguatera fish poisoning with intravenous mannitol. JAMA 1988, 259, 2740–2742. [Google Scholar]
- Blythe, D.G.; De Sylva, D.P.; Fleming, L.E.; Ayyar, R.A.; Baden, D.G.; Shrank, K. Clinical experience with i.v. Mannitol in the treatment of ciguatera. Bull. Soc. Pathol. Exot. 1992, 85, 425–426. [Google Scholar]
- Mullins, M.E.; Hoffman, R.S. Is mannitol the treatment of choice for patients with ciguatera fish poisoning? Clin. Toxicol. 2017, 55, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schnorf, H.; Taurarii, M.; Cundy, T. Ciguatera fish poisoning: A double-blind randomized trial of mannitol therapy. Neurology 2002, 58, 873–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, M.J. An outbreak of ciguatera poisoning in a group of scuba divers. J. Wilderness Med. 1993, 4, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |


| CTX Effect | Model | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Nav-mediated depolarization ± spontaneous firing | Mouse differentiated neuroblastoma N1E 115 cells | [102] |
| Frog myelinated nerve fibers | [103,104] | |
| Guinea pig atrial heart muscle cells | [105] | |
| Frog motor nerve terminals of NMJs | [106] | |
| Guinea pig sympathetic ganglia | [107] | |
| Rat parasympathetic neurons | [108,109] | |
| Rat skeletal myotubes | [110] | |
| Rat and mouse DRG neurons/afferents | [111,112,113] | |
| Mouse cortical neurons | [114] | |
| Swelling | Ranvier nodes of frog myelinated nerve fibers | [104,115,116,117] |
| Rat DRG neurons | [118] | |
| Frog motor nerve terminals | [115,119,120] | |
| Human adaxonal Schwann cell cytoplasm | [59] | |
| Human intra-epidermal and sural nerve fibers | [70,121] | |
| Human corpus callosum | [122,123] | |
| Mice myenteric plexus nerves | [124,125] | |
| Mouse and frog erythrocytes | [124,126,127] | |
| Endothelial lining cells of heart capillaries | [128] | |
| Neuromediator release | ACh release from (parasympathetic innervation of): | |
| Cat cardiovascular system | [129] | |
| Guinea pig and mouse small intestine, taenia caeci and ileum | [125,130,131,132] | |
| Frog atrial muscle | [133] | |
| Frog motor nerve terminals of skeletal NMJs | [106,120] | |
| Torpedo cholinergic synaptosomes | [134] | |
| NAd release from sympathetic innervation of: | ||
| Guinea pig and human atria | [105,132,135,136,137] | |
| Guinea pig vas deferens | [130,131,138] | |
| Smooth muscle of rat tail artery | [139,140] | |
| Catecholamines from bovine chromaffin cells | [141,142] | |
| Dopamine and GABA from rat brain synaptosomes | [102] | |
| GABA from mouse cortical neurons | [143] | |
| CGRP and/or SP from mouse and rat sensory neurons/afferents | [72,144,145,146] | |
| [Ca2+]i increase | Influx through NCX in Torpedo cholinergic synaptosomes | [134,147] |
| Mobilization from internal stores: | ||
| Neuroblastoma x glioma hybrid NG108-15 cells | [106,148] | |
| Rat skeletal myotubes | [110] | |
| Bovine chromaffin cells | [141] | |
| Influx through TRPA1 in DRG neurons | [111] | |
| Influx through Cav in SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells | [72] | |
| Modulation of gene expression | Upregulation of iNOS and pro-inflammatory cytokines in RAW 264.7 macrophages | [149,150] |
| Gene expression modulation in mouse cortical neurons | [114,151] | |
| Expression modulation of genes involved in immune responses and detoxification in the blood, liver and brain | [152,153,154] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
L’Herondelle, K.; Talagas, M.; Mignen, O.; Misery, L.; Le Garrec, R. Neurological Disturbances of Ciguatera Poisoning: Clinical Features and Pathophysiological Basis. Cells 2020, 9, 2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102291
L’Herondelle K, Talagas M, Mignen O, Misery L, Le Garrec R. Neurological Disturbances of Ciguatera Poisoning: Clinical Features and Pathophysiological Basis. Cells. 2020; 9(10):2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102291
Chicago/Turabian StyleL’Herondelle, Killian, Matthieu Talagas, Olivier Mignen, Laurent Misery, and Raphaele Le Garrec. 2020. "Neurological Disturbances of Ciguatera Poisoning: Clinical Features and Pathophysiological Basis" Cells 9, no. 10: 2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102291
APA StyleL’Herondelle, K., Talagas, M., Mignen, O., Misery, L., & Le Garrec, R. (2020). Neurological Disturbances of Ciguatera Poisoning: Clinical Features and Pathophysiological Basis. Cells, 9(10), 2291. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9102291







