PVPred-SCM: Improved Prediction and Analysis of Phage Virion Proteins Using a Scoring Card Method
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Prediction Performance
2.2. Contribution and Effectiveness of Dipeptide Propensity Scores
2.3. Comparison with Existing Methods
2.4. Identification of Phage Virion Proteins
2.5. Analysis of Phage Virion Proteins Using Propensity Scores of Amino Acids and Dipeptides
2.6. Analysis of PVPs Using Informative Physicochemical Properties
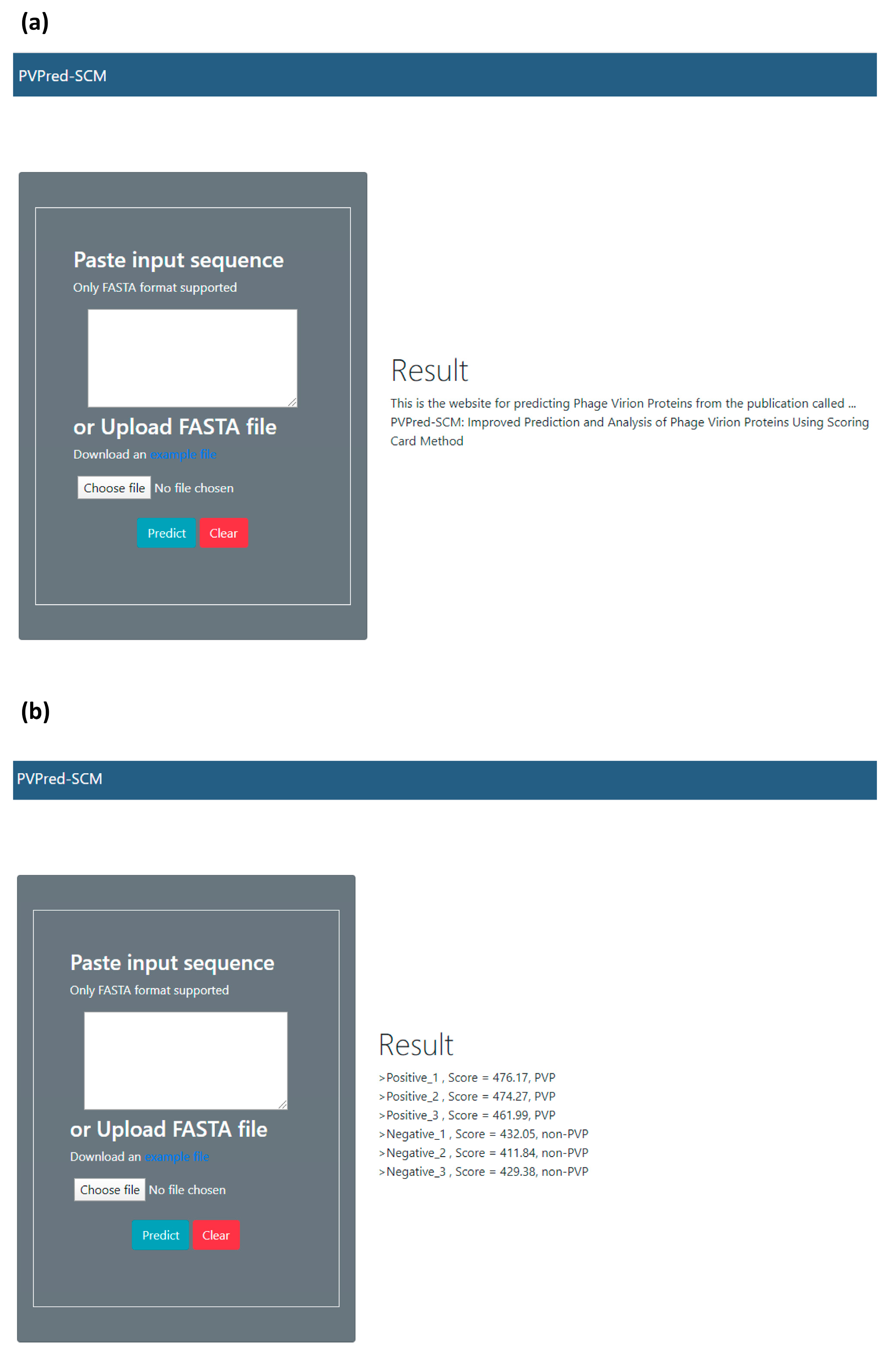
2.7. Web Server Implementation
2.8. Reproducible Research
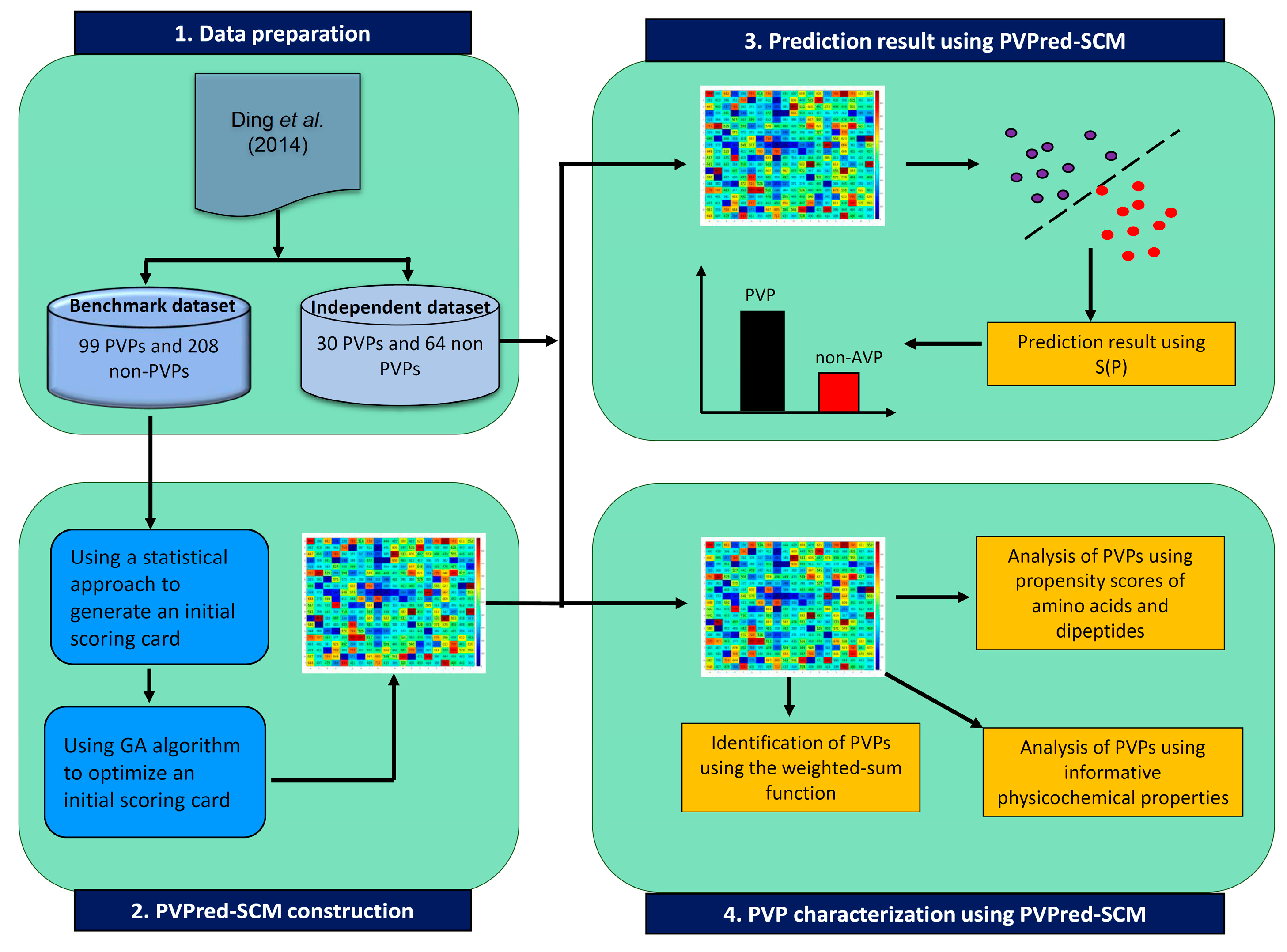
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Dataset Preparation
3.2. Feature Representation
3.3. Scoring Card Method
3.4. Characterization of Phage Virion Proteins
3.5. Performance Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clark, J.R.; March, J.B. Bacteriophages and biotechnology: Vaccines, gene therapy and antibacterials. Trends Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, J.E.; Magadan, A.H.; Sabri, M.; Moineau, S. Revenge of the phages: Defeating bacterial defences. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11, 675–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyon, J. Phage Therapy’s Role in Combating Antibiotic-Resistant Pathogens. JAMA 2017, 318, 1746–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lekunberri, I.; Subirats, J.; Borrego, C.M.; Balcazar, J.L. Exploring the contribution of bacteriophages to antibiotic resistance. Env. Pollut. 2017, 220 (Pt B), 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jara-Acevedo, R.; Díez, P.; González-González, M.; Dégano, R.M.; Ibarrola, N.; Góngora, R.; Orfao, A.; Fuentes, M. Screening phage-display antibody libraries using protein arrays. In Phage Display; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 365–380. [Google Scholar]
- Lavigne, R.; Ceyssens, P.-J.; Robben, J. Phage proteomics: Applications of mass spectrometry. In Bacteriophages; 2009; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA; pp. 239–251. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Gao, M. Proteomic analysis of a novel bacillus jumbo phage revealing glycoside hydrolase as structural component. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seguritan, V.; Alves Jr, N.; Arnoult, M.; Raymond, A.; Lorimer, D.; Burgin Jr, A.B.; Salamon, P.; Segall, A.M. Artificial neural networks trained to detect viral and phage structural proteins. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2012, 8, e1002657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, P.-M.; Ding, H.; Chen, W.; Lin, H. Naive Bayes Classifier with Feature Selection to Identify Phage Virion Proteins. Comput. Math. Methods Med. 2013, 2013, 530696. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, H.; Feng, P.-M.; Chen, W.; Lin, H. Identification of bacteriophage virion proteins by the ANOVA feature selection and analysis. Mol. Biosyst. 2014, 10, 2229–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Gao, R.; Yang, R. An ensemble method to distinguish bacteriophage virion from non-virion proteins based on protein sequence characteristics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21734–21758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Shin, T.H.; Lee, G. PVP-SVM: Sequence-based prediction of phage virion proteins using a support vector machine. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Gao, H.; Lin, H.; Liu, Z.; Tang, L.; Li, S. Identification of Bacteriophage Virion Proteins Using Multinomial Naive Bayes with g-Gap Feature Tree. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.-X.; Dao, F.-Y.; Lv, H.; Feng, P.-M.; Ding, H. Identifying phage virion proteins by using two-step feature selection methods. Molecules 2018, 23, 2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ru, X.; Li, L.; Wang, C. Identification of phage viral proteins with hybrid sequence features. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arif, M.; Ali, F.; Ahmad, S.; Kabir, M.; Ali, Z.; Hayat, M. Pred-BVP-Unb: Fast prediction of bacteriophage Virion proteins using un-biased multi-perspective properties with recursive feature elimination. Genomics 2019, 112, 1565–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoombuatong, W.; Schaduangrat, N.; Pratiwi, R.; Nantasenamat, C. THPep: A machine learning-based approach for predicting tumor homing peptides. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 80, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hongjaisee, S.; Nantasenamat, C.; Carraway, T.S.; Shoombuatong, W. HIVCoR: A sequence-based tool for predicting HIV-1 CRF01_AE coreceptor usage. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2019, 80, 419–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laengsri, V.; Nantasenamat, C.; Schaduangrat, N.; Nuchnoi, P.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Shoombuatong, W. TargetAntiAngio: A Sequence-Based Tool for the Prediction and Analysis of Anti-Angiogenic Peptides. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaduangrat, N.; Nantasenamat, C.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Shoombuatong, W. ACPred: A Computational Tool for the Prediction and Analysis of Anticancer Peptides. Molecules 2019, 24, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasylenko, T.; Liou, Y.-F.; Chiou, P.-C.; Chu, H.-W.; Lai, Y.-S.; Chou, Y.-L.; Huang, H.-L.; Ho, S.-Y. SCMBYK: Prediction and characterization of bacterial tyrosine-kinases based on propensity scores of dipeptides. BMC Bioinform. 2016, 17, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Vasylenko, T.; Liou, Y.-F.; Chen, H.-A.; Charoenkwan, P.; Huang, H.-L.; Ho, S.-Y. SCMPSP: Prediction and characterization of photosynthetic proteins based on a scoring card method. BMC Bioinform. 2015, 16, S8. [Google Scholar]
- Liou, Y.-F.; Vasylenko, T.; Yeh, C.-L.; Lin, W.-C.; Chiu, S.-H.; Charoenkwan, P.; Shu, L.-S.; Ho, S.-Y.; Huang, H.-L. SCMMTP: Identifying and characterizing membrane transport proteins using propensity scores of dipeptides. Bmc Genom. 2015, 16, S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Huang, H.-L. Propensity scores for prediction and characterization of bioluminescent proteins from sequences. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, Y.-F.; Charoenkwan, P.; Srinivasulu, Y.S.; Vasylenko, T.; Lai, S.-C.; Lee, H.-C.; Chen, Y.-H.; Huang, H.-L.; Ho, S.-Y. SCMHBP: Prediction and analysis of heme binding proteins using propensity scores of dipeptides. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15, S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charoenkwan, P.; Shoombuatong, W.; Lee, H.-C.; Chaijaruwanich, J.; Huang, H.-L.; Ho, S.-Y. SCMCRYS: Predicting protein crystallization using an ensemble scoring card method with estimating propensity scores of P-collocated amino acid pairs. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e72368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-L.; Charoenkwan, P.; Kao, T.-F.; Lee, H.-C.; Chang, F.-L.; Huang, W.-L.; Ho, S.-J.; Shu, L.-S.; Chen, W.-L.; Ho, S.-Y. Prediction and Analysis of Protein Solubility Using a Novel Scoring Card Method with Dipeptide Composition. BMC Bioinform. 2012; 13, S3. [Google Scholar]
- Win, T.S.; Schaduangrat, N.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Nantasenamat, C.; Shoombuatong, W. PAAP: A web server for predicting antihypertensive activity of peptides. Future Med. Chem. 2018, 10, 1749–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Win, T.S.; Malik, A.A.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Wikberg, J.E.S.; Nantasenamat, C.; Shoombuatong, W. HemoPred: A web server for predicting the hemolytic activity of peptides. Future Med. Chem. 2017, 9, 275–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoombuatong, W.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Anuwongcharoen, N.; Songtawee, N.; Monnor, T.; Prachayasittikul, S.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Nantasenamat, C. Navigating the chemical space of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 4515. [Google Scholar]
- Shoombuatong, W.; Nabu, S.; Simeon, S.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Lapins, M.; Wikberg, J.E.; Nantasenamat, C. Extending proteochemometric modeling for unraveling the sorption behavior of compound–soil interaction. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2016, 151, 219–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoombuatong, W.; Huang, H.-L.; Chaijaruwanich, J.; Charoenkwan, P.; Lee, H.-C.; Ho, S.-Y. Predicting Protein Crystallization Using a Simple Scoring Card Method. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Bioinformatics and Computational Biology (CIBCB), Singapore, 15–19 April 2013; pp. 22–30. [Google Scholar]
- Pratiwi, R.; Malik, A.A.; Schaduangrat, N.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Wikberg, J.E.; Nantasenamat, C.; Shoombuatong, W. CryoProtect: A Web Server for Classifying Antifreeze Proteins from Nonantifreeze Proteins. J. Chem. 2017, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoombuatong, W.; Schaduangrat, N.; Nantasenamat, C. Unraveling the bioactivity of anticancer peptides as deduced from machine learning. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 734. [Google Scholar]
- Shoombuatong, W.; Schaduangrat, N.; Nantasenamat, C. Towards understanding aromatase inhibitory activity via QSAR modeling. EXCLI J. 2018, 17, 688. [Google Scholar]
- Shoombuatong, W.; Prathipati, P.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Schaduangrat, N.; Malik, A.A.; Pratiwi, R.; Wanwimolruk, S.; Wikberg, J.E.; Gleeson, M.P.; Spjuth, O. Towards Predicting the Cytochrome P450 Modulation: From QSAR to Proteochemometric Modeling. Curr. Drug Metab. 2017, 18, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawashima, S.; Kanehisa, M. AAindex: Amino acid index database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoombuatong, W.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Nantasenamat, C. Prediction of aromatase inhibitory activity using the efficient linear method (ELM). EXCLI J. 2015, 14, 452. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simeon, S.; Shoombuatong, W.; Anuwongcharoen, N.; Preeyanon, L.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Wikberg, J.E.; Nantasenamat, C. osFP: A web server for predicting the oligomeric states of fluorescent proteins. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaduangrat, N.; Nantasenamat, C.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Shoombuatong, W. Meta-iAVP: A Sequence-Based Meta-Predictor for Improving the Prediction of Antiviral Peptides Using Effective Feature Representation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suvannang, N.; Preeyanon, L.; Malik, A.A.; Schaduangrat, N.; Shoombuatong, W.; Worachartcheewan, A.; Tantimongcolwat, T.; Nantasenamat, C. Probing the origin of estrogen receptor alpha inhibition via large-scale QSAR study. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 11344–11356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pederson, D.M.; Welsh, L.C.; Marvin, D.A.; Sampson, M.; Perham, R.N.; Yu, M.; Slater, M.R. The protein capsid of filamentous bacteriophage PH75 from Thermus thermophilus. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 309, 401–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ackermann, H.W. Bacteriophage taxonomy in 1987. Microbiol. Sci. 1987, 4, 214–218. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, J.Y.; Wu, C.C.; Kue, T.T. Amino acid analysis of the coat protein of the filamentous bacterial virus xf from Xanthomonas oryzae. Virology 1971, 45, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuzmicheva, G.; Jayanna, P.; Eroshkin, A.; Grishina, M.; Pereyaslavskaya, E.; Potemkin, V.; Petrenko, V. Mutations in fd phage major coat protein modulate affinity of the displayed peptide. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2009, 22, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pace, C.N.; Scholtz, J.M. A helix propensity scale based on experimental studies of peptides and proteins. Biophys. J. 1998, 75, 422–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfenden, R.V.; Cullis, P.M.; Southgate, C.C. Water, protein folding, and the genetic code. Science 1979, 575–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asija, K.; Teschke, C.M. Of capsid structure and stability: The partnership between charged residues of E-loop and P-domain of the bacteriophage P22 coat protein. Virology 2019, 534, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koehl, P.; Levitt, M. Structure-based conformational preferences of amino acids. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 12524–12529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.-B.; Chou, K.-C. PseAAC: A flexible web server for generating various kinds of protein pseudo amino acid composition. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 373, 386–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, T.A.; Weiss, G.A.; Eigenbrot, C.; Sidhu, S.S. A minimized M13 coat protein defines the requirements for assembly into the bacteriophage particle. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 322, 357–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Xiao, X.; Chou, K.-C. pLoc-mPlant: Predict subcellular localization of multi-location plant proteins by incorporating the optimal GO information into general PseAAC. Mol. Biosyst. 2017, 13, 1722–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, X.; Xiao, X.; Chou, K.-C. pLoc-mVirus: Predict subcellular localization of multi-location virus proteins via incorporating the optimal GO information into general PseAAC. Gene 2017, 628, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhao, S.-G.; Lin, W.-Z.; Xiao, X.; Chou, K.-C. pLoc-mAnimal: Predict subcellular localization of animal proteins with both single and multiple sites. Bioinformatics 2017, 33, 3524–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhao, S.-G.; Xiao, X.; Chou, K.-C. iATC-mISF: A multi-label classifier for predicting the classes of anatomical therapeutic chemicals. Bioinformatics 2016, 33, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhao, S.-G.; Xiao, X.; Chou, K.-C. iATC-mHyb: A hybrid multi-label classifier for predicting the classification of anatomical therapeutic chemicals. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 58494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Gao, X.; Zhang, H. BioSeq-Analysis2.0: An updated platform for analyzing DNA, RNA and protein sequences at sequence level and residue level based on machine learning approaches. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e127. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, P.; Li, F.; Leier, A.; Marquez-Lago, T.T.; Wang, Y.; Webb, G.I.; Smith, A.I.; Daly, R.J.; Chou, K.-C. iFeature: A python package and web server for features extraction and selection from protein and peptide sequences. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 2499–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, N.; Cao, D.-S.; Zhu, M.-F.; Xu, Q.-S. protr/ProtrWeb: R package and web server for generating various numerical representation schemes of protein sequences. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1857–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeon, S.; Li, H.; Win, T.S.; Malik, A.A.; Kandhro, A.H.; Piacham, T.; Shoombuatong, W.; Nuchnoi, P.; Wikberg, J.E.; Gleeson, M.P. PepBio: Predicting the bioactivity of host defense peptides. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 35119–35134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoombuatong, W.; Traisathit, P.; Prasitwattanaseree, S.; Tayapiwatana, C.; Cutler, R.; Chaijaruwanich, J. Prediction of the disulphide bonding state of cysteines in proteins using Conditional Random Fields. Int. J. Data Min. Bioinform. 2011, 5, 449–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoombuatong, W.; Hongjaisee, S.; Barin, F.; Chaijaruwanich, J.; Samleerat, T. HIV-1 CRF01_AE coreceptor usage prediction using kernel methods based logistic model trees. Comput. Biol. Med. 2012, 42, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Shin, T.H.; Wei, L.; Lee, G. mAHTPred: A sequence-based meta-predictor for improving the prediction of anti-hypertensive peptides using effective feature representation. Bioinformatics 2018, 35, 2757–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Basith, S.; Shin, T.H.; Wei, L.; Lee, G. Meta-4mCpred: A Sequence-Based Meta-Predictor for Accurate DNA 4mC Site Prediction Using Effective Feature Representation. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Govindaraj, R.G.; Shin, T.H.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, G. iBCE-EL: A new ensemble learning framework for improved linear B-cell epitope prediction. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manavalan, B.; Shin, T.H.; Kim, M.O.; Lee, G. PIP-EL: A new ensemble learning method for improved proinflammatory peptide predictions. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charoenkwan, P.; Schaduangrat, N.; Nantasenamat, C.; Piacham, T.; Shoombuatong, W. iQSP: A Sequence-Based Tool for the Prediction and Analysis of Quorum Sensing Peptides via Chou’s 5-Steps Rule and Informative Physicochemical Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worachartcheewan, A.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Anuwongcharoen, N.; Shoombuatong, W.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Nantasenamat, C. On the origins of hepatitis C virus NS5B polymerase inhibitory activity using machine learning approaches. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 1814–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prachayasittikul, V.; Worachartcheewan, A.; Shoombuatong, W.; Songtawee, N.; Simeon, S.; Prachayasittikul, V.; Nantasenamat, C. Computer-aided drug design of bioactive natural products. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 1780–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khatun, M.; Hasan, M.; Kurata, H. PreAIP: Computational prediction of anti-inflammatory peptides by integrating multiple complementary features. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.M.; Manavalan, B.; Khatun, M.S.; Kurata, H. i4mC-ROSE, a bioinformatics tool for the identification of DNA N4-methylcytosine sites in the Rosaceae genome. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.; Khatun, M.; Kurata, H. Large-Scale Assessment of Bioinformatics Tools for Lysine Succinylation Sites. Cells 2019, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Manavalan, B.; Khatun, M.S.; Kurata, H. Prediction of S-nitrosylation sites by integrating support vector machines and random forest. Mol. Omics 2019, 15, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, M.M.; Khatun, M.S.; Kurata, H. A comprehensive review of in silico analysis for protein S-sulfenylation sites. Protein Pept. Lett. 2018, 25, 815–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.-C. Some remarks on protein attribute prediction and pseudo amino acid composition. J. Theor. Biol. 2011, 273, 236–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoombuatong, W.; Mekha, P.; Waiyamai, K.; Cheevadhanarak, S.; Chaijaruwanicha, J. Prediction of human leukocyte antigen gene using k-nearest neighbour classifier based on spectrum kernel. ScienceAsia 2013, 39, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Fang, L.; Chou, K.-C. Pse-in-One: A web server for generating various modes of pseudo components of DNA, RNA, and protein sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W65–W71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.-C. Using amphiphilic pseudo amino acid composition to predict enzyme subfamily classes. Bioinformatics 2004, 21, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, K.-C. Impacts of bioinformatics to medicinal chemistry. Med. Chem. 2015, 11, 218–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, K.-C. An unprecedented revolution in medicinal chemistry driven by the progress of biological science. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 2337–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, K.-C. Progresses in predicting post-translational modification. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2019, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, K.-C. Advance in Predicting Subcellular Localization of Multi-label Proteins and its Implication for Developing Multi-target Drugs. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Method | Classifier a | Sequence Feature b | Independent Test | Webserver |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Seguritan et al.’s method [8] | ANN | AAC, PIP | - | - |
| Feng et al.’s method [9] | NB | AAC, DPC | - | - |
| PVPred [10] | SVM | g-gap DPC | ✓ | ✓ |
| PVP-SVM [12] | SVM | AAC, DPC, ATC, CTD, PCP | ✓ | ✓ |
| PhagePred [13] | Multinomial NB | g-gap DPC feature tree | - | ✓ c |
| Tan et al.’s method [14] | SVM | GDC | ✓ | - |
| Pred-BVP-Unb [16] | SVM | CT, SAAC, bi-PSSM | ✓ | - |
| PVPred-SCM (This study) | SCM | DPC | ✓ | ✓ |
| #Exp. | Fitness Score | Threshold | ACC (%) | SN (%) | SP (%) | MCC | auROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.955 | 443.96 | 92.50 | 99.00 | 89.41 | 0.849 | 0.952 |
| 2 | 0.955 | 459.91 | 93.15 | 91.89 | 93.76 | 0.851 | 0.954 |
| 3 | 0.968 | 471.80 | 95.11 | 94.00 | 95.64 | 0.894 | 0.966 |
| 4 | 0.946 | 476.36 | 92.15 | 95.89 | 90.31 | 0.840 | 0.942 |
| 5 | 0.960 | 455.34 | 94.44 | 96.00 | 93.74 | 0.882 | 0.960 |
| 6 | 0.956 | 458.08 | 93.16 | 96.00 | 91.81 | 0.856 | 0.953 |
| 7 | 0.950 | 446.56 | 92.50 | 96.00 | 90.81 | 0.846 | 0.947 |
| 8 | 0.954 | 446.24 | 92.51 | 98.00 | 89.88 | 0.849 | 0.953 |
| 9 | 0.950 | 461.75 | 92.52 | 95.89 | 90.86 | 0.846 | 0.948 |
| 10 | 0.960 | 463.10 | 93.82 | 94.78 | 93.29 | 0.866 | 0.960 |
| Mean | 0.955 | 458.31 | 93.18 | 95.74 | 91.95 | 0.858 | 0.954 |
| STD. | 0.006 | 10.77 | 0.98 | 1.97 | 2.05 | 0.018 | 0.007 |
| #Exp. | Fitness Score | Threshold | ACC (%) | SN (%) | SP (%) | MCC | auROC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.955 | 443.96 | 74.47 | 80.00 | 71.88 | 0.486 | 0.782 |
| 2 | 0.955 | 459.91 | 75.53 | 73.33 | 76.56 | 0.476 | 0.743 |
| 3 | 0.968 | 471.80 | 76.60 | 70.00 | 79.69 | 0.482 | 0.781 |
| 4 | 0.946 | 476.36 | 76.60 | 63.33 | 82.81 | 0.461 | 0.775 |
| 5 | 0.960 | 455.34 | 76.60 | 63.33 | 82.81 | 0.461 | 0.793 |
| 6 | 0.956 | 458.08 | 71.28 | 73.33 | 70.31 | 0.410 | 0.749 |
| 7 | 0.950 | 446.56 | 72.34 | 76.67 | 70.31 | 0.440 | 0.749 |
| 8 | 0.954 | 446.24 | 70.21 | 73.33 | 68.75 | 0.395 | 0.742 |
| 9 | 0.950 | 461.75 | 77.66 | 76.67 | 78.13 | 0.523 | 0.781 |
| 10 | 0.960 | 463.10 | 73.40 | 66.67 | 76.56 | 0.417 | 0.787 |
| Mean | 0.955 | 458.31 | 74.47 | 71.67 | 75.78 | 0.455 | 0.768 |
| STD. | 0.006 | 10.77 | 2.56 | 5.72 | 5.22 | 0.040 | 0.020 |
| Method | 10-fold CV | Independent Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC (%) | MCC | ACC (%) | SN (%) | SP (%) | MCC | |
| Init-DPS | 85.99 | 0.705 | 75.53 | 53.33 | 85.94 | 0.414 |
| opti-DPS | 92.52 | 0.846 | 77.66 | 76.67 | 78.13 | 0.523 |
| Method | 10-fold CV | Independent Test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACC (%) | MCC | ACC (%) | SN (%) | SP (%) | MCC | |
| Feng et al.’s method a | 79.15 | - | - | - | - | - |
| PVPred a | 85.02 | - | 71.30 | 60.00 | 76.50 | 0.357 |
| PVP-SVM a | 87.00 | 0.695 | 79.80 | 66.70 | 85.90 | 0.531 |
| PhagePred a | 98.05 | 0.963 | - | - | - | - |
| Tan et al.’s method a | 87.95 | 0.761 | 75.53 | 70.00 | 78.13 | 0.464 |
| PVPred-SCM | 92.52 | 0.846 | 77.66 | 76.67 | 78.13 | 0.523 |
| Name (Uniprot) | PVP Score | PDBID | UniProtID | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capsid protein G8P | 605.69 | 1HH0 | P82889 | Thermus phage PH75 |
| Capsid protein G8P | 581.12 | 2IFO | P03622 | Xanthomonas phage Xf |
| HIS6-pVII fusion protein | 541.13 | ADR00487 | VCSM13 HIS6-pVII modified interference-resistant helper phage | |
| G VIII capsid protein Precursor | 538.64 | 6A7F | NP_040575 | Enterobacteria phage Ike |
| P34 | 538.52 | YP_009639974 | Enterobacteria phage PRD1 | |
| Major coat protein | 534.58 | 1IFP | NP_040652 | Pseudomonas phage Pf3 |
| Structural protein P7 | 532.24 | NP_049902 | Pseudoalteromonas virus PM2 | |
| Transclycosylase | 529.49 | YP_009639979 | Enterobacteria phage PRD1 | |
| MULTISPECIES: major coat protein | 529.45 | WP_015979773 | Enterobacteriaceae | |
| Hypothetical protein | 519.23 | WP_015975197 | Salmonella enterica |
| Amino Acid | PVP (%) | Non-PVP (%) | Difference | Score | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-Ala | 9.98 | 8.09 | 1.89(1) | 529.50(1) | <0.05 |
| T-Thr | 6.90 | 5.49 | 1.41(4) | 511.43(2) | <0.05 |
| V-Val | 8.09 | 6.39 | 1.71(3) | 506.88(3) | <0.05 |
| G-Gly | 8.20 | 6.42 | 1.78(2) | 506.68(4) | <0.05 |
| S-Ser | 7.29 | 6.10 | 1.19(5) | 504.63(5) | <0.05 |
| Y-Tyr | 3.37 | 3.50 | −0.12(13) | 479.13(6) | 0.571 |
| N-Asn | 4.69 | 4.64 | 0.05(9) | 471.50(7) | 0.866 |
| P-Pro | 4.13 | 3.76 | 0.38(7) | 462.15(8) | 0.178 |
| Q-Gln | 4.18 | 3.72 | 0.46(6) | 452.83(9) | 0.106 |
| I-Ile | 6.23 | 6.06 | 0.17(8) | 443.18(10) | 0.629 |
| W-Trp | 1.38 | 1.50 | −0.12(12) | 442.33(11) | 0.408 |
| D-Asp | 5.23 | 5.87 | −0.64(16) | 435.45(12) | <0.05 |
| C-Cys | 0.66 | 1.05 | −0.39(14) | 426.58(13) | <0.05 |
| M-Met | 2.64 | 2.73 | −0.09(11) | 426.15(14) | 0.626 |
| F-Phe | 3.91 | 3.91 | 0.00(10) | 423.45(15) | 0.989 |
| L-Leu | 7.80 | 8.34 | −0.54(15) | 395.85(16) | 0.160 |
| R-Arg | 4.28 | 5.48 | −1.21(18) | 383.15(17) | <0.05 |
| H-His | 1.04 | 1.80 | −0.76(17) | 378.45(18) | <0.05 |
| E-Glu | 4.85 | 7.36 | −2.51(19) | 358.93(19) | <0.05 |
| K-Lys | 5.14 | 7.81 | −2.67(20) | 310.90(20) | <0.05 |
| Amino Acid | PS | KOEP990101 | Side-Chain [50] | WOLR790101 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A-Ala | 529.50(1) | −0.04(12) | 15(19) | 1.12(5) |
| T-Thr | 511.43(2) | 0.39(3) | 45(15) | −0.02(10) |
| V-Val | 506.88(3) | −0.06(13) | 43(16) | 1.13(4) |
| G-Gly | 506.68(4) | 1.24(1) | 1(20) | 1.20(1) |
| S-Ser | 504.63(5) | 0.15(7) | 31(18) | −0.05(11) |
| Y-Tyr | 479.13(6) | 0.05(8) | 107(2) | −0.23(13) |
| N-Asn | 471.50(7) | 0.25(5) | 58(11) | −0.83(16) |
| P-Pro | 462.15(8) | 0.00(9) | 42(17) | 0.54(9) |
| Q-Gln | 452.83(9) | −0.02(11) | 72(9) | −0.78(14) |
| I-Ile | 443.18(10) | −0.26(17) | 57(12) | 1.16(3) |
| W-Trp | 442.33(11) | 0.21(6) | 130(1) | −0.19(12) |
| D-Asp | 435.45(12) | 0.27(4) | 59(10) | −0.83(17) |
| C-Cys | 426.58(13) | 0.57(2) | 47(14) | 0.59(7) |
| M-Met | 426.15(14) | −0.09(14) | 75(6) | 0.55(8) |
| F-Phe | 423.45(15) | −0.01(10) | 91(4) | 0.67(6) |
| L-Leu | 395.85(16) | −0.38(20) | 57(13) | 1.18(2) |
| R-Arg | 383.15(17) | −0.30(18) | 101(3) | −2.55(20) |
| H-His | 378.45(18) | −0.11(15) | 82(5) | −0.93(19) |
| E-Glu | 358.93(19) | −0.33(19) | 73(7) | −0.92(18) |
| K-Lys | 310.90(20) | −0.18(16) | 73(8) | −0.80(15) |
| Correlation R | 1.000 | 0.502 | −0.516 | 0.484 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Charoenkwan, P.; Kanthawong, S.; Schaduangrat, N.; Yana, J.; Shoombuatong, W. PVPred-SCM: Improved Prediction and Analysis of Phage Virion Proteins Using a Scoring Card Method. Cells 2020, 9, 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020353
Charoenkwan P, Kanthawong S, Schaduangrat N, Yana J, Shoombuatong W. PVPred-SCM: Improved Prediction and Analysis of Phage Virion Proteins Using a Scoring Card Method. Cells. 2020; 9(2):353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020353
Chicago/Turabian StyleCharoenkwan, Phasit, Sakawrat Kanthawong, Nalini Schaduangrat, Janchai Yana, and Watshara Shoombuatong. 2020. "PVPred-SCM: Improved Prediction and Analysis of Phage Virion Proteins Using a Scoring Card Method" Cells 9, no. 2: 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020353
APA StyleCharoenkwan, P., Kanthawong, S., Schaduangrat, N., Yana, J., & Shoombuatong, W. (2020). PVPred-SCM: Improved Prediction and Analysis of Phage Virion Proteins Using a Scoring Card Method. Cells, 9(2), 353. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020353