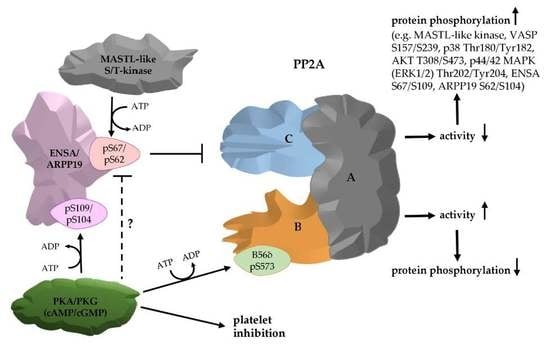
The Cell Cycle Checkpoint System MAST(L)-ENSA/ARPP19-PP2A is Targeted by cAMP/PKA and cGMP/PKG in Anucleate Human Platelets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Canonical Sequence of ENSA and ARPP19
2.3. Recombinant Wildtype and Mutant ENSA Protein Expression and Purification
2.4. Culture, Treatment, and Sample Generation of HEK293 Cells
2.5. Preparation of Washed Human Platelets
2.6. Generation of Platelet Lysates from Washed Human Platelets
2.7. Western Blot Analysis
2.8. Western blot Analysis Using Zn2+-PhostagTM-Gel Electrophoresis
2.9. Phosphorylation of GST-ARPP19 or HisENSA with Recombinant Kinases for Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Phosphorylation of GST-ARPP19 or HisENSA with Recombinant Kinases for Dephosphorylation Experiments in Platelet Lysates and for PP2A Phosphatase Activity Assay
2.11. Phosphorylation of Recombinant HisENSA and GST-ARPP19 in Platelet Lysates
2.12. Dephosphorylation of GST-ARPP19 in Platelet Lysates
2.13. Ser/Thr-Protein Phosphatase Inhibition by OA in Intact Human Platelets
2.14. PKA/PKG Effects in Intact Human Platelets
2.15. Colorimetric Ser/Thr/PP2A Phosphatase Activity Assay
2.16. Light Transmission Aggregometry
2.17. (Phospho-)Proteomic Sample Measurement
2.18. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The PP2A Inhibitors ENSA and ARPP19 are Present in Human Platelets and Phosphorylated by Both PKA and PKG
3.2. Phosphorylation of ENSA S67/ARPP19 S62 by a MASTL-Related Protein Kinase in Human Platelets
3.3. Phosphorylation of HisENSA and GST-ARPP19 by Human MASTL (S67/S62) and by PKA C-Subunit/ PKGIβ (S109/S104) or Combinations
- PKA phosphorylation of ARPP16 could interfere with the extent of PP2A inhibition by pS46 ARPP16
- PKA could phosphorylate and inhibit the ARPP16 S46 kinase MAST3
- Forskolin-stimulated PKA could activate PP2A by phosphorylation of PP2A B56δ [42] resulting in reduced S46 ARPP16 phosphorylation
3.4. Serine/Threonine Protein Phosphatases in Human Platelets
3.5. Effects of PP2A Inhibitors and MASTL-Phosphorylated HisENSA/GST-ARPP19 on Human Platelet PP2A Activity
3.6. Ser-Phosphorylated ARPP19 is Both a Substrate for and Inhibitor of Platelet PP2A
4. Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jurk, K.; Kehrel, B.E. Platelets: Physiology and biochemistry. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2005, 31, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Versteeg, H.H.; Heemskerk, J.W.; Levi, M.; Reitsma, P.H. New fundamentals in hemostasis. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 327–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jurk, K. Analysis of platelet function and dysfunction. Hamostaseologie 2015, 35, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, A.T.; Corken, A.; Ware, J. Platelets at the interface of thrombosis, inflammation, and cancer. Blood 2015, 126, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chatterjee, M.; Geisler, T. Inflammatory Contribution of Platelets Revisited: New Players in the Arena of Inflammation. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2016, 42, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maclachlan, A.; Watson, S.P.; Morgan, N.V. Inherited platelet disorders: Insight from platelet genomics using next-generation sequencing. Platelets 2017, 28, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golebiewska, E.M.; Poole, A.W. Platelet secretion: From haemostasis to wound healing and beyond. Blood Rev. 2015, 29, 153–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pagel, O.; Walter, E.; Jurk, K.; Zahedi, R.P. Taking the stock of granule cargo: Platelet releasate proteomics. Platelets 2017, 28, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, B.; Baber, U. Antiplatelet treatments: Recent evidence from randomized controlled trials. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2017, 32, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Offermanns, S. Activation of platelet function through G protein-coupled receptors. Circ. Res. 2006, 99, 1293–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senis, Y.A.; Mazharian, A.; Mori, J. Src family kinases: at the forefront of platelet activation. Blood 2014, 124, 2013–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heemskerk, J.W.M.; Harper, M.T.; Cosemans, J.; Poole, A.W. Unravelling the different functions of protein kinase C isoforms in platelets. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 1711–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aburima, A.; Naseem, K.M. Platelet myosin light chain phosphatase: Keeping it together. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 279–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunapuli, S.P.; Bhavanasi, D.; Kostyak, J.C.; Manne, B.K. Platelet Signaling: Protein Phosphorylation, in Platelets in Thrombotic and Non-Thrombotic Disorders: Pathophysiology, Pharmacology and Therapeutics: An Update; Gresele, P., Kleimann, N.S., Lopez, J.A., Page, C.P., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 297–308. [Google Scholar]
- Moncada, S.; Higgs, E.A.; Vane, J.R. Human Arterial and Venous Tissues Generate Prostacyclin (Prostaglandin-X), a Potent Inhibitor of Platelet-Aggregation. Lancet 1977, 1, 18–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, H.; Walter, U. NO at work. Cell 1994, 78, 919–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanhoutte, P.M.; Shimokawa, H.; Feletou, M.; Tang, E.H.C. Endothelial dysfunction and vascular disease—A 30th anniversary update. Acta Physiol. 2017, 219, 22–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Z.; Smolenski, A. Cyclic nucleotide-dependent inhibitory signaling interweaves with activating pathways to determine platelet responses. Res. Pract. Thromb. Haemost. 2018, 2, 558–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makhoul, S.; Walter, E.; Pagel, O.; Walter, U.; Sickmann, A.; Gambaryan, S.; Smolenski, A.; Zahedi, R.P.; Jurk, K. Effects of the NO/soluble guanylate cyclase/cGMP system on the functions of human platelets. Nitric Oxide 2018, 76, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coxon, C.H.; Geer, M.J.; Senis, Y.A. ITIM receptors: More than just inhibitors of platelet activation. Blood 2017, 129, 3407–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bye, A.P.; Unsworth, A.J.; Gibbins, J.M. Platelet signaling: A complex interplay between inhibitory and activatory networks. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2016, 14, 918–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senis, Y.A. Protein-tyrosine phosphatases: A new frontier in platelet signal transduction. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 11, 1800–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, V.; Goris, J. Protein phosphatase 2A: A highly regulated family of serine/threonine phosphatases implicated in cell growth and signalling. Biochem. J. 2001, 353, 417–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, M.H.A.; Held, M.; Janssens, V.; Hutchins, J.R.A.; Hudecz, O.; Ivanova, E.; Goris, J.; Trinkle-Mulcahy, L.; Lamond, A.I.; Poser, I.; et al. Live-cell imaging RNAi screen identifies PP2A-B55alpha and importin-beta1 as key mitotic exit regulators in human cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2010, 12, 886–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haesen, D.; Sents, W.; Lemaire, K.; Hoorne, Y.; Janssens, V. The Basic Biology of PP2A in Hematologic Cells and Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brautigan, D.L.; Shenolikar, S. Protein Serine/Threonine Phosphatases: Keys to Unlocking Regulators and Substrates. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018, 87, 921–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sangodkar, J.; Farrington, C.C.; McClinch, K.; Galsky, M.D.; Kastrinsky, D.B.; Narla, G. All roads lead to PP2A: Exploiting the therapeutic potential of this phosphatase. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 1004–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dulubova, I.; Horiuchi, A.; Snyder, G.L.; Girault, J.A.; Czernik, A.J.; Shao, L.; Ramabhadran, R.; Greengard, P.; Nairn, A.C. ARPP-16/ARPP-19: A highly conserved family of cAMP-regulated phosphoproteins. J. Neurochem. 2001, 77, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, S.; Maslen, S.L.; Skehel, M.; Hunt, T. Greatwall phosphorylates an inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A that is essential for mitosis. Science 2010, 330, 1670–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gharbi-Ayachi, A.; Labbe, J.C.; Burgess, A.; Vigneron, S.; Strub, J.M.; Brioudes, E.; Van-Dorsselaer, A.; Castro, A.; Lorca, T. The substrate of Greatwall kinase, Arpp19, controls mitosis by inhibiting protein phosphatase 2A. Science 2010, 330, 1673–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochida, S. Regulation of alpha-endosulfine, an inhibitor of protein phosphatase 2A, by multisite phosphorylation. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 1159–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labandera, A.M.; Vahab, A.R.; Chaudhuri, S.; Kerk, D.; Moorhead, G.B.G. The mitotic PP2A regulator ENSA/ARPP-19 is remarkably conserved across plants and most eukaryotes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. 2015, 458, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, A.; Lorca, T. Greatwall kinase at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs222364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burkhart, J.M.; Vaudel, M.; Gambaryan, S.; Radau, S.; Walter, U.; Martens, L.; Geiger, J.; Sickmann, A.; Zahedi, R.P. The first comprehensive and quantitative analysis of human platelet protein composition allows the comparative analysis of structural and functional pathways. Blood 2012, 120, e73–e82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Beck, F.; Geiger, J.; Gambaryan, S.; Veit, J.; Vaudel, M.; Nollau, P.; Kohlbacher, O.; Martens, L.; Walter, U.; Sickmann, A.; et al. Time-resolved characterization of cAMP/PKA-dependent signaling reveals that platelet inhibition is a concerted process involving multiple signaling pathways. Blood 2014, 123, e1–e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sundaresan, P.; Farndale, R.W. P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase dephosphorylation is regulated by protein phosphatase 2A in human platelets activated by collagen. FEBS Lett. 2002, 528, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Higashihara, M.; Takahata, K.; Kurokawa, K.; Ikebe, M. The inhibitory effects of okadaic acid on platelet function. FEBS Lett. 1992, 307, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Walker, T.R.; Watson, S.P. Okadaic Acid Inhibits Activation of Phospholipase-C in Human Platelets by Mimicking the Actions of Protein Kinase-A and Kinase-C. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1992, 105, 627–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, M.; Toyoda, H.; Saito, M.; Morita, K.; Tawara, I.; Deguchi, k.; Kuno, T.; Shima, H.; Nagaos, M.; Shirakawa, S. Calyculin-A and Okadaic Acid Inhibit Human Platelet-Aggregation by Blocking Protein Phosphatases Type-1 and Type-2A. Cell. Signal. 1994, 6, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, F.; Geiger, J.; Gambaryan, S.; Solari, F.A.; Dell’Aica, M.; Loroch, S.; Mattheij, N.J.; Mindukshev, I.; Pötz, O.; Jurk, K.; et al. Temporal quantitative phosphoproteomics of ADP stimulation reveals novel central nodes in platelet activation and inhibition. Blood 2017, 129, E1–E12. [Google Scholar]
- Reiss, C.; Mindukshev, I.; Bischoff, V.; Subramanian, H.; Kehrer, L.; Friebe, A.; Stasch, J.P.; Gambaryan, S.; Walter, U. The sGC stimulator riociguat inhibits platelet function in washed platelets but not in whole blood. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 172, 5199–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, J.H.; McAvoy, T.; Rakhilin, S.V.; Nishi, A.; Greengard, P.; Nairn, A.C. Protein kinase A activates protein phosphatase 2A by phosphorylation of the B56delta subunit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2979–2984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Williams, B.C.; Filter, J.J.; Blake-Hodek, K.A.; Wadzinski, B.E.; Fuda, N.J.; Shalloway, D.; Goldberg, M.L. Greatwall-phosphorylated Endosulfine is both an inhibitor and a substrate of PP2A-B55 heterotrimers. Elife 2014, 3, e01695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegarat, N.; Vesely, C.; Vinod, P.K.; Ocasio, C.; Peter, N.; Gannon, J.; Oliver, A.W.; Novak, B.; Hochegger, H. PP2A/B55 and Fcp1 regulate Greatwall and Ensa dephosphorylation during mitotic exit. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Voets, E.; Wolthuis, R.M. MASTL is the human orthologue of Greatwall kinase that facilitates mitotic entry, anaphase and cytokinesis. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 3591–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgess, A.; Vigneron, S.; Brioudes, E.; Labbe, J.C.; Lorca, T.; Castro, A. Loss of human Greatwall results in G2 arrest and multiple mitotic defects due to deregulation of the cyclin B-Cdc2/PP2A balance. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 12564–12569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Musante, V.; Li, L.; Kanyo, J.; Lam, T.T.; Colangelo, C.M.; Cheng, S.K.; Brody, A.H.; Greengard, P.; Le Novere, N.; Nairn, A.C. Reciprocal regulation of ARPP-16 by PKA and MAST3 kinases provides a cAMP-regulated switch in protein phosphatase 2A inhibition. Elife 2017, 6, e24998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, E.C.; Musante, V.; Horiuchi, A.; Matsuzaki, H.; Brody, A.H.; Wu, T.; Greengard, P.; Taylor, J.R.; Nairn, A.C. ARPP-16 Is a Striatal-Enriched Inhibitor of Protein Phosphatase 2A Regulated by Microtubule-Associated Serine/Threonine Kinase 3 (Mast 3 Kinase). J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 2709–2722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeiler, M.; Moser, M.; Mann, M. Copy Number Analysis of the Murine Platelet Proteome Spanning the Complete Abundance Range. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2014, 13, 3435–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rowley, J.W.; Oler, A.J.; Tolley, N.D.; Hunter, B.N.; Low, E.N.; Nix, D.A.; Yost, C.C.; Zimmerman, G.A.; Weyrich, A.S. Genome-wide RNA-seq analysis of human and mouse platelet transcriptomes. Blood 2011, 118, E101–E111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jurk, K.; Walter, U. New Insights into Platelet Signalling Pathways by Functional and Proteomic Approaches. Hamostaseologie 2018, 35, 60–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, M.J.; Cummings, C.L.; Drachman, J.G. FLJ14813 Missense mutation: A candidate for autosomal dominant thrombocytopenia on human chromosome 10. Hum. Hered. 2003, 55, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hurtado, B.; Trakala, M.; Ximénez-Embún, P.; El Bakkali, A.; Partida, D.; Sanz-Castillo, B.; Álvarez-Fernández, M.; Maroto, M.; Sánchez-Martínez, R.; Martínez, L.; et al. Thrombocytopenia-associated mutations in Ser/Thr kinase MASTL deregulate actin cytoskeletal dynamics in platelets. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 5351–5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dupre, A.I.; Haccard, O.; Jessus, C. The greatwall kinase is dominant over PKA in controlling the antagonistic function of ARPP19 in Xenopus oocytes. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 1440–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leslie, S.N.; Nairn, A.C. cAMP regulation of protein phosphatases PP1 and PP2A in brain. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, A.; Eto, M.; Hirano, K.; Takeya, K.; Wakimoto, T.; Watanabe, M. Protein phosphatases 1 and 2A and their naturally occurring inhibitors: Current topics in smooth muscle physiology and chemical biology. J. Physiol. Sci. 2018, 68, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Manning, G.; Whyte, D.B.; Martinez, R.; Hunter, T.; Sudarsanam, S. The protein kinase complement of the human genome. Science 2002, 298, 1912–1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, M.J.; Dixon, J.E.; Manning, G. Genomics and evolution of protein phosphatases. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaag1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Nie, Y.J.; Shi, H.R.; Ni, Z.F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, J.Z.; Liu, G.P. PTPA activates protein phosphatase-2A through reducing its phosphorylation at tyrosine-307 with upregulation of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 1235–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Pham, H.T.; Ruediger, R.; Walter, G. Characterization of the Aalpha and Abeta subunit isoforms of protein phosphatase 2A: Differences in expression, subunit interaction, and evolution. Biochem. J. 2003, 369, 387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McAvoy, T.; Nairn, A.C. Serine/threonine protein phosphatase assays. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2010, 92, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Swingle, M.R.; Honkanen, R.E. Inhibitors of Serine/Threonine Protein Phosphatases: Biochemical and Structural Studies Provide Insight for Further Development. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 2634–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuhashi, S.; Matsuura, N.; Ubukata, M.; Oikawa, H.; Shima, H.; Kikuchi, K. Tautomycetin is a novel and specific inhibitor of serine/threonine protein phosphatase type 1, PP1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 287, 328–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertz, E.P.T.; Kruse, T.; Davey, N.E.; Lopez-Mendez, B.; Sigurdsson, J.O.; Montoya, G.; Olsen, J.V.; Nilsson, J. A Conserved Motif Provides Binding Specificity to the PP2A-B56 Phosphatase. Mol. Cell 2016, 63, 686–695. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.G.; Chen, H.; Guo, F.; Yadav, K.V.; Mcilwain, S.J.; Rowse, M.; Choudhary, A.; Lin, Z.; Li, Y.; Gu, T.; et al. PP2A-B’ holoenzyme substrate recognition, regulation and role in cytokinesis. Cell Discov. 2017, 3, 17027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ocasio, C.A.; Rajasekaran, M.B.; Walker, S.; Le Grand, D.; Spencer, J.; Pearl, F.M.; Ward, S.E.; Savic, V.; Pearl, L.H.; Hochegger, H.; et al. A First Generation Inhibitor of Human Greatwall Kinase, Enabled by Structural and Functional Characterisation of a Minimal Kinase Domain Construct. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 71182–71197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.R.; Bajaj, R.; Bollen, M.; Peti, W.; Page, R. Expanding the PP2A Interactome by Defining a B56-Specific SLiM. Structure 2016, 24, 2174–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sommer, L.M.; Cho, H.; Choudhary, M.; Seeling, J.M. Evolutionary Analysis of the B56 Gene Family of PP2A Regulatory Subunits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 10134–10157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Booker, M.A.; DeLong, A. Atypical Protein Phosphatase 2A Gene Families Do Not Expand via Paleopolyploidization. Plant Physiol. 2017, 173, 1283–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cundell, M.J.; Hutter, L.H.; Bastos, R.N.; Poser, E.; Holder, J.; Mohammed, S.; Novak, B.; Barr, F.A. A PP2A-B55 recognition signal controls substrate dephosphorylation kinetics during mitotic exit. J. Cell Biol. 2016, 214, 539–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vigneron, S.; Robert, P.; Hached, K.; Sundermann, L.; Charrasse, S.; Labbe, J.C.; Castro, A.; Lorca, T. The master Greatwall kinase, a critical regulator of mitosis and meiosis. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2016, 60, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meeusen, B.; Janssens, V. Tumor suppressive protein phosphatases in human cancer: Emerging targets for therapeutic intervention and tumor stratification. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 96, 98–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, V.; Goris, J.; Van Hoof, C. PP2A: The expected tumor suppressor. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2005, 15, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junttila, M.R.; Li, S.P.; Westermarck, J. Phosphatase-mediated crosstalk between MAPK signalling pathways in the regulation of cell survival. FASEB J. 2008, 22, 954–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abel, K.; Mieskes, G.; Walter, U. Dephosphorylation of the focal adhesion protein VASP in vitro and in intact human platelets. FEBS Lett. 1995, 370, 184–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reinhard, M.; Jarchau, T.; Walter, U. Actin-based motility: Stop and go with Ena/VASP proteins. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2001, 26, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namboodiripad, A.N.; Jennings, M.L. Permeability characteristics of erythrocyte membrane to okadaic acid and calyculin A. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 1996, 270, C449–C456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aburima, A.; Walladbegi, K.; Wake, J.D.; Naseem, K.M. cGMP signaling inhibits platelet shape change through regulation of the RhoA-Rho Kinase-MLC phosphatase signaling pathway. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2017, 15, 1668–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Packham, M.A.; Livne, A.A.; Ruben, D.H.; Rand, M.L. Activation of Phospholipase-C and Protein-Kinase-C Has Little Involvement in Adp-Induced Primary Aggregation of Human Platelets—Effects of Diacylglycerols, The Diacylglycerol Kinase Inhibitor R59022, Staurosporine and Okadaic Acid. Biochem. J. 1993, 290, 849–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benz, P.M.; Blume, C.; Seifert, S.; Wilhelm, S.; Waschke, J.; Schuh, K.; Gertler, F.; Münzel, T.; Renné, T. Differential VASP phosphorylation controls remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton. J. Cell Sci. 2009, 122, 3954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Benz, P.M.; Blume, C.; Seifert, S.; Wilhelm, S.; Waschke, J.; Schuh, K.; Gertler, F.; Münzel, T.; Renné, T. Vasodilator-Stimulated Phosphoprotein (VASP)-dependent and -independent pathways regulate thrombin-induced activation of Rap1b in platelets. Cell Commun. Signal. 2016, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flaumenhaft, R. Stressed platelets ASK1 for a MAPK. Blood 2017, 129, 1066–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naik, M.U.; Patel, P.; Derstine, R.; Turaga, R.; Chen, X.; Golla, K.; Neeves, K.B.; Ichijo, H.; Naik, U.P. Ask1 regulates murine platelet granule secretion, thromboxane A(2) generation, and thrombus formation. Blood 2017, 129, 1197–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.; Naik, M.U.; Golla, K.; Shaik, N.F.; Naik, U.P. Calcium-induced dissociation of CIB1 from ASK1 regulates agonist-induced activation of the p38 MAPK pathway in platelets. Biochem. J. 2019, 476, 2835–2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moroi, A.J.; Watson, S.P. Impact of the PI3-kinase/Akt pathway on ITAM and hemITAM receptors: Haemostasis, platelet activation and antithrombotic therapy. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 94, 186–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moscardo, A.; Valles, J.; Pinon, M.; Aznar, J.; Martinez-Sales, V.; Santos, M.T. Regulation of cytosolic PlA2 activity by PP1/PP2A serine/threonine phosphatases in human platelets. Platelets 2006, 17, 405–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Blanco, N.; Vazquez-Bolado, A.; Moreno, S. Greatwall-Endosulfine: A Molecular Switch that Regulates PP2A/B55 Protein Phosphatase Activity in Dividing and Quiescent Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moyano-Rodriguez, Y.; Queralt, E. PP2A Functions during Mitosis and Cytokinesis in Yeasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reynhout, S.; Janssens, V. Physiologic functions of PP2A: Lessons from genetically modified mice. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2019, 1866, 31–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambrecht, C.; Libbrecht, L.; Sagaert, X.; Pauwels, P.; Hoorne, Y.; Crowther, J.; Louis, J.V.; Sents, W.; Sablina, A.; Janssens, V. Loss of protein phosphatase 2A regulatory subunit B56delta promotes spontaneous tumorigenesis in vivo. Oncogene 2017, 37, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hached, K.; Goguet, P.; Charrasse, S.; Vigneron, S.; Sacristan, M.P.; Lorca, T.; Castro, A. ENSA and ARPP19 differentially control cell cycle progression and development. J. Cell Biol. 2019, 18, 541–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Gene | Uniprot | P-Site | Av. Ratio Iloprost | Av. Ratio DEA-NO | Av. Ratio Riociguat | Av. Ratio SNC | Av. Ratio SNP | Copy Number/Platelet |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VASP | P50552 | S239 | 7.17 | 12.19 | 9.22 | 7.67 | 6.93 | 44,600 |
| ENSA | O43768 | S109 | 17.97 | 14.04 | 16.03 | 13.88 | 12.46 | 7800 |
| ENSA | O43768 | S67 | 0.53 | 0.82 | 0.62 | 0.72 | 0.82 | 7800 |
| Gene | Uniprot | Protein Name | Copy Number/Platelet | P-site (1st) (#of Averaged Peptides) | Iloprost (cA) | Riociguat (cG) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Av. Ratio | p-Value Fraction | Av. Ratio | p-Value Fraction | |||||
| ENSA | O43768 | ENSA/ARPP19e | 7800 | S109 (3) | 4.81 | 100% | 3.75 | 100% |
| ARPP19 | P56211 | ARPP19 | 2500 | S104 (1) | 3.53 | 100% | 2.18 | 100% |
| PPP2R5D | Q14738 | PP2A B-subunit B’-δ (B56δ) | 1300 | S573 (1) | 4.52 | 100% | 2.13 | 100% |
| VASP | P50552 | VASP | 44600 | S157* (1) | 2.03 | 100% | 1.67 | 100% |
| VASP | P50552 | VASP | 44600 | S239 (4) | 3.92 | 100% | 4.52 | 100% |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kumm, E.J.; Pagel, O.; Gambaryan, S.; Walter, U.; Zahedi, R.P.; Smolenski, A.; Jurk, K. The Cell Cycle Checkpoint System MAST(L)-ENSA/ARPP19-PP2A is Targeted by cAMP/PKA and cGMP/PKG in Anucleate Human Platelets. Cells 2020, 9, 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020472
Kumm EJ, Pagel O, Gambaryan S, Walter U, Zahedi RP, Smolenski A, Jurk K. The Cell Cycle Checkpoint System MAST(L)-ENSA/ARPP19-PP2A is Targeted by cAMP/PKA and cGMP/PKG in Anucleate Human Platelets. Cells. 2020; 9(2):472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020472
Chicago/Turabian StyleKumm, Elena J., Oliver Pagel, Stepan Gambaryan, Ulrich Walter, René P. Zahedi, Albert Smolenski, and Kerstin Jurk. 2020. "The Cell Cycle Checkpoint System MAST(L)-ENSA/ARPP19-PP2A is Targeted by cAMP/PKA and cGMP/PKG in Anucleate Human Platelets" Cells 9, no. 2: 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020472
APA StyleKumm, E. J., Pagel, O., Gambaryan, S., Walter, U., Zahedi, R. P., Smolenski, A., & Jurk, K. (2020). The Cell Cycle Checkpoint System MAST(L)-ENSA/ARPP19-PP2A is Targeted by cAMP/PKA and cGMP/PKG in Anucleate Human Platelets. Cells, 9(2), 472. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020472