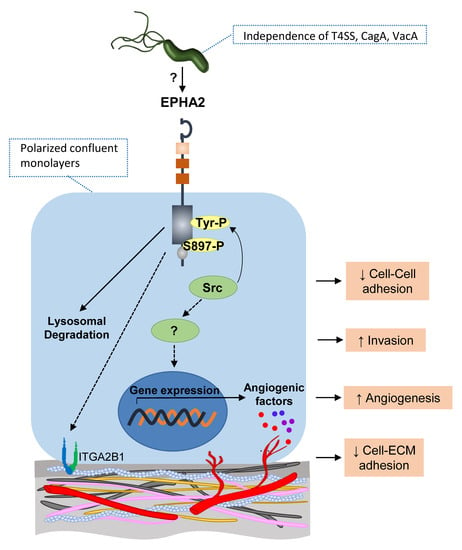
Helicobacter Pylori Targets the EPHA2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase in Gastric Cells Modulating Key Cellular Functions
Abstract
Share and Cite
Leite, M.; Marques, M.S.; Melo, J.; Pinto, M.T.; Cavadas, B.; Aroso, M.; Gomez-Lazaro, M.; Seruca, R.; Figueiredo, C. Helicobacter Pylori Targets the EPHA2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase in Gastric Cells Modulating Key Cellular Functions. Cells 2020, 9, 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020513
Leite M, Marques MS, Melo J, Pinto MT, Cavadas B, Aroso M, Gomez-Lazaro M, Seruca R, Figueiredo C. Helicobacter Pylori Targets the EPHA2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase in Gastric Cells Modulating Key Cellular Functions. Cells. 2020; 9(2):513. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020513
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeite, Marina, Miguel S. Marques, Joana Melo, Marta T. Pinto, Bruno Cavadas, Miguel Aroso, Maria Gomez-Lazaro, Raquel Seruca, and Ceu Figueiredo. 2020. "Helicobacter Pylori Targets the EPHA2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase in Gastric Cells Modulating Key Cellular Functions" Cells 9, no. 2: 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020513
APA StyleLeite, M., Marques, M. S., Melo, J., Pinto, M. T., Cavadas, B., Aroso, M., Gomez-Lazaro, M., Seruca, R., & Figueiredo, C. (2020). Helicobacter Pylori Targets the EPHA2 Receptor Tyrosine Kinase in Gastric Cells Modulating Key Cellular Functions. Cells, 9(2), 513. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9020513