Hidden Cardiotoxicity of Rofecoxib Can be Revealed in Experimental Models of Ischemia/Reperfusion
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethical Considerations
2.2. Sources of Chemicals
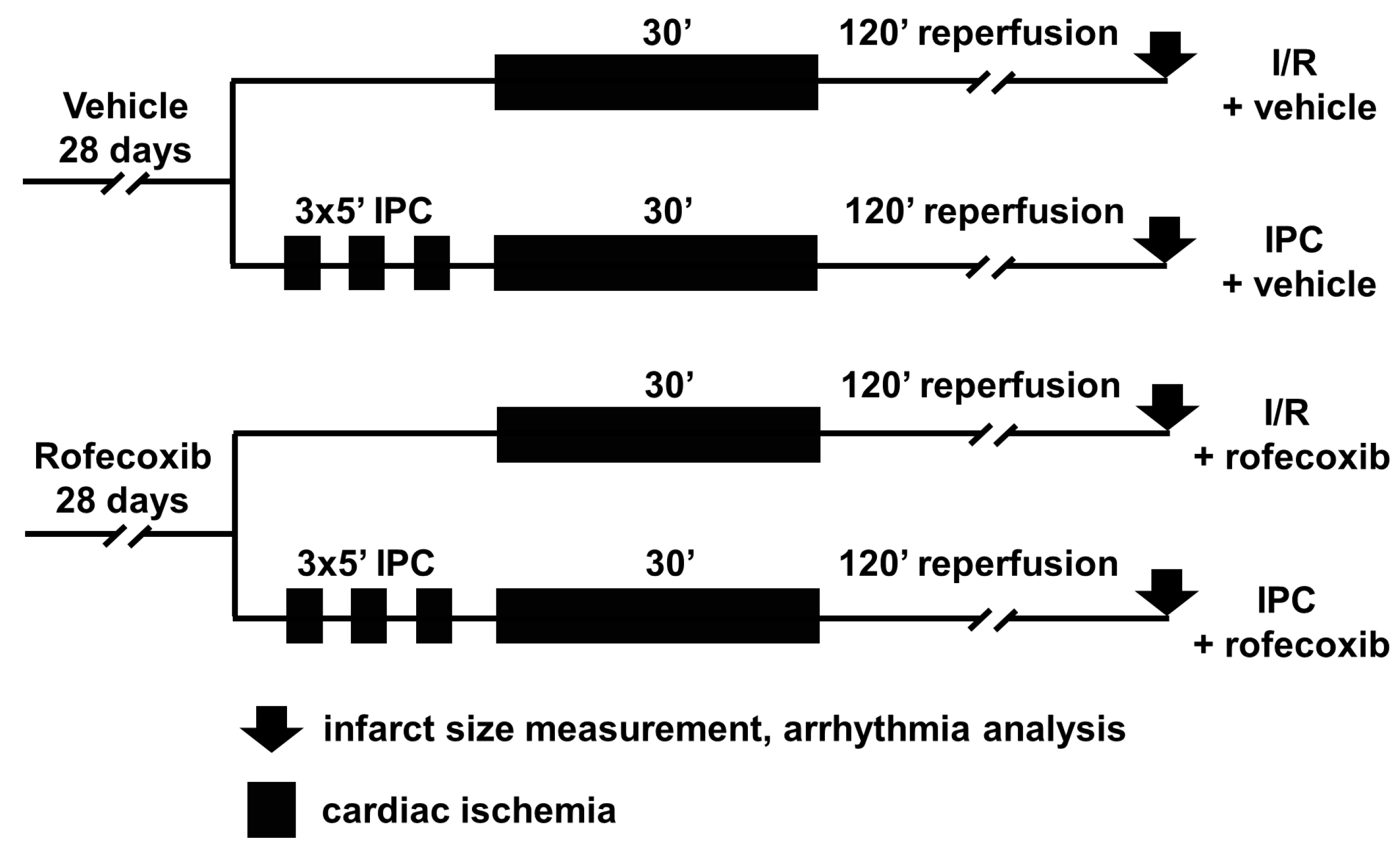
2.3. In Vivo Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Study
2.3.1. Mortality Analysis
2.3.2. Arrhythmia Analysis
2.3.3. Infarct Size Measurement
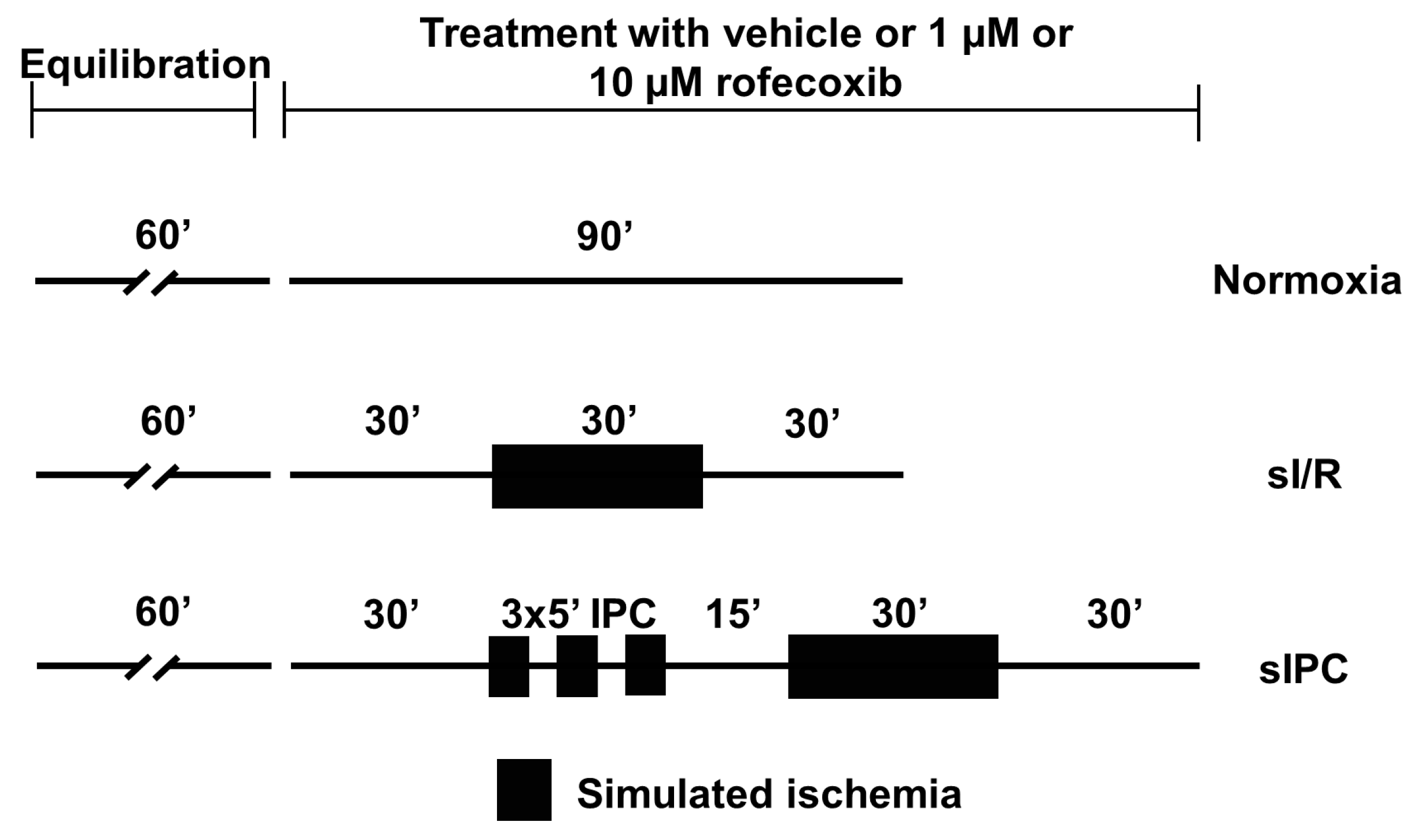
2.4. Ex Vivo Simulated Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Study
Evaluation of Action Potential Parameters
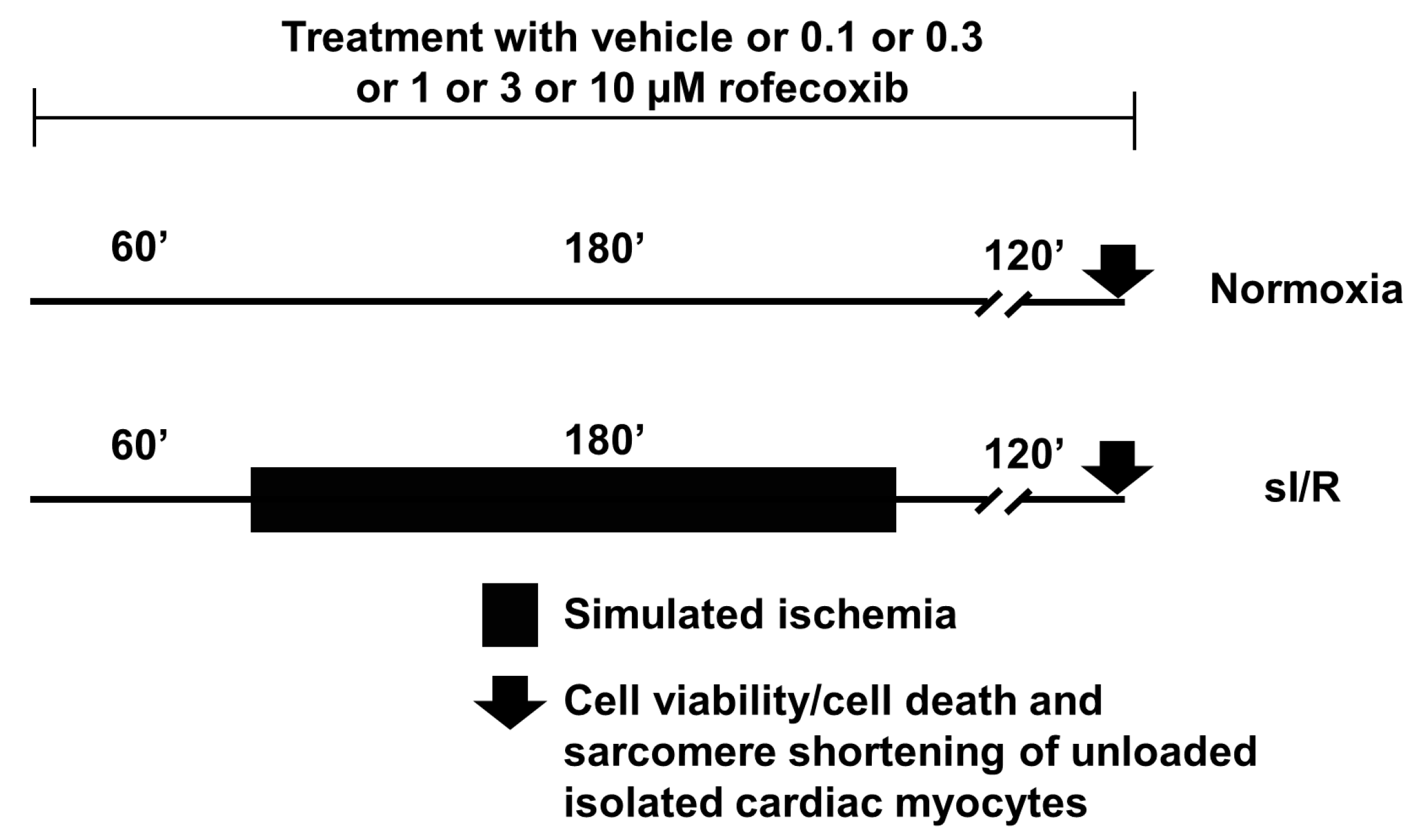
2.5. In Vitro Simulated Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury Study
Viability Assay
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chronic Rofecoxib Treatment Increased Acute Mortality During Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion
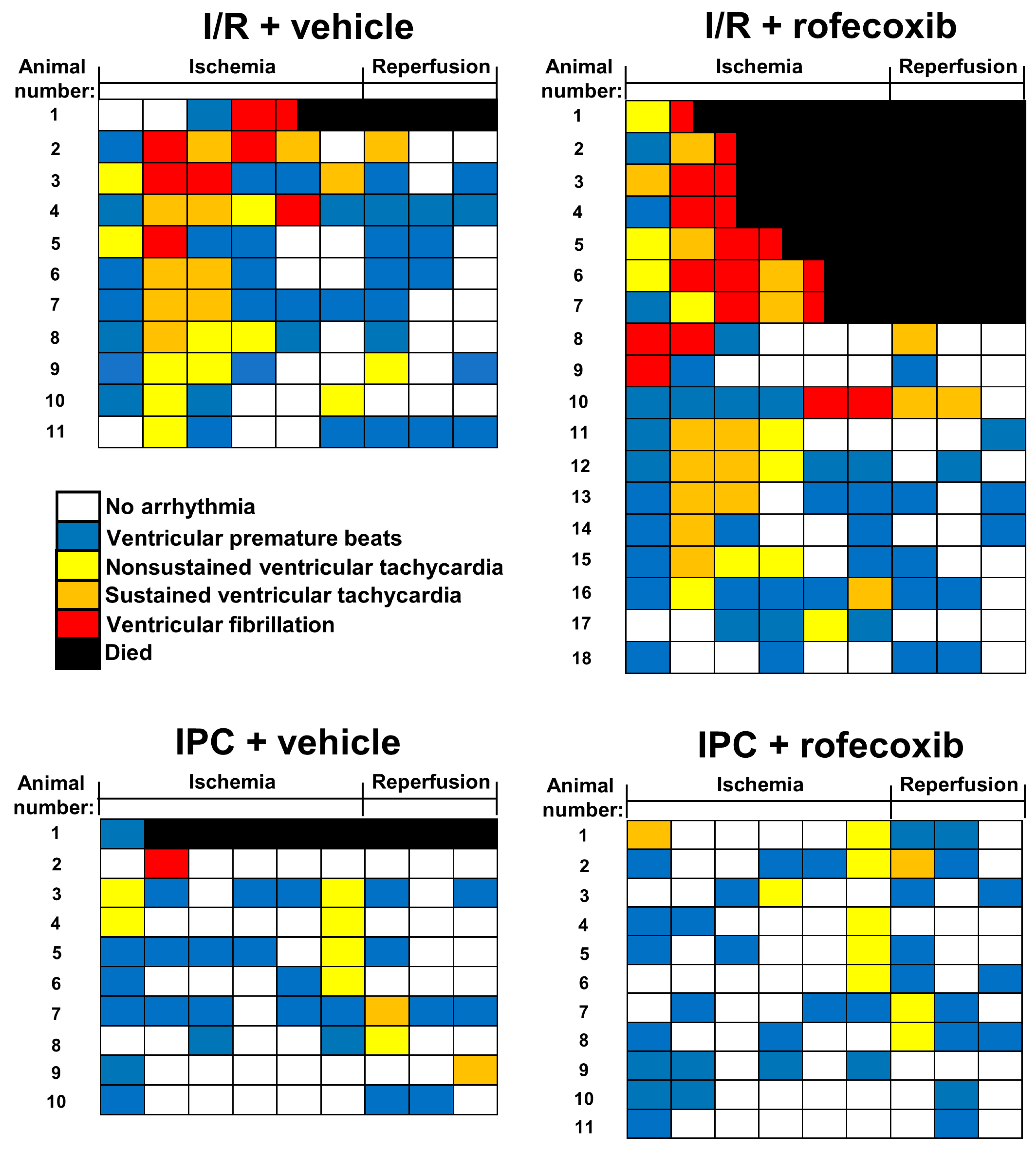
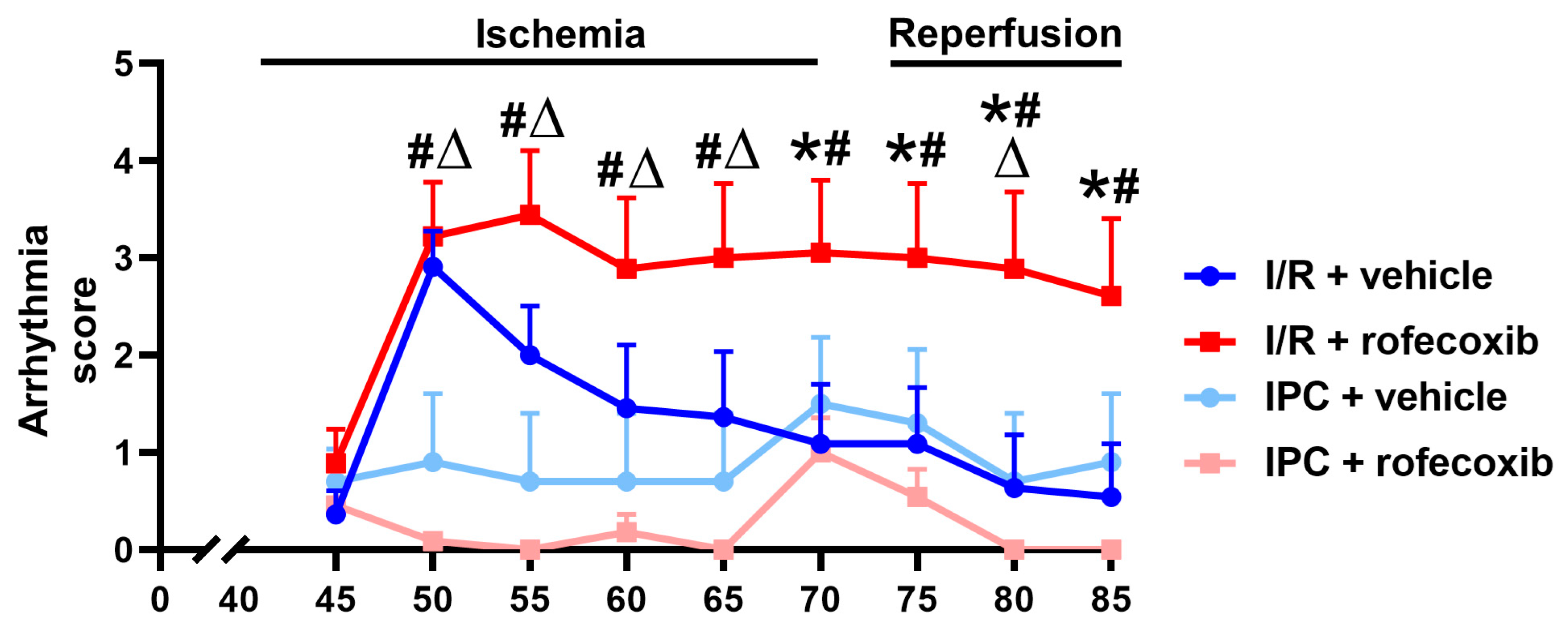
3.2. Chronic Rofecoxib Treatment Increased Arrhythmia Score in Cardiac Ischemia/Reperfusion
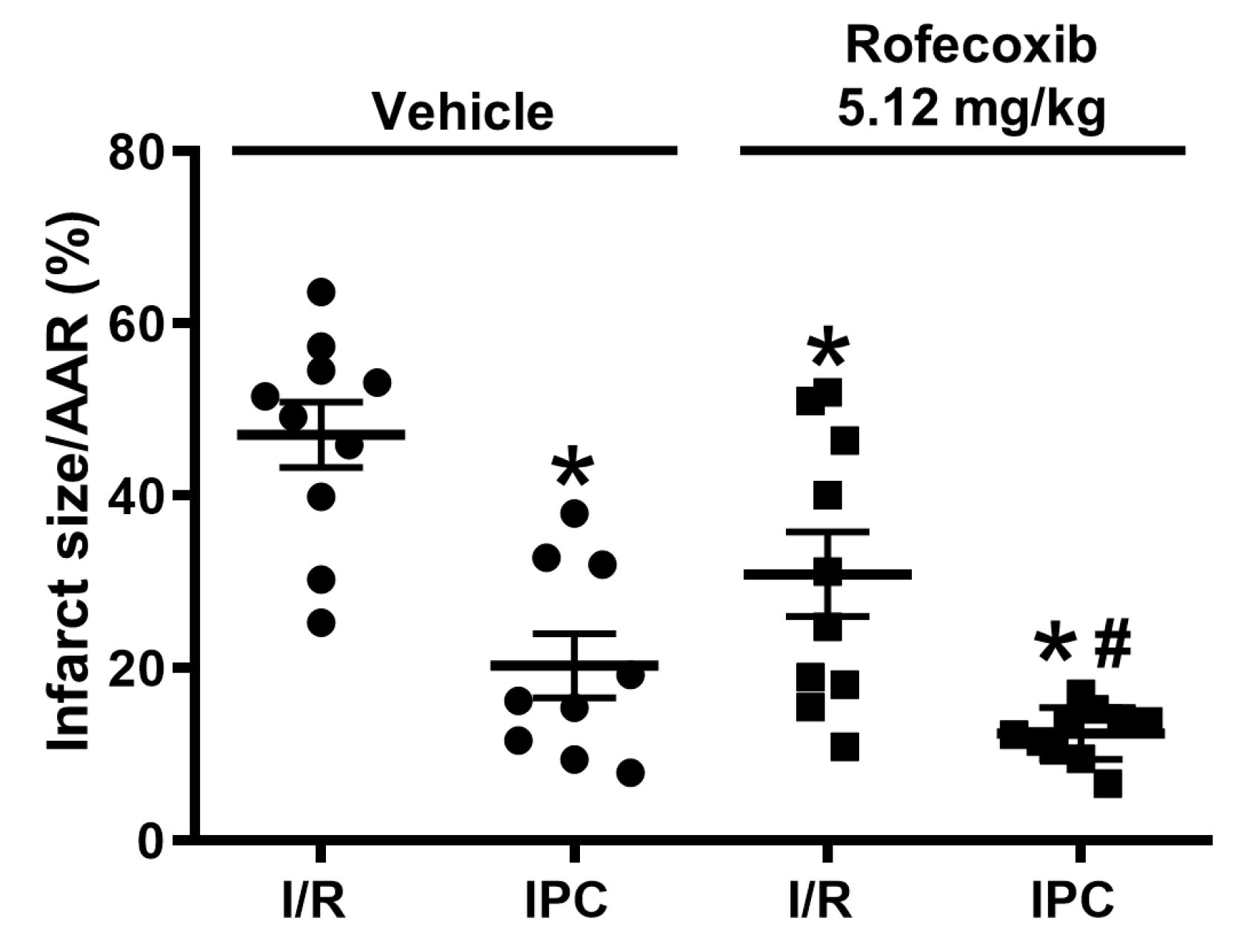
3.3. Rofecoxib Decreased Infarct Size and Did Not Interfere with Cardioprotection by Ischemic Preconditioning
3.4. Rofecoxib Increased the Action Potential Duration in Rat Isolated Papillary Muscles at the End of Simulated Ischemia/Reperfusion and this Effect Was Not Observed Ischemic Preconditioning Groups
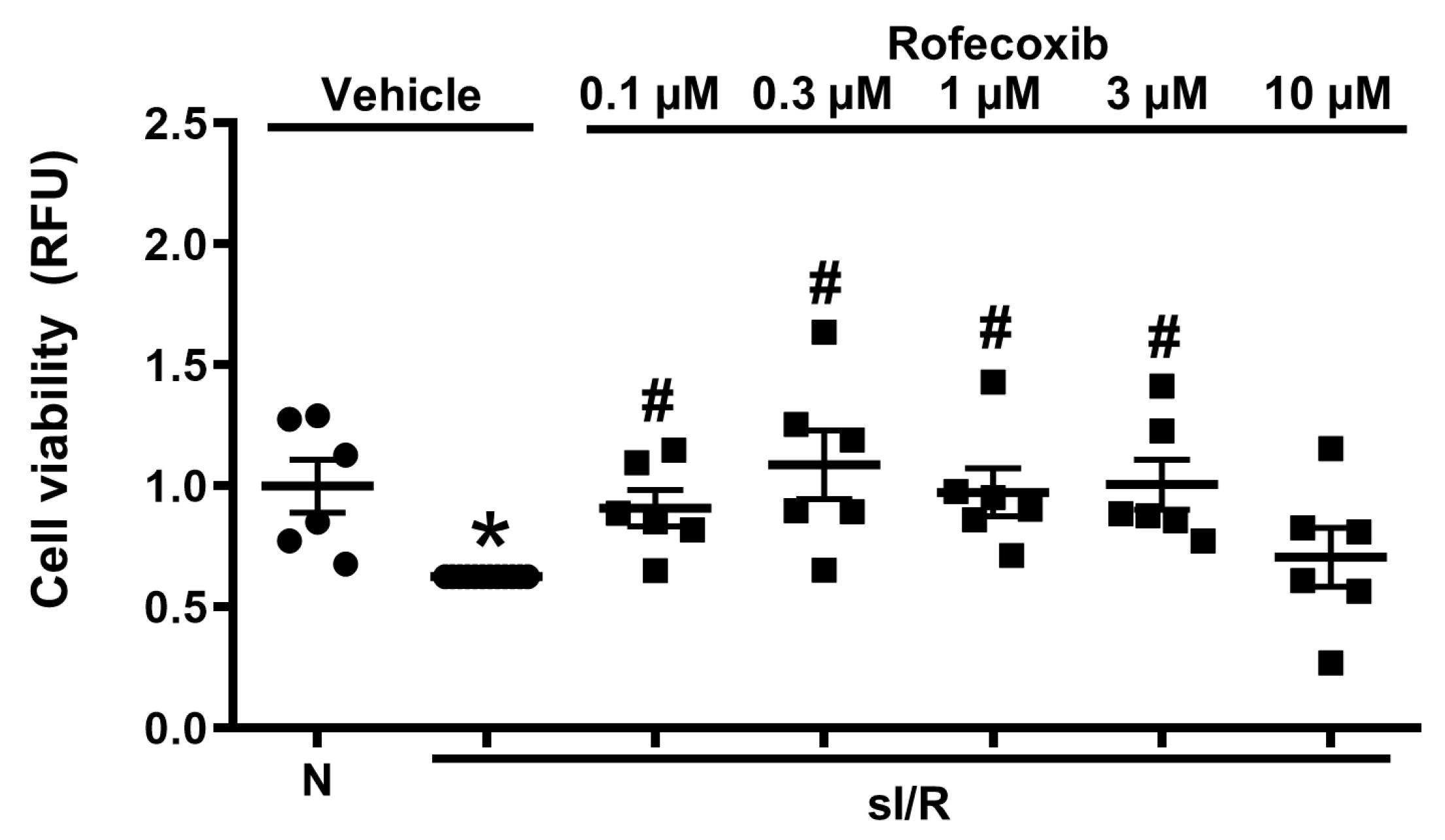
3.5. Rofecoxib Treatment Increased Viability of Isolated Adult Rat Cardiac Myocytes in Normoxia and in Simulated Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Madonna, R.; Cadeddu, C.; Deidda, M.; Mele, D.; Monte, I.; Novo, G.; Pagliaro, P.; Pepe, A.; Spallarossa, P.; Tocchetti, C.G.; et al. Improving the preclinical models for the study of chemotherapy-induced cardiotoxicity: A Position Paper of the Italian Working Group on Drug Cardiotoxicity and Cardioprotection. Heart Fail. Rev. 2015, 20, 621–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinandy, P.; Baczko, I.; Bencsik, P.; Giricz, Z.; Gorbe, A.; Pacher, P.; Varga, Z.V.; Varro, A.; Schulz, R. Definition of hidden drug cardiotoxicity: Paradigm change in cardiac safety testing and its clinical implications. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 1771–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, E.T.H.; Ewer, M.S.; Moslehi, J.; Dlugosz-Danecka, M.; Banchs, J.; Chang, H.M.; Minotti, G. Mechanisms and clinical course of cardiovascular toxicity of cancer treatment I. Oncology. Semin. Oncol. 2019, 46, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onakpoya, I.J.; Heneghan, C.J.; Aronson, J.K. Post-marketing withdrawal of 462 medicinal products because of adverse drug reactions: A systematic review of the world literature. BMC Med. 2016, 14, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pontes, H.; Clement, M.; Rollason, V. Safety signal detection: The relevance of literature review. Drug Saf. 2014, 37, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Conference on Harmonisation. Guidance on M3(R2) Nonclinical Safety Studies for the Conduct of Human Clinical Trials and Marketing Authorization for Pharmaceuticals; availability. Notice. Fed. Regist. 2010, 75, 3471–3472.
- Guideline on Repeated Dose Toxicity Corr—WC500079536.pdf. Available online: http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/Scientific_guideline/2010/03/WC500079536.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2019).
- International Conference on Harmonisation. Guidance on E14 Clinical Evaluation of QT/QTc Interval Prolongation and Proarrhythmic Potential for Non-Antiarrhythmic Drugs; availability. Notice. Fed. Regist. 2005, 70, 61134–61135.
- International Conference on Harmonisation. Guidance on S7B Nonclinical Evaluation of the Potential for Delayed Ventricular Repolarization (QT Interval Prolongation) by Human Pharmaceuticals; availability. Notice. Fed. Regist. 2005, 70, 61133–61134.
- Page, R.L.; O’Bryant, C.L.; Cheng, D.; Dow, T.J.; Ky, B.; Stein, C.M.; Spencer, A.P.; Trupp, R.J.; Lindenfeld, J. Drugs That May Cause or Exacerbate Heart Failure: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2016, 134, e32–e69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, T.F.; Liu, C.J.; Chen, S.J.; Wang, K.L.; Lin, Y.J.; Chang, S.L.; Lo, L.W.; Hu, Y.F.; Tuan, T.C.; Wu, T.J.; et al. The association between the use of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and atrial fibrillation: A nationwide case-control study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 312–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, C.W.; Jessup, M.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Drazner, M.H.; Fonarow, G.C.; Geraci, S.A.; Horwich, T.; Januzzi, J.L.; et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: Executive summary: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on practice guidelines. Circulation 2013, 128, 1810–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bombardier, C.; Laine, L.; Reicin, A.; Shapiro, D.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Davis, B.; Day, R.; Ferraz, M.B.; Hawkey, C.J.; Hochberg, M.C.; et al. Comparison of upper gastrointestinal toxicity of rofecoxib and naproxen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. VIGOR Study Group. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bresalier, R.S.; Sandler, R.S.; Quan, H.; Bolognese, J.A.; Oxenius, B.; Horgan, K.; Lines, C.; Riddell, R.; Morton, D.; Lanas, A.; et al. Cardiovascular events associated with rofecoxib in a colorectal adenoma chemoprevention trial. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1092–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ding, E.L.; Song, Y. Adverse effects of cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitors on renal and arrhythmia events: Meta-analysis of randomized trials. JAMA 2006, 296, 1619–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, G.; Rangasetty, U.C.; Uretsky, B.F.; Birnbaum, Y. The cycloxygenase 2 (COX-2) story: It’s time to explain, not inflame. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 12, 98–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juni, P.; Nartey, L.; Reichenbach, S.; Sterchi, R.; Dieppe, P.A.; Egger, M. Risk of cardiovascular events and rofecoxib: Cumulative meta-analysis. Lancet 2004, 364, 2021–2029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullard, A. FDA reconsiders cardiovascular outcomes trials for diabetes drugs, 10 years on. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2018, 17, 850–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reagan-Shaw, S.; Nihal, M.; Ahmad, N. Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2008, 22, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lada-Moldovan, L.; Kaloustian, S.; Bah, T.M.; Girard, S.A.; Dery, M.A.; Rousseau, G. Chronic pretreatment with celecoxib reduces infarct size. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 54, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, M.J.; Hancox, J.C.; Farkas, A.; Wainwright, C.L.; Stables, C.L.; Saint, D.A.; Clements-Jewery, H.; Lambiase, P.D.; Billman, G.E.; Janse, M.J.; et al. The Lambeth Conventions (II): Guidelines for the study of animal and human ventricular and supraventricular arrhythmias. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 139, 213–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curtis, M.J.; Walker, M.J. Quantification of arrhythmias using scoring systems: An examination of seven scores in an in vivo model of regional myocardial ischaemia. Cardiovasc. Res. 1988, 22, 656–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halpin, R.A.; Geer, L.A.; Zhang, K.E.; Marks, T.M.; Dean, D.C.; Jones, A.N.; Melillo, D.; Doss, G.; Vyas, K.P. The absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion of rofecoxib, a potent and selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in rats and dogs. Drug Metab. Dispos. Biol. Fate Chem. 2000, 28, 1244–1254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barlaka, E.; Gorbe, A.; Gaspar, R.; Paloczi, J.; Ferdinandy, P.; Lazou, A. Activation of PPARbeta/delta protects cardiac myocytes from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis by suppressing generation of reactive oxygen/nitrogen species and expression of matrix metalloproteinases. Pharmacol. Res. 2015, 95–96, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Heinzel, F.R.; Boengler, K.; Schulz, R.; Heusch, G. Role of connexin 43 in ischemic preconditioning does not involve intercellular communication through gap junctions. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2004, 36, 161–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bencsik, P.; Paloczi, J.; Kocsis, G.F.; Pipis, J.; Belecz, I.; Varga, Z.V.; Csonka, C.; Gorbe, A.; Csont, T.; Ferdinandy, P. Moderate inhibition of myocardial matrix metalloproteinase-2 by ilomastat is cardioprotective. Pharmacol. Res. 2014, 80, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gislason, G.H.; Jacobsen, S.; Rasmussen, J.N.; Rasmussen, S.; Buch, P.; Friberg, J.; Schramm, T.K.; Abildstrom, S.Z.; Kober, L.; Madsen, M.; et al. Risk of death or reinfarction associated with the use of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors and nonselective nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs after acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 2006, 113, 2906–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antzelevitch, C.; Fish, J. Electrical heterogeneity within the ventricular wall. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2001, 96, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janse, M.J.; Wit, A.L. Electrophysiological mechanisms of ventricular arrhythmias resulting from myocardial ischemia and infarction. Physiol. Rev. 1989, 69, 1049–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleber, A.G.; Janse, M.J.; Wilms-Schopmann, F.J.; Wilde, A.A.; Coronel, R. Changes in conduction velocity during acute ischemia in ventricular myocardium of the isolated porcine heart. Circulation 1986, 73, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferdinandy, P.; Hausenloy, D.J.; Heusch, G.; Baxter, G.F.; Schulz, R. Interaction of risk factors, comorbidities, and comedications with ischemia/reperfusion injury and cardioprotection by preconditioning, postconditioning, and remote conditioning. Pharmacol. Rev. 2014, 66, 1142–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarapa, N.; Britto, M.R.; Cotton, B.; Cox, S.R.; Francom, S.F.; Jin, N.; Polasek, E.D.; Sainati, S.M.; Crosby-Sessoms, S.L.; Fleishaker, J.C. Valdecoxib, a COX-2-specific inhibitor, does not affect cardiac repolarization. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2003, 43, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussmeier, N.A.; Whelton, A.A.; Brown, M.T.; Joshi, G.P.; Langford, R.M.; Singla, N.K.; Boye, M.E.; Verburg, K.M. Safety and efficacy of the cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors parecoxib and valdecoxib after noncardiac surgery. Anesthesiology 2006, 104, 518–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nussmeier, N.A.; Whelton, A.A.; Brown, M.T.; Langford, R.M.; Hoeft, A.; Parlow, J.L.; Boyce, S.W.; Verburg, K.M. Complications of the COX-2 inhibitors parecoxib and valdecoxib after cardiac surgery. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timmers, L.; Sluijter, J.P.; Verlaan, C.W.; Steendijk, P.; Cramer, M.J.; Emons, M.; Strijder, C.; Grundeman, P.F.; Sze, S.K.; Hua, L.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition increases mortality, enhances left ventricular remodeling, and impairs systolic function after myocardial infarction in the pig. Circulation 2007, 115, 326–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, T.; Rodger, I.W.; Shennib, H.; Hu, F.; Tayara, L.; Giaid, A. Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in acute myocardial infarction: Cellular expression and use of selective COX-2 inhibitor. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2003, 81, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuren, N.; Jacobs, M.; Ertl, G.; Schorb, W. Cyclooxygenase-2 in myocardium stimulation by angiotensin-II in cultured cardiac fibroblasts and role at acute myocardial infarction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2002, 34, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salloum, F.N.; Hoke, N.N.; Seropian, I.M.; Varma, A.; Ownby, E.D.; Houser, J.E.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Abbate, A. Parecoxib inhibits apoptosis in acute myocardial infarction due to permanent coronary ligation but not due to ischemia-reperfusion. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2009, 53, 495–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaPointe, M.C.; Mendez, M.; Leung, A.; Tao, Z.; Yang, X.P. Inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 improves cardiac function after myocardial infarction in the mouse. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2004, 286, H1416–H1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnieto, A., Jr.; Dourado, P.M.; Luz, P.L.; Chagas, A.C. Selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibition protects against myocardial damage in experimental acute ischemia. Clinics 2009, 64, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inserte, J.; Molla, B.; Aguilar, R.; Traves, P.G.; Barba, I.; Martin-Sanz, P.; Bosca, L.; Casado, M.; Garcia-Dorado, D. Constitutive COX-2 activity in cardiomyocytes confers permanent cardioprotection Constitutive COX-2 expression and cardioprotection. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2009, 46, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Nong, Y.; Tukaye, D.N.; Rokosh, G.; Du, J.; Zhu, X.; Book, M.; Tomlin, A.; Li, Q.; Bolli, R. Inducible cardiac-specific overexpression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) confers resistance to ischemia/reperfusion injury. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2019, 114, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, L.; Cai, Y.; Tang, E.H.; Yan, D.; Kosuru, R.; Li, H.; Irwin, M.G.; Ma, H.; Xia, Z. Cox-2 Inhibition Protects against Hypoxia/Reoxygenation-Induced Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis via Akt-Dependent Enhancement of iNOS Expression. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivarajah, A.; McDonald, M.C.; Thiemermann, C. The cardioprotective effects of preconditioning with endotoxin, but not ischemia, are abolished by a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma antagonist. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2005, 313, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinmura, K.; Tang, X.L.; Wang, Y.; Xuan, Y.T.; Liu, S.Q.; Takano, H.; Bhatnagar, A.; Bolli, R. Cyclooxygenase-2 mediates the cardioprotective effects of the late phase of ischemic preconditioning in conscious rabbits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 10197–10202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolli, R.; Shinmura, K.; Tang, X.L.; Kodani, E.; Xuan, Y.T.; Guo, Y.; Dawn, B. Discovery of a new function of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2: COX-2 is a cardioprotective protein that alleviates ischemia/reperfusion injury and mediates the late phase of preconditioning. Cardiovasc. Res. 2002, 55, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, H.; Bolli, R.; Rokosh, G.D.; Bi, Q.; Dai, S.; Shirk, G.; Tang, X.L. The cardioprotection of the late phase of ischemic preconditioning is enhanced by postconditioning via a COX-2-mediated mechanism in conscious rats. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 293, H2557–H2564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maulik, A.; Davidson, S.M.; Piotrowska, I.; Walker, M.; Yellon, D.M. Ischaemic Preconditioning Protects Cardiomyocytes from Anthracycline-Induced Toxicity via the PI3K Pathway. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2018, 32, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, R.; Maulik, A.; Hamarneh, A.; Hochhauser, D.; Hausenloy, D.J.; Walker, J.M.; Yellon, D.M. Effect of Remote Ischaemic Conditioning in Oncology Patients Undergoing Chemotherapy: Rationale and Design of the ERIC-ONC Study—A Single-Center, Blinded, Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Cardiol. 2016, 39, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brenner, G.B.; Makkos, A.; Nagy, C.T.; Onódi, Z.; Sayour, N.V.; Gergely, T.G.; Kiss, B.; Görbe, A.; Sághy, É.; Zádori, Z.S.; et al. Hidden Cardiotoxicity of Rofecoxib Can be Revealed in Experimental Models of Ischemia/Reperfusion. Cells 2020, 9, 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030551
Brenner GB, Makkos A, Nagy CT, Onódi Z, Sayour NV, Gergely TG, Kiss B, Görbe A, Sághy É, Zádori ZS, et al. Hidden Cardiotoxicity of Rofecoxib Can be Revealed in Experimental Models of Ischemia/Reperfusion. Cells. 2020; 9(3):551. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030551
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrenner, Gábor B., András Makkos, Csilla Terézia Nagy, Zsófia Onódi, Nabil V. Sayour, Tamás G. Gergely, Bernadett Kiss, Anikó Görbe, Éva Sághy, Zoltán S. Zádori, and et al. 2020. "Hidden Cardiotoxicity of Rofecoxib Can be Revealed in Experimental Models of Ischemia/Reperfusion" Cells 9, no. 3: 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030551
APA StyleBrenner, G. B., Makkos, A., Nagy, C. T., Onódi, Z., Sayour, N. V., Gergely, T. G., Kiss, B., Görbe, A., Sághy, É., Zádori, Z. S., Lázár, B., Baranyai, T., Varga, R. S., Husti, Z., Varró, A., Tóthfalusi, L., Schulz, R., Baczkó, I., Giricz, Z., & Ferdinandy, P. (2020). Hidden Cardiotoxicity of Rofecoxib Can be Revealed in Experimental Models of Ischemia/Reperfusion. Cells, 9(3), 551. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030551





