Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Regulate Endothelial Cell Migration Under PDGF Stimulation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Exosome Isolation
2.3. Quantitative Reverse Transcriptase-PCR (qRT-PCR)
2.4. MiRNA mimics and anti-miRNA oligonucleotides
2.5. Immunoblotting
2.6. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.7. In Vitro Scratch Wound Assay
2.8. Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS)-Based Small RNA Sequencing
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
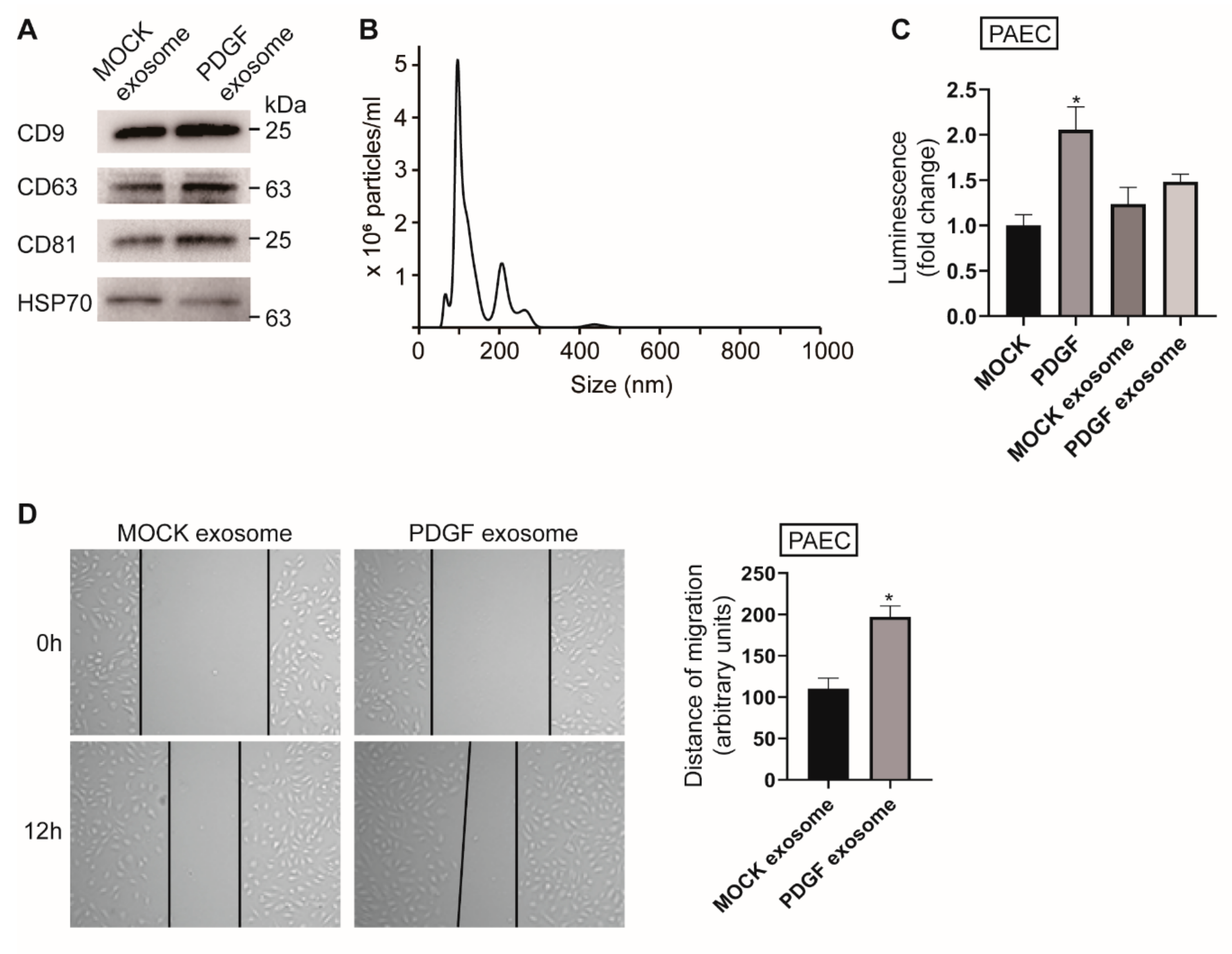
3.1. PASMC-Derived Exosomes Affect PAEC Migration under PDGF Stimulation
3.2. Exosomal miRNA Profile is Regulated by PDGF Signaling
3.3. PASMC-Derived Exosomes Affect Cellular Levels of miRNA in PAECs
3.4. Downregulation of miR-1246, miR-182, and miR-486 Elicits a Pro-Migratory Effect in Vascular Cells
3.5. Exosome-Derived miR-1246, miR-182, and miR-486 Counteract the Effect of Exosomes from PDGF-Stimulated PASMCs on PAEC Migration
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Marmur, J.D.; Poon, M.; Rossikhina, M.; Taubman, M.B. Induction of PDGF-responsive genes in vascular smooth muscle. Implications for the early response to vessel injury. Circulation 1992, 86, III53–III60. [Google Scholar]
- Barst, R.J. PDGF signaling in pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2691–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schermuly, R.T.; Dony, E.; Ghofrani, H.A.; Pullamsetti, S.; Savai, R.; Roth, M.; Sydykov, A.; Lai, Y.J.; Weissmann, N.; Seeger, W.; et al. Reversal of experimental pulmonary hypertension by PDGF inhibition. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 115, 2811–2821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.; El Andaloussi, S.; Wood, M.J. Exosomes and microvesicles: Extracellular vesicles for genetic information transfer and gene therapy. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, R125–R134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Johnstone, R.M.; Adam, M.; Hammond, J.R.; Orr, L.; Turbide, C. Vesicle formation during reticulocyte maturation. Association of plasma membrane activities with released vesicles (exosomes). J. Biol. Chem. 1987, 262, 9412–9420. [Google Scholar]
- Valadi, H.; Ekstrom, K.; Bossios, A.; Sjostrand, M.; Lee, J.J.; Lotvall, J.O. Exosome-mediated transfer of mRNAs and microRNAs is a novel mechanism of genetic exchange between cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Raposo, G.; Stoorvogel, W. Extracellular vesicles: Exosomes, microvesicles, and friends. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 200, 373–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- de Jong, O.G.; Verhaar, M.C.; Chen, Y.; Vader, P.; Gremmels, H.; Posthuma, G.; Schiffelers, R.M.; Gucek, M.; van Balkom, B.W. Cellular stress conditions are reflected in the protein and RNA content of endothelial cell-derived exosomes. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2012, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hergenreider, E.; Heydt, S.; Treguer, K.; Boettger, T.; Horrevoets, A.J.; Zeiher, A.M.; Scheffer, M.P.; Frangakis, A.S.; Yin, X.; Mayr, M.; et al. Atheroprotective communication between endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells through miRNAs. Nat. Cell Biol. 2012, 14, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loyer, X.; Vion, A.C.; Tedgui, A.; Boulanger, C.M. Microvesicles as cell-cell messengers in cardiovascular diseases. Circ. Res. 2014, 114, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jansen, F.; Nickenig, G.; Werner, N. Extracellular Vesicles in Cardiovascular Disease: Potential Applications in Diagnosis, Prognosis, and Epidemiology. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 1649–1657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, S.A.; Xie, Y.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.A.; Xiang, M. Emerging role of exosome-mediated intercellular communication in vascular remodeling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 25700–25712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aliotta, J.M.; Pereira, M.; Wen, S.; Dooner, M.S.; Del Tatto, M.; Papa, E.; Goldberg, L.R.; Baird, G.L.; Ventetuolo, C.E.; Quesenberry, P.J.; et al. Exosomes induce and reverse monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in mice. Cardiovasc. Res. 2016, 110, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhao, L.; Luo, H.; Li, X.; Li, T.; He, J.; Qi, Q.; Liu, Y.; Yu, Z. Exosomes Derived from Human Pulmonary Artery Endothelial Cells Shift the Balance between Proliferation and Apoptosis of Smooth Muscle Cells. Cardiology 2017, 137, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Blanco, F.J.; Stevens, H.; Lu, R.; Caudrillier, A.; McBride, M.; McClure, J.D.; Grant, J.; Thomas, M.; Frid, M.; et al. MicroRNA-143 Activation Regulates Smooth Muscle and Endothelial Cell Crosstalk in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 870–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuwabara, Y.; Ono, K.; Horie, T.; Nishi, H.; Nagao, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Watanabe, S.; Baba, O.; Kojima, Y.; Shizuta, S.; et al. Increased microRNA-1 and microRNA-133a levels in serum of patients with cardiovascular disease indicate myocardial damage. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2011, 4, 446–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figueroa, J.; Phillips, L.M.; Shahar, T.; Hossain, A.; Gumin, J.; Kim, H.; Bean, A.J.; Calin, G.A.; Fueyo, J.; Walters, E.T.; et al. Exosomes from Glioma-Associated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Increase the Tumorigenicity of Glioma Stem-like Cells via Transfer of miR-1587. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5808–5819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kapustin, A.N.; Chatrou, M.L.; Drozdov, I.; Zheng, Y.; Davidson, S.M.; Soong, D.; Furmanik, M.; Sanchis, P.; De Rosales, R.T.; Alvarez-Hernandez, D.; et al. Vascular smooth muscle cell calcification is mediated by regulated exosome secretion. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 1312–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tan, M.; Yan, H.B.; Li, J.N.; Li, W.K.; Fu, Y.Y.; Chen, W.; Zhou, Z. Thrombin Stimulated Platelet-Derived Exosomes Inhibit Platelet-Derived Growth Factor Receptor-Beta Expression in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2016, 38, 2348–2365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzau, V.J.; Braun-Dullaeus, R.C.; Sedding, D.G. Vascular proliferation and atherosclerosis: New perspectives and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1249–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kishore, R.; Garikipati, V.N.; Gumpert, A. Tiny Shuttles for Information Transfer: Exosomes in Cardiac Health and Disease. J. Cardiovasc. Transl. Res. 2016, 9, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kapustin, A.N.; Davies, J.D.; Reynolds, J.L.; McNair, R.; Jones, G.T.; Sidibe, A.; Schurgers, L.J.; Skepper, J.N.; Proudfoot, D.; Mayr, M.; et al. Calcium regulates key components of vascular smooth muscle cell-derived matrix vesicles to enhance mineralization. Circ. Res. 2011, 109, e1–e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhagirath, D.; Yang, T.L.; Bucay, N.; Sekhon, K.; Majid, S.; Shahryari, V.; Dahiya, R.; Tanaka, Y.; Saini, S. microRNA-1246 Is an Exosomal Biomarker for Aggressive Prostate Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 1833–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, Z.; Meng, C.; Wang, S.; Zhou, N.; Guan, M.; Bai, C.; Lu, S.; Han, Q.; Zhao, R.C. MicroRNA-1246 enhances migration and invasion through CADM1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Zeng, Y.; Zhou, J.M.; Nie, S.L.; Peng, Q.; Gong, J.; Huo, J.R. MicroRNA-1246 promotes growth and metastasis of colorectal cancer cells involving CCNG2 reduction. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Cao, L.; Zhang, Y.; Lian, H.; Sun, Z.; Cui, Y. MicroRNA-1246 inhibits cell invasion and epithelial mesenchymal transition process by targeting CXCR4 in lung cancer cells. Cancer Biomark. Sect. A Dis. Markers 2018, 21, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.Q.; You, A.B.; Zhu, X.D.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Zhang, S.Z.; Zhang, K.W.; Cai, H.; Shi, W.K.; Li, X.L.; et al. miR-182-5p promotes hepatocellular carcinoma progression by repressing FOXO3a. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 11, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, N.; Nan, C.C.; Zhong, X.Y.; Weng, J.Q.; Fan, H.D.; Sun, H.P.; Tang, S.; Shi, L.; Huang, S.X. miR-182-5p Promotes Growth in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Inhibiting CAMK2N1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 49, 1329–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Chen, S.; Shan, Z.; Bi, L.; Yu, S.; Li, Y.; Xu, S. miR-182-5p improves the viability, mitosis, migration, and invasion ability of human gastric cancer cells by down-regulating RAB27A. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sarver, A.E.; Sarver, A.L.; Thayanithy, V.; Subramanian, S. Identification, by systematic RNA sequencing, of novel candidate biomarkers and therapeutic targets in human soft tissue tumors. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2015, 95, 1077–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Hu, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhu, Y.; Liang, Z.; Wang, X.; Lin, Y.; Mao, Y.; et al. Downregulation of microRNA-182-5p contributes to renal cell carcinoma proliferation via activating the AKT/FOXO3a signaling pathway. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, C.; Zheng, X.; Li, W.; Bai, F.; Lyu, J.; Meng, Q.H. Serum miR-486-5p as a diagnostic marker in cervical cancer: With investigation of potential mechanisms. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.; Ji, C.; Guo, S.; Su, X.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, S.; Liu, G.; Qiu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, H.; et al. The miR-486-5p plays a causative role in prostate cancer through negative regulation of multiple tumor suppressor pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 72835–72846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.P.; Hou, J.; Shen, X.Y.; Huang, C.Y.; Zhang, X.H.; Xie, Y.A.; Luo, X.L. MicroRNA-486-5p, which is downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma, suppresses tumor growth by targeting PIK3R1. FEBS J. 2015, 282, 579–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, C.; Li, M.; Hu, Y.; Shi, N.; Yu, H.; Liu, H.; Lian, H. miR-486-5p attenuates tumor growth and lymphangiogenesis by targeting neuropilin-2 in colorectal carcinoma. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 2865–2871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Shen, Y.Q.; Li, Y.L.; Liang, C.; Zhang, B.J.; Lu, S.D.; He, Y.Y.; Wang, P.; Sun, Q.L.; Jin, Y.X.; et al. Direct repression of the oncogene CDK4 by the tumor suppressor miR-486-5p in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 34011–34021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, S.; Geng, S.; Hu, Y. miR-486-5p inhibits cell proliferation and invasion through repressing GAB2 in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 3525–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, Z.; Cui, G.; Wang, X.; Yang, Z. MicroRNA-486-5p targeting PIM-1 suppresses cell proliferation in breast cancer cells. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 11137–11145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, T.; Yang, K.; Zhang, M.; Wang, K. miR-486-5p suppresses prostate cancer metastasis by targeting Snail and regulating epithelial-mesenchymal transition. OncoTargets Ther. 2016, 9, 6909–6914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Qin, H. miR-486-5p regulates the migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells through targeting PIK3R1. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 7243–7248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stoorvogel, W. Resolving sorting mechanisms into exosomes. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 531–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Li, S.; Li, L.; Li, M.; Guo, C.; Yao, J.; Mi, S. Exosome and exosomal microRNA: Trafficking, sorting, and function. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2015, 13, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gray, W.D.; French, K.M.; Ghosh-Choudhary, S.; Maxwell, J.T.; Brown, M.E.; Platt, M.O.; Searles, C.D.; Davis, M.E. Identification of therapeutic covariant microRNA clusters in hypoxia-treated cardiac progenitor cell exosomes using systems biology. Circ. Res. 2015, 116, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]





| Downregulated miRNA | Fold Change (PDGF Exosome/MOCK Exosome) | Upregulated miRNA | Fold Change (PDGF Exosome/MOCK Exosome) |
|---|---|---|---|
| miR-1246 | −13.33 | miR-409 | 9.24 |
| miR-195-3p | −4.35 | miR-576-3p | 4.77 |
| miR-4682 | −3.91 | miR-874 | 4.42 |
| miR-320d | −3.86 | miR-92a-1 | 4.03 |
| miR-4645-3p | −3.80 | miR-4741 | 3.91 |
| miR-6511a | −3.73 | miR-561-3p | 3.91 |
| miR-6511b | −3.64 | miR-1273d | 3.73 |
| miR-1290 | −3.52 | miR-340-3p | 3.52 |
| miR-5189 | −3.52 | miR-412 | 3.41 |
| miR-103a-2 | −3.43 | miR-193b | 3.35 |
| miR-320c | −3.40 | miR-5100 | 3.29 |
| miR-3613 | −3.37 | miR-26a-2-3p | 3.26 |
| miR-3074 | −3.13 | miR-147b | 3.13 |
| miR-3653-3p | −3.13 | let-7g-3p | 3.09 |
| miR-1270 | −3.10 | miR-190a | 3.00 |
| miR-1249-3p | −3.09 | miR-33b-3p | 2.92 |
| miR-375 | −3.09 | miR-1271-3p | 2.81 |
| miR-4775 | −2.98 | miR-4638-3p | 2.81 |
| miR-5010-3p | −2.81 | miR-188 | 2.80 |
| miR-3913 | −2.79 | miR-2277-3p | 2.75 |
| miR-939 | −2.74 | miR-1260b | 2.60 |
| miR-548h | −2.69 | miR-3173 | 2.56 |
| miR-182 | −2.68 | miR-3911 | 2.56 |
| miR-486 | −2.56 | miR-6500-3p | 2.56 |
| miR-302b-3p | −2.56 | miR-30b-3p | 2.53 |
| miR-3605-3p | −2.56 | miR-5000-3p | 2.50 |
| miR-3619-3p | −2.56 | miR-4485-3p | 2.47 |
| miR-580-3p | −2.56 | miR-1271 | 2.46 |
| miR-579 | −2.53 | miR-501-3p | 2.39 |
| miR-4466 | −2.44 | miR-1260a | 2.30 |
| miR-4449 | −2.44 | miR-1972 | 2.27 |
| miR-6723 | −2.43 | let-7c-3p | 2.25 |
| miR-1228 | −2.40 | miR-29b-2 | 2.25 |
| miR-668-3p | −2.31 | miR-627-3p | 2.25 |
| miR-362-3p | −2.27 | miR-193a-3p | 2.25 |
| miR-664a-3p | −2.26 | miR-1224 | 2.25 |
| miR-643 | −2.25 | miR-1306-3p | 2.20 |
| miR-664b-3p | −2.25 | miR-4745 | 2.20 |
| miR-485-3p | −2.15 | miR-4787 | 2.20 |
| miR-1273f | −2.06 | miR-487a | 2.20 |
| miR-374a-3p | −2.06 | miR-769-3p | 2.19 |
| miR-656 | 2.17 | ||
| miR-6886 | 2.17 | ||
| miR-138 | 2.13 | ||
| miR-214 | 2.10 | ||
| let-7f-1-3p | 2.10 | ||
| miR-221 | 2.09 | ||
| miR-100 | 2.08 | ||
| miR-1908-3p | 2.06 | ||
| miR-337 | 2.05 | ||
| miR-99b | 2.03 | ||
| miR-4792 | 2.03 | ||
| miR-1287 | 2.01 | ||
| miR-4767 | 2.00 | ||
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heo, J.; Yang, H.C.; Rhee, W.J.; Kang, H. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Regulate Endothelial Cell Migration Under PDGF Stimulation. Cells 2020, 9, 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030639
Heo J, Yang HC, Rhee WJ, Kang H. Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Regulate Endothelial Cell Migration Under PDGF Stimulation. Cells. 2020; 9(3):639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030639
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeo, Jeongyeon, Hee Cheol Yang, Won Jong Rhee, and Hara Kang. 2020. "Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Regulate Endothelial Cell Migration Under PDGF Stimulation" Cells 9, no. 3: 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030639
APA StyleHeo, J., Yang, H. C., Rhee, W. J., & Kang, H. (2020). Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell-Derived Exosomal MicroRNAs Regulate Endothelial Cell Migration Under PDGF Stimulation. Cells, 9(3), 639. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030639






