Diversity of RNA-Binding Proteins Modulating Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Protein Expression in the Maturing Mammalian Oocyte
Abstract
:1. Introduction
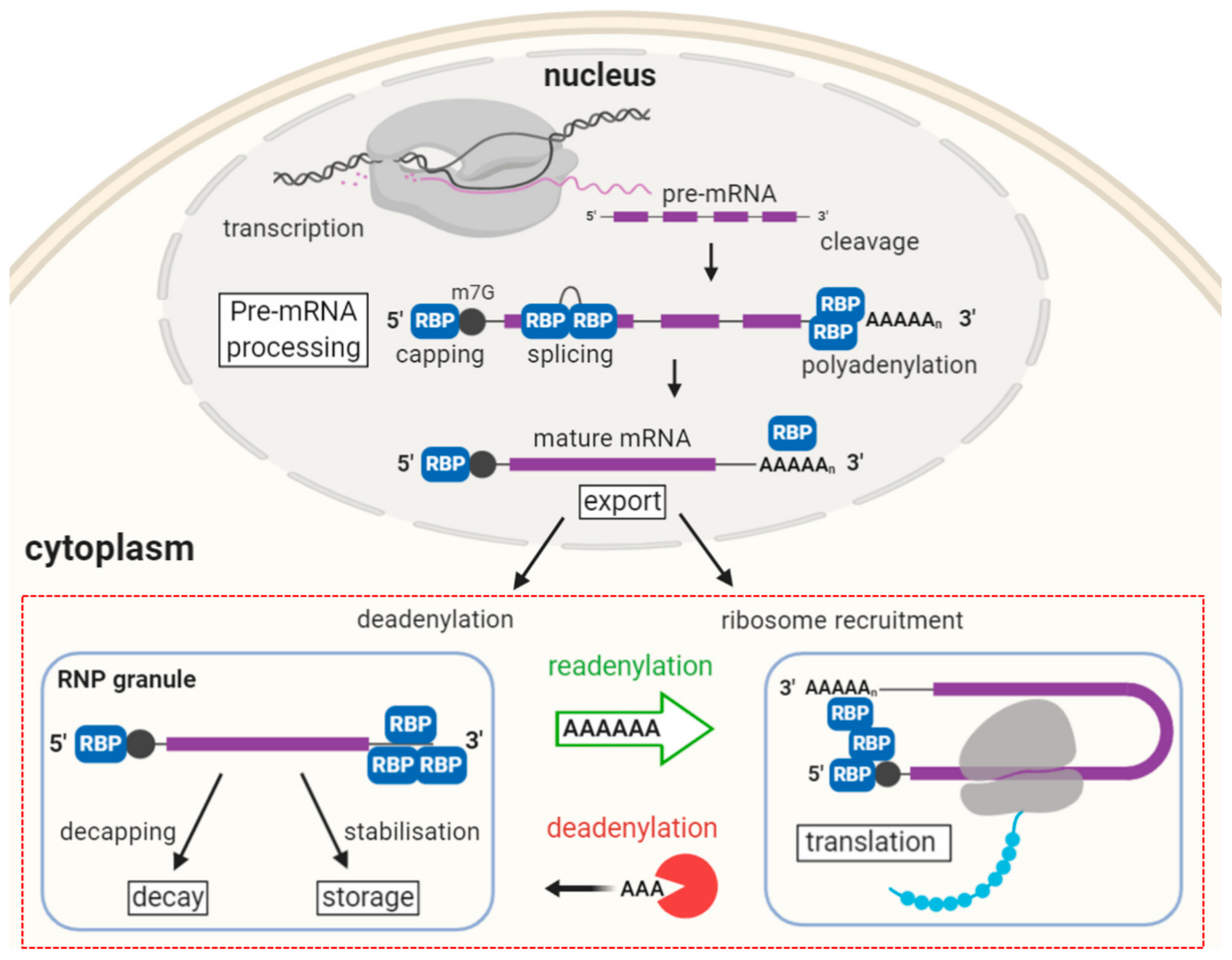
2. The Journey of a Messenger RNA Guided by Bound Proteins
2.1. Pre-mRNA Synthesis and Processing
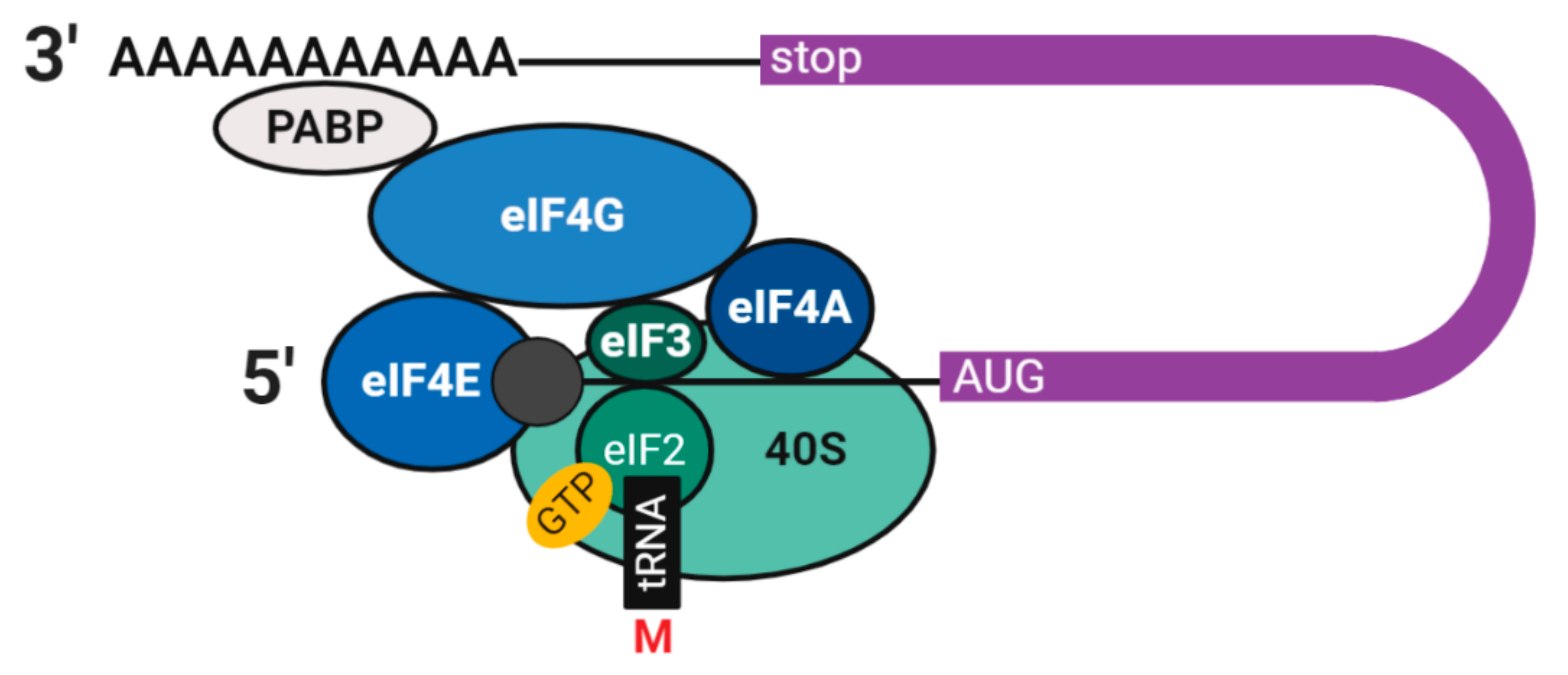
2.2. Translation and Decay
2.3. Somatic RNP Granules
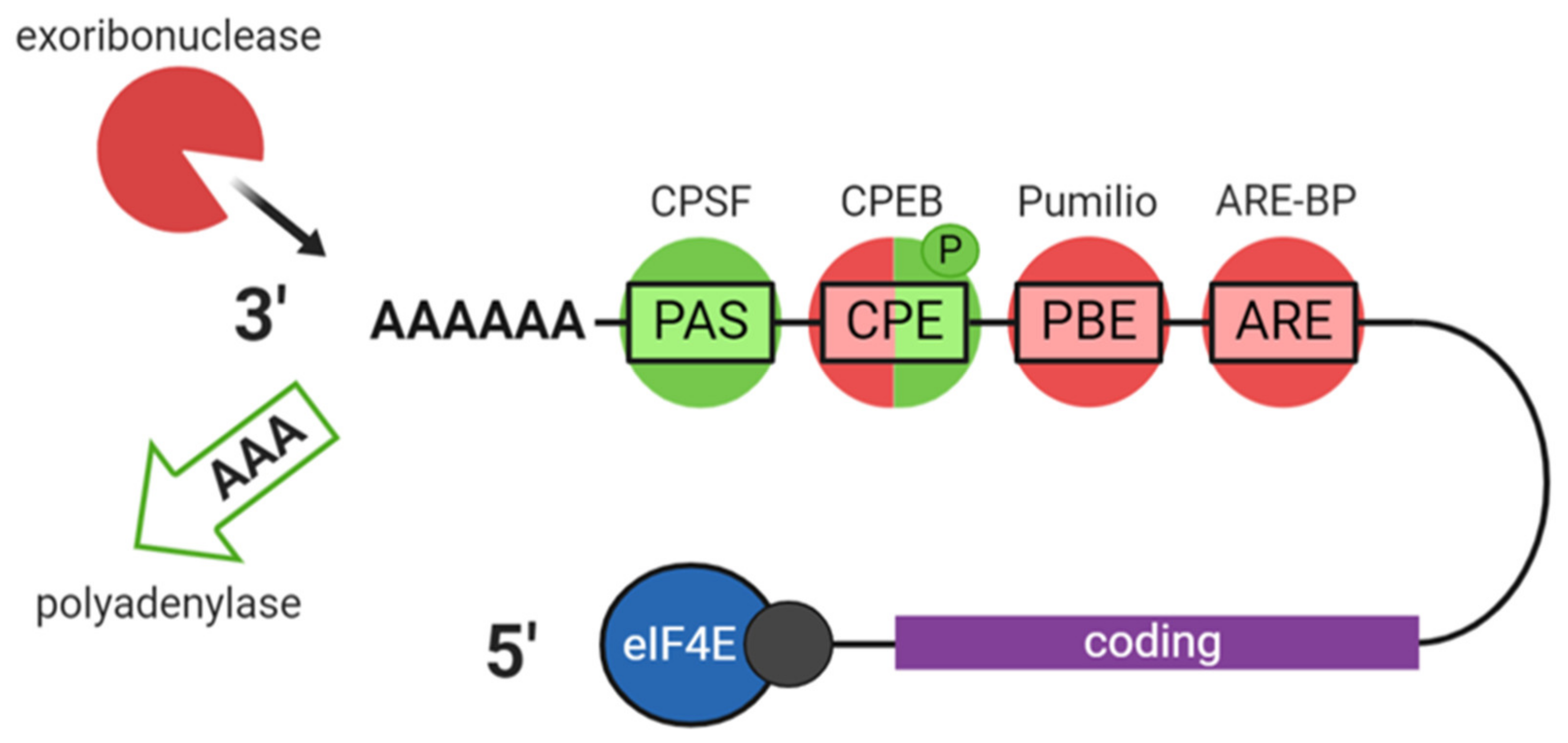
3. Oocyte RBPs and Post-Transcriptional Regulation
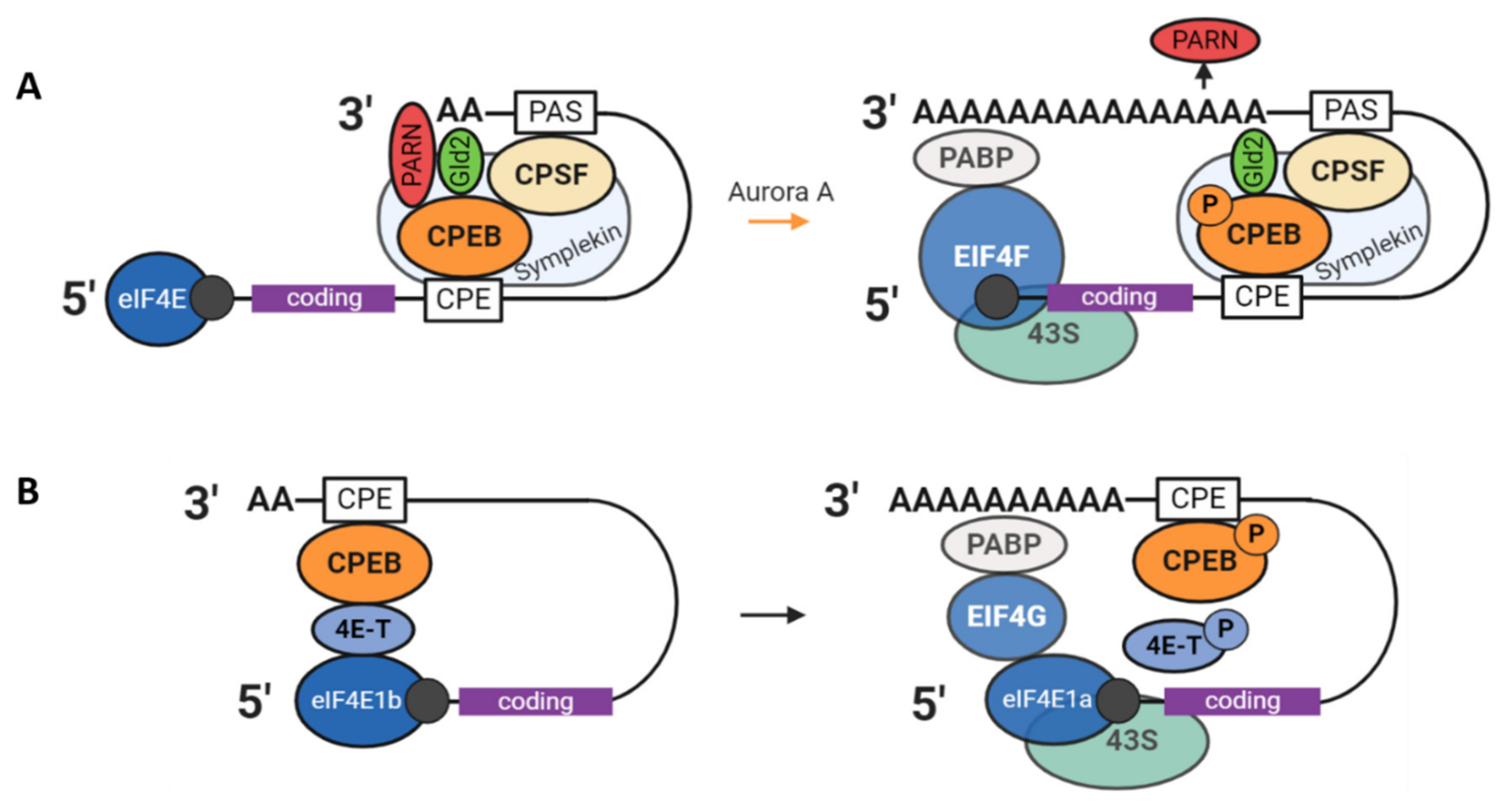
3.1. The CPEB1 Mechanism
3.2. PUM2-DAZL-EPABP
3.3. PATL2
3.4. MSY2/FRGY2
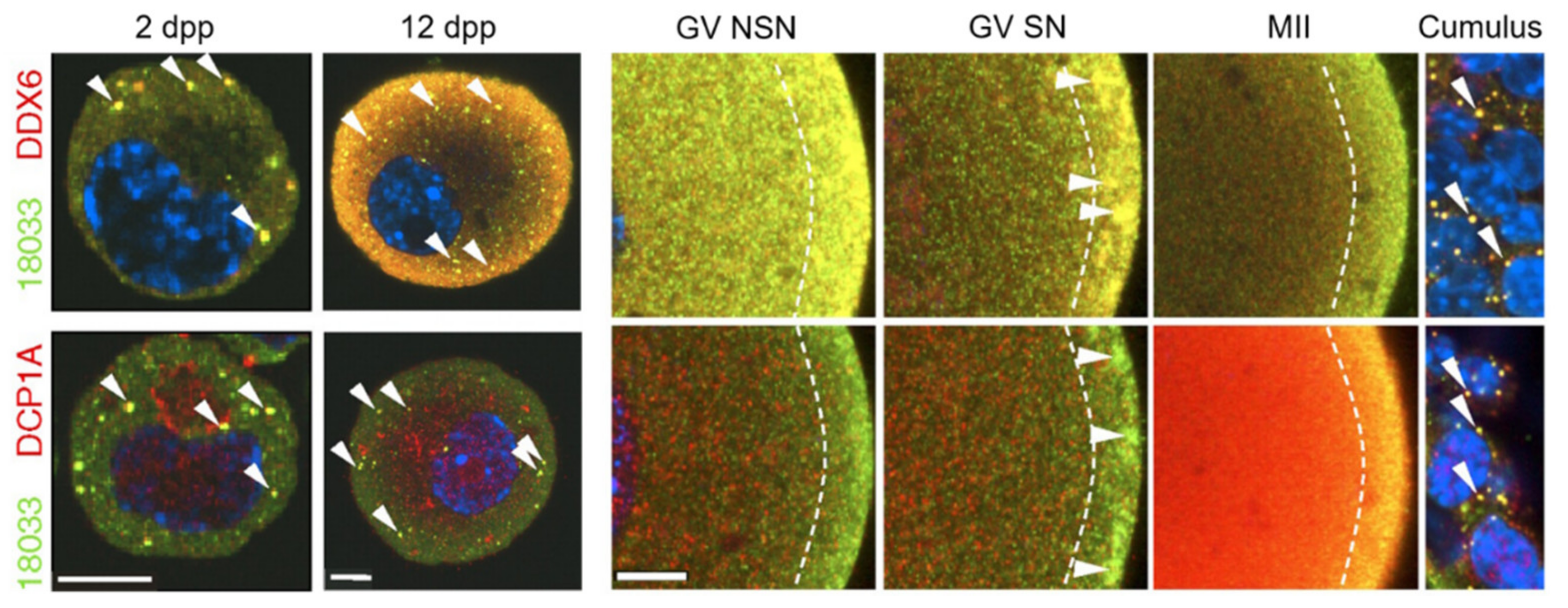
3.5. DDX6 (Rck/p54)
3.6. Musashi (MSI)
3.7. RAP55B/LSM14B
3.8. Somatic Cell-Mediated Translational Regulation
3.9. Small Non-Coding RNAs
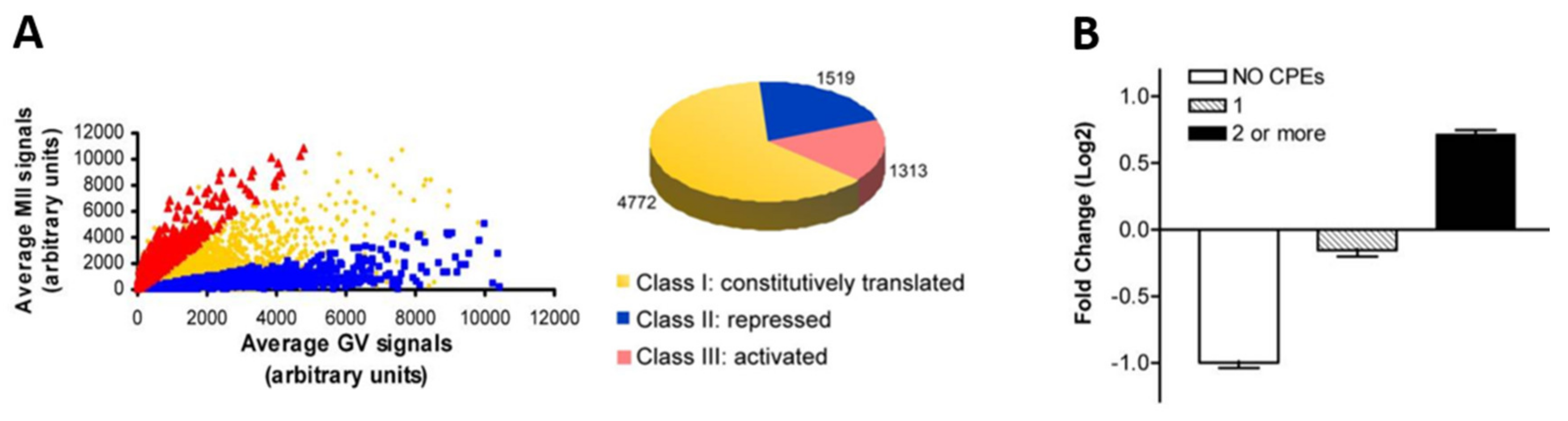
4. Waves of Translation and Degradation
4.1. Translational Activation after GVBD
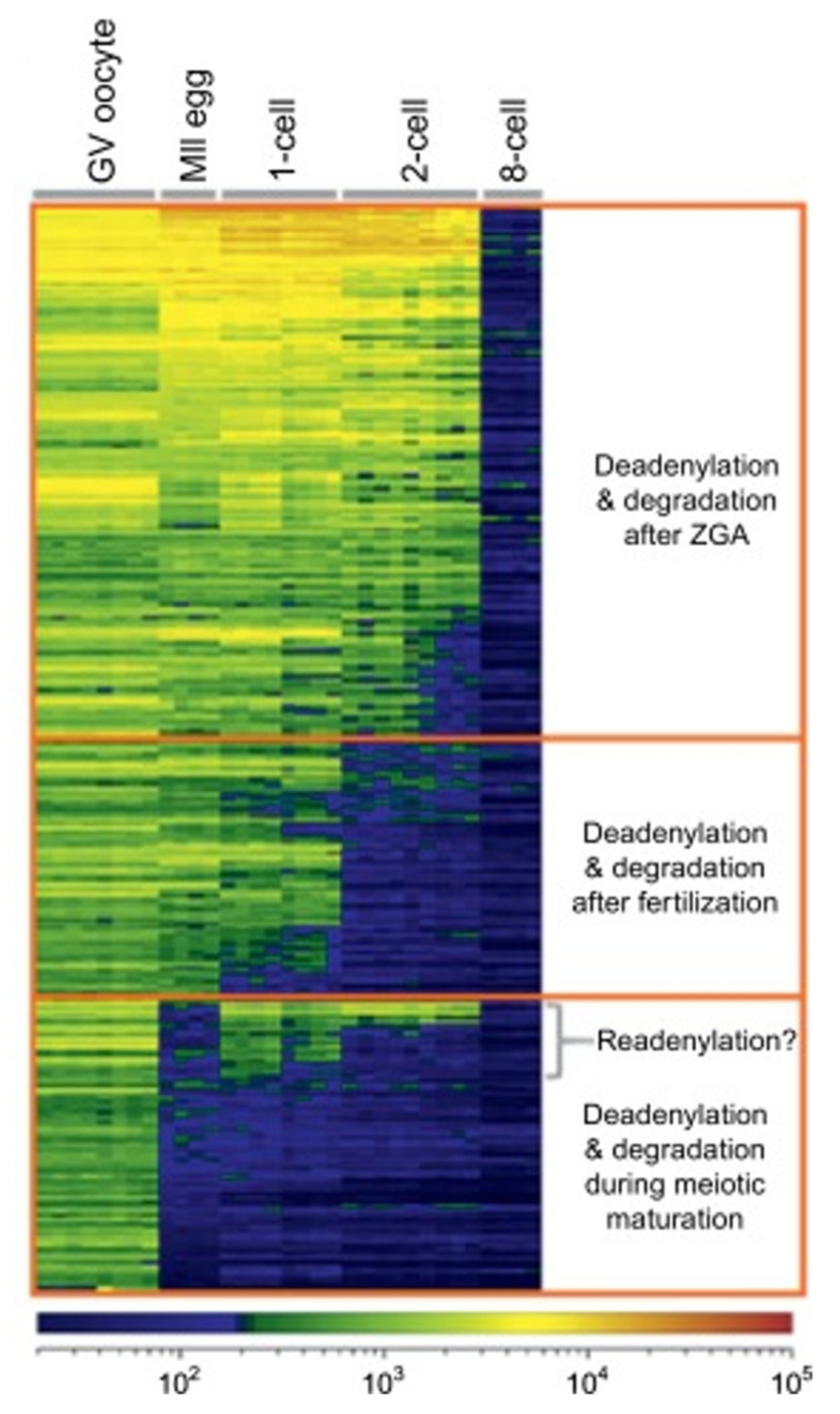
4.2. Degradation of Maternal Elements
5. RBPs and Human Infertility
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alberts, B.; Johnson, A.; Lewis, J.; Raff, M.; Roberts, K.; Walter, P. Molecular Biology of the Cell, 4th ed.; Garland Science: New York, NY, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Russell, J.E. Structural and functional analysis of an mRNP complex that mediates the high stability of human beta-globin mRNA. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 5879–5888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwanhäusser, B.; Busse, D.; Li, N.; Dittmar, G.; Schuchhardt, J.; Wolf, J.; Chen, W.; Selbach, M. Global quantification of mammalian gene expression control. Nature 2011, 473, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carpenter, S.; Ricci, E.P.; Mercier, B.C.; Moore, M.J.; Fitzgerald, K.A. Post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 361–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svoboda, P.; Franke, V.; Schultz, R.M. Sculpting the Transcriptome During the Oocyte-to-Embryo Transition in Mouse. Curr. Top. Dev. Biol. 2015, 113, 305–349. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Medvedev, S.; Pan, H.; Schultz, R.M. Absence of MSY2 in mouse oocytes perturbs oocyte growth and maturation, RNA stability, and the transcriptome. Biol. Reprod. 2011, 85, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luong, X.G.; Conti, M. RNA Binding Protein Networks and Translational Regulation in Oocytes. In Human Reproductive and Prenatal Genetics; Academic Press/Elsevier: London, UK; San Diego, CA, USA; Cambridge, MA, USA; Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 193–220. [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski, S. Transcription initiation unwrapped. Nature 2012, 483, 286–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richard, P.; Manley, J.L. Transcription termination by nuclear RNA polymerases. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 1247–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katahira, J. Nuclear export of messenger RNA. Genes 2015, 6, 163–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maquat, L.E.; Tarn, W.-Y.; Isken, O. The pioneer round of translation: Features and functions. Cell 2010, 142, 368–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- López-Lastra, M.; Rivas, A.; Barría, M.I. Protein synthesis in eukaryotes: The growing biological relevance of cap-independent translation initiation. Biol. Res. 2005, 38, 121–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gebauer, F.; Hentze, M.W. Molecular mechanisms of translational control. Nat. Rev. 2004, 5, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiederhold, K.; Passmore, L.A. Cytoplasmic deadenylation: Regulation of mRNA fate. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2010, 38, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tharun, S.; He, W.; Mayes, A.E.; Lennertz, P.; Beggs, J.D.; Parker, R. Yeast Sm-like proteins function in mRNA decapping and decay. Nature 2000, 404, 515–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garneau, N.L.; Wilusz, J.; Wilusz, C.J. The highways and byways of mRNA decay. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 113–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, M.; Stoecklin, G. On track with P-bodies. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2010, 38, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brengues, M.; Teixeira, D.; Parker, R. Movement of Eukaryotic mRNAs Between Polysomes and Cytoplasmic Processing Bodies. Science 2005, 310, 486–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Standart, N.; Weil, D. P-Bodies: Cytosolic Droplets for Coordinated mRNA Storage. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubstenberger, A.; Courel, M.; Bénard, M.; Souquere, S.; Ernoult-Lange, M.; Chouaib, R.; Yi, Z.; Morlot, J.B.; Munier, A.; Fradet, M.; et al. P-Body Purification Reveals the Condensation of Repressed mRNA Regulons. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Standart, N.; Minshall, N. Translational control in early development: CPEB, P-bodies and germinal granules. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Piqué, M.; López, J.M.; Foissac, S.; Guigó, R.; Méndez, R. A Combinatorial Code for CPE-Mediated Translational Control. Cell 2008, 132, 434–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, M.J. From Birth to Death: The Complex Lives of Eukaryotic mRNAs. Science 2005, 309, 1514–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mak, W.; Fang, C.; Holden, T.; Dratver, M.B.; Lin, H. An Important Role of Pumilio 1 in Regulating the Development of the Mammalian Female Germline. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 94, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa Martins, J.P.; Liu, X.; Oke, A.; Arora, R.; Franciosi, F.; Viville, S.; Laird, D.J.; Fung, J.C.; Conti, M. DAZL and CPEB1 regulate mRNA translation synergistically during oocyte maturation. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 1271–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Voronina, E.; Seydoux, G.; Sassone-Corsi, P.; Nagamori, I. RNA granules in germ cells. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a002774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Swetloff, A.; Conne, B.; Huarte, J.; Pitetti, J.L.; Nef, S.; Vassalli, J.D. Dcp1-bodies in mouse oocytes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 4951–4961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Flemr, M.; Ma, J.; Schultz, R.M.; Svoboda, P. P-Body Loss Is Concomitant with Formation of a Messenger RNA Storage Domain in Mouse Oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 82, 1008–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boke, E.; Mitchison, T.J. The balbiani body and the concept of physiological amyloids. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 153–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pepling, M.E. A Novel Maternal mRNA Storage Compartment in Mouse Oocytes. Biol. Reprod. 2010, 82, 807–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, J.; Richter, J.D. Germ cell differentiation and synaptonemal complex formation are disrupted in CPEB knockout mice. Dev. Cell 2001, 1, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hyon, C.; Mansour-Hendili, L.; Chantot-Bastaraud, S.; Donadille, B.; Kerlan, V.; Dodé, C.; Jonard, S.; Delemer, B.; Gompel, A.; Reznik, Y.; et al. Deletion of CPEB1 Gene: A Rare but Recurrent Cause of Premature Ovarian Insufficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 2099–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Igea, A.; Méndez, R. Meiosis requires a translational positive loop where CPEB1 ensues its replacement by CPEB4. EMBO J. 2010, 29, 2182–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Melton, C.; Suh, N.; Oh, J.S.; Horner, K.; Xie, F.; Sette, C.; Blelloch, R.; Conti, M. Genome-wide analysis of translation reveals a critical role for deleted in azoospermia-like (Dazl) at the oocyte-to-zygote transition. Genes Dev. 2011, 25, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tung, J.Y.; Rosen, M.P.; Nelson, L.M.; Turek, P.J.; Witte, J.S.; Cramer, D.W.; Cedars, M.I.; Reijo-Pera, R.A. Novel missense mutations of the Deleted-in-AZoospermia-Like (DAZL) gene in infertile women and men. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2006, 4, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guzeloglu-Kayisli, O.; Lalioti, M.D.; Aydiner, F.; Sasson, I.; Ilbay, O.; Sakkas, D.; Lowther, K.M.; Mehlmann, L.M.; Seli, E. Embryonic poly(A)-binding protein (EPAB) is required for oocyte maturation and female fertility in mice. Biochem. J. 2012, 446, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, T.; Li, Y.; Li, H.; Ma, X.S.; Ouyang, Y.C.; Hou, Y.; Schatten, H.; Sun, Q.Y. RNA-associated protein LSM family member 14 controls oocyte meiotic maturation through regulating mRNA pools. J. Reprod. Dev. 2017, 63, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sutherland, J.M.; Sobinoff, A.P.; Gunter, K.M.; Fraser, B.A.; Pye, V.; Bernstein, I.R.; Boon, E.; Siddall, N.A.; De Andres, L.I.; Hime, G.R.; et al. Knockout of rna binding protein msi2 impairs follicle development in the mouse ovary: Characterization of msi1 and msi2 during folliculogenesis. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1228–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Medvedev, S.; Yu, J.; Tang, L.C.; Agno, J.E.; Matzuk, M.M.; Schultz, R.M.; Hecht, N.B. Absence of the DNA-/RNA-binding protein MSY2 results in male and female infertility. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5755–5760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Christou-Kent, M.; Kherraf, Z.-E.; Amiri-Yekta, A.; Le Blévec, E.; Karaouzène, T.; Conne, B.; Escoffier, J.; Assou, S.; Guttin, A.; Lambert, E.; et al. PATL2 is a key actor of oocyte maturation whose invalidation causes infertility in women and mice. Embo Mol. Med. 2018, 10, e8515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maddirevula, S.; Coskun, S.; Alhassan, S.; Elnour, A.; Alsaif, H.S.; Ibrahim, N.; Abdulwahab, F.; Arold, S.T.; Alkuraya, F.S. Female Infertility Caused by Mutations in the Oocyte-Specific Translational Repressor PATL2. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Chen, H.; Li, D.; Song, D.; Chen, B.; Yan, Z.; Lyu, Q.; Wang, L.; Kuang, Y.; Li, B.; et al. Novel mutations in PATL2: Expanding the mutational spectrum and corresponding phenotypic variability associated with female infertility. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 64, 379–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Tong, X.; Wang, F.; Luo, L.; Jin, R.; Fu, Y.; Zhou, G.; Li, D.; Song, G.; Liu, Y.; et al. Novel mutations in PATL2 cause female infertility with oocyte germinal vesicle arrest. Hum. Reprod. 2018, 33, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.; Zhang, Z.; Sun, X.; Kuang, Y.; Mao, X.; Wang, X.; Yan, Z.; Li, B.; Xu, Y.; Yu, M.; et al. Biallelic Mutations in PATL2 Cause Female Infertility Characterized by Oocyte Maturation Arrest. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mak, W.; Xia, J.; Cheng, E.-C.; Lowther, K.; Lin, H. A role of Pumilio 1 in mammalian oocyte maturation and maternal phase of embryogenesis. Cell Biosci. 2018, 8, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Ke, H.; Liu, R.; Qin, Y.; Mak, W.; Ma, J.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Z.-J. Variation analysis of PUM1 gene in Chinese women with primary ovarian insufficiency. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2018, 35, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, K.; Zhang, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, D.; Zhu, M.; Xu, E.Y. Generation and functional characterization of a conditional Pumilio2 null allele. J. Biomed. Res. 2018, 32, 434–441. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, M.J.; Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Lim, E.L.; Wang, Z.; Yeager, M.; Wong, M.P.; Sham, P.C.; Chanock, S.J.; Wang, J. GWASdb: A database for human genetic variants identified by genome-wide association studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D1047–D1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Viveiros, M.M.; Eppig, J.J.; Bai, Y.; Fitzpatrick, S.L.; Matzuk, M.M. Zygote arrest 1 (Zar1) is a novel maternal-effect gene critical for the oocyte-to-embryo transition. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Ji, S.-Y.; Zhu, Y.-Z.; Wu, Y.-W.; Shen, L.; Fan, H.-Y. ZAR1 and ZAR2 are required for oocyte meiotic maturation by regulating the maternal transcriptome and mRNA translational activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 11387–11402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wang, F.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, Y.; Ding, M.; Gao, S. Mouse ZAR1-like (XM_359149) colocalizes with mRNA processing components and its dominant-negative mutant caused two-cell-stage embryonic arrest. Dev. Dyn. 2010, 239, 407–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, S.B.V.; Stumpo, D.J.; Kennington, E.A.; Phillips, R.S.; Bock, C.B.; Ribeiro-Neto, F.; Blackshear, P.J. The CCCH tandem zinc-finger protein Zfp36l2 is crucial for female fertility and early embryonic development. Development 2004, 131, 4883–4893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ball, C.B.; Rodriguez, K.F.; Stumpo, D.J.; Ribeiro-Neto, F.; Korach, K.S.; Blackshear, P.J.; Birnbaumer, L.; Ramos, S.B.V. The RNA-binding protein, ZFP36L2, influences ovulation and oocyte maturation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e97324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Udagawa, T.; Swanger, S.A.; Takeuchi, K.; Kim, J.H.; Nalavadi, V.; Shin, J.; Lorenz, L.J.; Zukin, R.S.; Bassell, G.J.; Richter, J.D. Bidirectional control of mRNA translation and synaptic plasticity by the cytoplasmic polyadenylation complex. Mol. Cell 2012, 47, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Richter, J.D. CPEB: A life in translation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakanishi, T.; Kumagai, S.; Kimura, M.; Watanabe, H.; Sakurai, T.; Kimura, M.; Kashiwabara, S.; Baba, T. Disruption of mouse poly(A) polymerase mGLD-2 does not alter polyadenylation status in oocytes and somatic cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 364, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, M.K.; Han, S.J. Post-transcriptional and post-translational regulation during mouse oocyte maturation. BMB Rep. 2011, 44, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kozak, M. Rethinking some mechanisms invoked to explain translational regulation in eukaryotes. Gene 2006, 382, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villaescusa, J.C.; Allard, P.; Carminati, E.; Kontogiannea, M.; Talarico, D.; Blasi, F.; Farookhi, R.; Verrotti, A.C. Clast4, the murine homologue of human eIF4E-Transporter, is highly expressed in developing oocytes and post-translationally modified at meiotic maturation. Gene 2006, 367, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minshall, N.; Reiter, M.H.; Weil, D.; Standart, N. CPEB interacts with an ovary-specific eIF4E and 4E-T in early Xenopus oocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 37389–37401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esencan, E.; Seli, E. Translational Regulation of Gene Expression During Oogenesis and Preimplantation Embryo Development. In Human Reproductive and Prenatal Genetics; Academic Press/Elsevier: London, UK; San Diego, CA, USA; Cambridge, MA, USA; Oxford, UK, 2019; pp. 221–239. [Google Scholar]
- Nakahata, S.; Kotani, T.; Mita, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Katsu, Y.; Nagahama, Y.; Yamashita, M. Involvement of Xenopus Pumilio in the translational regulation that is specific to cyclin B1 mRNA during oocyte maturation. Mech. Dev. 2003, 120, 865–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padmanabhan, K.; Richter, J.D. Regulated Pumilio-2 binding controls RINGO/Spy mRNA translation and CPEB activation. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Collier, B.; Gorgoni, B.; Loveridge, C.; Cooke, H.J.; Gray, N.K. The DAZL family proteins are PABP-binding proteins that regulate translation in germ cells. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 2656–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, C.-R.; Lowther, K.M.; Lalioti, M.D.; Seli, E. Embryonic Poly(A)-Binding Protein (EPAB) Is Required for Granulosa Cell EGF Signaling and Cumulus Expansion in Female Mice. Endocrinology 2016, 157, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, Y.; Tanaka, K.J.; Miyauchi, M.; Huang, L.; Tsujimoto, M.; Matsumoto, K. Translational repression by the oocyte-specific protein P100 in Xenopus. Dev. Biol. 2010, 344, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marnef, A.; Maldonado, M.; Bugaut, A.; Balasubramanian, S.; Kress, M.; Weil, D.; Standart, N. Distinct functions of maternal and somatic Pat1 protein paralogs. RNA 2010, 16, 2094–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.; Hecht, N.B.; Schultz, R.M. Expression of MSY2 in mouse oocytes and preimplantation embryos. Biol. Reprod. 2001, 65, 1260–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ayache, J.; Bénard, M.; Ernoult-Lange, M.; Minshall, N.; Standart, N.; Kress, M.; Weil, D. P-body assembly requires DDX6 repression complexes rather than decay or Ataxin2/2L complexes. Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 2579–2595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smillie, D.A.; Sommerville, J. RNA helicase p54 (DDX6) is a shuttling protein involved in nuclear assembly of stored mRNP particles. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 395–407. [Google Scholar]
- Minshall, N.; Kress, M.; Weil, D.; Standart, N. Role of p54 RNA helicase activity and its c-terminal domain in translational repression, p-body localization and assembly. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 2464–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Weston, A.; Sommerville, J. Xp54 and related (DDX6-like) RNA helicases: Roles in messenger RNP assembly, translation regulation and RNA degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, 3082–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cragle, C.E.; MacNicol, M.C.; Byrum, S.D.; Hardy, L.L.; Mackintosh, S.G.; Richardson, W.A.; Gray, N.K.; Childs, G.V.; Tackett, A.J.; MacNicol, A.M. Musashi interaction with poly(A)-binding protein is required for activation of target mRNA translation. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 10969–10986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.J.; Ogawa, K.; Takagi, M.; Imamoto, N.; Matsumoto, K.; Tsujimoto, M. RAP55, a cytoplasmic mRNP component, represses translation in Xenopus oocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 40096–40106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pepling, M.E.; Wilhelm, J.E.; O’Hara, A.L.; Gephardt, G.W.; Spradling, A.C. Mouse oocytes within germ cell cysts and primordial follicles contain a Balbiani body. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Marnef, A.; Sommerville, J.; Ladomery, M.R. RAP55: Insights into an evolutionarily conserved protein family. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2009, 41, 977–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susor, A.; Jansova, D.; Cerna, R.; Danylevska, A.; Anger, M.; Toralova, T.; Malik, R.; Supolikova, J.; Cook, M.S.; Oh, J.S.; et al. Temporal and spatial regulation of translation in the mammalian oocyte via the mTOR-eIF4F pathway. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, J.; Torcia, S.; Xie, F.; Lin, C.-J.; Cakmak, H.; Franciosi, F.; Horner, K.; Onodera, C.; Song, J.S.; Cedars, M.I.; et al. Somatic cells regulate maternal mRNA translation and developmental competence of mouse oocytes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2013, 15, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansova, D.; Koncicka, M.; Tetkova, A.; Cerna, R.; Malik, R.; del Llano, E.; Kubelka, M.; Susor, A. Regulation of 4E-BP1 activity in the mammalian oocyte. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 927–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraldez, A.J.; Mishima, Y.; Rihel, J.; Grocock, R.J.; Van Dongen, S.; Inoue, K.; Enright, A.J.; Schier, A.F. Zebrafish MiR-430 Promotes Deadenylation and Clearance of Maternal mRNAs. Science 2006, 312, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suh, N.; Baehner, L.; Moltzahn, F.; Melton, C.; Shenoy, A.; Chen, J.; Blelloch, R. MicroRNA function is globally suppressed in mouse oocytes and early embryos. Curr. Biol. 2010, 20, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Flemr, M.; Malik, R.; Franke, V.; Nejepinska, J.; Sedlacek, R.; Vlahovicek, K.; Svoboda, P. A Retrotransposon-Driven Dicer Isoform Directs Endogenous Small Interfering RNA Production in Mouse Oocytes. Cell 2013, 155, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jong, H.K.; Richter, J.D. RINGO/cdk1 and CPEB mediate poly(A) tail stabilization and translational regulation by ePAB. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 2571–2579. [Google Scholar]
- Conti, M.; Franciosi, F. Acquisition of oocyte competence to develop as an embryo: Integrated nuclear and cytoplasmic events. Hum. Reprod. Update 2018, 24, 245–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luong, X.G.; Maria Daldello, E.; Rajkovic, G.; Yang, C.-R. Genome-wide analysis reveals a switch in the translational program upon oocyte meiotic resumption. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Walser, C.B.; Lipshitz, H.D. Transcript clearance during the maternal-to-zygotic transition. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2011, 21, 431–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashirullah, A.; Halsell, S.R.; Cooperstock, R.L.; Kloc, M.; Karaiskakis, A.; Fisher, W.W.; Weili, F.; Hamilton, J.K.; Etkin, L.D.; Lipshitz, H.D. Joint action of two RNA degradation pathways controls the timing of maternal transcript elimination at the midblastula transition in Drosophila melanogaster. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 2610–2620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semotok, J.L.; Cooperstock, R.L.; Pinder, B.D.; Vari, H.K.; Lipshitz, H.D.; Smibert, C.A. Smaug recruits the CCR4/POP2/NOT deadenylase complex to trigger maternal transcript localization in the early Drosophila embryo. Curr. Biol. 2005, 15, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.T.; Bonneau, A.R.; Giraldez, A.J. Zygotic genome activation during the maternal-to-zygotic transition. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 581–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Medvedev, S.; Yang, J.; Hecht, N.B.; Schultz, R.M. CDC2A (CDK1)-mediated phosphorylation of MSY2 triggers maternal mRNA degradation during mouse oocyte maturation. Dev. Biol. 2008, 321, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Clarke, H.J. Post-transcriptional Control of Gene Expression During Mouse Oogenesis. Results Probl. Cell Differ. 2012, 55, 1–21. [Google Scholar]
- DeRenzo, C.; Seydoux, G. A clean start: Degradation of maternal proteins at the oocyte-to-embryo transition. Trends Cell Biol. 2004, 14, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vos, M.; Devroey, P.; Fauser, B.C.J. Primary ovarian insufficiency. Lancet 2010, 376, 911–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogli, A.; Rodriguez, D.; Eymard-Pierre, E.; Bouhour, F.; Labauge, P.; Meaney, B.F.; Zeesman, S.; Kaneski, C.R.; Schiffmann, R.; Boespflug-Tanguy, O. Ovarian failure related to eukaryotic initiation factor 2B mutations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2003, 72, 1544–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rosario, R.; Childs, A.J.; Anderson, R.A. RNA-binding proteins in human oogenesis: Balancing differentiation and self-renewal in the female fetal germline. Stem Cell Res. 2017, 21, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Gene Name | Mouse Phenotypes | Association to Reproductive Disease in Women |
|---|---|---|
| CPEB1 Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 1 | KO: females sterile. Embryonic oocyte development suspended at the pachytene stage of prophase I [31] | Heterozygous deletion associated with POI [32] |
| CPEB4 Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 4 | KD: oocytes show impaired MI to MII transition and absence of first polar body extrusion [33] | - |
| DAZL Deleted in azoospermia-like | KD: oocytes showed decreased translation during late meiosis and improper spindle assembly KO: females (and males) sterile [34] | Missense mutations associated with POI in homozygous and heterozygous states [35] |
| EPABP Embryonic poly(A)-binding protein | KO: females infertile. Impaired growth and lack of transcriptional silencing in GV oocytes; failed translation activation in MII oocytes [36] | - |
| LSM14B LSM Family Member 14B | KD: high proportion of metaphase-1 arrested oocytes [37] | - |
| MSI2 Musashi homolog 2 (Drosophila) | KO: females showed impaired folliculogenesis and decrease in number of MII oocytes [38] | - |
| MSY2 Y-box-binding protein 2 | KO: females (and males) infertile with impaired folliculogenesis and oocyte loss [39] | - |
| PATL2 Protein associated with Topoisomerase II (yeast)-like 2 | KO: females subfertile, high incidence of 1) oocytes not maturing to MII stage, 2) aberrant response to fertilisation and 3) developmental arrest before blastocyst stage [40] | Nonsense, missense, frameshift and splicing variants associated with OMD with GV arrest for homozygous variants and GV to early embryo arrest for compound heterozygous mutations [40,41,42,43,44] |
| PUM1 Pumilio 1 (Drosophila) | KO: diminished ovarian reserve, oocytes showed delayed meiosis [24], higher rate of abnormal embryo development [45] | No pathogenic variants identified in study of POI patients [46] |
| PUM2 Pumilio 1 (Drosophila) | KO: Females of normal fertility, possible redundancy with PUM1/species difference [47] | GWAS association with POI [48] |
| ZAR1/2 Zygote arrest 1/2 | ZAR1 KO: failed cleavage after fertilisation, some blastocysts with impaired EGA [49] ZAR1/2 KO: delayed meiotic resumption and first polar body extrusion, high frequency of abnormal meiotic spindle and chromosome aneuploidy [50]. | - |
| ZAR1L Zar1-like | KD: two-cell stage embryonic arrest [51] | - |
| ZFP36L2 mRNA decay activator protein | KO (C57BL/6NTac): embryonic arrest at the two-cell stage KO (F3 strain): females anovulatory, oocytes did not mature [52,53] | - |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Christou-Kent, M.; Dhellemmes, M.; Lambert, E.; Ray, P.F.; Arnoult, C. Diversity of RNA-Binding Proteins Modulating Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Protein Expression in the Maturing Mammalian Oocyte. Cells 2020, 9, 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030662
Christou-Kent M, Dhellemmes M, Lambert E, Ray PF, Arnoult C. Diversity of RNA-Binding Proteins Modulating Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Protein Expression in the Maturing Mammalian Oocyte. Cells. 2020; 9(3):662. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030662
Chicago/Turabian StyleChristou-Kent, Marie, Magali Dhellemmes, Emeline Lambert, Pierre F. Ray, and Christophe Arnoult. 2020. "Diversity of RNA-Binding Proteins Modulating Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Protein Expression in the Maturing Mammalian Oocyte" Cells 9, no. 3: 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030662
APA StyleChristou-Kent, M., Dhellemmes, M., Lambert, E., Ray, P. F., & Arnoult, C. (2020). Diversity of RNA-Binding Proteins Modulating Post-Transcriptional Regulation of Protein Expression in the Maturing Mammalian Oocyte. Cells, 9(3), 662. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030662





