The Significance of the Dysregulation of Canonical Wnt Signaling in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas
Abstract
1. Introduction
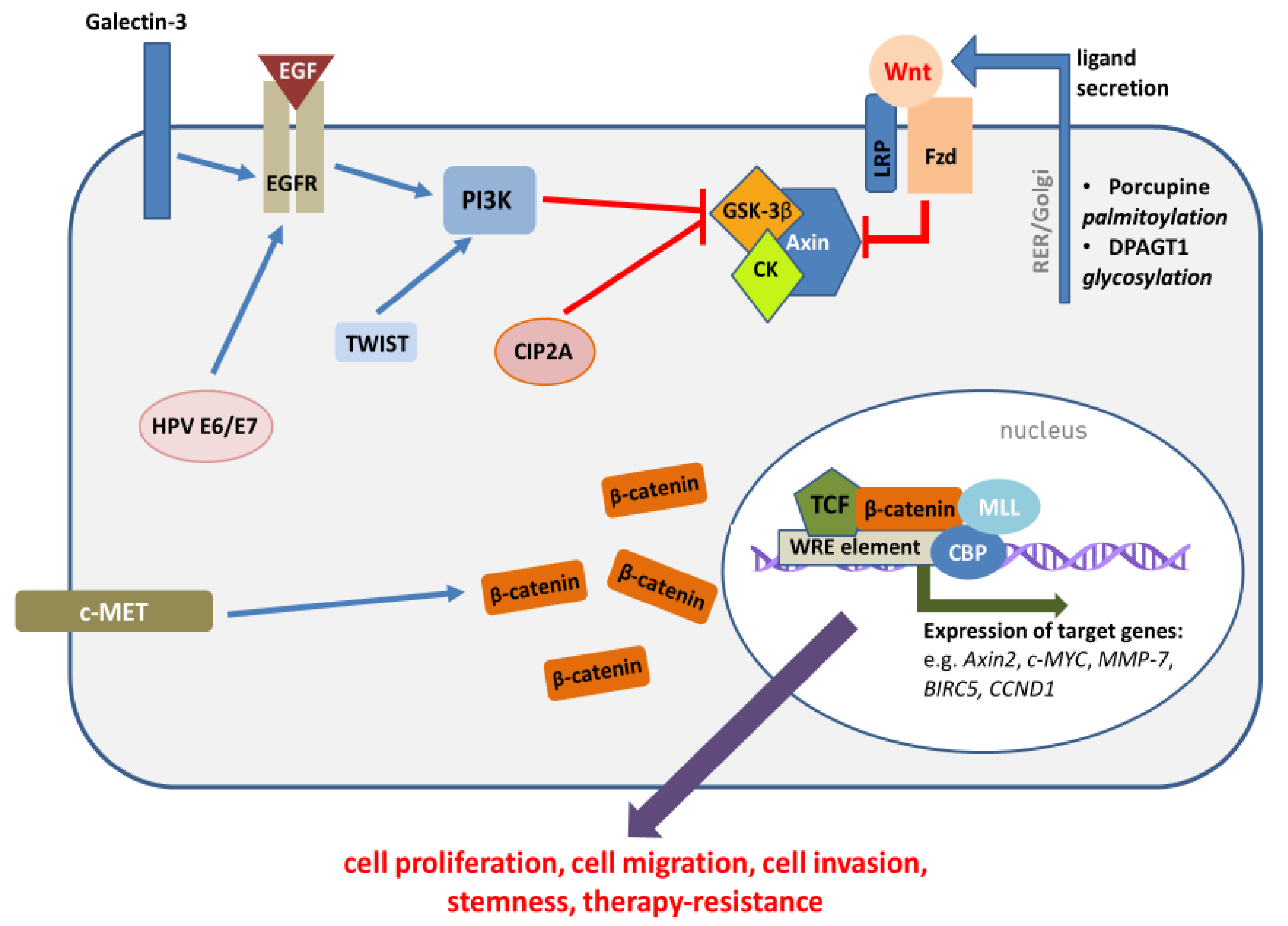
2. Mechanisms of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Activation in HNSCC
2.1. The Role of Epigenetic Mechanisms in Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Activation
2.2. The Role of HNSCC Etiological Factors in Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Activation
3. Functional Significance of Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway Dysregulation
4. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Mathers, C.; Parkin, D.M.; Piñeros, M.; Znaor, A.; Bray, F. Estimating the global cancer incidence and mortality in 2018: GLOBOCAN sources and methods. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 144, 1941–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferlay, J.; Colombet, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Dyba, T.; Randi, G.; Bettio, M.; Gavin, A.; Visser, O.; Bray, F. Cancer incidence and mortality patterns in Europe: Estimates for 40 countries and 25 major cancers in 2018. Eur. J. Cancer. 2018, 103, 356–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szyfter, K.; Kiwerska, K.; Wierzbicka, M. HPV-related HNC—New challenge and hope for head and neck cancer subjects. J. Med. Sci. 2018, 87, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.; Johnson, N.W.; Kumar, N. Global Epidemiology of Head and Neck Cancers: A Continuing Challenge. Oncology 2016, 91, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, K.; Agrawal, N.; Gooi, Z. Head and Neck Masses. Med. Clin. North. Am. 2018, 102, 1013–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braig, F.; Kriegs, M.; Voigtlaender, M.; Habel, B.; Grob, T.; Biskup, K.; Blanchard, V.; Sack, M.; Thalhammer, A.; Ben Batalla, I.; et al. Cetuximab Resistance in Head and Neck Cancer Is Mediated by EGFR-K(521) Polymorphism. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1188–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheth, S.; Weiss, J. Pembrolizumab and its use in the treatment of recurrent or metastatic head and neck cancer. Future Oncol. Lond. Engl. 2018, 14, 1547–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iorio, F.; Knijnenburg, T.A.; Vis, D.J.; Bignell, G.R.; Menden, M.P.; Schubert, M.; Aben, N.; Gonçalves, E.; Barthorpe, S.; Lightfoot, H.; et al. A Landscape of Pharmacogenomic Interactions in Cancer. Cell 2016, 166, 740–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Vega, F.; Mina, M.; Armenia, J.; Chatila, W.K.; Luna, A.; La, K.C.; Dimitriadoy, S.; Liu, D.L.; Kantheti, H.S.; Saghafinia, S.; et al. Oncogenic Signaling Pathways in The Cancer Genome Atlas. Cell 2018, 173, 321–337.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, K.-T.; Chang, J.-G.; Lin, T.-H.; Wang, Y.-F.; Chang, J.-Y.; Shih, M.-C.; Lin, C.-C. Correlation between protein expression and epigenetic and mutation changes of Wnt pathway-related genes in oral cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2003, 23, 1001–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, R.; Yamamoto, G.; Nagoshi, Y.; Aida, T.; Irie, T.; Tachikawa, T. Expression of adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) in tumorigenesis of human oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Oncol. 2004, 40, 932–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, S.; Katagiri, W.; Kong, C.; Amekawa, S.; Nakazawa, M.; Yura, Y. Mutations of the APC, beta-catenin, and axin 1 genes and cytoplasmic accumulation of beta-catenin in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 131, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odajima, T.; Sasaki, Y.; Tanaka, N.; Kato-Mori, Y.; Asanuma, H.; Ikeda, T.; Satoh, M.; Hiratsuka, H.; Tokino, T.; Sawada, N. Abnormal β-catenin expression in oral cancer with no gene mutation: Correlation with expression of cyclin D1 and epidermal growth factor receptor, Ki-67 labeling index, and clinicopathological features. Hum. Pathol. 2005, 36, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Weinberger, P.M.; Provost, E.; Haffty, B.G.; Sasaki, C.; Joe, J.; Camp, R.L.; Rimm, D.L.; Psyrri, A. B-Catenin Functions Mainly as an Adhesion Molecule in Patients with Squamous Cell Cancer of the Head and Neck. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2471–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lea, I.A.; Jackson, M.A.; Li, X.; Bailey, S.; Peddada, S.D.; Dunnick, J.K. Genetic pathways and mutation profiles of human cancers: Site- and exposure-specific patterns. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 1851–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogabe, Y.; Suzuki, H.; Toyota, M.; Ogi, K.; Imai, T.; Nojima, M.; Sasaki, Y.; Hiratsuka, H.; Tokino, T. Epigenetic inactivation of SFRP genes in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2008, 32, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Morris, L.G.T.; Kaufman, A.M.; Gong, Y.; Ramaswami, D.; Walsh, L.A.; Turcan, Ş.; Eng, S.; Kannan, K.; Zou, Y.; Peng, L.; et al. Recurrent somatic mutation of FAT1 in multiple human cancers leads to aberrant Wnt activation. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Hung, H.-W.; Hung, P.-H.; Shieh, Y.-S. Epidermal growth factor receptor regulates β-catenin location, stability, and transcriptional activity in oral cancer. Mol. Cancer 2010, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varelas, X.; Bouchie, M.P.; Kukuruzinska, M.A. Protein N-glycosylation in oral cancer: Dysregulated cellular networks among DPAGT1, E-cadherin adhesion and canonical Wnt signaling. Glycobiology 2014, 24, 579–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, Z.; Liu, S.; Dong, Z.; Dalin, M.; Bao, S.; Hu, Y.; Wei, F. Galectin-3 gene silencing inhibits migration and invasion of human tongue cancer cells in vitro via downregulating β-catenin. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeets, S.J.; van der Plas, M.; Schaaij-Visser, T.B.M.; van Veen, E.A.M.; van Meerloo, J.; Braakhuis, B.J.M.; Steenbergen, R.D.M.; Brakenhoff, R.H. Immortalization of oral keratinocytes by functional inactivation of the p53 and pRb pathways. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleszcz, R. The canonical Wnt pathway—Functional structure and importance for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Postępy Biochem. 2019, 65, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heuberger, J.; Birchmeier, W. Interplay of Cadherin-Mediated Cell Adhesion and Canonical Wnt Signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a002915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Silva, B.S.F.; de Castro, C.A.; Von Zeidler, S.L.V.; de Sousa, S.C.O.M.; Batista, A.C. Altered β-catenin expression in oral mucosal dysplasia: A comparative study. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2015, 23, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagerakis, P.; Pannone, G.; Shabana, A.-H.; Depondt, J.; Santoro, A.; Ghirtis, K.; Berdal, A.; Papagerakis, S. Aberrant β-Catenin and Lef1 Expression May Predict the Clinical Outcome for Patients with Oropharyngeal Cancer. Int. J. Immunopathol. Pharmacol. 2012, 25, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, K.; Ito, S.; Wada, N.; Deguchi, H.; Hata, T.; Hosoda, M.; Nohno, T. Nuclear localization of beta-catenin involved in precancerous change in oral leukoplakia. Mol. Cancer 2007, 6, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Z.; Shi, X.; Gao, Y.; Wei, M.; Wang, C.; Yu, G. β-catenin expression pattern in primary oral squamous cell carcinoma. Chin. Med. J. (Engl.) 2008, 121, 1866–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.K.; Sanders, D.S.A.; Jankowski, J.A.Z.; Landini, G.; Brown, A.M.S. Expression of cadherins and catenins in oral epithelial dysplasia and squamous cell carcinoma. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2007, 27, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzio, L.L.; Russo, L.L.; Falaschini, S.; Ciavarella, D.; Pentenero, M.; Arduino, P.; Favia, G.; Maiorano, E.; Rubini, C.; Pieramici, T.; et al. β- and γ-catenin expression in oral dysplasia. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 501–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaw, S.Y.; Abdul Majeed, A.; Dalley, A.J.; Chan, A.; Stein, S.; Farah, C.S. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT) biomarkers—E-cadherin, beta-catenin, APC and Vimentin—In oral squamous cell carcinogenesis and transformation. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaya, K.; Sudo, H.; Maeda, G.; Kawashiri, S.; Imai, K. Concomitant Loss of p120-Catenin and β-Catenin Membrane Expression and Oral Carcinoma Progression with E-Cadherin Reduction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e69777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pectasides, E.; Rampias, T.; Sasaki, C.; Perisanidis, C.; Kouloulias, V.; Burtness, B.; Zaramboukas, T.; Rimm, D.; Fountzilas, G.; Psyrri, A. Markers of Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition in Association with Survival in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC). PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.-S.; Tsai, C.-H.; Tsai, L.-L.; Chou, M.-C.; Chou, M.-Y.; Chang, Y.-C. β-catenin expression in areca quid chewing-associated oral squamous cell carcinomas and upregulated by arecoline in human oral epithelial cells. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2012, 111, 194–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, J.; Sawhney, M.; DattaGupta, S.; Shukla, N.K.; Srivastava, A.; Walfish, P.G.; Ralhan, R. Clinical Significance of Altered Expression of β-Catenin and E-Cadherin in Oral Dysplasia and Cancer: Potential Link with ALCAM Expression. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, M.; Peña-Oyarzun, D.; Maturana, A.; Torres, V.A. Nuclear localization of β-catenin and expression of target genes are associated with increased Wnt secretion in oral dysplasia. Oral Oncol. 2019, 94, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Marcos, C.; López, F.; Alonso-Guervós, M.; Domínguez, F.; Suárez, C.; Hermsen, M.A.; Llorente, J.L. Genetic and protein markers related to laryngeal epithelial precursor lesions and their neoplastic progression. Acta Otolaryngol. (Stockh.) 2013, 133, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, F.; Álvarez-Marcos, C.; Alonso-Guervós, M.; Domínguez, F.; Suárez, C.; Hermsen, M.A.; Llorente, J.L. From laryngeal epithelial precursor lesions to squamous carcinoma of the larynx: The role of cell cycle proteins and β-catenin. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2013, 270, 3153–3162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarado, C.G.; Maruyama, S.; Cheng, J.; Ida-Yonemochi, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Yamazaki, M.; Takagi, R.; Saku, T. Nuclear translocation of β-catenin synchronized with loss of E-cadherin in oral epithelial dysplasia with a characteristic two-phase appearance. Histopathology 2011, 59, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galera-Ruiz, H.; Ríos-Moreno, M.J.; González-Cámpora, R.; Ortega, I.; Fernández, A.; García-Escudero, A.; Galera-Davidson, H. The cadherin–catenin complex in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2012, 269, 1183–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goulioumis, A.K.; Varakis, J.; Goumas, P.; Papadaki, H. Differential β-catenin expression between glottic and supraglottic laryngeal carcinoma. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2010, 267, 1573–1578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.; Pannone, G.; Papagerakis, S.; McGuff, H.S.; Cafarelli, B.; Lepore, S.; De Maria, S.; Rubini, C.; Mattoni, M.; Staibano, S.; et al. Beta-Catenin and Epithelial Tumors: A Study Based on 374 Oropharyngeal Cancers. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxmidevi, L.B.; Angadi, P.V.; Pillai, R.K.; Chandreshekar, C. Aberrant β-catenin expression in the histologic differentiation of oral squamous cell carcinoma and verrucous carcinoma: An immunohistochemical study. J. Oral Sci. 2010, 52, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ravindran, G.; Sawant, S.S.; Hague, A.; Kingsley, K.; Devaraj, H. Association of differential β-catenin expression with Oct-4 and Nanog in oral squamous cell carcinoma and their correlation with clinicopathological factors and prognosis: Association of β-catenin, with Oct-4 and NANOG in OSCC. Head Neck 2015, 37, 982–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahomed, F.; Altini, M.; Meer, S. Altered E-cadherin/β-catenin expression in oral squamous carcinoma with and without nodal metastasis. Oral Dis. 2007, 13, 386–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.-K.; Jiang, X.-Y.; Zhou, X.-X.; Wang, D.-M.; Song, X.-L.; Jiang, H.-B. Upregulation of vimentin and aberrant expression of E-cadherin/β-catenin complex in oral squamous cell carcinomas: Correlation with the clinicopathological features and patient outcome. Mod. Pathol. 2010, 23, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, G.; Sunakawa, H.; Nakamori, K.; Shinya, T.; Tsuhako, W.; Tamura, Y.; Kosugi, T.; Sato, N.; Ogi, K.; Hiratsuka, H. Aberrant expression of β- and γ-catenin is an independent prognostic marker in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2006, 35, 356–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Z.; Müller, S.; Qian, G.; Xu, J.; Kim, S.; Chen, Z.; Jiang, N.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Saba, N.F.; et al. Human papillomavirus 16 oncoprotein regulates the translocation of β-catenin via the activation of epidermal growth factor receptor: HPV Inducing β-Catenin Translocation. Cancer 2015, 121, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.; Kar, M.; Roy, S.; Saha, A.; Padhi, S.; Banerjee, B. Role of β-catenin in cisplatin resistance, relapse and prognosis of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Cell. Oncol. 2018, 41, 185–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pukkila, M.J.; Virtaniemi, J.A.; Kumpulainen, E.J.; Pirinen, R.T.; Johansson, R.T.; Valtonen, H.J.; Juhola, M.T.; Kosma, V.M. Nuclear beta catenin expression is related to unfavourable outcome in oropharyngeal and hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Clin. Pathol. 2001, 54, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, F.F.; da Costa Miguel, M.C.; Pereira, A.L.A.; da Cruz, M.C.F.N.; de Almeida Freitas, R.; Pinto, L.P.; de Souza, L.B. Changes in immunoexpression of E-cadherin and β-catenin in oral squamous cell carcinoma with and without nodal metastasis. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2009, 13, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Jiao, J.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, M. An essential role for N-cadherin and β-catenin for progression in tongue squamous cell carcinoma and their effect on invasion and metastasis of Tca8113 tongue cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 21, 1223–1233. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- García-Pedrero, J.M.; García-Cabo, P.; Ángeles Villaronga, M.; Hermida-Prado, F.; Granda-Díaz, R.; Allonca, E.; Rodrigo, J.P. Prognostic significance of E-cadherin and β-catenin expression in HPV-negative oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas. Head Neck 2017, 39, 2293–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaid, K.W. Immunohistochemical Assessment of E-cadherin and β-catenin in the Histological Differentiations of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2014, 15, 8847–8853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparoni, A.; Chaves, A.; Fonzi, L.; Johnson, G.K.; Schneider, G.B.; Squier, C.A. Subcellular localization of beta-catenin in malignant cell lines and squamous cell carcinomas of the oral cavity. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2002, 31, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosado, P.; Lequerica-Fernández, P.; Fernández, S.; Allonca, E.; Villallaín, L.; de Vicente, J.C. E-cadherin and β-catenin expression in well-differentiated and moderately-differentiated oral squamous cell carcinoma: Relations with clinical variables. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 51, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujii, M.; Katase, N.; Lefeuvre, M.; Gunduz, M.; Buery, R.R.; Tamamura, R.; Tsujigiwa, H.; Nagatsuka, H. Dickkopf (Dkk)-3 and β-catenin expressions increased in the transition from normal oral mucosal to oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Mol. Histol. 2011, 42, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Andrews, N.; Jones, A.; Helliwell, T.; Kinsella, A. Expression of the E-cadherin-catenin cell adhesion complex in primary squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck and their nodal metastases. Br. J. Cancer 1997, 75, 1474–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kudo, Y.; Kitahima, S.; Ogawa, I.; Hiraoka, M.; Sargolzaei, S.; Keikhaee, M.R.; Sato, S.; Miyauchi, M.; Takata, T. Invasion and Metastasis of Oral Cancer Cells Require Methylation of E-Cadherin and/or Degradation of Membranous Beta-Catenin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5455–5463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamal, B.; Sengupta, P.K.; Gao, Z.; Nita-Lazar, M.; Amin, B.; Jalisi, S.; Bouchie, M.P.; Kukuruzinska, M.A. Aberrant amplification of the crosstalk between canonical Wnt signaling and N-glycosylation gene DPAGT1 promotes oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishikawa, Y.; Miyazaki, T.; Nkashiro, K.-I.; Yamagata, H.; Isokane, M.; Goda, H.; Tanaka, H.; Oka, R.; Hamakawa, H. Human FAT1 cadherin controls cell migration and invasion of oral squamous cell carcinoma through the localization of β-catenin. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 26, 587–592. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz Prado, S.M.; Medina Villaamil, V.; Aparicio Gallego, G.; Blanco Calvo, M.; López Cedrún, J.L.; Sironvalle Soliva, S.; Valladares Ayerbes, M.; García Campelo, R.; Antón Aparicio, L.M. Expression of Wnt gene family and frizzled receptors in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Virchows Arch. 2009, 455, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiah, S.-G.; Hsiao, J.-R.; Chang, W.-M.; Chen, Y.-W.; Jin, Y.-T.; Wong, T.-Y.; Huang, J.-S.; Tsai, S.-T.; Hsu, Y.-M.; Chou, S.-T.; et al. Downregulated miR329 and miR410 Promote the Proliferation and Invasion of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma by Targeting Wnt-7b. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7560–7572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uraguchi, M.; Morikawa, M.; Shirakawa, M.; Sanada, K.; Imai, K. Activation of WNT Family Expression and Signaling in Squamous Cell Carcinomas of the Oral Cavity. J. Dent. Res. 2004, 83, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Li, G.; Chen, X.; Jing, Q.; Liu, C.; Lu, S.; Huang, D.; Wang, Y.; Tan, P.; Chen, J.; et al. Wnt3a protein overexpression predicts worse overall survival in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4633–4638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.-C.; Chen, C.-T.; Huang, F.-I.; Chen, Y.-L.; Jeng, Y.-M.; Lin, C.-Y. Expression of LEF1 is an independent prognostic factor for patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2014, 113, 934–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, P.N.; Keysar, S.B.; Miller, B.; Eagles, J.R.; Chimed, T.-S.; Reisinger, J.; Gomez, K.E.; Nieto, C.; Jackson, B.C.; Somerset, H.L.; et al. Wnt signaling dynamics in head and neck squamous cell cancer tumor-stroma interactions. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 398–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katz, J.; Jakymiw, A.; Ducksworth, M.K.; Stewart, C.M.; Bhattacharyya, I.; Cha, S.; Chan, E.K.L. CIP2A expression and localization in oral carcinoma and dysplasia. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2010, 10, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böckelman, C.; Hagström, J.; Mäkinen, L.K.; Keski-Säntti, H.; Häyry, V.; Lundin, J.; Atula, T.; Ristimäki, A.; Haglund, C. High CIP2A immunoreactivity is an independent prognostic indicator in early-stage tongue cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 104, 1890–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, J.; Williams, C. Protein Phosphatase 2A in the Regulation of Wnt Signaling, Stem Cells, and Cancer. Genes 2018, 9, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leopoldino, A.M.; Squarize, C.H.; Garcia, C.B.; Almeida, L.O.; Pestana, C.R.; Sobral, L.M.; Uyemura, S.A.; Tajara, E.H.; Silvio Gutkind, J.; Curti, C. SET protein accumulates in HNSCC and contributes to cell survival: Antioxidant defense, Akt phosphorylation and AVOs acidification. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsit, C.J.; McClean, M.D.; Furniss, C.S.; Kelsey, K.T. Epigenetic inactivation of the SFRP genes is associated with drinking, smoking and HPV in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Cancer 2006, 119, 1761–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, C.; Wang, L.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, C.; Zhou, J. Secreted frizzled-related protein 2 is epigenetically silenced and functions as a tumor suppressor in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol. Med. Rep. 2014, 10, 2293–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhou, S.; Chen, L.; Mashrah, M.; Zhu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.; He, Z.; Wang, L.; Xiang, T.; Yao, Z.; et al. Deregulation of secreted frizzled-related proteins is associated with aberrant β-catenin activation in the carcinogenesis of oral submucous fibrosis. OncoTargets Ther. 2015, 2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paluszczak, J.; Hemmerling, D.; Kostrzewska-Poczekaj, M.; Jarmuż-Szymczak, M.; Grenman, R.; Wierzbicka, M.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Frequent hypermethylation of WNT pathway genes in laryngeal squamous cell carcinomas. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2014, 43, 652–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, G.; Bufo, P.; Santoro, A.; Franco, R.; Aquino, G.; Longo, F.; Botti, G.; Serpico, R.; Cafarelli, B.; Abbruzzese, A.; et al. WNT pathway in oral cancer: Epigenetic inactivation of WNT-inhibitors. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 24, 1035–1041. [Google Scholar]
- Towle, R.; Truong, D.; Hogg, K.; Robinson, W.P.; Poh, C.F.; Garnis, C. Global analysis of DNA methylation changes during progression of oral cancer. Oral Oncol. 2013, 49, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluszczak, J.; Sarbak, J.; Kostrzewska-Poczekaj, M.; Kiwerska, K.; Jarmuż-Szymczak, M.; Grenman, R.; Mielcarek-Kuchta, D.; Baer-Dubowska, W. The negative regulators of Wnt pathway—DACH1, DKK1, and WIF1 are methylated in oral and oropharyngeal cancer and WIF1 methylation predicts shorter survival. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 2855–2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Supic, G.; Kozomara, R.; Jovic, N.; Zeljic, K.; Magic, Z. Hypermethylation of RUNX3 but not WIF1 gene and its association with stage and nodal status of tongue cancers. Oral Dis. 2011, 17, 794–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, G.; Zhao, D.; Xu, J.; Li, B. Expression of CBY and Methylation of CBY at Promoter Region in Human Laryngeal Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Tumori J. 2015, 101, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Wang, L.; Song, H.; Wu, C. MiR-29a inhibits the progression of oral squamous cell carcinoma by targeting Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2019, 47, 3037–3042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, A.; Yanamoto, S.; Yamada, S.; Naruse, T.; Takahashi, H.; Kawasaki, G.; Umeda, M. MicroRNA-21 Promotes Oral Cancer Invasion via the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway by Targeting DKK2. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2014, 20, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Q.; Jin, L.; Yang, X.; Zhang, F. LncRNA MINCR activates Wnt/β-catenin signals to promote cell proliferation and migration in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2019, 215, 924–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Qi, S.; Zhang, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, R. lncRNA PLAC2 activated by H3K27 acetylation promotes cell proliferation and invasion via the activation of Wnt/β-catenin pathway in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 54, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Gong, C.; Yuan, K. LncRNA UCA1 promotes cell proliferation, invasion and migration of laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma cells by activating Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 17, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepore, S.; Lettini, G.; Condelli, V.; Sisinni, L.; Piscazzi, A.; Simeon, V.; Zoppoli, P.; Pedicillo, M.C.; Natalicchio, M.I.; Pietrafesa, M.; et al. Comparative Gene Expression Profiling of Tobacco-Associated HPV-Positive versus Negative Oral Squamous Carcinoma Cell Lines. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carrero, I.; Liu, H.-C.; Sikora, A.G.; Milosavljevic, A. Histoepigenetic analysis of HPV- and tobacco-associated head and neck cancer identifies both subtype-specific and common therapeutic targets despite divergent microenvironments. Oncogene 2019, 38, 3551–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenner, M.; Yosef, B.; Huebbers, C.U.; Preuss, S.F.; Dienes, H.-P.; Speel, E.-J.M.; Odenthal, M.; Klussmann, J.P. Nuclear translocation of β-catenin and decreased expression of epithelial cadherin in human papillomavirus-positive tonsillar cancer: An early event in human papillomavirus-related tumour progression?: Nuclear β-catenin and HPV in OSCC. Histopathology 2011, 58, 1117–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.; Hu, Z.; Xu, H.; Müller, S.; Wang, D.; Zhang, H.; Kim, S.; Chen, Z.; Saba, N.F.; Shin, D.M.; et al. A novel prediction model for human papillomavirus-associated oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma using p16 and subcellular β-catenin expression. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2016, 45, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rampias, T.; Boutati, E.; Pectasides, E.; Sasaki, C.; Kountourakis, P.; Weinberger, P.; Psyrri, A. Activation of Wnt Signaling Pathway by Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7 Oncogenes in HPV16-Positive Oropharyngeal Squamous Carcinoma Cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2010, 8, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Moustafa, A.-E.; Foulkes, W.D.; Benlimame, N.; Wong, A.; Yen, L.; Bergeron, J.; Batist, G.; Alpert, L.; Alaoui-Jamali, M.A. E6/E7 proteins of HPV type 16 and ErbB-2 cooperate to induce neoplastic transformation of primary normal oral epithelial cells. Oncogene 2004, 23, 350–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanojia, D.; Vaidya, M.M. 4-Nitroquinoline-1-oxide induced experimental oral carcinogenesis. Oral Oncol. 2006, 42, 655–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, K.; Okazaki, Y.; Tonogi, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Yamane, G. Expression of β-catenin in rat oral epithelial dysplasia induced by 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide. Oral Oncol. 2002, 38, 772–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, I.; Sakaki, T.; Chaqour, B.; Howard, P.S.; Ikeo, T.; Macarak, E.J. Correlation of P-cadherin and β-catenin expression and phosphorylation with carcinogenesis in rat tongue cancer induced with 4-nitroquinoline 1-oxide. Oral Oncol. 2003, 39, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakita, D.; Matsuo, K. Alcohol and head and neck cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2017, 36, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osei-Sarfo, K.; Tang, X.-H.; Urvalek, A.M.; Scognamiglio, T.; Gudas, L.J. The molecular features of tongue epithelium treated with the carcinogen 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide and alcohol as a model for HNSCC. Carcinogenesis 2013, 34, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidya Priyadarsini, R.; Senthil Murugan, R.; Nagini, S. Aberrant activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway contributes to the sequential progression of DMBA-induced HBP carcinomas. Oral Oncol. 2012, 48, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemjabbar-Alaoui, H.; Dasari, V.; Sidhu, S.S.; Mengistab, A.; Finkbeiner, W.; Gallup, M.; Basbaum, C. Wnt and Hedgehog Are Critical Mediators of Cigarette Smoke-Induced Lung Cancer. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalley, A.J.; Abdul Majeed, A.A.; Pitty, L.P.; Major, A.G.; Farah, C.S. LGR5 expression in oral epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oral Surg. Oral Med. Oral Pathol. Oral Radiol. 2015, 119, 436–440.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Liu, S.; Duan, S.Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Shi, C.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, Z. Targeting the c-Met/FZD8 Signaling Axis Eliminates Patient-Derived Cancer Stem-like Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 7546–7559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Chang, I.; Chen, Z.; Kang, M.; Wang, C.-Y. Characterization of Side Populations in HNSCC: Highly Invasive, Chemoresistant and Abnormal Wnt Signaling. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e11456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Ma, B.; Chen, J. Biological characteristics of CD133+ cancer stem cells derived from human laryngeal carcinoma cell line. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 2453–2462. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Koo, B.S.; Kim, J.M.; Huang, S.; Rho, Y.S.; Bae, W.J.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Moon, J.H.; Lim, Y.C. Wnt/β-catenin signalling maintains self-renewal and tumourigenicity of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma stem-like cells by activating Oct4. J. Pathol. 2014, 234, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Zeng, Q.; Yu, G.; Li, S.; Wang, C.-Y. Wnt/β-catenin signaling inhibits death receptor-mediated apoptosis and promotes invasive growth of HNSCC. Cell. Signal. 2006, 18, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, C.; Shi, L.; Huang, Y.; Shen, L.; Peng, H.; Zhu, X.; Zhou, G. Nanoparticle delivery of Wnt-1 siRNA enhances photodynamic therapy by inhibiting epithelial–mesenchymal transition for oral cancer. Biomater. Sci. 2017, 5, 494–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwai, S.; Yonekawa, A.; Harada, C.; Hamada, M.; Katagiri, W.; Nakazawa, M.; Yura, Y. Involvement of the Wnt-β-catenin pathway in invasion and migration of oral squamous carcinoma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2010, 37, 1095–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Wei, D.; Wang, W.; Shen, B.; Xu, S.; Cao, Y. TRAF4 enhances oral squamous cell carcinoma cell growth, invasion and migration by Wnt-β-catenin. Signaling pathway. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2015, 8, 11837–11846. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, Y.; Fan, M. Lentivirus-mediated gene silencing of beta-catenin inhibits growth of human tongue cancer cells: Beta-catenin silencing in tongue cancer. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2011, 40, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.W.; Lee, Y.S.; Nam, H.Y.; Han, M.W.; Kim, H.J.; Moon, S.Y.; Jeon, H.; Park, J.J.; Carey, T.E.; Chang, S.E.; et al. Knockdown of β-catenin controls both apoptotic and autophagic cell death through LKB1/AMPK signaling in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Cell. Signal. 2013, 25, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhee, C.-S.; Sen, M.; Lu, D.; Wu, C.; Leoni, L.; Rubin, J.; Corr, M.; Carson, D.A. Wnt and frizzled receptors as potential targets for immunotherapy in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Oncogene 2002, 21, 6598–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.; Li, N.; Guo, F.; Jian, X.-C.; Jiang, C.-H.; Yin, P.; Min, A.-J.; Huang, L. Twist-related protein 1 enhances oral tongue squamous cell carcinoma cell invasion through β-catenin signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 11, 2255–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Way, T.-D.; Huang, J.-T.; Chou, C.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Yang, M.-H.; Ho, C.-T. Emodin represses TWIST1-induced epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells by inhibiting the β-catenin and Akt pathways. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 366–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.-P.; Chen, S.-W.; Zhuang, S.-M.; Li, H.; Song, M. Galectin-3 Accelerates the Progression of Oral Tongue Squamous Cell Carcinoma via a Wnt/β-catenin-Dependent Pathway. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2013, 19, 461–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yue, D. CUL4B promotes aggressive phenotypes of HNSCC via the activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Cancer Med. 2019, 8, 2278–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, R.; Kasamatsu, A.; Koyama, T.; Fukumoto, C.; Kouzu, Y.; Higo, M.; Endo-Sakamoto, Y.; Ogawara, K.; Shiiba, M.; Tanzawa, H.; et al. Glutamate acid decarboxylase 1 promotes metastasis of human oral cancer by β-catenin translocation and MMP7 activation. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Xie, T.-X.; Zhao, M.; Jasser, S.; Younes, M.; Sano, D.; Lin, J.; Kupferman, M.; Santillan, A.; Patel, V.; et al. Reciprocal negative regulation between S100A7/psoriasin and β-catenin signaling plays an important role in tumor progression of squamous cell carcinoma of oral cavity. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3527–3538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anitha, P.; Priyadarsini, R.V.; Kavitha, K.; Thiyagarajan, P.; Nagini, S. Ellagic acid coordinately attenuates Wnt/β-catenin and NF-κB signaling pathways to induce intrinsic apoptosis in an animal model of oral oncogenesis. Eur. J. Nutr. 2013, 52, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavitha, K.; Kowshik, J.; Kishore, T.K.K.; Baba, A.B.; Nagini, S. Astaxanthin inhibits NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathways via inactivation of Erk/MAPK and PI3K/Akt to induce intrinsic apoptosis in a hamster model of oral cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830, 4433–4444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.-J.; Lai, G.-M.; Yeh, C.-T.; Lai, M.-T.; Shih, P.-H.; Chao, W.-J.; Whang-Peng, J.; Chuang, S.-E.; Lai, T.-Y. Honokiol Eliminates Human Oral Cancer Stem-Like Cells Accompanied with Suppression of Wnt/ β-Catenin Signaling and Apoptosis Induction. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, G.; Matta, A.; Fu, G.; Somasundaram, R.T.; Datti, A.; Walfish, P.G.; Ralhan, R. Anticancer activity of pyrithione zinc in oral cancer cells identified in small molecule screens and xenograft model: Implications for oral cancer therapy. Mol. Oncol. 2015, 9, 1720–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, A.; Siddharth, S.; Das, S.; Nayak, D.; Sethy, C.; Kundu, C.N. Nanoquinacrine caused apoptosis in oral cancer stem cells by disrupting the interaction between GLI1 and β-catenin through activation of GSK3β. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 330, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, Y.C.; Kang, H.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Choi, E.C. All-trans-retinoic acid inhibits growth of head and neck cancer stem cells by suppression of Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 3310–3318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleszcz, R.; Paluszczak, J.; Baer-Dubowska, W. The effect of niclosamide on the head and neck carcinoma cells survival and the expression of Wnt/β-catenin signaling and glycolysis pathway components. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2019, 76, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-H.; Xu, M.; Fu, L.-Q.; Chen, X.-Y.; Yang, F. The Antihelminthic Niclosamide Inhibits Cancer Stemness, Extracellular Matrix Remodeling, and Metastasis through Dysregulation of the Nuclear β-catenin/c-Myc axis in OSCC. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleszcz, R.; Szymańska, A.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V.; Baer-Dubowska, W.; Paluszczak, J. Inhibition of CBP/β-catenin and porcupine attenuates Wnt signaling and induces apoptosis in head and neck carcinoma cells. Cell. Oncol. 2019, 42, 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Pan, S.; Hsieh, M.H.; Ng, N.; Sun, F.; Wang, T.; Kasibhatla, S.; Schuller, A.G.; Li, A.G.; Cheng, D.; et al. Targeting Wnt-driven cancer through the inhibition of Porcupine by LGK974. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 20224–20229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmerli, D.; Cecconi, V.; Valenta, T.; Hausmann, G.; Cantù, C.; Restivo, G.; Hafner, J.; Basler, K.; van den Broek, M. WNT ligands control initiation and progression of human papillomavirus-driven squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3753–3762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goto, M.; Mitra, R.S.; Liu, M.; Lee, J.; Henson, B.S.; Carey, T.; Bradford, C.; Prince, M.; Wang, C.-Y.; Fearon, E.R.; et al. Rap1 Stabilizes -Catenin and Enhances β-Catenin-Dependent Transcription and Invasion in Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Head and Neck. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sogutlu, F.; Kayabasi, C.; Ozmen Yelken, B.; Asik, A.; Gasimli, R.; Dogan, F.; Yilmaz Süslüer, S.; Biray Avcı, C.; Gunduz, C. The effect of ICRT-3 on Wnt signaling pathway in head and neck cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2019, 120, 380–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluszczak, A.; Kleszcz, R.; Witczak, O.; Krajka-Kuźniak, V. The comparison of the effects of panobinostat and PKF118-310 on β-catenin-dependent transcription in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cell lines. Acta Pol. Pharm. Drug Res. 2020, 77, 77–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wend, P.; Fang, L.; Zhu, Q.; Schipper, J.H.; Loddenkemper, C.; Kosel, F.; Brinkmann, V.; Eckert, K.; Hindersin, S.; Holland, J.D.; et al. Wnt/β-catenin signalling induces MLL to create epigenetic changes in salivary gland tumours. EMBO J. 2013, 32, 1977–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartha, V.K.; Alamoud, K.A.; Sadykov, K.; Nguyen, B.-C.; Laroche, F.; Feng, H.; Lee, J.; Pai, S.I.; Varelas, X.; Egloff, A.M.; et al. Functional and genomic analyses reveal therapeutic potential of targeting β-catenin/CBP activity in head and neck cancer. Genome Med. 2018, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Q.; Fang, L.; Heuberger, J.; Kranz, A.; Schipper, J.; Scheckenbach, K.; Vidal, R.O.; Sunaga-Franze, D.Y.; Müller, M.; Wulf-Goldenberg, A.; et al. The Wnt-Driven Mll1 Epigenome Regulates Salivary Gland and Head and Neck Cancer. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 415–428.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Jia, X.; Xiong, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, N.; Deng, Y.; Luo, K.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Z.; et al. The 14-3-3σ/GSK3β/β-catenin/ZEB1 regulatory loop modulates chemo-sensitivity in human tongue cancer. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 20177–20189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, S.-J.; Yang, X.-N.; Qian, H.-Y. Antitumor effects of WNT2B silencing in GLUT1 overexpressing cisplatin resistant head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2014, 5, 300–308. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.W.; Nam, H.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Moon, S.Y.; Kim, M.R.; Lee, M.; Kim, G.C.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.Y. Effect of β-catenin silencing in overcoming radioresistance of head and neck cancer cells by antagonizing the effects of AMPK on Ku70/Ku80: β-Catenin Controls Radiation Sensitivity. Head Neck 2016, 38, E1909–E1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.W.; Roh, J.-L.; Jeong, E.-J.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-W.; Choi, S.-H.; Park, S.-K.; Kim, S.Y. Wnt signaling controls radiosensitivityvia cyclooxygenase-2-mediated Ku expression in head and neck cancer. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 122, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-F.; Liu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, G.-H. Research progress in the radioprotective effect of the canonical Wnt pathway. Cancer Biol. Med. 2013, 10, 61–71. [Google Scholar]

| Gene/Protein | Type of Alteration | Molecular Effects | Functional Significance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drivers of Wnt activation | ||||
| WNT ligands | overexpression | translocation of β-catenin | lymph node invasion | [61,62,63,64] |
| APC | mutational loss | stabilization of β-catenin | enhanced cell growth | [10,11,12,13,14,15,16] |
| FAT1 | mutational loss | reduced sequestration of β-catenin | enhanced cell growth, loss of cell adhesion | [60] |
| CDH1 | (epi)mutational loss | release of β-catenin from cell-cell junctions | enhanced cell growth, loss of cell adhesion | [51,55,57,58] |
| EGFR | overexpression | stabilization and nuclear translocation of β-catenin | enhanced cell proliferation | [13,18] |
| c-MET | overexpression | Wnt activation via FZD8 | increased stemness | [99] |
| SFRP1-5 | epigenetic silencing | reduced Wnt ligand sequestration | worse prognosis | [73] |
| WIF-1 | epigenetic silencing | reduced Wnt ligand sequestration | worse prognosis | [73,77] |
| HPV E6/E7 oncogenes | overexpression | stabilization of β-catenin | neoplastic transformation | [47,89] |
| β-catenin | nuclear accumulation | enhanced expression of Wnt target genes (CCND1, c-MYC, MMP7) | invasiveness, lymph node metastasis, recurrence, dedifferentiation | [26,28,38,42,44,45,46,47,48] |
| LEF1 | overexpression | transcriptional activation | lymph node invasion | [25,65] |
| Targets for therapeutic inhibition of Wnt signaling | ||||
| WNT-1 | knockdown | reduced Vimentin expression | inhibition of epithelial-to- mesenchymal transition | [104] |
| inhibition by antibody | reduced expression of Wnt target genes | reduced HNSCC cell viability | [109] | |
| FZD-DVL complex | niclosamide | altered gene expression | reduced stemness | [123] |
| β-catenin | knockdown | decreased gene expression of CCND1, c-MYC, MMP-7 | reduced stemness | [102] |
| decreased cell invasion | [106] | |||
| cell cycle arrest, reduced cell migration, induction of apoptosis | [51,107] | |||
| decreased cisplatin resistance | [102] | |||
| increased radiosensitivity | [135] | |||
| Porcupine | IWP-2 inhibitor | inhibition of UCA1- dependent Wnt activation | reduced cell proliferation and migration | [84] |
| LGK974 inhibitor | reduced Wnt target gene expression | reduced tumor growth | [125] | |
| C59 inhibitor | reduced secretion of WNT-3A, reduced CCND1 and BIRC5 expression | impaired HPV-driven transformation | [126] | |
| CBP | ICG-001 inhibitor | altered gene expression | cell cycle arrest, induction of apoptosis, reduced stemness, tumor growth and metastasis | [130,131] |
| PI3K pathway | emodin | inhibition of PI3K/Akt/ β-catenin pathway | reduced cell invasiveness | [111] |
| pyrithione zinc | reduced expression of CCND1 and c-MYC | reduced cell proliferation and invasion, apoptosis | [119] | |
| CUL4B | knockdown | reduced expression of CCND1, c-MYC, MMP-7 | reduced cell growth, migration and invasion | [113] |
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Paluszczak, J. The Significance of the Dysregulation of Canonical Wnt Signaling in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cells 2020, 9, 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030723
Paluszczak J. The Significance of the Dysregulation of Canonical Wnt Signaling in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cells. 2020; 9(3):723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030723
Chicago/Turabian StylePaluszczak, Jarosław. 2020. "The Significance of the Dysregulation of Canonical Wnt Signaling in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas" Cells 9, no. 3: 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030723
APA StylePaluszczak, J. (2020). The Significance of the Dysregulation of Canonical Wnt Signaling in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinomas. Cells, 9(3), 723. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9030723





