Delayed Demyelination and Impaired Remyelination in Aged Mice in the Cuprizone Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Induction of De- and Remyelination
2.3. Tissue Processing
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
2.5. Determination of Demyelination and Quantification of Glial Reaction
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. The Standard 0.2% Cuprizone Treatment is Not Sufficient to Induce Demyelination of the Corpus Callosum in Aged Mice
3.2. Feeding of 0.4% Cuprizone for 6.5 Weeks Results in Complete Demyelination of the Corpus Callosum in Aged Mice
3.3. Cuprizone Treatment Leads to Significant Oligodendrocyte Loss Independent of Cuprizone Concentration
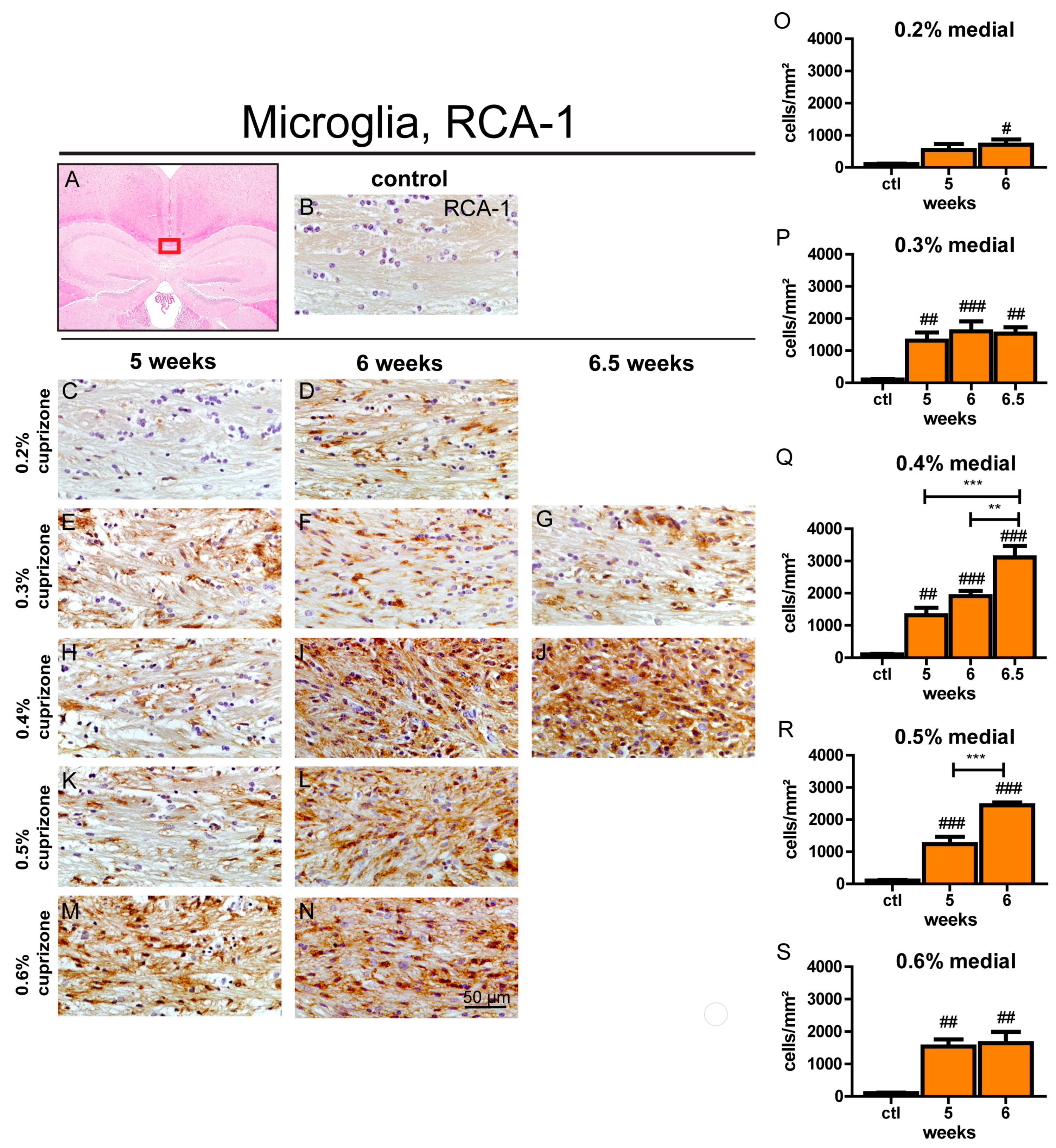
3.4. Maximum Microglia Activation and Accumulation is Evident after 6.5 Weeks with 0.4% Cuprizone Treatment
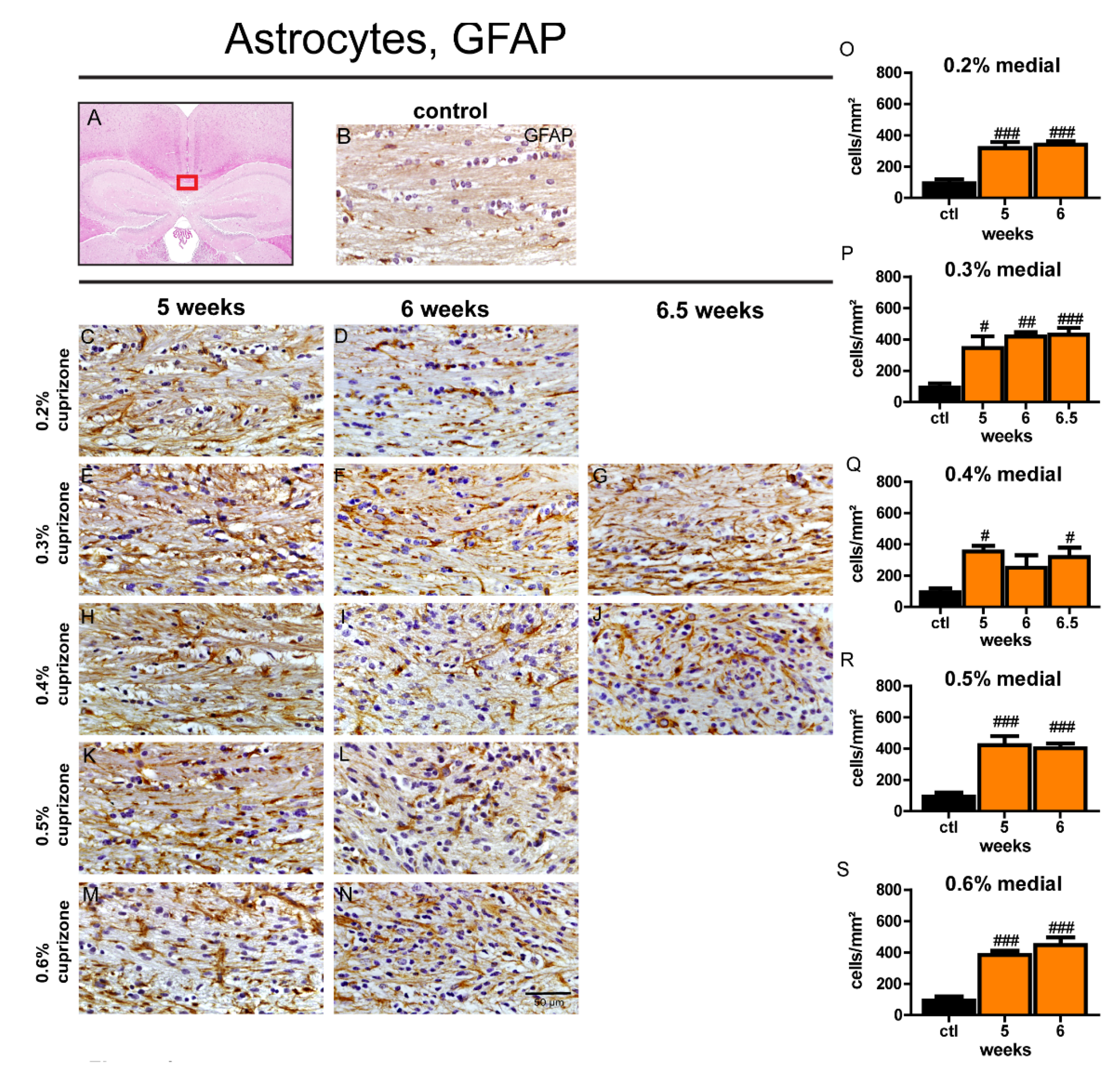
3.5. The Extent of Astrocytosis is Independent of Duration and Dose of Cuprizone Treatment
3.6. Aged Mice Show Rapid Induction of Remyelination but Remyelination Remains Incomplete
3.7. Repopulation of Oligodendrocytes in the Corpus Callosum during Remyelination is Less Efficient Compared to Young Mice
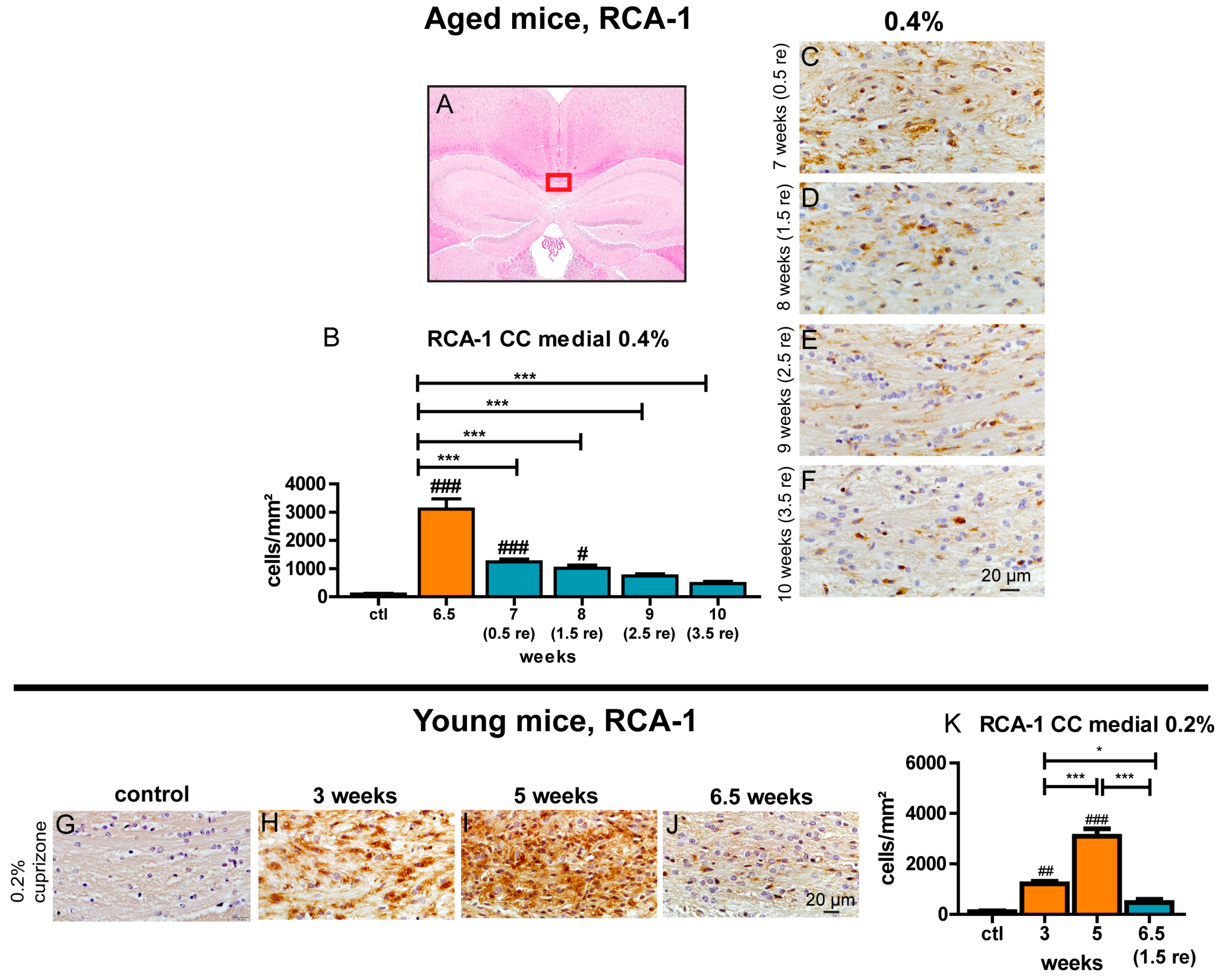
3.8. Prolonged Activation of Microglia during the Recovery Period
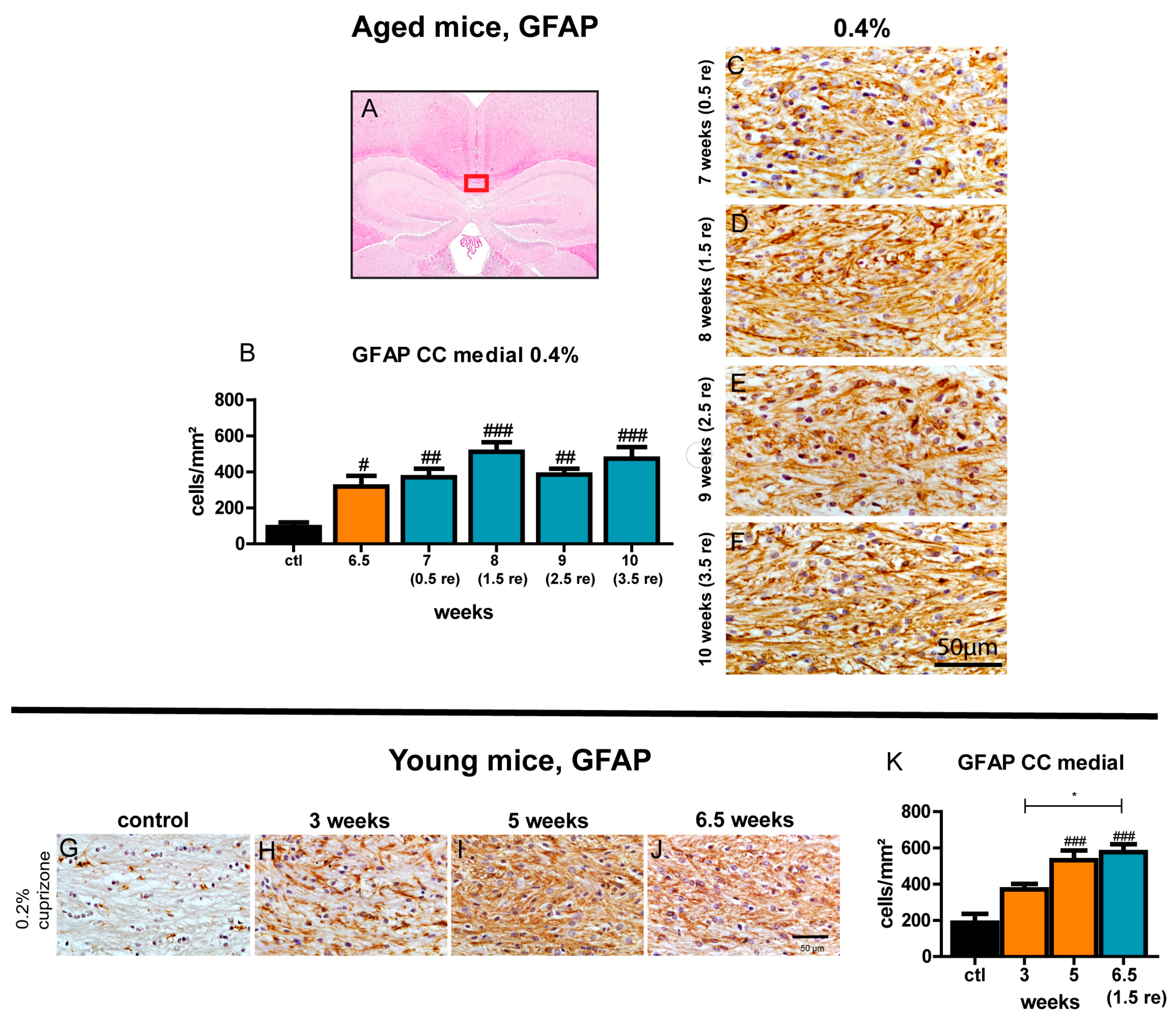
3.9. Astrogliosis Remains Unchanged Despite Ongoing Remyelination
3.10. Axonal Pathology Occurs during Cuprizone-Induced Demyelination in Aged Mice and Corresponds to Microglia Activation
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lassmann, H. Multiple Sclerosis Pathology. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8, a028936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Smith, K.J.; Blakemore, W.F.; McDonald, W.I. Central remyelination restores secure conduction. Nature 1979, 280, 395–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, I.D.; Brower, A.; Kondo, Y.; Curlee, J.F., Jr.; Schultz, R.D. Extensive remyelination of the CNS leads to functional recovery. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 6832–6836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeffery, N.D.; Blakemore, W.F. Locomotor deficits induced by experimental spinal cord demyelination are abolished by spontaneous remyelination. Brain 1997, 120, 27–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, F.; Lehmann-Horn, K.; Shen, Y.A.; Rankin, K.A.; Stebbins, K.J.; Lorrain, D.S.; Pekarek, K.; Sagan, A.S.; Xiao, L.; Teuscher, C.; et al. Accelerated remyelination during inflammatory demyelination prevents axonal loss and improves functional recovery. Elife 2016, 5, e18246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, K.A.; Blakemore, W.F. Remyelination protects axons from demyelination-associated axon degeneration. Brain 2008, 131, 1464–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Franklin, R.J.M.; Ffrench-Constant, C. Regenerating CNS myelin—from mechanisms to experimental medicines. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2017, 18, 753–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patrikios, P.; Stadelmann, C.; Kutzelnigg, A.; Rauschka, H.; Schmidbauer, M.; Laursen, H.; Sorensen, P.S.; Bruck, W.; Lucchinetti, C.; Lassmann, H. Remyelination is extensive in a subset of multiple sclerosis patients. Brain 2006, 129, 3165–3172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Goldschmidt, T.; Antel, J.; Konig, F.B.; Bruck, W.; Kuhlmann, T. Remyelination capacity of the MS brain decreases with disease chronicity. Neurology 2009, 72, 1914–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skripuletz, T.; Manzel, A.; Gropengiesser, K.; Schafer, N.; Gudi, V.; Singh, V.; Salinas Tejedor, L.; Jorg, S.; Hammer, A.; Voss, E.; et al. Pivotal role of choline metabolites in remyelination. Brain 2015, 138, 398–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hiremath, M.M.; Saito, Y.; Knapp, G.W.; Ting, J.P.; Suzuki, K.; Matsushima, G.K. Microglial/macrophage accumulation during cuprizone-induced demyelination in C57BL/6 mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 1998, 92, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skripuletz, T.; Gudi, V.; Hackstette, D.; Stangel, M. De- and remyelination in the CNS white and grey matter induced by cuprizone: The old, the new, and the unexpected. Histol. Histopathol. 2011, 26, 1585–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flurkey, K.; Currer, J.M.; Harrison, D.E. Mouse Models in Aging Research. In The Mouse in Biomedical Research, 2nd ed.; Fox, J., Barthold, S., Davisson, M., Newcomer, C., Quimby, F., Smith, A., Eds.; Elsevier: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 3, pp. 637–672. [Google Scholar]
- Goodin, D.S. The epidemiology of multiple sclerosis: Insights to disease pathogenesis. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2014, 122, 231–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Sengupta, P. Men and mice: Relating their ages. Life Sci. 2016, 152, 244–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, S.A.; Gilson, J.M.; Blakemore, W.F.; Franklin, R.J. Remyelination occurs as extensively but more slowly in old rats compared to young rats following gliotoxin-induced CNS demyelination. Glia 1999, 28, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chari, D.M.; Crang, A.J.; Blakemore, W.F. Decline in rate of colonization of oligodendrocyte progenitor cell (OPC)-depleted tissue by adult OPCs with age. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2003, 62, 908–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruckh, J.M.; Zhao, J.W.; Shadrach, J.L.; van Wijngaarden, P.; Rao, T.N.; Wagers, A.J.; Franklin, R.J. Rejuvenation of regeneration in the aging central nervous system. Cell Stem Cell 2012, 10, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cantuti-Castelvetri, L.; Fitzner, D.; Bosch-Queralt, M.; Weil, M.T.; Su, M.; Sen, P.; Ruhwedel, T.; Mitkovski, M.; Trendelenburg, G.; Lutjohann, D.; et al. Defective cholesterol clearance limits remyelination in the aged central nervous system. Science 2018, 359, 684–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Neumann, B.; Baror, R.; Zhao, C.; Segel, M.; Dietmann, S.; Rawji, K.S.; Foerster, S.; McClain, C.R.; Chalut, K.; van Wijngaarden, P.; et al. Metformin Restores CNS Remyelination Capacity by Rejuvenating Aged Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 25, 473–485.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blakemore, W.F. Remyelination of the superior cerebellar peduncle in old mice following demyelination induced by cuprizone. J. Neurol. Sci. 1974, 22, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irvine, K.A.; Blakemore, W.F. Age increases axon loss associated with primary demyelination in cuprizone-induced demyelination in C57BL/6 mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 2006, 175, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Sandoval, J.; Swiss, V.A.; Li, J.; Dupree, J.; Franklin, R.J.; Casaccia-Bonnefil, P. Age-dependent epigenetic control of differentiation inhibitors is critical for remyelination efficiency. Nat. Neurosci. 2008, 11, 1024–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Doucette, J.R.; Jiao, R.; Nazarali, A.J. Age-related and cuprizone-induced changes in myelin and transcription factor gene expression and in oligodendrocyte cell densities in the rostral corpus callosum of mice. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2010, 30, 607–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, J.L.; Jones, J.J.; Taniike, M.; Morell, P.; Suzuki, K.; Matsushima, G.K. Mature oligodendrocyte apoptosis precedes IGF-1 production and oligodendrocyte progenitor accumulation and differentiation during demyelination/remyelination. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 61, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudi, V.; Gingele, S.; Skripuletz, T.; Stangel, M. Glial response during cuprizone-induced de- and remyelination in the CNS: Lessons learned. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mahler, M.; Berard, M.; Feinstein, R.; Gallagher, A.; Illgen-Wilcke, B.; Pritchett-Corning, K.; Raspa, M. FELASA recommendations for the health monitoring of mouse, rat, hamster, guinea pig and rabbit colonies in breeding and experimental units. Lab. Anim. 2014, 48, 178–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudi, V.; Gai, L.; Herder, V.; Tejedor, L.S.; Kipp, M.; Amor, S.; Suhs, K.W.; Hansmann, F.; Beineke, A.; Baumgartner, W.; et al. Synaptophysin Is a Reliable Marker for Axonal Damage. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2017, 76, 109–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudi, V.; Moharregh-Khiabani, D.; Skripuletz, T.; Koutsoudaki, P.N.; Kotsiari, A.; Skuljec, J.; Trebst, C.; Stangel, M. Regional differences between grey and white matter in cuprizone induced demyelination. Brain Res. 2009, 1283, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skripuletz, T.; Hackstette, D.; Bauer, K.; Gudi, V.; Pul, R.; Voss, E.; Berger, K.; Kipp, M.; Baumgartner, W.; Stangel, M. Astrocytes regulate myelin clearance through recruitment of microglia during cuprizone-induced demyelination. Brain 2013, 136, 147–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paxinos, G.; Franklin, K.B.J.; Franklin, K.B.J. The mouse brain in stereotaxic coordinates, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Lindner, M.; Heine, S.; Haastert, K.; Garde, N.; Fokuhl, J.; Linsmeier, F.; Grothe, C.; Baumgartner, W.; Stangel, M. Sequential myelin protein expression during remyelination reveals fast and efficient repair after central nervous system demyelination. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2008, 34, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudi, V.; Skuljec, J.; Yildiz, O.; Frichert, K.; Skripuletz, T.; Moharregh-Khiabani, D.; Voss, E.; Wissel, K.; Wolter, S.; Stangel, M. Spatial and temporal profiles of growth factor expression during CNS demyelination reveal the dynamics of repair priming. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skuljec, J.; Gudi, V.; Ulrich, R.; Frichert, K.; Yildiz, O.; Pul, R.; Voss, E.V.; Wissel, K.; Baumgartner, W.; Stangel, M. Matrix metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors in cuprizone-induced demyelination and remyelination of brain white and gray matter. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2011, 70, 758–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acs, P.; Kipp, M.; Norkute, A.; Johann, S.; Clarner, T.; Braun, A.; Berente, Z.; Komoly, S.; Beyer, C. 17beta-estradiol and progesterone prevent cuprizone provoked demyelination of corpus callosum in male mice. Glia 2009, 57, 807–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stangel, M.; Kuhlmann, T.; Matthews, P.M.; Kilpatrick, T.J. Achievements and obstacles of remyelinating therapies in multiple sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 742–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilson, J.; Blakemore, W.F. Failure of remyelination in areas of demyelination produced in the spinal cord of old rats. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 1993, 19, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natrajan, M.S.; de la Fuente, A.G.; Crawford, A.H.; Linehan, E.; Nunez, V.; Johnson, K.R.; Wu, T.; Fitzgerald, D.C.; Ricote, M.; Bielekova, B.; et al. Retinoid X receptor activation reverses age-related deficiencies in myelin debris phagocytosis and remyelination. Brain 2015, 138, 3581–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sim, F.J.; Zhao, C.; Penderis, J.; Franklin, R.J. The age-related decrease in CNS remyelination efficiency is attributable to an impairment of both oligodendrocyte progenitor recruitment and differentiation. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 2451–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hinks, G.L.; Franklin, R.J. Delayed changes in growth factor gene expression during slow remyelination in the CNS of aged rats. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2000, 16, 542–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gingele, S.; Henkel, F.; Heckers, S.; Moellenkamp, T.M.; Hümmert, M.W.; Skripuletz, T.; Stangel, M.; Gudi, V. Delayed Demyelination and Impaired Remyelination in Aged Mice in the Cuprizone Model. Cells 2020, 9, 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040945
Gingele S, Henkel F, Heckers S, Moellenkamp TM, Hümmert MW, Skripuletz T, Stangel M, Gudi V. Delayed Demyelination and Impaired Remyelination in Aged Mice in the Cuprizone Model. Cells. 2020; 9(4):945. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040945
Chicago/Turabian StyleGingele, Stefan, Florian Henkel, Sandra Heckers, Thiemo M. Moellenkamp, Martin W. Hümmert, Thomas Skripuletz, Martin Stangel, and Viktoria Gudi. 2020. "Delayed Demyelination and Impaired Remyelination in Aged Mice in the Cuprizone Model" Cells 9, no. 4: 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040945
APA StyleGingele, S., Henkel, F., Heckers, S., Moellenkamp, T. M., Hümmert, M. W., Skripuletz, T., Stangel, M., & Gudi, V. (2020). Delayed Demyelination and Impaired Remyelination in Aged Mice in the Cuprizone Model. Cells, 9(4), 945. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040945





