Chromosome Dynamics Regulating Genomic Dispersion and Alteration of Nucleolus Organizer Regions (NORs)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Methods Used for Inferring Genomic Dispersion Mechanism
3. Relationship of rDNA and Other Repeat Arrays
4. Manifestations of Chromosomal Configuration in Meiotic Prophase
5. Conditions of the “Molecular Effect” System of Genomic Dispersion
6. Variation in rDNA Loci
7. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Montgomery, T.H. Comparative cytological studies, with especial regard to the morphology of the nucleolus. J. Morphol. 1898, 15, 265–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ghosh, S. The nucleolar structure. Int. Rev. Cytol. 1976, 44, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sumner, A.T.; Unwin, H. Chromosome banding. Trends Genet. 1990, 7, 306. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, A.S.; Warburton, D.; Atwood, K.C. Location of ribosomal DNA in the human chromosome complement. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1972, 69, 3394–3398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hsu, T.C.; Spirito, S.E.; Pardue, M.L. Distribution of 18 + 28S ribosomal genes in mammalian genomes. Chromosoma 1975, 53, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.N. The structure and organization of human ribosomal genes. In The Cell Nucleus; Bush, X.H., Rothblum, L., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1982; Volume 10, pp. 287–318. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, A.S.; Warburton, D.; Megraw-Ripley, S.; Atwood, K.C. The chromosomal location of rDNA in selected lower primates. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1977, 19, 281–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodpasture, C.; Bloom, S.E. Visualization of nucleolar organizer regions in mammalian chromosomes using silver staining. Chromosoma 1975, 53, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, W.M.; Denton, T.E.; Diamond, J.R. Differential staining of the satellite regions of human acrocentric chromosomes. Experientia 1975, 15, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buys, C.H.C.M.; Osinga, J. Abundance of protein-bound sulfhydryl and disulfide groups at chromosomal nucleolus organizing regions. Chromosoma 1980, 77, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tantravahi, R.; Miller, D.A.; Dev, V.G.; Miller, O.J. Detection of nucleolus organizer regions in chromosomes of human, chimpanzee, gorilla, orangutan and gibbon. Chromosoma 1976, 56, 15–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohno, S.; Trujilo, J.M.; Kaplan, W.D.; Kinosita, R. Nucleolus-organizers in the causation of chromosomal anomalies in man. Lancet 1961, 2, 123–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, S.R.; Lubs, H.A. Non-random association of human acrocentric chromosomes. Humangenetik 1971, 13, 157–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, E.A.; Martin, S.L.; Beverley, S.M.; Kan, Y.W.; Wilson, A.C. Rapid duplication and loss of genes coding for the α chains of hemoglobin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 2158–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dover, G.; Coen, E. Springcleaning ribosomal DNA: A model for multigene evolution? Nature 1981, 290, 731–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnheim, N.; Krystal, M.; Schmickel, R.; Wilson, G.; Ryder, O.; Zimmer, E. Molecular evidence for genetic exchanges among ribosomal genes on nonhomologous chromosomes in man and apes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1980, 77, 7323–7327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maeda, N.; Smithies, O. The evolution of multigene families: Human haptoglobin genes. Ann. Rev. Genet. 1986, 20, 81–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlötterrere, C.; Tautz, D. Chromosomal homogeneity of Drosophila ribosomal DNA arrays suggested intrachromosomal exchanges drive concerted evolution. Curr. Biol. 1994, 4, 777–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H.; Taguchi, T.; Godwin, A.K. Genomic differentiation of 18S ribosomal DNA and ß-satellite DNA in the hominoid and its evolutionary aspects. Chromosome Res. 1999, 7, 531–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H.; Yamamoto, M.-T.; Ogura, K.; Satta, Y.; Yamada, M.; Taylor, R.W.; Imai, H.T. Multiplication of 28S rDNA and NOR activity in chromosome evolution among ants of the Myrmecia pilosula species complex. Chromosoma 1994, 103, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, H.T.; Taylor, R.W.; Crosland, M.W.; Crozier, R.H. Modes of spontaneous chromosomal mutation and karyotype evolution in ants with reference to the minimum interaction hypothesis. Jpn. J. Genet. 1988, 63, 159–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hirai, H.; Matsubayashi, K.; Kumazaki, K.; Kato, A.; Maeda, N.; Kim, H.-S. Chimpanzee chromosomes: Retrotransposable compound repeat DNA organization (RCRO) and its influence on meiotic prophase and crossing-over. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2005, 108, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, H.; Hirai, Y. FISH mapping for helminth genome. In Methods in Molecular Biology; Melville, S.E., Ed.; Humana Press: Totowana, NJ, USA, 2004; pp. 379–394. [Google Scholar]
- Imai, H.T.; Taylor, R.W. Chromosomal polymorphisms involving telomere fusion, centromeric inactivation and centromere shift in the ant Myrmecia (pilosula) n = 1. Chromosoma 1989, 98, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H.; Hirai, Y.; Udono, T.; Matsubayashi, K.; Tosi, A.J.; Koga, A. Structural variation of subterminal satellite blocks and their source mechanisms as inferred from the meiotic configurations of chimpanzee chromosome terminal. Chromosome Res. 2019, 27, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schempp, W.; Zeitler, S.; Reitschel, W. Chromosomal localization of rDNA in the gorilla. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1998, 80, 185–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yunis, J.; Prakash, O. The origin of man: A chromosomal pictorial legacy. Science 1982, 215, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scherthan, H. A bouquet makes ends meet. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 621–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suderakis, M.; Tarsounds, M. Telomere regulation and function during meiosis. Chromosome Res. 2007, 15, 667–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schethan, H.; Jerratsch, M.; Li, B.; Smith, S.; Hulten, M.; Lock, T.; de Lange, T. Mammalian meiotic telomeres: Protein composition and redistribution in relation to nuclear pores. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 4189–4203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shibuya, H.; Ishiguro, K.; Watanabe, Y. The TRF1-binding protein TERB1 promotes chromosome movement and telomere rigidity in meiosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, L.; Smith, G.R. The meiotic bouquet promotes homolog interactions and restricts ectopic recombination in Schizosaccaromyces pombe. Genetics 2006, 174, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hiraoka, Y.; Dernburg, A.F. The SUN rises on meiotic chromosome dynamics. Dev. Cell 2009, 17, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armstrong, S.J.; Franklin, C.F.; Jones, G.H. Nucleolus-associated telomere clustering and paring precede meiotic chromosome synapsis in Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 4207–4217. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vader, G.; Blitzblau, H.G.; Tame, M.A.; Falk, J.E.; Curtin, L.; Hochwagen, A. Protection of repetitive DNA borders from self-induced meiotic instability. Nature 2012, 477, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- van Sluis, M.; McStay, B. A localized nucleolar DNA damage response facilitates recuruitment of the homology-directed repair machinery independent of cell cycle stage. Genes Dev. 2015, 29, 1151–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cechova, M.; Harris, R.S.; Tomaszliewicz, M.; Arbeithuber, B.; Chiaromonte, F.; Makova, K.D. High satellite repeat turnover in Grate apes studied with short- and long-read technologies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 2415–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imai, H.T. On-Line Monograph: The Minimum Interaction Theory. Available online: https://minimum-interaction-theory.jimdofree.com/ (accessed on 15 September 2018).
- Zang, K.D.; Back, E. Quantitative studies on the arrangement of human metaphase chromosomes. I. Individual features in the association pattern of the acrocentric chromosomes of normal males and females. Cytogenetics 1968, 7, 455–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Müller, H.J.; Stasch, S.; Engel, W. Silver staining of nucleolus organizer regions during human spermatogenesis. Hum. Genet. 1983, 64, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmid, M.; Grunert, D.; Haaf, T.; Engel, W. A direct demonstration of somatically paired heterochromatin of human chromosomes. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1983, 36, 554–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, D.J.; Palmer, C.G.; Melman, A. Nonhomologous associations of C-heterochromatin at human male meiotic prophase. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1979, 23, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuck-Muller, C.M.; Bordson, B.L.; Varela, M.; Bennet, J.W. NOR association with heterochromatin. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 1984, 38, 165–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guillén, A.K.Z.; Hirai, Y.; Tanoue, T.; Hirai, H. Transcriptional repression mechanisms of nucleolus organizer regions (NORs) in humans and chimpanzees. Chromosome Res. 2004, 12, 225–237. [Google Scholar]
- Gerbault-Seureau, M.; Cacheux, L.; Dutrillaux, B. The relationship between the (In-)Stability of NORs and their chromosomal location: The example of Cercopithecidae and a short review of other primates. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2017, 153, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, H.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kawamoto, Y.; Tokita, E. Tandem duplication of nucleolus organizer region (NOR) in the Japanese macaque, Macaca fuscata fuscata. Chromosome Res. 1998, 6, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirai, H.; Yamamoto, M.T.; Taylor, R.W.; Imai, H.T. Genomic dispersion of 28S rDNA during karyotype evolution in the ant genus Myrmecia (Formicidae). Chromosoma 1996, 105, 190–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, H.T.; Taylor, R.W.; Crozier, R.H. Experimental bases for the minimum interaction theory.1. Chromosome evolution in the ant Myrmecia pilosula species complex. Jpn. J. Genet. 1994, 69, 137–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Royle, N.J.; Baird, D.M.; Jefferys, A.J. A subterminal satellite located adjacent to telomeres in chimpanzees is absent from the human genome. Nat. Genet. 1994, 6, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schempp, W.; Toder, R.; Reitschel, W.; Grützner, F.; Mayerová, A.; Gauckler, A. Inverted and satellited Y chromosome in the orangutan (Pongo pygmaeus). Chromosome Res. 1993, 1, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meneveri, R.; Agresti, A.; Rocchi, M.; Marozzi, A.; Ginelli, E. Analysis of GC-rich repetitive nucleotide sequences in great apes. J. Mol. Evol. 1995, 40, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assum, G.; Pasantes, J.; Glaser, B.; Schempp, W.; Wohr, G. Concerted evolution of members of the multisequence family chAB4 located on various nonhomologous chromosomes. Mamm. Genome 1998, 9, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Sluis, M.; Gailín, M.Ó.; McCarter, J.G.W.; Mangan, H.; Grob, A.; McStay, B. Human NORs, comprising rDNA arrays and functionally conserved distal elements, are located within dynamic chromosomal regions. Genes Dev. 2019, 33, 1688–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floutsakou, I.; Agrawal, S.; Nguyen, T.T.; Seoighe, C.; Ganley, A.R.D.; McStay, B. The shared genomic architecture of human nucleolar organizer regions. Genome Res. 2013, 23, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scherthan, H. Telomere attachment and clustering during meiosis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harper, L.; Golubovskaya, I.; Cande, W.Z. A bouquet of chromosome. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 4025–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jacobs, P.A.; Melville, M.; Ratcliffe, S.; Keay, A.J.; Syme, J. A cytogenetic survaey of 11,680 newborn infants. Ann. Hum. Genet. 1974, 37, 359–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, P.A.; Mayer, M.; Morton, N.E. Acrocentric chromosome associations in man. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1976, 28, 567–576. [Google Scholar]
- Baicharoen, S.; Hirai, Y.; Srikulnath, K.; Kongprom, U.; Hirai, H. Hypervariability of nucleolus organizer regions in Bengal slow lorises, Nyctcebus bengalensis (Primates, Lorisidae). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2016, 149, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, A.S.; Atwood, K.C.; Warburton, D. Chromosomal distribution of rDNA in Pan paniscus, Gorilla gorilla beringei, and Symphalangus syndactylus: Comparison to related primates. Chromosoma 1976, 59, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giusto, J.P.; Margulis, L. Karyotypic fission theory and the evolution of old world monkeys and apes. BioSystems 1981, 13, 267–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirai, H.; Hirai, Y.; Kawamoto, Y.; Endo, H.; Kimura, J.; Rerkamnuaychoke, W. Cytogenetic differentiation of two sympatric tree shrew taxa found in the southern part of the Isthmus of Kra. Chromosome Res. 2002, 10, 313–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardhan, A.; Sharma, A. Dynamic of nucleolus organizer regions and karyotype evolution in Indian pygmy field mice. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 2000, 91, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskina, O.; Belyayev, A.; Nevo, E. Activity of the En/Spm-like transposon in meiosis as a base for chromosome repatterning in a small, isolated, peripheral population of Aegilops speltoides Tausch. Chromosome Res. 2004, 12, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Datson, P.M.; Murray, B.G. Ribosomal DNA locus evolution in Nemesia: Transposition rather than structural rearrangement as the key mechanism? Chromosome Res. 2006, 14, 845–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, I.; Wobus, U. In situ hybridization confirms jumping nucleolus organizing regions in Allium. Chromosoma 1985, 92, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricroch, A.; Peffley, E.B.; Baker, R.J. Chromosomal location of rDNA in Allium: In situ hybridization using biotin- and fluorescein-labelled probe. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1992, 83, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raskina, O.; Barber, J.C.; Nevo, E.; Belyayev, A. Repetitive DNA and chromosomal rearrangements: Speciation-related events in plant genomes. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2008, 120, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eickbush, T.H.; Eickbush, D.G. Finely orchestrated movements: Evolution of the ribosomal RNA genes. Genetics 2007, 175, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dutrillaux, A.-M.; Dutrilaux, B. Chromosome analysis of 82 species of Scarabaeoidaea (Coleoptera), with special focus on NOR localization. Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2012, 136, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutrillaux, A.-M.; Carton, B.; Cacheux, L.; Dutrillaux, B. Interstitial NORs, fragile sites, and chromosome evolution: A not so simple relationship—The example of Melolontha melolontha and genus Protaetia (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2016, 149, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roa, F.; Guerra, M. Distribution of 45S rDNA sites in chromosomes of plants: Structural and evolutionary implications. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cazaux, B.; Catalan, J.; Veyrunes, F.; Douzery, E.J.P.; Britton-Davidian, J. Are ribosomal DNA clusters rearrangement hotspots? A case study in the genus Mus (Rodentia, Muridae). BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Imai, H.T.; Wada, M.Y.; Hirai, H.; Matsuda, Y.; Tsuchiya, K. Cytological, genetic and evolutionary functions of chiasmata based on chiasma graph analysis. J. Theor. Biol. 1999, 198, 239–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, R.; Grummt, I. Molecular mechanisms mediating methylation-dependent silencing of ribosomal gene transcription. Mol. Cell 2001, 8, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalmárová, M.; Sminrov, E.; Masata, M.; Koberna, K.; Ligasová, A.; Popov, A.; Raska, I. Positioning of NORs and NOR-bearing chromosomes in relation to nucleoli. J. Struct. Biol. 2007, 160, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerqueira, A.V.; Lemos, B. Ribosomal DNA and the nucleolus as keystones of nuclear architecture, organization, and function. Trends Genet. 2019, 35, 710–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
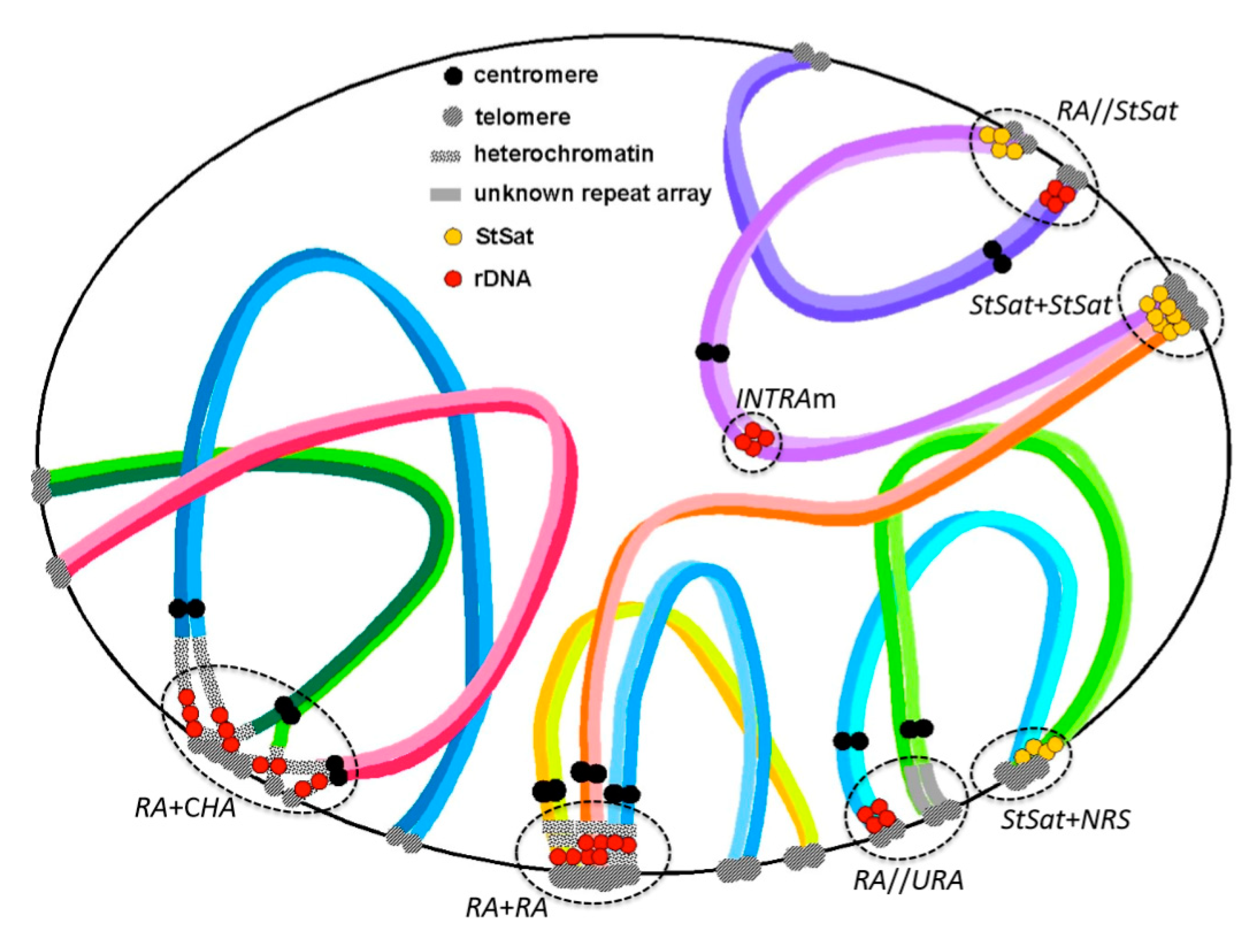


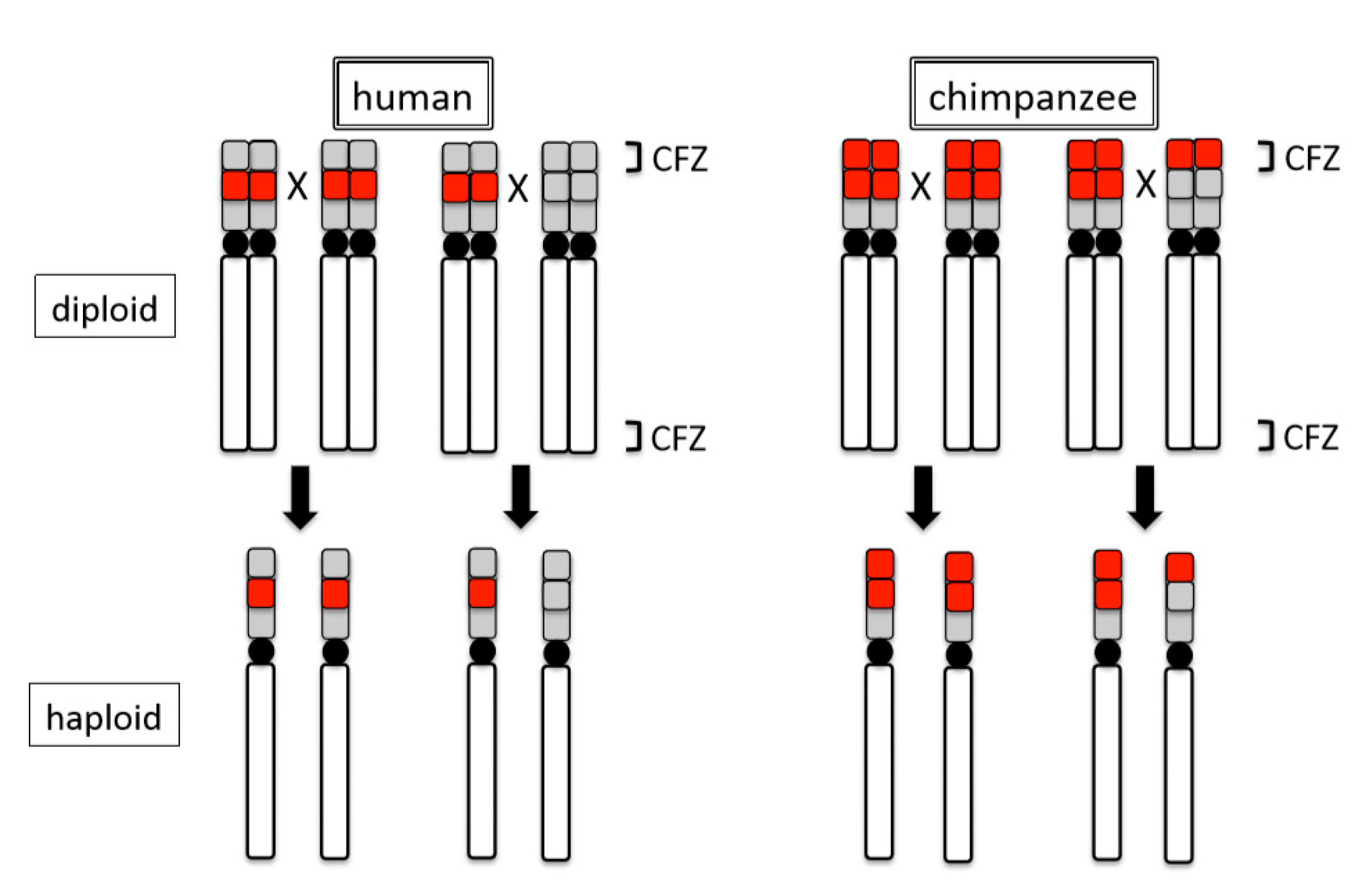
© 2020 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hirai, H. Chromosome Dynamics Regulating Genomic Dispersion and Alteration of Nucleolus Organizer Regions (NORs). Cells 2020, 9, 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040971
Hirai H. Chromosome Dynamics Regulating Genomic Dispersion and Alteration of Nucleolus Organizer Regions (NORs). Cells. 2020; 9(4):971. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040971
Chicago/Turabian StyleHirai, Hirohisa. 2020. "Chromosome Dynamics Regulating Genomic Dispersion and Alteration of Nucleolus Organizer Regions (NORs)" Cells 9, no. 4: 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040971
APA StyleHirai, H. (2020). Chromosome Dynamics Regulating Genomic Dispersion and Alteration of Nucleolus Organizer Regions (NORs). Cells, 9(4), 971. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9040971



