Large-Scale Profiling of Signaling Pathways Reveals a Distinct Demarcation between Normal and Extended Liver Resection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Animal Surgery
2.3. Liver and RNA Isolation
2.4. cDNA Library Construction and RNA Deep Sequencing
2.5. Functional Annotation of Gene Expression Data
2.6. Source Datasets
2.7. Statistical Tests
2.8. miRNA Target Prediction
3. Results
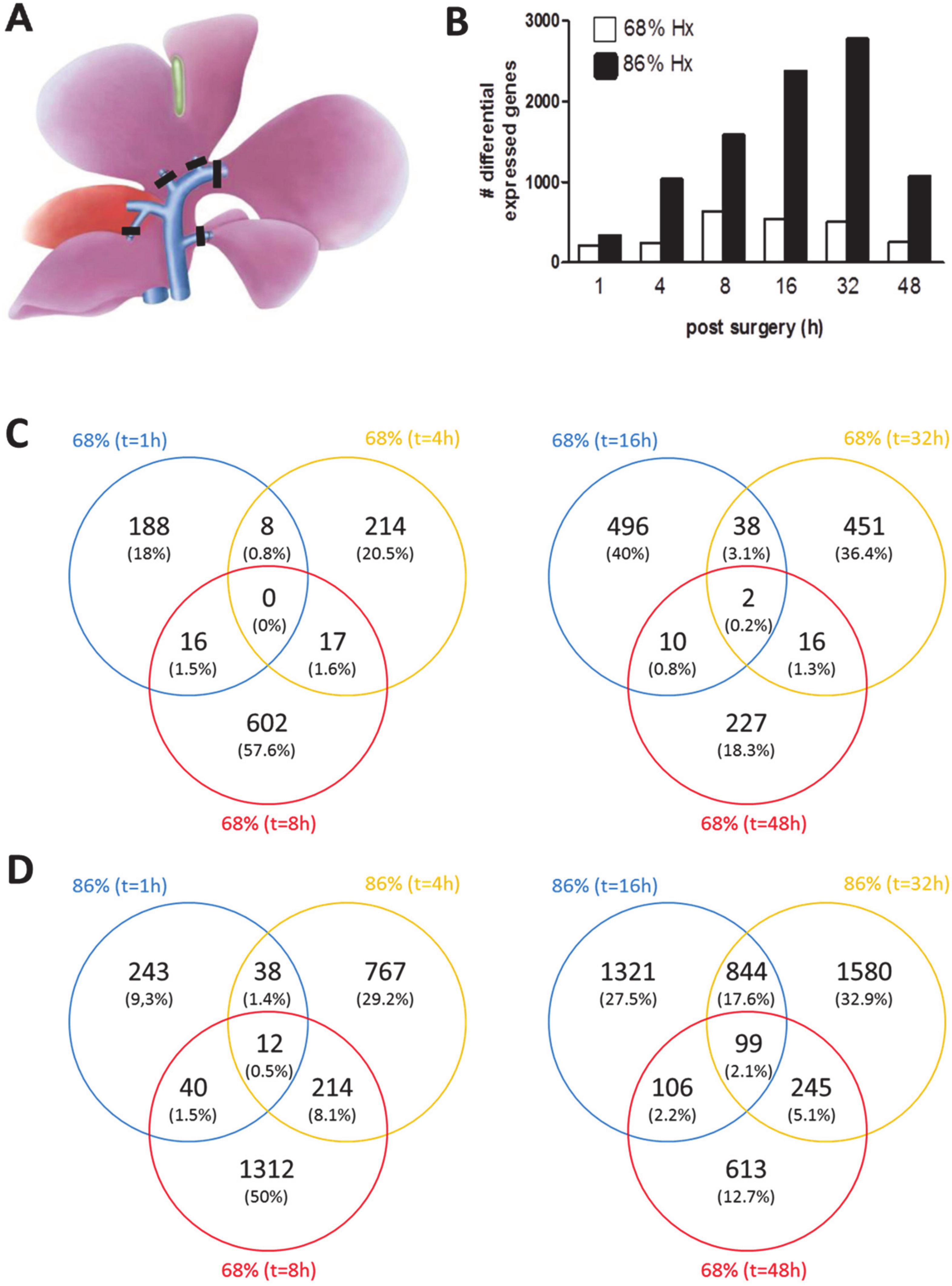
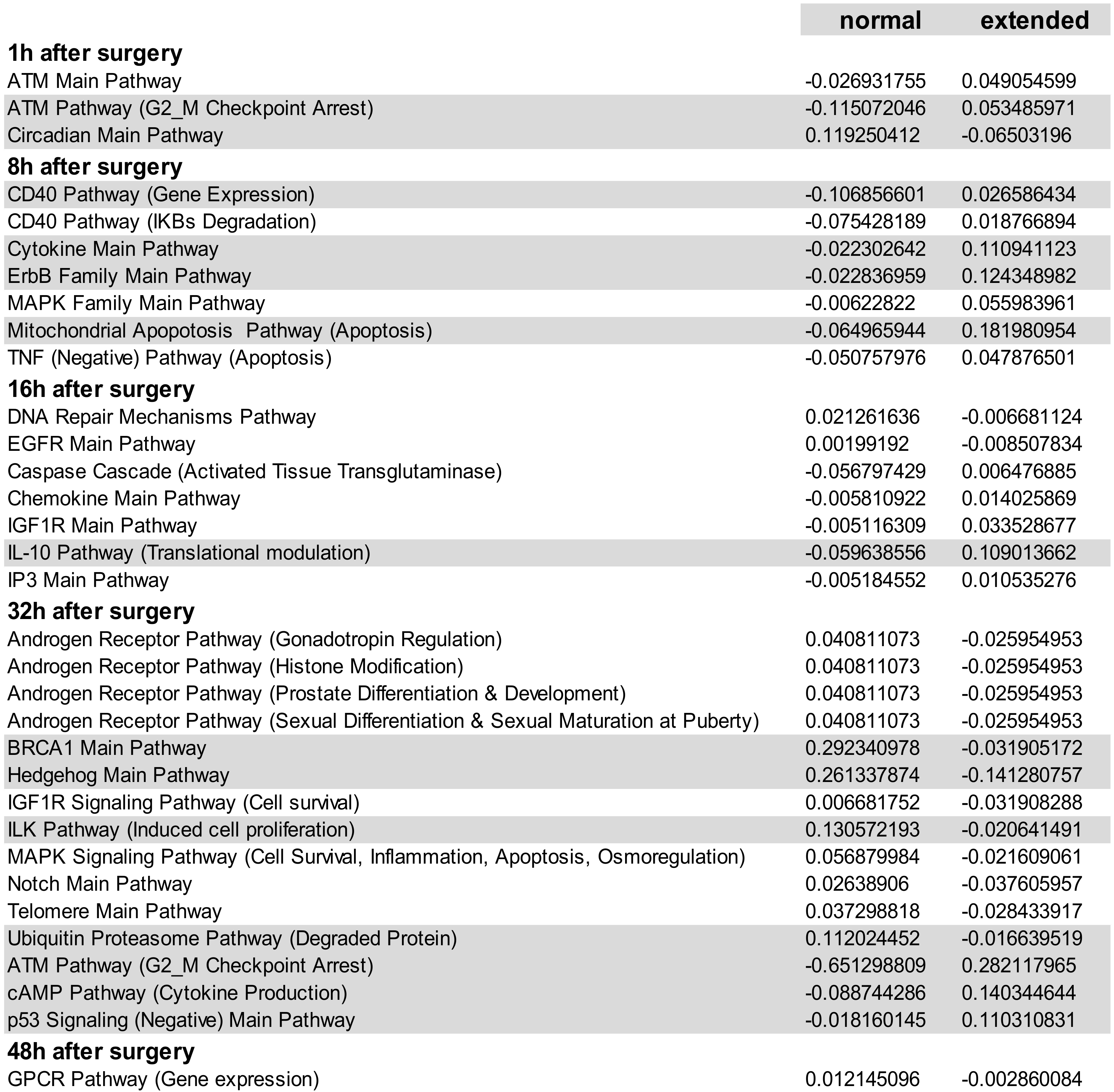
3.1. Transcriptional Landscape of nHx and eHx Changes Over Time
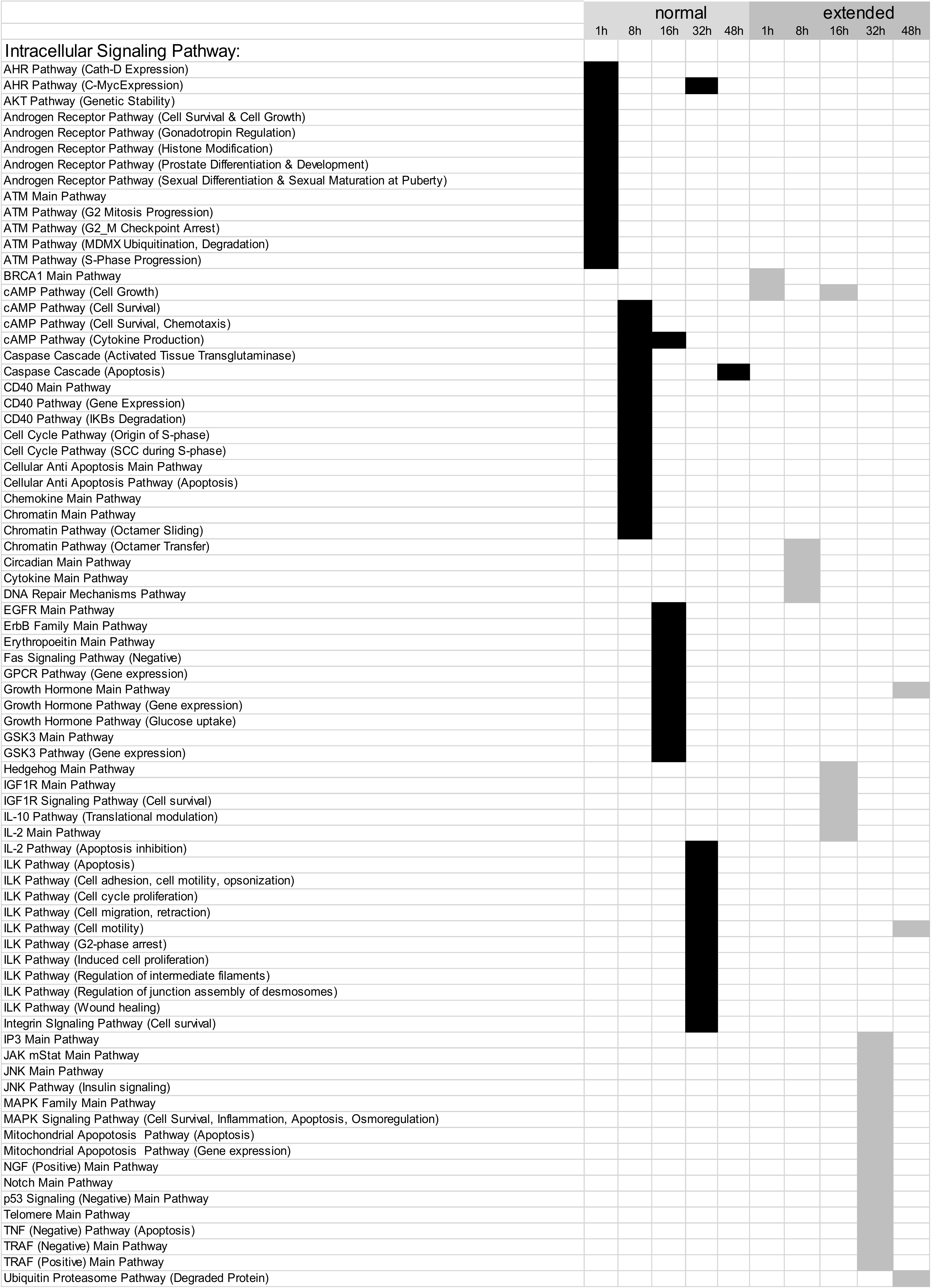
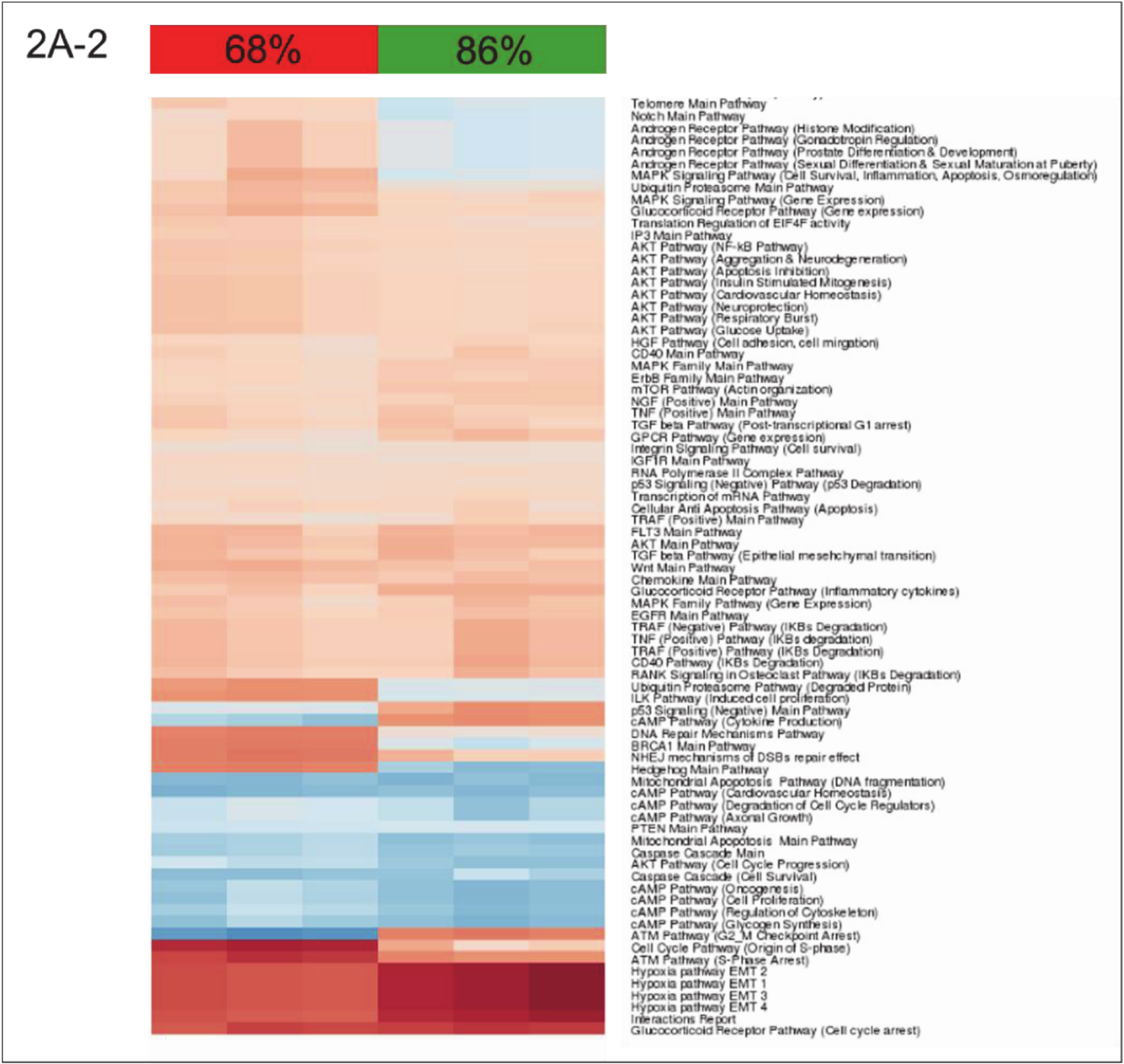
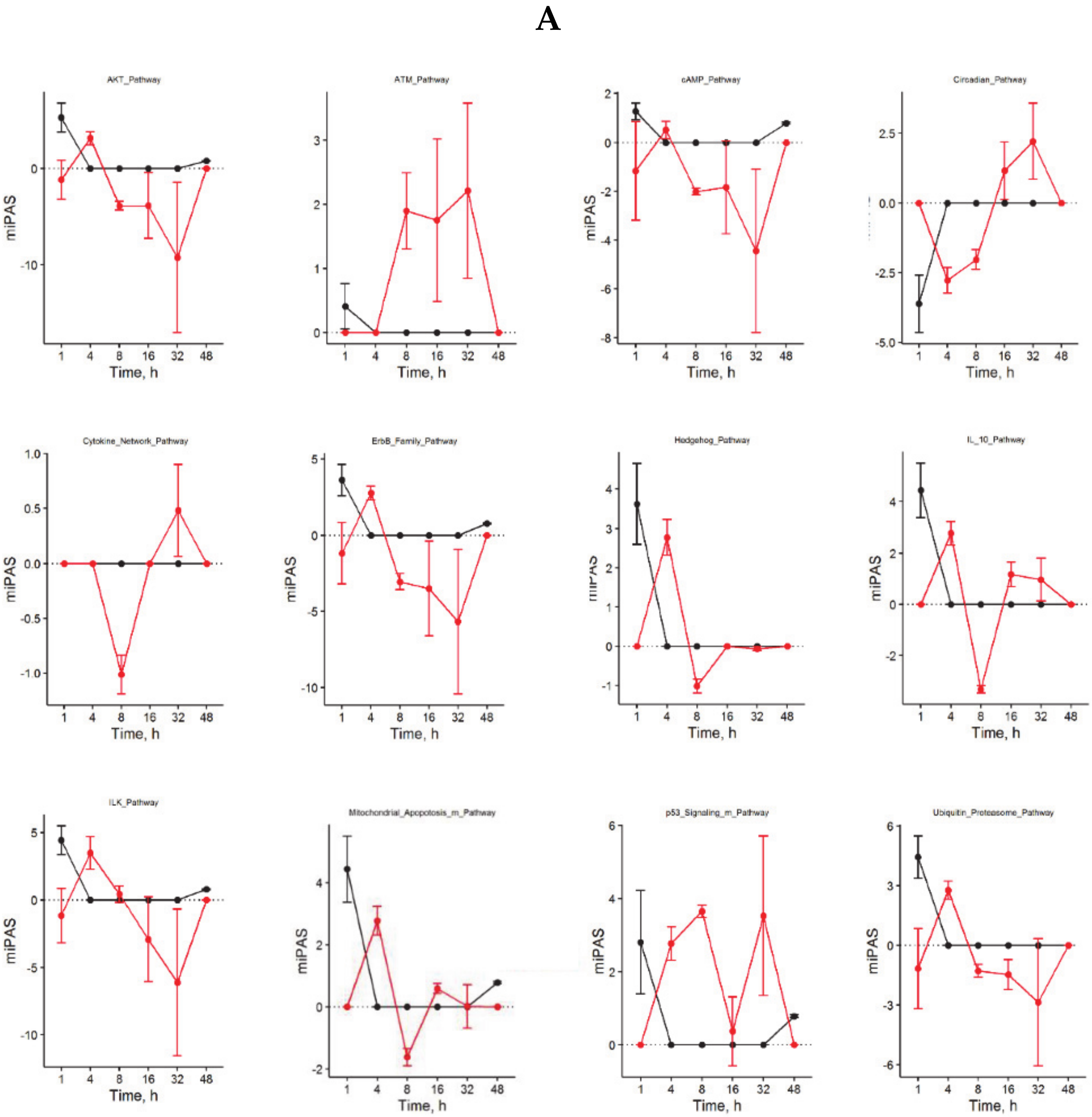
3.2. Building ISPs Activation Profiles
3.3. Common and Unique ISPs after nHx and eHx
3.4. Inversely Regulated ISPs after nHx and eHx
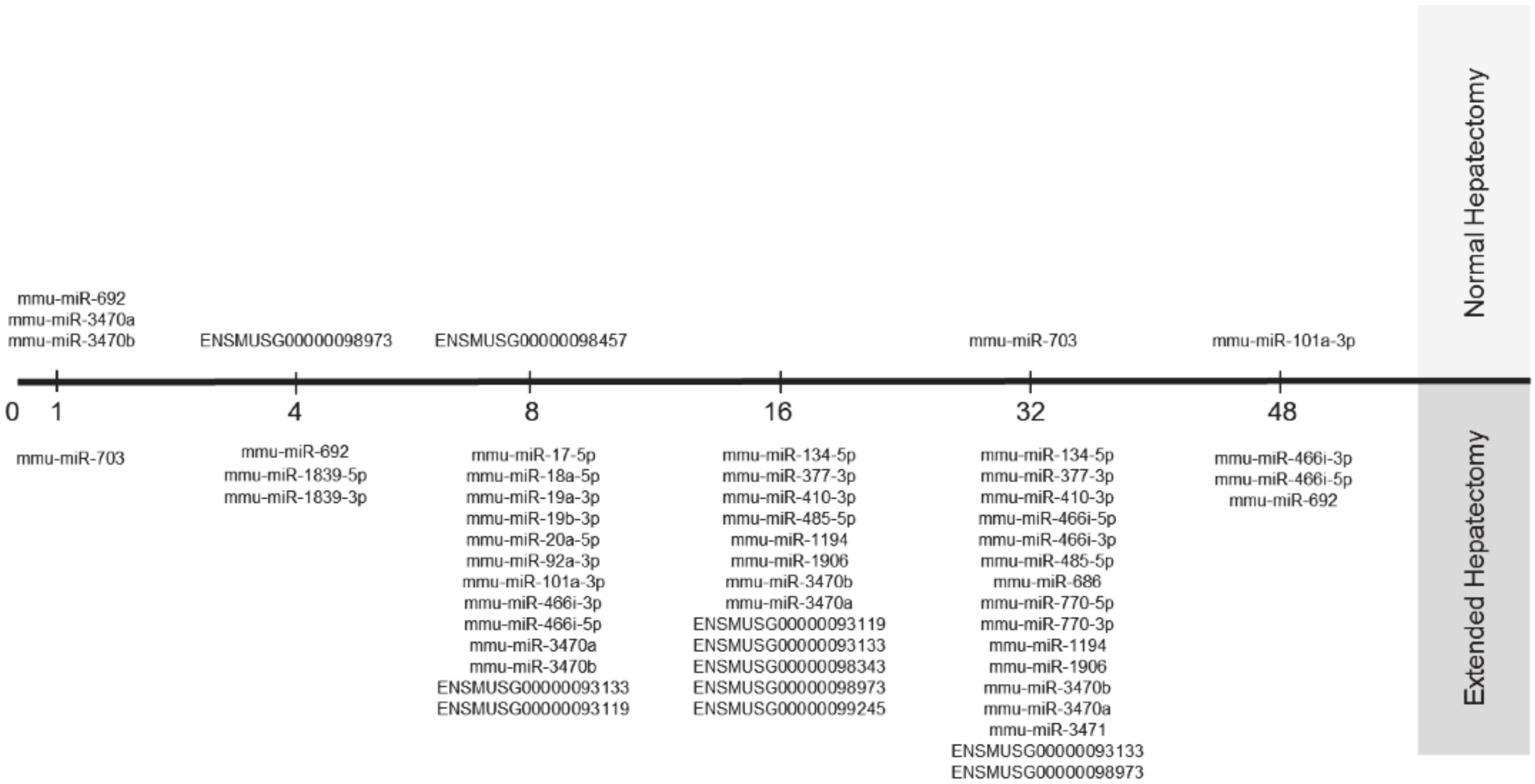
3.5. Target Prediction for Differentially Expressed miRNAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clavien, P.A.; Petrowsky, H.; DeOliveira, M.L.; Graf, R. Strategies for safer liver surgery and partial liver transplantation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1545–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, E.; Tang, H. Liver Regeneration: Analysis of the Main Relevant Signaling Molecules. Mediators Inflamm. 2017, 17, 4256352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Chen, P. Proliferation-inhibiting pathways in liver regeneration (Review). Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 1, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, K.; Tschuor, C.; Rickenbacher, A.; Jang, J.H.; Oberkofler, C.E.; Tschopp, O.; Schultze, S.M.; Raptis, D.A.; Weber, A.; Graf, R.; et al. Liver failure after extended hepatectomy in mice is mediated by a p21-dependent barrier to liver regeneration. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1609–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Buzdin, A.A.; Zhavoronkov, A.A.; Korzinkin, M.B.; Venkova, L.S.; Zenin, A.A.; Smirnov, P.Y.; Borisov, N.M. Oncofinder, a new method for the analysis of intracellular signaling pathway activation using transcriptomic data. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Alexandrova, E.; Nassa, G.; Corleone, G.; Buzdin, A.; Aliper, A.M.; Terekhanova, N.; Shepelin, D.; Zhavoronkov, A.; Tamm, M.; Milanesi, L.; et al. Large-scale profiling of signalling pathways reveals an asthma specific signature in bronchial smooth muscle cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 25150–25161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Illumina, TruSeq® RNASample Preparation v2 Guide. Available online: https://support.illumina.com/content/dam/illumina-support/documents/documentation/chemistry_documentation/samplepreps_truseq/truseqrna/truseq-rna-sample-prep-v2-guide-15026495-f.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2020).
- Nikitin, D.; Garazha, A.; Sorokin, M.; Penzar, D.; Tkachev, V.; Markov, A.; Gaifullin, N.; Borger, P.; Poltorak, A.; Buzdin, A. Retroelement—Linked Transcription Factor Binding Patterns Point to Quickly Developing Molecular Pathways in Human Evolution. Cells 2019, 8, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Culhane, A.C.; Thioulouse, J.; Perriere, G.; Higgins, D.G. MADE4: An R package for multivariate analysis of gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2789–2790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scales, M.; Jager, R.; Migliorini, G.; Houlston, R.S.; Henrion, M.Y. VisPIG—a web tool for producing multi-region, multi-track, multi-scale plots of genetic data. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Karagkouni, D.; Georgakilas, G.; Vergoulis, T.; Kanellos, I.; Anastasopoulos, I.-L.; Maniou, S.; Karathanou, K.; Kalfakakou, D.; et al. DIANA-TarBase v7.0: Indexing more than half a million experimentally supported miRNA:mRNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D153–D159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, F.; Zuo, Z.; Cai, G.; Kang, S.; Gao, X.; Li, T. miRecords: An integrated resource for microRNA-target interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D105–D110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aplan, P.D.; Johnson, B.E.; Russell, E.; Chervinsky, D.S.; Kirsch, I.R. Cloning and characterization of TCTA, a gene located at the site of a t(1;3) translocation. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 1917–1921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Williams, L.M.; Ricchetti, G.; Sarma, U.; Smallie, T.; Foxwell, B.M. Interleukin-10 suppression of myeloid cell activation—A continuing puzzle (review). Immunology 2004, 113, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servillo, G.; Della-Fazia, M.A.; Sassone-Corsi, P. Coupling cAMP signaling to transcription in the liver: Pivotal role of CREB and CREM. Exp. Cell Res. 2002, 275, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, F.M.; Guimaraes, E.L.; Grivicich, I.; Trindade, V.M.T.; Guaragna, R.M.; Borojevic, R.; Guma, F.C. Hepatic stellate cell activation in vitro: Cell cycle arrest at G2/M and modification of cell motility. J. Cell Biochem. 2003, 90, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, U.; Gkretsi, V.; Bowen, W.C.; Mars, W.M.; Luo, J.H.; Donthamsetty, S.; Orr, A.; Monga, S.P.S.; Wu, C.; Michalopoulos, G.K. Enhanced liver regeneration following changes induced by hepatocyte-specific genetic ablation of integrin-linked kinase. Hepatology 2009, 50, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kron, P.; Linecker, M.; Limani, P.; Schlegel, A.; Kambakamba, P.; Lehn, J.M.; Nicolau, C.; Graf, R.; Humar, B.; Clavien, P.-A. Hypoxia-driven Hif2a coordinates mouse liver regeneration by coupling parenchymal growth to vascular expansion. Hepatology 2016, 64, 2198–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gardner, L.B.; Li, Q.; Park, M.S.; Flanagan, W.M.; Semenza, G.L.; Dang, C.V. Hypoxia inhibits G1/S transition through regulation of p27 expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 7919–7926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayashi, E.; Yasui, A.; Oda, K.; Nagino, M.; Nimura, Y.; Nakanishi, M.; Motoyama, N.; Ikeda, K.; Matsuura, A. Loss of p27(Kip1) accelerates DNA replication after partial hepatectomy in mice. J. Surg. Res. 2003, 111, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyaoka, Y.; Miyajima, A. To divide or not to divide: Revisitingliver regeneration. Cell Div. 2013, 8, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rudnick, D.A.; Davidson, N.O. Functional relationships betweenlipid metabolism and liver regeneration. Int. J. Hepatol. 2012, 2012, 549241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tautenhahn, H.M.; Brückner, S.; Baumann, S.; Winkler, S.; Otto, W.; von Bergen, M.; Bartels, M.; Christ, B. Attenuation of Postoperative Acute Liver Failure by Mesenchymal Stem Cell Treatment Due to Metabolic Implications. Ann. Surg. 2016, 263, 546–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauschke, V.M.; Mkrtchian, S.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. The role of microRNAs in liver injury at the crossroad between hepatic cell death and regeneration. Biochem. Biophys Res. Commun. 2017, 482, 399–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borger, P.; Buzdin, A.; Sorokin, M.; Kachaylo, E.; Humar, B.; Graf, R.; Clavien, P.-A. Large-Scale Profiling of Signaling Pathways Reveals a Distinct Demarcation between Normal and Extended Liver Resection. Cells 2020, 9, 1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051149
Borger P, Buzdin A, Sorokin M, Kachaylo E, Humar B, Graf R, Clavien P-A. Large-Scale Profiling of Signaling Pathways Reveals a Distinct Demarcation between Normal and Extended Liver Resection. Cells. 2020; 9(5):1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051149
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorger, Pieter, Anton Buzdin, Maksim Sorokin, Ekaterina Kachaylo, Bostjan Humar, Rolf Graf, and Pierre-Alien Clavien. 2020. "Large-Scale Profiling of Signaling Pathways Reveals a Distinct Demarcation between Normal and Extended Liver Resection" Cells 9, no. 5: 1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051149
APA StyleBorger, P., Buzdin, A., Sorokin, M., Kachaylo, E., Humar, B., Graf, R., & Clavien, P.-A. (2020). Large-Scale Profiling of Signaling Pathways Reveals a Distinct Demarcation between Normal and Extended Liver Resection. Cells, 9(5), 1149. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051149






