NF-?B and tPA Signaling in Kidney and Other Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. NF-κB Pathway
2.1. Discovery and Structure
2.2. NF-κB Activation and Signaling Pathways
2.3. NF-κB as a Regulator of Inflammation
3. tPA Signaling
3.1. Discovery and Structure
3.2. Dual Function as a Protease and a Cytokine
3.3. tPA Associated Receptors
4. tPA and NF-κB in Kidney Disease
4.1. NF-κB and Renal Inflammation
4.2. tPA Signaling in Kidney Fibrosis and Inflammation
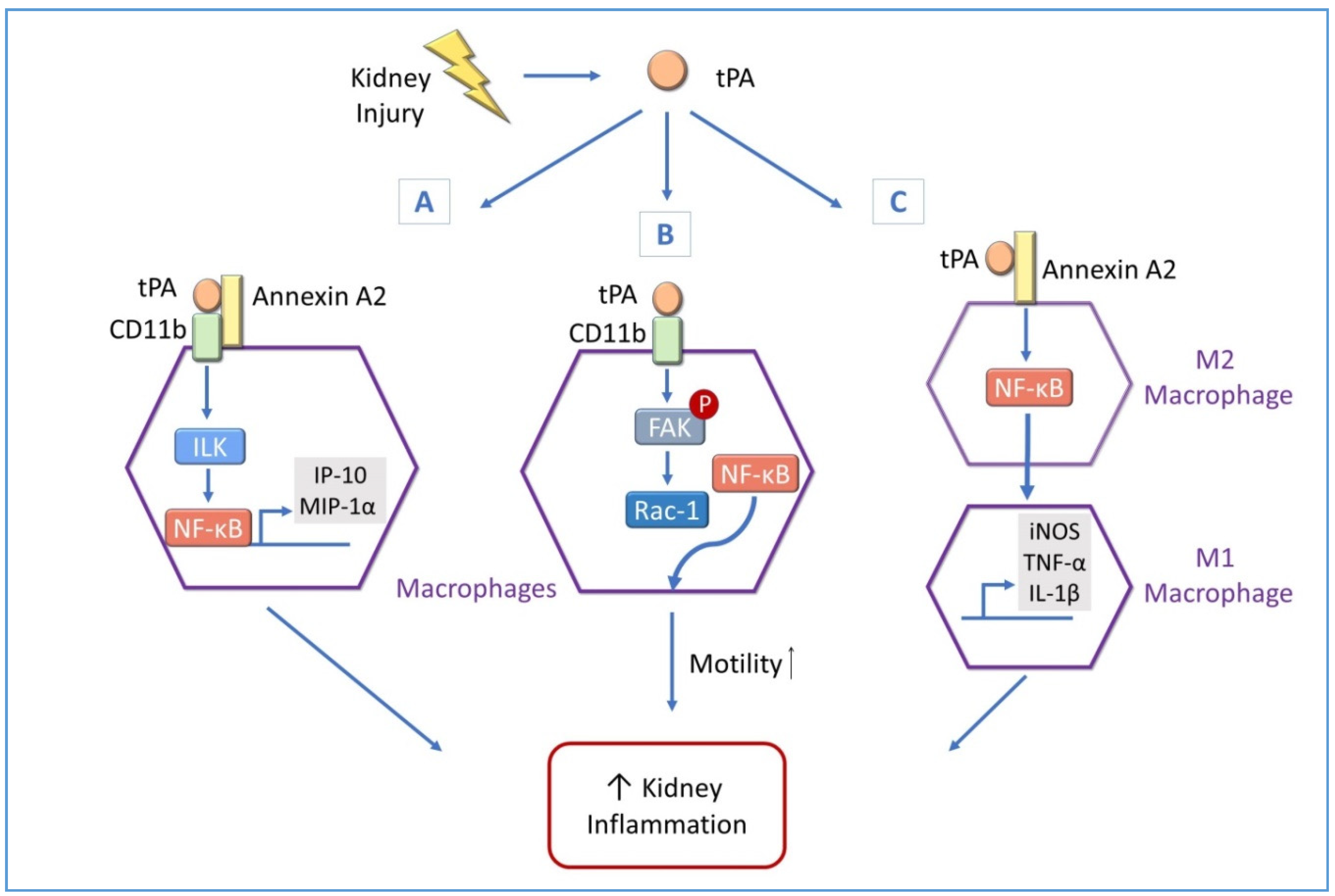
4.3. tPA Modulates Renal Inflammation through NF-κB in Macrophages
4.3.1. tPA and NF-κB Promote Macrophage Motility in Obstructive Kidney Diseases
4.3.2. tPA and NF-κB Modulate Renal Macrophage Polarization
5. tPA and NF-κB in Other Diseases
5.1. tPA and NF-κB in Cerebral Ischemic Stroke
5.2. tPA and NF-κB in Cardiovascular Diseases
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKI | acute kidney injury |
| BAFFR | B cell activating factor receptor |
| CCL21 | chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 21 |
| CD11b | cluster of differentiation molecule 11b |
| CKD | chronic kidney disease |
| CNS | central nervous system |
| CVD | cardiovascular disease |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| ERSD | end-stage renal disease |
| FAK | focal adhesion kinase |
| FDA | U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
| Fn14 | fibroblast growth factor-inducible factor 14 |
| HGF | hepatocyte growth factor |
| IBD | inflammatory bowel disease |
| IκB | inhibitory κB |
| IKK | inhibitory κB kinase |
| IL-1 β | interleukin 1β |
| ILK | integrin-linked kinase |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| IP-10 | interferon-γ-inducible protein 10 |
| I/R | ischemia/reperfusion |
| LRP-1 | low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 |
| LTβR | lymphotoxin-β receptor |
| MCAO | middle cerebral artery occlusion |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 |
| MIP-1 | macrophage inflammatory protein 1 |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| NEMO | NF-κB essential modulator |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor-κB |
| NIK | nuclear factor -κB inducing kinase |
| OGD/R | oxygen/glucose deprivation and reperfusion |
| p90RSK | the 90kDa ribosomal s6 kinase |
| PAI-1 | plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| PAMPs | pathogen-associated molecular patterns |
| PRRs | pattern-recognition receptors |
| RHD | Rel homology domain |
| Rac1 | Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| TAD | transactivation domain |
| TCR | T-cell receptor |
| TLR | toll-like receptor |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| TNFR | tumor necrosis factor receptors |
| tPA | tissue plasminogen activator |
| TWEAK | TNF-like weak inducer of apoptosis |
| uPA | urokinase plasminogen activator |
| UUO | unilateral ureteral obstruction |
| UV | ultraviolet |
References
- Ruggenenti, P.; Cravedi, P.; Remuzzi, G. Mechanisms and treatment of CKD. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Go, A.S.; Chertow, G.M.; Fan, D.; McCulloch, C.E.; Hsu, C.Y. Chronic kidney disease and the risks of death, cardiovascular events, and hospitalization. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 1296–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Na, S.Y.; Sung, J.Y.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, S.; Lee, H.H.; Park, Y.H.; Chung, W.; Oh, K.H.; Jung, J.Y. Chronic kidney disease in cancer patients: An independent predictor of cancer-specific mortality. Am. J. Nephrol. 2011, 33, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saran, R.; Robinson, B.; Abbott, K.C.; Agodoa, L.Y.C.; Bragg-Gresham, J.; Balkrishnan, R.; Bhave, N.; Dietrich, X.; Ding, Z.; Eggers, P.W.; et al. US Renal Data System 2018 Annual Data Report: Epidemiology of Kidney Disease in the United States. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2019, 73, A7–A8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Imig, J.D.; Ryan, M.J. Immune and inflammatory role in renal disease. Compr. Physiol. 2013, 3, 957–976. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB in inflammation and renal diseases. Cell Biosci. 2015, 5, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, K.; Yang, J.; Tanaka, S.; Gonias, S.L.; Mars, W.M.; Liu, Y. Tissue-type plasminogen activator acts as a cytokine that triggers intracellular signal transduction and induces matrix metalloproteinase-9 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 2120–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, K.; Mars, W.M.; Liu, Y. Novel actions of tissue-type plasminogen activator in chronic kidney disease. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 5174–5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sen, R.; Baltimore, D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell 1986, 46, 705–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Ghosh, S. The NF-kappaB family of transcription factors and its regulation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; May, M.J.; Kopp, E.B. NF-kappa B and Rel proteins: Evolutionarily conserved mediators of immune responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 225–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beinke, S.; Ley, S.C. Functions of NF-kappaB1 and NF-kappaB2 in immune cell biology. Biochem. J. 2004, 382, 393–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.C. The non-canonical NF-kappaB pathway in immunity and inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, G.; Fong, A.; Sun, S.C. Induction of p100 processing by NF-kappaB-inducing kinase involves docking IkappaB kinase alpha (IKKalpha) to p100 and IKKalpha-mediated phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30099–30105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Zhang, L.; Joo, D.; Sun, S.C. NF-kappaB signaling in inflammation. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2017, 2, e17023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mercurio, F.; Manning, A.M. NF-kappaB as a primary regulator of the stress response. Oncogene 1999, 18, 6163–6171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mussbacher, M.; Salzmann, M.; Brostjan, C.; Hoesel, B.; Schoergenhofer, C.; Datler, H.; Hohensinner, P.; Basilio, J.; Petzelbauer, P.; Assinger, A.; et al. Cell Type-Specific Roles of NF-kappaB Linking Inflammation and Thrombosis. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lawrence, T. The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, a001651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hebert, M.; Lesept, F.; Vivien, D.; Macrez, R. The story of an exceptional serine protease, tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA). Rev. Neurol. 2016, 172, 186–197. [Google Scholar]
- Binder, B.R.; Spragg, J.; Austen, K.F. Purification and characterization of human vascular plasminogen activator derived from blood vessel perfusates. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 1998–2003. [Google Scholar]
- Rijken, D.C.; Wijngaards, G.; Zaal-de Jong, M.; Welbergen, J. Purification and partial characterization of plasminogen activator from human uterine tissue. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1979, 580, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennica, D.; Holmes, W.E.; Kohr, W.J.; Harkins, R.N.; Vehar, G.A.; Ward, C.A.; Bennett, W.F.; Yelverton, E.; Seeburg, P.H.; Heyneker, H.L.; et al. Cloning and expression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator cDNA in E. coli. Nature 1983, 301, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chevilley, A.; Lesept, F.; Lenoir, S.; Ali, C.; Parcq, J.; Vivien, D. Impacts of tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) on neuronal survival. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 9, 415. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kattula, S.; Byrnes, J.R.; Wolberg, A.S. Fibrinogen and Fibrin in Hemostasis and Thrombosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, e13–e21. [Google Scholar]
- Mondino, A.; Blasi, F. uPA and uPAR in fibrinolysis, immunity and pathology. Trends Immunol. 2004, 25, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellino, F.J.; Ploplis, V.A. Structure and function of the plasminogen/plasmin system. Thromb. Haemost. 2005, 93, 647–654. [Google Scholar]
- Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1581–1587. [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Shultz, R.W.; Mars, W.M.; Wegner, R.E.; Li, Y.; Dai, C.; Nejak, K.; Liu, Y. Disruption of tissue-type plasminogen activator gene in mice reduces renal interstitial fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1525–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donate, L.E.; Gherardi, E.; Srinivasan, N.; Sowdhamini, R.; Aparicio, S.; Blundell, T.L. Molecular evolution and domain structure of plasminogen-related growth factors (HGF/SF and HGF1/MSP). Protein Sci. 1994, 3, 2378–2394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gherardi, E.; Gonzalez Manzano, R.; Cottage, A.; Hawker, K.; Aparicio, S. Evolution of plasminogen-related growth factors (HGF/SF and HGF1/MSP). Ciba Found. Symp. 1997, 212, 24–35. [Google Scholar]
- Higazi, A.A.; El-Haj, M.; Melhem, A.; Horani, A.; Pappo, O.; Alvarez, C.E.; Muhanna, N.; Friedman, S.L.; Safadi, R. Immunomodulatory effects of plasminogen activators on hepatic fibrogenesis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2008, 152, 163–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Polavarapu, R.; She, H.; Mao, Z.; Yepes, M. Tissue-type plasminogen activator and the low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein mediate cerebral ischemia-induced nuclear factor-kappaB pathway activation. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1281–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bu, G.; Williams, S.; Strickland, D.K.; Schwartz, A.L. Low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein/alpha 2-macroglobulin receptor is an hepatic receptor for tissue-type plasminogen activator. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 7427–7431. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Hu, K. Tissue plasminogen activator and inflammation: From phenotype to signaling mechanisms. Am. J. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2014, 3, 30–36. [Google Scholar]
- Obermoeller-McCormick, L.M.; Li, Y.; Osaka, H.; FitzGerald, D.J.; Schwartz, A.L.; Bu, G. Dissection of receptor folding and ligand-binding property with functional minireceptors of LDL receptor-related protein. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 899–908. [Google Scholar]
- Herz, J.; Strickland, D.K. LRP: A multifunctional scavenger and signaling receptor. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 779–784. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Bu, G.; Mars, W.M.; Reeves, W.B.; Tanaka, S.; Hu, K. tPA activates LDL receptor-related protein 1-mediated mitogenic signaling involving the p90RSK and GSK3beta pathway. Am. J. Pathol. 2010, 177, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, L.; Hu, K. LRP-1: Functions, signaling and implications in kidney and other diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 22887–22901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salama, Y.; Lin, S.Y.; Dhahri, D.; Hattori, K.; Heissig, B. The fibrinolytic factor tPA drives LRP1-mediated melanoma growth and metastasis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 3465–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; An, J.; Strickland, D.K.; Yepes, M. The low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1 mediates tissue-type plasminogen activator-induced microglial activation in the ischemic brain. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 586–594. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, K.; Wu, C.; Mars, W.M.; Liu, Y. Tissue-type plasminogen activator promotes murine myofibroblast activation through LDL receptor-related protein 1-mediated integrin signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 3821–3832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Siao, C.J.; Tsirka, S.E. Tissue plasminogen activator mediates microglial activation via its finger domain through annexin II. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 3352–3358. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rescher, U.; Gerke, V. Annexins--unique membrane binding proteins with diverse functions. J. Cell Sci. 2004, 117, 2631–2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cesarman, G.M.; Guevara, C.A.; Hajjar, K.A. An endothelial cell receptor for plasminogen/tissue plasminogen activator (t-PA). II. Annexin II-mediated enhancement of t-PA-dependent plasminogen activation. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 21198–21203. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ortiz-Zapater, E.; Peiro, S.; Roda, O.; Corominas, J.M.; Aguilar, S.; Ampurdanes, C.; Real, F.X.; Navarro, P. Tissue plasminogen activator induces pancreatic cancer cell proliferation by a non-catalytic mechanism that requires extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 activation through epidermal growth factor receptor and annexin A2. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, M.; Ownbey, R.T.; Sharma, M.C. Breast cancer cell surface annexin II induces cell migration and neoangiogenesis via tPA dependent plasmin generation. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2010, 88, 278–286. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.Y.; Lin, C.F. Annexin A2: Its molecular regulation and cellular expression in cancer development. Dis. Markers 2014, 2014, 308976. [Google Scholar]
- Hajjar, K.A.; Mauri, L.; Jacovina, A.T.; Zhong, F.; Mirza, U.A.; Padovan, J.C.; Chait, B.T. Tissue plasminogen activator binding to the annexin II tail domain. Direct modulation by homocysteine. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 9987–9993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Paciucci, R.; Tora, M.; Diaz, V.M.; Real, F.X. The plasminogen activator system in pancreas cancer: Role of t-PA in the invasive potential in vitro. Oncogene 1998, 16, 625–633. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y. Cellular and molecular mechanisms of renal fibrosis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 684–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffield, J.S. Macrophages and immunologic inflammation of the kidney. Semin. Nephrol. 2010, 30, 234–254. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Iturbe, B.; Garcia Garcia, G. The role of tubulointerstitial inflammation in the progression of chronic renal failure. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2010, 116, c81–c88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewitson, T.D. Renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis: Common but never simple. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2009, 296, F1239–F1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lo, W.K. Serum parameters, inflammation, renal function and patient outcome. Contrib. Nephrol. 2006, 150, 152–155. [Google Scholar]
- Sterner, R.M.; Hartono, S.P.; Grande, J.P. The Pathogenesis of Lupus Nephritis. J. Clin. Cell. Immunol. 2014, 5, 205. [Google Scholar]
- Kiryluk, K.; Novak, J. The genetics and immunobiology of IgA nephropathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 2325–2332. [Google Scholar]
- Guijarro, C.; Egido, J. Transcription factor-kappa B (NF-kappa B) and renal disease. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, 415–424. [Google Scholar]
- Sanz, A.B.; Sanchez-Nino, M.D.; Ramos, A.M.; Moreno, J.A.; Santamaria, B.; Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Egido, J.; Ortiz, A. NF-kappaB in renal inflammation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 21, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morrissey, J.; Klahr, S. Transcription factor NF-kappaB regulation of renal fibrosis during ureteral obstruction. Semin. Nephrol. 1998, 18, 603–611. [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, F.L.; Patel, N.S.A.; Purvis, G.S.D.; Chiazza, F.; Chen, J.; Sordi, R.; Hache, G.; Merezhko, V.V.; Collino, M.; Yaqoob, M.M.; et al. Inhibition of IkappaB Kinase at 24 Hours After Acute Kidney Injury Improves Recovery of Renal Function and Attenuates Fibrosis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e005092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, N.; Thaiss, F.; Guo, L. NFkappaB and Kidney Injury. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpini, R.A.; Costa, R.S.; da Silva, C.G.; Coimbra, T.M. Inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB activation attenuates tubulointerstitial nephritis induced by gentamicin. Nephron Physiol. 2004, 98, p97–p106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujihara, C.K.; Antunes, G.R.; Mattar, A.L.; Malheiros, D.M.; Vieira, J.M., Jr.; Zatz, R. Chronic inhibition of nuclear factor-kappaB attenuates renal injury in the 5/6 renal ablation model. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2007, 292, F92–F99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donnahoo, K.K.; Shames, B.D.; Harken, A.H.; Meldrum, D.R. Review article: The role of tumor necrosis factor in renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. J. Urol. 1999, 162, 196–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poveda, J.; Tabara, L.C.; Fernandez-Fernandez, B.; Martin-Cleary, C.; Sanz, A.B.; Selgas, R.; Ortiz, A.; Sanchez-Nino, M.D. TWEAK/Fn14 and Non-Canonical NF-kappaB Signaling in Kidney Disease. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Esteban, V.; Lorenzo, O.; Ruperez, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Mezzano, S.; Blanco, J.; Kretzler, M.; Sugaya, T.; Egido, J.; Ruiz-Ortega, M. Angiotensin II, via AT1 and AT2 receptors and NF-kappaB pathway, regulates the inflammatory response in unilateral ureteral obstruction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 1514–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Ruperez, M.; Lorenzo, O.; Esteban, V.; Blanco, J.; Mezzano, S.; Egido, J. Angiotensin II regulates the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines in the kidney. Kidney Int. Suppl. 2002, 62, S12–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roelofs, J.J.; Rouschop, K.M.; Leemans, J.C.; Claessen, N.; de Boer, A.M.; Frederiks, W.M.; Lijnen, H.R.; Weening, J.J.; Florquin, S. Tissue-type plasminogen activator modulates inflammatory responses and renal function in ischemia reperfusion injury. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Jin, Y.; Hu, K. Tissue-type plasminogen activator (tPA) promotes M1 macrophage survival through p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 7910–7917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ferrario, F.; Castiglione, A.; Colasanti, G.; Barbiano di Belgioioso, G.; Bertoli, S.; D’Amico, G. The detection of monocytes in human glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1985, 28, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eardley, K.S.; Kubal, C.; Zehnder, D.; Quinkler, M.; Lepenies, J.; Savage, C.O.; Howie, A.J.; Kaur, K.; Cooper, M.S.; Adu, D.; et al. The role of capillary density, macrophage infiltration and interstitial scarring in the pathogenesis of human chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2008, 74, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Wu, C.; Hu, K. Tissue plasminogen activator activates NF-kappaB through a pathway involving annexin A2/CD11b and integrin-linked kinase. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 1329–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liot, G.; Roussel, B.D.; Lebeurrier, N.; Benchenane, K.; Lopez-Atalaya, J.P.; Vivien, D.; Ali, C. Tissue-type plasminogen activator rescues neurones from serum deprivation-induced apoptosis through a mechanism independent of its proteolytic activity. J. Neurochem. 2006, 98, 1458–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Jin, Y.; Mars, W.M.; Reeves, W.B.; Hu, K. Myeloid-derived tissue-type plasminogen activator promotes macrophage motility through FAK, Rac1, and NF-kappaB pathways. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 2757–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Guan, J.L. Focal adhesion kinase and its signaling pathways in cell migration and angiogenesis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 610–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nobes, C.D.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases control polarity, protrusion, and adhesion during cell movement. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 144, 1235–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ginhoux, F.; Greter, M.; Leboeuf, M.; Nandi, S.; See, P.; Gokhan, S.; Mehler, M.F.; Conway, S.J.; Ng, L.G.; Stanley, E.R.; et al. Fate mapping analysis reveals that adult microglia derive from primitive macrophages. Science 2010, 330, 841–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ricardo, S.D.; van Goor, H.; Eddy, A.A. Macrophage diversity in renal injury and repair. J. Clin. Investig. 2008, 118, 3522–3530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, S.; Chen, S.Y. Macrophage polarization in kidney diseases. Macrophage (Houst) 2015, 2, e679. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, S.; Huen, S.; Nishio, H.; Nishio, S.; Lee, H.K.; Choi, B.S.; Ruhrberg, C.; Cantley, L.G. Distinct macrophage phenotypes contribute to kidney injury and repair. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braga, T.T.; Correa-Costa, M.; Azevedo, H.; Silva, R.C.; Cruz, M.C.; Almeida, M.E.; Hiyane, M.I.; Moreira-Filho, C.A.; Santos, M.F.; Perez, K.R.; et al. Early infiltration of p40IL12(+)CCR7(+)CD11b(+) cells is critical for fibrosis development. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2016, 4, 300–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, L.; Hu, K. Tissue-type plasminogen activator modulates macrophage M2 to M1 phenotypic change through annexin A2-mediated NF-kappaB pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 88094–88103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yaghi, S.; Willey, J.Z.; Cucchiara, B.; Goldstein, J.N.; Gonzales, N.R.; Khatri, P.; Kim, L.J.; Mayer, S.A.; Sheth, K.N.; Schwamm, L.H. Treatment and Outcome of Hemorrhagic Transformation After Intravenous Alteplase in Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Scientific Statement for Healthcare Professionals From the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 2017, 48, e343–e361. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.J.; Simpson, J.R.; Silver, B. Safety of thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke: A review of complications, risk factors, and newer technologies. Neurohospitalist 2011, 1, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seeds, N.W.; Basham, M.E.; Ferguson, J.E. Absence of tissue plasminogen activator gene or activity impairs mouse cerebellar motor learning. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 7368–7375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsirka, S.E.; Rogove, A.D.; Strickland, S. Neuronal cell death and tPA. Nature 1996, 384, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yepes, M.; Sandkvist, M.; Moore, E.G.; Bugge, T.H.; Strickland, D.K.; Lawrence, D.A. Tissue-type plasminogen activator induces opening of the blood-brain barrier via the LDL receptor-related protein. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1533–1540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uhl, B.; Zuchtriegel, G.; Puhr-Westerheide, D.; Praetner, M.; Rehberg, M.; Fabritius, M.; Hessenauer, M.; Holzer, M.; Khandoga, A.; Furst, R.; et al. Tissue plasminogen activator promotes postischemic neutrophil recruitment via its proteolytic and nonproteolytic properties. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1495–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schneider, A.; Martin-Villalba, A.; Weih, F.; Vogel, J.; Wirth, T.; Schwaninger, M. NF-kappaB is activated and promotes cell death in focal cerebral ischemia. Nat. Med. 1999, 5, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzi, M.; Goffi, F.; Boroni, F.; Benarese, M.; Perkins, S.E.; Liou, H.C.; Spano, P. Opposing roles for NF-kappa B/Rel factors p65 and c-Rel in the modulation of neuron survival elicited by glutamate and interleukin-1beta. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 20717–20723. [Google Scholar]
- Pizzi, M.; Sarnico, I.; Boroni, F.; Benarese, M.; Steimberg, N.; Mazzoleni, G.; Dietz, G.P.; Bahr, M.; Liou, H.C.; Spano, P.F. NF-kappaB factor c-Rel mediates neuroprotection elicited by mGlu5 receptor agonists against amyloid beta-peptide toxicity. Cell Death Differ. 2005, 12, 761–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, X.D.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Chen, L.F. Functional interplay between acetylation and methylation of the RelA subunit of NF-kappaB. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 2170–2180. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarnico, I.; Branca, C.; Lanzillotta, A.; Porrini, V.; Benarese, M.; Spano, P.F.; Pizzi, M. NF-kappaB and epigenetic mechanisms as integrative regulators of brain resilience to anoxic stress. Brain Res. 2012, 1476, 203–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iadecola, C.; Zhang, F.; Casey, R.; Nagayama, M.; Ross, M.E. Delayed reduction of ischemic brain injury and neurological deficits in mice lacking the inducible nitric oxide synthase gene. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 9157–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheon, S.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Kam, E.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, T.W.; Koo, B.N. Isoflurane preconditioning inhibits the effects of tissue-type plasminogen activator on brain endothelial cell in an in vitro model of ischemic stroke. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 14, 425–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Agnic, I.; Filipovic, N.; Vukojevic, K.; Saraga-Babic, M.; Vrdoljak, M.; Grkovic, I. Effects of isoflurane postconditioning on chronic phase of ischemia-reperfusion heart injury in rats. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2015, 24, 94–101. [Google Scholar]
- Salomaa, V.; Stinson, V.; Kark, J.D.; Folsom, A.R.; Davis, C.E.; Wu, K.K. Association of fibrinolytic parameters with early atherosclerosis. The ARIC Study. Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Circulation 1995, 91, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Vaughan, D.E.; Stampfer, M.J.; Manson, J.E.; Hennekens, C.H. Endogenous tissue-type plasminogen activator and risk of myocardial infarction. Lancet 1993, 341, 1165–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, G.D.; Danesh, J.; Lewington, S.; Walker, M.; Lennon, L.; Thomson, A.; Rumley, A.; Whincup, P.H. Tissue plasminogen activator antigen and coronary heart disease. Prospective study and meta-analysis. Eur. Heart J. 2004, 25, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tofler, G.H.; Massaro, J.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Vasan, R.S.; Sutherland, P.A.; Meigs, J.B.; Levy, D.; D’Agostino, R.B., Sr. Plasminogen activator inhibitor and the risk of cardiovascular disease: The Framingham Heart Study. Thromb. Res. 2016, 140, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Winther, M.P.; Kanters, E.; Kraal, G.; Hofker, M.H. Nuclear factor kappaB signaling in atherogenesis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 904–914. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Heiden, K.; Cuhlmann, S.; Luong le, A.; Zakkar, M.; Evans, P.C. Role of nuclear factor kappaB in cardiovascular health and disease. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2010, 118, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ulfhammer, E.; Larsson, P.; Karlsson, L.; Hrafnkelsdottir, T.; Bokarewa, M.; Tarkowski, A.; Jern, S. TNF-alpha mediated suppression of tissue type plasminogen activator expression in vascular endothelial cells is NF-kappaB- and p38 MAPK-dependent. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2006, 4, 1781–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
White, S.; Lin, L.; Hu, K. NF-?B and tPA Signaling in Kidney and Other Diseases. Cells 2020, 9, 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061348
White S, Lin L, Hu K. NF-?B and tPA Signaling in Kidney and Other Diseases. Cells. 2020; 9(6):1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061348
Chicago/Turabian StyleWhite, Samantha, Ling Lin, and Kebin Hu. 2020. "NF-?B and tPA Signaling in Kidney and Other Diseases" Cells 9, no. 6: 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061348
APA StyleWhite, S., Lin, L., & Hu, K. (2020). NF-?B and tPA Signaling in Kidney and Other Diseases. Cells, 9(6), 1348. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061348





