miR-615 Fine-Tunes Growth and Development and Has a Role in Cancer and in Neural Repair
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Functions of miR-615
3. miR-615 Targets Under Physiological and Pathological Conditions
4. mir-615-3p Dual Role as Oncogene and Tumor Suppressor in Cancer
5. miR-615-5p as a Tumor Suppressor in Several Types of Cancer
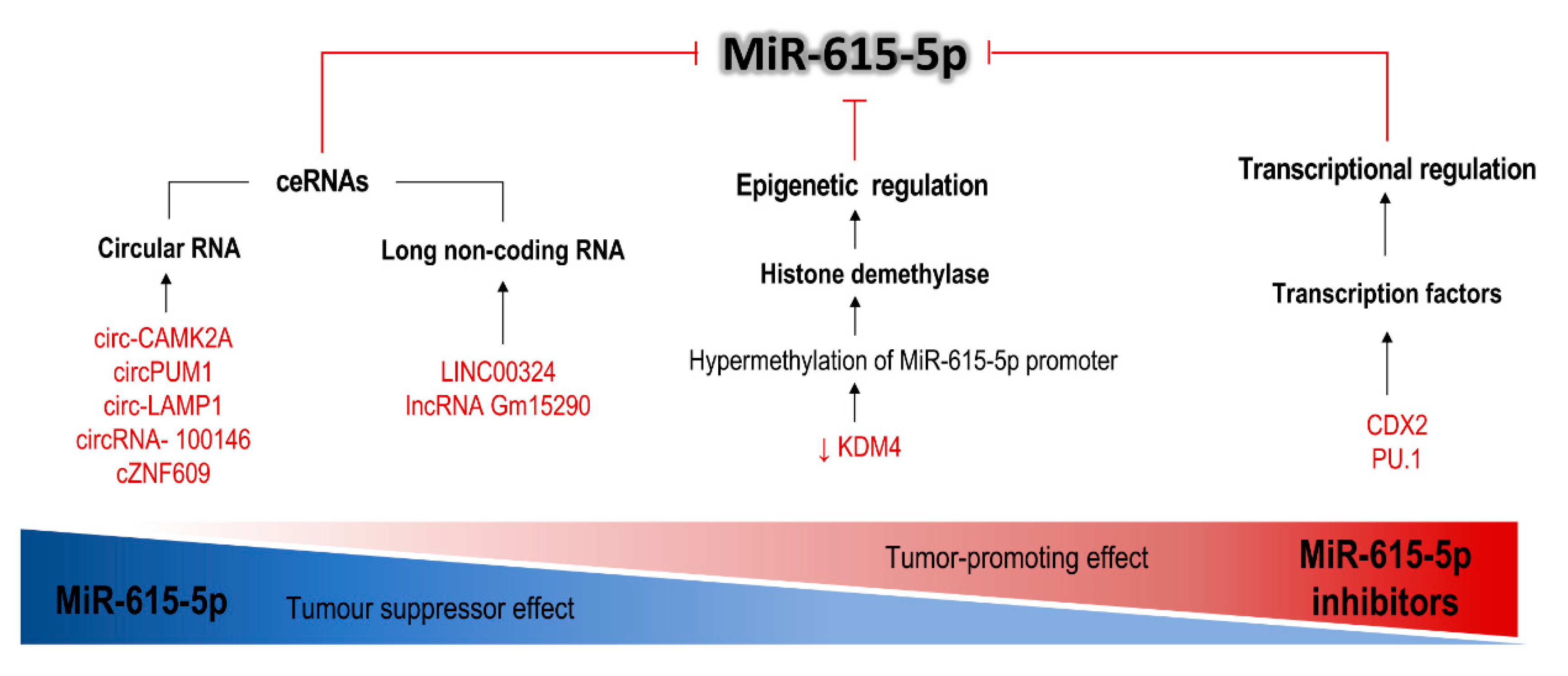
6. Competing Endogenous RNAs, Like lncRNAs and circRNAs, Act as a Regulatory Sponge of miR-615
7. Other miR-615-5p Repressor Mechanisms Which Contribute to the Promotion of Tumor Growth
8. miR-615 Involvement in Neural Plasticity
9. Future Challenges
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holland, P.W.H. Evolution of homeobox genes: Evolution of homeobox genes. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Dev. Biol. 2013, 2, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deschamps, J.; Duboule, D. Embryonic timing, axial stem cells, chromatin dynamics, and the Hox clock. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 1406–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, C.S.; Le Boiteux, E.; Arnaud, P.; Costa, B.M. HOX gene cluster (de)regulation in brain: From neurodevelopment to malignant gliaal tumours. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filipowicz, W.; Bhattacharyya, S.N.; Sonenberg, N. Mechanisms of post-transcriptional regulation by microRNAs: Are the answers in sight? Nat. Rev. Genet. 2008, 9, 102–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woltering, J.M.; Durston, A.J. MiR-10 Represses HoxB1a and HoxB3a in Zebrafish. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quah, S.; Holland, P.W.H. The Hox cluster microRNA miR-615: A case study of intronic microRNA evolution. EvoDevo 2015, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landgraf, P.; Rusu, M.; Sheridan, R.; Sewer, A.; Iovino, N.; Aravin, A.; Pfeffer, S.; Rice, A.; Kamphorst, A.O.; Landthaler, M.; et al. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 2007, 129, 1401–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-X.; Tian, Z.-G.; Zhu, L.-F.; Wu, W.-D.; Zhou, S.-L.; Zhao, Y.-T.; Huang, S. MicroRNA-615-3p promotes the osteoarthritis progression by inhibiting chondrogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 6212–6220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Gu, Y.; Li, Z.; Cai, H.; Peng, Q.; Tu, M.; Kondo, Y.; Shinjo, K.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, J.; et al. miR-615-5p is epigenetically inactivated and functions as a tumor suppressor in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, R.; Tomimaru, Y.; Nagano, H.; Eguchi, H.; Mimori, K.; Tomokuni, A.; Asaoka, T.; Wada, H.; Kawamoto, K.; Marubashi, S.; et al. miR-615-3p expression level in bone marrow is associated with tumor recurrence in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 3, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Sun, Y.; Xue, Y.; Qu, J.; Pan, S.; Li, H.; Qu, H.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. miR-615-3p promotes proliferation and migration and inhibits apoptosis through its potential target CELF2 in gastric cancer. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 101, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laursen, E.B.; Fredsøe, J.; Schmidt, L.; Strand, S.H.; Kristensen, H.; Rasmussen, A.K.I.; Daugaard, T.F.; Mouritzen, P.; Høyer, S.; Kristensen, G.; et al. Elevated miR-615-3p Expression Predicts Adverse Clinical Outcome and Promotes Proliferation and Migration of Prostate Cancer Cells. Am. J. Pathol. 2019, 189, 2377–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, A.; Zhang, S.; Li, Z.; Liang, R.; Ren, S.; Li, J.; Pu, Y.; Yang, J. miR-615-3p promotes the phagocytic capacity of splenic macrophages by targeting ligand-dependent nuclear receptor corepressor in cirrhosis-related portal hypertension. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 236, 672–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyamoto, Y.; Mauer, A.S.; Kumar, S.; Mott, J.L.; Malhi, H. Mmu-miR-615-3p Regulates Lipoapoptosis by Inhibiting C/EBP Homologous Protein. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, J.; Zhuang, G.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhang, R.; Guo, H.; Fan, X.; Cao, Y. MiR-615-3p inhibits the osteogenic differentiation of human lumbar ligamentum flavum cells via suppression of osteogenic regulators GDF5 and FOXO1: MiR-615-3p blocks ligamentum ossification. Cell Biol. Int. 2017, 41, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-Q.; Ding, Y.-J. Overexpressed microRNA-615-3p promotes progression of neonatal acute respiratory distress syndrome by inhibiting differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells to alveolar type II epithelial cells. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 4625–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Wang, D.; Zhang, M.; Deng, Y.; Jiang, H.; Li, Y. miR-615-3p promotes the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of breast cancer by targeting PICK1/TGFBRI axis. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2020, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jia, Y.; Jia, L.; Li, T.; Yang, L.; Zhang, G. MicroRNA 615-3p Inhibits the Tumor Growth and Metastasis of NSCLC via Inhibiting IGF2. Oncol. Res. 2019, 27, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Wu, G.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Q.; Zheng, W.; Chen, X.; Chen, F.; Li, Q.; Che, X. Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP promotes renal cell carcinoma progression through the regulation of the miR-615/IGF-2 pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Ooi, W.F.; Qamra, A.; Cheung, A.; Ma, D.; Sundaram, G.M.; Xu, C.; Xing, M.; Poon, L.; Wang, J.; et al. HoxC5 and miR-615-3p target newly evolved genomic regions to repress hTERT and inhibit tumorigenesis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Wang, H.; Feng, W.; Huang, S.; An, J.; Qiu, Y.; Wu, K. Long non-coding RNA HOTTIP promotes hypoxia-induced glycolysis through targeting miR-615-3p/HMGB3 axis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 862, 172615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Pan, S.; Yang, T.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y.; Shi, X.; Zhao, X.; Guo, J.; Zhang, X. LINC00657 played oncogenic roles in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting miR-615-3p and JunB. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 108, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, N.; Yu, L.; Han, S.; Li, D.; Li, J. Identification of differentially expressed microRNAs and their PKC-isoform specific gene network prediction during hypoxic pre-conditioning and focal cerebral ischemia of mice: Differential miRNAs in HPC and MCAO mouse brain. J. Neurochem. 2012, 120, 830–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.; Ding, L.; Wang, Y.; Zou, T.-B.; Wang, T.; Fu, W.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, K.; Lei, Y.; et al. MiR-615 Regulates NSC Differentiation In Vitro and Contributes to Spinal Cord Injury Repair by Targeting LINGO-1. Mol. Neurobiol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hessert, D.; Tanzer, D.; Brunstetter, T.; Kaupp, S.; Murdoch, D.; Mirzaoff, M. Topical cyclosporine A for postoperative photorefractive keratectomy and laser in situ keratomileusis. J. Cataract Refract. Surg. 2013, 39, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, S.; Huang, C.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Wei, B. MicroRNAome of Splenic Macrophages in Hypersplenism due to Portal Hypertension in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Cirrhosis. Exp. Biol. Med. 2008, 233, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Tayebi, H.M.; Hosny, K.A.; Esmat, G.; Breuhahn, K.; Abdelaziz, A.I. miR-615-5p is restrictedly expressed in cirrhotic and cancerous liver tissues and its overexpression alleviates the tumorigenic effects in hepatocellular carcinoma. FEBS Lett. 2012, 586, 3309–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Maraghy, S.A.; Adel, O.; Zayed, N.; Yosry, A.; El-Nahaas, S.M.; Gibriel, A.A. Circulatory miRNA-484, 524, 615 and 628 expression profiling in HCV mediated HCC among Egyptian patients; implications for diagnosis and staging of hepatic cirrhosis and fibrosis. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 22, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icli, B.; Wu, W.; Ozdemir, D.; Li, H.; Cheng, H.S.; Haemmig, S.; Liu, X.; Giatsidis, G.; Avci, S.N.; Lee, N.; et al. MicroRNA-615-5p Regulates Angiogenesis and Tissue Repair by Targeting AKT/eNOS (Protein Kinase B/Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase) Signaling in Endothelial Cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2019, 39, 1458–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.-J.; Liu, C.; Shan, K.; Liu, B.-H.; Li, X.-M.; Zhang, S.-J.; Zhou, R.-M.; Dong, R.; Yan, B.; Sun, X.-H. Circular RNA-ZNF609 regulates retinal neurodegeneration by acting as miR-615 sponge. Theranostics 2018, 8, 3408–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmoon, M.A.; Youness, R.A.; Gomaa, A.I.; Hamza, M.T.; Waked, I.; El Tayebi, H.M.; Abdelaziz, A.I. MiR-615-5p depresses natural killer cells cytotoxicity through repressing IGF-1R in hepatocellular carcinoma patients. Growth Factors 2017, 35, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kermorvant-Duchemin, E.; Sapieha, P.; Sirinyan, M.; Beauchamp, M.; Checchin, D.; Hardy, P.; Sennlaub, F.; Lachapelle, P.; Chemtob, S. Understanding ischemic retinopathies: Emerging concepts from oxygen-induced retinopathy. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2010, 120, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Yao, M.-D.; Li, C.-P.; Shan, K.; Yang, H.; Wang, J.-J.; Liu, B.; Li, X.-M.; Yao, J.; Jiang, Q.; et al. Silencing Of Circular RNA-ZNF609 Ameliorates Vascular Endothelial Dysfunction. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2863–2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacilotto, N.; Chouliaras, K.M.; Nikitenko, L.L.; Lu, Y.W.; Fritzsche, M.; Wallace, M.D.; Nornes, S.; García-Moreno, F.; Payne, S.; Bridges, E.; et al. MEF2 transcription factors are key regulators of sprouting angiogenesis. Genes Dev. 2016, 30, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teichert, M.; Milde, L.; Holm, A.; Stanicek, L.; Gengenbacher, N.; Savant, S.; Ruckdeschel, T.; Hasanov, Z.; Srivastava, K.; Hu, J.; et al. Pericyte-expressed Tie2 controls angiogenesis and vessel maturation. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallinga, M.G.; Yetkin-Arik, B.; Kayser, R.P.; Vogels, I.M.C.; Nowak-Sliwinska, P.; Griffioen, A.W.; van Noorden, C.J.F.; Klaassen, I.; Schlingemann, R.O. IGF2 and IGF1R identified as novel tip cell genes in primary microvascular endothelial cell monolayers. Angiogenesis 2018, 21, 823–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Aaser, A.A.; El-Merzabani, M.M. Simultaneous determination of 5′-nucleotidase and alkaline phosphatase activities in serum. Z. Klin. Chem. Klin. Biochem. 1975, 13, 453–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Kouwenhove, M.; Kedde, M.; Agami, R. MicroRNA regulation by RNA-binding proteins and its implications for cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2011, 11, 644–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalmay, T. Mechanism of miRNA-mediated repression of mRNA translation. Essays Biochem. 2013, 54, 29–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, H.-Y.; Xu, R.; Zhang, M.-Y.; Yuan, L.-J.; Hu, J.-Y.; Huang, G.-L.; Wang, H.-Y. Identification of microRNA-615-3p as a novel tumor suppressor in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2403–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.W.; Sokoloski, J.A.; Perez, J.R.; Maltese, J.Y.; Sartorelli, A.C.; Stein, C.A.; Nichols, G.; Khaled, Z.; Telang, N.T.; Narayanan, R. Differentiation of immortal cells inhibits telomerase activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 12343–12346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, C.; Dragowska, W.; Kim, N.W.; Vaziri, H.; Yui, J.; Thomas, T.E.; Harley, C.B.; Lansdorp, P.M. Differential Expression of Telomerase Activity in Hematopoietic Progenitors from Adult Human Bone Marrow. Stem Cells 1996, 14, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Piatyszek, M.; Prowse, K.; Harley, C.; West, M.; Ho, P.; Coviello, G.; Wright, W.; Weinrich, S.; Shay, J. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science 1994, 266, 2011–2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar, M.; Wyman, S.K.; Fritz, B.R.; Qi, J.; Garg, K.S.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Bendoraite, A.; Mitchell, P.S.; Nelson, A.M.; et al. MicroRNA Discovery and Profiling in Human Embryonic Stem Cells by Deep Sequencing of Small RNA Libraries. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 2496–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.; Jin, P.; Wang, E.; Marincola, F.M.; Stroncek, D.F. MicroRNA and gene expression patterns in the differentiation of human embryonic stem cells. J. Transl. Med. 2009, 7, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guled, M.; Lahti, L.; Lindholm, P.M.; Salmenkivi, K.; Bagwan, I.; Nicholson, A.G.; Knuutila, S. CDKN2A, NF2, and JUN are dysregulated among other genes by miRNAs in malignant mesothelioma-A miRNA microarray analysis. Genes. Chromosomes Cancer 2009, 48, 615–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schee, K.; Lorenz, S.; Worren, M.M.; Günther, C.-C.; Holden, M.; Hovig, E.; Fodstad, Ø.; Meza-Zepeda, L.A.; Flatmark, K. Deep Sequencing the MicroRNA Transcriptome in Colorectal Cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mjelle, R.; Sjursen, W.; Thommesen, L.; Sætrom, P.; Hofsli, E. Small RNA expression from viruses, bacteria and human miRNAs in colon cancer tissue and its association with microsatellite instability and tumor location. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.R.; Islam, T.; Gov, E.; Turanli, B.; Gulfidan, G.; Shahjaman, M.; Banu, N.A.; Mollah, M.N.H.; Arga, K.Y.; Moni, M.A. Identification of Prognostic Biomarker Signatures and Candidate Drugs in Colorectal Cancer: Insights from Systems Biology Analysis. Medicina 2019, 55, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Giridhar, K.V.; Tian, Y.; Tschannen, M.R.; Zhu, J.; Huang, C.-C.; Kilari, D.; Kohli, M.; Wang, L. Plasma exosomal miRNAs-based prognosis in metastatic kidney cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 63703–63714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Deng, L.; Tang, D.; Ying, G.; Yao, X.; Liu, F.; Liang, G. miR-615-5p prevents proliferation and migration through negatively regulating serine hydromethyltransferase 2 (SHMT2) in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 6813–6821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Zhang, G.; Qiu, H.; Yu, H.; Yuan, W. The novel circular RNA circ-CAMK2A enhances lung adenocarcinoma metastasis by regulating the miR-615-5p/fibronectin 1 pathway. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2019, 24, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, X.; Zong, Z.; Liu, Y.; Chen, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y. circPUM1 Promotes Tumorigenesis and Progression of Ovarian Cancer by Sponging miR-615-5p and miR-6753-5p. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2019, 18, 882–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, L.; Liu, G.; Zheng, C.; Zhang, L.; Kang, Y.; Yang, F. Circ-LAMP1 promotes T-cell lymphoblastic lymphoma progression via acting as a ceRNA for miR-615-5p to regulate DDR2 expression. Gene 2019, 701, 146–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Y.; Sun, Q.; Zhang, J.; Hu, H. MiR-615 inhibits cell proliferation, migration and invasion by targeting EGFR in human glioblastoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 499, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Huo, X.; Sun, R.; Liu, Z.; Huang, M.; Yang, S. lncRNA Gm15290 promotes cell proliferation and invasion in lung cancer through directly interacting with and suppressing the tumor suppressor miR-615-5p. Biosci. Rep. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, F.; Du, X.; Zhang, J. CDX2 inhibits pancreatic adenocarcinoma cell proliferation via promoting tumor suppressor miR-615-5p. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 1041–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Xie, R.; Wu, S.-N.; Gao, C.-C.; Yang, X.-Z.; Zhou, J.-F. MicroRNA-615-5p targets insulin-like growth factor 2 and exerts tumor-suppressing functions in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 255–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, T.; Wang, C.; Jin, X.; Jia, C.; Yu, S.; Chen, J. MiRNA-615-5p Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma by Targeting AKT2. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Z.-H.; Guo, X.-Q.; Shan, J.; Luo, S.-X. LINC00324 exerts tumor-promoting functions in lung adenocarcinoma via targeting miR-615-5p/AKT1 axis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 8333–8342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Nan, A.; Zhang, N.; Jia, Y.; Li, X.; Ling, Y.; Dai, J.; Zhang, S.; Yang, Q.; Yi, Y.; et al. Circular RNA 100146 functions as an oncogene through direct binding to miR-361-3p and miR-615-5p in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, F.; Zhao, H.; Du, Z.; Jiang, H. miR-615 Inhibits Prostate Cancer Cell Proliferation and Invasion by Directly Targeting Cyclin D2. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2019, 27, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Liu, R.; Chen, L.; Yi, J.; Qi, B.; Shuang, Z.; Liu, M.; Li, X.; Li, S.; et al. KDM4B-mediated epigenetic silencing of miRNA-615-5p augments RAB24 to facilitate malignancy of hepatoma cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17712–17725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.-J.; Zhang, W.-J.; Chang, Z.-W.; Pan, Y.-F.; Zong, H.; Fan, Q.-X.; Wang, L.-X. PU.1 Is Identified as a Novel Metastasis Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Regulating the miR-615-5p/IGF2 Axis. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 3667–3671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, B.; Liu, M.; Liu, L.; Chen, S.; Ren, M.; Wang, Y.; Yu, M.; et al. SHMT2 Desuccinylation by SIRT5 Drives Cancer Cell Proliferation. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 372–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alexander, R.P.; Fang, G.; Rozowsky, J.; Snyder, M.; Gerstein, M.B. Annotating non-coding regions of the genome. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2010, 11, 559–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergun, S.; Oztuzcu, S. Oncocers: ceRNA-mediated cross-talk by sponging miRNAs in oncogenic pathways. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 3129–3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmena, L.; Poliseno, L.; Tay, Y.; Kats, L.; Pandolfi, P.P. A ceRNA Hypothesis: The Rosetta Stone of a Hidden RNA Language? Cell 2011, 146, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Militello, G.; Weirick, T.; John, D.; Döring, C.; Dimmeler, S.; Uchida, S. Screening and validation of lncRNAs and circRNAs as miRNA sponges. Brief. Bioinform. 2016, bbw053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kopp, F.; Chang, T.-C.; Sataluri, A.; Chen, B.; Sivakumar, S.; Yu, H.; Xie, Y.; Mendell, J.T. Noncoding RNA NORAD Regulates Genomic Stability by Sequestering PUMILIO Proteins. Cell 2016, 164, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Li, J.; Koirala, P.; Ding, X.; Chen, B.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Mo, Y.-Y. Long non-coding RNAs as prognostic markers in human breast cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Li, X.-Y.; Hu, P.; Ding, Y.-S. LncRNA NORAD contributes to colorectal cancer progression by inhibition of miR-202-5p. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2018, 26, 1411–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Cai, H.; Zheng, R.; Yang, S.; Zhou, Z.; Tu, J. Long non-coding RNA 657 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-106a-5p to regulate PTEN expression. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2017, 92, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, B.K.; Xia, L.; Palandjian, L.; Gozani, O.; Chyung, Y.; Reed, R. Characterization of a Protein Complex Containing Spliceosomal Proteins SAPs 49, 130, 145, and 155. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1999, 19, 6796–6802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, N.; Kim, D.; Kim, W.-U. Role of NFAT5 in the Immune System and Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leask, A. A centralized communication network: Recent insights into the role of the cancer associated fibroblast in the development of drug resistance in tumors. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 101, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, K.; Chan, J.K.L.; Zhu, G.; Wu, Z. Myocyte Enhancer Factor 2 Acetylation by p300 Enhances Its DNA Binding Activity, Transcriptional Activity, and Myogenic Differentiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 3575–3582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabi, Z.A.; Todorović-Raković, N.; Vujasinović, T.; Milovanović, J.; Nikolić-Vukosavljević, D. Markers of progression and invasion in short term follow up of untreated breast cancer patients. Cancer Biomark. 2015, 15, 745–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chawengsaksophak, K. Cdx2 Animal Models Reveal Developmental Origins of Cancers. Genes 2019, 10, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stelow, E.B.; Yaziji, H. Immunohistochemistry, carcinomas of unknown primary, and incidence rates. Semin. Diagn. Pathol. 2018, 35, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, N.; Feng, Y.; Stolfi, C.; Kurosu, Y.; Green, M.; Lin, J.; Green, M.E.; Sentani, K.; Yasui, W.; McMahon, M.; et al. BRAFV600E cooperates with CDX2 inactivation to promote serrated colorectal tumorigenesis. eLife 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuki, H.; Ueno, S.; Tatetsu, H.; Niiro, H.; Iino, T.; Endo, S.; Kawano, Y.; Komohara, Y.; Takeya, M.; Hata, H.; et al. PU.1 is a potent tumor suppressor in classical Hodgkin lymphoma cells. Blood 2013, 121, 962–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, W.D.; McCaw, B.J.; Herring, C.; John, D.L.; Foote, S.J.; Nutt, S.L.; Adams, J.M. PU.1 is a suppressor of myeloid leukemia, inactivated in mice by gene deletion and mutation of its DNA binding domain. Blood 2004, 104, 3437–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castellini, L.; Moon, E.J.; Razorenova, O.V.; Krieg, A.J.; von Eyben, R.; Giaccia, A.J. KDM4B/JMJD2B is a p53 target gene that modulates the amplitude of p53 response after DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, 3674–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaya, K.D.; Karakülah, G.; Yakıcıer, C.M.; Acar, A.C.; Konu, Ö. mESAdb: microRNA Expression and Sequence Analysis Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D170–D180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoss, A.G.; Kartha, V.K.; Dong, X.; Latourelle, J.C.; Dumitriu, A.; Hadzi, T.C.; MacDonald, M.E.; Gusella, J.F.; Akbarian, S.; Chen, J.-F.; et al. MicroRNAs Located in the Hox Gene Clusters Are Implicated in Huntington’s Disease Pathogenesis. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez-Iglesias, J.; Liu, C.-C.; Morgan, T.E.; Finch, C.E.; Zhou, X.J. Joint Genome-Wide Profiling of miRNA and mRNA Expression in Alzheimer’s Disease Cortex Reveals Altered miRNA Regulation. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meseguer, S.; Mudduluru, G.; Escamilla, J.M.; Allgayer, H.; Barettino, D. MicroRNAs-10a and -10b Contribute to Retinoic Acid-induced Differentiation of Neuroblastoma Cells and Target the Alternative Splicing Regulatory Factor SFRS1 (SF2/ASF). J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 4150–4164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gareev, I.; Beylerli, O.; Yang, G.; Sun, J.; Pavlov, V.; Izmailov, A.; Shi, H.; Zhao, S. The current state of MiRNAs as biomarkers and therapeutic tools. Clin. Exp. Med. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Titze-de-Almeida, S.S.; Soto-Sánchez, C.; Fernandez, E.; Koprich, J.B.; Brotchie, J.M.; Titze-de-Almeida, R. The Promise and Challenges of Developing miRNA-Based Therapeutics for Parkinson’s Disease. Cells 2020, 9, 841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christopher, A.; Kaur, R.; Kaur, G.; Kaur, A.; Gupta, V.; Bansal, P. MicroRNA therapeutics: Discovering novel targets and developing specific therapy. Perspect. Clin. Res. 2016, 7, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
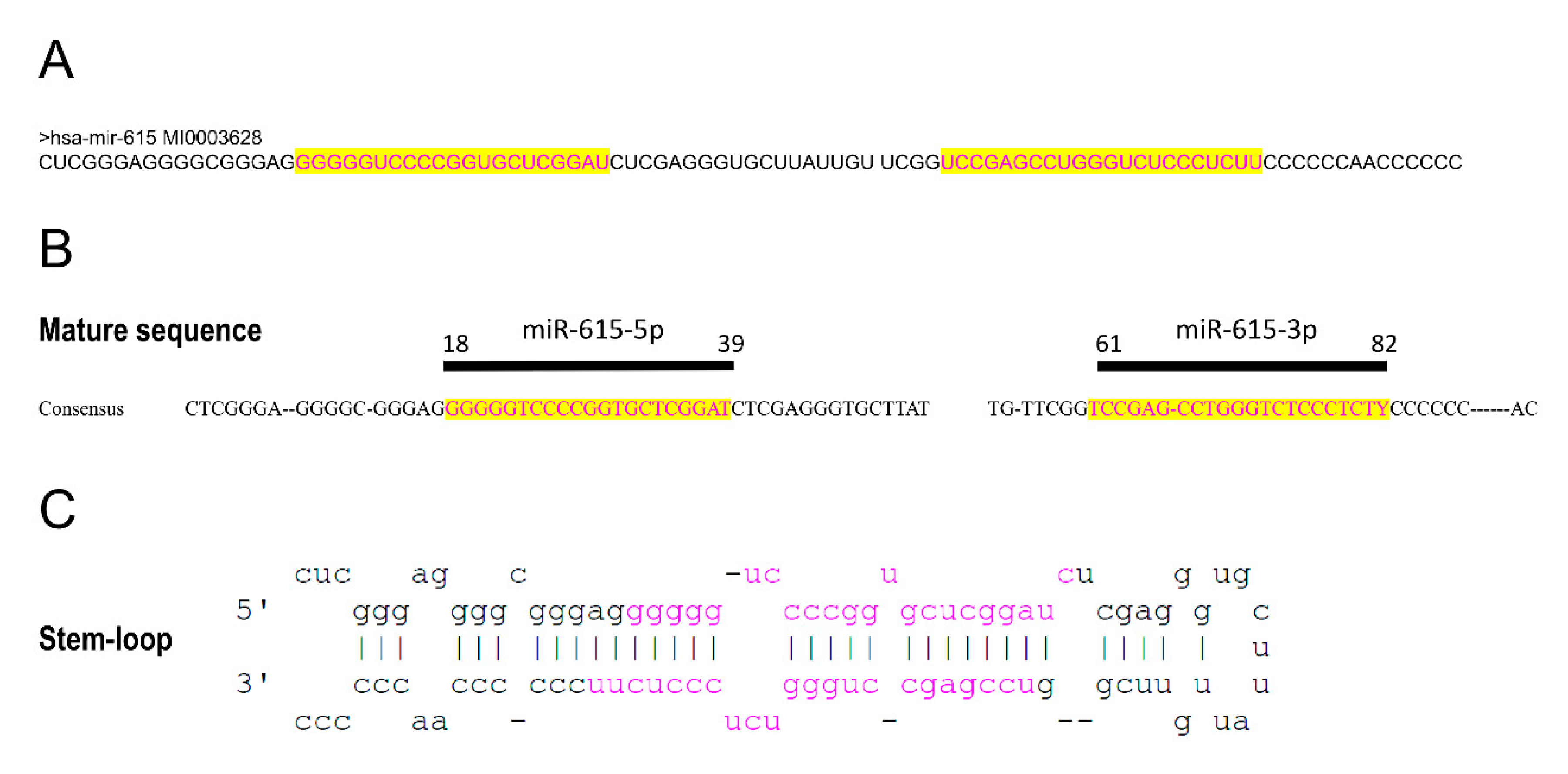
| Target Gene | Description | Gene Action or Effect | Cell Line | Interaction | Effect | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LCoR | Ligand-dependent nuclear receptor corepressor | Suppress PPARδ | THP-1 cells/splenic macrophages | At the 3’UTR of LCoR, located at the 193 bp downstream of the stop codon | Downregulated | [13] |
| CHOP | C/EBP homologous protein | A proapoptotic transcription factor | Mouse hepatocytes/hepatoma cell line | A single predicted binding site in the 3´UTR, located at 195 bp | Upregulated | [14] |
| FOXO1 | Forkhead box protein O1 | A transcription factor regulating insulin signaling pathway, and played roles in adipogenesis, gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis | hBMSCs/hFOB1.19 human osteoblast cell line | n.d. | Downregulated | [15] |
| GDF5 | Growth/ differentiation factor 5 | A member of the TGF-β superfamily and closely related to the bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) | hBMSCs/hFOB1.19 human osteoblast cell line | n.d. | Downregulated | [15] |
| OCLN | Occludin | Major component of tight junction | MSCs/ATII cells | n.d. | Downregulated | [16] |
| CK18 | Cytokeratin 18 | Component of cytoskeleton intermediate filaments | MSCs/ATII cells | n.d. | Downregulated | [16] |
| PICK1 | Protein interacting with C kinase 1 | Regulation of traffic between surface receptors | Human breast cancer cell lines | Targeting the 3′-UTR | Downregulated | [17] |
| IGF2 | Insulin-like growth factor 2 | Growth factor has growth-regulating, insulin-like and mitogenic activities | MKN28, MKN45, SGC7901 and GES-1 cell lines; NSCLC cell lines. | Directly binds to the 3´-UTR | Downregulated | [18,19] |
| hTERT | Telomerase reverse transcriptase | A catalytic subunit of the enzyme telomerase | 56 different NCI-60 cell lines | Targeting its 3′UTR | Downregulated | [20] |
| CELF2 | CUGBP Elav-like family member 2 | A tumor suppressor RNA-binding protein implicated in the regulation of several post-transcriptional events | MKN28, MKN45, SGC7901 and GES-1 cell lines | n.d. | Downregulated | [11] |
| HMGB3 | High mobility group box 3 | Multifunctional protein with various roles in different cellular compartments | Human normal bronchial epithelial cell line 16HBE/NSCLC cell lines (A549 and H1299) | n.d. | Downregulated | [21] |
| JunB | JunB proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | Transcription factor involved in regulating gene activity following the primary growth factor response | Human ESCC cell lines (Eca-109, TE-1 and KY-SE) and human normal esophageal cell line | Downregulated by NORAD | Upregulated | [22] |
| AP-1 | Transcription factor subunit | Involved in several cellular processes (cell growth, differentiation and apoptosis) | Human ESCC cell lines (Eca-109, TE-1, and KY-SE) and Human normal esophageal cell line | Downregulated by NORAD | Upregulated | [22] |
| Ywhag | 14-3-3-δ, protein kinase C inhibitor protein 1 | An abundant, cytosolic and brain-specific protein, which mediates signal transduction | Mice cerebral anterior cortex | Downregulated | [23] | |
| LINGO-1 | LRR and Ig domain containing NOGO receptor interacting protein 1 | Transmembrane protein selectively expressed in neurons and oligodendrocytes in CNS and the spinal cord, mediating axon growth | NSCs fetal brain 14th E.D. | Bind with the target sites (GGACCCC) in the 3′-UTR located in 202-223bp | Downregulated | [24] |
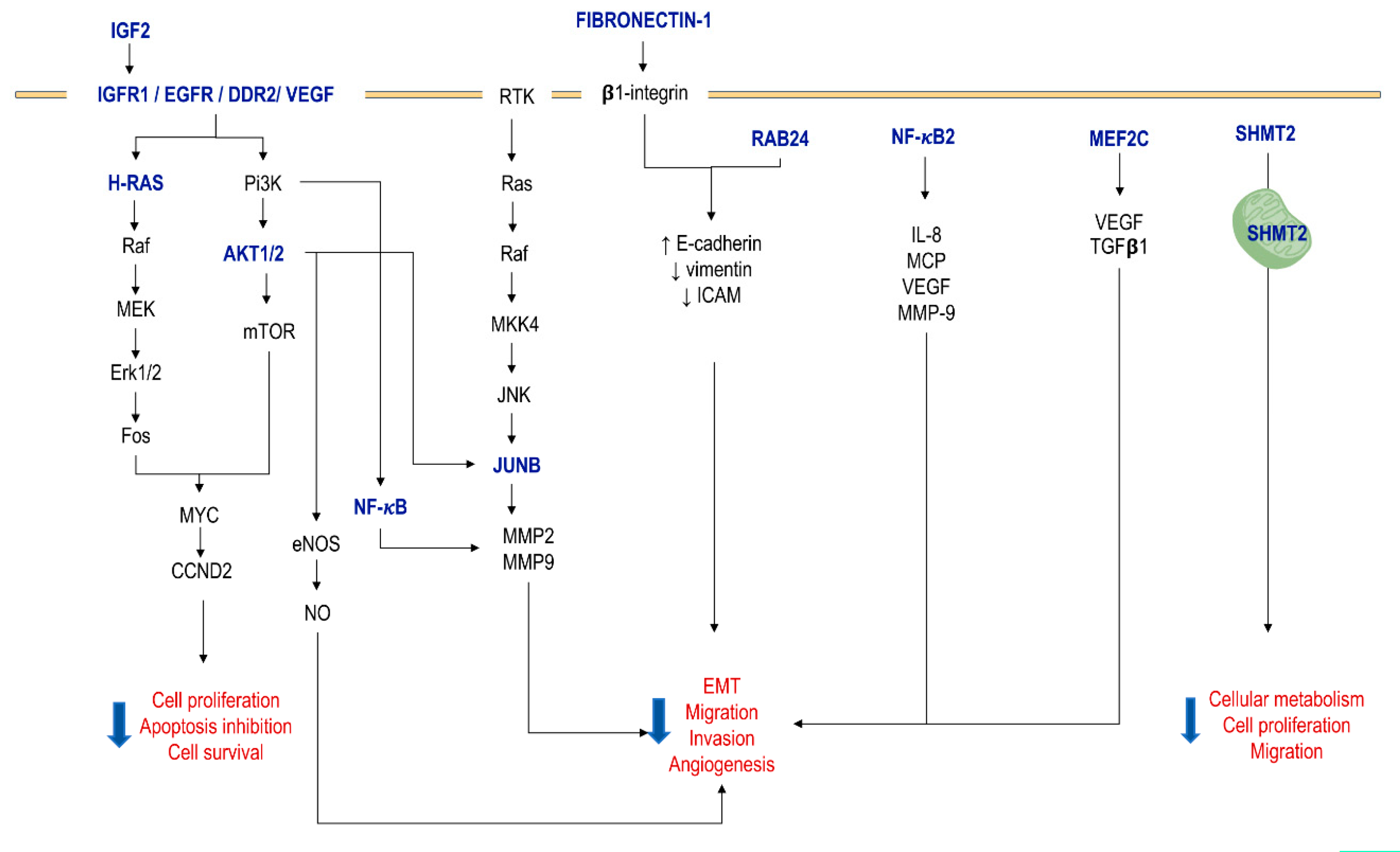
| Target Gene | Description | Gene Action or Effect | Model | Status in Cancer Cells | 3′-UTR Targeting Sequence | Effect | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IGF2 | Insulin-like growth factor 2 | Growth factor | NSLCC, ESCC, HCC, PAC | Upregulated | 5’GGACCCCA3’ | Good prognosis (clinically); ↓ cell motility, migration, cell proliferation and tumor growth | [9,27,56,57,58] |
| AKT1 AKT2 | Serine/threonine protein kinase B 1 and 2 | Regulation of metabolism, apoptosis, cell cycle and transcription | LUAD, PAC | Upregulated | 5’GACCCCA3’ 5’GACCCCU3’ | ↓ tumor growth and metastasis in vivo and cell proliferation, migration and invasion in vitro. ↑ apoptosis | [56,59,60] |
| SHMT2 | Serine Hydroxymethyltransferase 2 | Cellular energy metabolism, proliferation and migration | NSLCC, HCC | Upregulated | 5’GGACCCC3’ | ↓ proliferation, migration, and prevented growth of HCC cells | [51,56] |
| IGFR1 | Insulin-like growth factor type 1 receptor | Receptor tyrosine kinase | HCC | Downregulated | 5’GGACCC3’ | Tumor suppressor effect; ↓ downstream mediators like mTOR | [31] |
| DDR2 | Discoidin Domain Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 2 | Receptor tyrosine kinase | T-cell lympho-blastic lymphoma | Upregulated | 5’GACCCCAA3’ | ↑ apoptosis; ↓ cell viability | [54] |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor | Receptor tyrosine kinase | Glioblastoma | Upregulated | 5’CCACGAGC3’ | Good prognosis (clinically); ↓ cell growth, migration and invasion | [55] |
| NF-kB2 | Nuclear factor NF-kappa-B p100 subunit | Transcription factor related to immunity, differentiation, cell growth, tumorigenesis and apoptosis | Ovarian cancer | Upregulated | 5’GGACCCC3’ | ↓ viability, cell migration and invasion; ↑ apoptosis | [53] |
| MEF2C | Myocyte-specific enhancer factor 2C | Transcription factor, role in myogenesis, neurogenesis and vasculogenesis | NSLCC | Upregulated | n.d. | ↓ cell proliferation, survival, tumor growth, migration and invasion | [61] |
| JUNB | JunB Proto-Oncogene | Transcription factor, AP-1 transcription factor subunit | PAC | Upregulated | n.d. | ↓ cell motility, migration and cell proliferation ↓ HRas/Raf/MAPK and PI3/Akt cascades; ↓ AKT and ERK phosphorylation | [9] |
| CCND2 | Cyclin D2 | Cell cycle regulator | Prostate cancer | Upregulated | 5’GGACCCC3’ | ↓ proliferation, migration and invasion of cancer cells in vitro and in vivo | [62] |
| SF3B3 | Splicing Factor 3b Subunit 3 | Forms small nuclear ribonucleoproteins complex | NSLCC | Upregulated | 5’GACCCC3’ | ↓ cell proliferation, survival, tumor growth, migration and invasion | [61] |
| RAB24 | Ras-related protein 24 | Cytoskeletal remodeling, motility and adhesion | HCC | Upregulated | 5’GGACCCC3’ | ↓ EMT process promotion (↑ E-cadherin, ↓ vimentin, ICAM and β-integrin); ↓ proliferation, survival, motility, adhesion and angiogenesis in vitro and in vivo | [63] |
| FIBRO-NECTIN-1 | ECM protein | LUAD | Upregulated | 5′GUGGACCCC3′ | ↓ MMP2 and MMP9; ↓ migratory and invasive capability | [52] |
| Molecule | Description | Effect | Cell Line | Status in Cancer Cells | Axis Documented | Effects Associated with Inhibition of miR-615 | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| circ-CAMK2A | Circular RNA | Sponge miR-615-5p | LUAD cell lines, HBE | Upregulated | circ-CAMK2A/miR-615-5p/fibronectin-1/MMP | Metastasis, advanced TNM stage and poor prognosis; ↑ migration, and invasion | [52] |
| circPUM1 | Circular RNA | Sponge miR-615-5p | Ovarian cancer cell lines and human peritoneal mesothelial cell line | Upregulated | circPUM1/miR-615-5p/NF-κB | Associated with FIGO stage (poor prognosis); ↑ proliferation, survival, migration, tumor growth and metastasis | [53] |
| circ-LAMP1 | Circular RNA | Sponge miR-615-5p | T-LBL cells Jurkat, CCRF-CEM and SUP-T1 | Upregulated | circ-LAMP1/miR-615-5p/DDR2 | ↑ cell proliferation and viability; ↓ apoptosis | [54] |
| circRNA-100146 | Circular RNA | Sponge miR-615-5p and 3p | 16HBE, LUAD cell line | Upregulated | circRNA- 100146/ miR-615-5p and 3p/MEF2C and SF3B3 | Poor clinical prognosis; ↑ cell proliferation, survival, tumor growth, migration and invasion | [61] |
| LINC00324 | Long noncoding RNA | Sponge miR-615-5p | LUAD cell lines and 16HBE | Upregulated | LINC00324/ miR-615-5p/AKT1 | ↑ cell proliferation, migration and invasion ↓ apoptosis | [60] |
| lncRNA Gm15290 | Long noncoding RNA | Sponge miR-615-5p | HBE and NSCLC cell lines | Upregulated | Gm1529/ miR-615-5p/AKT2, IGF2 and SHMT2 | ↑ proliferation and invasion; ↓ apoptosis | [56] |
| HOTTIP | HOXA transcript at the distal tip | Sponge miR-615-3p | 16HBE/NSCLC cell lines. Human RCC cell lines, normal renal epithelial cells HK-2, 293T. | Upregulated | HOTTIP/miR-615-3p/HMBG3 HOTTIP/miR615-3p/IGF2 | Endogenous sponge; promotion of glycolysis under hypoxic conditions in LUAD; lead to suppression of IGF-2 in RCC | [19,21] |
| NORAD (LIN-C00657) | Noncoding RNA Activated by DNA Damage | Sponge miR-615-3p | Human ESCC cell lines and HEEC | Upregulated | NORAD/miR-615-3p/JunB | Upregulated after DNA damage Oncogenic | [22] |
| KDM4B | Histone demethylase | Lysine demethylase | HCC cell lines | Downregulated | KDM4/miR-615-5p/RAB24 | Demethylation of the miR-615-5p promoter; ↑ proliferation, motility, adhesion and angiogenesis | [63] |
| CDX2 | Caudal type homeobox 2 | Transcriptional activator | Pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Downregulated | CDX2/ miR-615-5p/IGF2 | Induction of transcription of miR-615-5p; neoplastic cell growth. | [57] |
| PU.1 | Transcription factor | Transcriptional activator | HCC cell lines (Hep3B, MHCC97L and MHCC97H). | Downregulated (in metastatic HCC) | PU.1/ miR-615-5p/IGF2 | Induction of transcription of miR-615-5p; ↑ migration and invasion | [64] |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Godínez-Rubí, M.; Ortuño-Sahagún, D. miR-615 Fine-Tunes Growth and Development and Has a Role in Cancer and in Neural Repair. Cells 2020, 9, 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071566
Godínez-Rubí M, Ortuño-Sahagún D. miR-615 Fine-Tunes Growth and Development and Has a Role in Cancer and in Neural Repair. Cells. 2020; 9(7):1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071566
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodínez-Rubí, Marisol, and Daniel Ortuño-Sahagún. 2020. "miR-615 Fine-Tunes Growth and Development and Has a Role in Cancer and in Neural Repair" Cells 9, no. 7: 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071566
APA StyleGodínez-Rubí, M., & Ortuño-Sahagún, D. (2020). miR-615 Fine-Tunes Growth and Development and Has a Role in Cancer and in Neural Repair. Cells, 9(7), 1566. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9071566






