MicroRNA-221: A Fine Tuner and Potential Biomarker of Chronic Liver Injury
Abstract
1. Introduction
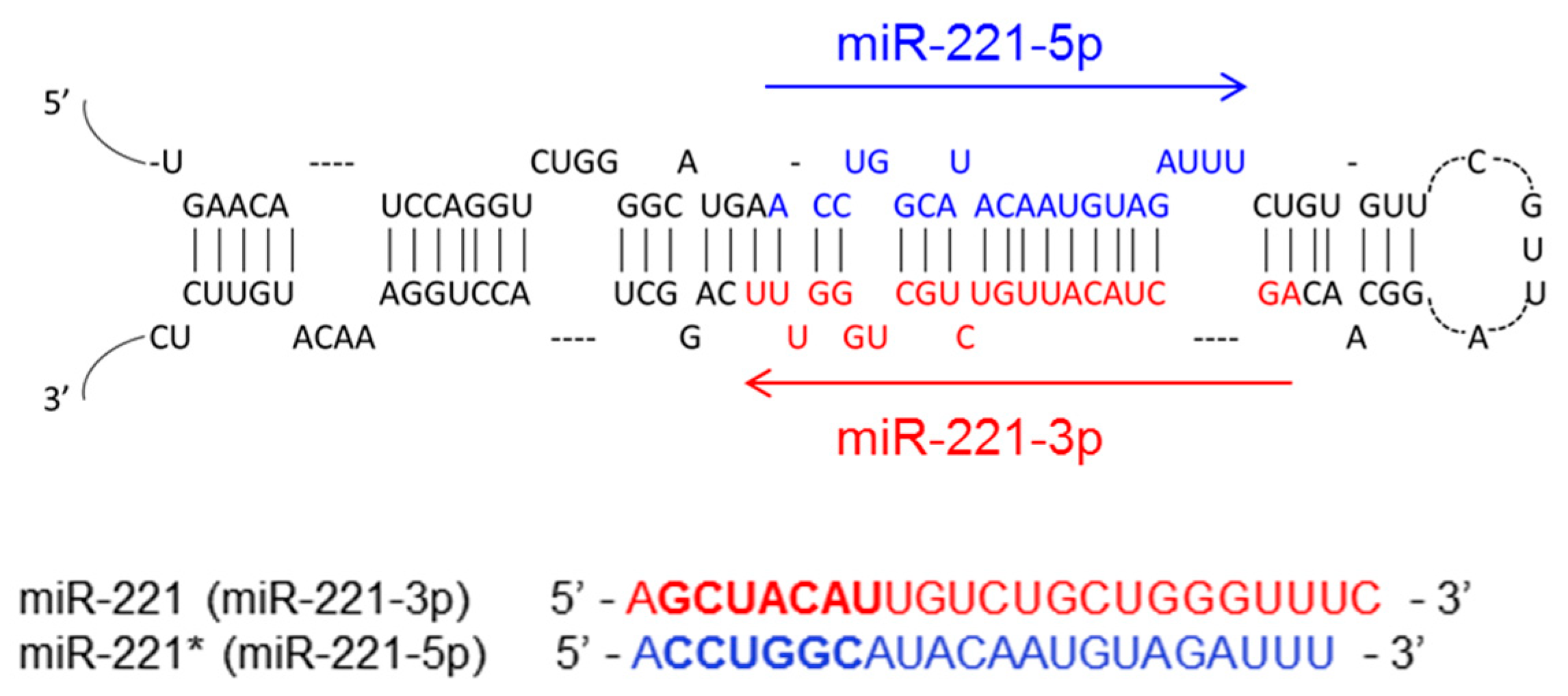
2. The Biogenesis of miR-221
3. MiR-221 is Upregulated During Liver Fibrosis and Other Chronic Liver Diseases
4. Regulation of miRNA-221
5. Potential Mechanism of Fibrosis Regulation by miR-221
6. In vivo miR-221 Inhibition: A Potential Approach for Mitigating Liver Fibrosis
6.1. Tough Decoys
6.2. Locked Nucleic Acids
6.3. MiRNA Sponges
6.4. MiR-221 as A Serum Biomarker
7. Unanswered Questions
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schueller, F.; Roy, S.; Vucur, M.; Trautwein, C.; Luedde, T.; Roderburg, C. The Role of miRNAs in the Pathophysiology of Liver Diseases and Toxicity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Q.; Kumar, V.; Sud, N.; Mahato, R.I. MicroRNAs in the pathogenesis and treatment of progressive liver injury in NAFLD and liver fibrosis. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 129, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.D.; Narain, N.; Händel, E.-M.; Iken, M.; Singhal, N.; Cathomen, T.; Manns, M.P.; Schöler, H.R.; Ott, M.; Cantz, T. MicroRNA-221 regulates FAS-induced fulminant liver failure. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1651–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Medvid, R.; Melton, C.; Jaenisch, R.; Blelloch, R. DGCR8 is essential for microRNA biogenesis and silencing of embryonic stem cell self-renewal. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Denli, A.M.; Tops, B.B.J.; Plasterk, R.H.A.; Ketting, R.F.; Hannon, G.J. Processing of primary microRNAs by the Microprocessor complex. Nature 2004, 432, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Ahn, C.; Han, J.; Choi, H.; Kim, J.; Yim, J.; Lee, J.; Provost, P.; Rådmark, O.; Kim, S.; et al. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature 2003, 425, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gramantieri, L.; Fornari, F.; Ferracin, M.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.; Calin, G.A.; Grazi, G.L.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; Negrini, M. MicroRNA-221 targets Bmf in hepatocellular carcinoma and correlates with tumor multifocality. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 5073–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, F.; Gramantieri, L.; Ferracin, M.; Veronese, A.; Sabbioni, S.A.; Calin, G.; Grazi, G.L.; Giovannini, C.; Croce, C.M.; Bolondi, L.; et al. MiR-221 controls CDKN1C/p57 and CDKN1B/p27 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene 2008, 27, 5651–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pineau, P.; Volinia, S.; McJunkin, K.; Marchio, A.; Battiston, C.; Terris, B.; Mazzaferro, V.; Lowe, S.; Croce, C.; Dejean, A. 579 MIR-221 Overexpression Contributes to Liver Tumorigenesis. J. Hepatol. 2010, 52, S229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roderburg, C.; Urban, G.-W.; Bettermann, K.; Vucur, M.; Zimmermann, H.; Schmidt, S.; Janssen, J.; Koppe, C.; Knolle, P.A.; Castoldi, M.; et al. Micro-RNA profiling reveals a role for miR-29 in human and murine liver fibrosis. Hepatology 2010, 53, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, T.; Enomoto, M.; Fujii, H.; Sekiya, Y.; Yoshizato, K.; Ikeda, K.; Kawada, N. MicroRNA-221/222 upregulation indicates the activation of stellate cells and the progression of liver fibrosis. Gut 2012, 61, 1600–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsay, H.-C.; Yuan, Q.; Balakrishnan, A.; Kaiser, M.; Möbus, S.; Kozdrowska, E.; Farid, M.; Tegtmeyer, P.-K.; Borst, K.; Vondran, F.W.R.; et al. Hepatocyte-specific suppression of microRNA-221-3p mitigates liver fibrosis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 722–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Jiao, X.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J. miR-221 promotes growth and invasion of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by constitutive activation of NFkappaB. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 4764–4777. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Li, M.; Hu, S.; Cheng, X.; Gao, Y.; Jiang, S.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Sun, P.; Xian, W.; et al. MiR-221 mediates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting AdipoR1. Int. J. Boil. Macromol. 2017, 103, 1054–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhou, D.; Li, Y.-X.; Ming, Z.-Y.; Li, K.-Z.; Wu, G.-B.; Chen, C.; Zhao, Y.-N. In vivo and in vitro effects of microRNA-221 on hepatocellular carcinoma development and progression through the JAK-STAT3 signaling pathway by targeting SOCS3. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 234, 3500–3514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galardi, S.; Mercatelli, N.; Farace, M.G.; Ciafrè, S.A. NF-kB and c-Jun induce the expression of the oncogenic miR-221 and miR-222 in prostate carcinoma and glioblastoma cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, 3892–3902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellerbrand, C.; Jobin, C.; Iimuro, Y.; Licato, L.; Sartor, R.B.; Brenner, D.A. Inhibition of NFkappaB in activated rat hepatic stellate cells by proteasome inhibitors and an IkappaB super-repressor. Hepatology 1998, 27, 1285–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, D.; Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Han, J.; Jiang, H. Short interfering RNA targetting NF-kappa B induces apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells and attenuates extracellular matrix production. Dig. Liver Dis. 2010, 42, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eferl, R.; Ricci, R.; Kenner, L.; Zenz, R.; David, J.P.; Rath, M.; Wagner, E.F. Liver tumor development. c-Jun antagonizes the proapoptotic activity of p53. Cell 2003, 112, 181–192. [Google Scholar]
- Trierweiler, C.; Hockenjos, B.; Zatloukal, K.; Thimme, R.; Blum, H.E.; Wagner, E.F.; Hasselblatt, P. The transcription factor c-JUN/AP-1 promotes HBV-related liver tumorigenesis in mice. Cell Death Differ 2016, 23, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulien, I.; Hockenjos, B.; Schmitt-Graeff, A.; Perdekamp, M.G.; Follo, M.; Thimme, R.; Hasselblatt, P. The transcription factor c-Jun/AP-1 promotes liver fibrosis during non-alcoholic steatohepatitis by regulating Osteopontin expression. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 1688–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernig, G.; Chen, S.Y.; Cui, L.; Van Neste, C.; Tsai, J.M.; Kambham, N.; Vogel, H.; Natkunam, Y.; Gilliland, D.G.; Nolan, G.; et al. Unifying mechanism for different fibrotic diseases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 4757–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.; Di Leva, G.; Romano, G.; Nuovo, G.; Suh, S.-S.; Ngankeu, A.; Taccioli, C.; Pichiorri, F.; Alder, H.; Secchiero, P.; et al. miR-221&222 Regulate TRAIL Resistance and Enhance Tumorigenicity through PTEN and TIMP3 Downregulation. Cancer Cell 2009, 16, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garofalo, M.; Quintavalle, C.; Romano, G.; Croce, C.M.; Condorelli, G. miR221/222 in cancer: Their role in tumor progression and response to therapy. Curr. Mol. Med. 2012, 12, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Li, W.; Guo, K.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, J.G. miR-181b Promotes hepatic stellate cells proliferation by targeting p27 and is elevated in the serum of cirrhosis patients. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 421, 4–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.G.; Xu, L.; Wang, T.; Wei, J.; Meng, W.Y.; Wang, N.; Shi, M. Givinostat inhibition of hepatic stellate cell proliferation and protein acetylation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8326–8339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Q.; Loya, K.; Rani, B.; Möbus, S.; Balakrishnan, A.; Lamlé, J.; Cathomen, T.; Vogel, A.; Manns, M.P.; Ott, M.; et al. MicroRNA-221 overexpression accelerates hepatocyte proliferation during liver regeneration. Hepatology 2013, 57, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehgal, M.; Zeremski, M.; Talal, A.H.; Ginwala, R.; Elrod, E.; Grakoui, A.; Li, Q.G.; Philip, R.; Khan, Z.K.; Jain, P. IFN-α-Induced Downregulation of miR-221 in Dendritic Cells: Implications for HCV Pathogenesis and Treatment. J. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2015, 35, 698–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafanda, E.K.; Kandhi, R.; Bobbala, D.; Khan, G.M.; Nandi, M.; Menendez, A.; Ramanathan, S.; Ilangumaran, S. Essential role of suppressor of cytokine signaling 1 (SOCS1) in hepatocytes and macrophages in the regulation of liver fibrosis. Cytokine 2019, 124, 154501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeck, C.; Wehr, A.; Karlmark, K.R.; Heymann, F.; Vucur, M.; Gassler, N.; Huss, S.; Klussmann, S.; Eulberg, D.; Luedde, T.; et al. Pharmacological inhibition of the chemokine CCL2 (MCP-1) diminishes liver macrophage infiltration and steatohepatitis in chronic hepatic injury. Gut 2011, 61, 416–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, N.; Liang, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Zen, K.; Gu, H. Slug-upregulated miR-221 promotes breast cancer progression through suppressing E-cadherin expression. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaimori, A.; Potter, J.; Kaimori, J.-Y.; Wang, C.; Mezey, E.; Koteish, A. Transforming Growth Factor-beta1 Induces an Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition State in Mouse Hepatocytes in Vitro. J. Boil. Chem. 2007, 282, 22089–22101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeisberg, M.; Yang, C.; Martino, M.; Duncan, M.B.; Rieder, F.; Tanjore, H.; Kalluri, R. Fibroblasts Derive from Hepatocytes in Liver Fibrosis via Epithelial to Mesenchymal Transition. J. Boil. Chem. 2007, 282, 23337–23347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, W.F.; Zhou, C.F.; Wu, X.G.; He, L.N.; Wu, L.F.; Chen, X.J.; Yan, R.M.; Zhong, M.; Yu, Y.H.; Liang, L.; et al. MicroRNA-221-3p, a TWIST2 target, promotes cervical cancer metastasis by directly targeting THBS2. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, 3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Yao, L.; Li, G.; Ma, D.; Sun, C.; Gao, S.; Zhang, P.; Gao, F. miR-221 Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition through Targeting PTEN and Forms a Positive Feedback Loop with beta-catenin/c-Jun Signaling Pathway in Extra-Hepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taura, K.; Miura, K.; Iwaisako, K.; Österreicher, C.H.; Kodama, Y.; Penz-Österreicher, M.; Brenner, D.A. Hepatocytes do not undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition in liver fibrosis in mice. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scholten, D.; Österreicher, C.H.; Scholten, A.; Iwaisako, K.; Gu, G.; Brenner, D.A.; Kisseleva, T. Genetic Labeling Does Not Detect Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition of Cholangiocytes in Liver Fibrosis in Mice. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Gubbins, J.; Peng, Z.; Medina, V.; Fei, F.; Asahina, K.; Wang, J.; Kahn, M.; Rountree, C.B.; Stiles, B.L. Activation of hepatic stellate cell in Pten null liver injury model. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair 2016, 9, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Jiang, L.; Shan, A.; Su, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Song, D.; Ji, H.; Ning, G.; Wang, W.; Cao, Y. Targeting hepatic miR-221/222 for therapeutic intervention of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in mice. EBioMedicine 2018, 37, 307–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhao, S.; Chen, X.; Li, F.; Tao, X. miR-221-3p and miR-15b-5p promote cell proliferation and invasion by targeting Axin2 in liver cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2019, 18, 6491–6500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Chou, X.; Guan, F.; Fang, Z.; Lu, S.; Lei, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, W. Enhanced Wnt Signalling in Hepatocytes is Associated with Schistosoma japonicum Infection and Contributes to Liver Fibrosis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Huang, Y.; Chen, L.; Wang, J. miR-221 regulates proliferation and apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells by targeting BMF. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 16, 6697–6704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraguchi, T.; Ozaki, Y.; Iba, H. Vectors expressing efficient RNA decoys achieve the long-term suppression of specific microRNA activity in mammalian cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, R.O.; Hollensen, A.K.; Primo, M.; Sørensen, C.D.; Mikkelsen, J.G. Potent microRNA suppression by RNA Pol II-transcribed ‘Tough Decoy’ inhibitors. RNA 2012, 19, 280–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Sun, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, Y.; Zheng, D.; Shi, J. Combination of AAV-TRAIL with miR-221-Zip Therapeutic Strategy Overcomes the Resistance to TRAIL Induced Apoptosis in Liver Cancer. Theranostics 2017, 7, 3228–3242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünweller, A.; Hartmann, R.K. Locked nucleic acid oligonucleotides: The next generation of antisense agents? BioDrugs 2007, 21, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmen, J.; Lindow, M.; Schütz, S.; Lawrence, M.; Petri, A.; Obad, S.; Lindholm, M.W.; Hedtjärn, M.; Hansen, H.F.; Berger, U.; et al. LNA-mediated microRNA silencing in non-human primates. Nature 2008, 452, 896–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrell, R.E. RNA Methodologies. Encycl. Mol. Cell Biol. Mol. Med. 2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ottosen, S.; Parsley, T.B.; Yang, L.; Zeh, K.; Van Doorn, L.-J.; Van Der Veer, E.; Raney, A.K.; Hodges, M.R.; Patick, A.K. In VitroAntiviral Activity and Preclinical and Clinical Resistance Profile of Miravirsen, a Novel Anti-Hepatitis C Virus Therapeutic Targeting the Human Factor miR-122. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 59, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jopling, C.; Yi, M.; Lancaster, A.M.; Lemon, S.M.; Sarnow, P. Modulation of Hepatitis C Virus RNA Abundance by a Liver-Specific MicroRNA. Science 2005, 309, 1577–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, H.; Honda, M.; Campbell, J.S.; Takegoshi, K.; Sakai, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Shirasaki, T.; Takabatake, R.; Nakamura, M.; Tanaka, T.; et al. Inhibition of microRNA-214 ameliorates hepatic fibrosis and tumor incidence in platelet-derived growth factor C transgenic mice. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 1143–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, J.; Fu, J.; Chen, C.; Jiao, C.; Kong, W.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, D.; Illei, G.G.; et al. LNA-anti-miR-150 ameliorated kidney injury of lupus nephritis by inhibiting renal fibrosis and macrophage infiltration. Arthritis Res. 2019, 21, 276–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Putta, S.; Lanting, L.; Sun, G.; Lawson, G.; Kato, M.; Natarajan, R. Inhibiting MicroRNA-192 Ameliorates Renal Fibrosis in Diabetic Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2012, 23, 458–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernardo, B.C.; Nguyen, S.S.; Winbanks, C.E.; Gao, X.; Boey, E.J.H.; Tham, Y.K.; Kiriazis, H.; Ooi, J.Y.Y.; Porrello, E.R.; Igoor, S.; et al. Therapeutic silencing of miR-652 restores heart function and attenuates adverse remodeling in a setting of established pathological hypertrophy. Faseb J. 2014, 28, 5097–5110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, M.S.; Neilson, J.R.A.; Sharp, P. MicroRNA sponges: Competitive inhibitors of small RNAs in mammalian cells. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moshiri, F.; Callegari, E.; D’Abundo, L.; Corrà, F.; Lupini, L.; Sabbioni, S.; Negrini, M. Inhibiting the oncogenic mir-221 by microRNA sponge: Toward microRNA-based therapeutics for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Bed Bench 2014, 7, 43–54. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Cai, L.; Wang, C.; Deng, X.; Yi, S.; Lei, Z.; Xiao, Q.; Xu, H.; Luo, H.; Sun, J. CASC2/miR-24/miR-221 modulates the TRAIL resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cell through caspase-8/caspase-3. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, F.; Zhu, C.; Wei, Q.; Zhang, T.; Zhou, Y.L. miR-221 suppression through nanoparticle-based miRNA delivery system for hepatocellular carcinoma therapy and its diagnosis as a potential biomarker. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 2295–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, H.; Yang, Y.; Peng, F.; Liu, Y.; Fu, X.; Ji, B. Gold nanoparticles-loaded anti-miR221 enhances antitumor effect of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 16, 1541–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, J.; Kanchagar, C.; Veksler-Lublinsky, I.; Lee, R.C.; McGill, M.R.; Jaeschke, H.; Curry, S.C.; Ambros, V. Circulating microRNA profiles in human patients with acetaminophen hepatotoxicity or ischemic hepatitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 12169–12174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Yuan, Q.; Balakrishnan, A.; Bantel, H.; Klusmann, J.-H.; Manns, M.P.; Ott, M.; Cantz, T.; Sharma, A.D. MicroRNA-125b-5p mimic inhibits acute liver failure. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, C.L.; Xu, G.; Ren, H.; Zhao, L.J.; Zhao, P.; Qi, Z.T.; Wang, W. HCV infection induces the upregulation of miR-221 in NF-κB dependent manner. Virus Res. 2015, 196, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, G.; Yang, F.; Ding, C.L.; Wang, J.; Zhao, P.; Wang, W.; Ren, H. MiR-221 accentuates IFN’s anti-HCV effect by downregulating SOCS1 and SOCS3. Virology 2014, 463, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, W.; Kim, J.; Kang, S.H.; Yang, S.R.; Cho, J.Y.; Cho, H.C.; Shim, S.G.; Paik, Y.H. Serum exosomal microRNAs as novel biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Exp. Mol. Med. 2015, 47, e184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Yu, W.; Chen, J.; Luo, J. Expression of serum miR-221 in human hepatocellular carcinoma and its prognostic significance. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 406, 70–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornari, F.; Ferracin, M.; Treré, D.; Milazzo, M.; Marinelli, S.; Galassi, M.; Venerandi, L.; Pollutri, D.; Patrizi, C.; Borghi, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs, miR-939, miR-595, miR-519d and miR-494, Identify Cirrhotic Patients with HCC. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Wang, Q.; Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Chen, X.; Cao, L.; Tan, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, L.; Bi, J.; et al. Clinical significance of miR-221 and its inverse correlation with p27Kip1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol. Boil. Rep. 2010, 38, 3029–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Zhang, W.; Qian, H.; Tang, H.; Lin, W.; Lu, B.-C. SOCS1 regulates hepatic regenerative response and provides prognostic makers for acute obstructive cholangitis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Organ, S.L.; Tsao, M.-S. An overview of the c-MET signaling pathway. Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2011, 3, S7–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Y.; Yeganeh, M.; Ramanathan, S.; Leblanc, C.; Pomerleau, V.; Ferbeyre, G.; Saucier, C.; Ilangumaran, S. SOCS1 controls liver regeneration by regulating HGF signaling in hepatocytes. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, A.; Suzuki, M.; Sakaguchi, R.; Hanada, T.; Yasukawa, H. SOCS, Inflammation, and Autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, G.M.; Ghosh, A.; Variya, B.; Santharam, M.A.; Kandhi, R.; Ramanathan, S.; Ilangumaran, S. Hepatocyte growth control by SOCS1 and SOCS3. Cytokine 2019, 121, 154733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markovic, J.; Sharma, A.D.; Balakrishnan, A. MicroRNA-221: A Fine Tuner and Potential Biomarker of Chronic Liver Injury. Cells 2020, 9, 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081767
Markovic J, Sharma AD, Balakrishnan A. MicroRNA-221: A Fine Tuner and Potential Biomarker of Chronic Liver Injury. Cells. 2020; 9(8):1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081767
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkovic, Jovana, Amar Deep Sharma, and Asha Balakrishnan. 2020. "MicroRNA-221: A Fine Tuner and Potential Biomarker of Chronic Liver Injury" Cells 9, no. 8: 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081767
APA StyleMarkovic, J., Sharma, A. D., & Balakrishnan, A. (2020). MicroRNA-221: A Fine Tuner and Potential Biomarker of Chronic Liver Injury. Cells, 9(8), 1767. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081767



