circRNAome Profiling in Oral Carcinoma Unveils a Novel circFLNB that Mediates Tumour Growth-Regulating Transcriptional Response
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sequencing Data Analysis and Bioinformatics Analysis
2.2. RNA-Sequencing and Gene Expression Analysis
2.3. Circular RNA Identification and miRNA Sponge Prediction
2.4. RNA Extraction, Reverse Transcription (RT)-PCR, and Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
2.5. Cell Culture
2.6. MTT Cell Proliferation Assay and Colony Formation Assay
2.7. Plasmids Construction for Gene Knockdown and Overexpression
2.8. Wound Healing Assay and Transwell Experiments
2.9. In Vivo Mouse Xenograft Experiment
2.10. Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
3. Results
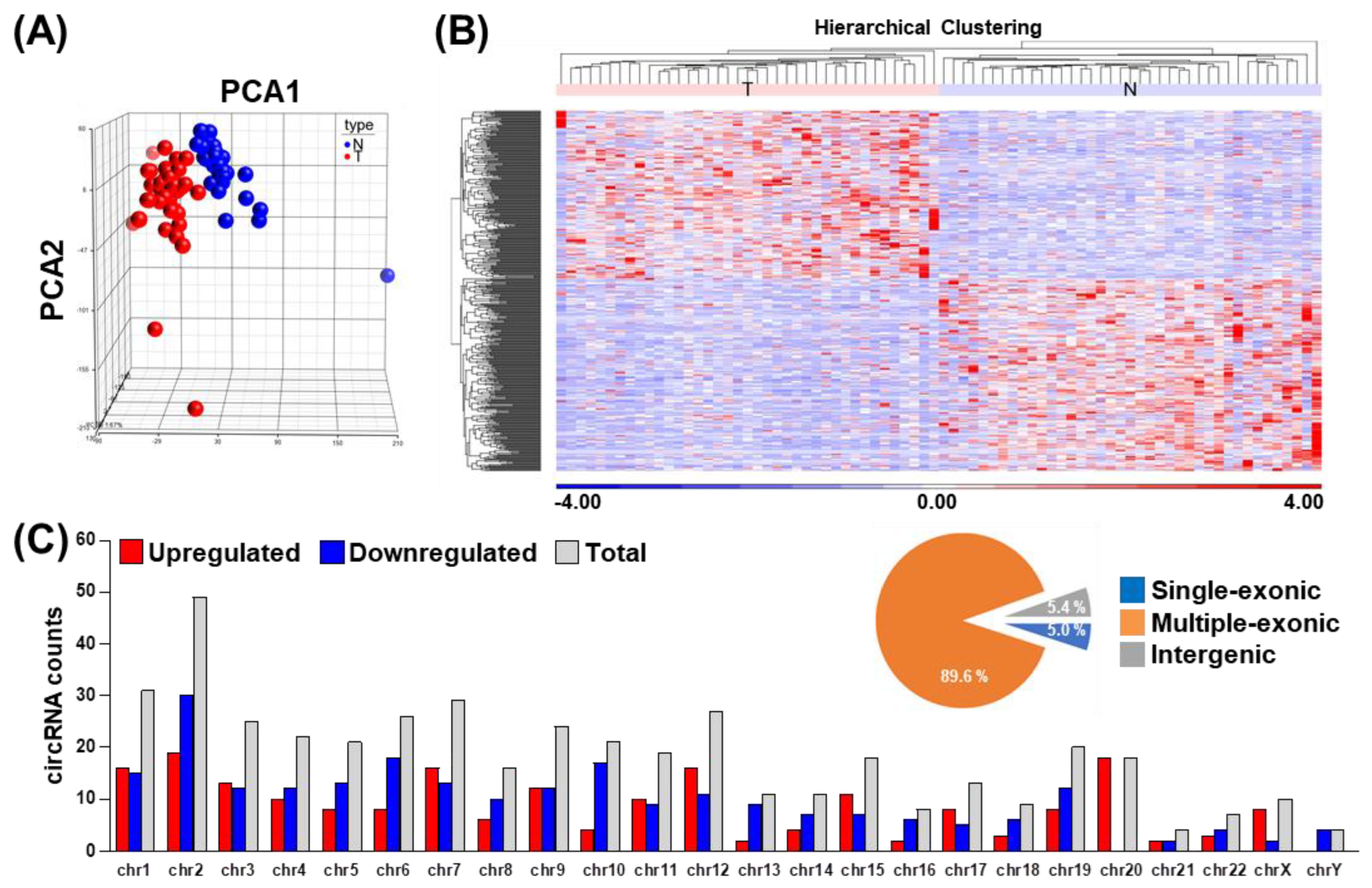
3.1. Integrated Transcriptome-Wide Profiling of the OSCC-Associated circRNA Landscape
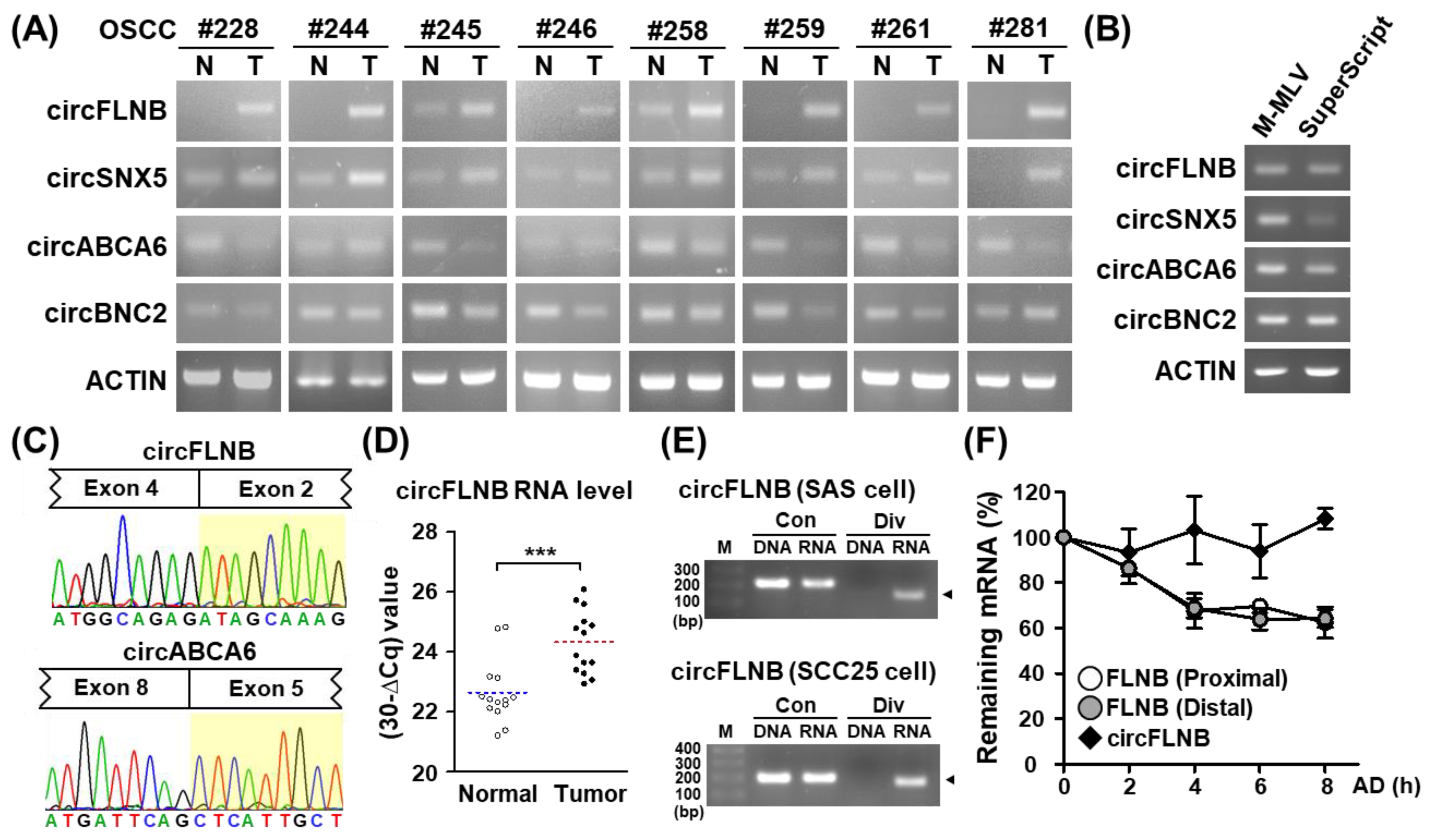
3.2. Identification and Validation of circRNAs Differentially Expressed in OSCC Patients
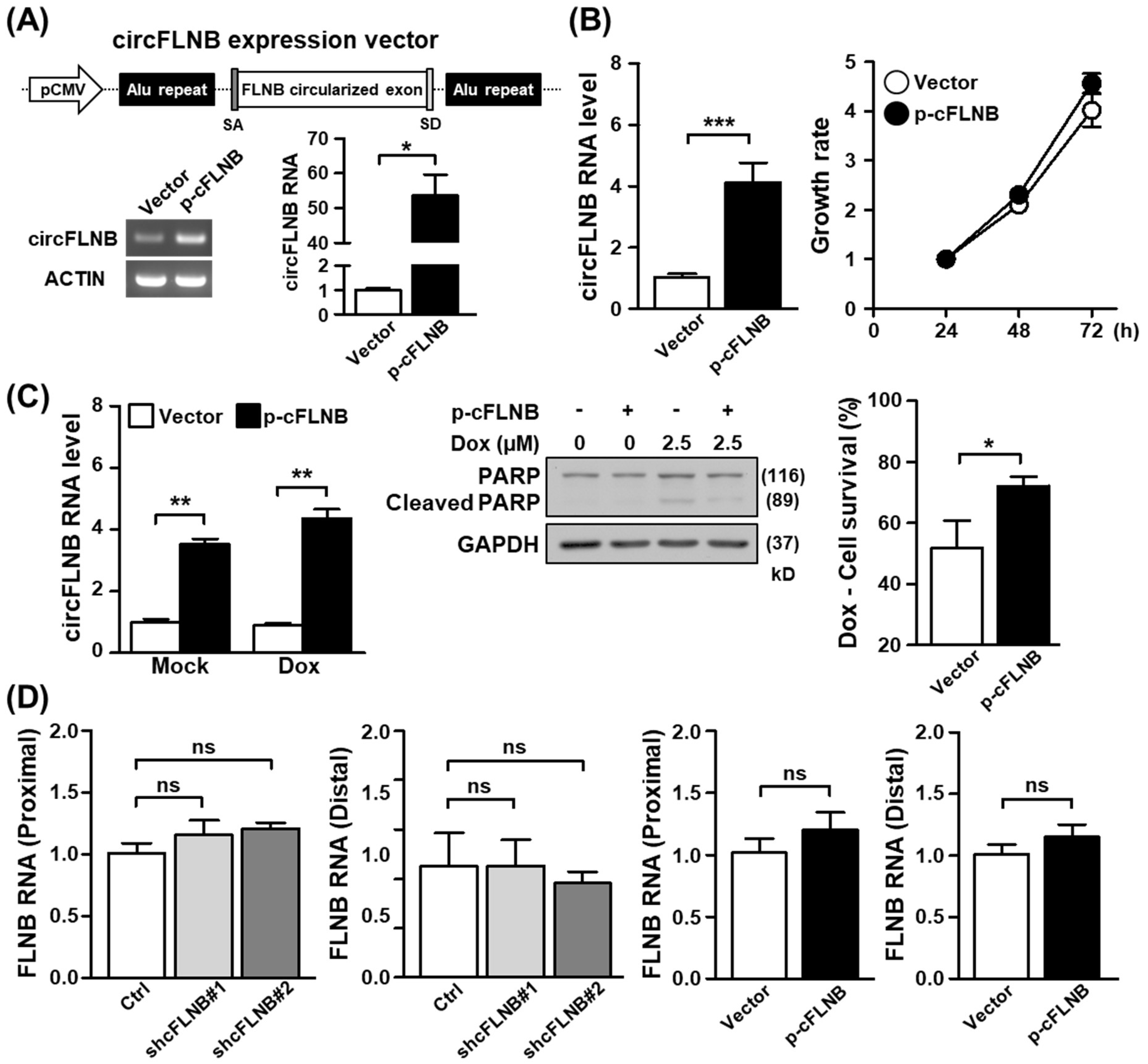
3.3. Characterization of an OSCC-Associated circRNA, circFLNB
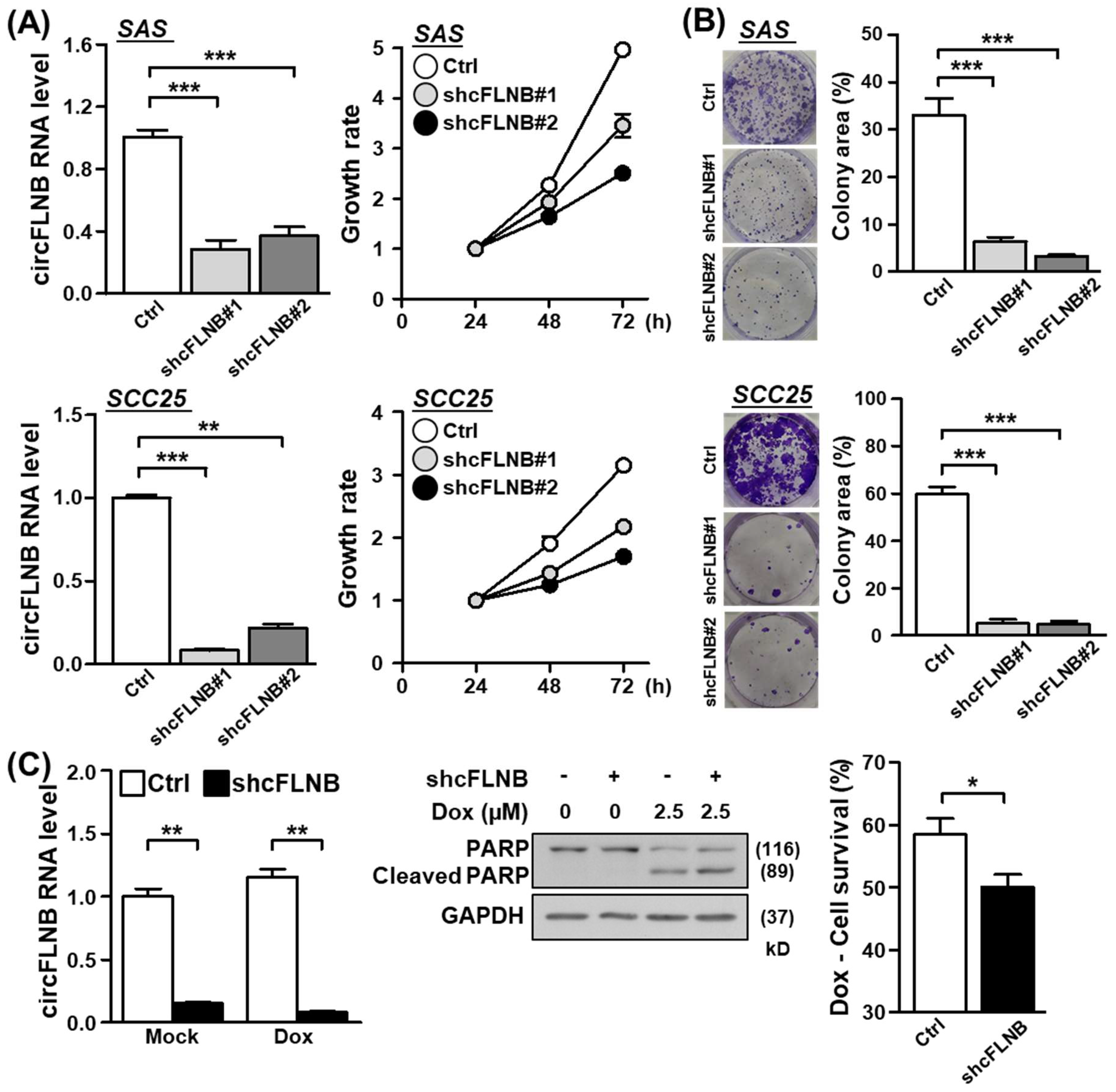
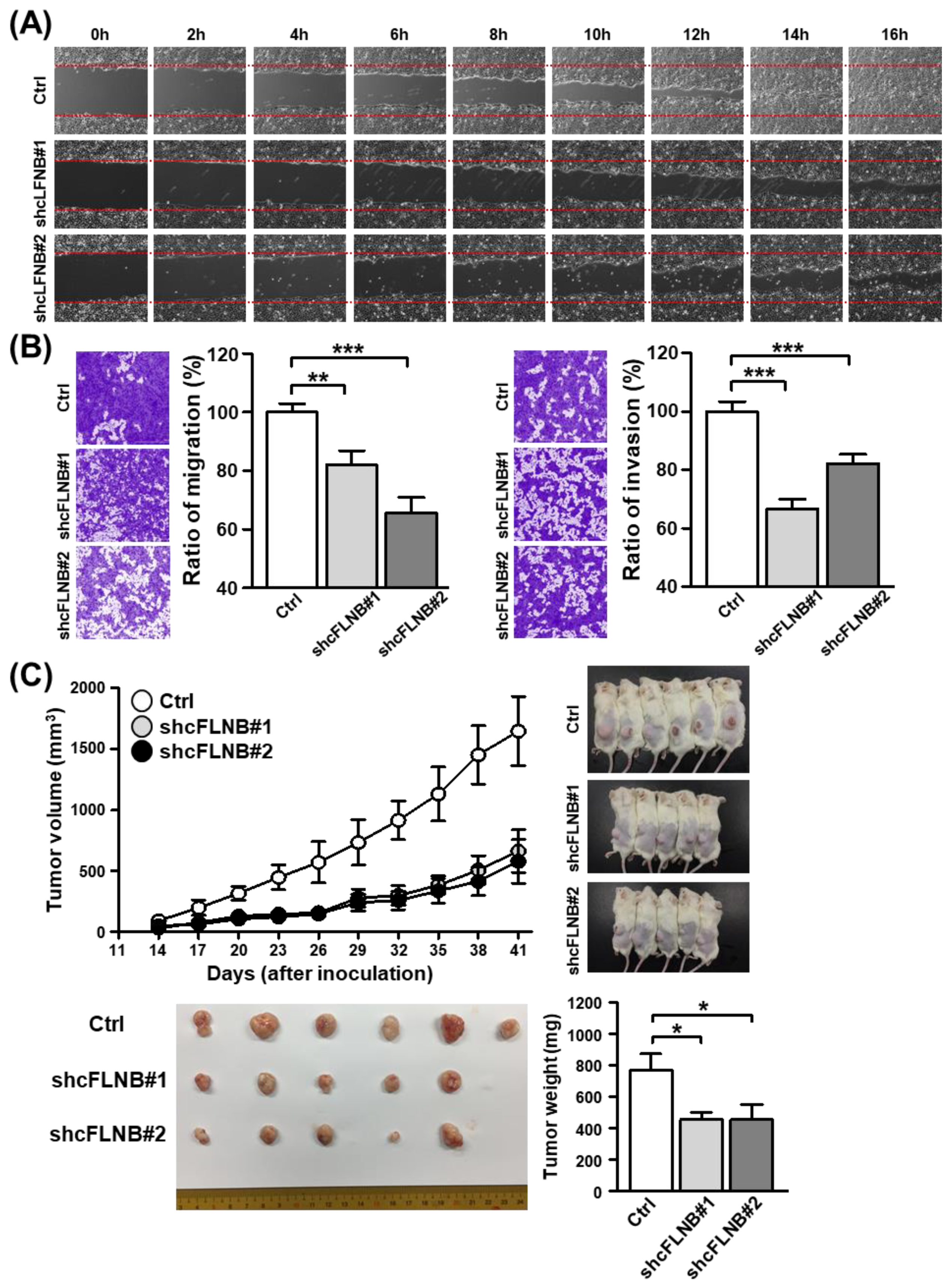
3.4. Knockdown of circFLNB Compromised Tumor Attributes In Vitro and In Vivo
3.5. Knockdown of circFLNB Reduced Cell Metastasis and Tumor Formation
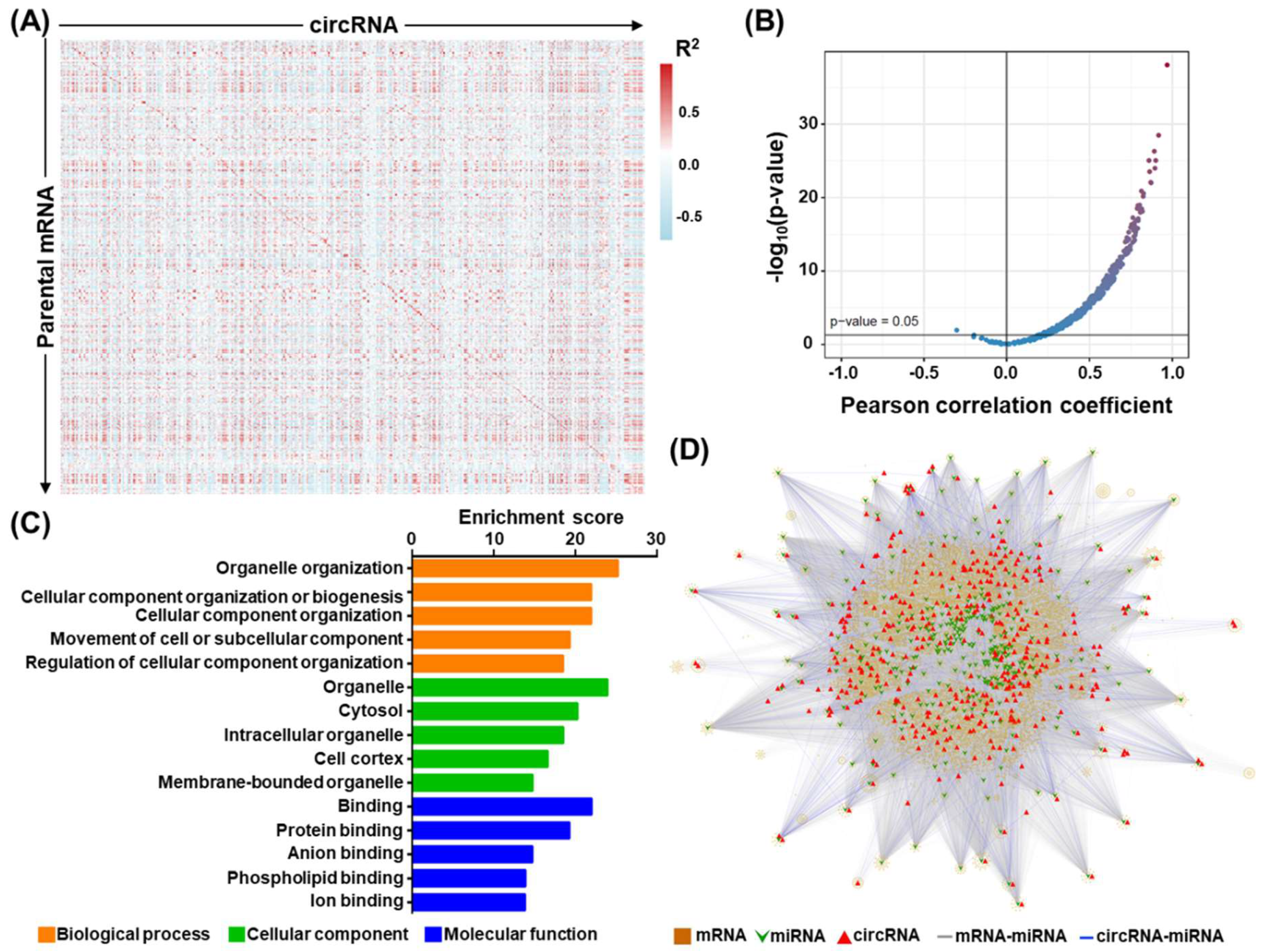
3.6. Exploration of the circFLNB-Mediated Regulatory Network
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chaturvedi, A.K.; Udaltsova, N.; Engels, E.A.; Katzel, J.A.; Yanik, E.L.; Katki, H.A.; Lingen, M.W.; Silverberg, M.J. Oral leukoplakia and risk of progression to oral cancer: A population-based cohort study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shield, K.D.; Ferlay, J.; Jemal, A.; Sankaranarayanan, R.; Chaturvedi, A.K.; Bray, F.; Soerjomataram, I. The global incidence of lip, oral cavity, and pharyngeal cancers by subsite in 2012. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 51–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.A.; Huang, C.G.; Tsao, K.C.; Liao, C.T.; Kang, C.J.; Chang, K.P.; Huang, S.F.; Chen, I.H.; Fang, T.J.; Li, H.Y.; et al. Increasing rates of low-risk human papillomavirus infections in patients with oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma: Association with clinical outcomes. J. Clin. Virol. 2013, 57, 331–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.A.; Huang, C.G.; Tsao, K.C.; Liao, C.T.; Kang, C.J.; Chang, K.P.; Huang, S.F.; Chen, I.H.; Fang, T.J.; Li, H.Y.; et al. Human papillomavirus infections are common and predict mortality in a retrospective cohort study of taiwanese patients with oral cavity cancer. Medicine 2015, 94, e2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ndiaye, C.; Mena, M.; Alemany, L.; Arbyn, M.; Castellsague, X.; Laporte, L.; Bosch, F.X.; de Sanjose, S.; Trottier, H. HPV DNA, E6/E7 mRNA, and p16INK4a detection in head and neck cancers: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet. Oncol. 2014, 15, 1319–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, S.; Yue, K.; Wang, X.D. The recurrence and survival of oral squamous cell carcinoma: A report of 275 cases. Chin. J. Cancer 2013, 32, 614–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinolo, A.A.; Amornphimoltham, P.; Squarize, C.H.; Castilho, R.M.; Patel, V.; Gutkind, J.S. Dysregulated molecular networks in head and neck carcinogenesis. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Zhou, H.; Feng, Z.; Xu, Z.; Tang, Y.; Li, P.; Wu, M. CircRNA: Functions and properties of a novel potential biomarker for cancer. Mol. Cancer 2017, 16, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.Y.; Yang, J.M.; Xiong, X.D. The emerging landscape of circular RNA in cardiovascular diseases. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2018, 122, 134–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Qi, X.; Liu, L.; Hu, X.; Liu, J.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, S.; et al. Emerging epigenetic regulation of circular RNAs in human cancer. Mol. Therapy Nucleic Acids 2019, 16, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, K.; He, B.; Yang, B.B.; Xu, T.; Chen, X.; Xu, M.; Liu, X.; Sun, H.; Pan, Y.; Wang, S. The pro-metastasis effect of circANKS1B in breast cancer. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Deng, T.; Ge, S.; Liu, Y.; Bai, M.; Zhu, K.; Fan, Q.; Li, J.; Ning, T.; Tian, F.; et al. Exosome circRNA secreted from adipocytes promotes the growth of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting deubiquitination-related USP7. Oncogene 2019, 38, 2844–2859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.W.; Yang, W.; Li, X.; Awan, F.M.; Yang, Z.; Fang, L.; Lyu, J.; Li, F.; Peng, C.; Krylov, S.N.; et al. A circular RNA circ-DNMT1 enhances breast cancer progression by activating autophagy. Oncogene 2018, 37, 5829–5842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Li, B.W.; Sun, S.; Li, X.; Su, W.; Wang, Z.H.; Wang, F.; Zhang, W.; Yang, H.Y. Circular RNA expression in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, W.; Sun, S.; Wang, F.; Shen, Y.; Yang, H. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0055538 regulates the malignant biological behavior of oral squamous cell carcinoma through the p53/Bcl-2/caspase signaling pathway. J. Transl. Med. 2019, 17, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Hansen, T.B.; Veno, M.T.; Kjems, J. Circular RNAs in cancer: Opportunities and challenges in the field. Oncogene 2018, 37, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, M.; Xiao, Y.; Ma, J.; Tang, Y.; Tian, B.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Wu, Z.; Yang, D.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Circular RNAs in cancer: Emerging functions in hallmarks, stemness, resistance and roles as potential biomarkers. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Du, Y.; Yang, X.; Mo, Y.; Fan, C.; Xiong, F.; Ren, D.; Ye, X.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Circular RNAs function as ceRNAs to regulate and control human cancer progression. Mol. Cancer 2018, 17, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Guo, W.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Luo, Y.; Lyu, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.W.; Lee, C.C.; Liu, H.; Wu, C.S.; Pickering, C.R.; Huang, P.J.; Wang, J.; Chang, I.Y.; Yeh, Y.M.; Chen, C.D.; et al. APOBEC3A is an oral cancer prognostic biomarker in Taiwanese carriers of an APOBEC deletion polymorphism. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobin, A.; Davis, C.A.; Schlesinger, F.; Drenkow, J.; Zaleski, C.; Jha, S.; Batut, P.; Chaisson, M.; Gingeras, T.R. STAR: Ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrow, J.; Frankish, A.; Gonzalez, J.M.; Tapanari, E.; Diekhans, M.; Kokocinski, F.; Aken, B.L.; Barrell, D.; Zadissa, A.; Searle, S.; et al. GENCODE: The reference human genome annotation for The ENCODE project. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szabo, L.; Morey, R.; Palpant, N.J.; Wang, P.L.; Afari, N.; Jiang, C.; Parast, M.M.; Murry, C.E.; Laurent, L.C.; Salzman, J. Statistically based splicing detection reveals neural enrichment and tissue-specific induction of circular RNA during human fetal development. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, J.; Rehmsmeier, M. RNAhybrid: MicroRNA target prediction easy, fast and flexible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006, 34, W451–W454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, D.W.; Dinger, M.E. Endogenous microRNA sponges: Evidence and controversy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, B.P.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Conserved seed pairing, often flanked by adenosines, indicates that thousands of human genes are microRNA targets. Cell 2005, 120, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legnini, I.; Di Timoteo, G.; Rossi, F.; Morlando, M.; Briganti, F.; Sthandier, O.; Fatica, A.; Santini, T.; Andronache, A.; Wade, M.; et al. Circ-ZNF609 is a circular RNA that can be translated and functions in myogenesis. Mol. Cell 2017, 66, 22–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaiz, E.; Sole, C.; Manterola, L.; Iparraguirre, L.; Otaegui, D.; Lawrie, C.H. CircRNAs and cancer: Biomarkers and master regulators. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2019, 58, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Cui, Y.; Liu, L.; Qi, X.; Liu, J.; Ma, S.; Hu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; et al. Splicing factor derived circular RNA circUHRF1 accelerates oral squamous cell carcinoma tumorigenesis via feedback loop. Cell Death Differ. 2020, 27, 919–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.X.; Liu, Y.; Jia, X.J.; Liu, S.X.; Dong, J.H.; Ren, X.M.; Xu, O.; Zhang, H.Z.; Duan, H.J.; Shan, C.G. Upregulation of circFLNA contributes to laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma migration by circFLNA-miR-486-3p-FLNA axis. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. CircRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Marabti, E.; Younis, I. The cancer spliceome: Reprograming of alternative splicing in cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Yao, Z.; Wang, L.; Ding, H.; Shao, J.; Chen, A.; Zhang, F.; Zheng, S. Activation of ferritinophagy is required for the RNA-binding protein ELAVL1/HuR to regulate ferroptosis in hepatic stellate cells. Autophagy 2018, 14, 2083–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Li, X.X.; Chung, H.K.; Kalakonda, S.; Cai, J.Z.; Cao, S.; Chen, N.; Liu, Y.; Rao, J.N.; Wang, H.Y.; et al. RNA-binding protein HuR regulates paneth cell function by altering membrane localization of TLR2 via post-transcriptional control of CNPY3. Gastroenterology 2019, 157, 731–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Panda, A.C.; Munk, R.; Grammatikakis, I.; Dudekula, D.B.; De, S.; Kim, J.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Martindale, J.L.; et al. Identification of HuR target circular RNAs uncovers suppression of PABPN1 translation by CircPABPN1. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakuguchi, W.; Kitamura, T.; Kuroshima, T.; Ishikawa, M.; Kitagawa, Y.; Totsuka, Y.; Shindoh, M.; Higashino, F. HuR knockdown changes the oncogenic potential of oral cancer cells. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2010, 8, 520–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muralidharan, R.; Mehta, M.; Ahmed, R.; Roy, S.; Xu, L.; Aube, J.; Chen, A.; Zhao, Y.D.; Herman, T.; Ramesh, R.; et al. HuR-targeted small molecule inhibitor exhibits cytotoxicity towards human lung cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, F.; Fang, E.; Xiao, W.; Mei, H.; Li, H.; Li, D.; Song, H.; Wang, J.; Hong, M.; et al. Circular RNA circAGO2 drives cancer progression through facilitating HuR-repressed functions of AGO2-miRNA complexes. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 1346–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Liu, L.; Fu, H.; Wang, Q.; Shi, Y. Association of decreased expression of serum miR-9 with poor prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma patients. Med. Sci. Monit. Int. Med. J. Exp. Clin. Res. 2016, 22, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Liu, K.; Wu, Y.; Fan, J.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Yang, Q.; Wang, Z. MicroRNA-9 inhibits the proliferation of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells by suppressing expression of CXCR4 via the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5017–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, A.; Lu, W.Y.; Yang, M.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, H.; Cai, Z.X.; Wang, W.W.; Wang, W.X.; Wu, G.Q. MiR-9 induces cell arrest and apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma via CDK 4/6 pathway. Artif. Cells Nanomed. Biotechnol. 2018, 46, 1754–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Tan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, S.; Liu, D.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, S. MiR-9-5p inhibits glioblastoma cells proliferation through directly targeting FOXP2 (forkhead box P2). Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, H.; Yao, L.; Tao, X.; Yu, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, R.; Xu, C. MiR-9 functions as a tumor suppressor in ovarian serous carcinoma by targeting TLN1. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 32, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arora, H.; Qureshi, R.; Jin, S.; Park, A.K.; Park, W.Y. MiR-9 and let-7g enhance the sensitivity to ionizing radiation by suppression of NFkappaB1. Exp. Mol. Med. 2011, 43, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, M.; Xiong, G.; Cao, Z.; Yang, G.; Zheng, S.; Qiu, J.; You, L.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, Y. LAT2 regulates glutamine-dependent mTOR activation to promote glycolysis and chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. CR 2018, 37, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.-T.; Chang, I.Y.-F.; Kan, C.-H.; Liu, Y.-H.; Kuo, Y.-P.; Tseng, H.-H.; Chen, H.-C.; Liu, H.; Chang, Y.-S.; Yu, J.-S.; et al. circRNAome Profiling in Oral Carcinoma Unveils a Novel circFLNB that Mediates Tumour Growth-Regulating Transcriptional Response. Cells 2020, 9, 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081868
Chen Y-T, Chang IY-F, Kan C-H, Liu Y-H, Kuo Y-P, Tseng H-H, Chen H-C, Liu H, Chang Y-S, Yu J-S, et al. circRNAome Profiling in Oral Carcinoma Unveils a Novel circFLNB that Mediates Tumour Growth-Regulating Transcriptional Response. Cells. 2020; 9(8):1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081868
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yi-Tung, Ian Yi-Feng Chang, Chia-Hua Kan, Yu-Hao Liu, Yu-Ping Kuo, Hsin-Hao Tseng, Hsing-Chun Chen, Hsuan Liu, Yu-Sun Chang, Jau-Song Yu, and et al. 2020. "circRNAome Profiling in Oral Carcinoma Unveils a Novel circFLNB that Mediates Tumour Growth-Regulating Transcriptional Response" Cells 9, no. 8: 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081868
APA StyleChen, Y.-T., Chang, I. Y.-F., Kan, C.-H., Liu, Y.-H., Kuo, Y.-P., Tseng, H.-H., Chen, H.-C., Liu, H., Chang, Y.-S., Yu, J.-S., Chang, K.-P., & Tan, B. C.-M. (2020). circRNAome Profiling in Oral Carcinoma Unveils a Novel circFLNB that Mediates Tumour Growth-Regulating Transcriptional Response. Cells, 9(8), 1868. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081868




