Alcohol and Smoking Mediated Modulations in Adaptive Immunity in Pancreatitis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
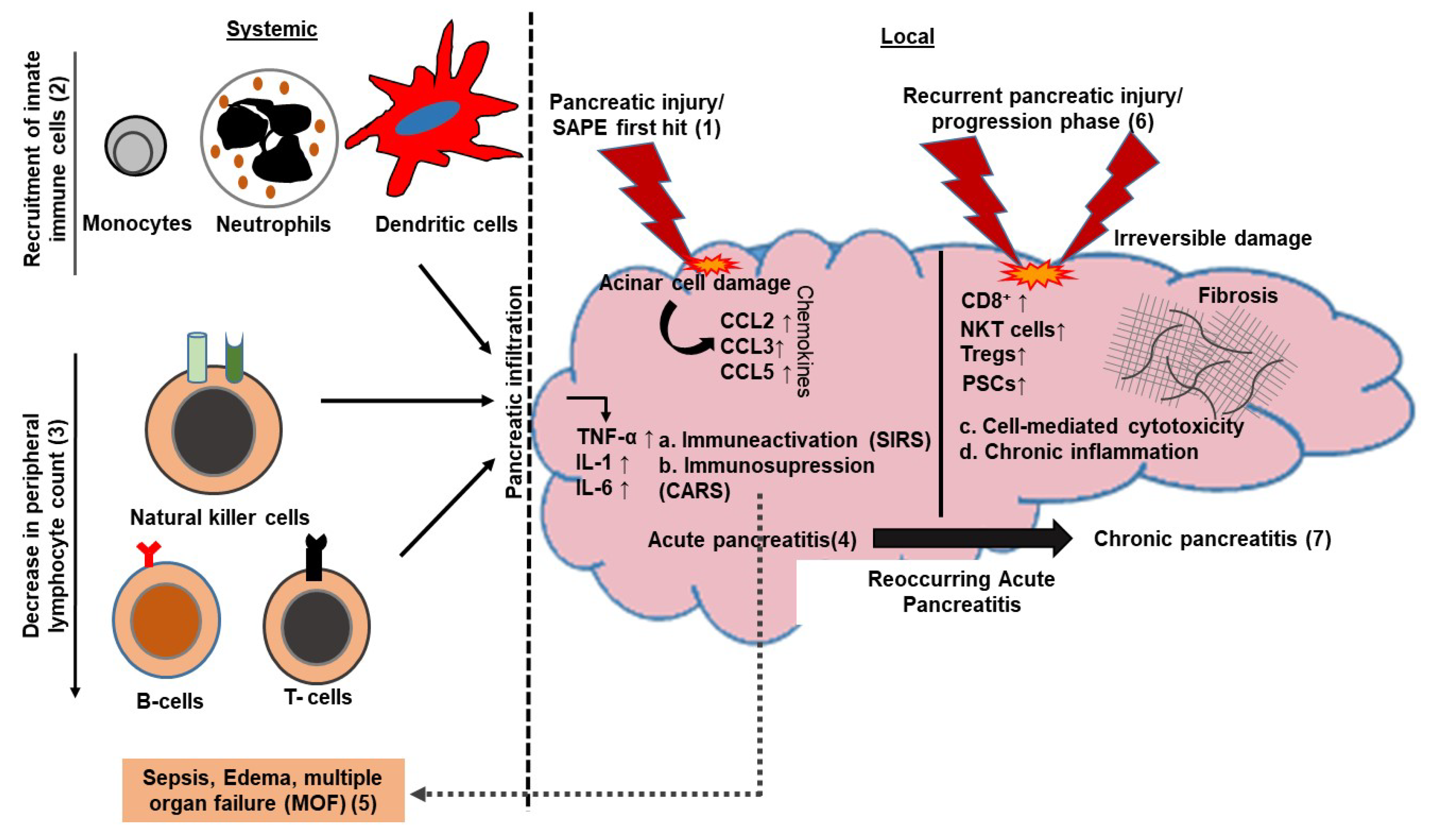
2. Role of Adaptive Immune Mediators in Pancreatitis
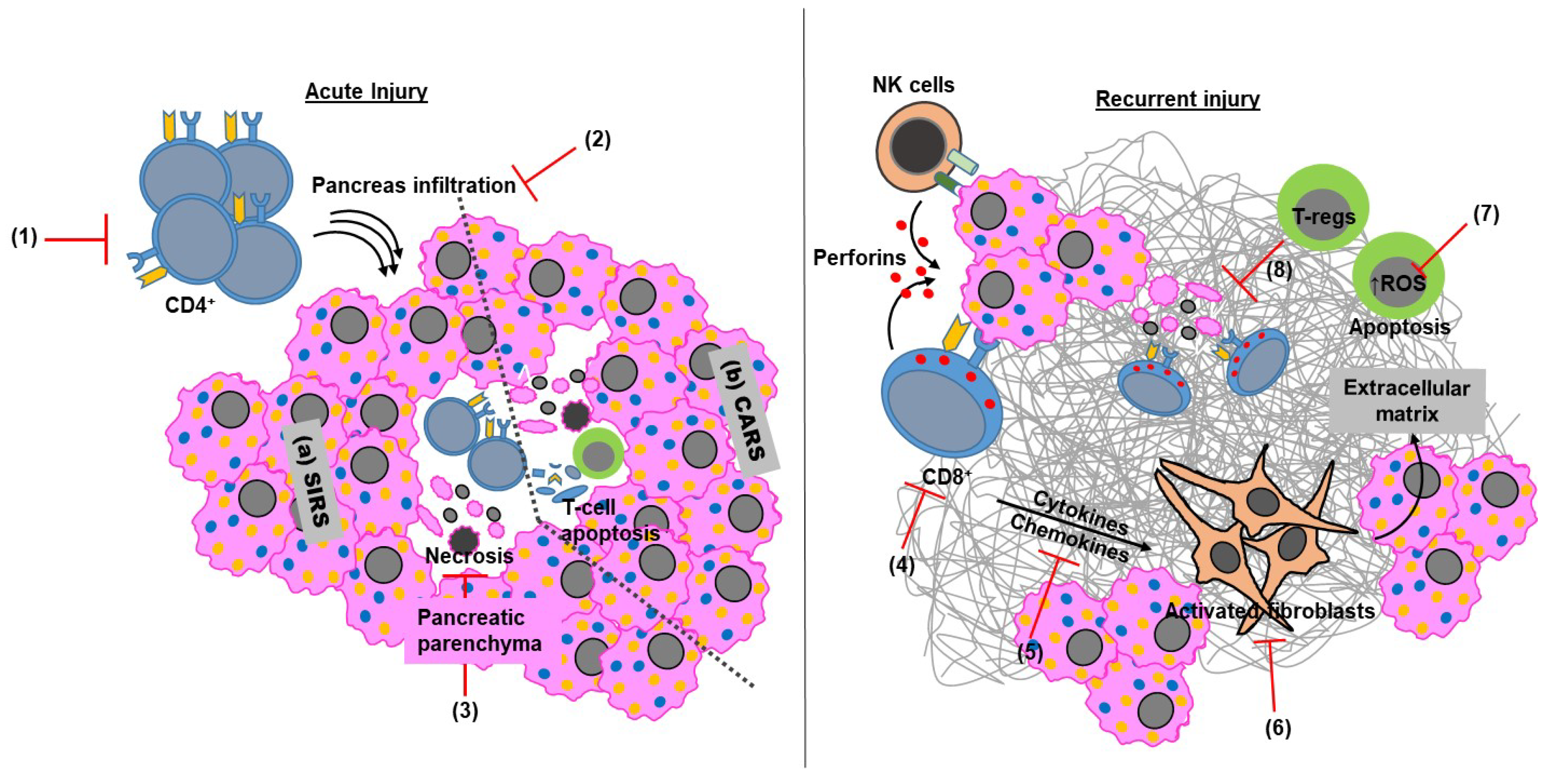
2.1. Adaptive Immunity in Acute Pancreatitis
2.2. Adaptive Immunity in Chronic Pancreatitis
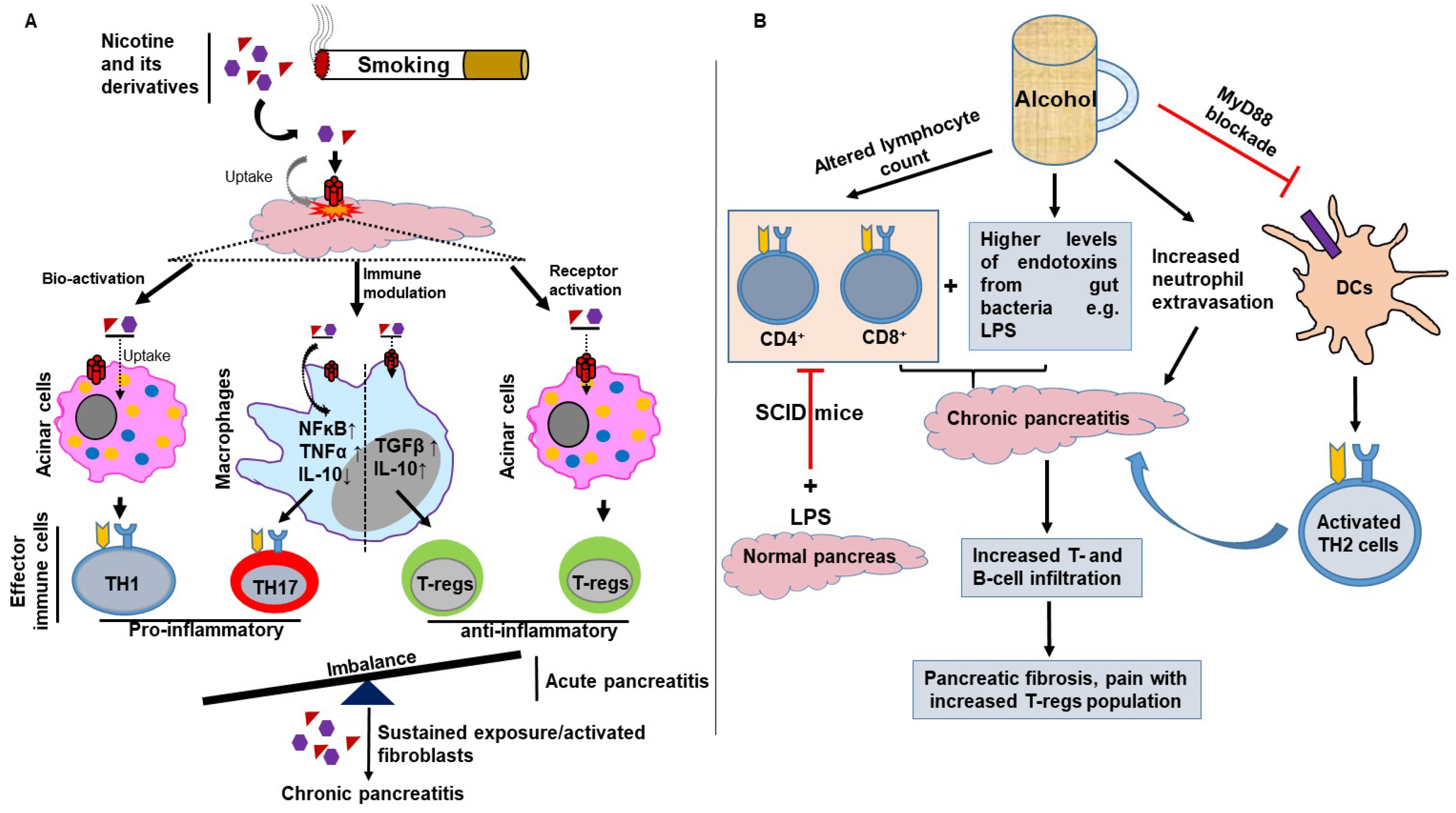
3. Smoking and Alcohol-Mediated Modulation of Adaptive Immunity in Pancreatitis
4. Other Factors Influencing Adaptive Immunity in Pancreatitis
5. Impact of Targeting the Adaptive Immune Arm in Pancreatitis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarles, H.; Sarles, J.C.; Muratore, R.; Guien, C. Chronic inflammatory sclerosis of the pancreas--an autonomous pancreatic disease? Am. J. Dig. Dis. 1961, 6, 688–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, D.; Gukovskaya, A.; Reavey, P.; Gukovsky, S.; Sisk, A.; Braquet, P.; Pandol, S.J.; Poucell-Hatton, S. The role of neutrophils and platelet-activating factor in mediating experimental pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 1996, 111, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gukovskaya, A.S.; Vaquero, E.; Zaninovic, V.; Gorelick, F.S.; Lusis, A.J.; Brennan, M.L.; Holland, S.; Pandol, S.J. Neutrophils and NADPH oxidase mediate intrapancreatic trypsin activation in murine experimental acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 974–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gukovskaya, A.S.; Gukovsky, I.; Zaninovic, V.; Song, M.; Sandoval, D.; Gukovsky, S.; Pandol, S.J. Pancreatic acinar cells produce, release, and respond to tumor necrosis factor-alpha. Role in regulating cell death and pancreatitis. J. Clin. Invest. 1997, 100, 1853–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bhatia, M.; Brady, M.; Shokuhi, S.; Christmas, S.; Neoptolemos, J.P.; Slavin, J. Inflammatory mediators in acute pancreatitis. J. Pathol. 2000, 190, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Neuhofer, P.; Song, L.; Rabe, B.; Lesina, M.; Kurkowski, M.U.; Treiber, M.; Wartmann, T.; Regner, S.; Thorlacius, H.; et al. IL-6 trans-signaling promotes pancreatitis-associated lung injury and lethality. J. Clin. Invest. 2013, 123, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takeyama, Y.; Nishikawa, J.; Ueda, T.; Hori, Y.; Yamamoto, M.; Kuroda, Y. Involvement of peritoneal macrophage in the induction of cytotoxicity due to apoptosis in ascitic fluid associated with severe acute pancreatitis. J. Surg. Res. 1999, 82, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, J.; Sharma, V.; Habtezion, A. Immune cells and immune-based therapy in pancreatitis. Immunol. Res. 2014, 58, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtezion, A. Inflammation in acute and chronic pancreatitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 31, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bedrosian, A.S.; Nguyen, A.H.; Hackman, M.; Connolly, M.K.; Malhotra, A.; Ibrahim, J.; Cieza-Rubio, N.E.; Henning, J.R.; Barilla, R.; Rehman, A.; et al. Dendritic cells promote pancreatic viability in mice with acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, L.; Xue, J.; Jaffee, E.M.; Habtezion, A. Role of immune cells and immune-based therapies in pancreatitis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yadav, D.; Lowenfels, A.B. The epidemiology of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1252–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, J.; Sharma, V.; Hsieh, M.H.; Chawla, A.; Murali, R.; Pandol, S.J.; Habtezion, A. Alternatively activated macrophages promote pancreatic fibrosis in chronic pancreatitis. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Demols, A.; Le Moine, O.; Desalle, F.; Quertinmont, E.; Van Laethem, J.L.; Deviere, J. CD4(+)T cells play an important role in acute experimental pancreatitis in mice. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz-Winnenthal, H.; Pietsch, D.H.; Schimmack, S.; Bonertz, A.; Udonta, F.; Ge, Y.; Galindo, L.; Specht, S.; Volk, C.; Zgraggen, K.; et al. Chronic pancreatitis is associated with disease-specific regulatory T-cell responses. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1178–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmrich, J.; Weber, I.; Nausch, M.; Sparmann, G.; Koch, K.; Seyfarth, M.; Lohr, M.; Liebe, S. Immunohistochemical characterization of the pancreatic cellular infiltrate in normal pancreas, chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic carcinoma. Digestion 1998, 59, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietruczuk, M.; Dabrowska, M.I.; Wereszczynska-Siemiatkowska, U.; Dabrowski, A. Alteration of peripheral blood lymphocyte subsets in acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 5344–5351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curley, P.J.; McMahon, M.J.; Lancaster, F.; Banks, R.E.; Barclay, G.R.; Shefta, J.; Boylston, A.W.; Whicher, J.T. Reduction in circulating levels of CD4-positive lymphocytes in acute pancreatitis: Relationship to endotoxin, interleukin 6 and disease severity. Br. J. Surg. 1993, 80, 1312–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pezzilli, R.; Billi, P.; Beltrandi, E.; Maldini, M.; Mancini, R.; Morselli Labate, A.M.; Miglioli, M. Circulating lymphocyte subsets in human acute pancreatitis. Pancreas 1995, 11, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempuraj, D.; Twait, E.C.; Williard, D.E.; Yuan, Z.; Meyerholz, D.K.; Samuel, I. The novel cytokine interleukin-33 activates acinar cell proinflammatory pathways and induces acute pancreatic inflammation in mice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e56866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Uehara, S.; Gothoh, K.; Handa, H.; Tomita, H.; Tomita, Y. Immune function in patients with acute pancreatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2003, 18, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curley, P.; Nestor, M.; Collins, K.; Saporoschetz, I.; Mendez, M.; Mannick, J.A.; Rodrick, M.L. Decreased interleukin-2 production in murine acute pancreatitis: Potential for immunomodulation. Gastroenterology 1996, 110, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oiva, J.; Mustonen, H.; Kylanpaa, M.L.; Kyhala, L.; Kuuliala, K.; Siitonen, S.; Kemppainen, E.; Puolakkainen, P.; Repo, H. Acute pancreatitis with organ dysfunction associates with abnormal blood lymphocyte signaling: Controlled laboratory study. Crit. Care 2010, 14, R207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mylona, V.; Koussoulas, V.; Tzivras, D.; Makrygiannis, E.; Georgopoulou, P.; Koratzanis, G.; Giamarellos-Bourboulis, E.J.; Tzivras, M.D. Changes in adaptive and innate immunity in patients with acute pancreatitis and systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Pancreatology 2011, 11, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inman, K.S.; Francis, A.A.; Murray, N.R. Complex role for the immune system in initiation and progression of pancreatic cancer. World J. Gastroenterol 2014, 20, 11160–11181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerem, E. Treatment of severe acute pancreatitis and its complications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 13879–13892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beger, H.G.; Bittner, R.; Block, S.; Buchler, M. Bacterial contamination of pancreatic necrosis. A prospective clinical study. Gastroenterology 1986, 91, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, P.A.; Bollen, T.L.; Dervenis, C.; Gooszen, H.G.; Johnson, C.D.; Sarr, M.G.; Tsiotos, G.G.; Vege, S.S. Classification of acute pancreatitis--2012: Revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 2013, 62, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Dong, L.; Yang, C.; Gou, S.; Yin, T.; Wu, H.; Wang, C. The Reduction of Peripheral Blood CD4+ T Cell Indicates Persistent Organ Failure in Acute Pancreatitis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Hou, C.; Zhu, X.; Peng, Y.; Guo, F.; Zhang, K.; Huang, D.; Li, Q.; Miao, Y. New Predictor of Organ Failure in Acute Pancreatitis: CD4+ T Lymphocytes and CD19+ B Lymphocytes. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1012584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, J.; Nguyen, D.T.; Habtezion, A. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor regulates pancreatic IL-22 production and protects mice from acute pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2012, 143, 1670–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, L.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, Q.; Yu, J.; Li, Q.; Sun, R. Decreased levels of regulatory B cells in patients with acute pancreatitis: Association with the severity of the disease. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 36067–36082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McKay, C.J.; Glen, P.; McMillan, D.C. Chronic inflammation and pancreatic cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2008, 22, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitone, L.J.; Greenhalf, W.; Howes, N.R.; Neoptolemos, J.P. Hereditary pancreatitis and secondary screening for early pancreatic cancer. Rocz. Akad. Med. Bialymst. 2005, 50, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ebert, M.P.; Ademmer, K.; Muller-Ostermeyer, F.; Friess, H.; Buchler, M.W.; Schubert, W.; Malfertheiner, P. CD8+CD103+ T cells analogous to intestinal intraepithelial lymphocytes infiltrate the pancreas in chronic pancreatitis. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 1998, 93, 2141–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunger, R.E.; Mueller, C.; Z’Graggen, K.; Friess, H.; Buchler, M.W. Cytotoxic cells are activated in cellular infiltrates of alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 1997, 112, 1656–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Sogawa, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Kaneda, K.; Nakamura, S.; Kuno, A.; Sano, H.; Ando, T.; Kobayashi, S.; et al. Role of T cells in development of chronic pancreatitis in male Wistar Bonn/Kobori rats: Effects of tacrolimus. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2001, 281, G1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gansauge, F.; Gansauge, S.; Eh, M.; Schlosser, W.; Ramadani, M.; Kern, P.; Beger, H.G. Distributional and functional alterations of immunocompetent peripheral blood lymphocytes in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Ann. Surg. 2001, 233, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Ma, C.; Bian, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, T.; Su, L.; Lu, J. Hydrogen Treatment Protects Mice Against Chronic Pancreatitis by Restoring Regulatory T Cells Loss. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 2005–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grundsten, M.; Liu, G.Z.; Permert, J.; Hjelmstrom, P.; Tsai, J.A. Increased central memory T cells in patients with chronic pancreatitis. Pancreatology 2005, 5, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochi, A.; Nguyen, A.H.; Bedrosian, A.S.; Mushlin, H.M.; Zarbakhsh, S.; Barilla, R.; Zambirinis, C.P.; Fallon, N.C.; Rehman, A.; Pylayeva-Gupta, Y.; et al. MyD88 inhibition amplifies dendritic cell capacity to promote pancreatic carcinogenesis via Th2 cells. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1671–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ammann, R.W.; Muellhaupt, B.; Meyenberger, C.; Heitz, P.U. Alcoholic nonprogressive chronic pancreatitis: Prospective long-term study of a large cohort with alcoholic acute pancreatitis (1976–1992). Pancreas 1994, 9, 365–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lankisch, P.G.; Breuer, N.; Bruns, A.; Weber-Dany, B.; Lowenfels, A.B.; Maisonneuve, P. Natural history of acute pancreatitis: A long-term population-based study. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 104, 2797–2805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lugea, A.; Gerloff, A.; Su, H.Y.; Xu, Z.; Go, A.; Hu, C.; French, S.W.; Wilson, J.S.; Apte, M.V.; Waldron, R.T.; et al. The Combination of Alcohol and Cigarette Smoke Induces Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Cell Death in Pancreatic Acinar Cells. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1674–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sahin-Toth, M.; Hegyi, P. Smoking and Drinking Synergize in Pancreatitis: Multiple Hits on Multiple Targets. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1479–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yadav, D.; Whitcomb, D.C. The role of alcohol and smoking in pancreatitis. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 131–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Batra, S.K. Interleukin-22 Connects Smoking and Pancreatic Fibrosis During Chronic Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 1067–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galitovskiy, V.; Qian, J.; Chernyavsky, A.I.; Marchenko, S.; Gindi, V.; Edwards, R.A.; Grando, S.A. Cytokine-induced alterations of alpha7 nicotinic receptor in colonic CD4 T cells mediate dichotomous response to nicotine in murine models of Th1/Th17- versus Th2-mediated colitis. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 2677–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skok, M.V.; Kalashnik, E.N.; Koval, L.N.; Tsetlin, V.I.; Utkin, Y.N.; Changeux, J.P.; Grailhe, R. Functional nicotinic acetylcholine receptors are expressed in B lymphocyte-derived cell lines. Mol. Pharmacol. 2003, 64, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnson, Y.; Shoenfeld, Y.; Amital, H. Effects of tobacco smoke on immunity, inflammation and autoimmunity. J. Autoimmun. 2010, 34, J258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalra, R.; Singh, S.P.; Savage, S.M.; Finch, G.L.; Sopori, M.L. Effects of cigarette smoke on immune response: Chronic exposure to cigarette smoke impairs antigen-mediated signaling in T cells and depletes IP3-sensitive Ca(2+) stores. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2000, 293, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maeno, T.; Houghton, A.M.; Quintero, P.A.; Grumelli, S.; Owen, C.A.; Shapiro, S.D. CD8+ T Cells are required for inflammation and destruction in cigarette smoke-induced emphysema in mice. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 8090–8096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Muto, H.; Takizawa, Y. Dioxins in cigarette smoke. Arch. Environ. Health 1989, 44, 171–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stedman, R.L. The chemical composition of tobacco and tobacco smoke. Chem. Rev. 1968, 68, 153–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Zhao, Q.; Sharma, V.; Nguyen, L.P.; Lee, Y.N.; Pham, K.L.; Edderkaoui, M.; Pandol, S.J.; Park, W.; Habtezion, A. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Ligands in Cigarette Smoke Induce Production of Interleukin-22 to Promote Pancreatic Fibrosis in Models of Chronic Pancreatitis. Gastroenterology 2016, 151, 1206–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mili, F.; Flanders, W.D.; Boring, J.R.; Annest, J.L.; DeStefano, F. The associations of alcohol drinking and drinking cessation to measures of the immune system in middle-aged men. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1992, 16, 688–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheorghiu, M.; Bara, C.; Pasarica, D.; Brasoveanu, L.; Bleotu, C.; Toparceanu, F.; Trandafir, T.; Diaconu, C.C. Ethanol-induced dysfunction of hepatocytes and leukocytes in patients without liver failure. Roum. Arch. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 63, 5–33. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyadjieva, N.I.; Dokur, M.; Advis, J.P.; Meadows, G.G.; Sarkar, D.K. Beta-endorphin modulation of lymphocyte proliferation: Effects of ethanol. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2002, 26, 1719–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slukvin, II.; Jerrells, T.R. Different pathways of in vitro ethanol-induced apoptosis in thymocytes and splenic T and B lymphocytes. Immunopharmacology 1995, 31, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasala, S.; Barr, T.; Messaoudi, I. Impact of Alcohol Abuse on the Adaptive Immune System. Alcohol Res. 2015, 37, 185–197. [Google Scholar]
- Hakim, F.T.; Gress, R.E. Immunosenescence: Deficits in adaptive immunity in the elderly. Tissue Antigens 2007, 70, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, J.P.; Effros, R.B. T cell replicative senescence in human aging. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 1680–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhlbauer, E.; Karsten, U.; Rottmann, M.; Rommelspacher, H. Impaired immunoglobulin M production by incubation of hybridoma cells with ethanol. Alcohol 2001, 24, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, G.M.; Duryee, M.J.; Willis, M.S.; Tuma, D.J.; Radio, S.J.; Hunter, C.D.; Schaffert, C.S.; Klassen, L.W. Autoimmune hepatitis induced by syngeneic liver cytosolic proteins biotransformed by alcohol metabolites. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2010, 34, 2126–2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clemens, D.L.; Schneider, K.J.; Arkfeld, C.K.; Grode, J.R.; Wells, M.A.; Singh, S. Alcoholic pancreatitis: New insights into the pathogenesis and treatment. World J. Gastrointest. Pathophysiol. 2016, 7, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, P.; Gupta, P. Pathophysiology of alcoholic pancreatitis: An overview. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 7421–7427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vonlaufen, A.; Xu, Z.; Daniel, B.; Kumar, R.K.; Pirola, R.; Wilson, J.; Apte, M.V. Bacterial endotoxin: A trigger factor for alcoholic pancreatitis? Evidence from a novel, physiologically relevant animal model. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1293–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vonlaufen, A.; Phillips, P.A.; Xu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yang, L.; Pirola, R.C.; Wilson, J.S.; Apte, M.V. Withdrawal of alcohol promotes regression while continued alcohol intake promotes persistence of LPS-induced pancreatic injury in alcohol-fed rats. Gut 2011, 60, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wang, L.; Elm, M.S.; Gabazadeh, D.; Diorio, G.J.; Eagon, P.K.; Whitcomb, D.C. Chronic alcohol consumption accelerates fibrosis in response to cerulein-induced pancreatitis in rats. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 166, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gukovsky, I.; Lugea, A.; Shahsahebi, M.; Cheng, J.H.; Hong, P.P.; Jung, Y.J.; Deng, Q.G.; French, B.A.; Lungo, W.; French, S.W.; et al. A rat model reproducing key pathological responses of alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Perides, G.; Tao, X.; West, N.; Sharma, A.; Steer, M.L. A mouse model of ethanol dependent pancreatic fibrosis. Gut 2005, 54, 1461–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.T.; Xu, Z.; Pothula, S.P.; Patel, M.B.; Pirola, R.C.; Wilson, J.S.; Apte, M.V. Alcohol and cigarette smoke components activate human pancreatic stellate cells: Implications for the progression of chronic pancreatitis. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 2015, 39, 2123–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Jin, T.; Hao, J. Nicotine promotes activation of human pancreatic stellate cells through inducing autophagy via alpha7nAChR-mediated JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. Life Sci. 2020, 243, 117301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gryshchenko, O.; Gerasimenko, J.V.; Gerasimenko, O.V.; Petersen, O.H. Calcium signalling in pancreatic stellate cells: Mechanisms and potential roles. Cell Calcium 2016, 59, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimosegawa, T.; Chari, S.T.; Frulloni, L.; Kamisawa, T.; Kawa, S.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Kim, M.H.; Kloppel, G.; Lerch, M.M.; Lohr, M.; et al. International consensus diagnostic criteria for autoimmune pancreatitis: Guidelines of the International Association of Pancreatology. Pancreas 2011, 40, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fritz, S.; Bergmann, F.; Grenacher, L.; Sgroi, M.; Hinz, U.; Hackert, T.; Buchler, M.W.; Werner, J. Diagnosis and treatment of autoimmune pancreatitis types 1 and 2. Br. J. Surg. 2014, 101, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Yamashita, K.; Fujikawa, S.; Sakurai, T.; Kudo, M.; Shiokawa, M.; Kodama, Y.; Uchida, K.; Okazaki, K.; Chiba, T. Involvement of activation of toll-like receptors and nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors in enhanced IgG4 responses in autoimmune pancreatitis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 914–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T.; Yamashita, K.; Sakurai, T.; Kudo, M.; Shiokawa, M.; Uza, N.; Kodama, Y.; Uchida, K.; Okazaki, K.; Chiba, T. Toll-like receptor activation in basophils contributes to the development of IgG4-related disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 48, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukui, Y.; Uchida, K.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Fukui, T.; Nishio, A.; Shikata, N.; Sakaida, N.; Uemura, Y.; Satoi, S.; Okazaki, K. Possible involvement of Toll-like receptor 7 in the development of type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis. J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 50, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishi, H.; Tojo, A.; Onozato, M.L.; Jimbo, R.; Nangaku, M.; Uozaki, H.; Hirano, K.; Isayama, H.; Omata, M.; Kaname, S.; et al. Anti-carbonic anhydrase II antibody in autoimmune pancreatitis and tubulointerstitial nephritis. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 1273–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okazaki, K.; Uchida, K.; Ohana, M.; Nakase, H.; Uose, S.; Inai, M.; Matsushima, Y.; Katamura, K.; Ohmori, K.; Chiba, T. Autoimmune-related pancreatitis is associated with autoantibodies and a Th1/Th2-type cellular immune response. Gastroenterology 2000, 118, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, O.; Tan, S. From Pathogenesis, Clinical Manifestation, and Diagnosis to Treatment: An Overview on Autoimmune Pancreatitis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2017, 2017, 3246459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endo, T.; Takizawa, S.; Tanaka, S.; Takahashi, M.; Fujii, H.; Kamisawa, T.; Kobayashi, T. Amylase alpha-2A autoantibodies: Novel marker of autoimmune pancreatitis and fulminant type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2009, 58, 732–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.C.; Dong, F.; Pan, J.F.; Zhuang, Z.H.; Gao, F.; Liu, G.Z.; Chen, Q.Q.; Chen, S.; Weng, S.H.; Lin, L.Q.; et al. Antibodies to Type IV Collagen Induce Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis. Inflammation 2016, 39, 592–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smyk, D.S.; Rigopoulou, E.I.; Koutsoumpas, A.L.; Kriese, S.; Burroughs, A.K.; Bogdanos, D.P. Autoantibodies in autoimmune pancreatitis. Int J. Rheumatol 2012, 2012, 940831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, H.; Uchida, K.; Taniguchi, T.; Yazumi, S.; Matsushita, M.; Takaoka, M.; Okazaki, K. Circulating naive and CD4+CD25high regulatory T cells in patients with autoimmune pancreatitis. Pancreas 2008, 36, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, K.; Kusuda, T.; Koyabu, M.; Miyoshi, H.; Fukata, N.; Sumimoto, K.; Fukui, Y.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Ikeura, T.; Shimatani, M.; et al. Regulatory T cells in type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis. Int. J. Rheumatol. 2012, 2012, 795026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raphael, K.L.; Willingham, F.F. Hereditary pancreatitis: Current perspectives. Clin. Exp. Gastroenterol. 2016, 9, 197–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Whitcomb, D.C. Genetic aspects of pancreatitis. Annu. Rev. Med. 2010, 61, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dani, R.; Antunes, L.J.; Rocha, W.M.; Nogueira, C.E. AW23 and AW24 associated with chronic calcifying pancreatitis of alcoholic origin (author’s transl). Arq. Gastroenterol. 1978, 15, 163–166. (In Portuguese) [Google Scholar]
- Forbes, A.; Schwarz, G.; Mirakian, R.; Drummond, V.; Chan, C.K.; Cotton, P.B.; Bottazzo, G.F. HLA antigens in chronic pancreatitis. Tissue Antigens 1987, 30, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Homma, T.; Kubo, K.; Sato, T. HLA antigen and chronic pancreatitis in Japan. Digestion 1981, 21, 267–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gullo, L.; Tabacchi, P.L.; Corazza, G.R.; Calanca, F.; Campione, O.; Labo, G. HLA-B13 and chronic calcific pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 1982, 27, 214–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, R.J.; Dyer, P.A.; Donnai, D.; Klouda, P.T.; Jennison, R.; Braganza, J.M. Chronic pancreatitis, HLA and autoimmunity. Int. J. Pancreatol. 1988, 3, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavestro, G.M.; Frulloni, L.; Neri, T.M.; Seghini, P.; Nouvenne, A.; Zanetti, A.; Bovo, P.; Di Mario, F.; Okolicsanyi, L.; Cavallini, G. Association of HLA-DRB1*0401 allele with chronic pancreatitis. Pancreas 2003, 26, 388–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Adamska, J.Z.; Namkoong, H.; Bellin, M.D.; Wilhelm, J.; Szot, G.L.; Louis, D.M.; Davis, M.M.; Pandol, S.J.; Habtezion, A. Distinct immune characteristics distinguish hereditary and idiopathic chronic pancreatitis. J. Clin. Invest. 2020, 130, 2705–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buch, S.; Schafmayer, C.; Volzke, H.; Seeger, M.; Miquel, J.F.; Sookoian, S.C.; Egberts, J.H.; Arlt, A.; Pirola, C.J.; Lerch, M.M.; et al. Loci from a genome-wide analysis of bilirubin levels are associated with gallstone risk and composition. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1942–1951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Kampen, O.; Buch, S.; Nothnagel, M.; Azocar, L.; Molina, H.; Brosch, M.; Erhart, W.; Von Schonfels, W.; Egberts, J.; Seeger, M.; et al. Genetic and functional identification of the likely causative variant for cholesterol gallstone disease at the ABCG5/8 lithogenic locus. Hepatology 2013, 57, 2407–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtezion, A.; Algul, H. Immune modulation in acute and chronic pancreatitis. Pancreapedia Exocrine Pancreas Knowl. Base 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mrazek, A.A.; Porro, L.J.; Bhatia, V.; Falzon, M.; Spratt, H.; Zhou, J.; Chao, C.; Hellmich, M.R. Apigenin inhibits pancreatic stellate cell activity in pancreatitis. J. Surg. Res. 2015, 196, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rickmann, M.; Vaquero, E.C.; Malagelada, J.R.; Molero, X. Tocotrienols induce apoptosis and autophagy in rat pancreatic stellate cells through the mitochondrial death pathway. Gastroenterology 2007, 132, 2518–2532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsang, S.W.; Zhang, H.; Lin, C.; Xiao, H.; Wong, M.; Shang, H.; Yang, Z.J.; Lu, A.; Yung, K.K.; Bian, Z. Rhein, a natural anthraquinone derivative, attenuates the activation of pancreatic stellate cells and ameliorates pancreatic fibrosis in mice with experimental chronic pancreatitis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, W.G.; Li, L.; Appana, S.; Wei, W.; Stello, K.; Andersen, D.K.; Hughes, S.J.; Whitcomb, D.C.; Brand, R.E.; Yadav, D.; et al. Unique circulating immune signatures for recurrent acute pancreatitis, chronic pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer: A pilot study of these conditions with and without diabetes. Pancreatology 2020, 20, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Shi, J.; Zhang, R.; Ni, J.; Habtezion, A.; Wang, X.; Hu, G.; Xue, J. Expanded CD14(hi)CD16(-) Immunosuppressive Monocytes Predict Disease Severity in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis. J. Immunol. 2019, 202, 2578–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhatia, R.; Thompson, C.; Ganguly, K.; Singh, S.; Batra, S.K.; Kumar, S. Alcohol and Smoking Mediated Modulations in Adaptive Immunity in Pancreatitis. Cells 2020, 9, 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081880
Bhatia R, Thompson C, Ganguly K, Singh S, Batra SK, Kumar S. Alcohol and Smoking Mediated Modulations in Adaptive Immunity in Pancreatitis. Cells. 2020; 9(8):1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081880
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhatia, Rakesh, Christopher Thompson, Koelina Ganguly, Shailender Singh, Surinder K. Batra, and Sushil Kumar. 2020. "Alcohol and Smoking Mediated Modulations in Adaptive Immunity in Pancreatitis" Cells 9, no. 8: 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081880
APA StyleBhatia, R., Thompson, C., Ganguly, K., Singh, S., Batra, S. K., & Kumar, S. (2020). Alcohol and Smoking Mediated Modulations in Adaptive Immunity in Pancreatitis. Cells, 9(8), 1880. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9081880




