Evidence for Strong Kinship Influence on the Extent of Linkage Disequilibrium in Cultivated Common Beans
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
2.2. DNA Extraction, Genotyping by Sequencing Library Preparation, Sequencing, and SNP Calling
2.3. Filtering and Imputing Genotyping by Sequencing SNP Calls
2.4. Population Structure, Kinship, and Linkage Disequilibrium Investigation
3. Results
3.1. Single Nucleotide Polymorphism Calling and Imputation
3.2. Population Structure and Kinship
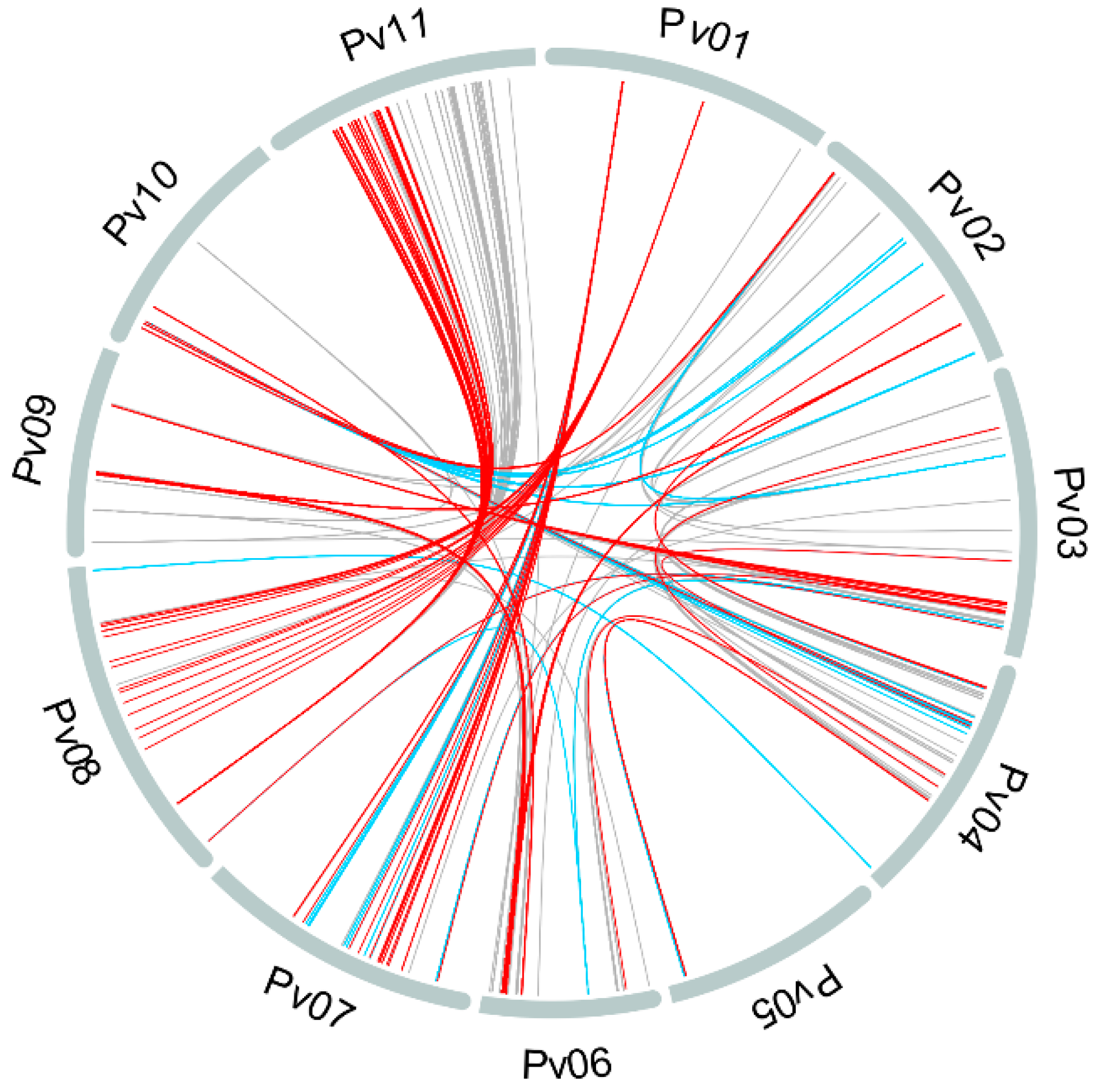
3.3. Linkage Disequilibrium
4. Discussion
4.1. Population Structure and Kinship
4.2. Linkage Disequilibrium
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gepts, P.; Beavis, W.D.; Brummer, E.C.; Shoemaker, R.C.; Stalker, H.T.; Weeden, N.F.; Young, N.D. Legumes as a model plant family. Genomics for food and feed report of the cross-legume advances through genomics conference. Plant Physiol. 2005, 137, 1228–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debouck, D.G.; Toro, O.; Paredes, O.M.; Johnson, W.C.; Gepts, P. Genetic diversity and ecological distribution of Phaseolus vulgaris (Fabaceae) in northwestern South America. Econ. Bot. 1993, 47, 408–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gepts, P.; Osborn, T.C.; Rashka, K.; Bliss, F.A. Phaseolin-protein variability in wild forms and landraces of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): Evidence for multiple centers of domestication. Econ. Bot. 1986, 40, 451–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, M.; Gepts, P. Structure of genetic diversity in the two major gene pools of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L., Fabaceae). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2009, 118, 979–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitocchi, E.; Nanni, L.; Bellucci, E.; Rossi, M.; Giardini, A.; Zeuli, P.S.; Logozzo, G.; Stougaard, J.; McClean, P.; Attene, G.; et al. Mesoamerican origin of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) is revealed by sequence data. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mamidi, S.; Rossi, M.; Moghaddam, S.M.; Annam, D.; Lee, R.; Papa, R.; McClean, P.E. Demographic factors shaped diversity in the two gene pools of wild common bean Phaseolus vulgaris L. Heredity 2013, 110, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myers, J.R.; Kmiecik, K. Common bean: Economic importance and relevance to biological science research. In The Common Bean Genome; Pérez de la Vega, M., Santalla, M., Marsolais, F., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 1–20. ISBN 978-3-319-63526-2. [Google Scholar]
- Beebe, S. Common bean breeding in the tropics. In Plant Breeding Reviews; Janick, J., Ed.; Wiley Online Books; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2012; pp. 357–412. ISBN 9781118358566. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.K.; Allard, R.W. The Effects of linkage, epistasis, and inbreeding on population changes under selection. Genetics 1966, 53, 633–659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flint-Garcia, S.A.; Thornsberry, J.M.; Buckler IV, E.S. Structure of linkage disequilibrium in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 357–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freyre, R.; Skroch, P.W.; Geffroy, V.; Adam-Blondon, A.-F.; Shirmohamadali, A.; Johnson, W.C.; Llaca, V.; Nodari, R.O.; Pereira, P.A.; Tsai, S.-M.; et al. Towards an integrated linkage map of common bean. 4. Development of a core linkage map and alignment of RFLP maps. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1998, 97, 847–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blair, M.W.; Pedraza, F.; Buendia, H.F.; Gaitan-Solis, E.; Beebe, S.E.; Gepts, P.; Tohme, J. Development of a genome-wide anchored microsatellite map for common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2003, 107, 1362–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miklas, P.N.; Kelly, J.D.; Beebe, S.E.; Blair, M.W. Common bean breeding for resistance against biotic and abiotic stresses: From classical to MAS breeding. Euphytica 2006, 147, 105–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Checa, O.; Blair, M. Mapping QTL for climbing ability and component traits in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Mol. Breed. 2008, 22, 201–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanai, L.R.; Santini, L.; Camargo, L.E.A.; Fungaro, M.H.P.; Gepts, P.; Tsai, S.M.; Vieira, M.L.C. Extension of the core map of common bean with EST-SSR, RGA, AFLP, and putative functional markers. Mol. Breed. 2010, 25, 25–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, T.; Oblessuc, P.R.; Sforça, D.A.; Cardoso, J.M.K.; Baroni, R.M.; de Sousa, A.C.B.; Carbonell, S.A.M.; Chioratto, A.F.; Garcia, A.A.F.; Rubiano, L.B.; et al. Inheritance of growth habit detected by genetic linkage analysis using microsatellites in the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Mol. Breed. 2011, 27, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oblessuc, P.; Baroni, R.; Garcia, A.A.; Chioratto, A.; Carbonell, S.A.; Camargo, L.E.; Benchimol, L. Mapping of angular leaf spot resistance QTL in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) under different environments. BMC Genet. 2012, 13, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oblessuc, P.R.; Baroni, R.M.; da Silva Pereira, G.; Chiorato, A.F.; Carbonell, S.A.M.; Briñez, B.; Da Costa, E.; Silva, L.; Garcia, A.A.F.; Camargo, L.E.A.; et al. Quantitative analysis of race-specific resistance to Colletotrichum lindemuthianum in common bean. Mol. Breed. 2014, 34, 1313–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, B.; Manzanares, C.; Jara, C.; Lobaton, J.D.; Studer, B.; Raatz, B. Fine-mapping of a major QTL controlling angular leaf spot resistance in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oraguzie, N.C.; Rikkerink, E.H.A.; Gardiner, S.E.; Silva, H.N. Association Mapping in Plants; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.; Navabi, A.; Yu, K. Association mapping of common bacterial blight resistance QTL in Ontario bean breeding populations. BMC Plant Biol. 2011, 11, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tock, A.J.; Fourie, D.; Walley, P.G.; Holub, E.B.; Soler, A.; Cichy, K.A.; Pastor-Corrales, M.A.; Song, Q.; Porch, T.G.; Hart, J.P.; et al. Genome-Wide linkage and association mapping of Halo Blight resistance in common bean to race 6 of the globally important bacterial pathogen. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perseguini, J.M.K.C.; Oblessuc, P.R.; Rosa, J.R.B.F.; Gomes, K.A.; Chiorato, A.F.; Carbonell, S.A.M.; Garcia, A.A.F.; Vianello, R.P.; Benchimol-Reis, L.L. Genome-wide association studies of anthracnose and angular leaf spot resistance in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galeano, C.H.; Cortés, A.J.; Fernández, A.C.; Soler, Á.; Franco-Herrera, N.; Makunde, G.; Vanderleyden, J.; Blair, M.W. Gene-Based Single nucleotide polymorphism markers for genetic and association mapping in common bean. BMC Genet. 2012, 13, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemli, S.; Asciogul, T.K.; Kaya, H.B.; Kahraman, A.; Eşiyok, D.; Tanyolac, B. Association mapping for five agronomic traits in the common bean ( Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J. Sci. Food Agric. 2014, 94, 3141–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamfwa, K.; Cichy, K.A.; Kelly, J.D. Genome-wide association study of agronomic traits in common bean. Plant Genome 2015, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ates, D.; Asciogul, T.K.; Nemli, S.; Erdogmus, S.; Esiyok, D.; Tanyolac, M.B. Association mapping of days to flowering in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) revealed by DArT markers. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nascimento, M.; Nascimento, A.C.C.; e Silva, F.F.; Barili, L.D.; do Vale, N.M.; Carneiro, J.E.; Cruz, C.D.; Carneiro, P.C.S.; Serão, N.V.L. Quantile regression for genome-wide association study of flowering time-related traits in common bean. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichy, K.A.; Wiesinger, J.A.; Mendoza, F.A. Genetic diversity and genome-wide association analysis of cooking time in dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 1555–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, J.K.; Przeworski, M. Linkage disequilibrium in humans: Models and data. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2001, 69, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stram, D.O. Tag SNP selection for association studies. Genet. Epidemiol. 2004, 27, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hedrick, P.W. Gametic disequilibrium measures: Proceed with caution. Genetics 1987, 117, 331–341. [Google Scholar]
- Hill, W.G.; Robertson, A. Linkage disequilibrium in finite populations. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1968, 38, 226–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Pressoir, G.; Briggs, W.H.; Vroh Bi, I.; Yamasaki, M.; Doebley, J.F.; McMullen, M.D.; Gaut, B.S.; Nielsen, D.M.; Holland, J.B.; et al. A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangin, B.; Siberchicot, A.; Nicolas, S.; Doligez, A.; This, P.; Cierco-Ayrolles, C. Novel measures of linkage disequilibrium that correct the bias due to population structure and relatedness. Heredity 2012, 108, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cericola, F.; Portis, E.; Lanteri, S.; Toppino, L.; Barchi, L.; Acciarri, N.; Pulcini, L.; Sala, T.; Rotino, G. Linkage disequilibrium and genome-wide association analysis for anthocyanin pigmentation and fruit color in eggplant. BMC Genom. 2014, 15, 896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graebner, R.C.; Wise, M.; Cuesta-Marcos, A.; Geniza, M.; Blake, T.; Blake, V.C.; Butler, J.; Chao, S.; Hole, D.J.; Horsley, R.; et al. Quantitative trait loci associated with the tocochromanol (vitamin E) pathway in barley. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangin, B.; Sandron, F.; Henry, K.; Devaux, B.; Willems, G.; Devaux, P.; Goudemand, E. Breeding patterns and cultivated beets origins by genetic diversity and linkage disequilibrium analyses. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2015, 128, 2255–2271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.-F.; Poland, J.A.; Wight, C.P.; Jackson, E.W.; Tinker, N.A. Using genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) for genomic discovery in cultivated oat. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Kirk, C.; Deng, C.; Wiedow, C.; Knaebel, M.; Brewer, L. Genotyping-by-sequencing of pear (Pyrus spp.) accessions unravels novel patterns of genetic diversity and selection footprints. Hortic. Res. 2017, 4, 17015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, S.D.; Péros, J.-P.; Lacombe, T.; Launay, A.; Le Paslier, M.-C.; Bérard, A.; Mangin, B.; Valière, S.; Martins, F.; Le Cunff, L.; et al. Genetic diversity, linkage disequilibrium and power of a large grapevine (Vitis vinifera L) diversity panel newly designed for association studies. BMC Plant Biol. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, R.; Acosta, J.; Delgado-Salinas, A.; Gepts, P. A genome-wide analysis of differentiation between wild and domesticated Phaseolus vulgaris from Mesoamerica. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2005, 111, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papa, R.; Bellucci, E.; Rossi, M.; Leonardi, S.; Rau, D.; Gepts, P.; Nanni, L.; Attene, G. Tagging the signatures of domestication in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) by means of pooled DNA samples. Ann. Bot. 2007, 100, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blair, M.W.; Cortés, A.J.; Farmer, A.D.; Huang, W.; Ambachew, D.; Penmetsa, R.V.; Carrasquilla-Garcia, N.; Assefa, T.; Cannon, S.B. Uneven recombination rate and linkage disequilibrium across a reference SNP map for common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campa, A.; Murube, E.; Ferreira, J.J. Genetic diversity, population structure, and linkage disequilibrium in a spanish common bean diversity panel revealed through genotyping-by-sequencing. Genes (Basel) 2018, 9, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burle, M.L.; Fonseca, J.R.; Kami, J.A.; Gepts, P. Microsatellite diversity and genetic structure among common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) landraces in Brazil, a secondary center of diversity. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2010, 121, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, M.; Bitocchi, E.; Bellucci, E.; Nanni, L.; Rau, D.; Attene, G.; Papa, R. Linkage disequilibrium and population structure in wild and domesticated populations of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Evol. Appl. 2009, 2, 504–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdisser, P.A.M.R.; Pereira, W.J.; Almeida Filho, J.E.; Müller, B.S.F.; Coelho, G.R.C.; de Menezes, I.P.P.; Vianna, J.P.G.; Zucchi, M.I.; Lanna, A.C.; Coelho, A.S.G.; et al. In-depth genome characterization of a Brazilian common bean core collection using DArTseq high-density SNP genotyping. BMC Genom. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Resende, R.T.; de Resende, M.D.V.; Azevedo, C.F.; Fonseca e Silva, F.; Melo, L.C.; Pereira, H.S.; Souza, T.L.P.O.; Valdisser, P.A.M.R.; Brondani, C.; Vianello, R.P. Genome-wide association and regional heritability mapping of plant architecture, lodging and productivity in Phaseolus vulgaris. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2018, 8, 2841–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nodari, R.O.; Tsail, S.M.; Gilbertson, R.L.; Gepts, P. Towards an integrated linkage map of common bean 2. Development of an RFLP-based linkage map. Theor. Appl. Genet. 1993, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, S.; Gomes, L.A.A.; Maluf, W.R.; Furtini, I.V.; Campos, V.P. Genetic control of resistance to Meloidogyne incognita race 1 in the Brazilian common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cv. Aporé. Euphytica 2012, 186, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perseguini, J.M.K.C.; Silva, G.M.B.; Rosa, J.R.B.F.; Gazaffi, R.; Marçal, J.F.; Carbonell, S.A.M.; Chiorato, A.F.; Zucchi, M.I.; Garcia, A.A.F.; Benchimol-Reis, L.L. Developing a common bean core collection suitable for association mapping studies. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2015, 38, 67–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kami, J.; Velásquez, V.B.; Debouck, D.G.; Gepts, P. Identification of presumed ancestral DNA sequences of phaseolin in Phaseolus vulgaris. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elshire, R.J.; Glaubitz, J.C.; Sun, Q.; Poland, J.A.; Kawamoto, K.; Buckler, E.S.; Mitchell, S.E. A robust, simple genotyping-by-sequencing (GBS) approach for high diversity species. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glaubitz, J.C.; Casstevens, T.M.; Lu, F.; Harriman, J.; Elshire, R.J.; Sun, Q.; Buckler, E.S. TASSEL-GBS: A high capacity genotyping by sequencing analysis pipeline. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmutz, J.; McClean, P.E.; Mamidi, S.; Wu, G.A.; Cannon, S.B.; Grimwood, J.; Jenkins, J.; Shu, S.; Song, Q.; Chavarro, C.; et al. A reference genome for common bean and genome-wide analysis of dual domestications. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 707–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roberts, A.; McMillan, L.; Wang, W.; Parker, J.; Rusyn, I.; Threadgill, D. Inferring missing genotypes in large SNP panels using fast nearest-neighbor searches over sliding windows. Bioinformatics 2007, 23, i401–i407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Tracy, C.A.; Widom, H. Level-spacing distributions and the Airy kernel. Commun. Math. Phys. 1994, 159, 151–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patterson, N.; Price, A.L.; Reich, D. Population structure and eigenanalysis. PLoS Genet. 2006, 2, e190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nei, M. Molecular Evolutionary Genetics; Columbia University Press: New York, NY, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayes, B.J.; Goddard, M.E. Technical note: Prediction of breeding values using marker-derived relationship matrices. J. Anim. Sci. 2008, 86, 2089–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wimmer, V.; Albrecht, T.; Auinger, H.-J.; Schon, C.-C. synbreed: A framework for the analysis of genomic prediction data using R. Bioinformatics 2012, 28, 2086–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warnes, G.; Leisch, F. Genetics: Population Genetics; Warnes, G., Ed.; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2005; pp. 1–36. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marroni, F.; Pinosio, S.; Zaina, G.; Fogolari, F.; Felice, N.; Cattonaro, F.; Morgante, M. Nucleotide diversity and linkage disequilibrium in Populus nigra cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD4) gene. Tree Genet. Genomes 2011, 7, 1011–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, W.G.; Weir, B.S. Variances and covariances of squared linkage disequilibria in finite populations. Theor. Popul. Biol. 1988, 33, 54–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oblessuc, P.R.; Cardoso Perseguini, J.M.K.; Baroni, R.M.; Chiorato, A.F.; Carbonell, S.A.M.; Mondego, J.M.C.; Vidal, R.O.; Camargo, L.E.A.; Benchimol-Reis, L.L. Increasing the density of markers around a major QTL controlling resistance to angular leaf spot in common bean. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2013, 126, 2451–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, E.; Bitocchi, E.; Ferrarini, A.; Benazzo, A.; Biagetti, E.; Klie, S.; Minio, A.; Rau, D.; Rodriguez, M.; Panziera, A.; et al. Decreased nucleotide and expression diversity and modified coexpression patterns characterize domestication in the common bean. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 1901–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Gou, Z.; Lyu, J.; Li, W.; Yu, Y.; Shu, L.; Zhao, Y.; Ma, Y.; et al. Resequencing 302 wild and cultivated accessions identifies genes related to domestication and improvement in soybean. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Wei, X.; Sang, T.; Zhao, Q.; Feng, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, C.; Lu, T.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Genome-wide asociation studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhakta, M.S.; Jones, V.A.; Vallejos, C.E. Punctuated distribution of recombination hotspots and demarcation of pericentromeric regions in Phaseolus vulgaris L. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, W.C.; Gepts, P. The role of epistasis in controlling seed yield and other agronomic traits in an Andean × Mesoamerican cross of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Euphytica 2002, 125, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-H.; Yang, H.-J.; Jung, K.-H.; Yoo, S.-C.; Paek, N.-C. Quantitative trait locus mapping and candidate gene analysis for plant architecture traits using whole genome re-sequencing in rice. Mol. Cells 2014, 37, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Number of SNPs | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chromosome | Physical Length (Mb) 1 | Number of Genes 1 | MD ≤ 0.10 | MAF ≥ 0.05 |
| Pv01 | 52.18 | 2116 | 2100 | 993 |
| Pv02 | 49.03 | 2695 | 2678 | 1261 |
| Pv03 | 52.21 | 2294 | 2407 | 1063 |
| Pv04 | 45.79 | 1035 | 1378 | 748 |
| Pv05 | 40.23 | 1349 | 1335 | 695 |
| Pv06 | 31.97 | 1649 | 1635 | 841 |
| Pv07 | 51.69 | 2146 | 2133 | 1082 |
| Pv08 | 59.63 | 2067 | 2453 | 1188 |
| Pv09 | 37.39 | 2134 | 1935 | 869 |
| Pv10 | 43.21 | 1020 | 1379 | 680 |
| Pv11 | 50.20 | 1274 | 1848 | 942 |
| Total | − | 19,779 | 21,281 | 10,362 |
| Institution of Origin | N | S | π |
|---|---|---|---|
| IAC | 87 | 10,354 | 0.256 |
| CIAT | 62 | 10,346 | 0.309 |
| Embrapa | 12 | 9632 | 0.272 |
| Other | 19 | 9984 | 0.251 |
| Total | 180 | 10,362 | 0.277 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Diniz, A.L.; Giordani, W.; Costa, Z.P.; Margarido, G.R.A.; Perseguini, J.M.K.C.; Benchimol-Reis, L.L.; Chiorato, A.F.; Garcia, A.A.F.; Vieira, M.L.C. Evidence for Strong Kinship Influence on the Extent of Linkage Disequilibrium in Cultivated Common Beans. Genes 2019, 10, 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10010005
Diniz AL, Giordani W, Costa ZP, Margarido GRA, Perseguini JMKC, Benchimol-Reis LL, Chiorato AF, Garcia AAF, Vieira MLC. Evidence for Strong Kinship Influence on the Extent of Linkage Disequilibrium in Cultivated Common Beans. Genes. 2019; 10(1):5. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10010005
Chicago/Turabian StyleDiniz, Augusto Lima, Willian Giordani, Zirlane Portugal Costa, Gabriel R. A. Margarido, Juliana Morini K. C. Perseguini, Luciana L. Benchimol-Reis, Alisson F. Chiorato, Antônio Augusto F. Garcia, and Maria Lucia Carneiro Vieira. 2019. "Evidence for Strong Kinship Influence on the Extent of Linkage Disequilibrium in Cultivated Common Beans" Genes 10, no. 1: 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10010005
APA StyleDiniz, A. L., Giordani, W., Costa, Z. P., Margarido, G. R. A., Perseguini, J. M. K. C., Benchimol-Reis, L. L., Chiorato, A. F., Garcia, A. A. F., & Vieira, M. L. C. (2019). Evidence for Strong Kinship Influence on the Extent of Linkage Disequilibrium in Cultivated Common Beans. Genes, 10(1), 5. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10010005






