Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Genetic Variants Associated with Risk for Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease in Taiwanese Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. SNP Selection and Genotyping
2.3. T2D Mouse Model
2.4. Western Blot
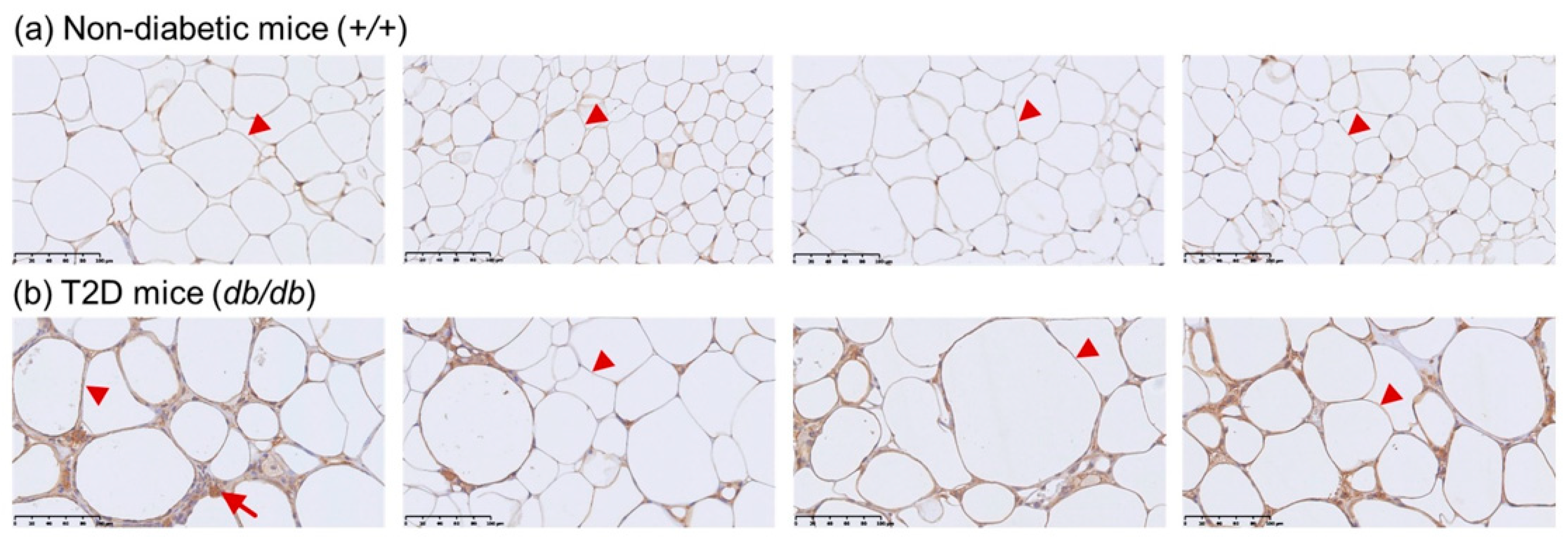
2.5. Immunohistochemistry
2.6. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liao, W.L.; Tsai, F.J. Personalized medicine in type 2 diabetes. Biomedicine (Taipei) 2014, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokopenko, I.; McCarthy, M.I.; Lindgren, C.M. Type 2 diabetes: New genes, new understanding. Trends Genet. 2008, 24, 613–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.; King, G.L. Microvascular complications of diabetes. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. North Am. 2004, 33, 215–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Angelantonio, E.; Sarwar, N.; Perry, P.; Kaptoge, S.; Ray, K.K.; Thompson, A.; Wood, A.M.; Lewington, S.; Sattar, N.; Packard, C.J.; et al. Major lipids, apolipoproteins, and risk of vascular disease. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2009, 302, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, P.W.; Meigs, J.B.; Sullivan, L.; Fox, C.S.; Nathan, D.M.; D’Agostino, R.B. Prediction of incident diabetes mellitus in middle-aged adults: The Framingham offspring study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1068–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.I.; Duncan, B.B.; Bang, H.; Pankow, J.S.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Golden, S.H.; Folsom, A.R.; Chambless, L.E. Identifying individuals at high risk for diabetes: The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Diabetes Care 2005, 28, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snieder, H.; van Doornen, L.J.; Boomsma, D.I. Dissecting the genetic architecture of lipids, lipoproteins, and apolipoproteins: Lessons from twin studies. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 2826–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.A.; Deckelbaum, R.J. Crystal structure of cetp: New hopes for raising hdl to decrease risk of cardiovascular disease? Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millwood, I.Y.; Bennett, D.A.; Holmes, M.V.; Boxall, R.; Guo, Y.; Bian, Z.; Yang, L.; Sansome, S.; Chen, Y.; Du, H.; et al. Association of CETP gene variants with risk for vascular and nonvascular diseases among chinese adults. J. Am. Med. Assoc. Cardiol. 2018, 3, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.; Di Angelantonio, E.; Sarwar, N.; Erqou, S.; Saleheen, D.; Dullaart, R.P.; Keavney, B.; Ye, Z.; Danesh, J. Association of cholesteryl ester transfer protein genotypes with cetp mass and activity, lipid levels, and coronary risk. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2008, 299, 2777–2788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridker, P.M.; Pare, G.; Parker, A.N.; Zee, R.Y.; Miletich, J.P.; Chasman, D.I. Polymorphism in the CETP gene region, hdl cholesterol, and risk of future myocardial infarction: Genomewide analysis among 18245 initially healthy women from the women’s genome health study. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2009, 2, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, W.; Qi, Y. Circulating cholesteryl ester transfer protein and coronary heart disease: Mendelian randomization meta-analysis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2015, 8, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, A.; Won, H.H.; Khera, A.V.; Takeuchi, F.; Ito, K.; McCarthy, S.; Emdin, C.A.; Klarin, D.; Natarajan, P.; Zekavat, S.M.; et al. Protein-truncating variants at the cholesteryl ester transfer protein gene and risk for coronary heart disease. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.M.; Hsu, Y.M.; Ying, M.C.; Tsai, F.J.; Tsai, C.H.; Chung, J.G.; Yang, J.S.; Tang, C.H.; Cheng, L.Y.; Su, P.H.; et al. High-density lipoprotein ameliorates palmitic acid-induced lipotoxicity and oxidative dysfunction in h9c2 cardiomyoblast cells via ros suppression. Nutr. Metab. (London) 2019, 16, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.A.; Ko, Y.L.; Hsu, K.H.; Ko, Y.H.; Lee, Y.S. Genetic variations in the cholesteryl ester transfer protein gene and high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in Taiwanese Chinese. Hum. Genet. 2002, 110, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.C.; Tien, K.J.; Chang, S.J.; Lo, C.S.; Hsin, S.C.; Hsiao, J.Y.; Hsu, S.C.; Liang, H.T.; Chen, H.C.; Shin, S.J.; et al. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein B1B1 genotype as a predictor of coronary artery disease in Taiwanese with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2007, 56, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsieh, M.C.; Chen, C.C.; Wang, J.Y.; Chong, I.W.; Yhe, C.J.; Shin, S.J.; Lin, S.R. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein B1B1 genotype is associated with a parental history of cardiovascular diseases in Taiwanese people. Med. Princ. Pract. 2008, 17, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2013, 36 (Suppl. 1), S67–S74. [Google Scholar]
- Musso, C.G.; Alvarez-Gregori, J.; Jauregui, J.; Macias-Nunez, J.F. Glomerular filtration rate equations: A comprehensive review. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2016, 48, 1105–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, C.P.; Ferris, F.L., III; Klein, R.E.; Lee, P.P.; Agardh, C.D.; Davis, M.; Dills, D.; Kampik, A.; Pararajasegaram, R.; Verdaguer, J.T. Proposed international clinical diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema disease severity scales. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 1677–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.H.; Yang, J.H.; Chiang, C.W.K.; Hsiung, C.N.; Wu, P.E.; Chang, L.C.; Chu, H.W.; Chang, J.; Song, I.W.; Yang, S.L.; et al. Population structure of Han Chinese in the modern Taiwanese population based on 10,000 participants in the Taiwan Biobank project. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 5321–5331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schierer, A.; Been, L.F.; Ralhan, S.; Wander, G.S.; Aston, C.E.; Sanghera, D.K. Genetic variation in cholesterol ester transfer protein, serum CETP activity, and coronary artery disease risk in Asian Indian diabetic cohort. Pharmacogenet. Genomics 2012, 22, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haase, C.L.; Tybjaerg-Hansen, A.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Frikke-Schmidt, R. Hdl cholesterol and risk of type 2 diabetes: A mendelian randomization study. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3328–3333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, F.J.; Yang, C.F.; Chen, C.C.; Chuang, L.M.; Lu, C.H.; Chang, C.T.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, R.H.; Shiu, C.F.; Liu, Y.M.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies susceptibility variants for type 2 diabetes in Han Chinese. PLoS Genet. 2010, 6, e1000847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, J.C.; Fry, B.; Maller, J.; Daly, M.J. Haploview: Analysis and visualization of ld and haplotype maps. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, B.G.; Rye, K.A.; Duffy, S.J.; Barter, P.; Kingwell, B.A. The emerging role of HDL in glucose metabolism. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.T.; De Cosmo, S.; Viazzi, F.; Pacilli, A.; Ceriello, A.; Genovese, S.; Guida, P.; Giorda, C.; Cucinotta, D.; Pontremoli, R.; et al. Plasma triglycerides and HDL-C levels predict the development of diabetic kidney disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes: The AMD annals initiative. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 2278–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobrin, L.; Chong, Y.H.; Fan, Q.; Gan, A.; Stanwyck, L.K.; Kaidonis, G.; Craig, J.E.; Kim, J.; Liao, W.L.; Huang, Y.C.; et al. Genetically determined plasma lipid levels and risk of diabetic retinopathy: A mendelian randomization study. Diabetes 2017, 66, 3130–3141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, G.T.; Giandalia, A.; Romeo, E.L.; Muscianisi, M.; Ruffo, M.C.; Alibrandi, A.; Bitto, A.; Forte, F.; Grillone, A.; Asztalos, B.; et al. HDL subclasses and the common CETP TaqIB variant predict the incidence of microangiopatic complications in type 2 diabetic women: A 9years follow-up study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 132, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahri, J.; Groop, P.H.; Elliott, T.; Viberti, G.; Taskinen, M.R. Plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein and its relationship to plasma lipoproteins and apolipoprotein AI-containing lipoproteins in IDDM patients with microalbuminuria and clinical nephropathy. Diabetes Care 1994, 17, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadjadj, S.; Gallois, Y.; Simard, G.; Bouhanick, B.; Passa, P.; Grimaldi, A.; Drouin, P.; Tichet, J.; Marre, M. Lack of relationship in long-term type 1 diabetic patients between diabetic nephropathy and polymorphisms in apolipoprotein epsilon, lipoprotein lipase and cholesteryl ester transfer protein. Genetique de la nephropathie diabetique study group. Donnees epidemiologiques sur le syndrome d’insulino-resistance study group. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2000, 15, 1971–1976. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, T.Y.; Zhang, C.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Qi, L.; Rimm, E.; Hunter, D.J.; Hu, F.B. Interaction between dietary fat intake and the cholesterol ester transfer protein TaqIB polymorphism in relation to HDL-cholesterol concentrations among US diabetic men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 86, 1524–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Liao, W.L.; Lin, J.M.; Liu, S.P.; Chen, S.Y.; Lin, H.J.; Wang, Y.H.; Lei, Y.J.; Huang, Y.C.; Tsai, F.J. Loss of response gene to complement 32 (RGC-32) in diabetic mouse retina is involved in retinopathy development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.C.; Barter, P.J. Differences in plasma cholesteryl ester transfer activity in sixteen vertebrate species. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B 1982, 71, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacLean, P.S.; Bower, J.F.; Vadlamudi, S.; Osborne, J.N.; Bradfield, J.F.; Burden, H.W.; Bensch, W.H.; Kauffman, R.F.; Barakat, H.A. Cholesteryl ester transfer protein expression prevents diet-induced atherosclerotic lesions in male db/db mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 1412–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Non-Diabetic Control N = 1383 | T2D Patients N = 1640 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | |||
| Male | 48.1% | 50.8% | 0.138 |
| Female | 51.9% | 49.2% | |
| Age at study (mean ± SD, years) | 46.0 ± 10.6 | 62.0 ± 11.3 | <0.001 |
| Duration of diabetes (mean ± SD, years) | -- | 11.0 ± 8.7 | -- |
| HbA1C (%) | 5.5 ± 0.3 | 7.9 ± 1.6 | <0.001 |
| Body mass index (kg/m2) | 23.9 ± 3.5 | 25.4 ± 4.0 | <0.001 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mean ± SD, mmHg) | 112.9 ± 16.6 | 140.4 ± 19.5 | <0.001 |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mean ± SD, mmHg) | 71.2 ± 11.4 | 79.4 ± 12.1 | <0.001 |
| Waist–hip ratio (mean ± SD) | 0.87± 0.23 | 0.93 ± 0.07 | <0.001 |
| Total cholesterol (mean ± SD, mg/dL) | 190.9 ± 34.9 | 185.4 ± 41.8 | <0.001 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mean ± SD, mg/dL) | 54.8 ± 12.9 | 48.3 ± 14.9 | <0.001 |
| LDL-cholesterol (mean ± SD, mg/dL) | 119.7 ± 31.9 | 115.1 ± 37.0 | 0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mean ± SD, mg/dL) | 106.8 ± 67.2 | 166.0 ± 131.5 | <0.001 |
| eGFR (mean ± SD, mL/min/1.73 m2) 1 ≥60 <60 (diabetic kidney disease, DKD) | 109.8 ± 26.0 1371 (99.1%) 12 (0.9%) | 83.8 ± 40.6 958 (72.3%) 367 (27.7%) | <0.001 <0.001 |
| Diabetic retinopathy severity scales 2,3 | |||
| Non-DR | -- | 588 (55.3%) | -- |
| Non-proliferative DR | -- | 201 (18.9%) | -- |
| Proliferative DR | -- | 274 (25.8%) | -- |
| dbSNP ID/Physical Position (bp) | Genotype | Non-Diabetic Controls N = 1383 | Total Cholesterol (mg/dL) | p Value | Triglycerides (mg/dL) | p Value | HDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | p Value | LDL-Cholesterol (mg/dL) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3764261/ | AA | 51 (3.7) | 189.5 ± 31.9 | 0.759 | 107.4 ± 57.8 | 0.910 | 58.9 ± 12.9 | 1.34 × 10−4 | 114.2 ± 30.6 | 0.421 |
| 56959412 | AC | 357 (25.9) | 192.0 ± 34.8 | 105.5 ± 61.3 | 56.7 ± 13.4 | 119.3 ± 32.2 | ||||
| CC | 971 (70.4) | 190.5 ± 35.2 | 107.3 ± 69.8 | 53.9 ± 12.7 | 120.1 ± 31.9 | |||||
| rs4783961/ | AA | 91 (6.7) | 194.0 ± 34.6 | 0.603 | 109.6 ± 58.1 | 0.736 | 57.6 ± 12.5 | 0.011 | 119.7 ± 32.4 | 0.829 |
| 56960982 | AG | 457 (33.4) | 191.6 ± 34.0 | 107.7 ± 77.3 | 55.7 ± 13.1 | 119.1 ± 31.7 | ||||
| GG | 820 (59.9) | 190.5 ± 35.5 | 105.3 ± 60.6 | 54.1 ± 12.8 | 120.2 ± 32.1 | |||||
| rs1800775/ | AA | 369 (26.7) | 191.7 ± 35.8 | 0.328 | 103.3 ± 53.3 | 0.499 | 56.0 ± 13.0 | 0.094 | 119.7 ± 33.3 | 0.198 |
| 56961324 | AC | 686 (49.7) | 189.6 ± 35.3 | 108.4 ± 74.8 | 54.3 ± 13.0 | 118.5 ± 31.9 | ||||
| CC | 326 (23.6) | 192.9 ± 3.0 | 107.2 ± 64.4 | 54.3 ± 12.7 | 122.4 ± 29.9 | |||||
| rs5882/ | AA | 400 (28.9) | 191.7 ± 32.6 | 0.394 | 111.9 ± 78.8 | 0.193 | 54.0 ± 12.7 | 0.264 | 121.2 ± 29.6 | 0.330 |
| 56982180 | AG | 698 (50.5) | 189.7 ± 36.0 | 104.9 ± 63.3 | 54.9 ± 13.1 | 118.5 ± 32.8 | ||||
| GG | 284 (20.5) | 192.7 ± 35.5 | 104.4 ± 57.8 | 55.6 ± 12.8 | 120.8 ± 32.7 |
| Effect/Other Allele 1 | N | Per Effect Allele (mg/dL) | SE | p Value 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HDL-cholesterol | |||||
| rs3764261 | A/C | 1379 | 2.86 | 0.59 | 1.00 × 10−6 |
| rs4783961 | A/G | 1368 | 1.71 | 0.52 | 0.001 |
| rs1800775 | A/C | 1381 | 0.91 | 0.46 | 0.045 |
| rs5882 | G/A | 1382 | 0.56 | 0.65 | 0.231 |
| LDL-cholesterol | |||||
| rs3764261 | A/C | 1379 | −2.24 | 1.55 | 0.150 |
| rs4783961 | A/G | 1368 | −1.11 | 1.37 | 0.417 |
| rs1800775 | A/C | 1381 | −1.44 | 1.19 | 0.227 |
| rs5882 | G/A | 1382 | −0.53 | 1.21 | 0.660 |
| Total cholesterol | |||||
| rs3764261 | A/C | 1379 | −0.03 | 1.68 | 0.988 |
| rs4783961 | A/G | 1368 | 0.84 | 1.49 | 0.571 |
| rs1800775 | A/C | 1381 | −0.73 | 1.29 | 0.572 |
| rs5882 | G/A | 1382 | −0.12 | 1.31 | 0.928 |
| Triglycerides | |||||
| rs3764261 | A/C | 1379 | −2.09 | 3.21 | 0.515 |
| rs4783961 | A/G | 1368 | 1.76 | 2.80 | 0.529 |
| rs1800775 | A/C | 1381 | −2.23 | 2.46 | 0.364 |
| rs5882 | G/A | 1382 | −3.41 | 2.49 | 0.172 |
| dbSNP ID/Effect Allele 1 | Genotype/Effect Allele Number | T2D Patients N = 1640 | Non-Diabetic Controls N = 1383 | T2D vs. Non-Diabetic Controls OR (95% CI) p-Value | Non-Diabetic Controls (Age ≥ 55 Years) N = 349 | T2D vs. Non-Diabetic Controls (Age ≥ 55 Years) OR (95% CI) p-Value | Non-Diabetic Controls (Geographical Region Control) 2 N = 253 | T2D vs. Non-Diabetic Controls (Geographical Region Control) (95% CI) p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3764261/A | CC/0 | 1104 (70.9) | 971 (70.4) | 0.91 (0.77–1.08) 0.270 3 0.90 (0.76–1.07) 0.231 4 | 243 (69.6) | 0.90 (0.72–1.12) 0.334 3 0.90 (0.72–1.12) 0.340 4 | 168 (66.9) | 0.88 (0.66–1.16) 0.352 3 0.87 (0.65–1.15) 0.322 4 |
| AC/1 | 420 (27.0) | 357 (25.9) | 92 (26.4) | 73 (29.1) | ||||
| AA/2 | 34 (2.2) | 51 (3.7) | 14 (4.0) | 10 (4.0) | ||||
| rs4783961/A | GG/0 | 970 (62.3) | 820 (59.9) | 0.82 (0.71–0.96) 0.011 3 0.81 (0.70–0.95) 0.007 4 | 200 (57.3) | 0.80 (0.66–0.97) 0.021 3 0.79 (0.65–0.96) 0.016 4 | 138 (54.8) | 0.76 (0.59–0.97) 0.027 3 0.74 (0.57–0.95) 0.020 4 |
| AG/1 | 523 (33.6) | 457 (33.4) | 124 (35.5) | 96 (38.1) | ||||
| AA/2 | 65 (4.2) | 91 (6.7) | 25 (7.2) | 18 (7.1) | ||||
| rs1800775/A | CC/0 | 375 (24.1) | 326 (23.6) | 0.94 (0.83–1.07) 0.339 3 0.93 (0.82–1.06) 0.272 4 | 81 (23.2) | 0.94 (0.79–1.11) 0.448 3 0.93 (0.79–1.10) 0.411 4 | 58 (22.9) | 0.95 (0.77–1.18) 0.648 3 0.94 (0.75–1.17) 0.563 4 |
| AC/1 | 790 (50.7) | 686 (49.7) | 172 (49.3) | 126 (49.8) | ||||
| AA/2 | 393 (25.2) | 369 (26.7) | 96 (27.5) | 69 (27.3) | ||||
| rs5882/G | AA/0 | 474 (30.5) | 400 (28.9) | 0.94 (0.83–1.07) 0.379 3 0.93 (0.82–1.06) 0.269 4 | 100 (28.7) | 0.97 (0.82–1.14) 0.693 3 0.95 (0.81–1.13) 0.580 4 | 74 (29.2) | 1.03 (0.83–1.28) 0.786 3 1.00 (0.80–1.25) 0.975 4 |
| AG/1 | 760 (48.9) | 698 (50.5) | 178 (51.0) | 131 (51.8) | ||||
| GG/2 | 319 (20.5) | 284 (20.5) | 71 (20.3) | 48 (19.0) |
| dbSNP ID/Effect Allele 1 | Genotype/Effect Allele Number | T2D Patients with DKD/without DKD N = 367/958 | T2D with DKD vs. without DKD OR (95% CI), p-Value | T2D Patients With DR/ Non-DR N = 475/588 | DR vs. Non-DR OR (95% CI), p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3764261/A | CC/0 | 235 (74.4)/650 (70.0) | 0.78 (0.58–1.04), 0.094 2 | 335 (70.5)/406 (69.2) | 0.90 (0.70–1.16), 0.408 2 |
| AC/1 | 74 (23.4)/254 (27.4) | 0.80 (0.60–1.08), 0.154 3 | 133 (28.0)/169 (28.8) | 0.90 (0.70–1.16), 0.414 3 | |
| AA/2 | 7 (2.2)/24 (2.6) | 7 (1.5)/12 (2.0) | |||
| rs4783961/A | GG/0 | 207 (65.5)/574 (61.9) | 0.82 (0.63–1.06), 0.126 2 | 295 (62.1)/360 (61.2) | 0.90 (0.72–1.12), 0.341 2 |
| AG/1 | 97 (30.7)/310 (33.4) | 0.84 (0.65–1.09), 0.186 3 | 164 (34.5)/202 (34.4) | 0.89 (0.71–1.12), 0.318 3 | |
| AA/2 | 12 (3.8)/44 (4.7) | 16 (3.4)/26 (4.4) | |||
| rs1800775/A | CC/0 | 85 (26.9)/221 (23.8) | 0.78 (0.64–0.96), 0.019 2 | 104 (21.9)/142 (24.1) | 0.98 (0.82–1.17), 0.816 2 |
| AC/1 | 169 (53.5)/456 (49.1) | 0.80 (0.65–0.98), 0.032 3 | 251 (53.0)/290 (49.3) | 0.98 (0.82–1.17), 0.810 3 | |
| AA/2 | 62 (19.6)/252 (27.1) | 119 (25.1)/156 (26.5) | |||
| rs5882/G | AA/0 | 105 (33.4)/270 (29.2) | 0.83 (0.68–1.02), 0.083 2 | 144 (30.4)/175 (29.9) | 0.94 (0.79–1.13), 0.506 2 |
| AG/1 | 155 (49.4)/458 (49.5) | 0.83 (0.67–1.03), 0.086 3 | 237 (50.0)/277 (47.4) | 0.94 (0.79–1.13), 0.506 3 | |
| GG/2 | 54 (17.2)/197 (21.3) | 93 (19.6)/133 (22.7) |
| Haplotype rs3764261/rs4783961/rs1800775 | Non-Diabetic Controls | T2D Patients | T2D vs. Non-Diabetic Controls | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | OR (95% CI) | ||
| CGC | 1322 (48.2) | 1686 (51.7) | 1.00 (ref) | |
| CGA | 804 (29.3) | 939 (28.8) | 0.92 (0.81–1.03) | 0.146 |
| AAA | 458 (16.7) | 487 (14.9) | 0.83 (0.72–0.97) | 0.015 |
| CAA | 161 (5.9) | 149 (4.6) | 0.73 (0.57–0.92) | 0.007 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Huang, Y.-C.; Chen, S.-Y.; Liu, S.-P.; Lin, J.-M.; Lin, H.-J.; Lei, Y.-J.; Chung, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.-C.; Wang, Y.-H.; Liao, W.-L.; et al. Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Genetic Variants Associated with Risk for Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease in Taiwanese Population. Genes 2019, 10, 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100782
Huang Y-C, Chen S-Y, Liu S-P, Lin J-M, Lin H-J, Lei Y-J, Chung Y-C, Chen Y-C, Wang Y-H, Liao W-L, et al. Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Genetic Variants Associated with Risk for Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease in Taiwanese Population. Genes. 2019; 10(10):782. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100782
Chicago/Turabian StyleHuang, Yu-Chuen, Shih-Yin Chen, Shih-Ping Liu, Jane-Ming Lin, Hui-Ju Lin, Yu-Jie Lei, Yun-Chih Chung, Yu-Chi Chen, Yeh-Han Wang, Wen-Ling Liao, and et al. 2019. "Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Genetic Variants Associated with Risk for Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease in Taiwanese Population" Genes 10, no. 10: 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100782
APA StyleHuang, Y.-C., Chen, S.-Y., Liu, S.-P., Lin, J.-M., Lin, H.-J., Lei, Y.-J., Chung, Y.-C., Chen, Y.-C., Wang, Y.-H., Liao, W.-L., & Tsai, F.-J. (2019). Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Genetic Variants Associated with Risk for Type 2 Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease in Taiwanese Population. Genes, 10(10), 782. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10100782






