Identification and Description of the Key Molecular Components of the Egg Strings of the Salmon Louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Candidate Gene Identification
2.2. Animal Culture
2.3. RNA Extraction and cDNA Synthesis
2.4. Gene Sequencing and Characterization
2.5. Quantitative PCR
2.6. In Situ Hybridization
2.7. RNAi Knockdown
2.8. Histological Analysis
2.9. Protein Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Gene Structure
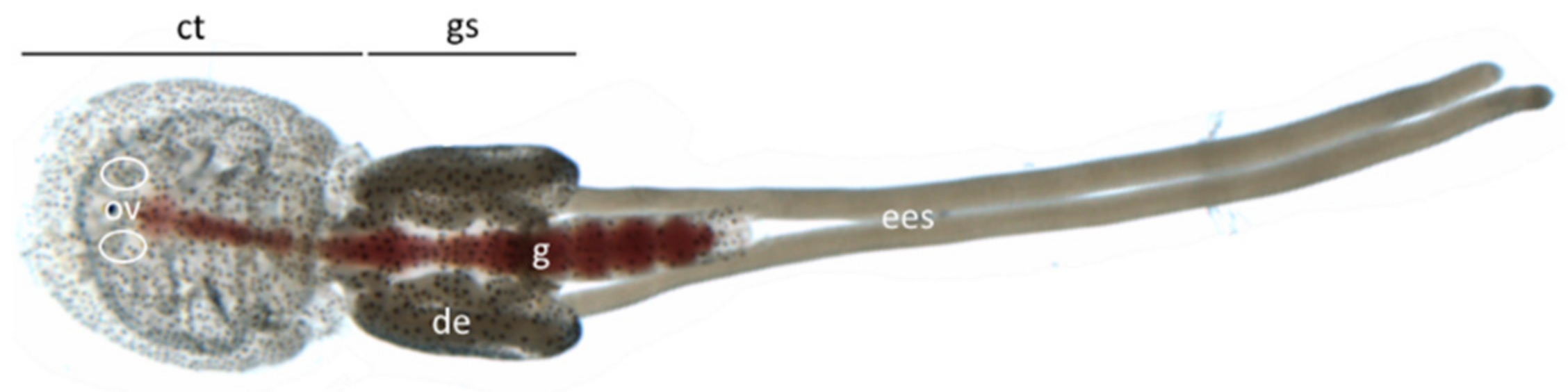
3.2. Gene Localization
3.3. Gene Expression
3.4. RNAi-Mediated Knockdown
3.5. RNAi Knockdown Interactions
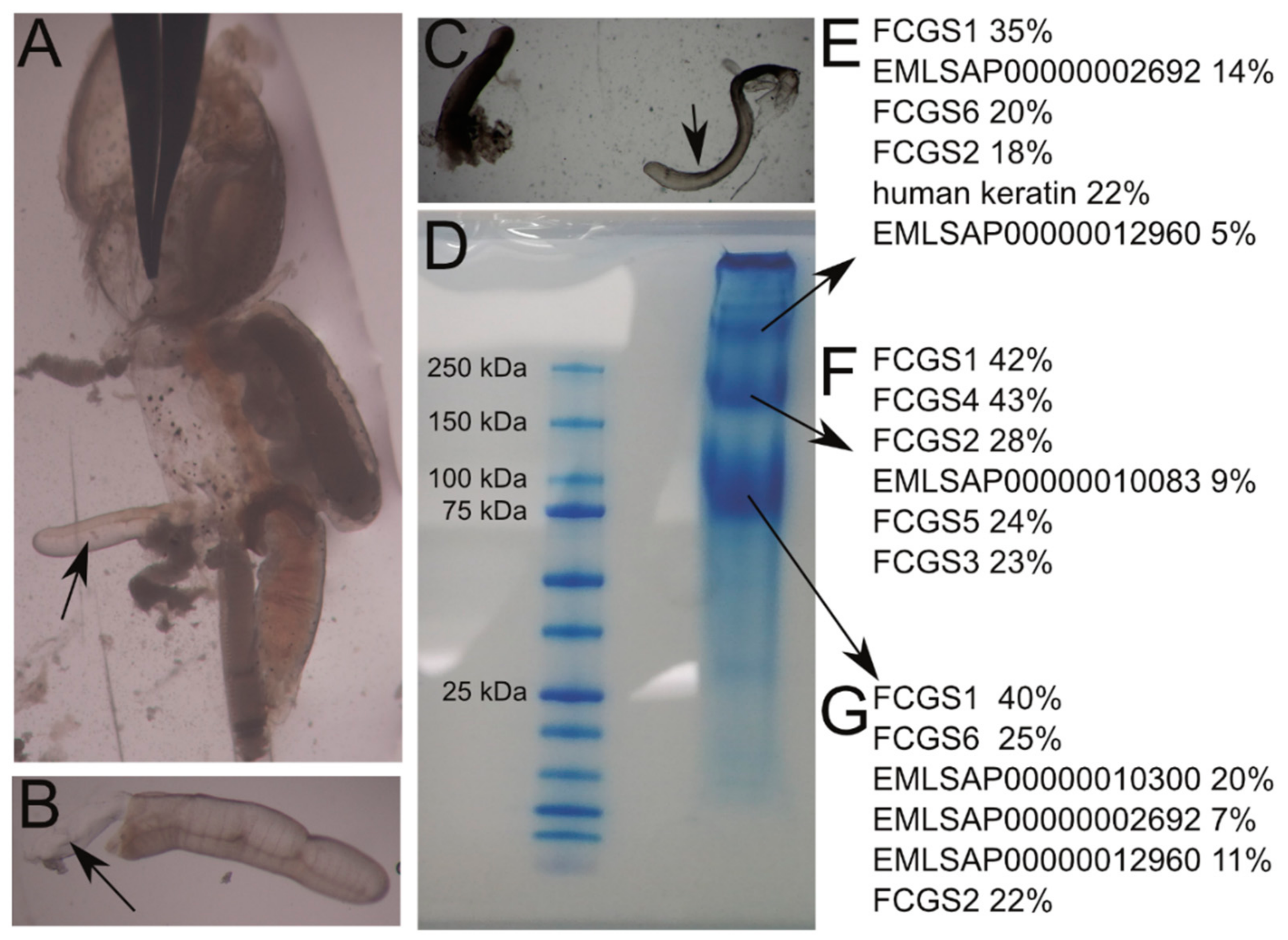
3.6. Protein Analysis
4. Discussion
4.1. FCGS Are the Building Blocks of the Egg Strings
4.2. FCGS Forms a New Protein Class
4.3. Genes of the Cement Gland Are Co-Regulated
4.4. FCGMB1 and FCGPO1 and 2 Are Essential for Egg String Formation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walter, T.C.; Boxshall, G. World of Copepods Database. Lepeophtheirus Salmonis (Krøyer, 1837). Available online: http://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=135782 (accessed on 27 August 2018).
- Boxaspen, K. A review of the biology and genetics of sea lice. ICES J. Mar. Sci. J. Du Cons. 2006, 63, 1304–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Costello, M.J. The global economic cost of sea lice to the salmonid farming industry. J. Fish Dis. 2009, 32, 115–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abolofia, J.; Asche, F.; Wilen, J.E. The Cost of Lice: Quantifying the Impacts of Parasitic Sea Lice on Farmed Salmon. Mar. Resour. Econ. 2017, 32, 329–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamre, L.A.; Eichner, C.; Caipang, C.M.A.; Dalvin, S.T.; Bron, J.E.; Nilsen, F.; Boxshall, G.; Skern-Mauritzen, R. The Salmon Louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Copepoda: Caligidae) Life Cycle Has Only Two Chalimus Stages. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ritchie, G.; Mordue, A.J.; Pike, A.W.; Rae, G.H. Morphology and Ultrastructure of the Reproductive System of Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Krøyer, 1837) (Copepoda: Caligidae). J. Crustacean Biol. 1996, 16, 330–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvin, S.; Frost, P.; Loeffen, P.; SkernMauritzen, R.; Baban, J.; Rnnestad, I.; Nilsen, F. Characterisation of two vitellogenins in the salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis: Molecular, functional and evolutional analysis. Dis. Aquat. Org. 2011, 94, 211–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.T.; Dalvin, S.; Waheed, Q.; Nilsen, F.; Male, R. Molecular characterization of the lipophorin receptor in the crustacean ectoparasite Lepeophtheirus salmonis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalvin, S.; Frost, P.; Biering, E.; Hamre, L.A.; Eichner, C.; Krossøy, B.; Nilsen, F. Functional characterisation of the maternal yolk-associated protein (LsYAP) utilising systemic RNA interference in the salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) (Crustacea: Copepoda). Int. J. Parasitol. 2009, 39, 1407–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandlund, L.; Kongshaug, H.; Nilsen, F.; Dalvin, S. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of components of the TOR pathway of the salmon louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Krøyer, 1838). Exp. Parasitol. 2018, 188, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandlund, L.; Nilsen, F.; Male, R.; Grotmol, S.; Kongshaug, H.; Dalvin, S. Molecular characterisation of the salmon louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis salmonis (Krøyer, 1837), ecdysone receptor with emphasis on functional studies of female reproduction. Int. J. Parasitol. 2015, 45, 175–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schram, T.A. The egg string attachment mechanism in salmon lice Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Copepoda: Caligidae). Contrib. Zool. 2000, 69, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hamre, L.A.; Glover, K.A.; Nilsen, F. Establishment and characterisation of salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Krøyer 1837)) laboratory strains. Parasitol. Int. 2009, 58, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsing, F.; Oppedal, F.; Dalvin, S.; Johnsen, I.; Vågseth, T.; Dempster, T. Salmon lice (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) development times, body size, and reproductive outputs follow universal models of temperature dependence. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci. 2016, 73, 1841–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heuch, P.A.; Nordhagen, J.R.; Schram, T.A. Egg production in the salmon louse [Lepeophtheirus salmonis (Kroyer)] in relation to origin and water temperature. Aquac. Res. 2000, 31, 805–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Styf, H.K.; Nilsson Sköld, H.; Eriksson, S.P. Embryonic response to long-term exposure of the marine crustacean Nephrops norvegicus to ocean acidification and elevated temperature. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 3, 5055–5065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, P.; Binns, D.; Chang, H.-Y.; Fraser, M.; Li, W.; McAnulla, C.; McWilliam, H.; Maslen, J.; Mitchell, A.; Nuka, G.; et al. InterProScan 5: Genome-scale protein function classification. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 1236–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frost, P.; Nilsen, F. Validation of reference genes for transcription profiling in the salmon louse, Lepeophtheirus salmonis, by quantitative real-time PCR. Vet. Parasitol. 2003, 118, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichner, C.; Øvergård, A.-C.; Nilsen, F.; Dalvin, S. Molecular characterization and knock-down of salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) prostaglandin E synthase. Exp. Parasitol. 2015, 159, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Øvergård, A.-C.; Eichner, C.; Nilsen, F.; Dalvin, S. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of a salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis, Krøyer 1838) heme peroxidase with a potential role in extracellular matrixes. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A 2017, 206, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borchel, A.; Nilsen, F. A novel gene-family involved in spermatophore generation in the economically important salmon louse Lepeophtheirus salmonis. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2018, 85, 478–489. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heggland, E.I.; Eichner, C.; Støve, S.I.; Martinez, A.; Nilsen, F.; Dondrup, M. A scavenger receptor B (CD36)-like protein is a potential mediator of intestinal heme absorption in the hematophagous ectoparasite Lepeophtheirus salmonis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 4218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, M.C.; Maclean, B.; Burke, R.; Amodei, D.; Ruderman, D.L.; Neumann, S.; Gatto, L.; Fischer, B.; Pratt, B.; Egertson, J.; et al. A cross-platform toolkit for mass spectrometry and proteomics. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 918–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsnes, H.; Vaudel, M. SearchGUI: A Highly Adaptable Common Interface for Proteomics Search and de Novo Engines. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 2552–2555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaudel, M.; Burkhart, J.M.; Zahedi, R.P.; Oveland, E.; Berven, F.S.; Sickmann, A.; Martens, L.; Barsnes, H. PeptideShaker enables reanalysis of MS-derived proteomics data sets. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Xie, Y.; Ma, J.; Luo, X.; Nie, P.; Zuo, Z.; Lahrmann, U.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. IBS: An illustrator for the presentation and visualization of biological sequences: Fig. 1. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 3359–3361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wilson, C.B. North American parasitic copepods belonging to the family Caligidae, Part I.—The Caliginae. Proc. United States Natl. Mus. 1905, 28, 479–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, B.E.; Muriel, J.M.; Dong, C.; Xu, X. Hemicentins: What have we learned from worms? Cell Res. 2006, 16, 872–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, X.; Xu, M.; Zhou, X.; Jones, O.B.; Moharomd, E.; Pan, Y.; Yan, G.; Anthony, D.D.; Isaacs, W.B. Specific structure and unique function define the hemicentin. Cell Biosci. 2013, 3, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Adams, J.C.; Lawler, J. The thrombospondins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a009712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, A.L.; Bartz, S.R.; Schelter, J.; Kobayashi, S.V.; Burchard, J.; Mao, M.; Li, B.; Cavet, G.; Linsley, P.S. Expression profiling reveals off-target gene regulation by RNAi. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichner, C.; Frost, P.; Dysvik, B.; Jonassen, I.; Kristiansen, B.; Nilsen, F. Salmon louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis) transcriptomes during post molting maturation and egg production, revealed using EST-sequencing and microarray analysis. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Heck, T.; Faccio, G.; Richter, M.; Thöny-Meyer, L. Enzyme-catalyzed protein crosslinking. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2013, 97, 461–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heijnis, W.H.; Dekker, H.L.; de Koning, L.J.; Wierenga, P.A.; Westphal, A.H.; de Koster, C.G.; Gruppen, H.; van Berkel, W.J.H. Identification of the Peroxidase-Generated Intermolecular Dityrosine Cross-Link in Bovine α-Lactalbumin. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Gene Symbol | Gene Name | ENSEMBL Stable Gene id(s) | GenBank Accession | Signal Peptide | Trans-Membrane Domain | mRNA Length (bp) 1 | CDS Length (bp)/Protein Length (aa)/Protein Size (kDa) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FCGS1 | Female cement gland secreted 1 | EMLSAG00000005417 EMLSAG00000002486 EMLSAG00000002488 EMLSAG00000002798 EMLSAG00000009842 | MK933815 | + | - | 2811 | 2691/896/97 |
| FCGS2 | Female cement gland secreted 2 | EMLSAG00000002328 | MK933816 | + | - | 2801 | 2661/886/97 |
| FCGS3 | Female cement gland secreted 3 | EMLSAG00000008518 | MK933817 | + | - | 2564 | 2463/820/92 |
| FCGS4 | Female cement gland secreted 4 | EMLSAG00000011195 | MK933818 | + | - | 2423 | 2298/765/84 |
| FCGS5 | Female cement gland secreted 5 | EMLSAG00000010070 | MK933819 | + | - | 2632 | 2568/855/94 |
| FCGS6 | Female cement gland secreted 6 | EMLSAG00000010397 | MK933820 | + | - | 5501 | 5109/1702/186 |
| FCGMB1 | Female cement gland membrane bound 1 | EMLSAG00000000454 | MK933821 | − | N-terminal | 2334 | 2127/708/77 |
| FCGPO1 | Female cement gland peroxidase 1 | EMLSAG00000007125 | MK933822 | − | - | 1884 | 1566/521/60 |
| FCGPO2 | Female cement gland peroxidase 2 | EMLSAG00000010106 | MK933823 | − | C-terminal | 3303 | 2856/951/109 |
| Gene Symbol | Cysteine Content |
|---|---|
| FCGS1 | 11.7% |
| FCGS2 | 11.9% |
| FCGS3 | 11.8% |
| FCGS4 | 15.8% |
| FCGS5 | 16.3% |
| FCGS6 | 11.2% |
| FCGMB1 | 11.7% |
| FCGPO1 | 1.7% |
| FCGPO2 | 2.7% |
| ⌀ L. salmonis proteins | 2.1% |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borchel, A.; Kongshaug, H.; Nilsen, F. Identification and Description of the Key Molecular Components of the Egg Strings of the Salmon Louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis). Genes 2019, 10, 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121004
Borchel A, Kongshaug H, Nilsen F. Identification and Description of the Key Molecular Components of the Egg Strings of the Salmon Louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis). Genes. 2019; 10(12):1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121004
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorchel, Andreas, Heidi Kongshaug, and Frank Nilsen. 2019. "Identification and Description of the Key Molecular Components of the Egg Strings of the Salmon Louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis)" Genes 10, no. 12: 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121004
APA StyleBorchel, A., Kongshaug, H., & Nilsen, F. (2019). Identification and Description of the Key Molecular Components of the Egg Strings of the Salmon Louse (Lepeophtheirus salmonis). Genes, 10(12), 1004. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10121004





