High Frequency of Either Altered Pre-Core Start Codon or Weakened Kozak Sequence in the Core Promoter Region in Hepatitis B Virus A1 Strains from Rwanda
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Serum Samples
2.2. PCR Amplification
2.3. Sequencing
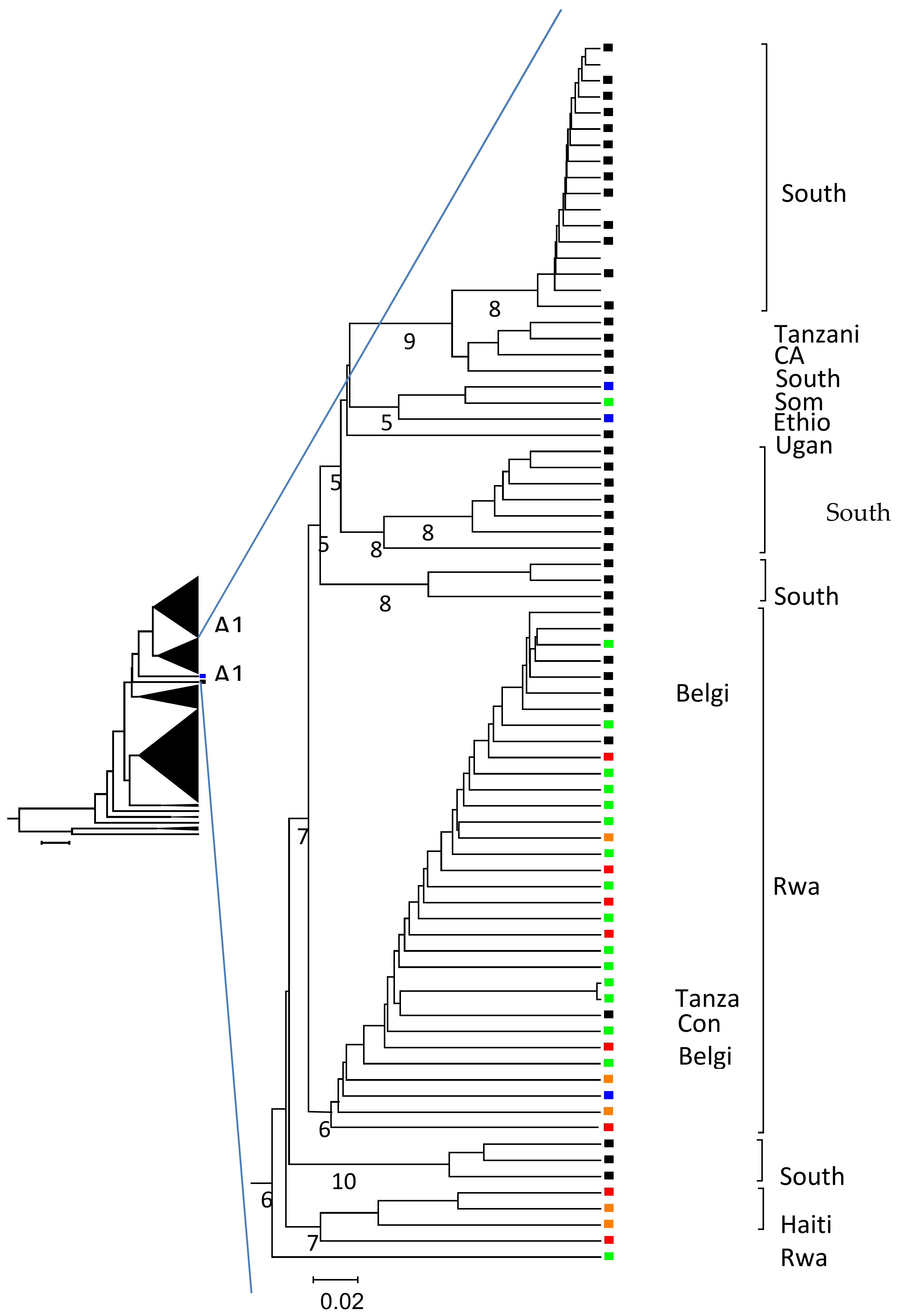
2.4. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Complete HBV Genomes
3.2. Core Promoter and Precore Regions of Complete and Partial Genomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Norder, H.; Courouce, A.M.; Coursaget, P.; Echevarria, J.M.; Lee, S.D.; Mushahwar, I.K.; Robertson, B.H.; Locarnini, S.; Magnius, L.O. Genetic diversity of hepatitis B virus strains derived worldwide: Genotypes, subgenotypes, and HBsAg subtypes. Intervirology 2004, 47, 289–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannoun, C.; Norder, H.; Lindh, M. An aberrant genotype revealed in recombinant hepatitis B virus strains from Vietnam. J. Gen. Virol. 2000, 81, 2267–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olinger, C.M.; Jutavijittum, P.; Hubschen, J.M.; Yousukh, A.; Samountry, B.; Thammavong, T.; Toriyama, K.; Muller, C.P. Possible new hepatitis B virus genotype, southeast Asia. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 1777–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.T.; Trinh, T.N.; Abe, K. New complex recombinant genotype of hepatitis B virus identified in Vietnam. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 5657–5663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramvis, A.; Kew, M.C. Epidemiology of hepatitis B virus in Africa, its genotypes and clinical associations of genotypes. Hepatol. Res. Off. J. Jpn. Soc. Hepatol. 2007, 37, S9–S19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramvis, A. Genotypes and genetic variability of hepatitis B virus. Intervirology 2014, 57, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twagirumugabe, T.; Swaibu, G.; Walker, T.D.; Lindh, M.; Gahutu, J.B.; Bergstrom, T.; Norder, H. Hepatitis B virus strains from Rwandan blood donors are genetically similar and form one clade within subgenotype A1. BMC Infect. Dis 2017, 17, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.; Revill, P. Overview of hepatitis B viral replication and genetic variability. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, S4–S16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, R.H.; Kaneko, S.; Chung, C.T.; Girones, R.; Purcell, R.H. Compact organization of the hepatitis B virus genome. Hepatology 1989, 9, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassal, M.; Schaller, H. Hepatitis B virus replication. Trends Microbiol. 1993, 1, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnius, L.O.; Espmark, J.A. New specificities in Australia antigen positive sera distinct from the Le Bouvier determinants. J. Immunol. 1972, 109, 1017–1021. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Milich, D.R.; Jones, J.E.; Hughes, J.L.; Price, J.; Raney, A.K.; McLachlan, A. Is a function of the secreted hepatitis B e antigen to induce immunologic tolerance in utero? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 6599–6603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.T.; Billaud, J.N.; Sallberg, M.; Guidotti, L.G.; Chisari, F.V.; Jones, J.; Hughes, J.; Milich, D.R. A function of the hepatitis B virus precore protein is to regulate the immune response to the core antigen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14913–14918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, H.; Tsuda, F.; Akahane, Y.; Sugai, Y.; Yoshiba, M.; Moriyama, K.; Tanaka, T.; Miyakawa, Y.; Mayumi, M. Hepatitis B virus with mutations in the core promoter for an e-antigen-negative phenotype in carriers with antibody to e antigen. J. Virol. 1994, 68, 8102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buckwold, V.E.; Xu, Z.; Chen, M.; Yen, T.S.; Ou, J.H. Effects of a naturally occurring mutation in the hepatitis B virus basal core promoter on precore gene expression and viral replication. J. Virol. 1996, 70, 5845–5851. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.L.; Hussain, M.; Lok, A.S. Different hepatitis B virus genotypes are associated with different mutations in the core promoter and precore regions during hepatitis B e antigen seroconversion. Hepatology 1999, 29, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.L.; Leung, N.W.; Hussain, M.; Wong, M.L.; Lok, A.S. Hepatitis B e antigen-negative chronic hepatitis B in Hong Kong. Hepatology 2000, 31, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moriyama, K.; Okamoto, H.; Tsuda, F.; Mayumi, M. Reduced precore transcription and enhanced core-pregenome transcription of hepatitis B virus DNA after replacement of the precore-core promoter with sequences associated with e antigen-seronegative persistent infections. Virology 1996, 226, 269–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiordalisi, G.; Cariani, E.; Mantero, G.; Zanetti, A.; Tanzi, E.; Chiaramonte, M.; Primi, D. High genomic variability in the pre-C region of hepatitis B virus in anti-HBe, HBV DNA-positive chronic hepatitis. J. Med. Virol. 1990, 31, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parekh, S.; Zoulim, F.; Ahn, S.H.; Tsai, A.; Li, J.; Kawai, S.; Khan, N.; Trepo, C.; Wands, J.; Tong, S. Genome replication, virion secretion, and e antigen expression of naturally occurring hepatitis B virus core promoter mutants. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 6601–6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishizawa, T.; Hoshino, T.; Naganuma, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Nagashima, S.; Takahashi, M.; Takagi, H.; Okamoto, H. Enhanced pregenomic RNA levels and lowered precore mRNA transcription efficiency in a genotype A hepatitis B virus genome with C1766T and T1768A mutations obtained from a fulminant hepatitis patient. J. Gen. Virol. 2016, 97, 2643–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskus, T.; Rakela, J.; Tong, M.J.; Nowicki, M.J.; Mosley, J.W.; Persing, D.H. Naturally occurring hepatitis B virus mutants with deletions in the core promoter region. J. Hepatol. 1994, 20, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pult, I.; Chouard, T.; Wieland, S.; Klemenz, R.; Yaniv, M.; Blum, H.E. A hepatitis B virus mutant with a new hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 binding site emerging in transplant-transmitted fulminant hepatitis B. Hepatology 1997, 25, 1507–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, S.P.; Li, J.S.; Vitvitski, L.; Trepo, C. Active hepatitis B virus replication in the presence of anti-HBe is associated with viral variants containing an inactive pre-C region. Virology 1990, 176, 596–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carman, W.F.; Jacyna, M.R.; Hadziyannis, S.; Karayiannis, P.; McGarvey, M.J.; Makris, A.; Thomas, H.C. Mutation preventing formation of hepatitis B e antigen in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection. Lancet 1989, 2, 588–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, H.; Yotsumoto, S.; Akahane, Y.; Yamanaka, T.; Miyazaki, Y.; Sugai, Y.; Tsuda, F.; Tanaka, T.; Miyakawa, Y.; Mayumi, M. Hepatitis B viruses with precore region defects prevail in persistently infected hosts along with seroconversion to the antibody against e antigen. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 1298–1303. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Santantonio, T.; Jung, M.C.; Miska, S.; Pastore, G.; Pape, G.R.; Will, H. Prevalence and type of pre-C HBV mutants in anti-HBe positive carriers with chronic liver disease in a highly endemic area. Virology 1991, 183, 840–844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimondo, G.; Schneider, R.; Stemler, M.; Smedile, V.; Rodino, G.; Will, H. A new hepatitis B virus variant in a chronic carrier with multiple episodes of viral reactivation and acute hepatitis. Virology 1990, 179, 64–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Twagirumugabe, T.M.C.; Habarurema, S.; Seruyange, E.; Bergström, T.; Gahutu, J.B.; Walker, T.D.; Norder, H. Different Epidemiology of Two Blood Borne Infections, Hepatitis B and C, in Rwanda. 2018; to be submitted. [Google Scholar]
- Radziwill, G.; Tucker, W.; Schaller, H. Mutational analysis of the hepatitis B virus P gene product: Domain structure and RNase H activity. J. Virol. 1990, 64, 613–620. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kimbi, G.C.; Kramvis, A.; Kew, M.C. Distinctive sequence characteristics of subgenotype A1 isolates of hepatitis B virus from South Africa. J. Gen. Virol. 2004, 85, 1211–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozak, M. Recognition of AUG and alternative initiator codons is augmented by G in position +4 but is not generally affected by the nucleotides in positions +5 and +6. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 2482–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.H.; Kramvis, A.; Kawai, S.; Spangenberg, H.C.; Li, J.; Kimbi, G.; Kew, M.; Wands, J.; Tong, S. Sequence variation upstream of precore translation initiation codon reduces hepatitis B virus e antigen production. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1370–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.H.; Huang, C.J.; Ting, L.P. Overlapping initiator and TATA box functions in the basal core promoter of hepatitis B virus. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3647–3657. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kimbi, G.C.; Kew, M.C.; Kramvis, A. The effect of the G1888A mutation of subgenotype A1 of hepatitis B virus on the translation of the core protein. Virus Res. 2012, 163, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochwoto, M.; Chauhan, R.; Gopalakrishnan, D.; Chen, C.Y.; Ng’ang’a, Z.; Okoth, F.; Kioko, H.; Kimotho, J.; Kaiguri, P.; Kramvis, A. Genotyping and molecular characterization of hepatitis B virus in liver disease patients in Kenya. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2013, 20, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andernach, I.E.; Nolte, C.; Pape, J.W.; Muller, C.P. Slave trade and hepatitis B virus genotypes and subgenotypes in Haiti and Africa. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2009, 15, 1222–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubschen, J.M.; Mbah, P.O.; Forbi, J.C.; Otegbayo, J.A.; Olinger, C.M.; Charpentier, E.; Muller, C.P. Detection of a new subgenotype of hepatitis B virus genotype A in Cameroon but not in neighbouring Nigeria. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2011, 17, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touriol, C.; Bornes, S.; Bonnal, S.; Audigier, S.; Prats, H.; Prats, A.C.; Vagner, S. Generation of protein isoform diversity by alternative initiation of translation at non-AUG codons. Biol. Cell 2003, 95, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dever, T.E. Molecular biology. A new start for protein synthesis. Science 2012, 336, 1645–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norder, H.; Galli, C.; Magnil, E.; Sikora, P.; Ekvarn, E.; Nystrom, K.; Magnius, L.O. Hepatitis E virus genotype 3 genomes from RNA-positive but serologically negative plasma donors have CUG as the start codon for ORF3. Intervirology 2018, 61, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firth, A.E.; Brierley, I. Non-canonical translation in RNA viruses. J. Gen. Virol. 2012, 93, 1385–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.S.; Tong, S.P.; Wen, Y.M.; Vitvitski, L.; Zhang, Q.; Trepo, C. Hepatitis B virus genotype A rarely circulates as an HBe-minus mutant: Possible contribution of a single nucleotide in the precore region. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 5402–5410. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wei, F.; Zheng, Q.; Li, M.; Wu, M. The association between hepatitis B mutants and hepatocellular carcinoma: A meta-analysis. Medicine 2017, 96, e6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.S.; Yamashiro, T.; Sumie, A.; Terao, H.; Mifune, K.; Nishizono, A. Hepatitis B virus harboring nucleotide deletions in the core promoter region and genotype B correlate with low viral replication activity in anti-HBe positive carriers. J. Clin. Virol. Off. Publ. Pan Am. Soc. Clin. Virol. 2001, 23, 97–106. [Google Scholar]
- Kohno, K.; Nishizono, A.; Terao, H.; Hiraga, M.; Mifune, K. Reduced transcription and progeny virus production of hepatitis B virus containing an 8-bp deletion in basic core promoter. J. Med. Virol. 2000, 61, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| N | HBeAg | Anti-HBe | Both HBeAg and Anti-HBe | No HBe Marker | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No known liver disease | 25 (14) | 9 (7) | 14 (5) | 2 (2) | 0 |
| Liver disease patients | 16 (9) | 6 (5) | 8 (3) | 1 (1) | 1 (0) |
| TOTAL | 41 (23) | 15 (12) | 22 (8) | 3 (3) | 1 (0) |
| All | A1762T/G1764A | Changed Kozak Sequence a | Precore Start Codon Mutation | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | Viral Loadb | N | Viral Load b | N | Viral Load b | N | Viral Load b | |
| No known liver disease | ||||||||
| HBeAg | 9 | 9.27 | ||||||
| Anti-HBe | 14 | 4.55 | 2 | 3.91 | 6 | 4.53 | 5 | 4.68 |
| Both HBe markers | 2 | 6.80 | 1 | 7.10 | ||||
| Subtotal | 25 | 3 | 6 | 5 | ||||
| Liver disease patients | ||||||||
| HBeAg | 6 | 7.43 | ||||||
| Anti-HBe | 8 | 6.61 | 2 | 5.79 | 2 | 7.08 | 4c | 5.50 |
| Both HBe markers | 1 | 5.43 | ||||||
| No HBe marker | 1 | 3.11 | 1 | 3.11 | ||||
| Subtotal | 16 | 3 | 2 | 4 | ||||
| All samples | ||||||||
| HBeAg | 15 | 9.07 | ||||||
| Anti-HBe | 22 | 6.20 | 4 | 5.49 | 8 | 6.48 | 9 | 5.22 |
| Both HBe markers | 3 | 6.64 | 1 | 7.10 | ||||
| No HBe marker | 1 | 3.11 | 1 | 3.11 | ||||
| TOTAL | 41 | 6 | 6.10 | 8 | 6.48 | 9 | 5.22 | |
| N Strains with Respective Precore Start Codons | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AUG | CUG | ACG | UUG | AAG | AUA | |
| Without known liver disease | ||||||
| HBeAg reactive | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Anti-HBe reactive | 9 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| Both markers | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Subtotal | 20 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| With known liver disease | ||||||
| HBeAg reactive | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Anti-HBe reactive | 4 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Both markers | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| No HBe marker | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Subtotal | 12 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| All patients | ||||||
| HBeAg reactive | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Anti-HBe reactive | 13 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| Both markers | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| No HBe marker | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 32 | 3 | 1 | 3 | 2 | 0 |
| A1 sequences in GenBank | 237 | 21 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 0 |
| A2 sequences in GenBank | 218 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| A3 sequences in GenBank | 37 | 8 | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 |
| N Strains with Respective Kozak Sequence At positions 1809–1813 | Other Kozak Sequences | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A1 wild Type TCATC/ GCACC | TGGTC | TTCTC | TACTC | TCTTC | TCCTC | TCTGC | ||
| Without known liver disease | ||||||||
| HBeAg reactive | 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Anti-HBe reactive | 9 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| Both markers | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Subtotal | 19 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | |
| With known liver disease | ||||||||
| HBeAg reactive | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Anti-HBe reactive | 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Both markers | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| No HBe marker | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Subtotal | 14 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| All patients | ||||||||
| HBeAg reactive | 15 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Anti-HBe reactive | 15 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| Both markers | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| No HBe marker | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| TOTAL | 33 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | |
| A1 sequences in GenBank | 225 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 4 | 21 | 0 | 13 |
| A2 sequences in GenBank | 220 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 5 |
| A3 sequences in GenBank | 35 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 9 | 0 | 1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Norder, H.; Twagirumugabe, T.; Said, J.; Tian, Y.; Tang, K.-W.; Magnius, L.; Lindh, M. High Frequency of Either Altered Pre-Core Start Codon or Weakened Kozak Sequence in the Core Promoter Region in Hepatitis B Virus A1 Strains from Rwanda. Genes 2019, 10, 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10030182
Norder H, Twagirumugabe T, Said J, Tian Y, Tang K-W, Magnius L, Lindh M. High Frequency of Either Altered Pre-Core Start Codon or Weakened Kozak Sequence in the Core Promoter Region in Hepatitis B Virus A1 Strains from Rwanda. Genes. 2019; 10(3):182. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10030182
Chicago/Turabian StyleNorder, Heléne, Theogene Twagirumugabe, Joanna Said, Yarong Tian, Ka-Wei Tang, Lars Magnius, and Magnus Lindh. 2019. "High Frequency of Either Altered Pre-Core Start Codon or Weakened Kozak Sequence in the Core Promoter Region in Hepatitis B Virus A1 Strains from Rwanda" Genes 10, no. 3: 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10030182
APA StyleNorder, H., Twagirumugabe, T., Said, J., Tian, Y., Tang, K.-W., Magnius, L., & Lindh, M. (2019). High Frequency of Either Altered Pre-Core Start Codon or Weakened Kozak Sequence in the Core Promoter Region in Hepatitis B Virus A1 Strains from Rwanda. Genes, 10(3), 182. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10030182





